Branko Mišković
Independent, Novi Sad, Serbia
Correspondence to: Branko Mišković, Independent, Novi Sad, Serbia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
Looking for the deeper essence of natural phenomena and minimal number of physical laws describing them, a hypothetical vacuum medium is stratified into structural layers, as the levels of observation of respective processes. Instead of a fluidic, the dielectric medium successfully explains all EM phenomena at least. More or less convincingly, inertia and gravitation are explained on EM bases, and the speed of light propagation, with respective reference frame, is conditioned by gravitation itself. The unification of physics is thus initialized, just on the advanced classical bases.
Keywords:
Philosophy, Cosmology, Gravitation, Vacuum medium, Reference frame
Cite this paper: Branko Mišković, Medium of Natural Phenomena, International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Vol. 4 No. 4, 2014, pp. 143-150. doi: 10.5923/j.ijtmp.20140404.01.
1. Introduction
Development of physics is dealt with material bodies or particles, accessible to perception or measurement. The finer structural levels, inaccessible even for instruments, are left to speculation, founded on the experience from already studied structures, and obeying the similar formal logic. Though the eternal dilemma – between infinite divisibility of matter and some final constituent particles – is still not resolved, it may be overcome. Namely, countless phenomenal bodies consist of very great number of chemical compounds, these ones – of a hundred of respective elements, and their own atoms – of a few stable particles only. The regressive sequence of these numbers just announces its – at least conditional – soon end. However, the former disappointment by divisible atoms directs the thoughts towards some further division even of the elementary particles. Their formal features are tried to explain by so called quarks, as respective constituent parts. This senseless name as if expects their own divisibility. In this sense, the abstract string theory is founded speculatively, without any palpable empirical bases.On the other hand, free space between material bodies, known as vacuum, always imposed the greatest quandaries in both, physics and philosophy. All physical forces and respective fields at least point to some their substratum. In analogy with the cruder waves at material media, possible interpretation of EM waves at vacuum demands the medium of their propagation. Thus used antique term ether was so abstract that even its aggregate state was uncertain. Instead, the principle of relativity and invariant speed of light were postulated at foundation of special relativity (SRT), with explicit negation of vacuum medium, as possible preferred frame. In spite of obvious inconsistencies of this speculation, it is accepted – at least conditionally, in the absence of a better solution. After its incorporation into modern physics, nobody more thinks about conditions of its acceptance. However, the production and annihilation of the particle pairs points to a real vacuum medium. The concepts of the invisible mass and energy cannot be even tried anyhow interpreted without such a medium.EM theory is the discipline nearest to vacuum medium. Though its differential equations were borrowed from fluid mechanics, the greater number of EM than mechanical quantities disabled the full analogy. By addition of temporal axis, this difficulty can be overcome in 4D space, with final elaboration of EM theory. After reduction of inertial mass to EM phenomena [1, 2], the opposite procedure of rational interpretation of all EM quantities by mechanics of some ideal fluid is tried in [3, 4]. The static, kinetic and dynamic forces, dependent on a distance, motion and acceleration, are to be explained by the compressible, super-fluidic and inert medium. However, this concept applied to the established equations calls in question their algebraic signs at least. This difficulty can be overcome by dielectric, non-resistive and reactive medium [5, 6]. The central part of this text considers the inconveniences of the former, as well as conveniences of the latter model of the vacuum medium.
2. Natural Philosophy
Physical processes develop in various constellations, from elementary particles – up to celestial bodies, in accord with respective physical laws. Going into the opposite direction, the regressive number of the elements is already mentioned: from countless bodies, via numerous constitutions of their molecules and a hundred types of atoms, up to a few distinct stable elementary particles only. The physical laws may be expected to follow a similar regress of their number and complexity. Not only that modern development of physics does not indicate such reduction, but shows just the opposite tendency. Instead of mutual relation of the known physical quantities and respective laws relating them, the increasing number of various formal concepts is included into separate, mutually incompatible, speculative theories. This tendency does not reflect a natural anomaly, but the hopeless scientific wander. This course is habituated and established, without attempts of its essential re-examination.However, we are not obliged to follow this course. The laws of mechanics are already reduced to EMT in [1-6], and its own laws will be explained by the three medium features. Nevertheless, the former laws are not neglected nor excluded from further application, but still serve as the convenient descriptions, in respective physical disciplines. Apart from the various approaches, the manner of thinking is determined by the scientific level of consideration. In this sense, there seems that physical laws somehow depend on the thinkers themselves. For instance, though a naïve observer directly perceives the daily path between sunrise and sunset, the science advocates the rotation of Earth. Similar relations in other sciences conditioned the foundation of various schools of subjective philosophies. Unfortunately, some of them also take place in the modern physics. Such a view in quantum theory neglects the events that are not, or cannot be, directly subjectively registered. With reliance on similar philosophy, SRT connected its reference frame to the passive observer or, at least, – to his measuring instruments.Physics is looking for objective natural facts, their formal relations and rational interpretations, instead of superficial experience and subjective impressions, or arbitrary formal concepts and unfounded speculation. The confrontation of empirical facts and intuitive ideas, their formal relations and /or rational interpretations, would finally follow into some acceptable results. Although subjective cognition establishes (more or less adequate) image of reality, it cannot influence the reality itself. The final exposition of physical theory must not contradict to any of the scientific criteria. If some of them, as the empirical evidence, are not applicable, the remaining ones should be more convincing. Just this condition is not satisfied in the speculations about Big Bang, black holes, and especially – in the string theory. Unlike scientific criteria at least implicitly understood in the 19th century, the sense of their application is finally lost in 20th century. With the vague or undefined technical terms and arbitrary formal concepts, modern physicists apply some speculative methodologies, as the thought experiments are or were.
3. Principal Views
Some doctrinal dilemmas and their solutions, in the form of respective principal views, determine actual development of physics. In such a case, the substantial fields, as volume densities of the continual scalar quantities, can be expressed alternatively, by the concentrations of respective particles. The convenience of the continual or discrete approaches depends on the levels of observation. More or less regularly, these two approaches have alternate periodically during the scientific history. Such the sequence is conditioned by the observed strata of the structures, thus also manifest in the zooming process or respective scientific development. As a rule, these two approaches accord to the predominance of the rational and formal investigation, respectively. In the former case, all scientific facts are understood as somehow mutually related. Active imagination of a process does not need its verbal descriptions, up to the public presentation. The classical field theory is such a typical example. In the latter case, formal features of the particles and their verbal terms are extremely emphasised. The particular features are considered rather separately, as the independent entities. Quark theory is the typical such example.In the next case, Maxwell’s differential equations define the carriers by field derivatives, and Thomson’s algebraic relations – the existence of one, by motion of the other EM field, at a point. Considering the moving fields – as the real entities, the field motion as if expresses the higher physical essence. However, the formal sense of the two algebraic relations exceeds the frames of the comparison, and so is restricted to the homogeneous speeds of the rigid moving fields, stably oriented in space. The applications of the three basic sets of EM theory further explicate their comparison. The algebraic relations directly observe moving bodies with their associated fields, central laws – kinematical states of punctual charges, and the differential equations – respective states of the medium. This hierarchy may be supported by the reduction of a field motion to successive changes in the medium, further reducible to some micro-motions in the medium. Though the macro-motions are thus reduced to visual impressions, they are followed by respective energy, as the final, very abstract, moving quantity. In the final instance, natural phenomena are transitory, with the phases of their formation, duration & dissolution. In the duration of a complex structure, some its components may be in formation, and some others – in dissolution, thus commonly manifest as the entity transformation. In the first and last phases, there appears considerable predominance of respective micro-process. Such the processes of anabolism, metabolism & catabolism are caused by respective chemical substances. The three physical substances – mass, energy & electricity – play the similar roles. Certain mass constitutes each structure, the energy partakes in its transformation, and electricity tends to its final dissolution, by attraction and annihilation of the two polarities. The three EM forces – static, kinetic and dynamic – related with three kinematical states – position, motion and acceleration – form such the triad. Similar triads are met in all structural layers, up to the highest – Holy Trinity. Owing to some similarities in a pair of the three members, the trinities are frequently treated approximately, as the apparent dualities.
4. Possible Cosmology
Kant’s antinomy between the finite or infinite cosmos is successfully resolved by Riemannian model of space, with three circular axes. The two field distributions – of evenly charged sphere and plane – are also reconciled by the same model in [1]. However, the cosmic expansion has not been incorporated into this model. The image of this process in 3D understands the boundary surface and background of the cosmos, being overcome in the model. On the other hand, though included into 4D space, time is understood very formally, or even – relatively. Instead, the lapse of time may be related with the matter motion along respective axis [6]. The equations of EM theory point to the speed 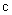 of this process, in the form of a hipper-spherical wave. This model also explains its own global curvature and circular axes. The projection into 3D space relates the cosmic expansion with the lapse of time, thus denying its relativity. Kant’s antinomy between a beginning and end in time – or infinite cosmic duration, can be also resolved, by some circular form of the temporal axis, alike spatial ones.The rectilinear t-axis, with a beginning and without end, implicates the inflationary cosmos, expanding into infinity. The circular t-axis points to the cosmos pulsating between two singularities, as the poles of 4D sphere. The Big Bang is thus followed by the Big Collapse, in the opposite pole. Of course, this process further alternates periodically. Though cosmic wave propagates at the speed
of this process, in the form of a hipper-spherical wave. This model also explains its own global curvature and circular axes. The projection into 3D space relates the cosmic expansion with the lapse of time, thus denying its relativity. Kant’s antinomy between a beginning and end in time – or infinite cosmic duration, can be also resolved, by some circular form of the temporal axis, alike spatial ones.The rectilinear t-axis, with a beginning and without end, implicates the inflationary cosmos, expanding into infinity. The circular t-axis points to the cosmos pulsating between two singularities, as the poles of 4D sphere. The Big Bang is thus followed by the Big Collapse, in the opposite pole. Of course, this process further alternates periodically. Though cosmic wave propagates at the speed 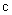 , its projection into 3D space varies. Starting by
, its projection into 3D space varies. Starting by 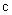 – in the tangential position, at the former pole, the decelerated expansion stops on the equator, with the maximal radius. This is followed by the accelerated contraction, up to the speed
– in the tangential position, at the former pole, the decelerated expansion stops on the equator, with the maximal radius. This is followed by the accelerated contraction, up to the speed 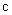 – in the latter pole. However, this model just contradicts to the assumed accelerated expansion, explaining the increasing red shift. Moreover, in spite of the speculations about Big Bang, the cosmic singularities are very difficult to be accepted. If the increasing red shift had none a better explanation, the accelerated expansion and decelerated contraction might be interpreted by some toroidal t-direction, with the cosmos oscillating between its two radii. Apart from the three spatial and one temporal axis, the matter demands a new axis. The zooming of structure – by its volume derivation, from the full cosmos – up to smallest particles, presents the matter by physical points
– in the latter pole. However, this model just contradicts to the assumed accelerated expansion, explaining the increasing red shift. Moreover, in spite of the speculations about Big Bang, the cosmic singularities are very difficult to be accepted. If the increasing red shift had none a better explanation, the accelerated expansion and decelerated contraction might be interpreted by some toroidal t-direction, with the cosmos oscillating between its two radii. Apart from the three spatial and one temporal axis, the matter demands a new axis. The zooming of structure – by its volume derivation, from the full cosmos – up to smallest particles, presents the matter by physical points 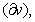 as the minimal relevant volumes. The logarithm of their radii gives the two infinite axis legs, with its zero determined by a unit of length. The motion of observation along this axis is enabled by the technical conversion of invisible into visible signals. The parallel development of chemical and nuclear processes in the same body, and the hierarchical scale of the energetic levels as well, are the indicative expressions of the fifth axis. In the same sense, EM processes develop in a few parallel structural layers. Inductive investigation is usually directed towards the finer, and deductive – towards cruder structures. Starting from the sensory domain, in the middle of the fifth axis, the science probably tends towards the same natural essence, at the common end of the two legs. Alike the former four, the fifth axis may be thus also expected to be somehow circularly closed into itself.
as the minimal relevant volumes. The logarithm of their radii gives the two infinite axis legs, with its zero determined by a unit of length. The motion of observation along this axis is enabled by the technical conversion of invisible into visible signals. The parallel development of chemical and nuclear processes in the same body, and the hierarchical scale of the energetic levels as well, are the indicative expressions of the fifth axis. In the same sense, EM processes develop in a few parallel structural layers. Inductive investigation is usually directed towards the finer, and deductive – towards cruder structures. Starting from the sensory domain, in the middle of the fifth axis, the science probably tends towards the same natural essence, at the common end of the two legs. Alike the former four, the fifth axis may be thus also expected to be somehow circularly closed into itself.
5. Energetic Homogeneity
The action-reaction law expresses the symmetry of two opposite forces. The action, changing the speed and/or path direction of a moving body, is opposed by the inertial and/or centrifugal reactions. This law is generalized to the zero sum of more force fields, as the gradients of respective energy densities (1). The two opposite energy gradients cause the opposite forces, action and reaction. Each of them tends to the even energy distribution in respective structural layer. With the complementary energy distributions in various layers, the summary energy density is constant (2). Though unevenly distributed in particular layers, the full energy density keeps a constant value, as the absolute expression of the energy conservation. The two opposite forces, action & reaction, play the roles in the energy transfer between two respective levels: the former of them invests, and the latter accepts the same energy. The medium reactivity, as one of its features, is thus explained. The zero time derivative of the total energy gives the energy conservation in 4D, known as the zero power of a closed composition.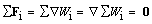 | (1) |
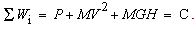 | (2) |
The zero force sum accords to a constant energy density, expressing its conservation. In Bernoulli’s equation (2) – as the typical example, the medium pressure, 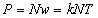 , represents its thermal energy, where
, represents its thermal energy, where 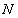 is the concentration of respective molecules, and
is the concentration of respective molecules, and 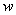 – the average molecular energy, proportional to the medium temperature
– the average molecular energy, proportional to the medium temperature 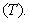 The second middle term represents the kinetic energy of the fluid flows, including its un-manifest half.
The second middle term represents the kinetic energy of the fluid flows, including its un-manifest half. 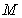 denotes the mass density, and
denotes the mass density, and 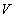 – the speed field of the fluid flow;
– the speed field of the fluid flow; 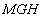 represents the static energy in gravitational field, where
represents the static energy in gravitational field, where 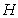 denotes the fluid depth at each point. Without energy transfer with surroundings, this sum keeps its constant value. At running out of the fluid, the static turns into kinetic energies. In addition, the oriented molecular motion causes some transverse pressure downfall, also transformed into motion. Owing to the decreased transverse pressure, two parallel flows attract each other. The two opposite flows form fluid vortices in between, causing the repulsion. Two crosswise flows thus form a torque tending to the same courses. The kinetic interactions are thus explained.In the discrete approach to various structures, the energy conservation – in the sense of its homogeneous density throughout 3D or 4D spaces – can be explained by even concentrations of various types of the particles carrying the different energetic charges. Namely, the particles themselves represent the energy disturbances, just formed on the finer structural levels. Not only that determined classes of these disturbances are mutually different quantitatively, but they also may express the positive or negative variations of the standard energy density on the level of their formation. With respect to the toroidal model of material particles [6], where the positive poles are of the greater mass and energy than the negative ones, the similar relations may be expected in the finer sub-structure of the vacuum medium. On these bases, the energy disturbances – in one, can be compensated by the medium polarization – in the other structural layers. This logic implicates that some of the medium layers or the finest of them may be even in the solid state.
denotes the fluid depth at each point. Without energy transfer with surroundings, this sum keeps its constant value. At running out of the fluid, the static turns into kinetic energies. In addition, the oriented molecular motion causes some transverse pressure downfall, also transformed into motion. Owing to the decreased transverse pressure, two parallel flows attract each other. The two opposite flows form fluid vortices in between, causing the repulsion. Two crosswise flows thus form a torque tending to the same courses. The kinetic interactions are thus explained.In the discrete approach to various structures, the energy conservation – in the sense of its homogeneous density throughout 3D or 4D spaces – can be explained by even concentrations of various types of the particles carrying the different energetic charges. Namely, the particles themselves represent the energy disturbances, just formed on the finer structural levels. Not only that determined classes of these disturbances are mutually different quantitatively, but they also may express the positive or negative variations of the standard energy density on the level of their formation. With respect to the toroidal model of material particles [6], where the positive poles are of the greater mass and energy than the negative ones, the similar relations may be expected in the finer sub-structure of the vacuum medium. On these bases, the energy disturbances – in one, can be compensated by the medium polarization – in the other structural layers. This logic implicates that some of the medium layers or the finest of them may be even in the solid state.
6. Mechanical Medium
A linear rotator, as a structural element, consists of a mass 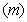 connected by elastic tie to the centre of rotation. Its stretch,
connected by elastic tie to the centre of rotation. Its stretch, 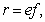 is proportional to the centrifugal force (3a). The division by
is proportional to the centrifugal force (3a). The division by 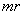 gives the invariant angular speed (3b), dependent on the factors
gives the invariant angular speed (3b), dependent on the factors 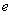 &
&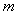 only. At each peripheral speed,
only. At each peripheral speed, 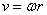 , the force balance is thus kept. The rotator may be substituted by sum of two orthogonal oscillators, of the resonant frequency (3b). On the other hand, the oscillator itself may be also understood as the rotator in the plane of a spatial and structural axes. The multiplication of (3a) by
, the force balance is thus kept. The rotator may be substituted by sum of two orthogonal oscillators, of the resonant frequency (3b). On the other hand, the oscillator itself may be also understood as the rotator in the plane of a spatial and structural axes. The multiplication of (3a) by 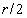 equals the two types of energy (3c), with their final sum (4a). The energy of a structural element is just proportional with the medium temperature,
equals the two types of energy (3c), with their final sum (4a). The energy of a structural element is just proportional with the medium temperature, 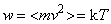 , where
, where 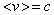 is the average speed. This is nothing else but Einstein’s equation. Its volume derivative gives the speed of wave propagation (4b), as the ratio of energy and mass densities. The interpretations of these two quantities depend on the medium type and respective waves. In general,
is the average speed. This is nothing else but Einstein’s equation. Its volume derivative gives the speed of wave propagation (4b), as the ratio of energy and mass densities. The interpretations of these two quantities depend on the medium type and respective waves. In general, 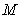 is the full energy density, and
is the full energy density, and 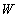 – its active component only, propagating through the transferring layer [5].
– its active component only, propagating through the transferring layer [5].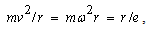 | (3a) |
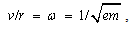 | (3b) |
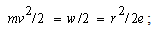 | (3c) |
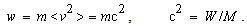 | (4a,b) |
Intermolecular forces link the elementary oscillators, as projections of the rotators. With respect to the weaker linking forces in relation to the internal centripetal ties, they cannot accept at once the complete energy of one oscillating period. The transfer of energy is thus slowed down and prolonged to more periods. Some indispensible phase difference between the adjacent oscillators determines their roles as the action and reaction. The former of them invests, and latter accepts the same energy, thus determining the course of the transfer. In the case of the two mutually linked oscillators, the energy is fully transferred for a number of wave cycles. For the same reasons as before, this one is followed by the inverse process, of the opposite energy transfer. This barter lasts up to energy dissipation into other layers, or – in the ideal non-resistive case – it would thus continue up to infinity.The alternating process of the energy transfer is implicitly considered as the theoretical basis for the barter of photons between two particles, as the modern attempt to explain all EM interactions. Not only that this exchange cannot explain repulsive interactions and satisfy energetic relations, but the resting particles do not oscillate at all. The single transfer of the kinetic energy from a moving particle, in the form of its associated wave, is only evident on the resonant frequency of the other particle, at their close meeting. In the typical natural case, of the continual sequence of such structural oscillators, the wave energy flows along this sequence through 3D space. The energy accumulation in, and discharging – from each element, may be considered as the ‘vertical’ flow along the structural axis. With respect to constant energy current on the path of propagation, the locally increased energy density accords to the decreased speed of propagation. These two facts are mathematically related in [5].
7. Electrical Neutrality
A free electric charge 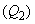 – in the conducting layer or free space, repels equipolar, and attracts opposite bound electricity – of the matter
– in the conducting layer or free space, repels equipolar, and attracts opposite bound electricity – of the matter 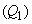 and/or – of vacuum
and/or – of vacuum 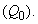 The attracted electricity compensates inserted charge, and repelled electricity forms the flux of electric displacement
The attracted electricity compensates inserted charge, and repelled electricity forms the flux of electric displacement 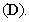 These two processes point to conservation of electric neutrality at each point (5a), where
These two processes point to conservation of electric neutrality at each point (5a), where 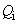 is the charge density in a layer. This relation is confirmed even by Faraday. Some charge inserted into a closed metallic sphere causes certain polarization of the surrounding medium, including the walls of the sphere. Its external surface thus obtains the equipolar, and internal one – the opposite polarities. The discharged external, is found to be equal with inserted charge. This latter inserted into one, forms the divergence of the displacement – in the other layers. With respect to summary neutrality, the full displacement must be closed into itself (5b). Unlike the vortical fields, already closed in 3D, the ‘non-vortical’ static field is thus also closed into itself, but in 5D-space. Therefore, all the types of EM fields, in their respective manners, are circularly closed into themselves.
is the charge density in a layer. This relation is confirmed even by Faraday. Some charge inserted into a closed metallic sphere causes certain polarization of the surrounding medium, including the walls of the sphere. Its external surface thus obtains the equipolar, and internal one – the opposite polarities. The discharged external, is found to be equal with inserted charge. This latter inserted into one, forms the divergence of the displacement – in the other layers. With respect to summary neutrality, the full displacement must be closed into itself (5b). Unlike the vortical fields, already closed in 3D, the ‘non-vortical’ static field is thus also closed into itself, but in 5D-space. Therefore, all the types of EM fields, in their respective manners, are circularly closed into themselves.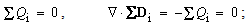 | (5) |
Unlike the above energy conservation, in some amount of its density – at each point, the neutrality means zero charge density at each location. Both facts just accord with the full balance of the two interacting forces at a point. With respect to the greater energies and masses of protons than that of electrons, constituting the usual crude matter, just the same relation may be expected in the substructure of the vacuum medium and its possible particles, or at least – of respective structural fractions. Therefore, the electric neutrality of each location in 3D space, irrespective of the specific material contents or vacuum, may be reduced to respective energetic homogeneity. On the other hand, the condition (5b) may be written in the form (6a) or (6b). The sum of the dielectric displacements is realized in the two non-conducting layers: 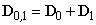 . The free material charge, in the continuity equation (6b), is inserted into the observed location as the displaced conducting electricity. In fact, (6b) is nothing else but the static Maxwell’s equation (10a), being equivalent with the absolute electrical neutrality.
. The free material charge, in the continuity equation (6b), is inserted into the observed location as the displaced conducting electricity. In fact, (6b) is nothing else but the static Maxwell’s equation (10a), being equivalent with the absolute electrical neutrality.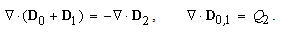 | (6) |
8. EM Fields
The well-known here needed equations of EM theory are presented below; only (7a) & (11a,b) are reaffirmed in the references. Starting from the static potential 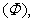 as the medium disturbance, with the two constants – electric
as the medium disturbance, with the two constants – electric 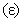 and magnetic
and magnetic 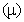 – meaning the elasticity and regular density of the medium, the equations (7) define the kinetic potential
– meaning the elasticity and regular density of the medium, the equations (7) define the kinetic potential 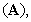 in the algebraic and differential forms. The gauge conditions (8) further introduce the three fields – electro-static, magnetic and electro-dynamic – as the formal features of the potentials. With respect to the constitutive relations (9), the equations (10) define the field carriers – electricity
in the algebraic and differential forms. The gauge conditions (8) further introduce the three fields – electro-static, magnetic and electro-dynamic – as the formal features of the potentials. With respect to the constitutive relations (9), the equations (10) define the field carriers – electricity 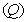 and respective current
and respective current 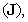 including the two displacement currents, electric and magnetic. Apparent field carriers are nothing else but the formal features of the fields. Apart from the static potential, as the starting EM quantity, the two EM constants should be convincingly interpreted. The two Thomson’s algebraic relations (11a,b), not indispensible at the theory constitution, are convenient in the following applications. Of course, they are already somehow formally related with (10) [5,6].
including the two displacement currents, electric and magnetic. Apparent field carriers are nothing else but the formal features of the fields. Apart from the static potential, as the starting EM quantity, the two EM constants should be convincingly interpreted. The two Thomson’s algebraic relations (11a,b), not indispensible at the theory constitution, are convenient in the following applications. Of course, they are already somehow formally related with (10) [5,6].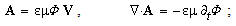 | (7) |
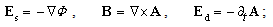 | (8) |
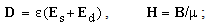 | (9) |
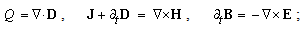 | (10) |
 | (11) |
These equations in the whole seem to be applicable to the dynamics of a compressible, super-fluidic and inert medium. With the bipolar static potential, as the opposite disturbances of the standard pressure, the two electric polarities just resemble the cyclones and anti-cyclones – in the atmosphere. The compressibility 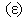 accumulates the static, and moving mass density
accumulates the static, and moving mass density 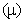 – kinetic energies. The super-fluidity just enables continual fluid flows. The product of compressibility, regular density and pressure disturbance – in a given fluid volume – just gives the disturbed density
– kinetic energies. The super-fluidity just enables continual fluid flows. The product of compressibility, regular density and pressure disturbance – in a given fluid volume – just gives the disturbed density 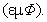 Its motion represents something as linear momentum density, or the kinetic potential (7). The radial gradient (8a) represents static, transverse gradient (8b) – kinetic, and accelerated flow (8c) – dynamic forces. The electric field terminals (10a) form the charge, and curls of magnetic field – electric current (10b). The electric current consists of the free and displacement flows. In absence of free magnetic poles, magnetic current in (10c) is reduced to its displacement component.
Its motion represents something as linear momentum density, or the kinetic potential (7). The radial gradient (8a) represents static, transverse gradient (8b) – kinetic, and accelerated flow (8c) – dynamic forces. The electric field terminals (10a) form the charge, and curls of magnetic field – electric current (10b). The electric current consists of the free and displacement flows. In absence of free magnetic poles, magnetic current in (10c) is reduced to its displacement component.
9. Causal Processes
Obtained from (10b,c), the equation (12a) determines the current of EM energy density (12b), with the speed of wave propagation (13a). The substitution of (11a) into (12b) gives the energy current of a moving electric field (13). Its former term expresses the moving energy density, in the double amount of its usual value 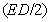 . With its invariant density, the moving energy can be increased only by extension of the spatial field domain. With conservation of its surrounding densities, the kinetic part of energy occupies the space close to the compressed particles, in the region of the stronger field. The letter part of energy (13) flows in the field direction: a particle accepts the energy in the front, and releases it behind itself, in accord with the opposite axial dynamic forces (14), transferring the energy. At the uniform motion, with equality of the two flows, these forces are in balance. In the fluidic medium model, this process is explained by compression and acceleration of the fluid in the front, and its expansion and deceleration – behind the moving charge.
. With its invariant density, the moving energy can be increased only by extension of the spatial field domain. With conservation of its surrounding densities, the kinetic part of energy occupies the space close to the compressed particles, in the region of the stronger field. The letter part of energy (13) flows in the field direction: a particle accepts the energy in the front, and releases it behind itself, in accord with the opposite axial dynamic forces (14), transferring the energy. At the uniform motion, with equality of the two flows, these forces are in balance. In the fluidic medium model, this process is explained by compression and acceleration of the fluid in the front, and its expansion and deceleration – behind the moving charge.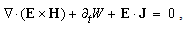 | (12a) |
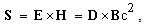 | (12b) |
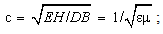 | (12c) |
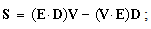 | (13) |
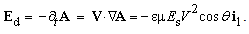 | (14) |
Physical processes are usually explained causally, from initial causes – up to final effects. If the final effect somehow influences the initial cause, the physical process is closed as a causal loop. This is the case at oscillations and waves. The electricity and its current (10a,b) are treated as the initial causes, given in advance, irrespective of their own former causes. The mutual relations of the two fields (10b,c) enable their causal loops. The equations (12), obtained from these two, in principle describe their causal loops. However, they also successfully treat the apparently open causal sequences. This fact is explained by the use of both equations (10b,c) at derivation of (12), pointing to the implicit causal loop. Alike all EM fields, already somehow closed, all causal processes are expected to be also closed, but in 5D space. This is also confirmed by the latter term of (13), as the continual barter of energy along the fifth axis, between a moving particle and a medium layer situated in the surroundings.
10. Dielectric Medium
The fluidic interpretation of (7a) demands a closed volume, with external award of the compressed fluid. The disturbed pressure around the particle model, irrespective of its cause, cannot be maintained in the open space, but will diffuse into surroundings, thus implying the opposite signs in (8c, 10c). On the other hand, the distinctions of the pressure differences – on the surfaces of the opposite particle polarities, result in the different radii and masses of a proton and electron. This antinomy just demands some re-examination of the former medium model. Instead of its untenable compression, its polarization is opposed by respective structural forces of the medium, preventing particle disperse. Though more massive positive fraction of the medium would be thus pushed radially, the compression of proton radius – into the stronger field – increases its energy and mass. The mass of the thus formed particle is not increased by the new fluid density, obtained by polarization, but by the extended domain of the field, around the compressed particle. Up to a certain electric field strength, vacuum medium conducts only displacement currents. Above this value, the free electrons are transferred between the electrodes. The ‘pulling out’ of the particle pairs from the medium demands much greater forces and energy densities. Thus obstructed displacements demand the continual motion of the toroidal vortices, through 3D or along temporal axis. Instead of the continual flows – at a place, they displace successively. For the energy conservation, the non-resistive dielectric, instead of super-fluidic medium, is needed. The kinetic forces result as Bernoulli’s effect – between displacement currents. The inertia is substituted by fluid reactivity, as the more general feature. It manifests as the dynamic field (10c), arisen at each medium disturbance. As EM induction, this field affects all present, including causing charge itself. In globally neutral media, these phenomena – reduced to the space between particles – are manifest as the inertia. EM and inertial forces are thus finally explained by this medium.
11. Gravitation
Gravitational field and potential (15) around a celestial body are obtained from respective law. The constant of integration 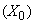 represents the referent potential, at infinity. Apart from the gravitational and EM forces, the physicists expect some nuclear forces, between the particles in the cluster model of the nuclei. Inertia is artificially united with gravitation, on the basis of proportionality of the two masses. Fully formally, they are further identified with the indistinct local curvature of space. EM forces are also arbitrarily united. The elaboration of EM theory [5] distinguishes the three forces (static, kinetic & dynamic) here explained by some processes in the vacuum medium. Inertia is identified as the dynamic effect, but assumed nuclear forces are overcome by the concentric model of the nuclei. After above explanation of EM and inertial forces, at least hypothetical explanation of gravitation is needed. At first look, the cosmic model, in the form of a hipper-spherical wave, just propagating along the temporal axis, points to certain kinetic effect between the parallel flows of all the cosmic matter.
represents the referent potential, at infinity. Apart from the gravitational and EM forces, the physicists expect some nuclear forces, between the particles in the cluster model of the nuclei. Inertia is artificially united with gravitation, on the basis of proportionality of the two masses. Fully formally, they are further identified with the indistinct local curvature of space. EM forces are also arbitrarily united. The elaboration of EM theory [5] distinguishes the three forces (static, kinetic & dynamic) here explained by some processes in the vacuum medium. Inertia is identified as the dynamic effect, but assumed nuclear forces are overcome by the concentric model of the nuclei. After above explanation of EM and inertial forces, at least hypothetical explanation of gravitation is needed. At first look, the cosmic model, in the form of a hipper-spherical wave, just propagating along the temporal axis, points to certain kinetic effect between the parallel flows of all the cosmic matter. | (15) |
The two forces – in the fully central form, electrostatic & gravitational, similarly origin from the temporal domain. However, they affect distinct objects, and so – are mutually exclusive. The idea of their superposition, so that the bipolar former, may be reduced to the variation of latter forces, must be thus refuted. Moreover, the former force is much stronger than latter one – between charge particles, further disabling the unification. Unlike electric field around separate charges, gravitation is dominant around neutral bodies, where the two opposite electric fields fully annul each other. However, the motion of one its polarity forms magnetic field, according to the relation (11a). This fact points to the implicit coexistence of the two opposite fields in the same location. Though thus electrically compensated, their community may be the real reason of gravitation, as the more subtle effect. In accord with the toroidal particle model [6], its flows are situated in 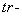 planes, thus only cutting 3D space. The kinetic effect, at some structural layer, may be expected between the neutral mixtures of the opposite charged particles.With respect to – already predicted and affirmed – bipolar structure of the vacuum medium, this medium itself may be the cause of some gravitational interactions. First of all, the magnetic constant
planes, thus only cutting 3D space. The kinetic effect, at some structural layer, may be expected between the neutral mixtures of the opposite charged particles.With respect to – already predicted and affirmed – bipolar structure of the vacuum medium, this medium itself may be the cause of some gravitational interactions. First of all, the magnetic constant 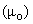 is identified in [5, 6] as the regular mass density of the medium. Moreover, apart from the micro toroidal vortices, forming elementary particles and photons, similar macro-vortices may be associated with some celestial bodies, and especially – with spiral galaxies. The additional gravitational fields, ascribed to the assumed invisible matter, may be possibly explained on these bases. On the other hand, though the electric constant
is identified in [5, 6] as the regular mass density of the medium. Moreover, apart from the micro toroidal vortices, forming elementary particles and photons, similar macro-vortices may be associated with some celestial bodies, and especially – with spiral galaxies. The additional gravitational fields, ascribed to the assumed invisible matter, may be possibly explained on these bases. On the other hand, though the electric constant 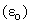 is inversely proportional to the modulus of elasticity or internal energy of the medium, it cannot be the reason of the assumed accelerated cosmic expansion. Identified as the hyper-spherical EM wave, this process is determined by the two constants. Their possible variation may possibly depend only on the shape of temporal axis. The empirical verification of this variation may be an additional difficult scientific problem.
is inversely proportional to the modulus of elasticity or internal energy of the medium, it cannot be the reason of the assumed accelerated cosmic expansion. Identified as the hyper-spherical EM wave, this process is determined by the two constants. Their possible variation may possibly depend only on the shape of temporal axis. The empirical verification of this variation may be an additional difficult scientific problem.
12. Reference Frame
The physical interactions – static, kinetic and dynamic – depend on the three kinematical states: position, motion and acceleration of interacting entities. With respect to reduction of all other – to EM forces, these ones are fully relevant. All of them depend on mutual distances of interacting charges. The kinetic forces also depend on the product of two parallel speeds. Apart from the object distance, and carrier speed – via variable mass, dynamic forces also depend on the carrier acceleration, as the time derivative of its speed. There arises the question of the valid frame of reference – for all the three kinematical quantities. At least tacitly or implicitly, some local frames, connected to predominant masses of nearby celestial bodies, are usually used in practice. E.g., a satellite path is hierarchically referred to the native planet, and of the planet – to respective star. However, the centrifugal force of a geostatic satellite is referred to some wider frame. The problematic reference of light propagation is especially interesting in the theory and practice.Just performed in the cosmic wave, light propagation is restricted to expanding 3D space. There is the question of its reference in this space. All other waves are naturally referred to their media, irrespective of their own motion. The invisible medium of light and its motion need be determined. Michelson-Morley’s experiment could not distinguish the speed of light – in the longitudinal and transverse directions of the orbital motion of Earth, as the moving frame. Instead of the subjective interpretation of this result, with respect to the passive observer, the objective interpretation concerns the Earth, as a predominant mass. Moreover, more accurate measurements during 20th century showed some delay of this frame behind Earth’s motion, merely a few percents of the expected full delay. Not only that SRT was already widely accepted, but this effect has none alternative interpretation, and so, is ignored. This delay may be ascribed to influence of remaining celestial bodies. Therefore, the frame motion is determined as the fractional effect (16a), with Fresnel factor (16b), concerning one of the bodies.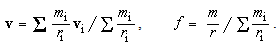 | (16) |
13. Propagation Speed
We examine the gravitational field and potential amongst a few nearby celestial bodies (17a,b). Integration in space of the former, gives latter quantity. The constant of integration 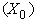 is the potential at relatively empty cosmic locations. With respect to square of speed – as its physical dimension, the attractive idea,
is the potential at relatively empty cosmic locations. With respect to square of speed – as its physical dimension, the attractive idea, 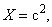 is worth of consideration. Of course, the potential and speed of light around a body (15b) are minimal on the body surface
is worth of consideration. Of course, the potential and speed of light around a body (15b) are minimal on the body surface 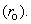 Possible compression of this body would reach the critical ratio of its mass and radius, with the zero potential, disabling light propagation. In the terms of the speed of light, (17b) describes a rectangular triangle (18a). Instead of the standard regular speed
Possible compression of this body would reach the critical ratio of its mass and radius, with the zero potential, disabling light propagation. In the terms of the speed of light, (17b) describes a rectangular triangle (18a). Instead of the standard regular speed 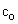 , the effective spatial propagation in 3D is
, the effective spatial propagation in 3D is 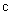 , and the value
, and the value 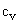 concerns the ‘depth’ of the potential. On the Sun surface it would be
concerns the ‘depth’ of the potential. On the Sun surface it would be 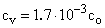 , and about ten times smaller – on Earth. The speed
, and about ten times smaller – on Earth. The speed 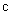 is thus very slightly distinct from the maximal value
is thus very slightly distinct from the maximal value 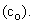 Therefore, its possible experimental verification is also under a question mark.
Therefore, its possible experimental verification is also under a question mark.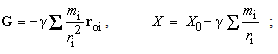 | (17) |
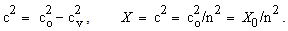 | (18) |
In (18b) 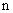 denotes the refraction factor of the summary potential. This factor is analogous with that in material media, but its value is here close to unit. As if, this fact is in some collision with above treatment of the frame of propagation. Namely, analogous Fresnel factor,
denotes the refraction factor of the summary potential. This factor is analogous with that in material media, but its value is here close to unit. As if, this fact is in some collision with above treatment of the frame of propagation. Namely, analogous Fresnel factor, 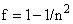 , would be here close to zero. However, calculated by (16b), it is close to unit, in accord with the experimental facts. The frame of propagation is here carried by the summary potential, with the separate fractional influences. The same bodies merely slightly influence the speed of propagation. Though fully carried by all the potentials, the medium of propagation is somehow stratified into the two structural layers. One of them, predominant in free space, transfers the wave energy at the full speed
, would be here close to zero. However, calculated by (16b), it is close to unit, in accord with the experimental facts. The frame of propagation is here carried by the summary potential, with the separate fractional influences. The same bodies merely slightly influence the speed of propagation. Though fully carried by all the potentials, the medium of propagation is somehow stratified into the two structural layers. One of them, predominant in free space, transfers the wave energy at the full speed 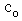 . The other of them, especially predominant in vicinity of extremely dense masses, temporarily withholds respective energetic fraction, increasing the local density and decreasing the propagation. At the critical ratio
. The other of them, especially predominant in vicinity of extremely dense masses, temporarily withholds respective energetic fraction, increasing the local density and decreasing the propagation. At the critical ratio 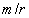 , this layer occupies the complete medium.The speed of propagation in fluidic media is determined by ratios of energy and mass densities (4b), or – of respective EM wave parameters (12b,c). In the cases of the material structures, each finer layer transfers the speedier signals. Stratifying the vacuum medium by the same principle, more and more speedy waves – of the much greater energies and smaller oscillations – may be thus expected. Exceeding the frames of the 3D space, they may be also directed along the temporal axis. Owing to the restriction of light propagation to 3D space, the temporal axis is called in Sanskrit as black dimension (kâla). Towards infinite density of a hypothetical Absolute Substance, the speed would tend into infinity, and oscillations are reduced close to zero. Thus being absolutely rigid, the subtlest medium would be invariable and eternal. Moreover, the signals from a point are instantly present in the whole cosmos. The cosmos thus behaves as one unique point, exceeding the notions of space and time. With respect to the finite speed of EM wave propagation, even the vacuum medium is considerably distant from God.
, this layer occupies the complete medium.The speed of propagation in fluidic media is determined by ratios of energy and mass densities (4b), or – of respective EM wave parameters (12b,c). In the cases of the material structures, each finer layer transfers the speedier signals. Stratifying the vacuum medium by the same principle, more and more speedy waves – of the much greater energies and smaller oscillations – may be thus expected. Exceeding the frames of the 3D space, they may be also directed along the temporal axis. Owing to the restriction of light propagation to 3D space, the temporal axis is called in Sanskrit as black dimension (kâla). Towards infinite density of a hypothetical Absolute Substance, the speed would tend into infinity, and oscillations are reduced close to zero. Thus being absolutely rigid, the subtlest medium would be invariable and eternal. Moreover, the signals from a point are instantly present in the whole cosmos. The cosmos thus behaves as one unique point, exceeding the notions of space and time. With respect to the finite speed of EM wave propagation, even the vacuum medium is considerably distant from God.
14. Conclusions
Not only that certain vacuum medium exists, but may be said that only it really exists. All material bodies and their constituent particles are only the dielectric images formed in this medium, as in the technical liquid crystal. These images interact by the known physical forces. Affecting respective human senses, they give the impression of the material existence. As the substratum of variable matter, the medium may be even a solid. Although various figures origin from, and move through it, the medium is globally resting. Respective its variations may be reduced to the deformations of its cruder layers. Transferring information in the form of EM or any other waves, the medium itself is invisible and impalpable. If a being had some higher sense for perception of the medium, by the signals unobstructed by matter, this matter would be transparent for it, as if being not existent. This may be the primary basis of the subjective philosophy, already mentioned. However, the conditions of its generalization to the material world and natural laws of its structural layers must be had in view.The action reaction law may be substituted by the law of energy conservation. Its additional generalization points to the constant sum of particular energy densities from various structural layers. The electric neutrality is also here reduced to the energy homogeneity. The uneven energy densities in particular layers are inevitably compensated by the opposite disturbances of the remaining layers, so that the complete medium energy is absolutely homogeneous. The energetic non-homogeneities of its particular layers just represent the structure of the world, so that their annulment would mean the world eradication. All variations and motions of the material bodies are followed by redistribution of the energy between various layers. Alike apparent wave motion – on a water surface, reducible to the vertical water oscillation, a body motion may be thus reduced to the energy exchanging. The moving particle accepts some energy in the front, and releases it behind itself, in the causal loop. This barter and its loop may be transferred analogically, into more complex – biological and social – relations.Energy seems to be a daily clear notion. Not only that is somehow produced, measured and transferred at distances, but as such it is bought and spent. Industrial production and biological existence are based on energy. On the other hand, being inaccessible by sensory perception, energy is a very abstract physical quantity. By the long sequence of formal procedures, the scientific concept is tacitly transferred into the daily notion. Energy manifests in all physical processes, in various forms. More or less successfully, these forms are transformed into each other, with full mutual equivalence. Energy density gradient in each structural layer is manifest as respective force field. Therefore, the force balance is equivalent with the energy homogeneity. Force interactions transfer the energy, so that the action invests, and reaction accepts the same energy, with motion in the action course. Being distributed along structural depths, it just forms all the structures. As the essence of the illusory phenomenal world, its own reality seems to be unquestionable. It may be regarded as the final physical quantity.
References
| [1] | B. Mišković, Essential Overview of EM Theory, Springer-Verlag, Selected Topics in Nonlinear Dynamics and TEE, Volume 459, 2013, pp 234-254, Chapter 13. |
| [2] | B. Mišković, Inductive elaboration of EM Theory, SAP, International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 3, 2013. |
| [3] | B. Mišković, Deductive Exposition of EM Theory, SAP, International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, 2013. |
| [4] | B. Mišković, Thematic Consideration of EM Theory, SAP, International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Vol. 3, No. 4, 2013. |
| [5] | B. Mišković, Systematic Foundation of EM Theory, SAP, International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications, Vol. 4, No. 1, 2014,http://article.sapub.org/10.5923/j.ijea.20140401.02. |
| [6] | B. Mišković, Boundary Questions of EM Theory, SAP, International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Vol. 4, No. 3, 2014,http://article.sapub.org/10.5923/j.ijtmp.20140403.01. |
| [7] | B. Mišković, Electrodynamics (in Serbo-Croatian), http://solair.eunet.rs/~brami/ |
| [8] | B. Mišković, General Physics (in Serbo-Croatian), http://solair.eunet.rs/~brami/ |
 of this process, in the form of a hipper-spherical wave. This model also explains its own global curvature and circular axes. The projection into 3D space relates the cosmic expansion with the lapse of time, thus denying its relativity. Kant’s antinomy between a beginning and end in time – or infinite cosmic duration, can be also resolved, by some circular form of the temporal axis, alike spatial ones.The rectilinear t-axis, with a beginning and without end, implicates the inflationary cosmos, expanding into infinity. The circular t-axis points to the cosmos pulsating between two singularities, as the poles of 4D sphere. The Big Bang is thus followed by the Big Collapse, in the opposite pole. Of course, this process further alternates periodically. Though cosmic wave propagates at the speed
of this process, in the form of a hipper-spherical wave. This model also explains its own global curvature and circular axes. The projection into 3D space relates the cosmic expansion with the lapse of time, thus denying its relativity. Kant’s antinomy between a beginning and end in time – or infinite cosmic duration, can be also resolved, by some circular form of the temporal axis, alike spatial ones.The rectilinear t-axis, with a beginning and without end, implicates the inflationary cosmos, expanding into infinity. The circular t-axis points to the cosmos pulsating between two singularities, as the poles of 4D sphere. The Big Bang is thus followed by the Big Collapse, in the opposite pole. Of course, this process further alternates periodically. Though cosmic wave propagates at the speed 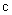 , its projection into 3D space varies. Starting by
, its projection into 3D space varies. Starting by 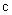 – in the tangential position, at the former pole, the decelerated expansion stops on the equator, with the maximal radius. This is followed by the accelerated contraction, up to the speed
– in the tangential position, at the former pole, the decelerated expansion stops on the equator, with the maximal radius. This is followed by the accelerated contraction, up to the speed 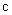 – in the latter pole. However, this model just contradicts to the assumed accelerated expansion, explaining the increasing red shift. Moreover, in spite of the speculations about Big Bang, the cosmic singularities are very difficult to be accepted. If the increasing red shift had none a better explanation, the accelerated expansion and decelerated contraction might be interpreted by some toroidal t-direction, with the cosmos oscillating between its two radii. Apart from the three spatial and one temporal axis, the matter demands a new axis. The zooming of structure – by its volume derivation, from the full cosmos – up to smallest particles, presents the matter by physical points
– in the latter pole. However, this model just contradicts to the assumed accelerated expansion, explaining the increasing red shift. Moreover, in spite of the speculations about Big Bang, the cosmic singularities are very difficult to be accepted. If the increasing red shift had none a better explanation, the accelerated expansion and decelerated contraction might be interpreted by some toroidal t-direction, with the cosmos oscillating between its two radii. Apart from the three spatial and one temporal axis, the matter demands a new axis. The zooming of structure – by its volume derivation, from the full cosmos – up to smallest particles, presents the matter by physical points 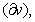 as the minimal relevant volumes. The logarithm of their radii gives the two infinite axis legs, with its zero determined by a unit of length. The motion of observation along this axis is enabled by the technical conversion of invisible into visible signals. The parallel development of chemical and nuclear processes in the same body, and the hierarchical scale of the energetic levels as well, are the indicative expressions of the fifth axis. In the same sense, EM processes develop in a few parallel structural layers. Inductive investigation is usually directed towards the finer, and deductive – towards cruder structures. Starting from the sensory domain, in the middle of the fifth axis, the science probably tends towards the same natural essence, at the common end of the two legs. Alike the former four, the fifth axis may be thus also expected to be somehow circularly closed into itself.
as the minimal relevant volumes. The logarithm of their radii gives the two infinite axis legs, with its zero determined by a unit of length. The motion of observation along this axis is enabled by the technical conversion of invisible into visible signals. The parallel development of chemical and nuclear processes in the same body, and the hierarchical scale of the energetic levels as well, are the indicative expressions of the fifth axis. In the same sense, EM processes develop in a few parallel structural layers. Inductive investigation is usually directed towards the finer, and deductive – towards cruder structures. Starting from the sensory domain, in the middle of the fifth axis, the science probably tends towards the same natural essence, at the common end of the two legs. Alike the former four, the fifth axis may be thus also expected to be somehow circularly closed into itself.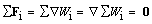
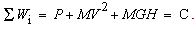
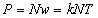 , represents its thermal energy, where
, represents its thermal energy, where 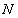 is the concentration of respective molecules, and
is the concentration of respective molecules, and 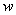 – the average molecular energy, proportional to the medium temperature
– the average molecular energy, proportional to the medium temperature 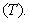 The second middle term represents the kinetic energy of the fluid flows, including its un-manifest half.
The second middle term represents the kinetic energy of the fluid flows, including its un-manifest half. 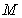 denotes the mass density, and
denotes the mass density, and 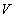 – the speed field of the fluid flow;
– the speed field of the fluid flow; 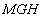 represents the static energy in gravitational field, where
represents the static energy in gravitational field, where 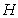 denotes the fluid depth at each point. Without energy transfer with surroundings, this sum keeps its constant value. At running out of the fluid, the static turns into kinetic energies. In addition, the oriented molecular motion causes some transverse pressure downfall, also transformed into motion. Owing to the decreased transverse pressure, two parallel flows attract each other. The two opposite flows form fluid vortices in between, causing the repulsion. Two crosswise flows thus form a torque tending to the same courses. The kinetic interactions are thus explained.In the discrete approach to various structures, the energy conservation – in the sense of its homogeneous density throughout 3D or 4D spaces – can be explained by even concentrations of various types of the particles carrying the different energetic charges. Namely, the particles themselves represent the energy disturbances, just formed on the finer structural levels. Not only that determined classes of these disturbances are mutually different quantitatively, but they also may express the positive or negative variations of the standard energy density on the level of their formation. With respect to the toroidal model of material particles [6], where the positive poles are of the greater mass and energy than the negative ones, the similar relations may be expected in the finer sub-structure of the vacuum medium. On these bases, the energy disturbances – in one, can be compensated by the medium polarization – in the other structural layers. This logic implicates that some of the medium layers or the finest of them may be even in the solid state.
denotes the fluid depth at each point. Without energy transfer with surroundings, this sum keeps its constant value. At running out of the fluid, the static turns into kinetic energies. In addition, the oriented molecular motion causes some transverse pressure downfall, also transformed into motion. Owing to the decreased transverse pressure, two parallel flows attract each other. The two opposite flows form fluid vortices in between, causing the repulsion. Two crosswise flows thus form a torque tending to the same courses. The kinetic interactions are thus explained.In the discrete approach to various structures, the energy conservation – in the sense of its homogeneous density throughout 3D or 4D spaces – can be explained by even concentrations of various types of the particles carrying the different energetic charges. Namely, the particles themselves represent the energy disturbances, just formed on the finer structural levels. Not only that determined classes of these disturbances are mutually different quantitatively, but they also may express the positive or negative variations of the standard energy density on the level of their formation. With respect to the toroidal model of material particles [6], where the positive poles are of the greater mass and energy than the negative ones, the similar relations may be expected in the finer sub-structure of the vacuum medium. On these bases, the energy disturbances – in one, can be compensated by the medium polarization – in the other structural layers. This logic implicates that some of the medium layers or the finest of them may be even in the solid state.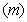 connected by elastic tie to the centre of rotation. Its stretch,
connected by elastic tie to the centre of rotation. Its stretch, 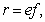 is proportional to the centrifugal force (3a). The division by
is proportional to the centrifugal force (3a). The division by 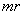 gives the invariant angular speed (3b), dependent on the factors
gives the invariant angular speed (3b), dependent on the factors 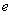 &
&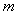 only. At each peripheral speed,
only. At each peripheral speed, 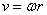 , the force balance is thus kept. The rotator may be substituted by sum of two orthogonal oscillators, of the resonant frequency (3b). On the other hand, the oscillator itself may be also understood as the rotator in the plane of a spatial and structural axes. The multiplication of (3a) by
, the force balance is thus kept. The rotator may be substituted by sum of two orthogonal oscillators, of the resonant frequency (3b). On the other hand, the oscillator itself may be also understood as the rotator in the plane of a spatial and structural axes. The multiplication of (3a) by 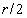 equals the two types of energy (3c), with their final sum (4a). The energy of a structural element is just proportional with the medium temperature,
equals the two types of energy (3c), with their final sum (4a). The energy of a structural element is just proportional with the medium temperature, 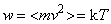 , where
, where 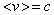 is the average speed. This is nothing else but Einstein’s equation. Its volume derivative gives the speed of wave propagation (4b), as the ratio of energy and mass densities. The interpretations of these two quantities depend on the medium type and respective waves. In general,
is the average speed. This is nothing else but Einstein’s equation. Its volume derivative gives the speed of wave propagation (4b), as the ratio of energy and mass densities. The interpretations of these two quantities depend on the medium type and respective waves. In general, 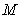 is the full energy density, and
is the full energy density, and 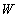 – its active component only, propagating through the transferring layer [5].
– its active component only, propagating through the transferring layer [5].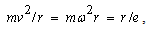
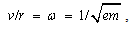
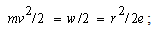
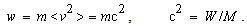
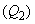 – in the conducting layer or free space, repels equipolar, and attracts opposite bound electricity – of the matter
– in the conducting layer or free space, repels equipolar, and attracts opposite bound electricity – of the matter 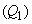 and/or – of vacuum
and/or – of vacuum 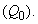 The attracted electricity compensates inserted charge, and repelled electricity forms the flux of electric displacement
The attracted electricity compensates inserted charge, and repelled electricity forms the flux of electric displacement 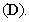 These two processes point to conservation of electric neutrality at each point (5a), where
These two processes point to conservation of electric neutrality at each point (5a), where 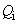 is the charge density in a layer. This relation is confirmed even by Faraday. Some charge inserted into a closed metallic sphere causes certain polarization of the surrounding medium, including the walls of the sphere. Its external surface thus obtains the equipolar, and internal one – the opposite polarities. The discharged external, is found to be equal with inserted charge. This latter inserted into one, forms the divergence of the displacement – in the other layers. With respect to summary neutrality, the full displacement must be closed into itself (5b). Unlike the vortical fields, already closed in 3D, the ‘non-vortical’ static field is thus also closed into itself, but in 5D-space. Therefore, all the types of EM fields, in their respective manners, are circularly closed into themselves.
is the charge density in a layer. This relation is confirmed even by Faraday. Some charge inserted into a closed metallic sphere causes certain polarization of the surrounding medium, including the walls of the sphere. Its external surface thus obtains the equipolar, and internal one – the opposite polarities. The discharged external, is found to be equal with inserted charge. This latter inserted into one, forms the divergence of the displacement – in the other layers. With respect to summary neutrality, the full displacement must be closed into itself (5b). Unlike the vortical fields, already closed in 3D, the ‘non-vortical’ static field is thus also closed into itself, but in 5D-space. Therefore, all the types of EM fields, in their respective manners, are circularly closed into themselves.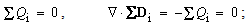
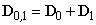 . The free material charge, in the continuity equation (6b), is inserted into the observed location as the displaced conducting electricity. In fact, (6b) is nothing else but the static Maxwell’s equation (10a), being equivalent with the absolute electrical neutrality.
. The free material charge, in the continuity equation (6b), is inserted into the observed location as the displaced conducting electricity. In fact, (6b) is nothing else but the static Maxwell’s equation (10a), being equivalent with the absolute electrical neutrality.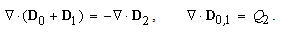
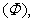 as the medium disturbance, with the two constants – electric
as the medium disturbance, with the two constants – electric 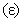 and magnetic
and magnetic 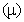 – meaning the elasticity and regular density of the medium, the equations (7) define the kinetic potential
– meaning the elasticity and regular density of the medium, the equations (7) define the kinetic potential 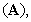 in the algebraic and differential forms. The gauge conditions (8) further introduce the three fields – electro-static, magnetic and electro-dynamic – as the formal features of the potentials. With respect to the constitutive relations (9), the equations (10) define the field carriers – electricity
in the algebraic and differential forms. The gauge conditions (8) further introduce the three fields – electro-static, magnetic and electro-dynamic – as the formal features of the potentials. With respect to the constitutive relations (9), the equations (10) define the field carriers – electricity 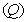 and respective current
and respective current 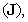 including the two displacement currents, electric and magnetic. Apparent field carriers are nothing else but the formal features of the fields. Apart from the static potential, as the starting EM quantity, the two EM constants should be convincingly interpreted. The two Thomson’s algebraic relations (11a,b), not indispensible at the theory constitution, are convenient in the following applications. Of course, they are already somehow formally related with (10) [5,6].
including the two displacement currents, electric and magnetic. Apparent field carriers are nothing else but the formal features of the fields. Apart from the static potential, as the starting EM quantity, the two EM constants should be convincingly interpreted. The two Thomson’s algebraic relations (11a,b), not indispensible at the theory constitution, are convenient in the following applications. Of course, they are already somehow formally related with (10) [5,6].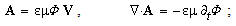
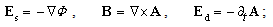
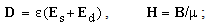
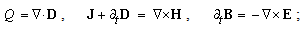

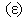 accumulates the static, and moving mass density
accumulates the static, and moving mass density 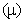 – kinetic energies. The super-fluidity just enables continual fluid flows. The product of compressibility, regular density and pressure disturbance – in a given fluid volume – just gives the disturbed density
– kinetic energies. The super-fluidity just enables continual fluid flows. The product of compressibility, regular density and pressure disturbance – in a given fluid volume – just gives the disturbed density 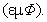 Its motion represents something as linear momentum density, or the kinetic potential (7). The radial gradient (8a) represents static, transverse gradient (8b) – kinetic, and accelerated flow (8c) – dynamic forces. The electric field terminals (10a) form the charge, and curls of magnetic field – electric current (10b). The electric current consists of the free and displacement flows. In absence of free magnetic poles, magnetic current in (10c) is reduced to its displacement component.
Its motion represents something as linear momentum density, or the kinetic potential (7). The radial gradient (8a) represents static, transverse gradient (8b) – kinetic, and accelerated flow (8c) – dynamic forces. The electric field terminals (10a) form the charge, and curls of magnetic field – electric current (10b). The electric current consists of the free and displacement flows. In absence of free magnetic poles, magnetic current in (10c) is reduced to its displacement component.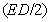 . With its invariant density, the moving energy can be increased only by extension of the spatial field domain. With conservation of its surrounding densities, the kinetic part of energy occupies the space close to the compressed particles, in the region of the stronger field. The letter part of energy (13) flows in the field direction: a particle accepts the energy in the front, and releases it behind itself, in accord with the opposite axial dynamic forces (14), transferring the energy. At the uniform motion, with equality of the two flows, these forces are in balance. In the fluidic medium model, this process is explained by compression and acceleration of the fluid in the front, and its expansion and deceleration – behind the moving charge.
. With its invariant density, the moving energy can be increased only by extension of the spatial field domain. With conservation of its surrounding densities, the kinetic part of energy occupies the space close to the compressed particles, in the region of the stronger field. The letter part of energy (13) flows in the field direction: a particle accepts the energy in the front, and releases it behind itself, in accord with the opposite axial dynamic forces (14), transferring the energy. At the uniform motion, with equality of the two flows, these forces are in balance. In the fluidic medium model, this process is explained by compression and acceleration of the fluid in the front, and its expansion and deceleration – behind the moving charge.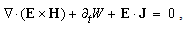
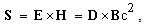
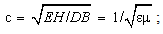
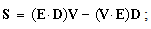
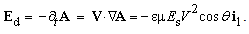
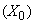 represents the referent potential, at infinity. Apart from the gravitational and EM forces, the physicists expect some nuclear forces, between the particles in the cluster model of the nuclei. Inertia is artificially united with gravitation, on the basis of proportionality of the two masses. Fully formally, they are further identified with the indistinct local curvature of space. EM forces are also arbitrarily united. The elaboration of EM theory [5] distinguishes the three forces (static, kinetic & dynamic) here explained by some processes in the vacuum medium. Inertia is identified as the dynamic effect, but assumed nuclear forces are overcome by the concentric model of the nuclei. After above explanation of EM and inertial forces, at least hypothetical explanation of gravitation is needed. At first look, the cosmic model, in the form of a hipper-spherical wave, just propagating along the temporal axis, points to certain kinetic effect between the parallel flows of all the cosmic matter.
represents the referent potential, at infinity. Apart from the gravitational and EM forces, the physicists expect some nuclear forces, between the particles in the cluster model of the nuclei. Inertia is artificially united with gravitation, on the basis of proportionality of the two masses. Fully formally, they are further identified with the indistinct local curvature of space. EM forces are also arbitrarily united. The elaboration of EM theory [5] distinguishes the three forces (static, kinetic & dynamic) here explained by some processes in the vacuum medium. Inertia is identified as the dynamic effect, but assumed nuclear forces are overcome by the concentric model of the nuclei. After above explanation of EM and inertial forces, at least hypothetical explanation of gravitation is needed. At first look, the cosmic model, in the form of a hipper-spherical wave, just propagating along the temporal axis, points to certain kinetic effect between the parallel flows of all the cosmic matter.
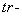 planes, thus only cutting 3D space. The kinetic effect, at some structural layer, may be expected between the neutral mixtures of the opposite charged particles.With respect to – already predicted and affirmed – bipolar structure of the vacuum medium, this medium itself may be the cause of some gravitational interactions. First of all, the magnetic constant
planes, thus only cutting 3D space. The kinetic effect, at some structural layer, may be expected between the neutral mixtures of the opposite charged particles.With respect to – already predicted and affirmed – bipolar structure of the vacuum medium, this medium itself may be the cause of some gravitational interactions. First of all, the magnetic constant 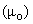 is identified in [5, 6] as the regular mass density of the medium. Moreover, apart from the micro toroidal vortices, forming elementary particles and photons, similar macro-vortices may be associated with some celestial bodies, and especially – with spiral galaxies. The additional gravitational fields, ascribed to the assumed invisible matter, may be possibly explained on these bases. On the other hand, though the electric constant
is identified in [5, 6] as the regular mass density of the medium. Moreover, apart from the micro toroidal vortices, forming elementary particles and photons, similar macro-vortices may be associated with some celestial bodies, and especially – with spiral galaxies. The additional gravitational fields, ascribed to the assumed invisible matter, may be possibly explained on these bases. On the other hand, though the electric constant 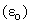 is inversely proportional to the modulus of elasticity or internal energy of the medium, it cannot be the reason of the assumed accelerated cosmic expansion. Identified as the hyper-spherical EM wave, this process is determined by the two constants. Their possible variation may possibly depend only on the shape of temporal axis. The empirical verification of this variation may be an additional difficult scientific problem.
is inversely proportional to the modulus of elasticity or internal energy of the medium, it cannot be the reason of the assumed accelerated cosmic expansion. Identified as the hyper-spherical EM wave, this process is determined by the two constants. Their possible variation may possibly depend only on the shape of temporal axis. The empirical verification of this variation may be an additional difficult scientific problem. 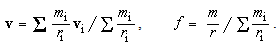
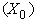 is the potential at relatively empty cosmic locations. With respect to square of speed – as its physical dimension, the attractive idea,
is the potential at relatively empty cosmic locations. With respect to square of speed – as its physical dimension, the attractive idea, 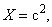 is worth of consideration. Of course, the potential and speed of light around a body (15b) are minimal on the body surface
is worth of consideration. Of course, the potential and speed of light around a body (15b) are minimal on the body surface 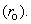 Possible compression of this body would reach the critical ratio of its mass and radius, with the zero potential, disabling light propagation. In the terms of the speed of light, (17b) describes a rectangular triangle (18a). Instead of the standard regular speed
Possible compression of this body would reach the critical ratio of its mass and radius, with the zero potential, disabling light propagation. In the terms of the speed of light, (17b) describes a rectangular triangle (18a). Instead of the standard regular speed 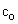 , the effective spatial propagation in 3D is
, the effective spatial propagation in 3D is 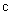 , and the value
, and the value 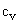 concerns the ‘depth’ of the potential. On the Sun surface it would be
concerns the ‘depth’ of the potential. On the Sun surface it would be 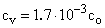 , and about ten times smaller – on Earth. The speed
, and about ten times smaller – on Earth. The speed 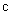 is thus very slightly distinct from the maximal value
is thus very slightly distinct from the maximal value 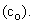 Therefore, its possible experimental verification is also under a question mark.
Therefore, its possible experimental verification is also under a question mark.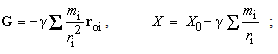
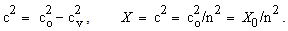
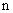 denotes the refraction factor of the summary potential. This factor is analogous with that in material media, but its value is here close to unit. As if, this fact is in some collision with above treatment of the frame of propagation. Namely, analogous Fresnel factor,
denotes the refraction factor of the summary potential. This factor is analogous with that in material media, but its value is here close to unit. As if, this fact is in some collision with above treatment of the frame of propagation. Namely, analogous Fresnel factor, 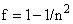 , would be here close to zero. However, calculated by (16b), it is close to unit, in accord with the experimental facts. The frame of propagation is here carried by the summary potential, with the separate fractional influences. The same bodies merely slightly influence the speed of propagation. Though fully carried by all the potentials, the medium of propagation is somehow stratified into the two structural layers. One of them, predominant in free space, transfers the wave energy at the full speed
, would be here close to zero. However, calculated by (16b), it is close to unit, in accord with the experimental facts. The frame of propagation is here carried by the summary potential, with the separate fractional influences. The same bodies merely slightly influence the speed of propagation. Though fully carried by all the potentials, the medium of propagation is somehow stratified into the two structural layers. One of them, predominant in free space, transfers the wave energy at the full speed 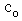 . The other of them, especially predominant in vicinity of extremely dense masses, temporarily withholds respective energetic fraction, increasing the local density and decreasing the propagation. At the critical ratio
. The other of them, especially predominant in vicinity of extremely dense masses, temporarily withholds respective energetic fraction, increasing the local density and decreasing the propagation. At the critical ratio 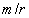 , this layer occupies the complete medium.The speed of propagation in fluidic media is determined by ratios of energy and mass densities (4b), or – of respective EM wave parameters (12b,c). In the cases of the material structures, each finer layer transfers the speedier signals. Stratifying the vacuum medium by the same principle, more and more speedy waves – of the much greater energies and smaller oscillations – may be thus expected. Exceeding the frames of the 3D space, they may be also directed along the temporal axis. Owing to the restriction of light propagation to 3D space, the temporal axis is called in Sanskrit as black dimension (kâla). Towards infinite density of a hypothetical Absolute Substance, the speed would tend into infinity, and oscillations are reduced close to zero. Thus being absolutely rigid, the subtlest medium would be invariable and eternal. Moreover, the signals from a point are instantly present in the whole cosmos. The cosmos thus behaves as one unique point, exceeding the notions of space and time. With respect to the finite speed of EM wave propagation, even the vacuum medium is considerably distant from God.
, this layer occupies the complete medium.The speed of propagation in fluidic media is determined by ratios of energy and mass densities (4b), or – of respective EM wave parameters (12b,c). In the cases of the material structures, each finer layer transfers the speedier signals. Stratifying the vacuum medium by the same principle, more and more speedy waves – of the much greater energies and smaller oscillations – may be thus expected. Exceeding the frames of the 3D space, they may be also directed along the temporal axis. Owing to the restriction of light propagation to 3D space, the temporal axis is called in Sanskrit as black dimension (kâla). Towards infinite density of a hypothetical Absolute Substance, the speed would tend into infinity, and oscillations are reduced close to zero. Thus being absolutely rigid, the subtlest medium would be invariable and eternal. Moreover, the signals from a point are instantly present in the whole cosmos. The cosmos thus behaves as one unique point, exceeding the notions of space and time. With respect to the finite speed of EM wave propagation, even the vacuum medium is considerably distant from God.  Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML