Hyun Seuk Rhee
Freelancer, Anyang, Kyeonggi, 13924 Republic of Korea
Correspondence to: Hyun Seuk Rhee, Freelancer, Anyang, Kyeonggi, 13924 Republic of Korea.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Current quantum mechanics faced divergence problem when calculating scattering amplitude using Feynman diagrams and corresponding rules. It solved this problem using the method called “Renormalization”. But the problem is that it is just calculating technique, it doesn’t show why divergence appears. This article shows the new answer for the renormalization problem in quantum mechanical Field. First, it reviews the concept of indistinguishability, The Mathematical 4 laws, The Physical 5 Laws introduced by Rhee. It introduces the concept of identity as well. Second, it explains the 3 relation among identity and the indistinguishability, The Mathematical 4 laws, The Physical 4 Laws, collision and reaction. It introduces new interpretation of complex number and pure imaginary number, and it provides the reason to perform multiplication and addition. After that, it explains the identity and corresponding equations of fermions. It shows that Dirac Lagrangian function can be obtained using the concept of identity. Using these 5 concepts and Feynman rules for the diagram, it shows a new way to obtain anomalous magnetic moment of fermion, especially without introducing divergence. Finally, this article will show the new way to solve the same divergence problem in non-inertial reference frame problem.
Keywords:
Indistinguishable, Identity, Renormalization
Cite this paper: Hyun Seuk Rhee, The Introduction of the New Solution of Renormalization Problem in Inertial and Non-inertial Frame Using the Concept of Identities, International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Vol. 14 No. 3, 2024, pp. 102-108. doi: 10.5923/j.ijtmp.20241403.03.
1. Introduction
There are several divergence problems in current quantum mechanics such as loops in Feynman Diagram. Currently this problem considered to be solved because the outcomes of these works correspond exactly to experimental results. However, the process of this calculation and obtaining the outcomes is not physical, easily understandable. Furthermore, this way cannot be applied to non-inertial reference frame.In this article, a new way to solve the divergence problem of current quantum mechanics using The 4 Laws of Mathematics, The Law of Existence and The Law of Movement introduced by Rhee and several new concepts such as identity will be introduced. This way of solution leads to exactly the same outcome, and is more physically understandable, can be applied easily to reality and the other fields of physics such as gravity and strong force physics. Finally, this article will show the new way to solve the same divergence problem in non-inertial reference problem.To achieve this object, the following condition is assumed.1. c and h are considered to be 1.2. Effect of fermion and boson spin is ignored (Except in the introduction of The Law of Movement).3. Einstein’s summation convention is introduced.4. Center of mass reference frame is assumed.
2. The 4 Laws of Mathematics
According to Rhee, the following 4 laws of mathematics can be applied to existences (fermion, boson) in indistinguishable or distinguishable physical status, quantities.1. If the ’change’ or ’difference’ of physical quantity while the change of spacetime is infinitesimal is the most symmetrical over all the other changes, then real infinitesimal number 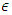 will be assigned to this change. If the change is in the time forward direction, then the number
will be assigned to this change. If the change is in the time forward direction, then the number 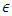 must be positive number, and if it is in the time backward direction, negative real number must be assigned to the change.2. If the ’change’ or ’difference’ of physical quantity while the change of spacetime is infinitesimal is the change which is not allowed by Einstein’s Relativity (the most non-symmetrical), then the pure imaginary number
must be positive number, and if it is in the time backward direction, negative real number must be assigned to the change.2. If the ’change’ or ’difference’ of physical quantity while the change of spacetime is infinitesimal is the change which is not allowed by Einstein’s Relativity (the most non-symmetrical), then the pure imaginary number 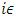 will be assigned to this change. This change is spacelike movement of certain particle, or the deviation of the object’s path from the General Relativity’s shortest path, for example. Assume there are 2 status of an object, and each is described by a number of each physical quantity. Then 2 following rules must be applied to these 2 numbers.3. The Rule of Addition: If the physical status (represented by complex number C) consists of 2 distinguishable status which is represented by the complex number A, B, then C is obtained by Addition of A and B. 4. The Rule of Multiplication: If the physical status (represented by complex number C) consists of 2 indistinguishable status which is represented by the complex number A, B, then C is obtained by multiplication of A and B.
will be assigned to this change. This change is spacelike movement of certain particle, or the deviation of the object’s path from the General Relativity’s shortest path, for example. Assume there are 2 status of an object, and each is described by a number of each physical quantity. Then 2 following rules must be applied to these 2 numbers.3. The Rule of Addition: If the physical status (represented by complex number C) consists of 2 distinguishable status which is represented by the complex number A, B, then C is obtained by Addition of A and B. 4. The Rule of Multiplication: If the physical status (represented by complex number C) consists of 2 indistinguishable status which is represented by the complex number A, B, then C is obtained by multiplication of A and B.
3. Meaning of Indistinguishable Between 2 Physical Quantities
In the introduction of The 4 Laws of Mathematics, additional explanation about the meaning of indistinguishable is needed. Assume there are 2 physical quantities (A and B). The 2 physical quantities are indistinguishable with each other if the following 2 physical changes are physically equivalent:  and
and 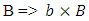 Here
Here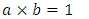 For example, consider time and energy of any fermion. The time change dt => 2dt is physically equivalent to
For example, consider time and energy of any fermion. The time change dt => 2dt is physically equivalent to 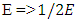 , therefore the 2 physical quantities is considered to be indistinguishable with each other.
, therefore the 2 physical quantities is considered to be indistinguishable with each other.
4. Identity
Identity of an existence (or particle, such as fermion and boson) is the value that represents whether each existence can be scientifically “distinguished”, or not. Assume there are 2 existences and each must be represented by “identity” of A and B. If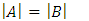 then the 2 existences cannot be scientifically distinguished. It means that if the 2 existences collide to each other and travel through different route from each other after collision, one cannot decide scientifically which one is A or B from the 2 existences after collision.Identity of an existence can be represented by the following formula:
then the 2 existences cannot be scientifically distinguished. It means that if the 2 existences collide to each other and travel through different route from each other after collision, one cannot decide scientifically which one is A or B from the 2 existences after collision.Identity of an existence can be represented by the following formula: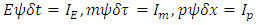 | (1) |
Where 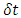 is the time interval during which the existence keeps its own path and energy in the reference frame of observer at one fixed space point,
is the time interval during which the existence keeps its own path and energy in the reference frame of observer at one fixed space point, 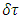 is the time interval during which the existence keeps its own path and mass in the reference frame of the existence at one fixed space point, and
is the time interval during which the existence keeps its own path and mass in the reference frame of the existence at one fixed space point, and 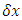 is space interval during which the existence keeps its own path and momentum when time difference is zero. E is energy, m is mass, p is momentum of the existence.
is space interval during which the existence keeps its own path and momentum when time difference is zero. E is energy, m is mass, p is momentum of the existence. 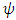 is called “wave function”.E and
is called “wave function”.E and 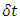 are indistinguishable to each other, and so are m and
are indistinguishable to each other, and so are m and 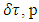 and
and 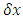 .The imaginary part of E, p means the amount of energy and momentum which violates the energy and momentum conservation laws, respectively. The imaginary part of wave function means swapping or deviating from its own traveling gravitational shortest path.
.The imaginary part of E, p means the amount of energy and momentum which violates the energy and momentum conservation laws, respectively. The imaginary part of wave function means swapping or deviating from its own traveling gravitational shortest path.
5. Identity and 2 Laws of Existence and 3 Laws of Motion
According to Rhee, to define macroscopic and microscopic fermion, the following 2 laws (laws of existence) must be introduced.1. The law of wave: Every existence including fermion and boson etc., which has energy of its own must be physically continuous to each other.2. The law of particle: The whole integration over wave (probability) density of every existence must be integer multiples of ℏ.(Physically Continuous: If the 2 existences have the same identity as each other, therefore if one cannot decide exactly whether they swap or ignore when they collide, then the 2 existences is said to be physically continuous to each other in this paper).One can define wave and particle with the 2 laws given above.Wave: an existence which satisfies The Law of Wave and violates The Law of Particle.Particle: an existence which violates The Law of Wave and satisfies The Law of Particle.One can also call “wave” as microscopic existence, and “particle” as macroscopic existence.To define the movement of the existence the following 3 laws (laws of movement) must also be introduced.1. The Law of Energy Conservation.2. The Law of Relativity - The same physical law must be applied to any reference frame. 3. The Law of speed limit - every physical element including fermion, boson, etc. must not exceed speed c, and The Law of momentum conservation (These 2 laws are combined to 1 law).The 3 laws of movement can also be defined by using the concept of Identity just introduced.1. The Law of Energy Conservation: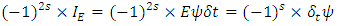 2. The Law of Relativity:
2. The Law of Relativity: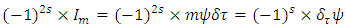 3. The Law of speed limit, The Law of momentum conservation:
3. The Law of speed limit, The Law of momentum conservation: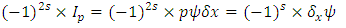
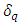 means partial differential operator with respect to q, s in the above equations is called “spin” of the existences.
means partial differential operator with respect to q, s in the above equations is called “spin” of the existences.
6. Relations Among Identities
The 3 identity quantities are related to the others by the following equations: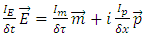 | (2) |
where 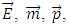 are unit vectors in energy-momentum space.
are unit vectors in energy-momentum space.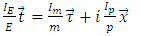 | (3) |
where 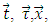 are unit vectors in spacetime and i is imaginary number unit.
are unit vectors in spacetime and i is imaginary number unit.
7. Reaction and Identity
If there are 2 existences A, B and each of their identities has the same magnitude, then when they collide to each other in the closed spacetime system, they are going to react to each other. Reacted existence of A and B must be described by the following identity: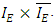 equation (2) can be:
equation (2) can be: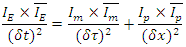 If the equation (1) is applied to the equation (2):
If the equation (1) is applied to the equation (2):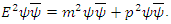
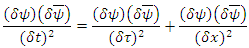 Change
Change 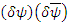 to
to  and
and  to
to 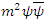 then
then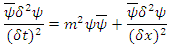 equation (3) can be:
equation (3) can be: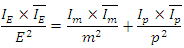 If the equation (1) is applied to the equation above:
If the equation (1) is applied to the equation above: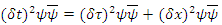 (Here
(Here 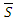 means conjugate complex number of S)
means conjugate complex number of S)
8. Identity of Wave (Probability) Density
Energy identity of wave density, allowing energy to be complex number, (imaginary part is energy non-conservation part) of microscopic fermion always have non real number and can be defined by the following equation: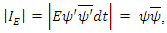 Or, using the integration,
Or, using the integration,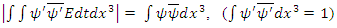 Where
Where 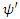 and
and 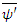 is wave functions of the same fermion with
is wave functions of the same fermion with 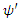 at the beginning of dt and
at the beginning of dt and  at the end of dt. Then the following relation must be satisfied by the whole macroscopic system of n fermions:
at the end of dt. Then the following relation must be satisfied by the whole macroscopic system of n fermions: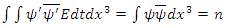 | (4) |
Where n is always integer and it means the number of fermions in the system, integration symbol for space means the entire integration over the entire physically continuous fermion wave density and integration symbol for time means the integration for the time interval between 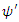 and
and 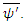 In this equation energy is not imaginary number anymore, because macroscopic system of fermions must always satisfy energy conservation law.Similar relations must be satisfied by momentum and mass identity.
In this equation energy is not imaginary number anymore, because macroscopic system of fermions must always satisfy energy conservation law.Similar relations must be satisfied by momentum and mass identity.
9. Identity and Fermion
According to Rhee, when 2 fermions react to each other during collision, they choose 1 of 2 options: swap or ignore. Furthermore, whether they swap their path with each other, or ignore each other cannot be decided precisely. Therefore, when they react to each other, one fermion with wave function 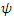 which is swapped and
which is swapped and  which keeps traveling on its path forms indistinguishable physical status.According to Rhee, Hamiltonian Picture is the kind of frame in which The Law of Relativity is satisfied while The Law of Energy Conservation, The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation are violated among The 3 Laws of Movement. In Hamiltonian Picture, the value of the identity of
which keeps traveling on its path forms indistinguishable physical status.According to Rhee, Hamiltonian Picture is the kind of frame in which The Law of Relativity is satisfied while The Law of Energy Conservation, The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation are violated among The 3 Laws of Movement. In Hamiltonian Picture, the value of the identity of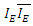 can be used to obtain the deviation of the movement of existence from the shortest path.Therefore, their identity after reaction can be described as follows:
can be used to obtain the deviation of the movement of existence from the shortest path.Therefore, their identity after reaction can be described as follows: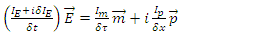 | (5) |
which becomes,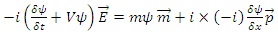 | (6) |
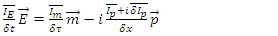 | (7) |
which becomes,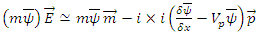 | (8) |
where  and
and  means violation of The Law of Energy, The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation, respectively, if
means violation of The Law of Energy, The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation, respectively, if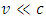 where v is the speed of the existence.
where v is the speed of the existence. and
and 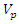 is the term which represents the violation of the 2 laws.Therefore,
is the term which represents the violation of the 2 laws.Therefore,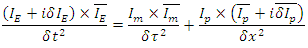 is
is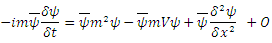 where O is the term which is so small that it can be ignored.or
where O is the term which is so small that it can be ignored.or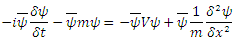 which is the Hamiltonian function of the fermion
which is the Hamiltonian function of the fermion 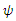 .The term
.The term  is related to the violation of The Law of Energy Conservation. If
is related to the violation of The Law of Energy Conservation. If  is the representation of macroscopic existence, this violation must be compensated by exchanging real macroscopic electric photon. The further violation of the value of the term
is the representation of macroscopic existence, this violation must be compensated by exchanging real macroscopic electric photon. The further violation of the value of the term 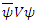 is
is 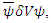 and it represents further violation of The Law of Energy Conservation by the entire microscopic part of system fermion + photon and the macroscopic one must satisfy following equation:
and it represents further violation of The Law of Energy Conservation by the entire microscopic part of system fermion + photon and the macroscopic one must satisfy following equation: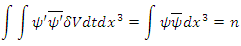 n can be any integer larger than 0.According to Rhee, there is also Lagrangian Picture in which The Law of Energy Conservation is satisfied while The Law of Relativity and The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation are violated among The 3 Laws of Movement.Therefore, their identity after reaction can be described as follows:
n can be any integer larger than 0.According to Rhee, there is also Lagrangian Picture in which The Law of Energy Conservation is satisfied while The Law of Relativity and The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation are violated among The 3 Laws of Movement.Therefore, their identity after reaction can be described as follows: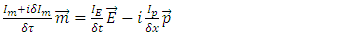 | (9) |
or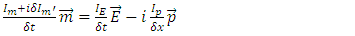 | (10) |
which becomes,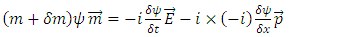 | (11) |
And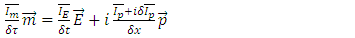 | (12) |
or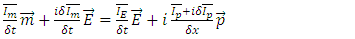 | (13) |
or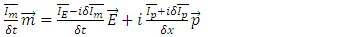 | (14) |
which becomes,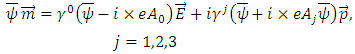 | (15) |
where 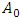 and
and 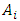 means the violation of energy conservation, speed limit and momentum conservation respectively of microscopic existence, wave. This violation must be compensated by real photon to satisfy The 3 Laws of Movement. Therefore,
means the violation of energy conservation, speed limit and momentum conservation respectively of microscopic existence, wave. This violation must be compensated by real photon to satisfy The 3 Laws of Movement. Therefore,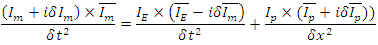 is
is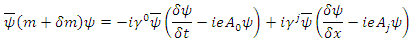 Where
Where 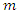 is fixed, and
is fixed, and 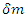 is variation of mass m.Above equation can be arranged to the following form:
is variation of mass m.Above equation can be arranged to the following form: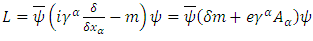 | (16) |
Where 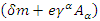 means the net rate of the change of the traveling path of
means the net rate of the change of the traveling path of 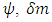 means the net rate of the change caused by the fermion itself and
means the net rate of the change caused by the fermion itself and 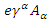 is the net rate of the change caused by external photon, and function L is called Dirac Lagrangian. Assuming that
is the net rate of the change caused by external photon, and function L is called Dirac Lagrangian. Assuming that 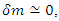
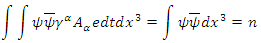 n can be any integer larger than 0.
n can be any integer larger than 0.
10. Alternative Calculation to Renormalization Using Feynman Diagram
According to current Capenhagen interpretation-based quantum mechanics, wave function of fermion represents the probability of existence in certain spacetime. on the process of applying Lagrangian method to this wave function on microscopical phenomenon like fermion photon scattering, Feynman Diagram and Feynman rules has been invented and applied to the analysis of the wave function. However, while applying Feynman Diagram and Feynman rules, especially to the Feynman Diagram which includes at least one “loop”, serious problems of infinity appears. Current quantum mechanics has been considered to solve this problem by using the method called renormalization. However, renormalization is just calculation skill which hide infinity using mathematical technique. Using the concept of identities, The Mathematical 4 Laws, The 2 Laws of Existence (the law of wave and the law of particle) and The 3 laws of movement introduced in the previous paragraphs in this article one can easily calculate and obtain proper result without hiding infinities, because infinity problem is not going to occur at all during calculational process. This can be done by introducing additional Feynman rules which are based on the concepts newly introduced in this article.Assume that there are fermion beam (like electron beam) which is influenced by external electric field.The situation of a fermion reacting to electric field must be described by the following picture: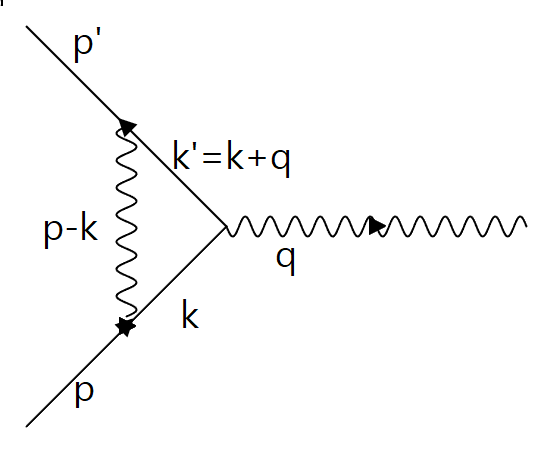 | Figure 1. Feynman Diagram of an electron in electric field |
10.1. Modification of Feynman Rules
First, Feynman rules must be modified. Different modification must be applied to microscopic and macroscopic existence (fermion).Because macroscopic existence is the one which violates The Law of wave and satisfy The Law of Particle, it must be physically discontinuous to the other part of existences (fermions). In the case of electron, it is the whole part of any individual electron in the N-electron system. Therefore, it is not identical (has different identity) to the other (part of) fermions, so each fermion can have various amplitude on any Feynman diagram. For example, in the case of one electron and one photon case like the picture figure 1, if the electron and the photon is exactly macroscopic, the amplitude for the Feynman diagram can have various values like 1 and 0. On the other hand if the internal loop is included in any Feynman diagram, then the effect of such a loop is ignored in the case of macroscopic existence. Following additional Feynman rules for macroscopic fermion and boson must be added: 1. The amplitude for each independent Feynman diagram can have more than one various values.2. Internal loop of each Feynman diagram must be ignored (Feynman diagram with and without internal loop must have the same value as each other.)On the other hand, microscopic system of fermion and boson must satisfy the following additional Feynman rules, as opposed to macroscopic one:1. The amplitude for each independent Feynman diagram must have only one consistent value.2. At each vertex additional identity must be multiplied, for example,  if there is no internal loop around the vertex, and if there is one loop, then
if there is no internal loop around the vertex, and if there is one loop, then 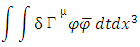 where
where  is the amplitude for internal loop obtained by the application of the other Feynman rules.Following Feynman rules must be applied to both microscopic and macroscopic one: 1. Each microscopic and macroscopic amplitude must be same if the number of fermions and bosons which are involved in calculating the amplitude is very big (N >> 1).
is the amplitude for internal loop obtained by the application of the other Feynman rules.Following Feynman rules must be applied to both microscopic and macroscopic one: 1. Each microscopic and macroscopic amplitude must be same if the number of fermions and bosons which are involved in calculating the amplitude is very big (N >> 1).
10.2. Application of the Modified Feynman Rules
Assume that the internal scattering amplitude of the above picture (Figure 1) is M. The value of M is only related to the coupling of external electromagnetic field and fermion, therefore, 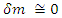 in equation (16). Applying equation (4), and if
in equation (16). Applying equation (4), and if  and
and 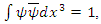 what the value of M becomes in the relatively short period of time is:
what the value of M becomes in the relatively short period of time is: 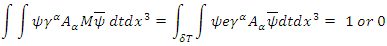 where
where 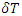 means the relatively short period of time between
means the relatively short period of time between 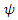 and
and 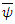 changing their energy and momentum by
changing their energy and momentum by 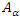 during the time. For the value of the above whole integration to be integer (1, or 0), the charge e must be 1 or 0 if
during the time. For the value of the above whole integration to be integer (1, or 0), the charge e must be 1 or 0 if 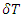 is relatively short. Both values 1 and 0 are possible because of additional Feynman rules for macroscopic existence. As
is relatively short. Both values 1 and 0 are possible because of additional Feynman rules for macroscopic existence. As  increases to infinity, and if
increases to infinity, and if  is integer,
is integer,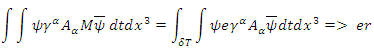 And e must converge to one fixed value (the renormalized coupling constant) for macroscopic and microscopic amplitude to be same.
And e must converge to one fixed value (the renormalized coupling constant) for macroscopic and microscopic amplitude to be same.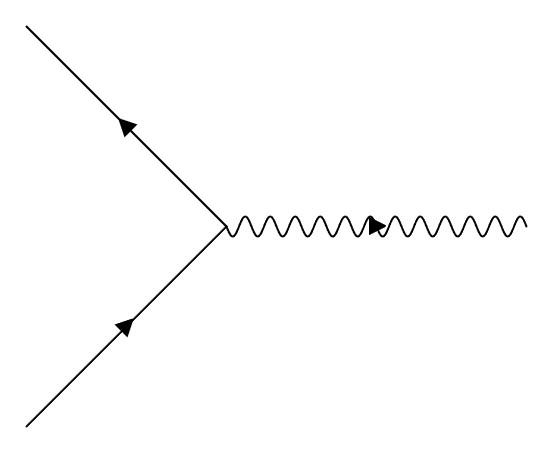 | Figure 2. Feynman Diagram of an electron with additional one loop |
First assume that the scattering amplitude of M can be represented by the following relation: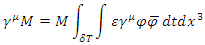 where
where 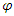 is a new kind of wave function which represents the internal deviation (or uncertainty) from the gravitational shortest path of figure 1.
is a new kind of wave function which represents the internal deviation (or uncertainty) from the gravitational shortest path of figure 1.  is real number which make the value of the following equation 1:
is real number which make the value of the following equation 1: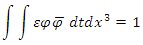 Then the scattering amplitude of Feynman Diagram figure 2 must have the following form:
Then the scattering amplitude of Feynman Diagram figure 2 must have the following form: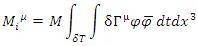 Where
Where  is the term calculated by the method obtained from the Feynman diagram according to current quantum mechanics, and
is the term calculated by the method obtained from the Feynman diagram according to current quantum mechanics, and 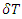 is the interval of time integration.According to Peskin,
is the interval of time integration.According to Peskin,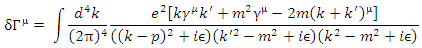 Therefore, the scattering amplitude of combined Feynman Diagram figure 1 and figure 2, M’ can be obtained by the following way:
Therefore, the scattering amplitude of combined Feynman Diagram figure 1 and figure 2, M’ can be obtained by the following way: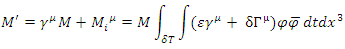
 energy part of identity of the wave function
energy part of identity of the wave function 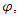 converges to
converges to 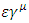 when the
when the 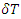 goes to infinity for this microscopic amplitude to be same as macroscopic one However, when
goes to infinity for this microscopic amplitude to be same as macroscopic one However, when 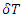 approaches to zero,
approaches to zero, 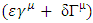 converges to
converges to 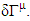 The one way to express this effect is to introduce following transformation like Pauli-villa regularization:
The one way to express this effect is to introduce following transformation like Pauli-villa regularization: 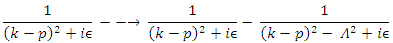 And let
And let 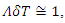
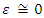 . Using this equation, one can obtain the same value to the physical observable such as anomalous magnetic moment.
. Using this equation, one can obtain the same value to the physical observable such as anomalous magnetic moment.
11. Alternative Calculation of Renormalization in Non-inertial Reference Frame
According to current Copenhagen-based quantum mechanics, when analyzing quantum mechanical process like fermion-boson scattering in non-inertial reference frame, a kind of existence called graviton must be introduced which represents gravitational force. According to , graviton can be represented by the following equation: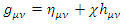 where
where 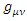 is gravitational ,
is gravitational , 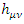 is the graviton field, and
is the graviton field, and 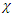 is the coupling constant. However, there is no evidence that such existence like graviton which satisfies The Law of Particle or The Law of Wave does exist. Therefore, instead of graviton, the special identity of energy tensor and metric tensor of matter wave function is going to be used, like the following equation which is suggested by Rhee:
is the coupling constant. However, there is no evidence that such existence like graviton which satisfies The Law of Particle or The Law of Wave does exist. Therefore, instead of graviton, the special identity of energy tensor and metric tensor of matter wave function is going to be used, like the following equation which is suggested by Rhee: 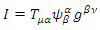 where
where 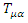 is the energy tensor which represents energy of fermion,
is the energy tensor which represents energy of fermion, 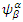 is wave function,
is wave function, 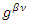 metric tensor. To make explanation simple, the wave function is assumed to be unity. Therefore, the identity is:
metric tensor. To make explanation simple, the wave function is assumed to be unity. Therefore, the identity is: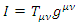 If the following identity
If the following identity 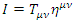 represents the identity of electron in inertial reference frame, and the gravitation is applied so that metric tensor is changed to
represents the identity of electron in inertial reference frame, and the gravitation is applied so that metric tensor is changed to  , then the identity becomes:
, then the identity becomes: The identity above is not the identity of electron (fermion with electron mass m) anymore because
The identity above is not the identity of electron (fermion with electron mass m) anymore because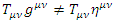 Therefore, the fermion which was electron when gravitational field was empty becomes the fermion with the different mass m’
Therefore, the fermion which was electron when gravitational field was empty becomes the fermion with the different mass m’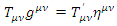 where
where 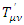 represents fermion with the mass m’When analyzing the quantum mechanical process in non-inertial reference, the way of calculating the scattering process is the same as inertial reference frame with the same Feynman rules as inertial reference frame one, except that the mass m must be changed to m’ which is obtained by the equation:
represents fermion with the mass m’When analyzing the quantum mechanical process in non-inertial reference, the way of calculating the scattering process is the same as inertial reference frame with the same Feynman rules as inertial reference frame one, except that the mass m must be changed to m’ which is obtained by the equation: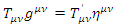 There is another way to obtain scattering amplitude of quantum mechanical process in non-inertial reference frame. This way of calculation can be explained by the following equation:
There is another way to obtain scattering amplitude of quantum mechanical process in non-inertial reference frame. This way of calculation can be explained by the following equation: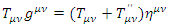 where
where 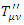 represents “virtual photon field” for compensation for the changing of the reference frame from non-inertial to inertial reference frame. In Feynman Diagram, this compensation can be described by photon field, which doesn’t exist in the reality but just exists for the description of “non-inertial reference frame” like the following diagram:
represents “virtual photon field” for compensation for the changing of the reference frame from non-inertial to inertial reference frame. In Feynman Diagram, this compensation can be described by photon field, which doesn’t exist in the reality but just exists for the description of “non-inertial reference frame” like the following diagram: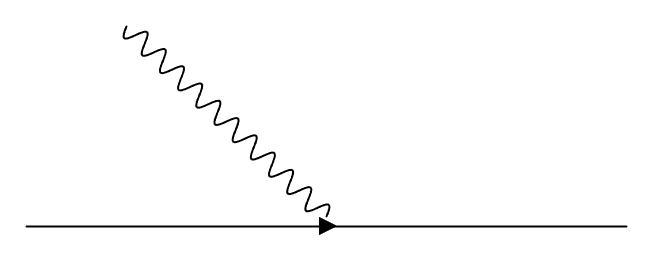 | Figure 3. Feynman Diagram with gravitation compensation. |
when virtual photon field is included in the Feynman diagram instead of non-inertial reference frame gravitational effect, real photon field must be changed from massless to massive photon field with non-zero mass 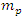 because the real photon field must be added by the “compensation” of the non-energy conservation term
because the real photon field must be added by the “compensation” of the non-energy conservation term 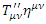 . Therefore, the following quantum mechanical process represented by Feynman diagram
. Therefore, the following quantum mechanical process represented by Feynman diagram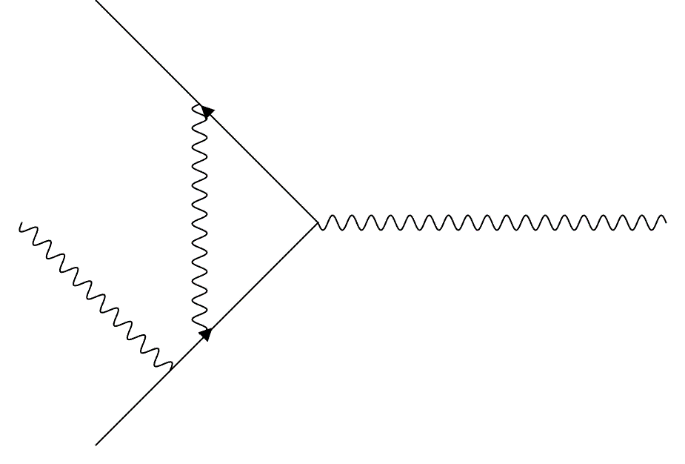 | Figure 4. Feynman Diagram of one fermion and pne photon in non-inertial reference frame. |
must be explained by internal photon propagator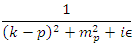 Instead of
Instead of 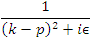
12. Conclusions
As explained in this article, in the process of the calculation of scattering amplitude, renormalization which is to hide infinity is not needed actually if The 4 Mathematical Law, The Law of Wave, The Law of Particle, The 3 Laws of Movement, and Identity introduced in this article is properly used. Only Feynman diagram and corresponding old Feynman rules, additional new Feynman rules derived from the laws mentioned above is needed and there was no infinity observed during the calculational process.
References
| [1] | Rhee, H. The New Interpretation of Quantum Mechanical Probability and Renormalization Using 4 Mathematical Laws and 5 Physical Laws. International Journal of Complementary and Internal Medicine. 2023, 4(1), 156–166. |
| [2] | M. Peskin, (1995), An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory, Colorado: Westview Press. |
| [3] | David Prinz, Renormalization of Gauge Theories and Gravity, arXiv: 2210.17510, 2022. |
| [4] | Rhee, H. The New Analysis of Quantum Gravity by Adding Uncertainty to Gravitational Spacetime and Modifying Einstein's Full Field Equation and Introduction of 5 Physical Laws. International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics. 2024, Volume 14, Number 1. |


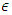 will be assigned to this change. If the change is in the time forward direction, then the number
will be assigned to this change. If the change is in the time forward direction, then the number 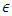 must be positive number, and if it is in the time backward direction, negative real number must be assigned to the change.2. If the ’change’ or ’difference’ of physical quantity while the change of spacetime is infinitesimal is the change which is not allowed by Einstein’s Relativity (the most non-symmetrical), then the pure imaginary number
must be positive number, and if it is in the time backward direction, negative real number must be assigned to the change.2. If the ’change’ or ’difference’ of physical quantity while the change of spacetime is infinitesimal is the change which is not allowed by Einstein’s Relativity (the most non-symmetrical), then the pure imaginary number 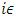 will be assigned to this change. This change is spacelike movement of certain particle, or the deviation of the object’s path from the General Relativity’s shortest path, for example. Assume there are 2 status of an object, and each is described by a number of each physical quantity. Then 2 following rules must be applied to these 2 numbers.3. The Rule of Addition: If the physical status (represented by complex number C) consists of 2 distinguishable status which is represented by the complex number A, B, then C is obtained by Addition of A and B. 4. The Rule of Multiplication: If the physical status (represented by complex number C) consists of 2 indistinguishable status which is represented by the complex number A, B, then C is obtained by multiplication of A and B.
will be assigned to this change. This change is spacelike movement of certain particle, or the deviation of the object’s path from the General Relativity’s shortest path, for example. Assume there are 2 status of an object, and each is described by a number of each physical quantity. Then 2 following rules must be applied to these 2 numbers.3. The Rule of Addition: If the physical status (represented by complex number C) consists of 2 distinguishable status which is represented by the complex number A, B, then C is obtained by Addition of A and B. 4. The Rule of Multiplication: If the physical status (represented by complex number C) consists of 2 indistinguishable status which is represented by the complex number A, B, then C is obtained by multiplication of A and B.  and
and 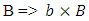 Here
Here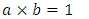 For example, consider time and energy of any fermion. The time change dt => 2dt is physically equivalent to
For example, consider time and energy of any fermion. The time change dt => 2dt is physically equivalent to 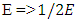 , therefore the 2 physical quantities is considered to be indistinguishable with each other.
, therefore the 2 physical quantities is considered to be indistinguishable with each other.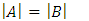 then the 2 existences cannot be scientifically distinguished. It means that if the 2 existences collide to each other and travel through different route from each other after collision, one cannot decide scientifically which one is A or B from the 2 existences after collision.Identity of an existence can be represented by the following formula:
then the 2 existences cannot be scientifically distinguished. It means that if the 2 existences collide to each other and travel through different route from each other after collision, one cannot decide scientifically which one is A or B from the 2 existences after collision.Identity of an existence can be represented by the following formula: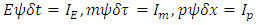
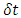 is the time interval during which the existence keeps its own path and energy in the reference frame of observer at one fixed space point,
is the time interval during which the existence keeps its own path and energy in the reference frame of observer at one fixed space point, 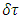 is the time interval during which the existence keeps its own path and mass in the reference frame of the existence at one fixed space point, and
is the time interval during which the existence keeps its own path and mass in the reference frame of the existence at one fixed space point, and 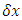 is space interval during which the existence keeps its own path and momentum when time difference is zero. E is energy, m is mass, p is momentum of the existence.
is space interval during which the existence keeps its own path and momentum when time difference is zero. E is energy, m is mass, p is momentum of the existence. 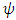 is called “wave function”.E and
is called “wave function”.E and 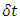 are indistinguishable to each other, and so are m and
are indistinguishable to each other, and so are m and 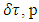 and
and 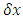 .The imaginary part of E, p means the amount of energy and momentum which violates the energy and momentum conservation laws, respectively. The imaginary part of wave function means swapping or deviating from its own traveling gravitational shortest path.
.The imaginary part of E, p means the amount of energy and momentum which violates the energy and momentum conservation laws, respectively. The imaginary part of wave function means swapping or deviating from its own traveling gravitational shortest path.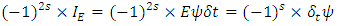 2. The Law of Relativity:
2. The Law of Relativity: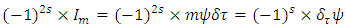 3. The Law of speed limit, The Law of momentum conservation:
3. The Law of speed limit, The Law of momentum conservation: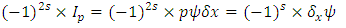
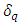 means partial differential operator with respect to q, s in the above equations is called “spin” of the existences.
means partial differential operator with respect to q, s in the above equations is called “spin” of the existences.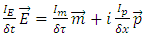
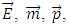 are unit vectors in energy-momentum space.
are unit vectors in energy-momentum space.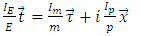
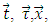 are unit vectors in spacetime and i is imaginary number unit.
are unit vectors in spacetime and i is imaginary number unit.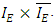 equation (2) can be:
equation (2) can be: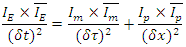 If the equation (1) is applied to the equation (2):
If the equation (1) is applied to the equation (2):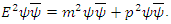
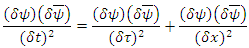 Change
Change  to
to  and
and  to
to 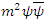 then
then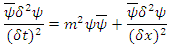 equation (3) can be:
equation (3) can be: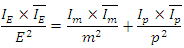 If the equation (1) is applied to the equation above:
If the equation (1) is applied to the equation above: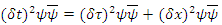 (Here
(Here 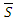 means conjugate complex number of S)
means conjugate complex number of S)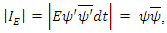 Or, using the integration,
Or, using the integration,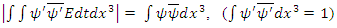 Where
Where 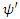 and
and 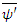 is wave functions of the same fermion with
is wave functions of the same fermion with 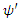 at the beginning of dt and
at the beginning of dt and  at the end of dt. Then the following relation must be satisfied by the whole macroscopic system of n fermions:
at the end of dt. Then the following relation must be satisfied by the whole macroscopic system of n fermions: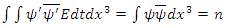
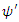 and
and 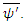 In this equation energy is not imaginary number anymore, because macroscopic system of fermions must always satisfy energy conservation law.Similar relations must be satisfied by momentum and mass identity.
In this equation energy is not imaginary number anymore, because macroscopic system of fermions must always satisfy energy conservation law.Similar relations must be satisfied by momentum and mass identity.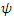 which is swapped and
which is swapped and  which keeps traveling on its path forms indistinguishable physical status.According to Rhee, Hamiltonian Picture is the kind of frame in which The Law of Relativity is satisfied while The Law of Energy Conservation, The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation are violated among The 3 Laws of Movement. In Hamiltonian Picture, the value of the identity of
which keeps traveling on its path forms indistinguishable physical status.According to Rhee, Hamiltonian Picture is the kind of frame in which The Law of Relativity is satisfied while The Law of Energy Conservation, The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation are violated among The 3 Laws of Movement. In Hamiltonian Picture, the value of the identity of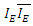 can be used to obtain the deviation of the movement of existence from the shortest path.Therefore, their identity after reaction can be described as follows:
can be used to obtain the deviation of the movement of existence from the shortest path.Therefore, their identity after reaction can be described as follows: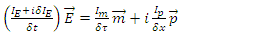
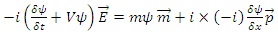
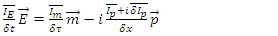
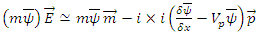
 and
and  means violation of The Law of Energy, The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation, respectively, if
means violation of The Law of Energy, The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation, respectively, if where v is the speed of the existence.
where v is the speed of the existence. and
and 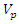 is the term which represents the violation of the 2 laws.Therefore,
is the term which represents the violation of the 2 laws.Therefore,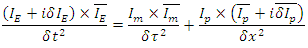 is
is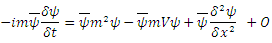 where O is the term which is so small that it can be ignored.or
where O is the term which is so small that it can be ignored.or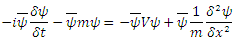 which is the Hamiltonian function of the fermion
which is the Hamiltonian function of the fermion 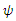 .The term
.The term  is related to the violation of The Law of Energy Conservation. If
is related to the violation of The Law of Energy Conservation. If  is the representation of macroscopic existence, this violation must be compensated by exchanging real macroscopic electric photon. The further violation of the value of the term
is the representation of macroscopic existence, this violation must be compensated by exchanging real macroscopic electric photon. The further violation of the value of the term 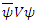 is
is 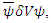 and it represents further violation of The Law of Energy Conservation by the entire microscopic part of system fermion + photon and the macroscopic one must satisfy following equation:
and it represents further violation of The Law of Energy Conservation by the entire microscopic part of system fermion + photon and the macroscopic one must satisfy following equation: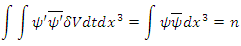 n can be any integer larger than 0.According to Rhee, there is also Lagrangian Picture in which The Law of Energy Conservation is satisfied while The Law of Relativity and The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation are violated among The 3 Laws of Movement.Therefore, their identity after reaction can be described as follows:
n can be any integer larger than 0.According to Rhee, there is also Lagrangian Picture in which The Law of Energy Conservation is satisfied while The Law of Relativity and The Law of Speed Limit and The Law of Momentum Conservation are violated among The 3 Laws of Movement.Therefore, their identity after reaction can be described as follows: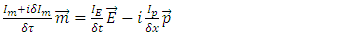
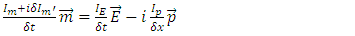
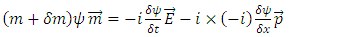
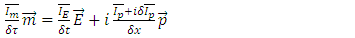
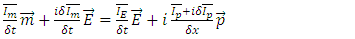
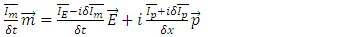
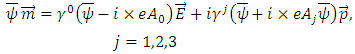
 and
and 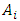 means the violation of energy conservation, speed limit and momentum conservation respectively of microscopic existence, wave. This violation must be compensated by real photon to satisfy The 3 Laws of Movement. Therefore,
means the violation of energy conservation, speed limit and momentum conservation respectively of microscopic existence, wave. This violation must be compensated by real photon to satisfy The 3 Laws of Movement. Therefore,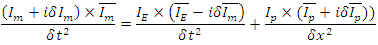 is
is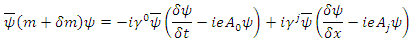 Where
Where 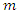 is fixed, and
is fixed, and 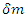 is variation of mass m.Above equation can be arranged to the following form:
is variation of mass m.Above equation can be arranged to the following form: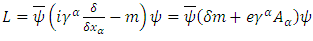
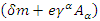 means the net rate of the change of the traveling path of
means the net rate of the change of the traveling path of 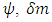 means the net rate of the change caused by the fermion itself and
means the net rate of the change caused by the fermion itself and 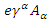 is the net rate of the change caused by external photon, and function L is called Dirac Lagrangian. Assuming that
is the net rate of the change caused by external photon, and function L is called Dirac Lagrangian. Assuming that 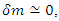
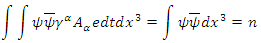 n can be any integer larger than 0.
n can be any integer larger than 0.
 if there is no internal loop around the vertex, and if there is one loop, then
if there is no internal loop around the vertex, and if there is one loop, then 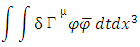 where
where  is the amplitude for internal loop obtained by the application of the other Feynman rules.Following Feynman rules must be applied to both microscopic and macroscopic one: 1. Each microscopic and macroscopic amplitude must be same if the number of fermions and bosons which are involved in calculating the amplitude is very big (N >> 1).
is the amplitude for internal loop obtained by the application of the other Feynman rules.Following Feynman rules must be applied to both microscopic and macroscopic one: 1. Each microscopic and macroscopic amplitude must be same if the number of fermions and bosons which are involved in calculating the amplitude is very big (N >> 1).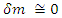 in equation (16). Applying equation (4), and if
in equation (16). Applying equation (4), and if 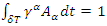 and
and 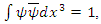 what the value of M becomes in the relatively short period of time is:
what the value of M becomes in the relatively short period of time is: 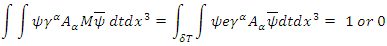 where
where 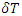 means the relatively short period of time between
means the relatively short period of time between 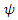 and
and 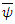 changing their energy and momentum by
changing their energy and momentum by 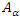 during the time. For the value of the above whole integration to be integer (1, or 0), the charge e must be 1 or 0 if
during the time. For the value of the above whole integration to be integer (1, or 0), the charge e must be 1 or 0 if 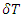 is relatively short. Both values 1 and 0 are possible because of additional Feynman rules for macroscopic existence. As
is relatively short. Both values 1 and 0 are possible because of additional Feynman rules for macroscopic existence. As  increases to infinity, and if
increases to infinity, and if  is integer,
is integer,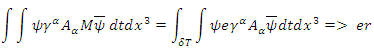 And e must converge to one fixed value (the renormalized coupling constant) for macroscopic and microscopic amplitude to be same.
And e must converge to one fixed value (the renormalized coupling constant) for macroscopic and microscopic amplitude to be same.
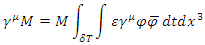 where
where 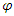 is a new kind of wave function which represents the internal deviation (or uncertainty) from the gravitational shortest path of figure 1.
is a new kind of wave function which represents the internal deviation (or uncertainty) from the gravitational shortest path of figure 1.  is real number which make the value of the following equation 1:
is real number which make the value of the following equation 1: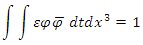 Then the scattering amplitude of Feynman Diagram figure 2 must have the following form:
Then the scattering amplitude of Feynman Diagram figure 2 must have the following form: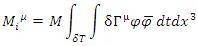 Where
Where  is the term calculated by the method obtained from the Feynman diagram according to current quantum mechanics, and
is the term calculated by the method obtained from the Feynman diagram according to current quantum mechanics, and 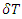 is the interval of time integration.According to Peskin,
is the interval of time integration.According to Peskin,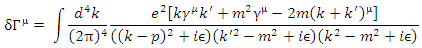 Therefore, the scattering amplitude of combined Feynman Diagram figure 1 and figure 2, M’ can be obtained by the following way:
Therefore, the scattering amplitude of combined Feynman Diagram figure 1 and figure 2, M’ can be obtained by the following way: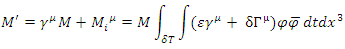
 energy part of identity of the wave function
energy part of identity of the wave function 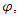 converges to
converges to 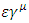 when the
when the 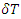 goes to infinity for this microscopic amplitude to be same as macroscopic one However, when
goes to infinity for this microscopic amplitude to be same as macroscopic one However, when 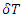 approaches to zero,
approaches to zero, 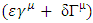 converges to
converges to 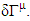 The one way to express this effect is to introduce following transformation like Pauli-villa regularization:
The one way to express this effect is to introduce following transformation like Pauli-villa regularization: 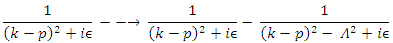 And let
And let 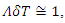
 . Using this equation, one can obtain the same value to the physical observable such as anomalous magnetic moment.
. Using this equation, one can obtain the same value to the physical observable such as anomalous magnetic moment.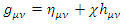 where
where 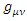 is gravitational ,
is gravitational , 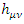 is the graviton field, and
is the graviton field, and 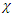 is the coupling constant. However, there is no evidence that such existence like graviton which satisfies The Law of Particle or The Law of Wave does exist. Therefore, instead of graviton, the special identity of energy tensor and metric tensor of matter wave function is going to be used, like the following equation which is suggested by Rhee:
is the coupling constant. However, there is no evidence that such existence like graviton which satisfies The Law of Particle or The Law of Wave does exist. Therefore, instead of graviton, the special identity of energy tensor and metric tensor of matter wave function is going to be used, like the following equation which is suggested by Rhee: 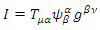 where
where 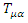 is the energy tensor which represents energy of fermion,
is the energy tensor which represents energy of fermion, 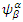 is wave function,
is wave function, 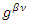 metric tensor. To make explanation simple, the wave function is assumed to be unity. Therefore, the identity is:
metric tensor. To make explanation simple, the wave function is assumed to be unity. Therefore, the identity is: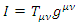 If the following identity
If the following identity 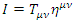 represents the identity of electron in inertial reference frame, and the gravitation is applied so that metric tensor is changed to
represents the identity of electron in inertial reference frame, and the gravitation is applied so that metric tensor is changed to  , then the identity becomes:
, then the identity becomes: The identity above is not the identity of electron (fermion with electron mass m) anymore because
The identity above is not the identity of electron (fermion with electron mass m) anymore because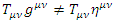 Therefore, the fermion which was electron when gravitational field was empty becomes the fermion with the different mass m’
Therefore, the fermion which was electron when gravitational field was empty becomes the fermion with the different mass m’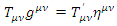 where
where 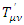 represents fermion with the mass m’When analyzing the quantum mechanical process in non-inertial reference, the way of calculating the scattering process is the same as inertial reference frame with the same Feynman rules as inertial reference frame one, except that the mass m must be changed to m’ which is obtained by the equation:
represents fermion with the mass m’When analyzing the quantum mechanical process in non-inertial reference, the way of calculating the scattering process is the same as inertial reference frame with the same Feynman rules as inertial reference frame one, except that the mass m must be changed to m’ which is obtained by the equation: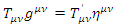 There is another way to obtain scattering amplitude of quantum mechanical process in non-inertial reference frame. This way of calculation can be explained by the following equation:
There is another way to obtain scattering amplitude of quantum mechanical process in non-inertial reference frame. This way of calculation can be explained by the following equation: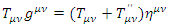 where
where 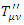 represents “virtual photon field” for compensation for the changing of the reference frame from non-inertial to inertial reference frame. In Feynman Diagram, this compensation can be described by photon field, which doesn’t exist in the reality but just exists for the description of “non-inertial reference frame” like the following diagram:
represents “virtual photon field” for compensation for the changing of the reference frame from non-inertial to inertial reference frame. In Feynman Diagram, this compensation can be described by photon field, which doesn’t exist in the reality but just exists for the description of “non-inertial reference frame” like the following diagram:
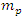 because the real photon field must be added by the “compensation” of the non-energy conservation term
because the real photon field must be added by the “compensation” of the non-energy conservation term 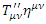 . Therefore, the following quantum mechanical process represented by Feynman diagram
. Therefore, the following quantum mechanical process represented by Feynman diagram
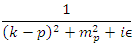 Instead of
Instead of 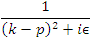
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML