Peter Okidi
Teacher, Bachelor’s of Science Degree, PGDE (Makerere University Uganda)
Correspondence to: Peter Okidi, Teacher, Bachelor’s of Science Degree, PGDE (Makerere University Uganda).
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Gravitational nature of space-time amalgamates Quantum gravity, Newtonian gravity and general theory of relativity to achieve a single integrated gravitational theory. The Weaker the gravitational potential, the faster the course of time, time dilation than official time. Since time and speed of light are inverse to the magnitude of gravity, space-time, and speed of light are considered as factors of gravitational effect. Time passes differently for the pair of identical atom clocks place in different gravitational fields. The magnitude of time and gravity of a specific location can therefore be explained by a single equation (Gravitational nature of space-time equation). 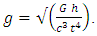 Relative differences in the acceleration due to gravity (g), relative differences in space-time (t), relative difference in the speed of light (an equivalent to relative difference in the speed of graviton) (c), Gravitational constant (G), Planck’s constant (h). Gravitational nature of space-time equation (theory), provide a universal explanation for the gravitational association of matter, space-time and speed. The theory of gravitational nature of space-time is applicable in the functioning of global positioning system, explanation of gravitational wave. Since time ticks at rates differently for different gravitational fields, implies gravity is time in nature.
Relative differences in the acceleration due to gravity (g), relative differences in space-time (t), relative difference in the speed of light (an equivalent to relative difference in the speed of graviton) (c), Gravitational constant (G), Planck’s constant (h). Gravitational nature of space-time equation (theory), provide a universal explanation for the gravitational association of matter, space-time and speed. The theory of gravitational nature of space-time is applicable in the functioning of global positioning system, explanation of gravitational wave. Since time ticks at rates differently for different gravitational fields, implies gravity is time in nature.
Keywords:
Gravitational time dilation, Special relativity, Graviton, Newtonian mechanics, and quantum mechanics
Cite this paper: Peter Okidi, Gravitational Nature of Space-Time, International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Vol. 7 No. 2, 2017, pp. 36-39. doi: 10.5923/j.ijtmp.20170702.03.
1. Introduction
We live in a very complex universe were a more accurate theory which incorporates all complexity is required.This research aims to relate Quantum gravity, Newtonian gravity and general theory of relativity to achieve a single gravitational theory.Quantum gravity describes gravity according to the principle of quantum mechanics, quantum gravity description of gravity is limited to quantum matter (particle).Newtonian gravity describes gravity according to the principle of Newtonian mechanics. Newtonian gravity is limited to constant mass and is not applicable to the subatomic particle moving at near the speed of light.The general theory of relativity describes gravity according to classical physics. General relativity accounts for every classical force but it’s not able to fully incorporate quantum mechanics without approximation.Consider a pair of identical atom clocks, one was placed on top of a mount Sunapee and other was place on at sea level, how will time pass for each of the two atomic clock? What will be the time difference when the two atomic clock are reunited after 4 days?Space-time and speed of light (speed of graviton) are factors of gravitational effect because time passes inversely to the magnitude of gravity and speed of light (speed of graviton) travels inversely to the magnitude of gravity.Gravitational nature of space-time equation (theory) describes gravity based on Planck’s constant, gravitational constant, space time and speed of graviton (speed of light).
2. Derivation of a Single Unified Gravitational Equation
Consider a single graviton particle moving at speed of light c in a gravitational field. From point A to B along the direction of the gravitational field.The speed of light c (an equivalent to speed of graviton) is considered to be constant, hence the rate of change distance per period is constant.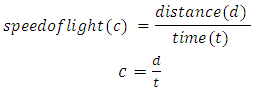 | (1) |
The acceleration (a) of the graviton from point A to point B is given as.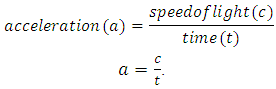 | (2) |
Substituting equation (1) into equation (2)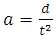 | (3) |
From newton’s second law of motion, the force due to graviton particle in motion (acceleration) is equal to the mass times the acceleration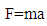 | (4) |
From the newton’s laws of gravitational force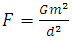 | (5) |
From equation 4 and equation 5 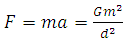 | (6) |
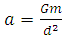 | (7) |
Substituting equation 3 into equation 7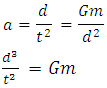 | (8) |
From equation 1, 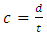 Speed of Light Square can be expressed as
Speed of Light Square can be expressed as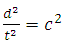 | (9) |
Substituting equation 9 into equation 8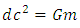 | (10) |
From Einstein equation 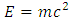 | (11) |
Planck-Einstein relation connects the particulate quantum energy (E) with its associated wave frequency (f)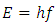 | (12) |
Energy of quantum particle travelling at speed of light given by 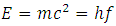
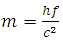 | (13) |
Substituting equation 13 into equation 10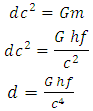 | (14) |
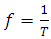 | (15) |
Substituting equation 15 into equation14 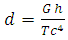 | (16) |
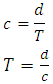 | (17) |
Substituting equation 17 into equation 16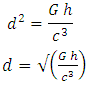 | (18) |
Acceleration is given by 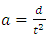
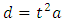 | (19) |
Substituting equation 19 into 18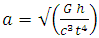 | (20) |
Considering acceleration to be equivalent to gravitational acceleration g.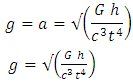 | (21) |
Derived Gravitational nature of space time equation (single unified gravitational equation)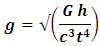
3. Experimental Design Required to Verify the Derived Equation
Instruments required are Gravimeter (gravity), Laser interferometer (speed of light) and Atomic clock (time).MethodTime is measured using an atomic clock for a duration of 4days (345600 seconds) at different altitudes. The data collected is computed to find the difference in time for one second.“NB” Its impossible measure Speed of graviton directly instead speed of light is measured which is conceded to be an equivalent to speed of graviton. Speed of light is measured at sea level and at mountain peak and data computed as followsRelative difference in speed of light at sea level and at mountain top = (Speed of light at sea level minus speed of light at mountain peak)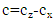 Gravity is measured at sea level and at mountain peak and data computed as followsRelative difference in gravity at sea level and at mountain peak = (Acceleration due to gravity at the sea level)-(acceleration due to gravity at mountain top)
Gravity is measured at sea level and at mountain peak and data computed as followsRelative difference in gravity at sea level and at mountain peak = (Acceleration due to gravity at the sea level)-(acceleration due to gravity at mountain top)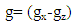 Results
ResultsFigure 1. Table of results
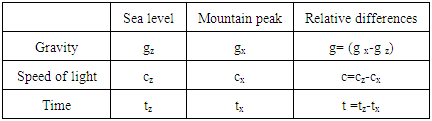 |
| |
|
4. Calculation
Consider time difference between mount Sunapee and sea level to be 20 nanoseconds after 4 daysConvert 4 days into seconds; 4days is equivalent as 345600seconds.Time difference between mount Sunapee and sea level was taken after a duration of 345600seconds, therefore 345600seconds is equated to 20nanoseconds.Time difference between mount Sunapee and sea level after duration one seconds = (20/345600) nanosecondsTime difference (t) = (20/345600) nanoseconds = (5.787037037037037 × 10-14seconds)Time difference (t4) = (1.215665478461× 10-53 s4)Consider the gravity at sea level =9.80665 ms-2The gravity at mount Sunapee peak =9.7975 ms-2The difference in the gravity at sea level and mount Sunapee g =0.00915 ms-2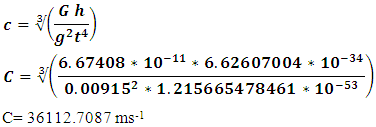 Relative difference in speed of light at mount Sunapee and sea level will be 36112.7087 ms-1.DiscussionA "positive" proof of general relativity is based on the fact that clocks works faster or slower when placed in different places within the gravitational potential of the Earth. For example, an atomic clock at the peak of Mountain runs faster than at sea level. Dilation of time has often been painted as the result of different quantities of gravitational potential that mysteriously affect the functioning of the clock energy. A gravitational time dilation is a form of time dilation were the time difference between two events as measured by observers located at distances varying from a gravitational mass. The weaker gravitational potential the faster time passes. Albert Einstein has originally expected this effect in his theory of relativity and has since been confirmed by tests of general relativity. This has been shown to point out that atomic clocks placed at different gravitational potential shows difference in time. The effects found in these experiments are related to Earths gravitational potential and are extremely small, measured in nanosecond differences.The cause of the dilation of gravitational times can be attributed to a simple Lorentz transformation of the mass resulting from the different speeds depleting these sites. Increased slope elevation speed causes an increase in the mass of the internal clock mechanism, and this reduces the clock speed through the retention of the angular momentum.A second lower factor in this mass of Lorentz transformation is the rotational speed of rotation of the earth to the latitude of these two places. To calculate the speed of a clock on the mount Sunapee peak, it is necessary only to determine the velocity vector produced by combining the speed with the horizontal vertical speed rotation. Lorentz's transformation at this speed increases the mass and slows down ticking in equal amounts. However, the greater the sea levels escape speed the slower the clock works.The difference between a velocity vector drawn form a position in space and vector acceleration of gravitational potential is the escape velocity is only a geometric potential gravitational position in space and is represented as part of the physical space structure.Space-time and speed of light (speed of graviton) are factors of gravitational effect because time passes inversely to the magnitude of gravity and speed of light travels inversely to the magnitude of gravity.Gravitational nature of space-time theory is an amalgamation of quantum gravity, Newtonian gravity and general theory of relativity to achieve a single gravitational (Gravitational nature of space time) theory.
Relative difference in speed of light at mount Sunapee and sea level will be 36112.7087 ms-1.DiscussionA "positive" proof of general relativity is based on the fact that clocks works faster or slower when placed in different places within the gravitational potential of the Earth. For example, an atomic clock at the peak of Mountain runs faster than at sea level. Dilation of time has often been painted as the result of different quantities of gravitational potential that mysteriously affect the functioning of the clock energy. A gravitational time dilation is a form of time dilation were the time difference between two events as measured by observers located at distances varying from a gravitational mass. The weaker gravitational potential the faster time passes. Albert Einstein has originally expected this effect in his theory of relativity and has since been confirmed by tests of general relativity. This has been shown to point out that atomic clocks placed at different gravitational potential shows difference in time. The effects found in these experiments are related to Earths gravitational potential and are extremely small, measured in nanosecond differences.The cause of the dilation of gravitational times can be attributed to a simple Lorentz transformation of the mass resulting from the different speeds depleting these sites. Increased slope elevation speed causes an increase in the mass of the internal clock mechanism, and this reduces the clock speed through the retention of the angular momentum.A second lower factor in this mass of Lorentz transformation is the rotational speed of rotation of the earth to the latitude of these two places. To calculate the speed of a clock on the mount Sunapee peak, it is necessary only to determine the velocity vector produced by combining the speed with the horizontal vertical speed rotation. Lorentz's transformation at this speed increases the mass and slows down ticking in equal amounts. However, the greater the sea levels escape speed the slower the clock works.The difference between a velocity vector drawn form a position in space and vector acceleration of gravitational potential is the escape velocity is only a geometric potential gravitational position in space and is represented as part of the physical space structure.Space-time and speed of light (speed of graviton) are factors of gravitational effect because time passes inversely to the magnitude of gravity and speed of light travels inversely to the magnitude of gravity.Gravitational nature of space-time theory is an amalgamation of quantum gravity, Newtonian gravity and general theory of relativity to achieve a single gravitational (Gravitational nature of space time) theory. 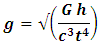 g -relative differences the acceleration due to gravity.t -relative differences in space-time.c- The Relative difference in the speed of light (an equivalent to speed of graviton).G - Gravitational constant (6.67408 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2)h- Planck’s constant (6.62607004 × 10-34 m2 kg s-1)The theory of gravitational nature of space-time, provide a universal explanation for the gravitational association of matter, space-time and speed. The theory of gravitational nature of space-time is applicable in the functioning of global positioning system, explanation of gravitational wave.
g -relative differences the acceleration due to gravity.t -relative differences in space-time.c- The Relative difference in the speed of light (an equivalent to speed of graviton).G - Gravitational constant (6.67408 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2)h- Planck’s constant (6.62607004 × 10-34 m2 kg s-1)The theory of gravitational nature of space-time, provide a universal explanation for the gravitational association of matter, space-time and speed. The theory of gravitational nature of space-time is applicable in the functioning of global positioning system, explanation of gravitational wave.
5. Conclusions
Gravitational nature of space-time and speed of light (speed of graviton) are correlating aspects centered on the magnitude of gravity, the speed of light (speed of graviton) and flow of space-time. Since time passes inversely to the magnitude of gravity and speed of light (speed of graviton) travels inversely to the magnitude of gravity, space-time, and speed of light (speed of graviton) are both factors of gravitational effect. Time passes slowly in strong gravitational field compared to the weak gravitational field. The speed of light (speed of graviton) travels faster in weak gravitational field compare to a strong gravitational field. Time slows down and speed of light (speed of graviton) decreases with increasing gravitational field verse versus.Since time passes differently for the pair of identical atom clocks place in different gravitational fields, there will be a difference in time when the atomic clocks are reunited after some duration of 4 days, this because gravity is time in nature.The magnitude of time and gravity of a specific location can therefore be explained by a single equation (Gravitational nature of space-time equation).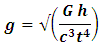
References
| [1] | Albert Einstein, On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies, Annalen der Physik 17 (1905) 891. |
| [2] | Isaac Newton, Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (“Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy”), (London, 1687). |
| [3] | Gupta, S. N. (1954). "Gravitation and Electromagnetism". Physical Review. 96 (6): 1683–1685. Bibcode: 1954PhRv...96.1683G. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.96.1683. |
| [4] | Sakurai, J. J.; Napolitano, Jim J. (2010-07-14). Modern Quantum Mechanics (2 ed.). Pearson. p. 68. ISBN 978-0-8053-8291-4. |



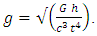 Relative differences in the acceleration due to gravity (g), relative differences in space-time (t), relative difference in the speed of light (an equivalent to relative difference in the speed of graviton) (c), Gravitational constant (G), Planck’s constant (h). Gravitational nature of space-time equation (theory), provide a universal explanation for the gravitational association of matter, space-time and speed. The theory of gravitational nature of space-time is applicable in the functioning of global positioning system, explanation of gravitational wave. Since time ticks at rates differently for different gravitational fields, implies gravity is time in nature.
Relative differences in the acceleration due to gravity (g), relative differences in space-time (t), relative difference in the speed of light (an equivalent to relative difference in the speed of graviton) (c), Gravitational constant (G), Planck’s constant (h). Gravitational nature of space-time equation (theory), provide a universal explanation for the gravitational association of matter, space-time and speed. The theory of gravitational nature of space-time is applicable in the functioning of global positioning system, explanation of gravitational wave. Since time ticks at rates differently for different gravitational fields, implies gravity is time in nature.
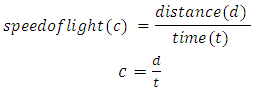
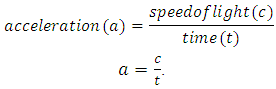
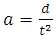
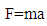
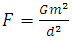
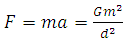
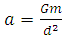
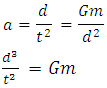
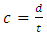 Speed of Light Square can be expressed as
Speed of Light Square can be expressed as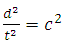
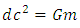
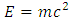
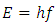
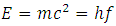
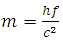
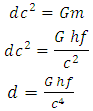
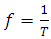
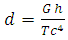
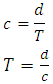
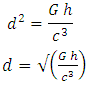
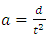
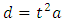
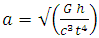
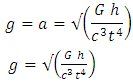
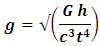
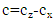 Gravity is measured at sea level and at mountain peak and data computed as followsRelative difference in gravity at sea level and at mountain peak = (Acceleration due to gravity at the sea level)-(acceleration due to gravity at mountain top)
Gravity is measured at sea level and at mountain peak and data computed as followsRelative difference in gravity at sea level and at mountain peak = (Acceleration due to gravity at the sea level)-(acceleration due to gravity at mountain top)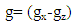 Results
Results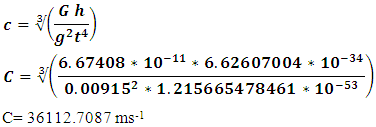 Relative difference in speed of light at mount Sunapee and sea level will be 36112.7087 ms-1.DiscussionA "positive" proof of general relativity is based on the fact that clocks works faster or slower when placed in different places within the gravitational potential of the Earth. For example, an atomic clock at the peak of Mountain runs faster than at sea level. Dilation of time has often been painted as the result of different quantities of gravitational potential that mysteriously affect the functioning of the clock energy. A gravitational time dilation is a form of time dilation were the time difference between two events as measured by observers located at distances varying from a gravitational mass. The weaker gravitational potential the faster time passes. Albert Einstein has originally expected this effect in his theory of relativity and has since been confirmed by tests of general relativity. This has been shown to point out that atomic clocks placed at different gravitational potential shows difference in time. The effects found in these experiments are related to Earths gravitational potential and are extremely small, measured in nanosecond differences.The cause of the dilation of gravitational times can be attributed to a simple Lorentz transformation of the mass resulting from the different speeds depleting these sites. Increased slope elevation speed causes an increase in the mass of the internal clock mechanism, and this reduces the clock speed through the retention of the angular momentum.A second lower factor in this mass of Lorentz transformation is the rotational speed of rotation of the earth to the latitude of these two places. To calculate the speed of a clock on the mount Sunapee peak, it is necessary only to determine the velocity vector produced by combining the speed with the horizontal vertical speed rotation. Lorentz's transformation at this speed increases the mass and slows down ticking in equal amounts. However, the greater the sea levels escape speed the slower the clock works.The difference between a velocity vector drawn form a position in space and vector acceleration of gravitational potential is the escape velocity is only a geometric potential gravitational position in space and is represented as part of the physical space structure.Space-time and speed of light (speed of graviton) are factors of gravitational effect because time passes inversely to the magnitude of gravity and speed of light travels inversely to the magnitude of gravity.Gravitational nature of space-time theory is an amalgamation of quantum gravity, Newtonian gravity and general theory of relativity to achieve a single gravitational (Gravitational nature of space time) theory.
Relative difference in speed of light at mount Sunapee and sea level will be 36112.7087 ms-1.DiscussionA "positive" proof of general relativity is based on the fact that clocks works faster or slower when placed in different places within the gravitational potential of the Earth. For example, an atomic clock at the peak of Mountain runs faster than at sea level. Dilation of time has often been painted as the result of different quantities of gravitational potential that mysteriously affect the functioning of the clock energy. A gravitational time dilation is a form of time dilation were the time difference between two events as measured by observers located at distances varying from a gravitational mass. The weaker gravitational potential the faster time passes. Albert Einstein has originally expected this effect in his theory of relativity and has since been confirmed by tests of general relativity. This has been shown to point out that atomic clocks placed at different gravitational potential shows difference in time. The effects found in these experiments are related to Earths gravitational potential and are extremely small, measured in nanosecond differences.The cause of the dilation of gravitational times can be attributed to a simple Lorentz transformation of the mass resulting from the different speeds depleting these sites. Increased slope elevation speed causes an increase in the mass of the internal clock mechanism, and this reduces the clock speed through the retention of the angular momentum.A second lower factor in this mass of Lorentz transformation is the rotational speed of rotation of the earth to the latitude of these two places. To calculate the speed of a clock on the mount Sunapee peak, it is necessary only to determine the velocity vector produced by combining the speed with the horizontal vertical speed rotation. Lorentz's transformation at this speed increases the mass and slows down ticking in equal amounts. However, the greater the sea levels escape speed the slower the clock works.The difference between a velocity vector drawn form a position in space and vector acceleration of gravitational potential is the escape velocity is only a geometric potential gravitational position in space and is represented as part of the physical space structure.Space-time and speed of light (speed of graviton) are factors of gravitational effect because time passes inversely to the magnitude of gravity and speed of light travels inversely to the magnitude of gravity.Gravitational nature of space-time theory is an amalgamation of quantum gravity, Newtonian gravity and general theory of relativity to achieve a single gravitational (Gravitational nature of space time) theory. 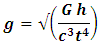 g -relative differences the acceleration due to gravity.t -relative differences in space-time.c- The Relative difference in the speed of light (an equivalent to speed of graviton).G - Gravitational constant (6.67408 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2)h- Planck’s constant (6.62607004 × 10-34 m2 kg s-1)The theory of gravitational nature of space-time, provide a universal explanation for the gravitational association of matter, space-time and speed. The theory of gravitational nature of space-time is applicable in the functioning of global positioning system, explanation of gravitational wave.
g -relative differences the acceleration due to gravity.t -relative differences in space-time.c- The Relative difference in the speed of light (an equivalent to speed of graviton).G - Gravitational constant (6.67408 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2)h- Planck’s constant (6.62607004 × 10-34 m2 kg s-1)The theory of gravitational nature of space-time, provide a universal explanation for the gravitational association of matter, space-time and speed. The theory of gravitational nature of space-time is applicable in the functioning of global positioning system, explanation of gravitational wave. 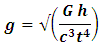
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML