Branko Mišković
Independent, Novi Sad, Serbia
Correspondence to: Branko Mišković , Independent, Novi Sad, Serbia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
In the aim to re-examine some already accepted concepts and speculations, EM theory (EMT) is applied to the wider context of physics. The comparison of some theses and anti-theses follows into respective syntheses, exceeding one or both of the alternatives, or removing their contradictions. EMT is thus related with mechanics, particle physics and cosmology, but confronted with quantum theory and special relativity (SRT) at least. Some inadequate concepts and unfounded speculations are substituted by more consistent and convincing alternative solutions. Respective discussion with a reviewer, representing the contemporary physics, is presented in an additional section.
Keywords:
Space, Time, Matter, Mass, Energy, Electricity, Particle, Cosmos
Cite this paper: Branko Mišković , Boundary Questions of EM Theory, International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 73-83. doi: 10.5923/j.ijtmp.20140403.01.
1. Introduction
Rational interpretation of empirical facts and their formal relations consist in their possible reduction to already known theories. The thermodynamics is thus reduced to molecular mechanics. However, formal similarities of the static, kinetic and dynamic laws of mechanics and EMT, dependent on the position, motion and acceleration of mass or electricity, were insufficient for explanation of their distinctions. Unlike the exclusive gravitational attraction, EM forces may be also repulsive. Inertia affects the accelerated body only, but EM induction affects surrounding electricity too. Solid moving masses do not manifest mutual kinetic forces, similar to that between moving charges. Moreover, EM kinetic central law was not formulated in general, and the algebraic relations, as direct interactions of moving fields, their carriers and objects, have not been fully elaborated so far.EM theory is founded in 19th century, by relatively new field theory, in the form of Maxwell’s differential equations. Owing to their implicit senses, these equations had not been accepted during author’s life. As broken by death (at 49), Maxwell did not succeed to elaborate their application to moving bodies. Merely Hertz’ realization of EM waves, in advance predicted by these equations, opened the door for their final wide acceptance. Moreover, Hertz tried to apply Maxwell’s theory to the moving bodies. With respect to the shorter life (of 36), his investigation stayed also unfinished. In spite of some additional partial contributions, EM theory has not been systematically completed. Founded intuitively and accepted by force of the empirical facts, it is now studied formally and superficially, without sufficient understanding of respective physical processes.Though EM phenomena are already successfully applied in practice, the unelaborated theory imposed some negative consequences in the science. Apart from its unsuccessful application in micro-structure, and erroneous conclusions derived from its incomplete laws, the way of its acceptance and further transfer caused the drastic slump of all scientific criteria. With doubtful reliance on the objective sources (empirical & formal), subjective criteria (rational & intuitive) are used on the rather miserly levels. Arbitrarily interpreted empirical results, with the artificial symmetries of various concepts and their relations, serve for foundation of some speculative, even fantastic, physical doctrines, from SRT up to the string theory. The inabilities of their understandings are ascribed to the imperfect powers of human reasoning and comprehension. All the scientific sources and criteria of cognition are thus called in question.Recent elaboration of EMT in [1-5] offers a possibility of adequate correction of the former confusion. If this job were made a hundred years ago, it would be accepted as the natural scientific development. However, now is the other situation. The radical renunciation of the contemporary, very diversified, in fact – quasi-scientific theories, cannot be even imagined. This event would cause a shock much greater than the famous Copernican U-turn. It would defeat almost of the scientific literature, the numerous titles and rewards, built into the careers of modern scientists. Such heretic scientific thoughts, being unacceptable for the institutionalized printed journals of 20th century, cannot be forbidden in the on-line scientific alternative. However, without the strict scientific criteria of the readers, lost in the former period, each such attempt is hopeless. On the other hand, the continuation of the modern courses would lead nowhere.
2. Scientific Methodology
Elaboration of a theory consists in mutual comparison and confrontation of its ideas and results, their formal relations and/or rational interpretations, as the theses and anti-theses. These starting alternatives represent the best challenges for decisive steps forward onto the higher scientific levels. This job consists in exhaustive re-examinations of each of the alternatives, the empirical and/or formal procedures of their introduction, their mathematical expressions and rational interpretations. In the final instance, the former models of thinking and established logic or mathematics may be called in question. Of course, the effective order of re-examination should start from the more probable, towards less probable faults. The synthesis may disprove one of the alternatives – or both of them, or rectify their apparent contradictions by adequate, more general interpretations.Principal views of historical periods influence the choices between the various alternatives. In this sense, the empirical impressions of local variations of mass, energy & electricity, as the continual substances, are usually confronted with possible formal symmetries of the discrete particles and their interactions, dependent on the three kinematical states. With their particular advantages and disadvantage, these two approaches alternate during the scientific history. In such the periodical alternation, they somehow supplement and correct each other. With respect to predominant position of one of them during more than a century, its views firmly establish in collective awareness, so that their painful substitution makes the impression of a great scientific revolution. Instead of the spiral progressive development, this alternation may seem as the senseless turning around a circle. Therefore, researches are not ever ready for fundamental scientific challenges. Instead of their final syntheses, they frequently arbitrarily choose one of the two alternatives – without convincing argumentation, or make some artificial, self-contradictory unifications of them. Depending on the personal authorities, such provisional solutions are gradually habituated by the scientific public, after some time of their uncritical repetition. In the further lapse of time, these solutions are accepted as the scientific miracles, on the mere level of subjective devotion. As the supreme unquestionable dogmas, they represent the main obstacles against the further scientific development. Modern physics uses a number of such unacceptable concepts. Some of them are the topics of the following consideration, and will be mainly surpassed by means of the presented methodology.
3. Extended Space
Physical processes are observed in 3D space, in the set of three equal axes, enabling three components of translation. The three components of rotation may be associated with respective planes or axes. Although in common oriented arbitrarily, perpendicular positions of the axes express their mutual independence. Human imagination, founded on the experience, is generally limited by the frames of 3D space. Noticed temporal variations of the phenomena demand an additional axis, as the fourth, perpendicular to spatial three. Unlike spatial freedom of motion, all matter is connected to the lapse of time – along respective axis, without possible stoppage or returning into the past. By continual sequences of the impressions in memory, the logical expectations and analogous generalizations from 3D space, the imagination is slightly extended into the past and future.As the combinations by two – of the four axes, 4D space contains six planes. Though formally equal with spatial axes, the fourth one is physically preferential, with respect to the temporal motion. The six planes are thus grouped by three: ‘longitudinal’ 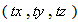 – in temporal, and ‘transverse’
– in temporal, and ‘transverse’ 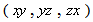 – in spatial domains. Apart from the three translations and enforced temporal motion, each rotation from 3D space may be associated with one spatial and the temporal axes. Similarly, each rotation from a
– in spatial domains. Apart from the three translations and enforced temporal motion, each rotation from 3D space may be associated with one spatial and the temporal axes. Similarly, each rotation from a 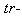 plane is associated with the two remaining spatial axes. These facts are the main difficulties in direct 4D imaginations. The sets of by three axes represent the four 3D subspaces. With the preferential sense of the
plane is associated with the two remaining spatial axes. These facts are the main difficulties in direct 4D imaginations. The sets of by three axes represent the four 3D subspaces. With the preferential sense of the 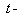 axis,
axis, 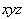 -subspace is manifest as the phenomenal world. Three ranks of tensor quantities, vectors, bi-vectors & tri-vectors, are associated to respective subspaces: axes, planes and 3D spaces.Without explicit empirical or logical argumentations, the intuitive hipper-spherical cosmic model is already widely accepted. However, some EM antinomies in the strait space are resolved by this model [1]. Moreover, the basic equations of EMT [2] point to the temporal motion, at speed
-subspace is manifest as the phenomenal world. Three ranks of tensor quantities, vectors, bi-vectors & tri-vectors, are associated to respective subspaces: axes, planes and 3D spaces.Without explicit empirical or logical argumentations, the intuitive hipper-spherical cosmic model is already widely accepted. However, some EM antinomies in the strait space are resolved by this model [1]. Moreover, the basic equations of EMT [2] point to the temporal motion, at speed 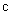 . With respect to this speed, the cosmic process may be understood as a hyper-spherical wave, directed along the temporal axis. With respect to the local image of strait axes, the spherical 3D space can also not be imagined. In the polar frame, t-axis would be set up radially. The propagation along it is projected into 3D, as continual process of cosmic expansion, the same for all the matter. The cosmic evolution depends on the t-axis form. Instead of this strait axis – with inflationary cosmos, its circular form would determine, maybe much more acceptable, pulsating cosmos.EM field tensor [3] explicates 4D senses of EM quantities and their relations. Space and time form 4D continuum, with the preference of t-axis. The addition of matter, as the third natural category, demands a new axis. In absence of a simple interpretation of the fifth axis, this idea was very difficult to be accepted. Its arbitrary closing on the elementary levels enabled only uncontrolled multiplication of such new axes. Instead, a convincing structural dimension is introduced in [3]. Poynting’s theorem, as a 5D continuity equation, is the example of its application. In this sense, EM processes develop in the four structural layers: vacuum, polarization, magnetization and conducting ones. The motion along the fifth axis would mean some structural transformation of the observed objects. Their zooming may be understood as the displacement of observation along this axis.
. With respect to this speed, the cosmic process may be understood as a hyper-spherical wave, directed along the temporal axis. With respect to the local image of strait axes, the spherical 3D space can also not be imagined. In the polar frame, t-axis would be set up radially. The propagation along it is projected into 3D, as continual process of cosmic expansion, the same for all the matter. The cosmic evolution depends on the t-axis form. Instead of this strait axis – with inflationary cosmos, its circular form would determine, maybe much more acceptable, pulsating cosmos.EM field tensor [3] explicates 4D senses of EM quantities and their relations. Space and time form 4D continuum, with the preference of t-axis. The addition of matter, as the third natural category, demands a new axis. In absence of a simple interpretation of the fifth axis, this idea was very difficult to be accepted. Its arbitrary closing on the elementary levels enabled only uncontrolled multiplication of such new axes. Instead, a convincing structural dimension is introduced in [3]. Poynting’s theorem, as a 5D continuity equation, is the example of its application. In this sense, EM processes develop in the four structural layers: vacuum, polarization, magnetization and conducting ones. The motion along the fifth axis would mean some structural transformation of the observed objects. Their zooming may be understood as the displacement of observation along this axis.
4. Variation or Motion
The noticed variation and imagined motion are not fully equivalent. Though each variation of a permanent substance can be reduced to respective motion, some motions do not cause any visible variations. For instance, unlike the motion of a vortical field along its gradient (in the field line planes), causing some convective variations, this one directed in the field homogeneity (across field line planes), does not change the field at any point. The two mathematical sets, Thomson’s – algebraic (1), and Maxwell’s – differential equations (6), are similarly related. The former pair concerns the imagined motions, and letter set – observed variations. Of course, the field variations are empirically much more accessible than respective motions. Therefore – in the standard EMT – the algebraic pair stays in the shadow of the differential set, being already affirmed and widely applied. | (1) |
 | (2) |
Here 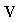 represents the speed of electric, and
represents the speed of electric, and 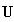 – of magnetic fields. The total fields
– of magnetic fields. The total fields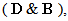 moving along their own gradients, produce the dissimilar vacuum fields
moving along their own gradients, produce the dissimilar vacuum fields 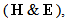 respectively, constitutively related with the former ones (2). The magnetic field – kinetically produced in (1a) – may be moved in the dynamic process (1b). There arises the question of some comparison of the two basic sets, algebraic and differential ones, in the sense of their complete or partial equivalence. Div & curl applied to the pair (1) give the four differential forms, wider than Maxwell’s equations are. The comparison points to the speed derivatives, in the excessive terms. They are eliminated by restriction of (1) to exclusively uniform and rectilinear field translation. Really, the former of them applied to circular motion follows into difficulties. Let us now transform the two restricted forms (3) and (4) into Maxwell’s differential equations (6).
respectively, constitutively related with the former ones (2). The magnetic field – kinetically produced in (1a) – may be moved in the dynamic process (1b). There arises the question of some comparison of the two basic sets, algebraic and differential ones, in the sense of their complete or partial equivalence. Div & curl applied to the pair (1) give the four differential forms, wider than Maxwell’s equations are. The comparison points to the speed derivatives, in the excessive terms. They are eliminated by restriction of (1) to exclusively uniform and rectilinear field translation. Really, the former of them applied to circular motion follows into difficulties. Let us now transform the two restricted forms (3) and (4) into Maxwell’s differential equations (6).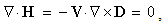 | (3a) |
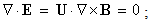 | (3b) |
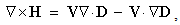 | (4a) |
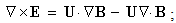 | (4b) |
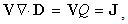 | (5a) |
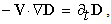 | (5b) |
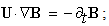 | (5c) |
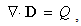 | (6a) |
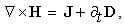 | (6b) |
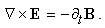 | (6c) |
Div-forms (3) express axial motions of the field vortices, across the field line planes. With the expected zero magnetic charge (3a), possible production of the electric charge (3b) – concerned by the static equation (6a) – cannot be obtained in 3D space, but origins from the temporal domain. On the other hand, with respect to (3a & 6a), the current field (5a) and the two convective derivatives (5b,c), – the two restricted curl-forms (4) just turn into the kinetic (6b) and dynamic (6c) equations, respectively. Though being mathematically more general, thus restricted application of the algebraic pair (1) mainly accords with the full sense of the differential set. In analogy with the electric displacement current (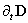 ) in (6b), respective term (
) in (6b), respective term (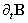 ) in (6c) may be formally considered as magnetic displacement current. Therefore, the equations (6) define the three carriers (electricity and the two currents) as the formal features of respective EM fields.Above restriction may be explained by the moving fields as the rigid structures, forming the gyroscopes in common with their carriers. This concept prefers the action – directly at a distance, instead of the assumed field transfer – at some finite speed. In the former opinion, a particle is considered as field carrier, and in latter – its source. Though was without convincing interpretation, the former principle is implicitly understood in all the equations of EMT. The observed fields are present at each point of 3D space, acting directly and instantly, as stretched arms. Not only that the latter principle is energetically problematic, but it is not built into Maxwell’s set, though accepted in common with it. Even this set does not take into account any time for the field transfer. However, this view is transferred into modern physics, where particles allegedly exchange some photons.
) in (6c) may be formally considered as magnetic displacement current. Therefore, the equations (6) define the three carriers (electricity and the two currents) as the formal features of respective EM fields.Above restriction may be explained by the moving fields as the rigid structures, forming the gyroscopes in common with their carriers. This concept prefers the action – directly at a distance, instead of the assumed field transfer – at some finite speed. In the former opinion, a particle is considered as field carrier, and in latter – its source. Though was without convincing interpretation, the former principle is implicitly understood in all the equations of EMT. The observed fields are present at each point of 3D space, acting directly and instantly, as stretched arms. Not only that the latter principle is energetically problematic, but it is not built into Maxwell’s set, though accepted in common with it. Even this set does not take into account any time for the field transfer. However, this view is transferred into modern physics, where particles allegedly exchange some photons.
5. Symmetry or Trinity
Some natural phenomena and their relations are usually manifest symmetrically, in the pairs of partial oppositions. In the wider groups, they form more or less symmetric concepts or relations. The two EM fields and their relations are thus described by two pairs of Maxwell’s equations. The former impression of the field duality has been founded on the phenomenal observation of the two forces: electric forces affect all the present electricity – in the field line direction, but magnetic ones affect electric currents only, transversally to the current and field. Apart from the magnetic, static and dynamic electric fields are mutually distinguished at least by their mathematical forms. As if the three relevant equations (6) operate by respective three fields. The trivial Maxwell’s equation (3a) only speaks against existence of free magnetic poles, possibly predicted in advance.Both EM fields are collinear with the forces acting on respective dipoles drawn along the field lines – towards the stronger fields [1,5]. Their initial introduction was founded on these phenomenal impressions. However, the relation of electric and magnetic phenomena reduced the two dipoles to the concept of electricity and its kinematics. In spite of the transverse magnetic forces, the former image of respective field is kept in application. The treatment is carried out by the cross product of the two vector quantities, perpendicular to both factors. The magnetic force acting on a punctual charge (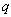 ) moving at some speed (
) moving at some speed (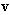 ) is determined by (7a). The same interaction may be also expressed by kinetic electric field (7b), collinear with this interaction. With respect to the perpendicular positions of the two thus related EM fields, the cross products are also applied in (1).
) is determined by (7a). The same interaction may be also expressed by kinetic electric field (7b), collinear with this interaction. With respect to the perpendicular positions of the two thus related EM fields, the cross products are also applied in (1). | (7) |
The duality of the two EM potentials is also apparent. Mutually related algebraically and differentially (8), these potentials just determine the three EM fields (9). The static potential may be understood as some strain of the medium, and its gradient determines respective forces (9a). Tending to statistic compensation of the strains, two equipolar charges mutually repel, and opposite ones attract each other. The motion (8a) or flow (8b) – of the static, just forms the kinetic potentials. These two relations point to at least quasi-fluidic interpretation of all EM phenomena. Owing to Bernoulli’s effect, transverse gradient of the flow (9b) determines its kinetic interactions with other such flows. The acceleration, as time derivative of the motion, may be considered as the third – dynamic potential (9c). Each field is thus defined as the formal feature of respective potential.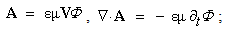 | (8) |
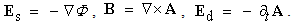 | (9) |
Instead of the former dual conception of the two EM fields and four Maxwell’s equations – emphasized by H. Hertz, a trilateral system of the static, kinetic and dynamic processes and respective three fields is thus reaffirmed. This system is founded on the three relevant Maxwell’s equations (6) and respective gauge conditions (9). The algebraic pair (1) is already reaffirmed and related with the differential equations. In addition, the central laws [5] will be further considered in the continuation. The differential sets (6) and (9) link the successive, – of the three types of EM quantities: carriers, fields and potentials. Gauge conditions (9) define the fields by potentials, and Maxwell’s equations (6) – the carriers by fields. Relating the quantities of the same type, the algebraic equations (1) link successive pairs of the three kinematical states: static, kinetic and dynamic ones.
6. Electricity or Mass
Electricity and mass are introduced as the two independent concepts. In analogy with elementary charges, reduced to respective particles, some elementary mass is predicted and allegedly confirmed. Even if this confirmation were reliable, the question would remain: why and how it behaves as mass? Of course, the same question may concern electricity and its elementary particles. The particles themselves are not the final, nor essential explanations of physical phenomena, but mere substitutes of the continual substances, by their discrete values. The distinction may concern the two levels of their observation only. Apart from its doubtful confirmation, the elementary mass would not explain too much. Alike relation of electric and magnetic phenomena, possible relation of electricity and mass, or – of respective forces – as their interactions, would be a half of the solution.Apart from mutual exclusivity, formal similarities of the two strictly central forces – electrostatic and gravitational – as the interactions of respective present particles, is disturbed by the bipolar or non-polar natures of the two respective substances. On the other hand, the two – at least apparently exclusive – dynamic effects, induction and inertia, as the reactions on some acceleration of respective carrying bodies, also somehow distinguish: the former of them affects all the surrounding electricity, including the carrier itself, but the latter is restricted to the carrier. To overcome at least one of the two distinctions between EM and mechanical phenomena, we start from the static central law – in its usual (10) and alternative (11) forms. Radial integration of the central force – via 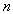 , gives respective potential energy, with the new factor
, gives respective potential energy, with the new factor 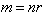 , where
, where 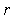 is particle radius, as the distance of the surface charge from its own centre.
is particle radius, as the distance of the surface charge from its own centre.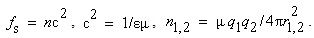 | (10) |
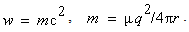 | (11) |
Kinetic interaction of moving charges is elaborated in [5]. Its particular form (12a) – of two commonly moving charges – at the speed 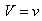 , at least conditionally – was accepted earlier. Respective alternative law (12b) is easily obtained by the radial integration. And finally, time derivative of (12b), partially – per
, at least conditionally – was accepted earlier. Respective alternative law (12b) is easily obtained by the radial integration. And finally, time derivative of (12b), partially – per 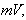 gives the dynamic, in fact – force action law (12c). The two factors
gives the dynamic, in fact – force action law (12c). The two factors 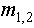 &
& 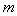 – of induction and self-induction, are thus identified as the mutual and proper masses. The alternative central law (11a) is nothing else than Einstein’s equation, giving the proper energy of a particle. As the condition of its equivalence with the usual law (10a), the relation (11b) was the basis for direct calculation of the ‘classical’ electron radius. With respect to the solid particle body implicitly expected, this result could not be practically confirmed, and was not accepted.
– of induction and self-induction, are thus identified as the mutual and proper masses. The alternative central law (11a) is nothing else than Einstein’s equation, giving the proper energy of a particle. As the condition of its equivalence with the usual law (10a), the relation (11b) was the basis for direct calculation of the ‘classical’ electron radius. With respect to the solid particle body implicitly expected, this result could not be practically confirmed, and was not accepted.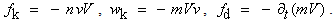 | (12) |
With respect to the Lorentz’ particle model, as the elastic, evenly distributed surface charge, the relation (11b) may be reaffirmed. Therefore, it relates the mass and electricity of a charged particle, in the function of its radius. Therefore, a lesser particle is of the greater mass, and vice versa. This fact points that the proper mass is at least partially contained in the surrounding electric field. Of course, majority of this portion is located at the smaller radii, of the stronger field. The mass of a globally neutral body, as the multi-pole, is thus located between adjacent poles. Owing to partial cancelation of the opposite elementary fields in the wider surroundings, this mass is in some extent defected in comparison with the full sum of separate masses of all the particles. All these expectations are already well-known, or will be confirmed and/or interpreted in the continuation.The force (12a) affects in return the carrying particle itself – as the object, at 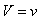 . Subtracted from the static force (10), this gives the total force (13), where
. Subtracted from the static force (10), this gives the total force (13), where 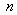 depends on the radius, and
depends on the radius, and 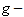 on speed. Tending to zero – approaching the speed
on speed. Tending to zero – approaching the speed 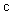 , from
, from 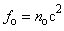 , where
, where 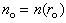 – at rest, this force strives to expand the particle. Therefore, it must be opposed by a constant external reaction, the same as at rest. The balance (
– at rest, this force strives to expand the particle. Therefore, it must be opposed by a constant external reaction, the same as at rest. The balance (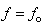 ) gives the relations (14). The latter of them is known as Lorentz’ mass function [5], introduced on the empirical bases. It is here derived directly, by the simple formal procedure. With the factor
) gives the relations (14). The latter of them is known as Lorentz’ mass function [5], introduced on the empirical bases. It is here derived directly, by the simple formal procedure. With the factor 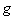 – dependent on speed, mass is minimal when resting in a – somehow preferred – reference frame, thus finally denying its relativity. Not only that the variable mass is none a relativistic effect, but just contradicts to this speculative doctrine.
– dependent on speed, mass is minimal when resting in a – somehow preferred – reference frame, thus finally denying its relativity. Not only that the variable mass is none a relativistic effect, but just contradicts to this speculative doctrine.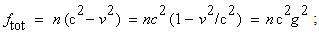 | (13) |
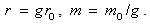 | (14) |
7. Mass or Energy
As the basis for indirect derivation of (11a), the relation (14b) further confirms the reduction of inertia to induction. With respect to the mass differential, 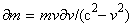 , the procedure (15a,b) relates the two differentials. The term
, the procedure (15a,b) relates the two differentials. The term 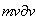 just accords to the classical kinetic energy, assuming the constant mass (with
just accords to the classical kinetic energy, assuming the constant mass (with 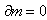 ). Really, the term
). Really, the term 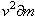 may be neglected at the smaller speeds. The integration gives the proper kinetic energy of the moving particle, as the difference of its two values – in accord with (11a). Mere substitution of respective two masses (15d) gives the final result, relating the kinetic energy of the moving charged particle with that of the electric field between the two radii (
may be neglected at the smaller speeds. The integration gives the proper kinetic energy of the moving particle, as the difference of its two values – in accord with (11a). Mere substitution of respective two masses (15d) gives the final result, relating the kinetic energy of the moving charged particle with that of the electric field between the two radii (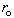 &
& 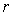 ) – of the resting and moving states. This is more transparent and advanced, further clarified and interpreted, well-known Einstein’s result, initially obtained accidentally, without the final EM explanation (15d).
) – of the resting and moving states. This is more transparent and advanced, further clarified and interpreted, well-known Einstein’s result, initially obtained accidentally, without the final EM explanation (15d).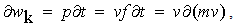 | (15a) |
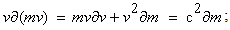 | (15b) |
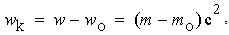 | (15c) |
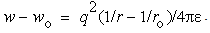 | (15d) |
There is the question of the different energies calculated by distinct procedures. The electric energy density (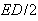 ) integrated between the radii – of the regular and compressed particle, as the difference of respective masses, gives a half of the energy obtained by the integration of the central forces (15). Apart from the field energy between the two particle radii, this value as if comprises the other its half, of unknown nature and location. Thus not manifest in the external 3D space – around the particle – on the observed structural level, it may be ascribed to the particle volume, or to the temporal domain out of 3D, or to finer structural levels of the medium. In each of the three cases, the two equal parts of energy point to the balance of respective forces, in 3D, 4D or 5D spaces. In the final instance, this is not a single such question which answer must be postponed into the future.Some well known and widely accepted relations are still not sufficiently interpreted. Let us compare Maxwell’s (10b), with Einstein’s (11a) relations. The former determines the speed of EM wave propagation by the two constants, as the abstract medium features. On the other hand, in the sense of the ratio of the energy and mass densities – inside the usual mechanical media, the latter relation determines the speed of propagation of respective its disturbances. In this sense, the elimination of the value
) integrated between the radii – of the regular and compressed particle, as the difference of respective masses, gives a half of the energy obtained by the integration of the central forces (15). Apart from the field energy between the two particle radii, this value as if comprises the other its half, of unknown nature and location. Thus not manifest in the external 3D space – around the particle – on the observed structural level, it may be ascribed to the particle volume, or to the temporal domain out of 3D, or to finer structural levels of the medium. In each of the three cases, the two equal parts of energy point to the balance of respective forces, in 3D, 4D or 5D spaces. In the final instance, this is not a single such question which answer must be postponed into the future.Some well known and widely accepted relations are still not sufficiently interpreted. Let us compare Maxwell’s (10b), with Einstein’s (11a) relations. The former determines the speed of EM wave propagation by the two constants, as the abstract medium features. On the other hand, in the sense of the ratio of the energy and mass densities – inside the usual mechanical media, the latter relation determines the speed of propagation of respective its disturbances. In this sense, the elimination of the value 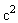 from the two equations directly relates the ratio of the energy and mass densities – in the medium, with the product
from the two equations directly relates the ratio of the energy and mass densities – in the medium, with the product 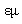 . The energy of the structural strains, as modulus of elasticity, is inversely proportional to electric constant. This comparison points to the analogous, electro-fluidic interpretation of EM phenomena, respective quantities and their mutual relations.In accord to (14b,15c), Fig. 1. presents the kinetic energy of a moving particle. At small speeds, it nearly equals to the classical kinetic energy (
. The energy of the structural strains, as modulus of elasticity, is inversely proportional to electric constant. This comparison points to the analogous, electro-fluidic interpretation of EM phenomena, respective quantities and their mutual relations.In accord to (14b,15c), Fig. 1. presents the kinetic energy of a moving particle. At small speeds, it nearly equals to the classical kinetic energy (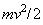 ), but considerably separates – at the greater speeds, tending into infinity – approaching the speed
), but considerably separates – at the greater speeds, tending into infinity – approaching the speed 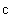 . In accord with Einstein’s relation (11a), the energy and mass of a resting or moving particle, as well as their differentials, are mutually proportional. Not only that the classical kinetic energy does not obey the greater speeds, but its interpretation was also inadequate. Instead of direct function of speed – at the constant mass, the kinetic energy accords to the mass difference. Though already renounced, the classical opinion is still implicitly understood in some physical disciplines, as the kinetic gas theory is. Such the inconsistencies are very frequent between various, or even inside particular physical disciplines.
. In accord with Einstein’s relation (11a), the energy and mass of a resting or moving particle, as well as their differentials, are mutually proportional. Not only that the classical kinetic energy does not obey the greater speeds, but its interpretation was also inadequate. Instead of direct function of speed – at the constant mass, the kinetic energy accords to the mass difference. Though already renounced, the classical opinion is still implicitly understood in some physical disciplines, as the kinetic gas theory is. Such the inconsistencies are very frequent between various, or even inside particular physical disciplines. 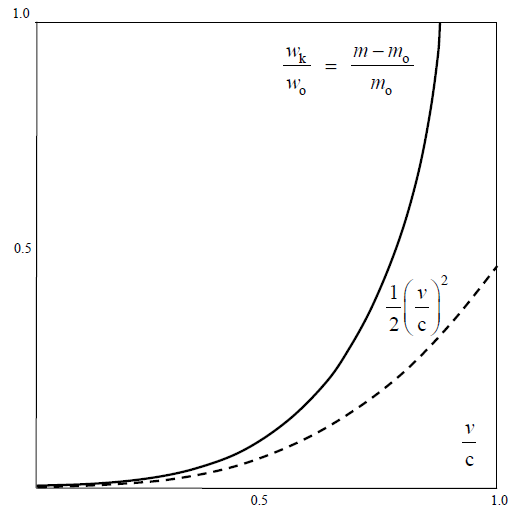 | Figure 1. Mass or energy function |
According to the diagram, the upper speed (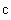 ) demands the infinite energy, and so cannot be attained. The functions of the radius and mass (14) physically explain this limitation, by zero particle volume. The mystification of this limitation – from SRT, founded on mere formal consideration of the square root – in (13b), is thus interpreted rationally. On the other hand, the standard speed of EM wave propagation (
) demands the infinite energy, and so cannot be attained. The functions of the radius and mass (14) physically explain this limitation, by zero particle volume. The mystification of this limitation – from SRT, founded on mere formal consideration of the square root – in (13b), is thus interpreted rationally. On the other hand, the standard speed of EM wave propagation (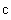 ) is determined by two respective constants, as the medium features, also without any mystics. This speed is diminished in the denser media, up to zero – in the critical gravitational field. Moreover, at some special media (mentioned in the next section), it may even exceed the upper limit. In the final instance, with respect to the slower waves (e. g. of sound) – at the cruder media, at possible finer media respective waves and particles may be much faster than
) is determined by two respective constants, as the medium features, also without any mystics. This speed is diminished in the denser media, up to zero – in the critical gravitational field. Moreover, at some special media (mentioned in the next section), it may even exceed the upper limit. In the final instance, with respect to the slower waves (e. g. of sound) – at the cruder media, at possible finer media respective waves and particles may be much faster than 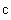 .Explicitly or implicitly, in classical and modern physics, mass denotes matter amount. On the other hand, with respect to its above EM interpretation, the notion of matter is mainly overcome. In the strictly scientific sense, mass can only represent the measures of inertia or gravitation, proportional to respective forces. Though EM waves and photons contain their energies, they seem to be mass-less. Due to the standard speed and inability of a force action, the longitudinal inertia cannot be manifest directly. However, the propagation of light along gravitational field changes the photon energy, equivalently to the acceleration of respective mass. The strait path is curved in inhomogeneous media or fields, reminding centripetal forces. The currents of energy and mass, related in the form of (11a), represent the linear momentum density (16), noticed as the pressure of EM waves.
.Explicitly or implicitly, in classical and modern physics, mass denotes matter amount. On the other hand, with respect to its above EM interpretation, the notion of matter is mainly overcome. In the strictly scientific sense, mass can only represent the measures of inertia or gravitation, proportional to respective forces. Though EM waves and photons contain their energies, they seem to be mass-less. Due to the standard speed and inability of a force action, the longitudinal inertia cannot be manifest directly. However, the propagation of light along gravitational field changes the photon energy, equivalently to the acceleration of respective mass. The strait path is curved in inhomogeneous media or fields, reminding centripetal forces. The currents of energy and mass, related in the form of (11a), represent the linear momentum density (16), noticed as the pressure of EM waves.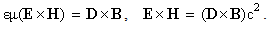 | (16) |
8. Particle or Wave
Though the eternal dilemma between the final constituent particles or endless divisibility of matter, is not resolved, the former alternative is preferred – as the implicit provisional supposition. Matter is usually considered in the solid state, and the fluidic states are reduced to, more or less free moving, constituent particles. Conditioned by such images, physicists expected the rigid, or at least solid elementary particles. This view was supported by the negation of any vacuum medium, for the sake of SRT. Moreover, both terms of ‘quantum mechanics’ further fix all these solid-mechanical concepts. Apart from some smallest particles, all their features and interactions by the fields are also expected to be somehow quantized. However, irrespective of the discrete particle measures, only electric charge is really quantized. In spite of some predictions, it is not divided so far.On the other hand, sound and EM radiation are reduced to respective waves. Longitudinal waves propagate in the radial direction, but transverse ones, as the expanding toroidal vortices, predominate in the plane of propagation. All of them spread and thus weak, more or less strictly, by square of the path. Light itself manifests EM features, but consists of photons, as some energetic particles. Though propagate at speed 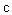 – of the waves, photons do not spread and weak in space. Their apparent dual nature is finally taken for granted by the term wave packet, formally supported by an abstract wave equation, which may mean everything or nothing. The relation of photon energy and frequency,
– of the waves, photons do not spread and weak in space. Their apparent dual nature is finally taken for granted by the term wave packet, formally supported by an abstract wave equation, which may mean everything or nothing. The relation of photon energy and frequency, 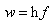 – noticed empirically, as if announces the quantization. However, the frequency (
– noticed empirically, as if announces the quantization. However, the frequency (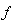 ) is not a discrete, but continual quantity, and so, neither the photon energy is quantized.The synthesis of the two natures of light is here obtained on EM bases. Namely, a convection current (
) is not a discrete, but continual quantity, and so, neither the photon energy is quantized.The synthesis of the two natures of light is here obtained on EM bases. Namely, a convection current (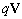 ) and its kinetic potential – as motion of the static potential (8), are mutually collinear. However, this current itself is continued in the surrounding space by the displacement current (17a). In the case of the central field (17b), this current is obtained in the form of a toroidal vortex (Fig. 2). With respect to the particle radius – dependent on speed, this vortex is manifest in the resting medium as the photon associated to the moving particle, of the frequency and energy proportional to the linear momentum. At the stoppage or deceleration of the particle, its kinetic energy (15d) would be released – fully or partially. Thus independent on the carrier, it continues its free motion at the speed
) and its kinetic potential – as motion of the static potential (8), are mutually collinear. However, this current itself is continued in the surrounding space by the displacement current (17a). In the case of the central field (17b), this current is obtained in the form of a toroidal vortex (Fig. 2). With respect to the particle radius – dependent on speed, this vortex is manifest in the resting medium as the photon associated to the moving particle, of the frequency and energy proportional to the linear momentum. At the stoppage or deceleration of the particle, its kinetic energy (15d) would be released – fully or partially. Thus independent on the carrier, it continues its free motion at the speed 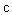 . In such a form, it manifests the mentioned features of a particle and wave.
. In such a form, it manifests the mentioned features of a particle and wave.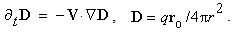 | (17) |
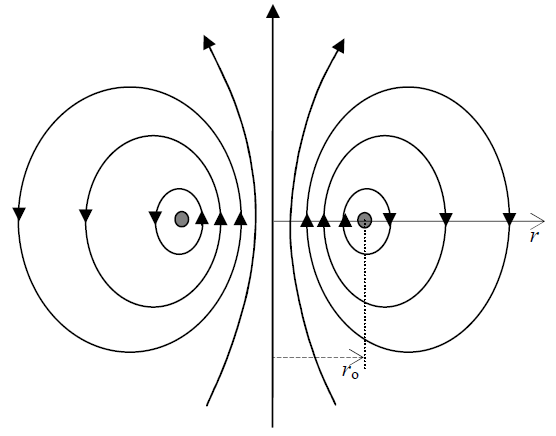 | Figure 2. Toroïdal vortex |
Of course, light propagation is referred to the expanding cosmos, as the moving medium. The formal speed  – in a
– in a  plane, is physically irrelevant. The expansion extends the photons themselves, equivalently to respective Doppler’s effect. This effect is manifest as the linear decrease of photon frequency and energy, with respective red shift, pointing to the cosmic expansion. The denser media or fields slow down the propagation. This is explained by temporary retaining of a fraction of wave energy by cruder structures [5]. At a given energy current, this effect increases the local energy density, and decreases the effective speed of propagation, in the ratio of the refraction factor (18a). Owing to sparser non-engaged medium, the remaining energy propagates at the wave speed (18b). The two obsolete terms – group and phase speeds – understood the wave packet concept.
plane, is physically irrelevant. The expansion extends the photons themselves, equivalently to respective Doppler’s effect. This effect is manifest as the linear decrease of photon frequency and energy, with respective red shift, pointing to the cosmic expansion. The denser media or fields slow down the propagation. This is explained by temporary retaining of a fraction of wave energy by cruder structures [5]. At a given energy current, this effect increases the local energy density, and decreases the effective speed of propagation, in the ratio of the refraction factor (18a). Owing to sparser non-engaged medium, the remaining energy propagates at the wave speed (18b). The two obsolete terms – group and phase speeds – understood the wave packet concept.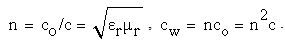 | (18) |
9. Bodies or Images
After relation of mass with energy and electricity, there is the question of the final nature of the last quantity. What is electricity? Does something as respective particles exist at all? In fact, a separate particle body, distinct from its fields, has never been practically evidenced. The measuring of electron radius stayed unsuccessful. Not only that its elastic surface cannot be estimated by the passing through various holes, but the same electron, alike a wave, passes through a few close holes, without destruction of its identity. With respect to the differential equations, the carriers are formal features of EM fields, and the fields – of potentials. In the final instance, a particle may be reduced to the centre, something as a knot of its surrounding manifestations. The only acceptable form of this knot, imagined intuitively, is the hipper-toroidal vortex of the flow (Fig. 2), but observed in 4D space.Axial orientation and motion of the vortex along 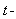 axis represent the necessary conditions for its existence. All the particles moving in common in the same direction form a hipper-spherical wave, as the expanding cosmos. This idea explains why and how 3D cosmos is globally curved and closed into itself. The continual lapse of time, the same for all celestial objects, may be determined by this wave, as well as gravitation, as the attraction in the parallel motion. Circular flow in a particle, superimposed to cosmic process, disturbs the local pressure, as the static potential. The positive flow thus causes the negative potential, and vice versa. This fact explains the two opposite polarities, and the opposite signs in the static and kinetic central laws (10a) & (12a). The two polarities obviously obey, somehow already predicted, CPT (circulation-polarity-time) symmetry.With respect to the four axes and six planes, cross product and curl-operation are not defined in 4D space. Possible application of the field theory in this space is partial, limited to its subspaces. Let us try to treat the above hipper-vortex mathematically. If its flows were understood as the closed contours of the kinetic potential in
axis represent the necessary conditions for its existence. All the particles moving in common in the same direction form a hipper-spherical wave, as the expanding cosmos. This idea explains why and how 3D cosmos is globally curved and closed into itself. The continual lapse of time, the same for all celestial objects, may be determined by this wave, as well as gravitation, as the attraction in the parallel motion. Circular flow in a particle, superimposed to cosmic process, disturbs the local pressure, as the static potential. The positive flow thus causes the negative potential, and vice versa. This fact explains the two opposite polarities, and the opposite signs in the static and kinetic central laws (10a) & (12a). The two polarities obviously obey, somehow already predicted, CPT (circulation-polarity-time) symmetry.With respect to the four axes and six planes, cross product and curl-operation are not defined in 4D space. Possible application of the field theory in this space is partial, limited to its subspaces. Let us try to treat the above hipper-vortex mathematically. If its flows were understood as the closed contours of the kinetic potential in 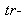 planes, its curl would represent something as the magnetic field, perpendicular to these planes. Apart from one spatial, each of its contours is thus coaxial with temporal axis. The common axial motion along this axis produces the central static field, according to (1b). The procedure (19) identifies the static and dynamic fields (20), under the condition:
planes, its curl would represent something as the magnetic field, perpendicular to these planes. Apart from one spatial, each of its contours is thus coaxial with temporal axis. The common axial motion along this axis produces the central static field, according to (1b). The procedure (19) identifies the static and dynamic fields (20), under the condition: 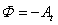 . This equality confirms the positive potential produced by negative flow, and vice versa. Though not fully strict and precise, this is the obvious mathematical correlation.
. This equality confirms the positive potential produced by negative flow, and vice versa. Though not fully strict and precise, this is the obvious mathematical correlation.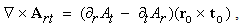 | (19a) |
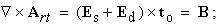 | (19b) |
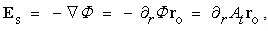 | (20a) |
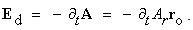 | (20b) |
EM quantities are reduced to the static potential and its motion. There is the question of some nature of the medium strains, as the possible essence of the mentioned potential. However, mechanical compressibility of a fluid cannot be fully accommodated with the established equations of EM theory. Instead, in analogy with EM structure of the cruder matter, the medium may be a similar dielectric continuum. With respect to the persistent strains and their motion, it must be dielectrically deformable, irresistive and reactive. The static potential is thus followed by the medium polarization, proportional to its gradient and electric constant. Similarly, the kinetic and dynamic effects are proportional to magnetic constant. Their product with the moving – static, thus give kinetic potentials (8a). Material structures thus seem to be nothing else than the moving EM images in the resting medium, similarly as on an LCD screen.The models of photon (in 3D) and particle (in 4D) are thus predicted. Their comparison points to some similarities and distinctions. The speeds of their propagations are determined by the medium features. Their existences are conditioned by the balance of two forces, concerning the linear and vortical motion. The projection from 4D into 3D spaces determines centrally symmetric particles, of the strict radii and masses, with the constant product 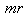 proportional to square of the elementary charge (11b). The energy of a photon is also inversely proportional to its radius, but – in the continual values. The charge enables a force action upon inert particle, accelerating it through 3D space – up to the speed
proportional to square of the elementary charge (11b). The energy of a photon is also inversely proportional to its radius, but – in the continual values. The charge enables a force action upon inert particle, accelerating it through 3D space – up to the speed  , limited by the zero volume. Formed in 3D – without electric charge, a photon is axially symmetric, free moving at the speed
, limited by the zero volume. Formed in 3D – without electric charge, a photon is axially symmetric, free moving at the speed  , and insensitive to the force action.
, and insensitive to the force action.
10. Compound Structures
With respect to the particle model and the cosmic wave directed in axis course, the faster summary flow inside the particle causes decreased pressure in the medium, and vice versa – outside the particle. The opposite circulation would give all the opposite effects. The two pressure disturbances on the surface cause the two different radii and masses of a proton and electron. Fig. 2 thus presents a proton, and Fig. 3 – respective potentials of the proton and electron. Their strict radii are finally determined by some resonant frequencies. The same such frequencies of respective antiparticles, as the unstable states, cause their less probability and inferiority of antimatter. With respect to the signs in the crucial equations (8a) & (9c), the medium may be incompressible, even as a solid. Its elastic deformation consists in its own polarization, storing respective (electro-static) energy.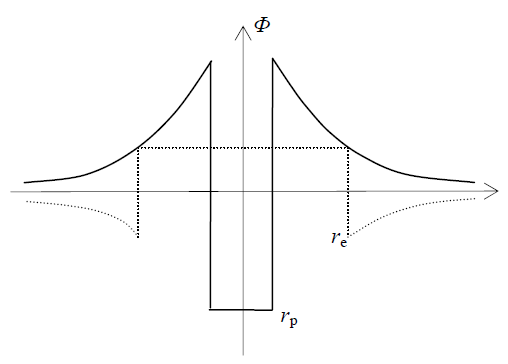 | Figure 3. Elementary central potentials |
Protons and electrons are sufficient elements for formation of other – at least stable – particles, as well as of the atoms and their nuclei. Instead of smearing of the particles about the shells, an electron embracing a proton, or vice versa, would form a hydrogen atom or neutron, respectively. The pairs or the concentric hipper-vortices mutually close, and thus annul their external fields. The same sequences of the quantum numbers in the atomic cover and nucleus point to the same principle of their own formation. The number of electronic shells – in the cover, accords to the difference of the opposite charges – in nucleus. Magnetic moments and quantum numbers of particles point to some disturbances of their 3D symmetries, tending to the minimal energies of the compositions. Of course, all these and other details demand much more serious investigation.Apart from the massive particles, photons and neutrinos seem to be mass-less. A toroidal vortex of the displacement current (17), as the photon model axial to own propagation, understands transverse circular vortex of its magnetic field. In the absence of its electric charge, photon energy is not manifest by noticeable mass. Such a vortex predominant at a longitudinal plane explains the light polarization. Atoms usually radiate the pairs of the opposite photon vortices, in the opposite courses. Their radii and energies are determined by the differences of the successive atomic energetic states. Due to the cosmic expansion or at gravitational field, photon energy & frequency are changed continually, with respective shift of spectral lines. Mutually concentric photons may form a neutrino. Without a mass and external field, this particle may be very fine, penetrable and elusive.
11. Physical Forces
Inertia and gravitation were introduced as the palpable mechanical forces. They were further supplemented by the similar EM, and assumed nuclear forces. Unlike the manifest EM and mechanical forces, nuclear ones intend to justify the cluster model of atomic nuclei, just overcome by above our concentric model. Not only that mutual relations of the few remaining forces were incomplete, but also their particular essences have been unknown. By superposition of various forces, R. Bošković (1711-86) tried their formal unification. Via Faraday, this idea was transferred to Einstein, without qualitative advances. In spite of real possibility far ago, mass is merely here explained by inertia of electricity, and inertia – by induction. EM forces are reduced to respective physical effects in vacuum medium. Independent similar explanation of gravitation is announced at least.The last but one idea is realized and elaborated [1-5]. EM quantities are interpreted and related by the standard, and less known or unapplied equations. The exposition starts by three EM forces – static, kinetic and dynamic, dependent on some disturbances of dielectric medium, their motion and/or acceleration. These processes demand dielectric, irresistive and reactive vacuum medium. The first of the three features enables the electro-static, and two latter – magneto-kinetic energies, with respective forces, as the gradients of their densities. Each physical force may be explained as the tendency to the full homogeneity of respective energy. The complementary energy densities in various layers accord to the mutual balances of the opposite forces. The structural non-resistance and reactivity of the medium maintain kinetic energies. The three medium features also enable the mutual transformations of the two types of energy.Some new ideas and obtained results demand respective physical interpretations. In this sense, as inertia is reduced to self-induction, the mutual induction must be a more general phenomenon than the inertia of finer structures, and demands a respective general interpretation. It really represents the dynamic electric field, as the opposite reaction against the polarization and depolarization of the surrounding medium, caused by the charge motion. Moreover, charge acceleration causes some difference of the two opposite dynamic forces, thus affecting all the present charges, including the causing charge. This interpretation does not concern the longitudinal kinetic induction in a parallel object conductor, caused by its own transverse motion. This effect is also manifest as the torque between two crosswise carrying conductors, by such interactions of their respective legs.The essence of gravitation and its relation with EM forces is an additional challenge. The attractive idea, relating the gravitation and lapse of time with cosmic expansion, is here already proposed. The central EM laws (10a & 12a) speak in favour of some relation of the two latter phenomena at least. The square of the light speed – in the static, instead of the speed product – in kinetic laws, points to the real motion along the fourth axis, at speed 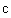 . This is further supported by convincing particle model. The parallel propagation of all cosmic particles or celestial bodies may be the real reason of their gravitational attraction. Apart from the particles, the surrounding fields are also included into the cosmic wave, as the invisible matter. The kinetic EM forces, caused by the spatial motion, are thus exclusive with respect to gravitation, caused by the temporal cosmic process.
. This is further supported by convincing particle model. The parallel propagation of all cosmic particles or celestial bodies may be the real reason of their gravitational attraction. Apart from the particles, the surrounding fields are also included into the cosmic wave, as the invisible matter. The kinetic EM forces, caused by the spatial motion, are thus exclusive with respect to gravitation, caused by the temporal cosmic process.
12. Orientation in Space
Apart from the static interactions, dependent on a mutual distance of interacting particles, the principle of relativity is artificially applied to the difference of kinetic and dynamic inductions [5], at mutual motion of the current carrying and object conductors, in the transverse direction, along the field gradient. The direction of the carrying conductor, along zero field gradient – without dynamic induction, is not taken into account. Moreover, with respect to dynamic forces (12c) – dependent on acceleration, the frame equivalence should be restricted to the inertial (un-accelerated) frames. For similar reasons, the kinetic interactions, dependent on speed, should be restricted to unmoving frames! In spite of inability of their definition, inertial frames are the deductive basis for SRT foundation. Subjective observer is substituted in practice by a field detector, as the moving object.In SRT foundation, a common detector moving at a speed 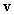 through resting EM fields causes the relative inductions. Their crosswise addition to similar fields gives the classical field transformations (22). This direct set, being inverted per the primed fields – by determinant theory, gives the inverse set (23). The set determinant,
through resting EM fields causes the relative inductions. Their crosswise addition to similar fields gives the classical field transformations (22). This direct set, being inverted per the primed fields – by determinant theory, gives the inverse set (23). The set determinant, 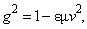 accidentally equal to the square of the factor
accidentally equal to the square of the factor 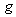 (14), just discriminates the two frames, speaking in favour of the preferred status of one of them. For the sake of the frame equivalence, SRT distributed this factor, – by
(14), just discriminates the two frames, speaking in favour of the preferred status of one of them. For the sake of the frame equivalence, SRT distributed this factor, – by 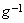 in each of the two sets. This arbitrary scaling of the transverse field components calls in question Maxwell’s equations, as the general distributions. To preserve their mathematical form, the two remaining 4D axes, longitudinal and temporal ones, are complementarily (in fact inversely) transformed (24).
in each of the two sets. This arbitrary scaling of the transverse field components calls in question Maxwell’s equations, as the general distributions. To preserve their mathematical form, the two remaining 4D axes, longitudinal and temporal ones, are complementarily (in fact inversely) transformed (24).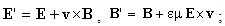 | (22) |
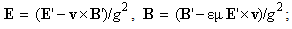 | (23) |
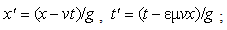 | (24) |
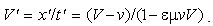 | (25) |
Unlike the functions (14), with the clear interpretations, the equations (24) cannot be anyhow understood. Their division gives the speed transformation (25). In the wave propagating at 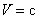 , this gives the identity:
, this gives the identity: 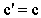 . It is interpreted as the invariant light propagation, in all (at least inertial) frames. Not only that this result is itself the obvious logical contradiction, but calls in question the medium of EM processes, and the wave nature of EM radiation. Following from the unfounded starting view, and carried out by the incorrect revision of the two sets (22 & 23), the full above procedure has none a support in reality. Michelson-Morley’s experiment concerns Earth, as the predominant mass – or locally preferred frame, and cannot be generalized to any other frame. Finally, there are the known wave effects, just determined by the variant speed of light.
. It is interpreted as the invariant light propagation, in all (at least inertial) frames. Not only that this result is itself the obvious logical contradiction, but calls in question the medium of EM processes, and the wave nature of EM radiation. Following from the unfounded starting view, and carried out by the incorrect revision of the two sets (22 & 23), the full above procedure has none a support in reality. Michelson-Morley’s experiment concerns Earth, as the predominant mass – or locally preferred frame, and cannot be generalized to any other frame. Finally, there are the known wave effects, just determined by the variant speed of light.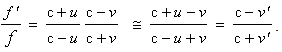 | (26) |
Her 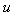 is the radar speed, and
is the radar speed, and 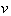 that of its object t;
that of its object t; 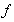 is the emitted, and
is the emitted, and 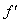 received signal frequency. The speeds of the two opposite beams, relative to the technical elements, cause a sequence of four Doppler’s effects. The particular of these effects can be confirmed by the additional receivers, on the light path and/or on object. The product
received signal frequency. The speeds of the two opposite beams, relative to the technical elements, cause a sequence of four Doppler’s effects. The particular of these effects can be confirmed by the additional receivers, on the light path and/or on object. The product 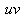 is neglected – in the continuation, with
is neglected – in the continuation, with 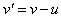 , as the mutual speed. In the aim of his originality, Einstein turned the last expression under a square root. Two of these effects arise at the mutual rotation of the dual star members, at their opposite speeds in the local medium of propagation. The distinct process causes the general red shift, ascribed to the cosmic expansion. Though the light source and receiver rest in respective local media, equivalent effect follows from permanent extension of the medium, along the light path.In the case of a common motion of the radar and object (
, as the mutual speed. In the aim of his originality, Einstein turned the last expression under a square root. Two of these effects arise at the mutual rotation of the dual star members, at their opposite speeds in the local medium of propagation. The distinct process causes the general red shift, ascribed to the cosmic expansion. Though the light source and receiver rest in respective local media, equivalent effect follows from permanent extension of the medium, along the light path.In the case of a common motion of the radar and object (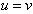 ), the particular effects mutually cancel, with equality of the two frequencies. Instead of this invariant quantity, the phase difference of the two signals is caused by the different paths through the medium, or the different speeds relative to the moving instrument. In this sense, Sagnac’s effect directly refutes the invariant light propagation, from SRT. This direct disprove of its main result is much more convincing than all the ‘experimental profs’ of SRT – in common. The absence of the similar result – in the case of Michelson-Morley’s experiment, is caused by the connection of the instrument to Earth, as the carrier of predominant gravitation and reference of light propagation. Some very minor delay of this medium behind Earth’s motion, registered more accurately during 20th century, may be ascribed to the influence of the remaining, nearby & distant, celestial bodies.
), the particular effects mutually cancel, with equality of the two frequencies. Instead of this invariant quantity, the phase difference of the two signals is caused by the different paths through the medium, or the different speeds relative to the moving instrument. In this sense, Sagnac’s effect directly refutes the invariant light propagation, from SRT. This direct disprove of its main result is much more convincing than all the ‘experimental profs’ of SRT – in common. The absence of the similar result – in the case of Michelson-Morley’s experiment, is caused by the connection of the instrument to Earth, as the carrier of predominant gravitation and reference of light propagation. Some very minor delay of this medium behind Earth’s motion, registered more accurately during 20th century, may be ascribed to the influence of the remaining, nearby & distant, celestial bodies.
13. Conclusions
Each section of this text offers at least one new or renewed idea, result or interpretation. The following ordinal numbers accord to respective sections of the body text.1. The former development of EM theory, as the central physical discipline, is related with a number of contemporary misconceptions, in the bases of modern physics.2. The classical method – thesis, anti-thesis, synthesis – is announced and reaffirmed. At least a few examples of its application are presented in the continuation.3. A model of 5D space, convenient for this consideration, further interprets the temporal dimension – as the fourth, and introduces structural one – as the fifth axes.4. Instead of the field carriers or sources, in central laws and differential set, algebraic relations affirm the direct field actions, at each point of space – separately.5. Instead of the field duality and symmetric equations, the three types of EM quantities are related by the three sets, treating the forces in the three kinematical states.6. Mass is related with electricity and interpreted as its effect, including mass variation, being independent – or even contradictory – to the principle of relativity.7. Mass is a proportional manifestation of the energy in the particle surroundings. The waves, photons and neutrinos do not manifest explicitly their own masses.8. Instead of the dual (wave-particle) nature, comprising the thesis and anti-thesis, a toroidal vortex, as the synthesis, exceeds and substitutes the two alternatives.9. The new models of a photon, particle and cosmos are reduced to vortices, their surfaces – to respective balloons, and their bodies – to EM images in the medium.10. The predicted concentric models of atoms, neutrons and nuclei do not need nuclear forces, unfoundedly assumed for the sake of the cluster model of nuclei.11. All physical forces are gradients of respective energies, in various structural layers. EM and mechanical forces are here mutually compared and mainly related.12. All the facts determining physical orientation in space contradict to the starting views, formal procedures and main final results of the special theory of relativity. Not only that the foundation and wide acceptance of the quantum, relativistic and some other modern theories were enabled by the incomplete EMT, but its own completion has been so far blocked by these scientific views, very firmly established as mere religious convictions.
14. Discussion
There follows the review of the paper, made by a typical contemporary physicist (R), with answers of the author (A), disputing the established concepts and prejudices. R. This paper investigated electromagnetism theory (EMT), one of the cornerstones of modern physics. The authors tried pointing out the mis-concepts in the methodology and theories. However the authors failed to present solid evidence to support their idea. In addition, several issues, such as the relation of particle and wave, proposed by authors are within the classical EMT framework, which have been addressed by quantum electrodynamics.A. EMT, already elaborated in [1-5], is recognized as the central discipline of complete physics. This paper presents its main theoretical implications, as the wider consequences, starting from the former solid scientific results. The unique nature understands a united natural science, without separate exclusive addresses. The continual theory is here extended to micro-structure, without artificial quantization. In fact, only elementary charge, as the product of two mutually reciprocal quantities, is ever constant. The modern intention of some quantization of everything has not any empirical basis nor methodological necessity, but may be understood as a mere arbitrary concept of the formalistic science.R. Physics is mainly an experimental science. Observation, assumption and derivation are typical procedures in which the physicists discover new theories. The investigation of rationale and consistency of a theory is non-trivial for any theoretical research. Nevertheless the final criteria to judge the validity of physical theories are the results from the experiments. For example, the failure of ether theory is due to non-experiment support, instead of logical defects. If merely replying on theses, anti-theses and synthesis, physics would have been just a sub-diary of philosophy.A. During inductive elaboration, physics usually starts by some established empirical facts. Their formal relations and rational interpretations merely give a theory. In the space of various external conditions, empirical results represent the separate singular points. A general physical theory demands their interpolation and extrapolation. Therefore, two distinct theories may cut each other through the same empirical facts, which may be thus explained by the both of these theories. A fact disobeying the theory disproves it or reduces its validity. Though each new result obeying the theory speaks in favour of its probability, it cannot judge of its general validity. The internal consistency and exhaustive comparison with wider knowledge and experience further affirm the theory. The theses and antitheses in physics also include the empirical results. However, the higher natural essence exceeds our empirical abilities. E. g., though invisible and impalpable, some vacuum medium is evident indirectly. The particle pair is produced from it, and cannot be annihilated into nothing. The vacuum medium is polarized by evident displacement currents and undulated by EM waves.R. There are several problems of this paper. First, the authors obscured the problems in quantum electromagnetism, relativity and EMT. They failed to provide convincing evidence to reveal the defects of EMT. With respect to quantum electrodynamics, the electromagnetic force arises due to an exchange of photons, while the authors created three mysterious interactions – static, kinetic and dynamic, which is poorly proved. Second, the authors attempted to answer the substantial questions which cannot be addressed by the classic EMT. But the assumption or reasoning is problematic. For instance, the authors claimed that the propagation speed of EM wave can exceed of the speed of light is trivial because of the difference in phase and group speed. Last but not least, the paper brought out some novel physical terms, for example, the fifth – structural dimension by presented the conclusions, relation between electricity and mass and etc.. Those newly-introduced concepts are redundant and/or non-experiment support.A. This paper confronts already elaborated EMT [5] with quantum theory and special relativity. The consistency of the former is preferred to the controversial speculations of the latter two. The main modern concepts are thus convincingly disproved. The photon exchange is founded on the classical thesis of the force transfer through the space, instead of the direct action at a distance. Not only that Maxwell’s equations do not take into account any time for the force transfer, but the photon barter may explain the repulsive forces only, and contradicts to the attraction. If understood at the carrier rest, why and how these interactions also depend on its speed and acceleration? All these difficulties are overcome by the three types of interactions, dependent on kinematical states. The distant action is explained by the external particle essence. Impossible wave packet and its dual speed is substituted by the vortical photon model. The standard wave propagation is slowed down by temporal retaining of a fraction of wave energy by cruder structures. The structure stratification is expressed by the fifth axis. Not only that these concepts remove the former difficulties, but obey at least the main empirical facts. Of course, they may be further practically tested and theoretically examined.R. Neither do I consider the modern physics is perfect, such as the inconsistency of quantum mechanics and general relativity on black hole theory, nor diminish the significance of logic or theoretical works. My point is the real revolution of physics happens as the experiments agree with the predictions of the theories. String theory shows great potential to be a quantum theory of gravity, but is criticized as a failure as a theory of everything for not providing novel experimental predictions at accessible energy scale. Higgs mechanism was admitted as the real theory of the origin of the mass only after the experimental confirmations.A. Less than inductive theories, these ones – founded on arbitrary assumptions and speculative conclusions – can be confirmed by any experimental results. This is especially impossible if the theory has some internal inconsistencies or contradicts to the wider knowledge and experience. SRT is such an example, convincingly disproved above. The last reviewer’s example would be here especially interesting. The mentioned assumption of elementary mass and its recent verification, both founded on the sequences of speculative thoughts, are extremely doubtful. Starting from the arbitrary formal concept – how a little Peter imagines a new particle, something similar to its possible manifestations has been evidenced in the probability about 50 %. On the other hand, above our considerations mutually relate mass, energy and electricity, as the various manifestations of the same particle model. Not only that the mass boson existence is uncertain, but this concept is theoretically excessive.Being unable to accept any new idea from the beginning, the reviewer neglected the remaining majority of the paper, as if that he did not read it. In fact, he is not very familiar with EM processes. Irrespective of the forces dependent on the speeds and accelerations of interacting charges, the kinetic and dynamic interactions are mysterious for him. Instead, he persistently repeats the controversial concepts, as the wave packet, its dual nature, twofold motion and barter between the particles. He forgot or newer knew that these concepts are just theses and anti-theses. Without adequate syntheses, they are tolerated as the scientific miracles.Though partial and tendentious, the review influenced the further affirmation of the re-examination – presented in the paper, on account of the modern scientific views. Of course, with respect to the very wide front of the re-examination, its understanding, and especially – the final acceptance, cannot be expected at once. On the other hand, in such its total form, the paper is more systematic and convincing. Instead of its extension or fraction into separate topics, its references and repeated readings may be recommended.
References
| [1] | B. Mišković, Essential Overview of EM Theory, Springer-Verlag, Selected Topics in Nonlinear Dynamics and TEE, Volume 459, 2013, pp 234-254, Ch. 13. |
| [2] | B. Mišković, Inductive Elaboration of EM Theory, SAP – International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications, Vol.3, No. 3, 2013. |
| [3] | B. Mišković, Deductive Exposition of EM Theory, SAP – International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, 2013. |
| [4] | B. Mišković, Thematic Consideration of EM Theory, SAP – International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Vol. 3, No. 5, 2013. |
| [5] | B. Mišković, Systematic Foundation of EM Theory, SAP – International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications, Vol. 4, No. 1 or 2, 2014. |
| [6] | B. Mišković, Electrodynamics (in Serbo-Croatian), http://solair.eunet.rs/~brami/ |
| [7] | B. Mišković, General Physics (in Serbo-Croatian), http://solair.eunet.rs/~brami/ |
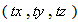 – in temporal, and ‘transverse’
– in temporal, and ‘transverse’ 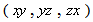 – in spatial domains. Apart from the three translations and enforced temporal motion, each rotation from 3D space may be associated with one spatial and the temporal axes. Similarly, each rotation from a
– in spatial domains. Apart from the three translations and enforced temporal motion, each rotation from 3D space may be associated with one spatial and the temporal axes. Similarly, each rotation from a  plane is associated with the two remaining spatial axes. These facts are the main difficulties in direct 4D imaginations. The sets of by three axes represent the four 3D subspaces. With the preferential sense of the
plane is associated with the two remaining spatial axes. These facts are the main difficulties in direct 4D imaginations. The sets of by three axes represent the four 3D subspaces. With the preferential sense of the  axis,
axis, 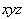 -subspace is manifest as the phenomenal world. Three ranks of tensor quantities, vectors, bi-vectors & tri-vectors, are associated to respective subspaces: axes, planes and 3D spaces.Without explicit empirical or logical argumentations, the intuitive hipper-spherical cosmic model is already widely accepted. However, some EM antinomies in the strait space are resolved by this model [1]. Moreover, the basic equations of EMT [2] point to the temporal motion, at speed
-subspace is manifest as the phenomenal world. Three ranks of tensor quantities, vectors, bi-vectors & tri-vectors, are associated to respective subspaces: axes, planes and 3D spaces.Without explicit empirical or logical argumentations, the intuitive hipper-spherical cosmic model is already widely accepted. However, some EM antinomies in the strait space are resolved by this model [1]. Moreover, the basic equations of EMT [2] point to the temporal motion, at speed 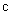 . With respect to this speed, the cosmic process may be understood as a hyper-spherical wave, directed along the temporal axis. With respect to the local image of strait axes, the spherical 3D space can also not be imagined. In the polar frame, t-axis would be set up radially. The propagation along it is projected into 3D, as continual process of cosmic expansion, the same for all the matter. The cosmic evolution depends on the t-axis form. Instead of this strait axis – with inflationary cosmos, its circular form would determine, maybe much more acceptable, pulsating cosmos.EM field tensor [3] explicates 4D senses of EM quantities and their relations. Space and time form 4D continuum, with the preference of t-axis. The addition of matter, as the third natural category, demands a new axis. In absence of a simple interpretation of the fifth axis, this idea was very difficult to be accepted. Its arbitrary closing on the elementary levels enabled only uncontrolled multiplication of such new axes. Instead, a convincing structural dimension is introduced in [3]. Poynting’s theorem, as a 5D continuity equation, is the example of its application. In this sense, EM processes develop in the four structural layers: vacuum, polarization, magnetization and conducting ones. The motion along the fifth axis would mean some structural transformation of the observed objects. Their zooming may be understood as the displacement of observation along this axis.
. With respect to this speed, the cosmic process may be understood as a hyper-spherical wave, directed along the temporal axis. With respect to the local image of strait axes, the spherical 3D space can also not be imagined. In the polar frame, t-axis would be set up radially. The propagation along it is projected into 3D, as continual process of cosmic expansion, the same for all the matter. The cosmic evolution depends on the t-axis form. Instead of this strait axis – with inflationary cosmos, its circular form would determine, maybe much more acceptable, pulsating cosmos.EM field tensor [3] explicates 4D senses of EM quantities and their relations. Space and time form 4D continuum, with the preference of t-axis. The addition of matter, as the third natural category, demands a new axis. In absence of a simple interpretation of the fifth axis, this idea was very difficult to be accepted. Its arbitrary closing on the elementary levels enabled only uncontrolled multiplication of such new axes. Instead, a convincing structural dimension is introduced in [3]. Poynting’s theorem, as a 5D continuity equation, is the example of its application. In this sense, EM processes develop in the four structural layers: vacuum, polarization, magnetization and conducting ones. The motion along the fifth axis would mean some structural transformation of the observed objects. Their zooming may be understood as the displacement of observation along this axis.

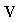 represents the speed of electric, and
represents the speed of electric, and 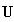 – of magnetic fields. The total fields
– of magnetic fields. The total fields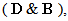 moving along their own gradients, produce the dissimilar vacuum fields
moving along their own gradients, produce the dissimilar vacuum fields 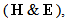 respectively, constitutively related with the former ones (2). The magnetic field – kinetically produced in (1a) – may be moved in the dynamic process (1b). There arises the question of some comparison of the two basic sets, algebraic and differential ones, in the sense of their complete or partial equivalence. Div & curl applied to the pair (1) give the four differential forms, wider than Maxwell’s equations are. The comparison points to the speed derivatives, in the excessive terms. They are eliminated by restriction of (1) to exclusively uniform and rectilinear field translation. Really, the former of them applied to circular motion follows into difficulties. Let us now transform the two restricted forms (3) and (4) into Maxwell’s differential equations (6).
respectively, constitutively related with the former ones (2). The magnetic field – kinetically produced in (1a) – may be moved in the dynamic process (1b). There arises the question of some comparison of the two basic sets, algebraic and differential ones, in the sense of their complete or partial equivalence. Div & curl applied to the pair (1) give the four differential forms, wider than Maxwell’s equations are. The comparison points to the speed derivatives, in the excessive terms. They are eliminated by restriction of (1) to exclusively uniform and rectilinear field translation. Really, the former of them applied to circular motion follows into difficulties. Let us now transform the two restricted forms (3) and (4) into Maxwell’s differential equations (6).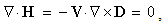
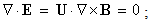
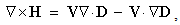
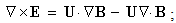
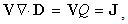
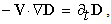
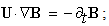
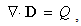
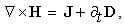
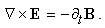
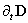 ) in (6b), respective term (
) in (6b), respective term (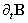 ) in (6c) may be formally considered as magnetic displacement current. Therefore, the equations (6) define the three carriers (electricity and the two currents) as the formal features of respective EM fields.Above restriction may be explained by the moving fields as the rigid structures, forming the gyroscopes in common with their carriers. This concept prefers the action – directly at a distance, instead of the assumed field transfer – at some finite speed. In the former opinion, a particle is considered as field carrier, and in latter – its source. Though was without convincing interpretation, the former principle is implicitly understood in all the equations of EMT. The observed fields are present at each point of 3D space, acting directly and instantly, as stretched arms. Not only that the latter principle is energetically problematic, but it is not built into Maxwell’s set, though accepted in common with it. Even this set does not take into account any time for the field transfer. However, this view is transferred into modern physics, where particles allegedly exchange some photons.
) in (6c) may be formally considered as magnetic displacement current. Therefore, the equations (6) define the three carriers (electricity and the two currents) as the formal features of respective EM fields.Above restriction may be explained by the moving fields as the rigid structures, forming the gyroscopes in common with their carriers. This concept prefers the action – directly at a distance, instead of the assumed field transfer – at some finite speed. In the former opinion, a particle is considered as field carrier, and in latter – its source. Though was without convincing interpretation, the former principle is implicitly understood in all the equations of EMT. The observed fields are present at each point of 3D space, acting directly and instantly, as stretched arms. Not only that the latter principle is energetically problematic, but it is not built into Maxwell’s set, though accepted in common with it. Even this set does not take into account any time for the field transfer. However, this view is transferred into modern physics, where particles allegedly exchange some photons.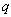 ) moving at some speed (
) moving at some speed (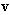 ) is determined by (7a). The same interaction may be also expressed by kinetic electric field (7b), collinear with this interaction. With respect to the perpendicular positions of the two thus related EM fields, the cross products are also applied in (1).
) is determined by (7a). The same interaction may be also expressed by kinetic electric field (7b), collinear with this interaction. With respect to the perpendicular positions of the two thus related EM fields, the cross products are also applied in (1).
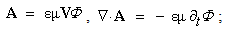
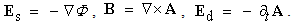
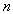 , gives respective potential energy, with the new factor
, gives respective potential energy, with the new factor 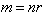 , where
, where 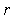 is particle radius, as the distance of the surface charge from its own centre.
is particle radius, as the distance of the surface charge from its own centre.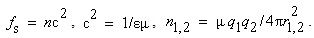
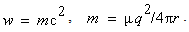
 , at least conditionally – was accepted earlier. Respective alternative law (12b) is easily obtained by the radial integration. And finally, time derivative of (12b), partially – per
, at least conditionally – was accepted earlier. Respective alternative law (12b) is easily obtained by the radial integration. And finally, time derivative of (12b), partially – per 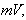 gives the dynamic, in fact – force action law (12c). The two factors
gives the dynamic, in fact – force action law (12c). The two factors 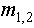 &
& 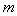 – of induction and self-induction, are thus identified as the mutual and proper masses. The alternative central law (11a) is nothing else than Einstein’s equation, giving the proper energy of a particle. As the condition of its equivalence with the usual law (10a), the relation (11b) was the basis for direct calculation of the ‘classical’ electron radius. With respect to the solid particle body implicitly expected, this result could not be practically confirmed, and was not accepted.
– of induction and self-induction, are thus identified as the mutual and proper masses. The alternative central law (11a) is nothing else than Einstein’s equation, giving the proper energy of a particle. As the condition of its equivalence with the usual law (10a), the relation (11b) was the basis for direct calculation of the ‘classical’ electron radius. With respect to the solid particle body implicitly expected, this result could not be practically confirmed, and was not accepted.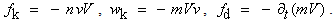
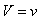 . Subtracted from the static force (10), this gives the total force (13), where
. Subtracted from the static force (10), this gives the total force (13), where 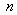 depends on the radius, and
depends on the radius, and 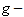 on speed. Tending to zero – approaching the speed
on speed. Tending to zero – approaching the speed 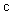 , from
, from 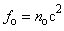 , where
, where 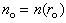 – at rest, this force strives to expand the particle. Therefore, it must be opposed by a constant external reaction, the same as at rest. The balance (
– at rest, this force strives to expand the particle. Therefore, it must be opposed by a constant external reaction, the same as at rest. The balance (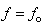 ) gives the relations (14). The latter of them is known as Lorentz’ mass function [5], introduced on the empirical bases. It is here derived directly, by the simple formal procedure. With the factor
) gives the relations (14). The latter of them is known as Lorentz’ mass function [5], introduced on the empirical bases. It is here derived directly, by the simple formal procedure. With the factor  – dependent on speed, mass is minimal when resting in a – somehow preferred – reference frame, thus finally denying its relativity. Not only that the variable mass is none a relativistic effect, but just contradicts to this speculative doctrine.
– dependent on speed, mass is minimal when resting in a – somehow preferred – reference frame, thus finally denying its relativity. Not only that the variable mass is none a relativistic effect, but just contradicts to this speculative doctrine.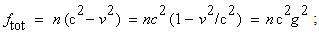
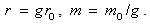
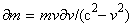 , the procedure (15a,b) relates the two differentials. The term
, the procedure (15a,b) relates the two differentials. The term 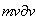 just accords to the classical kinetic energy, assuming the constant mass (with
just accords to the classical kinetic energy, assuming the constant mass (with 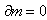 ). Really, the term
). Really, the term 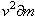 may be neglected at the smaller speeds. The integration gives the proper kinetic energy of the moving particle, as the difference of its two values – in accord with (11a). Mere substitution of respective two masses (15d) gives the final result, relating the kinetic energy of the moving charged particle with that of the electric field between the two radii (
may be neglected at the smaller speeds. The integration gives the proper kinetic energy of the moving particle, as the difference of its two values – in accord with (11a). Mere substitution of respective two masses (15d) gives the final result, relating the kinetic energy of the moving charged particle with that of the electric field between the two radii (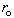 &
& 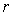 ) – of the resting and moving states. This is more transparent and advanced, further clarified and interpreted, well-known Einstein’s result, initially obtained accidentally, without the final EM explanation (15d).
) – of the resting and moving states. This is more transparent and advanced, further clarified and interpreted, well-known Einstein’s result, initially obtained accidentally, without the final EM explanation (15d).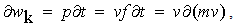
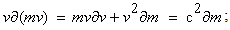
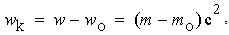
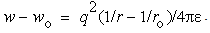
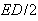 ) integrated between the radii – of the regular and compressed particle, as the difference of respective masses, gives a half of the energy obtained by the integration of the central forces (15). Apart from the field energy between the two particle radii, this value as if comprises the other its half, of unknown nature and location. Thus not manifest in the external 3D space – around the particle – on the observed structural level, it may be ascribed to the particle volume, or to the temporal domain out of 3D, or to finer structural levels of the medium. In each of the three cases, the two equal parts of energy point to the balance of respective forces, in 3D, 4D or 5D spaces. In the final instance, this is not a single such question which answer must be postponed into the future.Some well known and widely accepted relations are still not sufficiently interpreted. Let us compare Maxwell’s (10b), with Einstein’s (11a) relations. The former determines the speed of EM wave propagation by the two constants, as the abstract medium features. On the other hand, in the sense of the ratio of the energy and mass densities – inside the usual mechanical media, the latter relation determines the speed of propagation of respective its disturbances. In this sense, the elimination of the value
) integrated between the radii – of the regular and compressed particle, as the difference of respective masses, gives a half of the energy obtained by the integration of the central forces (15). Apart from the field energy between the two particle radii, this value as if comprises the other its half, of unknown nature and location. Thus not manifest in the external 3D space – around the particle – on the observed structural level, it may be ascribed to the particle volume, or to the temporal domain out of 3D, or to finer structural levels of the medium. In each of the three cases, the two equal parts of energy point to the balance of respective forces, in 3D, 4D or 5D spaces. In the final instance, this is not a single such question which answer must be postponed into the future.Some well known and widely accepted relations are still not sufficiently interpreted. Let us compare Maxwell’s (10b), with Einstein’s (11a) relations. The former determines the speed of EM wave propagation by the two constants, as the abstract medium features. On the other hand, in the sense of the ratio of the energy and mass densities – inside the usual mechanical media, the latter relation determines the speed of propagation of respective its disturbances. In this sense, the elimination of the value 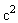 from the two equations directly relates the ratio of the energy and mass densities – in the medium, with the product
from the two equations directly relates the ratio of the energy and mass densities – in the medium, with the product 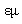 . The energy of the structural strains, as modulus of elasticity, is inversely proportional to electric constant. This comparison points to the analogous, electro-fluidic interpretation of EM phenomena, respective quantities and their mutual relations.In accord to (14b,15c), Fig. 1. presents the kinetic energy of a moving particle. At small speeds, it nearly equals to the classical kinetic energy (
. The energy of the structural strains, as modulus of elasticity, is inversely proportional to electric constant. This comparison points to the analogous, electro-fluidic interpretation of EM phenomena, respective quantities and their mutual relations.In accord to (14b,15c), Fig. 1. presents the kinetic energy of a moving particle. At small speeds, it nearly equals to the classical kinetic energy (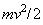 ), but considerably separates – at the greater speeds, tending into infinity – approaching the speed
), but considerably separates – at the greater speeds, tending into infinity – approaching the speed  . In accord with Einstein’s relation (11a), the energy and mass of a resting or moving particle, as well as their differentials, are mutually proportional. Not only that the classical kinetic energy does not obey the greater speeds, but its interpretation was also inadequate. Instead of direct function of speed – at the constant mass, the kinetic energy accords to the mass difference. Though already renounced, the classical opinion is still implicitly understood in some physical disciplines, as the kinetic gas theory is. Such the inconsistencies are very frequent between various, or even inside particular physical disciplines.
. In accord with Einstein’s relation (11a), the energy and mass of a resting or moving particle, as well as their differentials, are mutually proportional. Not only that the classical kinetic energy does not obey the greater speeds, but its interpretation was also inadequate. Instead of direct function of speed – at the constant mass, the kinetic energy accords to the mass difference. Though already renounced, the classical opinion is still implicitly understood in some physical disciplines, as the kinetic gas theory is. Such the inconsistencies are very frequent between various, or even inside particular physical disciplines. 
 ) demands the infinite energy, and so cannot be attained. The functions of the radius and mass (14) physically explain this limitation, by zero particle volume. The mystification of this limitation – from SRT, founded on mere formal consideration of the square root – in (13b), is thus interpreted rationally. On the other hand, the standard speed of EM wave propagation (
) demands the infinite energy, and so cannot be attained. The functions of the radius and mass (14) physically explain this limitation, by zero particle volume. The mystification of this limitation – from SRT, founded on mere formal consideration of the square root – in (13b), is thus interpreted rationally. On the other hand, the standard speed of EM wave propagation ( ) is determined by two respective constants, as the medium features, also without any mystics. This speed is diminished in the denser media, up to zero – in the critical gravitational field. Moreover, at some special media (mentioned in the next section), it may even exceed the upper limit. In the final instance, with respect to the slower waves (e. g. of sound) – at the cruder media, at possible finer media respective waves and particles may be much faster than
) is determined by two respective constants, as the medium features, also without any mystics. This speed is diminished in the denser media, up to zero – in the critical gravitational field. Moreover, at some special media (mentioned in the next section), it may even exceed the upper limit. In the final instance, with respect to the slower waves (e. g. of sound) – at the cruder media, at possible finer media respective waves and particles may be much faster than  .Explicitly or implicitly, in classical and modern physics, mass denotes matter amount. On the other hand, with respect to its above EM interpretation, the notion of matter is mainly overcome. In the strictly scientific sense, mass can only represent the measures of inertia or gravitation, proportional to respective forces. Though EM waves and photons contain their energies, they seem to be mass-less. Due to the standard speed and inability of a force action, the longitudinal inertia cannot be manifest directly. However, the propagation of light along gravitational field changes the photon energy, equivalently to the acceleration of respective mass. The strait path is curved in inhomogeneous media or fields, reminding centripetal forces. The currents of energy and mass, related in the form of (11a), represent the linear momentum density (16), noticed as the pressure of EM waves.
.Explicitly or implicitly, in classical and modern physics, mass denotes matter amount. On the other hand, with respect to its above EM interpretation, the notion of matter is mainly overcome. In the strictly scientific sense, mass can only represent the measures of inertia or gravitation, proportional to respective forces. Though EM waves and photons contain their energies, they seem to be mass-less. Due to the standard speed and inability of a force action, the longitudinal inertia cannot be manifest directly. However, the propagation of light along gravitational field changes the photon energy, equivalently to the acceleration of respective mass. The strait path is curved in inhomogeneous media or fields, reminding centripetal forces. The currents of energy and mass, related in the form of (11a), represent the linear momentum density (16), noticed as the pressure of EM waves.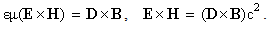
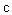 – of the waves, photons do not spread and weak in space. Their apparent dual nature is finally taken for granted by the term wave packet, formally supported by an abstract wave equation, which may mean everything or nothing. The relation of photon energy and frequency,
– of the waves, photons do not spread and weak in space. Their apparent dual nature is finally taken for granted by the term wave packet, formally supported by an abstract wave equation, which may mean everything or nothing. The relation of photon energy and frequency, 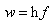 – noticed empirically, as if announces the quantization. However, the frequency (
– noticed empirically, as if announces the quantization. However, the frequency (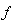 ) is not a discrete, but continual quantity, and so, neither the photon energy is quantized.The synthesis of the two natures of light is here obtained on EM bases. Namely, a convection current (
) is not a discrete, but continual quantity, and so, neither the photon energy is quantized.The synthesis of the two natures of light is here obtained on EM bases. Namely, a convection current (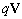 ) and its kinetic potential – as motion of the static potential (8), are mutually collinear. However, this current itself is continued in the surrounding space by the displacement current (17a). In the case of the central field (17b), this current is obtained in the form of a toroidal vortex (Fig. 2). With respect to the particle radius – dependent on speed, this vortex is manifest in the resting medium as the photon associated to the moving particle, of the frequency and energy proportional to the linear momentum. At the stoppage or deceleration of the particle, its kinetic energy (15d) would be released – fully or partially. Thus independent on the carrier, it continues its free motion at the speed
) and its kinetic potential – as motion of the static potential (8), are mutually collinear. However, this current itself is continued in the surrounding space by the displacement current (17a). In the case of the central field (17b), this current is obtained in the form of a toroidal vortex (Fig. 2). With respect to the particle radius – dependent on speed, this vortex is manifest in the resting medium as the photon associated to the moving particle, of the frequency and energy proportional to the linear momentum. At the stoppage or deceleration of the particle, its kinetic energy (15d) would be released – fully or partially. Thus independent on the carrier, it continues its free motion at the speed 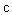 . In such a form, it manifests the mentioned features of a particle and wave.
. In such a form, it manifests the mentioned features of a particle and wave.

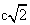 – in a
– in a 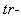 plane, is physically irrelevant. The expansion extends the photons themselves, equivalently to respective Doppler’s effect. This effect is manifest as the linear decrease of photon frequency and energy, with respective red shift, pointing to the cosmic expansion. The denser media or fields slow down the propagation. This is explained by temporary retaining of a fraction of wave energy by cruder structures [5]. At a given energy current, this effect increases the local energy density, and decreases the effective speed of propagation, in the ratio of the refraction factor (18a). Owing to sparser non-engaged medium, the remaining energy propagates at the wave speed (18b). The two obsolete terms – group and phase speeds – understood the wave packet concept.
plane, is physically irrelevant. The expansion extends the photons themselves, equivalently to respective Doppler’s effect. This effect is manifest as the linear decrease of photon frequency and energy, with respective red shift, pointing to the cosmic expansion. The denser media or fields slow down the propagation. This is explained by temporary retaining of a fraction of wave energy by cruder structures [5]. At a given energy current, this effect increases the local energy density, and decreases the effective speed of propagation, in the ratio of the refraction factor (18a). Owing to sparser non-engaged medium, the remaining energy propagates at the wave speed (18b). The two obsolete terms – group and phase speeds – understood the wave packet concept.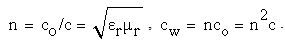
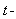 axis represent the necessary conditions for its existence. All the particles moving in common in the same direction form a hipper-spherical wave, as the expanding cosmos. This idea explains why and how 3D cosmos is globally curved and closed into itself. The continual lapse of time, the same for all celestial objects, may be determined by this wave, as well as gravitation, as the attraction in the parallel motion. Circular flow in a particle, superimposed to cosmic process, disturbs the local pressure, as the static potential. The positive flow thus causes the negative potential, and vice versa. This fact explains the two opposite polarities, and the opposite signs in the static and kinetic central laws (10a) & (12a). The two polarities obviously obey, somehow already predicted, CPT (circulation-polarity-time) symmetry.With respect to the four axes and six planes, cross product and curl-operation are not defined in 4D space. Possible application of the field theory in this space is partial, limited to its subspaces. Let us try to treat the above hipper-vortex mathematically. If its flows were understood as the closed contours of the kinetic potential in
axis represent the necessary conditions for its existence. All the particles moving in common in the same direction form a hipper-spherical wave, as the expanding cosmos. This idea explains why and how 3D cosmos is globally curved and closed into itself. The continual lapse of time, the same for all celestial objects, may be determined by this wave, as well as gravitation, as the attraction in the parallel motion. Circular flow in a particle, superimposed to cosmic process, disturbs the local pressure, as the static potential. The positive flow thus causes the negative potential, and vice versa. This fact explains the two opposite polarities, and the opposite signs in the static and kinetic central laws (10a) & (12a). The two polarities obviously obey, somehow already predicted, CPT (circulation-polarity-time) symmetry.With respect to the four axes and six planes, cross product and curl-operation are not defined in 4D space. Possible application of the field theory in this space is partial, limited to its subspaces. Let us try to treat the above hipper-vortex mathematically. If its flows were understood as the closed contours of the kinetic potential in 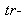 planes, its curl would represent something as the magnetic field, perpendicular to these planes. Apart from one spatial, each of its contours is thus coaxial with temporal axis. The common axial motion along this axis produces the central static field, according to (1b). The procedure (19) identifies the static and dynamic fields (20), under the condition:
planes, its curl would represent something as the magnetic field, perpendicular to these planes. Apart from one spatial, each of its contours is thus coaxial with temporal axis. The common axial motion along this axis produces the central static field, according to (1b). The procedure (19) identifies the static and dynamic fields (20), under the condition: 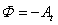 . This equality confirms the positive potential produced by negative flow, and vice versa. Though not fully strict and precise, this is the obvious mathematical correlation.
. This equality confirms the positive potential produced by negative flow, and vice versa. Though not fully strict and precise, this is the obvious mathematical correlation.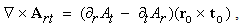
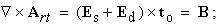
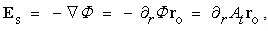
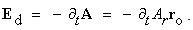
 proportional to square of the elementary charge (11b). The energy of a photon is also inversely proportional to its radius, but – in the continual values. The charge enables a force action upon inert particle, accelerating it through 3D space – up to the speed
proportional to square of the elementary charge (11b). The energy of a photon is also inversely proportional to its radius, but – in the continual values. The charge enables a force action upon inert particle, accelerating it through 3D space – up to the speed  , limited by the zero volume. Formed in 3D – without electric charge, a photon is axially symmetric, free moving at the speed
, limited by the zero volume. Formed in 3D – without electric charge, a photon is axially symmetric, free moving at the speed  , and insensitive to the force action.
, and insensitive to the force action.
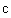 . This is further supported by convincing particle model. The parallel propagation of all cosmic particles or celestial bodies may be the real reason of their gravitational attraction. Apart from the particles, the surrounding fields are also included into the cosmic wave, as the invisible matter. The kinetic EM forces, caused by the spatial motion, are thus exclusive with respect to gravitation, caused by the temporal cosmic process.
. This is further supported by convincing particle model. The parallel propagation of all cosmic particles or celestial bodies may be the real reason of their gravitational attraction. Apart from the particles, the surrounding fields are also included into the cosmic wave, as the invisible matter. The kinetic EM forces, caused by the spatial motion, are thus exclusive with respect to gravitation, caused by the temporal cosmic process.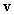 through resting EM fields causes the relative inductions. Their crosswise addition to similar fields gives the classical field transformations (22). This direct set, being inverted per the primed fields – by determinant theory, gives the inverse set (23). The set determinant,
through resting EM fields causes the relative inductions. Their crosswise addition to similar fields gives the classical field transformations (22). This direct set, being inverted per the primed fields – by determinant theory, gives the inverse set (23). The set determinant, 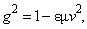 accidentally equal to the square of the factor
accidentally equal to the square of the factor 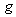 (14), just discriminates the two frames, speaking in favour of the preferred status of one of them. For the sake of the frame equivalence, SRT distributed this factor, – by
(14), just discriminates the two frames, speaking in favour of the preferred status of one of them. For the sake of the frame equivalence, SRT distributed this factor, – by 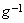 in each of the two sets. This arbitrary scaling of the transverse field components calls in question Maxwell’s equations, as the general distributions. To preserve their mathematical form, the two remaining 4D axes, longitudinal and temporal ones, are complementarily (in fact inversely) transformed (24).
in each of the two sets. This arbitrary scaling of the transverse field components calls in question Maxwell’s equations, as the general distributions. To preserve their mathematical form, the two remaining 4D axes, longitudinal and temporal ones, are complementarily (in fact inversely) transformed (24).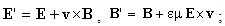
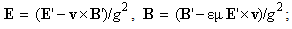
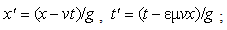
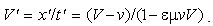
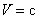 , this gives the identity:
, this gives the identity: 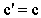 . It is interpreted as the invariant light propagation, in all (at least inertial) frames. Not only that this result is itself the obvious logical contradiction, but calls in question the medium of EM processes, and the wave nature of EM radiation. Following from the unfounded starting view, and carried out by the incorrect revision of the two sets (22 & 23), the full above procedure has none a support in reality. Michelson-Morley’s experiment concerns Earth, as the predominant mass – or locally preferred frame, and cannot be generalized to any other frame. Finally, there are the known wave effects, just determined by the variant speed of light.
. It is interpreted as the invariant light propagation, in all (at least inertial) frames. Not only that this result is itself the obvious logical contradiction, but calls in question the medium of EM processes, and the wave nature of EM radiation. Following from the unfounded starting view, and carried out by the incorrect revision of the two sets (22 & 23), the full above procedure has none a support in reality. Michelson-Morley’s experiment concerns Earth, as the predominant mass – or locally preferred frame, and cannot be generalized to any other frame. Finally, there are the known wave effects, just determined by the variant speed of light.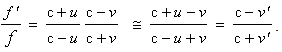
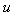 is the radar speed, and
is the radar speed, and 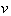 that of its object t;
that of its object t; 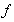 is the emitted, and
is the emitted, and 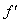 received signal frequency. The speeds of the two opposite beams, relative to the technical elements, cause a sequence of four Doppler’s effects. The particular of these effects can be confirmed by the additional receivers, on the light path and/or on object. The product
received signal frequency. The speeds of the two opposite beams, relative to the technical elements, cause a sequence of four Doppler’s effects. The particular of these effects can be confirmed by the additional receivers, on the light path and/or on object. The product 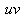 is neglected – in the continuation, with
is neglected – in the continuation, with 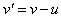 , as the mutual speed. In the aim of his originality, Einstein turned the last expression under a square root. Two of these effects arise at the mutual rotation of the dual star members, at their opposite speeds in the local medium of propagation. The distinct process causes the general red shift, ascribed to the cosmic expansion. Though the light source and receiver rest in respective local media, equivalent effect follows from permanent extension of the medium, along the light path.In the case of a common motion of the radar and object (
, as the mutual speed. In the aim of his originality, Einstein turned the last expression under a square root. Two of these effects arise at the mutual rotation of the dual star members, at their opposite speeds in the local medium of propagation. The distinct process causes the general red shift, ascribed to the cosmic expansion. Though the light source and receiver rest in respective local media, equivalent effect follows from permanent extension of the medium, along the light path.In the case of a common motion of the radar and object (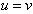 ), the particular effects mutually cancel, with equality of the two frequencies. Instead of this invariant quantity, the phase difference of the two signals is caused by the different paths through the medium, or the different speeds relative to the moving instrument. In this sense, Sagnac’s effect directly refutes the invariant light propagation, from SRT. This direct disprove of its main result is much more convincing than all the ‘experimental profs’ of SRT – in common. The absence of the similar result – in the case of Michelson-Morley’s experiment, is caused by the connection of the instrument to Earth, as the carrier of predominant gravitation and reference of light propagation. Some very minor delay of this medium behind Earth’s motion, registered more accurately during 20th century, may be ascribed to the influence of the remaining, nearby & distant, celestial bodies.
), the particular effects mutually cancel, with equality of the two frequencies. Instead of this invariant quantity, the phase difference of the two signals is caused by the different paths through the medium, or the different speeds relative to the moving instrument. In this sense, Sagnac’s effect directly refutes the invariant light propagation, from SRT. This direct disprove of its main result is much more convincing than all the ‘experimental profs’ of SRT – in common. The absence of the similar result – in the case of Michelson-Morley’s experiment, is caused by the connection of the instrument to Earth, as the carrier of predominant gravitation and reference of light propagation. Some very minor delay of this medium behind Earth’s motion, registered more accurately during 20th century, may be ascribed to the influence of the remaining, nearby & distant, celestial bodies.  Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML