-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Prevention and Treatment
p-ISSN: 2167-728X e-ISSN: 2167-7298
2016; 5(2): 17-21
doi:10.5923/j.ijpt.20160502.01

The Green Tea Extract Epigallocatechin Gallate Inhibits Human Platelet Function but not Plasma Coagulation
Sapha Mosawy 1, 2, Almottesembellah Gaiz 1, 2, Abdullah Karaksha 1, 2, Indu Singh 1, 2
1School of Medical Science, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Australia
2Menzies Health Institute Queensland, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Australia
Correspondence to: Sapha Mosawy , School of Medical Science, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The green tea extract epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) has been demonstrated to exert various biological activities including anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and anti-carcinogenic effects, as well as cardiovascular benefits. A limited number of studies have reported antiplatelet effects of EGCG. Furthermore, few studies have investigated its effect on the blood coagulation pathways. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of EGCG on platelet aggregation and activation and plasma coagulation times. EGCG at 50 or 100 µM significantly inhibited turbidimetric ADP stimulated platelet aggregation. Furthermore, the same concentrations significantly inhibited ADP induced platelet surface expression of P-selectin as measured by CD62P fluorescence. Coagulation studies were performed using platelet poor plasma in the presence of EGCG. At the concentrations tested, ECGC did not alter the coagulation times of both prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time. These results demonstrate that EGCG has an antiplatelet action without affecting the plasma coagulation cascade, suggesting that this green tea component could be used as a preventative strategy to lower the risk of thrombotic complications.
Keywords: Aggregation, Coagulation, EGCG, Platelets
Cite this paper: Sapha Mosawy , Almottesembellah Gaiz , Abdullah Karaksha , Indu Singh , The Green Tea Extract Epigallocatechin Gallate Inhibits Human Platelet Function but not Plasma Coagulation, International Journal of Prevention and Treatment, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2016, pp. 17-21. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpt.20160502.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Platelets are small anucleated blood cells which are essential for haemostasis and thrombosis [1]. It is well established that platelet-vessel wall interactions play a central role in the development of vascular thrombosis and the development of cardiovascular disease [2]. Platelets attach to thrombogenic substances exposed on the subendothelial matrix resulting in platelet activation and aggregation leading to thrombus formation at the site of injury [3]. Thrombus formation represents the main thrombotic complication in conditions such as myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis, peripheral vascular disease and stroke [4].Antiplatelet therapy remains the main treatment for patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and patients with cardiovascular disease. Despite the clinical benefits achieved with antiplatelet therapy, some patients still develop thrombotic events. Furthermore, there are many limitations associated with the current antiplatelet agents [5, 6].Green tea is the raw dried young leave of Camellia Sinensis that has undergone minimal oxidation [7]. Green tea is a commonly consumed beverage in many cultures [8]. It has been demonstrated that polyphenolic compounds from green tea exert a number of beneficial biological effects [9]. These effects include anti-oxidant, reduction of blood pressure, anti-thrombotic and anti-inflammatory activities [10-12]. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the major and the most abundant polyphenolic compound found in green tea [13], it has been demonstrated to induce many beneficial effects. Multiple studies have shown attenuation of platelet function in the presence of EGCG [14-16]. The mechanism by which EGCG inhibits platelets is still poorly understood. It has been reported that EGCG inhibits platelet aggregation induced by thrombin in a concentration dependant fashion, whereas, neither collagen nor ristocetin induced platelet aggregation was inhibited in the presence of ECGC [17]. A more recent data indicate one possible mechanism of action is the inhibition of cyclooxygenase 1 [18]. The effective concentration of EGCG that is able to inhibit platelet aggregation remains inconsistent. Indeed, a number of studies have demonstrated that EGCG was less effective in inhibiting agonist induced platelet function at low concentrations [16, 19], whereas a study by Ok et al suggested that EGCG significantly inhibited agonist induced platelet function at low concentrations [20]. Furthermore, a very limited number of studies have attempted to investigate the effect of EGCG on platelet activation markers (such as platelet surface expression of P-selectin) and plasma coagulation proteins. The aim of the present study is to investigate the effect of ECGC of platelet aggregation and activation, and plasma coagulation times. In this study a high EGCG concentration (100 µM) which has been found to significantly inhibit platelet aggregation and a lower concentration (50 µM) which has demonstrated to be less effective in inhibiting platelet aggregation as reported by Son et al [7] and Jin et al [19].
2. Methods
2.1. Human Volunteers
- Griffith University Human Research Ethics Committee approval and informed consent was obtained prior to blood collection. Subjects were healthy volunteers of both sexes, aged 18–60 years (4 Males and 2 Females) with no history of vascular disease, bleeding disorders or thrombosis and had not taken aspirin or any other medication that affects platelet function for at least two weeks prior to the study.
2.2. Sample Preparation
- Blood collection was performed using published methods for platelet function studies [3]. Briefly, fresh whole blood (n= 6) was collected by antecubital venepuncture into 3.8% (w/v) sodium citrate Vacuette tubes and used immediately for flow cytometric studies. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for platelet aggregation studies was obtained from the fresh blood after centrifugation at 200 x g for 10 minutes at room temperature. Platelet-poor plasma (PPP) was obtained by centrifugation of the remaining blood at 1800 x g for 15 minutes at room temperature. Aggregation studies were completed within three hours of blood collection. PPP was used for coagulation study. For full blood count analysis, blood was collected into Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) tubes. Blood counts were determined using Coulter AcT 5 Diff Haematology Analyser (Beckman Coulter (Fullerton, CA, USA).
2.3. Platelet Aggregation
- The effect of EGCG (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, US) or vehicle on agonist induced light transmittance platelet aggregation was determined as described previously [3]. Briefly, EGCG in PBS (pH 7.4) was incubated with PRP (n= 6) at 37°C for 10 minutes to achieve concentrations of 50 or 100 µM. Aggregation was stimulated by 6.5 mM ADP (sourced from Helena Laboratories, Beaumont, TX, USA). Turbidimetric platelet aggregation was calibrated against a PPP control (100% aggregation) and the maximal aggregation over a six minutes period was recorded using AggRAM® aggregation analyser (Helena Laboratories, Beaumont, TX, USA).
2.4. Flow Cytometric immunophenotyping
- The effect of EGCG on platelet activation was measured by whole blood flow cytometric evaluation of PAC-1 binding, a monoclonal antibody which recognises activated αIIbβ3 receptor and P-selectin expression [21] as previously described [3, 21]. Briefly, fresh citrated whole blood (n= 6) diluted 1:5 with HEPES saline buffer (10mM HEPES, 0.15M NaCl, pH 7.4) was incubated with EGCG at 50 or 100 µM or vehicle (PBS, pH 7.2) at 37°C for 10 minutes. For assessment of P-selectin expression, samples were labelled with fluorescently conjugated monoclonal CD42b PC5 (BD-Pharmingen, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) with anti-CD62p APC (BD-Pharmingen). Platelet activation was induced by 20 mM ADP. Samples were fixed with 1% (v/v) formaldehyde and analysed using a BD LSRFortessa cell analyser (BD Biosciences, North Ryde, NSW, Australia) and BD FACSDiva software (version 6.1.3, BD Biosciences, North Ryde, NSW, Australia). Platelets were identified by characteristic forward and side light scatter as well as expression of CD42b and 10,000 platelet events counted. The mean fluorescent intensity of CD62p was recorded.
2.5. Plasma Coagulation Study
- The coagulation times of plasma coagulation proteins (n= 6) were determined in the presence or absence of 50 or 100 µM EGCG. The coagulation study consisted of prothrombin clotting time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). The PT and aPTT were determined according to the C4-coagulation analyser operator’s manual (Helena Laboratories). All reagents and controls were purchased from Helena Laboratories.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- Data are expressed as S.E.M. of n independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s Comparisons test using GraphPad Prism software version 6.2 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). P < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Blood Counts
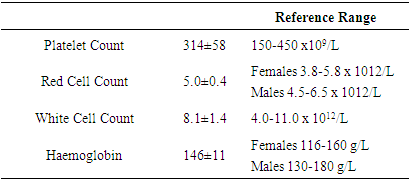
- Platelet count, red count, white count and haemoglobin levels were determined for each volunteer to ensure all volunteers had normal haematology counts. All volunteers were found to have normal haematological counts. The haematological counts are shown in table 1.
|
3.2. Effect of EGCG on Platelet Aggregation
- The effect of EGCG on platelet aggregation was assessed using light transmission aggregometry. Incubation of EGCG at 50 or 100 µM with PRP significantly inhibited platelet aggregation induced by ADP as shown in figure 1. Incubation with vehicle control did not affect platelet aggregation when compared to the baseline platelet aggregation (vehicle = 65.8% vs baseline =68.8%, p = ns). On the other hand, EGCG at 100 µM significantly inhibited platelet aggregation (31% decrease from baseline, P < 0.05). Similarly, 50 µM EGCG significantly reduced platelet aggregation (26% decrease from baseline, P < 0.05).
3.3. Effect of EGCG on α Granule Exocytosis
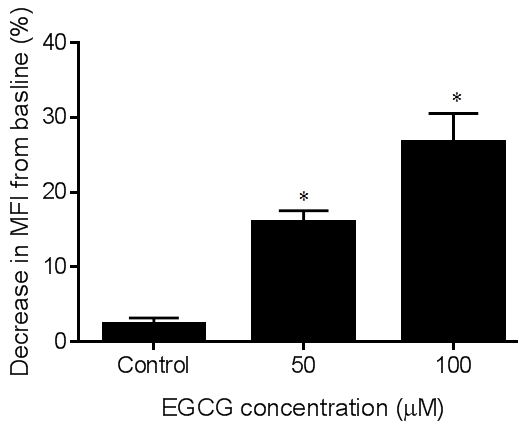
- α granule exocytosis was assessed by ADP stimulated platelet surface expression of P-selectin as measured by CD62P fluorescence. Incubation of the vehicle control with whole blood samples did not decrease platelet surface expression of P-selectin when compared to the baseline expression of P-selectin, whereas, ECGC at 50 or 100 µM significantly inhibited P-selectin expression induced by ADP as demonstrated by figure 2. EGCG at 100 µM significantly decreased CD62P fluorescence (26.6 ±3.8% decrease in fluorescence from baseline, P < 0.05). EGCG at 50 µM achieved 16.06 ± 1.5% decrease in fluorescence from baseline (P < 0.05).
3.4. Effect of EGCG on Coagulation Times
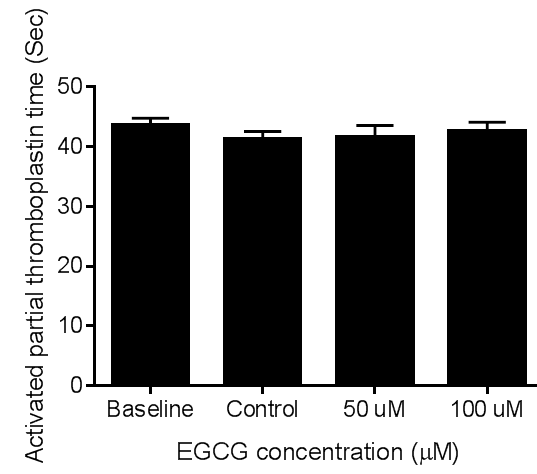
- The effect of ECGC on plasma coagulation protein was assessed by measuring the coagulation times of PT and aPTT using platelet poor plasma. At the concentrations tested EGCG did not affect the coagulation times of PT. figures 6 and 7 demonstrate the effect of EGCG on PT and aPTT, respectively.
4. Discussion
- In this study we have demonstrated that EGCG inhibits platelet aggregation and activation in response to AP stimulation. We also demonstrated that EGCG did not prolong the coagulation times of both PT and aPTT pathways, suggesting that the antithrombotic benefits of EGCG are mediated due at least in part to platelet inhibition. Platelet aggregation is one the last steps in thrombus formation [22]. It is initiated by several physiological agonists such as collagen and ADP [23]. In this study EGCG at 50 and 100 µM concentrations were found to significantly inhibit ADP induced aggregation. This finding of this study is consistent with previous data demonstrating that higher EGCG concentrations were required to produce significant inhibitory effects. Furthermore, this study demonstrated that EGCG 50 µM was able to inhibit platelet aggregation and activation, the same concentration that was previously found to be less effective in inhibiting platelet aggregation [7, 19]. More importantly, the concentrations tested were not toxic to platelets because Lill et al [16] demonstrated platelet aggregation reversibility upon EGCG removal. Platelet adhesion to the site of vascular injury is vital for platelet intracellular signalling, shape change and platelet release reaction in which dense and alpha granules release their granular contents [24]. P-selectin is expressed on activated platelets mediating platelet adhesion to monocytes and neutrophils [25]. Furthermore, P-selectin has been shown to play an essential role in atherosclerotic lesion development [26]. In this study we have shown that ADP induced P-selectin expression on platelet surface was significantly inhibited in the presence of EGCG at higher concentrations. The coagulation cascade consists of two distinct pathways, the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Platelet rich thrombus is stabilised by a fibrin clot resulting from the activation of the coagulation cascade, furthermore, the coagulation cascade is responsible for thrombin generation which is a potent platelet agonist and is important for platelet aggregation [27]. In this study we investigated the effect of EGCG on the coagulation times of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Our data show that EGCG at 50 and 100 µM concentrations did not affect the coagulation times of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. These data suggest that the observed antithrombotic effect of EGCG is mediated by inhibition of platelet function.ADP is a low molecular weight platelet agonist which is mainly stored in platelet dense granules [28]. It plays an essential role in propagating platelet activation process. The positive feedback mechanism induced by ADP has been found to be an important step in platelet aggregation, furthermore, it has been found to contribute to the initiation of the coagulation cascade [29]. Released ADP binds to platelet P2Y1 and PY12 receptors and induces further activation. Activated platelets exocytose their granular contents from both dense and alpha granules, the dense granules release ADP and other signalling molecules, while alpha granules release P-selectin which is important for platelet adhesion to leucocytes [28]. In addition, P2Y12 receptors have been reported to regulate platelet activation, thrombus growth and stability in injured arteries [30]. Therefore, inhibition of ADP mediated platelet function is an important step in reducing platelet function in patients with cardiovascular disease. Our data is consistent with other findings suggesting inhibition of platelet aggregation induced by ADP, but, not by collagen [17]. This is an important finding which means that platelet aggregation/ activation can be reduced but not complete abolished. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and activation by EGCG suggests that the green tea extract can be used to complement existing antiplatelet therapy in patients experiencing reduced responsiveness to the current antiplatelet regimes. In addition green tea consumption can be used a preventative measure to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.The concentrations tested in this study are high and unlikely to be achievable in vivo. Therefore, a comprehensive in vivo study investigating the achievable concentrations and the bioavailability of EGCG post consumption is warranted.
5. Conclusions
- This study demonstrates the inhibition of platelet aggregation and activation stimulated by ADP. This data suggests green tea consumption can be used as preventative strategy to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors wish to gratefully acknowledge Miss Sabrina Avendano and Mr Ian Dias for their help in obtaining the data.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML