-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Prevention and Treatment
p-ISSN: 2167-728X e-ISSN: 2167-7298
2017; 6(2): 34-44
doi:10.5923/j.ijpt.20170602.03

Assessment of the Preventive Effects of Salvia officinalis and Ruta graveolens Ethanolic Leaf Extracts on Chlorpyrifos- and Methomyl-induced Renal Toxicity and Oxidative Stress in Albino Rats
Mohamed B. Ashour 1, Osama M. Ahmed 1, Abd El Mawgoud A. Asran 2, Marwa A. Ali 2
1Physiology Division, Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt
2Department of Harmful Animals, Plant Protection Research Institute, Agricultural Research Center, Giza, Egypt
Correspondence to: Osama M. Ahmed , Physiology Division, Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Pesticides used for agricultural and other domestic practices not only produce adverse biological effects against the target species but also have the potential to affect the health of non-target species including human beings. Thus, the present work was designed to investigate the preventive effect of Salvia officinalis and Ruta graveolens ethanolic extracts against chlorpyrifos- and methomyl-induced renal toxicity in rats. The rats orally administered 1/20 LD50 of either chlorpyrifos (13.8 mg/kg b.w.) or methomyl (1.6 mg/kg b. w.) 2 times/week for 4 weeks were co-treated with ethanolic extracts of Salvia officinalis and Ruta graveolens at dose level of 50 mg/ kg b. w. six days/week by oral administration for 4 weeks. The administration of both chlorpyrifos and methomyl to rats induced renal toxicity which was manifested by the histological deleterious alterations and the significant elevation in serum creatinine, urea and uric acid levels. Chlorpyrifos and methomyl-administered rats also exhibited a significant increase in renal lipid peroxidation and a significant decrease in glutathione content and glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase and superoxide dismutase activities. Concomitant supplementation with S. officinalis or R. graveolens ethanolic extracts markedly prevented chlorpyrifos- and methomyl-induced biochemical and histopathological alterations. In conclusion, S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic extracts supplemented to albino rats could prevent chlorpyrifos- and methomyl-induced renal toxicity via attenuation of oxidative stress and enhancement of the antioxidant defense system.
Keywords: Renal toxicity, Oxidative Stress, Salvia officinalis, Ruta graveolens, Antioxidant effects
Cite this paper: Mohamed B. Ashour , Osama M. Ahmed , Abd El Mawgoud A. Asran , Marwa A. Ali , Assessment of the Preventive Effects of Salvia officinalis and Ruta graveolens Ethanolic Leaf Extracts on Chlorpyrifos- and Methomyl-induced Renal Toxicity and Oxidative Stress in Albino Rats, International Journal of Prevention and Treatment, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2017, pp. 34-44. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpt.20170602.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Insecticides are products of chemical or biological origin that control insects [1]. Insecticides are believed to be the major factors behind the increase in agricultural productivity in the 20th century [2].In USA, more than 18,000 products are licensed for use as pesticides and each year, more than 2 billion pounds of pesticides are applied to crops, gardens etc. [3]. The major economic and environmental losses due to the application of pesticides in public health were 1.1 billion dollars per year in USA [4]. Occupational exposure is known to result in an annual incidence of 18 cases of pesticides related illness for every 100,000 workers in U.S [5]. Moreover, pesticide poisoning is a major public health problem in many developing countries [6, 7], and pesticide poisoning among farmers and occupational workers is a major alarm in these countries [8].World Health Organization (WHO) estimated approximately 20,000 workers die from exposure every year and the majority were in developing countries [9-10]. The number of intoxications with organophosphates is estimated to be 3,000,000 per year and the number of deaths and casualties is determined to be 300,000 per year [11]. Chlorpirifos, an organophosphate insecticide, has been reported to cause developmental and neurobehavioural toxicity [12-14], hepatotoxicity [15, 16], immunotoxicity [17] and nephrotoxicity [18]. It is also believed to cause neuronal damage in the developing brain through other cellular mechanisms such as inhibition of adenyl cyclase and through oxidative stress [19-22].Methomyl is a degradation product of the carbamate thiodicarb [23, 24]. The activity of thiodicarb is closely related to that of methomyl [24]. Methomyl is highly effective for control of over 100 species of insects as an ovicide, as a larvicide, and as an adulticide [25]. It is also used as an acaricide to control ticks and spiders [23].Salvia officinalis (S. officinalis) has been extensively used as a medicinal plant in treating many diseases [26-30]. The leaves of S. officinalis possess some therapeutic effects due to the presence of mainly flavonoids; phenolic compounds such as carnosic, rosmarinic, caffeic, and salvianolic acids; and other phenolic structure-based compounds [26, 31, 32] especially found in alcohol-soluble fraction [33]. Several experimental studies have demonstrated the antioxidant properties of S. officinalis extract and some of its constituents [34, 35]. The major constituents identified in sage are terpenoids; the most commonly found of which are α- and β-thujone, camphor, 1,8-cineole, humulene, borneol acetate, limonene, viridiflorol, caryophyllene manool, muruleno, and ferruginol, each with established biological activity [36]. Ruta graveolens (R. graveolens) contains approximately 2% of rutin which is the main flavonoid of the plant [37]. Epidemiological studies have pointed out their possible role in preventing cardiovascular disease and cancer [38, 39]. This health-promoting activity seems to be related to the antioxidant (free-radical scavenging) activity to flavonoids [40]. Quercetin is one of the most common native flavonoids occurring mainly in glycosidic forms such as rutin [40, 41]. Rutin, one of active constituents in R. graveolens, exhibits multiple pharmacological activities including antibacterial, antitumor, antiinflammatory, antidiarrheal, antiulcer, antimutagenic, myocardial protecting, vasodilator, immunomodulator and hepatoprotective activities [42].Therefore, this study was designed to assess the preventive effects of S. officinalis) and R. graveolens ethanolic extracts against nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by two commonly used insecticides, chlorpyrifos and methomyl, in albino rats.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
- Adult male albino rats, weighing about 120-130 g and aging 9-10 weeks, were used in the present study. The animals were obtained from the National Institute of Ophthalmology, Giza, Egypt. They were kept under observation for two weeks before the experiment to exclude any intercurrent infection. The animals were housed in good aerated cages in the Animal House in Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Egypt at normal temperature (20-25°C) and normal daily lighting cycle (10-12hrs/day), and were given enough balanced standard diet and water ad libitum. All animal procedures are in accordance with the guidelines of Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Egypt. All efforts were done to minimize the number and suffering of animals.
2.2. Chemicals
- Both chlorpyrifos and methomyl were obtained from the Central Laboratories of Agricultural Pesticides, Doki, Egypt. Both S. officinalis and R. graveolens were obtained from Experimental Station of Medical Plants (ESMP), Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University, Egypt. Urea and uric acid were obtained from Spectrum Diagnostics (Egypt). Serum creatinine level was purchased from Diamond Diagnostics (Egypt).
2.3. Dose Preparation of Chlorpyrifos and Methomyl
- Chlorpyrifos was dissolved in 1% carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and was given to animals by oral gavage at dose level of 1/20 LD50 (13.8mg/kg b. w.) 2 times a week for 4 weeks [43]. Methomyl was dissolved in1% CMC and orally given to animals by gastric intubation at dose level of 1/20 LD50 (1.6mg/kg b. w.) 2 times a week for 4 weeks [44].
2.4. Preparation and dose of Ethanolic Extracts of S. officinalis and R. graveolens
- The leaves of S. officinalis and R. graveolens were washed and dried in good aerated shaded area. The dried leaves were powdered by an electric grinder. The powder was soaked in absolute ethyl alcohol for 72 hours. Then, the mixture was filtered. The solvent in the filtrate was evaporated by rotatory evaporator at 50°C and high pressure. The obtained viscous extract was kept in deep freezer until used. The ethanolic extract of both S. officinalis and R. graveolens was given to the rats by oral gavage at dose level of 50 mg/kg b. w. 6 days/week for 4 weeks The dose of S. officinalis was chosen according to Eidi et al. [45] and the dose of R. graveolens was chosen according to Pandey et al. [46].
2.5. Animal Grouping
- The male albino rats included in the present study were allocated into seven groups (6 rats in each group) designed as follows: Group 1 (Normal): Each animal was orally given the equivalent volume of 1% CMC (as vehicle), six days per week by oral gavage based on body weight (5 ml/kg b. w.). Group 2 (Chlorpyrifos-administered group): The rats in this group were administered chlorpyrifos at a dose level of 13.8 mg/kg b. w. 2 times/week and the equivalent volume of 1% CMC 6 times/week by oral gavage both for 4 weeks. Group 3 (Chlorpyrifos-administered group treated with S. officinalis leaf ethanolic extract): The rats in this group were administered ethanolic extract of S. officinalis leaves 6 days/week at dose level of 50 mg/kg b. w./day for 4 weeks along with chlorpyrifos oral administration. Group 4 (Chlorpyrifos-administered group treated with R. graveolens leaf ethanolic extract): The rats in this group were administered ethanolic extract of R. graveolens leaves 6 days/week at dose level of 50 mg/kg b. w./day for 4 weeks along with chlorpyrifos oral administration.Group 5 (Methomyl-administered group): The rats in this group were administered methomyl at a dose level of 1.6 mg/kg b. w. 2 times/week and the equivalent volume of 1% CMC 6 times/week by oral gavage both for 4 weeks. Group 6 (Methomyl-administered group treated with S. officinalis leaf ethanolic extract): The rats in this group were administered ethanolic extract of S. officinalis leaves 6 days/week at dose level of 50 mg/kg b. w./day for 4 weeks along with methomyl oral administration.Group 7 (Methomyl-administered group treated with R. graveolens leaf ethanolic extract): The rats in this group were administered ethanolic extract of R. graveolens leaves 6 days/week at dose level of 50 mg/kg b. w./day for 4 weeks along with methomyl oral administration.
2.6. Blood and Tissue Samples
- At the end of the experimental period, animals were weighed and sacrificed under diethyl ether anesthesia after 12 hours of food and water deprivation. Blood samples from jugular vein were collected. The blood was left to coagulate at room temperature then centrifuged at 3000 r.p.m. for 30 minutes. The clear non-haemolysed supernatant sera were quickly removed for analysis of various biochemical parameters related to kidney functions. The obtained serum was kept at -30°C until used. Animals were dissected and kidneys were rapidly excised. A 0.5 g from kidney of each animal were homogenized in 5 ml 0.9% NaCl (10%w/v) using Teflon homogenizer (Glas-Col, Terre Haute, USA). The obtained homogenates were centrifuged at 3000 r.p.m. for 10 minutes. The homogenate supernatants were fractioned into three sterile tubes and then kept in deep freezer at -30°C to be used later for determination of markers of oxidative stress and antioxidant defense system.
2.7. Biochemical Analysis
- Serum urea, uric acid and creatinine levels were detected according to the methods of Shephard and Mezzachi [47], Fossati et al. [48] and Young [49] respectively. Kidney glutathione content (GSH) and lipid peroxidation (LPO) were determined according to the procedures of Beutler et al. [50] and Preuss et al. [51] respectively. Glutathione content and peroxidase (GPx), glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities were determined according to the methods of Matkovics et al. [52], Mannervik and Gutenberg [53] and Marklund and Marklund [54] respectively.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
- Data are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE). The data were analyzed by one-way (ANOVA) [55] followed by Least Significant Difference (LSD) to compare various groups with each other. Values of P>0.05 were non-significantly different while values of P<0.05 and P<0.01 were significantly and highly significantly different respectively. F-probability of ANOVA expresses the general effect between groups.
3. Results
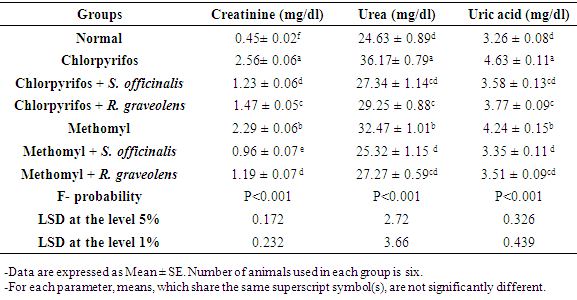
3.1. Effect on Kidney Function Parameters in Serum
- The chlorpyrifos-administered rats exhibited a highly significant increase (p<0.01; LSD) in serum creatinine, urea and uric acid concentrations as compared with normal ones. The treatment of chlorpyrifos-administered rats with S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic extracts induced a highly significant decrease (p<0.01; LSD) in the elevated creatinine, urea and uric acid concentrations (Table 1).At the same time, the methomyl-administered rats exhibited a highly significant increase (p<0.01; LSD) in serum creatinine, urea and uric acid concentrations as compared with normal ones. The treatment of methomyl-administered rats with S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic extracts induced a highly significant decrease (p<0.01; LSD) in the elevated creatinine, urea and uric acid concentrations (Table 1).Chlorpyrifos produced higher toxicity than the methomyl in increasing serum creatinine, urea and uric acid levels. Moreover, S. officinalis ethanolic extract seemed to be more potent than R. graveolens ethanolic extract in improving the impaired kidney function parameters creatinine, urea and uric acid concentrations (Table 1).
|
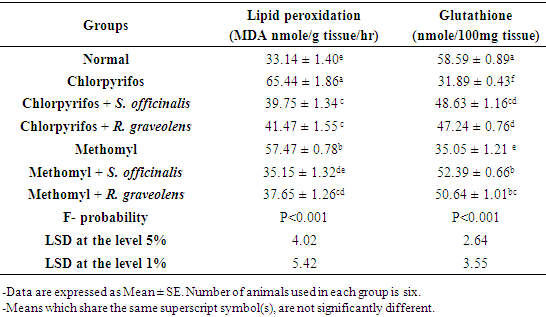
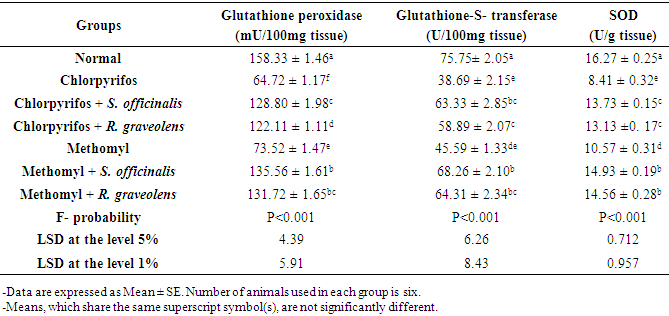
3.2. Effect on Indices of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense System in the Kidney
- Data showing the effect of S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic leaf extracts on kidney oxidative stress and antioxidant defense system markers of chlorpyrifos- and methomyl-administered rats were represented in tables 2 and 3.
|
|
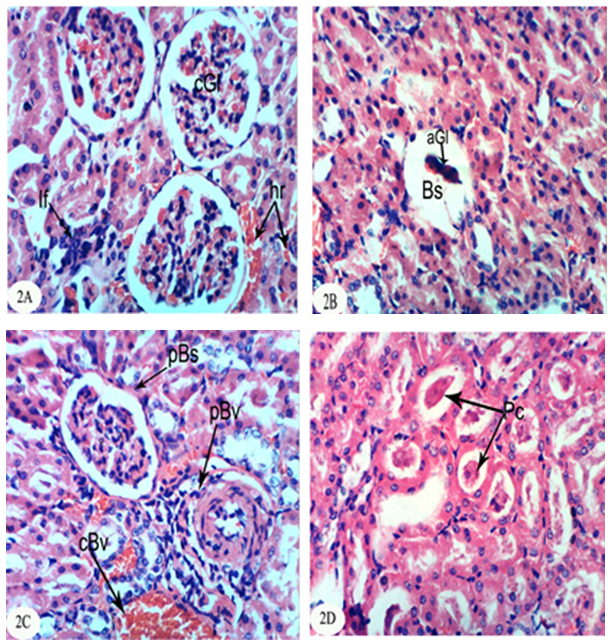
3.3. Histological Changes
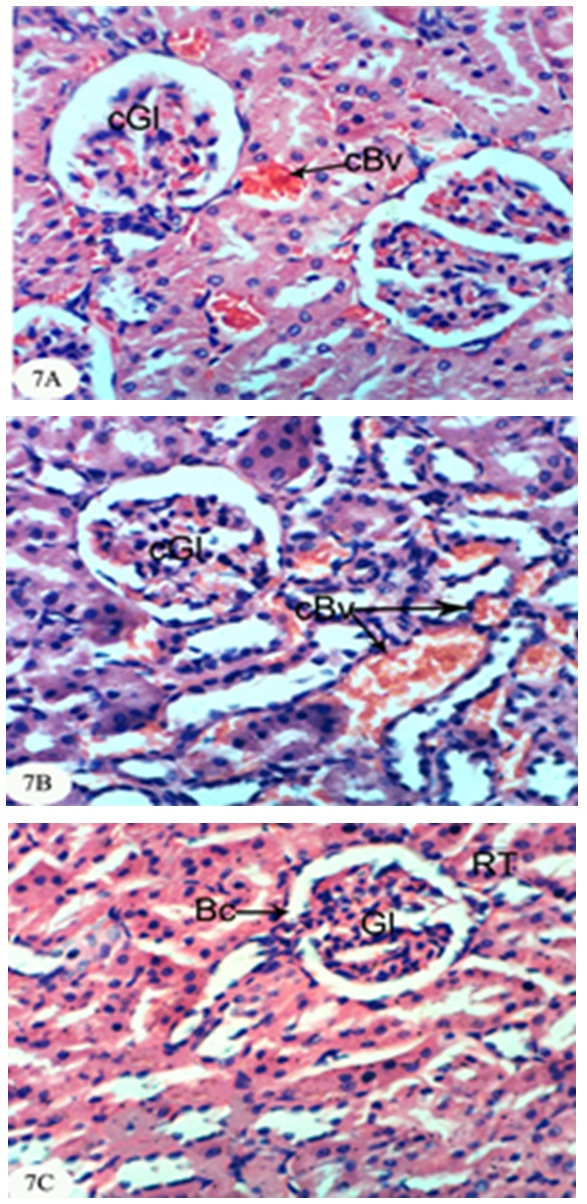
- The kidney section of normal rats exhibited normal histological structure and integrity of the glomeruli, urinary space, proximal tubules and distal tubules (Figure 1).
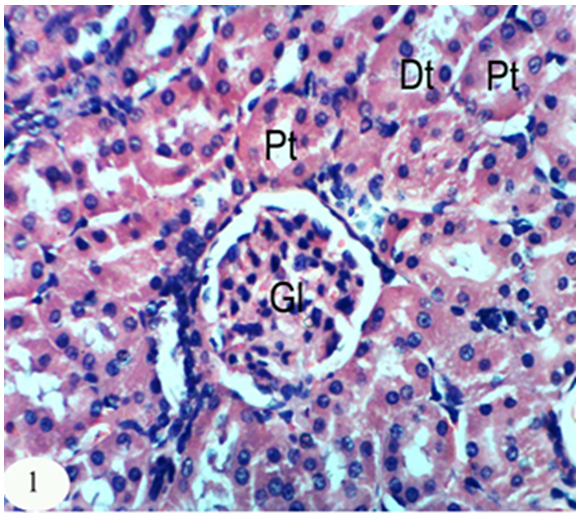 | Figure 1. Photomicrograph of kidney section of normal rat showing the normal histological structure of the glomeruli (Gl), proximal tubules (Pt) and distal tubules (Dt). (X400) |
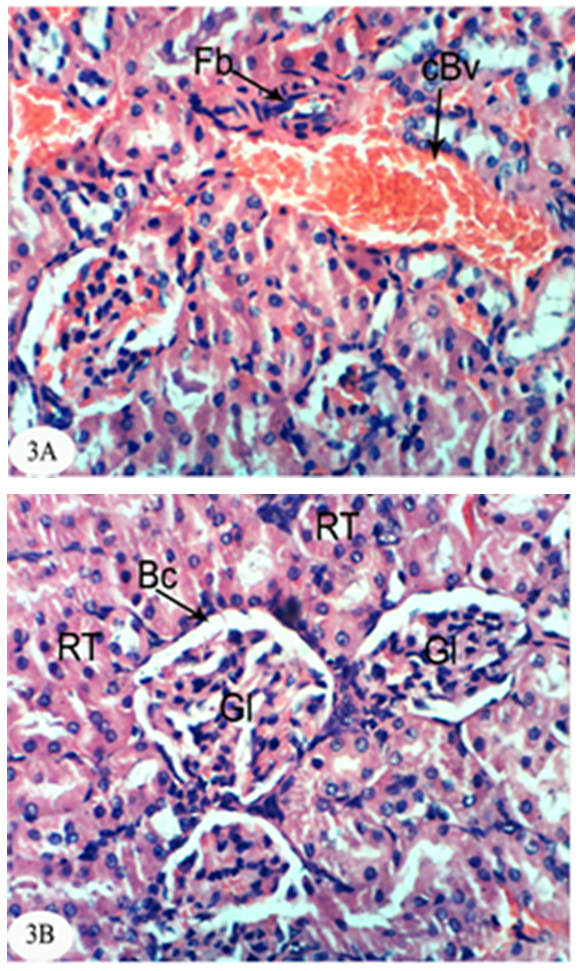
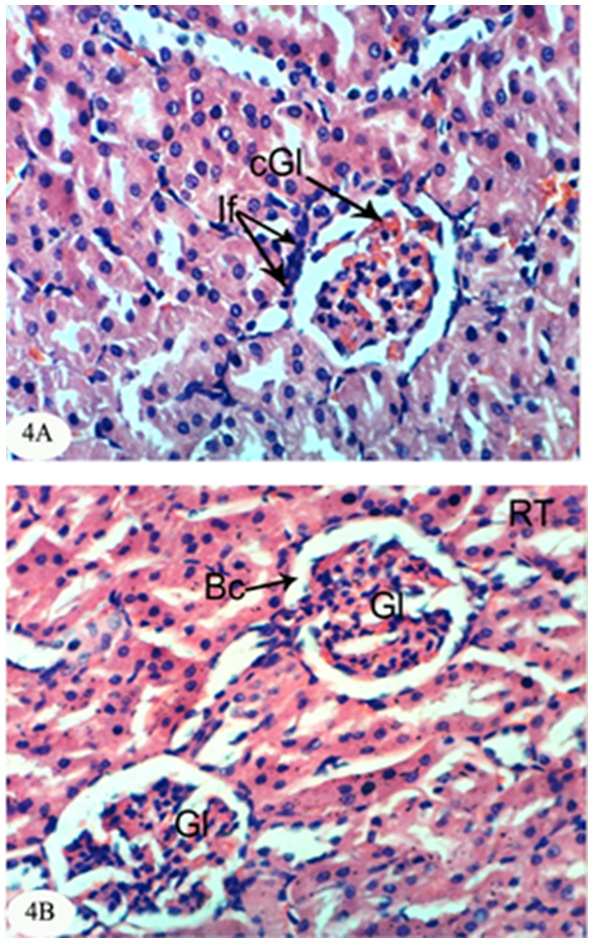
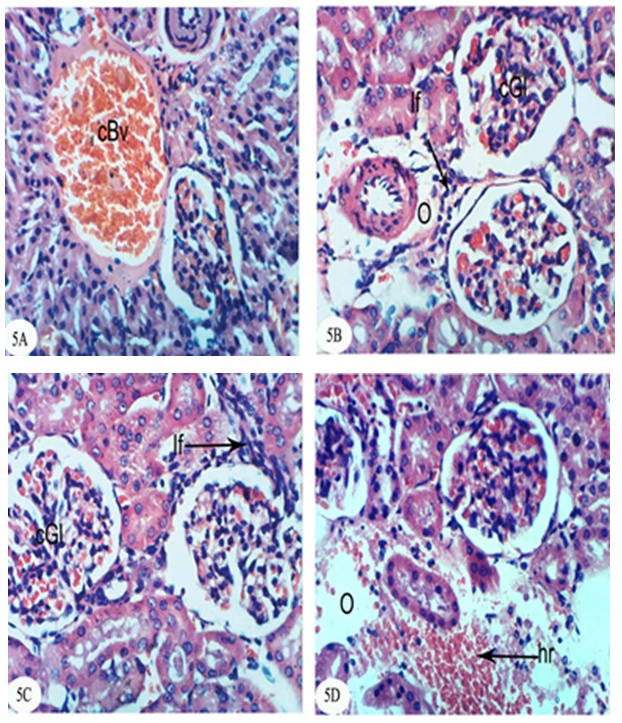
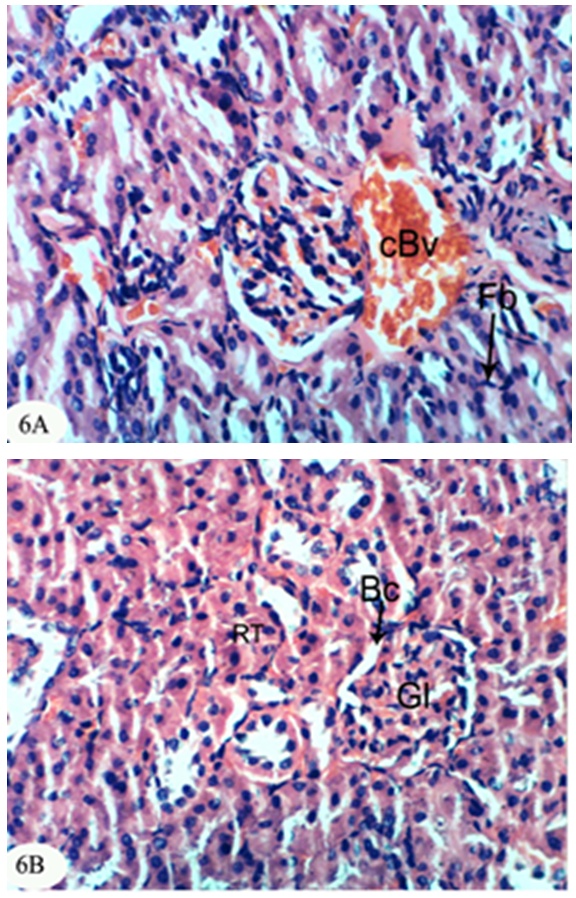
4. Discussion
- In the present study, both chlorpyrifos and methomyl caused a significant increase in serum urea, uric acid and creatinine levels. These results are in accordance with Mossa and Abbassy [56] who demonstrated that methomyl, chlorpyrifos-ethyl and chlorpyrifos-methyl increased the kidney dysfunction parameters in the serum of male rats. Nasr et al. [18] reported that the chlorpyrifos caused a significant increase in serum urea and creatinine levels of male rats. Moreover, Kammon et al. [57] found that the exposure to chlorpyrifos produced nephrotoxic damage in chickens.In the current study, treatment of chlorpyrifos- and methomyl-administered rats with S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic leaf extracts significantly improved the elevated levels of creatinine, urea and uric acid towards the normal levels. These biochemical results are concomitant with the histological results which indicated that S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic leaf extracts have the potentials of improving the histological architecture and integrity of the kidneys of chlorpyrifos- and methomyl-administered rats as sections obtained from this study showed a better histological organization of the kidneys in the extract treated rats.These results are in concurrence with other publication which elucidated that the hydroalcoholic extract of S. Officinalis exhibited nephroprotective effect in gentamicin-induced renal damage probably by its anti-oxidant activity, but further studies on its exact mechanism of action are wanted [58]. On the other hand, Hussein el al. [59] reported that R. graveolens protected against isoniazid/rifampicin-induced renal injury through attenuation of inflammation and oxidative stress, and potentiation of the antioxidant defense system. Moreover, Mahmoud et al. demonstrated the protective effect of R. graveolens leaf extract against diethylnitrosamine-induced kidney damage in rats [60].In the present study, the kidneys of the rats administered chlorpyrifos depicted marked changes such as congestion of glomeruler tufts, inflammatory cells infiltration, renal haemorrhage, atrophy of glomeruler tufts, distension of Bowman's space, perivasculitis and protein cast in the lumen of renal tubules. Concomitant supplementation with S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic leaf extracts markedly prevented chlorpyrifos-induced biochemical and histopathological alterations in the kidney. The chlorpyrifos-administered rats treated with S. officinalis ethanolic extract exhibited congestion of renal blood vessel and mild fibroplasia in some animals and potential improvements of the histopathological impacts to nearly normal histological architecture of glomeruli, Bowman's corpuscle and renal tubules in others. Similarly, the chlorpyrifos-administered group treated with R. graveolens ethanolic extract showed inflammatory cells infiltrations and congested glomeruler tufts in the kidney although there were improvements of the histopathological impacts to nearly normal histological architecture of glomerali, Bowman's corpuscle and renal tubules in various animals.Moreover, the kidney of methomyl-administered rats exhibited congestion of renal blood vessel and glomeruler tufts, inflammatory cells infiltration, perivascular oedema and renal haemorrhage. Concomitant supplementation with S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic extracts markedly prevented methomyl-induced biochemical and histopathological alterations on the kidney. The treatment of methomyl-administered rats with S. officinalis ethanolic extract greatly improved the histopathological impacts to nearly normal structure of Bowman's capsule, glomeruli and renal tubules although some of these treated animals exhibited congestion of renal blood vessels and moderate fibroplasia. The treatment of methomyl-administered rats with R. graveolens ethanolic extract also greatly amended the histopathological impacts to nearly normal structure of the kidney in spite of the presence of congested renal blood vessels and glomeruler tufts in some animals.In the present study, chlorpyrifos and methomyl administrations caused a significant increase in kidney LPO while they induced a significant depletion in GSH content and GPx, GST and SOD activities in the kidney of rats.It is worth mentioning that defense against oxidative stress are maintained by using several mechanisms which include antioxidant machinery [61]. The main cellular components susceptible to damage by free radicals are lipids (peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acids in cell membrane), proteins (denaturation), carbohydrates and nucleic acids; this in turn can impair cellular structure and function [61]. Among the antioxidant enzymes, SOD, GPx and GST are the first line of defense against oxidative injury. SOD is the primary step of the defense mechanism in the antioxidant system against oxidative stress by catalyzing the dismutation of 2 superoxide radicals (O2-) into molecular oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) [62]. GPx is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity whose main biological role is to protect the organism from oxidative damage. The biological function of GPx is to reduce lipid hydroperoxides conversion to their corresponding alcohols and to reduce free H2O2 reaction to water [63]. GPx activity was not altered in testicular tissue of rats exposed to chlorpyrifos [64-66] while other studies observed that GPx activity was increased [16, 67]. Such discrepancies could be related to the differences in the animals, doses and tissues. However, it has been also reported that organophosphate pesticides caused a decrease in GPx activity both in vivo and in vitro [68-69]. In the present study, a significant depletion in GSH level and suppression of GPx activity was observed in chlorpyrifos and methomyl-treated animals. This observation may be due to enhanced free radical production as evidenced by the increase of LPO in the present study and apart from GPx also involved in the H2O2 removal. H2O2 generated due to chlorpyrifos and methomyl toxicity, engage more GSH, which thereby gets converted to oxidized glutathione (GSSG) in presence of GPx. Hence, the kidney GSH content and GPx activity decreases due to chlorpyrifos and methomyl administration.GST is a family of phase II detoxifying enzymes with broad substrate specificities that catalyzes the conjugation of a variety of electrophilic substrates to the thiol group of GSH, producing less toxic forms [70, 71]. A decrease of GST activity in rats administered chlorpyrifos and methomyl was observed. This decrease may be due to the decrease in GSH content and glutathione dependent enzyme systems that provide major protection against the toxic agents. Several studies observed depletion of GSH level in chlorpyrifos intoxicated animals in different tissues [61, 72, 73]. GSH is an important naturally occurring antioxidant, which prevents free radical damaging effects and helps in detoxification process by conjugating with chemicals. In addition, GSH is central to the cellular antioxidant defenses and acts as an essential cofactor for antioxidant enzymes including GPx and GST [74]. Antioxidants such as GSH, GPx, GST and SOD are very important systems which protect the cell against free radicals. It is well known that endogenous non-enzymatic antioxidants and antioxidant enzymes are responsible for preventing and neutralizing the free radical-induced oxidative damage. In the present investigation, a striking decrease in these antioxidants in both chlorpyrifos- and methomyl-administered rats elicits strong evidence for the involvement of oxidative damage in the kidney inducing nephrotoxicity.The treatment with S. officinalis, in the present study, successfully prevented oxidative stress and enhanced the antioxidant defense system by increasing the activities of antioxidant enzymes and by decreasing LPO. This finding goes parallel with the results of various authors who reported that the leaves of S. officinalis L. (sage) are well known for their antioxidative properties [26, 27, 75, 76]. It is worth mentioning that the flavonoid, a group of polyphenolic compounds found mainly in plants of the Rutaceae family, have been shown to exhibit a series of biological effects among which stand out the inhibition of LPO and platelet aggregation, due to their antioxidant properties and their ability of removing free radicals and chelating divalent cations [77, 78]. Quercetin and rutin, a flavone glycoside and its aglycone, are the flavonoids that were most abundantly present in herbs and plant foods. Quercetin has been reported to exert numerous pharmacological activities, such as antioxidant [79], TNF-α inhibition [80], antiulcerogenic [81] and anticarcinogenic effects [82, 83]. Rutin has been reported to scavenge free radicals, to lower hepatic blood cholesterol levels, and showed antiplatelet activity [84, 85]. R. graveolens was known with its free radicals scavenging activity and this activity may be due to its phenolic and flavonoid compounds, which significantly increased the antioxidant status and decreased lipid peroxidation as indicated in the present study.
5. Conclusions
- In conclusion, chlorpyrifos and methomyl administration to rats increases the formation of oxygen free radicals, reduces antioxidants and increases lipid peroxidation and thereby lead to kidney injury and toxicity. S. officinalis and R. graveolens ethanolic extracts have potential chemopreventive effects against chlorpyrifos- and methomyl-induced renal toxicity and oxidative stress. Thus, the ameliorative chemopreventive effects of these extracts may be mediated via improving the antioxidant defense system and suppressing the oxidative stress.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML