Ahmed M. M. Elsheekh
PhD in Physics 2012, Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Egypt
Correspondence to: Ahmed M. M. Elsheekh, PhD in Physics 2012, Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
This article introduces a new vision by using simple mathematical process, this process created new theoretical quantized energy levels which leads to new theory. There are new ninety energy levels among the old seven energy levels in Hydrogen atom have been concluded. This new vision not only concluded and verified all previous energy levels , but also, is used to conclude and verify all known experimental ionization energy of elements in the periodic table. We introduce more acceptance explaining the completely dark lines appear in absorption line spectrum. These new energy levels can be used to explaining different physical and chemical phenomena. At last, the theoretical atomic physics will be in the front of experimental physics.
Keywords:
Key wordsBohr Theory, Atomic Physics, Spectroscopy
Cite this paper: Ahmed M. M. Elsheekh, New Theory and New Energy Levels in the Atom, International Journal of Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Vol. 3 No. 4, 2013, pp. 117-122. doi: 10.5923/j.ijtmp.20130304.04.
1. Introduction
Niels Bohr was the first leadership of atomic physics[1], he concluded the energy levels of the Hydrogen atom's electron and gave us the first module of atomic structure[2,3]. Bohr theory couldn't explain the emission spectra of any element except Hydrogen only. So that, quantum mechanics scientists and specialists used Schrödinger equation and generated three quantum numbers addition to the principle quantum number to create new energy levels, these energy levels have been used to explain the emission and absorption spectrum of elements[4]. But all explanations about absorption line spectra up till now tells us that, the completely dark lines[3] because of , the electron absorbs photon with energy equals the difference between tow energy levels. This is not convincing explanation because, if that is the true, then we must observe gray line(s) not completely dark line(s), because, the electron will lose its energy and back to its origin energy level by emitting photon, these emitted photons from several atoms will dispersed in all directions, it isn't acceptable we imagine the emitted photons will be in all directions except the direction of our detecting screen. There is other phenomenon, why the kinetic energy -related to the temperature- of material increases by passing electromagnetic wave through it ?. Kinetic energy increasing means that, the atom absorbs energy without re-emitting, it's not acceptable to say that, the nucleus –its mass 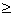 1836 electron's mass- will affected by photons more than the electron. We need new energy levels to answer these questions. Our new vision depends on Bohr's assumption, so that, there is shortly mentioned on his work and his derivation of energy levels of Hydrogen atom.
1836 electron's mass- will affected by photons more than the electron. We need new energy levels to answer these questions. Our new vision depends on Bohr's assumption, so that, there is shortly mentioned on his work and his derivation of energy levels of Hydrogen atom.
2. Overview
First, classical common universal equation of electron's total energy "kinetic energy and electric potential"[2,3], is given by,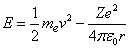 | (1) |
Where, (Z=1) is the atomic number of Hydrogen atom , (v) is the velocity of electron around the nucleus and (r) is the radius of the electron's orbit.Second, centrifugal force equals attractive Coulomb force[2,3], this equation is given by,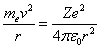 | (2) |
At last, Bohr assumption is given by[2,3],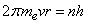 | (3) |
where (n) is a integer number. (n) is called principle quantum number By using equations(1,2 and 3), Bohr concluded the radius and energy of Hydrogen atom ,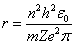 | (4) |
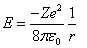 | (5) |
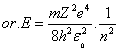 | (6) |
where (m) is the reduced mass[2,3].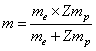 | (7) |
3. New Energy Levels
These new energy levels have been concluded by using Bohr assumption with equation (1) to get the equation of electron's total energy in this form.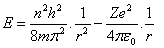 | (8) |
According to Newton's first law, the electron will stay in its stationary state unless it's affected by external force, in other words, the electron will change its radius if its energy changed. Mathematically it means the differential of energy (E) to the radius (r) in equation (8) must equal zero,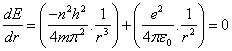 | (9) |
The result of differential process in equation(9) will be the radius of electron, it's as same as Bohr radius in equation(4), consequently, this differential process gives the energy of electron by substitution in equation(5) the result will be as same as equation(6).Can we use the mathematical differential process again? Can we get the radiuses and energy levels from the second, third, fourth …. and (n-order) -"n isn't the same term in radius and energy equations, which is called principle quantum number in quantum physics"- differential equations?.Let us do it and test the results. The second available radius is concluded from the second differential for equation (8) will be,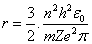 | (10) |
The third radius is concluded from the third differential ,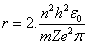 | (11) |
every new radius gives us new energy level. The general equation of available radiuses can be concluded and is given by,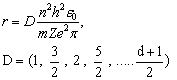 | (12) |
where (D) is the numbers those generated due to differential process, it's called differential generated numbers with symbol (D) because of its generation by Differential process. By substituting from the last equation into equation (5) we got : - The Modified form of Energy Equation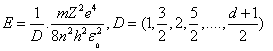 | (13) |
It's clear that, the energy and radius depend on two terms (D) and (n), (D) increases slower than (n), where, D is not square term but, (n) is squared, this leads to more energy levels and more flexibility dealing with electron.
4. New Energy Levels for Hydrogen Atom
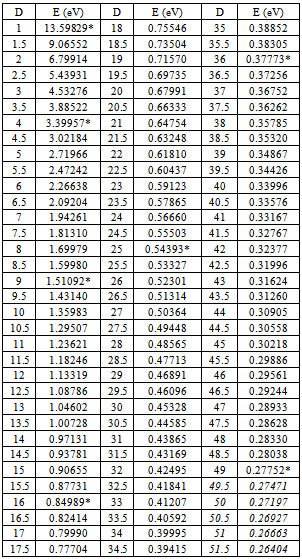
Table (1). Energy levels of Hydrogen atom those concluded by differential mathematical process
 |
| |
|
First, let us substituting (Z=1), (n=1 "which is called principle quantum number in quantum mechanics") and (D = all available numbers) in equation(13), the other terms are given previously. The results have been tabulated in table(1). All bold data those marked with (*) in agreement and coincident with Bohr results[2,3]. Italic data are addition data, where D=49 as same as n=7 in quantum mechanics.It is clear from table(1) that, this process generated Bohr's energy levels, in other words the old module of atom where (D = 1, 4, 9, 16, 25 ,36 and 49), equivalent to (n=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7) respectively.The new energy levels are these energy levels with values (D 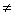 1, 4, 9, 16, 25 ,36 and 49) came directly from the differential process, the electron transition between two energy levels will be discussed later. It is clearly that, using series differential process gives us all old energy levels addition to new energy levels among the old energy levels in Hydrogen atom. At last, we need more evidence to trust in this differential process. So, we'll conclude the ionization energy of other elements.
1, 4, 9, 16, 25 ,36 and 49) came directly from the differential process, the electron transition between two energy levels will be discussed later. It is clearly that, using series differential process gives us all old energy levels addition to new energy levels among the old energy levels in Hydrogen atom. At last, we need more evidence to trust in this differential process. So, we'll conclude the ionization energy of other elements.
5. Ionization Energy of Elements
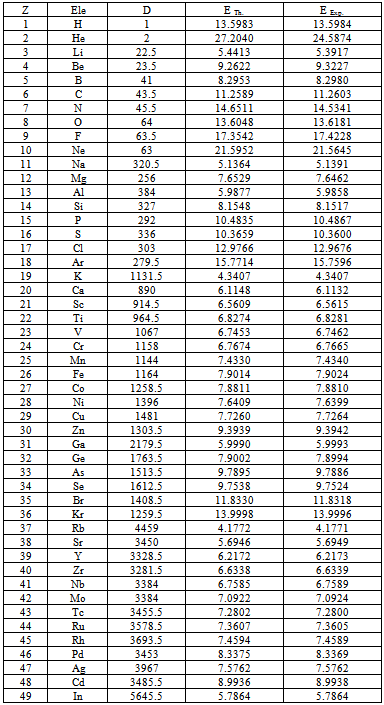
Table (2). Experimental ionization energy (EExp.) of elements from "NIST" comparing with theoretical ionization energy (ETh.) at differential order (D)
 |
| |
|
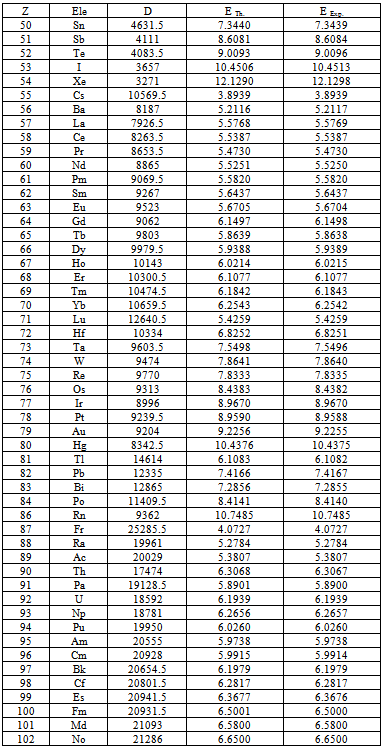
Table (2). Experimental ionization energy (EExp.) of elements from "NIST" comparing with theoretical ionization energy (ETh.) at differential order (D)
 |
| |
|
The first ionization "which means the energy required to extract one electron from the outer orbit outside the atom" energy of elements according to National Institute of Standers and Technology (NIST)[7] is symbolized by (EExp.) in table(2). Theoretical ionization energies is symbolized by (ETh) in table(2), (ETh) has been concluded by using differential mathematical process. We substituted in equation(13) with (n=1), (Z = atomic number of element) and reduced mass (m).It is clear that from table(2) (ETh) in agreement with (EExp.) for all elements except Helium. These data incentive us to trust the differential process seriously because, it gives us all data we need and more.
6. Results and Discussion
It's clear that, this simple sequence differential equation process not only concluded, approved and verified all experimental data, but also, concluded new quantized energy levels. Now, we need use these data to explain one physical phenomenon at least. The first step of our discussion is the module of Hydrogen atom. The electron can occupy one of these energy levels by absorbing or emitting energy. The ground state in the new module as same as the ground state in Bohr module. The squared values of D numbers (1, 4, 9, … etc.) as same as Bohr results (n= 1, 2, 3, etc.) respectively. Now the first explaining emission-absorption line spectra mechanism will different from the old module as the following:-The absorption line spectra can be explained according to the following, The absorbed photon by the electron leads to transferring the electron to higher energy level, for example, let the electron transfers from D = 1 to D = 9 (it was in Bohr module n=1 to n=3). After that, according to the new vision the electron will lose its energy by series emissions processes-not single emission photon- or series collisions process, or both of these two processes. The detail as the following: - First case, series of emission processes means that, the electron maybe transfers to lower energy level D=8 or D=7 …. etc., after that, the electron transfers to lower energy level again D=6 or D= 5 …. etc., and so on till it backs to its ground state. every transition generates photon with wavelength longer than the wavelength of absorbed photon. So, we expect the experimental data will detect more intensity of wavelength(s) in range longer than the range of the absorbed photon. Experimental detection will compare between in incident electromagnetic waves intensity over all its wavelengths before passing through the gas and its intensity after passing through the gas, we predict increasing the intensity in some wave lengths rang after passing of photons through the gas.Second case, the electron maybe loses energy by emitting photon(s) as same as first case but, during its transfer among these new energy levels it maybe stay in suitable energy level -one of these new energy levels only- which leads to the increasing of kinetic energy, this means that, it will not back to its ground state fast, but it will late, its energy will transfer to the nucleus due to changing the position of center of mass. This explains the kinetic energy increasing by electromagnetic waves. Where, the electron can interacts with the photon easier than the nucleus, the energy transfers from the electron to the nucleus, this is more acceptable than the interaction between the photon with nucleus directly. Third case, the electron maybe loses all or quantized part of its energy by collision(s) with an other atom, the electron of the second atom which will acquire the energy and will transfer to higher energy level and start lose its energy according one or more cases, those have been explained before.According to this new mechanism and new vision it is acceptable explanation completely dark line(s) appear(s) in absorption line spectra process. In other words "the path of going up is not the same path to back. The emission line spectra phenomenon can be explained according to new vision as the following:-When the gas is excited by external energy like electric potential or flame …etc. then, the electron will acquire energy and transfer to high energy level then there are two possibilities,First possibility if the electron transferred to one of these new energy levels only then, there are two cases, first case, it will jump to other higher energy level by acquiring more energy this process happens till the electron arrives to one of the old energy level (squared number of D numbers like D=4 or D= 9 ….etc.) , then, the electron will lose its energy suddenly in the form emitted photon. This leads to emission line spectrum.Second case, the electron loses its energy by collision only and back to its ground state.Second possibility, if the electron transferred to one of these old energy levels only (squared number of D numbers like D=4 or D= 9 ….etc.) then, it will lose its energy suddenly in the form emitted photon. In other words again "the path of going up is not the same path to back.The energy levels can be divided into two categories. First category the critical energy levels that allow electron lose its energy in forms different from -external applied energy- the acquiring energy. If the applied energy was electromagnetic waves then the electron loses its energy through these energy levels by other energy forms, so we observe completely dark lines in absorption line spectrum. If the applied energy was for example electric energy then the electron loses its energy through these energy levels by other energy forms, one of these forms is electromagnetic energy so we observe bright lines in emission line spectrum.New vision to quantization of kinetic energyThe variation of electron radius leads to the variation the center of mass between the nucleus and the electron. There are many new energy levels allow the electron to stay so long time this leads to more shift to the nucleus position –means vibration- we know this shift is so extremely very small, but the repeating this process millions times leads to noticeable vibration which leads to the temperature increasing. This is new vision for quantized kinetic energy of the atom.The most important thing in this paper is that " the differential process approved generated new energy levels and concluded all previous energy ".Elsheekh Vision.Emission and absorption phenomena are non-reversible processes to each other.Elsheekh Theory.Mathematical differential process for electron's energy equation generates new energy levels addition to the old energy levels are suggested to be occupied by the atom's electron(s).At last, the theoretical atomic physics now in the front of the experimental atomic physics, this is due to the so many numbers of energy levels which we can use them to explain currently and the next lab. observations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
To my friend and my professor Prof. Dr. Mohsen Barakat. Professor of physics, I hope him to be cured as soon as possible.Physical constants have be used[5,6].Dielectric constant 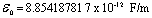 Electron rest mass
Electron rest mass 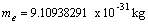 Proton rest mass
Proton rest mass 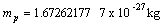 Elementary charge
Elementary charge 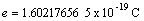 Planck's constant
Planck's constant 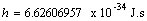 Constant (Pi)
Constant (Pi) 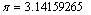
References
| [1] | N. Bohr, Philos. Mag. 26, 1 (1913). |
| [2] | Alan Giambattista, Betty Richardson andRobert C. Richardson., Cornell University -Ithaca. College Physics., 4th Ed., ISBN-13 9780073512143. (2013).http://dev5.mhhe.com/tbern/public_html/0073404470/pdf/ch27_07.pdf |
| [3] | Arthur Beiser., Concepts of Modern Physics, 2nd Ed., ISBN 0-07004363-4. (1973). |
| [4] | Nigel G. Adams et al., Gordon W. F. Drake (Ed.) Springer Handbooks of Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics., ISBN-13: 978-0-387-20802-2. (2006). |
| [5] | Peter J. Mohr, Barry N. Taylor, and David B. Newell., National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20899-8420, USA. (2012).http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Constants/Preprints/lsa2010.pdf. |
| [6] | National Institute of Standers and Technology. (NIST). http://physics.nist.gov/constants |
| [7] | National Institute of Standers and Technology. (NIST), Atomic Properties of the Elements., (2010).http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/upload/periodic_table_composite_2010.pdf |

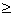 1836 electron's mass- will affected by photons more than the electron. We need new energy levels to answer these questions. Our new vision depends on Bohr's assumption, so that, there is shortly mentioned on his work and his derivation of energy levels of Hydrogen atom.
1836 electron's mass- will affected by photons more than the electron. We need new energy levels to answer these questions. Our new vision depends on Bohr's assumption, so that, there is shortly mentioned on his work and his derivation of energy levels of Hydrogen atom.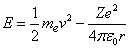
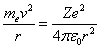
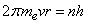
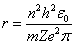
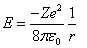
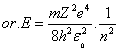
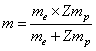
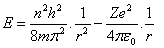
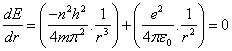
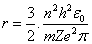
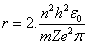
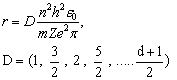
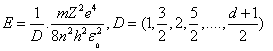
 1, 4, 9, 16, 25 ,36 and 49) came directly from the differential process, the electron transition between two energy levels will be discussed later. It is clearly that, using series differential process gives us all old energy levels addition to new energy levels among the old energy levels in Hydrogen atom. At last, we need more evidence to trust in this differential process. So, we'll conclude the ionization energy of other elements.
1, 4, 9, 16, 25 ,36 and 49) came directly from the differential process, the electron transition between two energy levels will be discussed later. It is clearly that, using series differential process gives us all old energy levels addition to new energy levels among the old energy levels in Hydrogen atom. At last, we need more evidence to trust in this differential process. So, we'll conclude the ionization energy of other elements.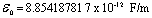 Electron rest mass
Electron rest mass 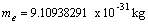 Proton rest mass
Proton rest mass 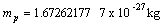 Elementary charge
Elementary charge 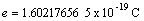 Planck's constant
Planck's constant 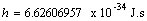 Constant (Pi)
Constant (Pi) 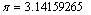
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML

