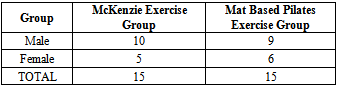-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Prevention and Treatment
p-ISSN: 2167-728X e-ISSN: 2167-7298
2013; 2(4): 47-54
doi:10.5923/j.ijpt.20130204.01
Effectiveness of Mckenzie Exercises and Mat Based Pilates Exercises in Subjects with Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain: A Comparative Study
Saravanan Kuppusamy1, Raghunath Narayanasamy2, JohnsonDillip Christopher3
1Masterskill global college, Kotabharu, 15050, Malaysia
2Modern institute of physical medicine and rehabilitation. Hyderabad, 500012, India
3PJKKMMRF College of physiotherapy, Komarapalayam. Tamilnadu, India
Correspondence to: Saravanan Kuppusamy, Masterskill global college, Kotabharu, 15050, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
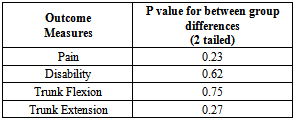
Study design: A single blinded, randomized control trial, pretest-posttest design, with 6 week treatment programme. Objectives: To compare the effectiveness of Mckenzie exercises to that of a mat based Pilates exercise in improving the pain, functional disability and trunk ROM associated with CNLBP (Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain).Background: Therapeutic approaches developed by Mckenzie and Pilates are becoming popular; however, there have been no reports on their difference effectiveness. Methods and measure: Thirty physically active subjects between 20 and 65 years old with CNLBP were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 groups. McKenzie exercise group (MEG) received McKenzie exercises for 6 weeks based on the assessment; while the Mat based pilates exercise (MBPE) group received Pilates exercise for the same 6 weeks duration. The outcome measures of pain are measured by the numeric pain rating scale (NPRS), functional disability is measured using a Rolland Morris disability questionnaire (RMDQ) and the trunk ROM is measured using modified Schobers method. Wilcoxon signed-rank tests and Mann-Whitney U test was used to analyze the data. The results: No statistical difference existed on posttest comparisons were made on outcome data between groups on pain (p<0.23), disability (p<0.62), trunk flexion (p<0.75) and trunk extension (p<0.27), While both the groups show improvements for all the measures that were assessed individually and they were significant (p<0.01). Conclusion: The results may help physiotherapists in clinical decision-making. Between group comparisons of changes in the dependent variable scores revealed no statistical differences between the groups.
Keywords: Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain, McKenzie Exercise, Mat Based Pilates Exercise, RMDQ
Cite this paper: Saravanan Kuppusamy, Raghunath Narayanasamy, JohnsonDillip Christopher, Effectiveness of Mckenzie Exercises and Mat Based Pilates Exercises in Subjects with Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain: A Comparative Study, International Journal of Prevention and Treatment, Vol. 2 No. 4, 2013, pp. 47-54. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpt.20130204.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Chronic non-specific low back pain(CNLBP) is a common musculoskeletal problem worldwide[1], It has been estimated that 80% of the population will suffer at least one episode of low back pain (LBP) at some point during their lives[2], reports proves that between 28% and 41% of persons with acute low back pain never completely recover, developing chronic low back pain[3,4.In addition to its high prevalence, the pain source is not well-established in the majority of individuals with back pain, and the term “chronic non-specific low back pain” is often used to describe this population[5,6]. fear of pain result in activity limitations, (e.g., lifting, walking, squatting, prolonged sitting positions, reaching and twisting), participation restriction (e.g., work, recreation activities, family and community) and functional disability[7,8]. Patients who experience this disability are limited in their daily living activities and may experience inappropriate neuromuscular adaptations to maintain and/or preserve functions such as walking, running, or other activities. Nonspecific low back pain is defined as pain located in the lower region of the spine (below the ribs and above the legs) due to an unknown cause. This condition can be mentioned as acute (< 3 months), chronic (> 3 months), or recurrent[9].About 90% of Low back pain (acute and chronic) is considered non-specific[14]. CNLBP, also known as ordinary or “simple backache”, and “common” or “garden variety low back pain”, is mechanical low back pain of musculoskeletal origin in which symptoms vary with physical activities[15]. CNLBP may be related to mechanical strain or dysfunction, although it often develops spontaneously, and can be painful and disabling; however the severity or intensity[14] of the pain gives very little information about the source of pain. Back pain often spreads to one or both of the buttocks or thighs, and this is usually somatic referred pain and not a sign of nerve root compression[2]. McKenzie approach and mat based Pilates are the two distinctly different interventions frequently used for the treatment of CNLBP.The McKenzie approach is one of the most frequently used types of physiotherapy for back pain[23–25]. It is based primarily on the identification of a directional preference for spinal movement and can form the basis for prescription of exercises[26]. Improvement in symptoms is subsequently assessed in terms of ‘centralization’, a phenomenon that has been commonly used[27]. It incorporates repeated end range movements by examination; the classification of direction for exercise depends upon the patient’s response to those repeated movements. Posture correction and to maintain the correction is the important aspect of McKenzie exercises[28].Modern Pilates focuses on maintaining a ‘neutral spine’, pelvic and spinal stability, along with activation of transverse abdominals and pelvic floor muscles in combination with controlled breathing[22]. Furthermore, in people with CNLBP, Pilates is sometimes promoted on the basis that it improves pain levels, flexibility, proprioception and the perception of positive general health[16]. Some researchers suggest that weakened muscles such as the transverse abdominals and multifidus may be responsible for decreased spinal stability and consequently the onset of LBP [21]. The Pilates method strengthens these muscles and hence may be an effective modality for LBP[22].Pilates has been applied in various musculoskeletal disorders. LBP is one of the most studied. However, the lack of definition regarding the time and frequency of the application required for each approach is a limiting factor for use of this technique[15]. In spite of many research studies performed in the McKenzie and mat Pilates, there is some disagreement about the most effective and safe method in improving the pain, disability and trunk ROM in CNLBP [8,17,31]. The controversy about this exercise prescription has motivated to conduct this present study.
2. Objective of this Study
- § To evaluate changes in pain, functional disability and trunk ROM in adults with CNLBP following a 6-week Mckenzie exercise programme.§ To evaluate changes in pain, functional disability and trunk ROM in adults with CNLBP following a 6-week mat based Pilate’s exercise programme.§ To compare the effectiveness of Mckenzie exercises to that of a mat based Pilates exercise in improving the pain, functional disability and trunk ROM associated with CNLBP.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design
- A pretest-posttest study design, randomized control trial. Single blinded study toassess the effectiveness of McKenzie and mat based Pilates exercises in subjects with chronic non-specific low back pain (CNLBP). Participants attended a total of 12 twelve treatment sessions over a 6 week period for two sessions per week. All participants signed the informed consent form to participate in the study. The study has been approved by the research committee of the institution.
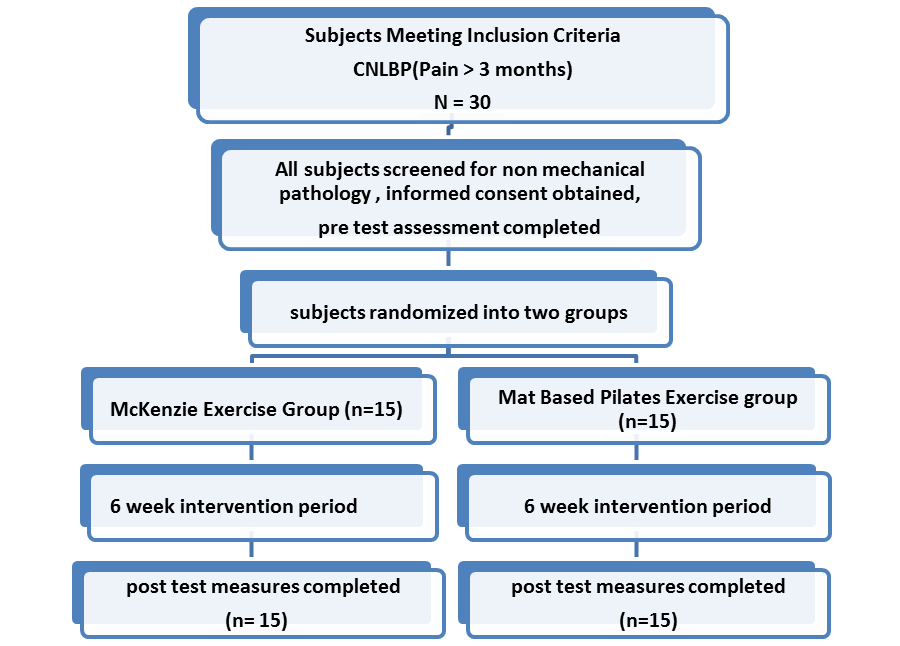 | Figure 1. Flow Diagram of Study Procedure |
3.2. Subjects and Study Setting
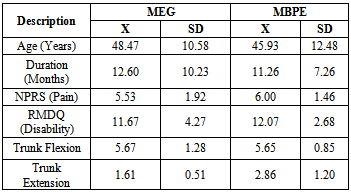
- Final sample composes of 30 patients who need care for chronic non-specific low back pain (CNLBP) with duration of symptoms more three months. Data from 30 participants (n=11, females, n=19 males), between 24 – 65 years of age (mean age 41.25 years) were analyzed. The sample size calculation was done based on the previous studies (30). We recruited over 6 months, referred subjects from various physicians from Hyderabad. The study was conducted in the modern physiocare rehabilitation Centre. Hyderabad. All the demographic data (Table 1 and 2) on Age, gender, duration of symptom, Pain, functional disability and trunk ROM were obtained at the time of baseline measurement.
|
3.3. Randomization
- A total of 30 subjects were randomly assigned into two treatment groups. Group 1 (McKenzie exercise group), and for Group 2 (mat based Pilates exercise group) using a random number table. Group 1 included 11 males 4 females and Group 2 included 10 male and 5 female subjects
4. Procedure
- Subjects who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria and who agreed to take part in this study were screened. If they were found to be eligible, informed written consent was obtained prior to being randomized. Subjects will be assessed by a researcher who will be unaware of the allocation of subjects. Researcher will determine the eligibility if the patients and collect the outcomes of the study. Outcome measures will be collected at baseline and the end of entire treatment. Physiotherapists who took part in the study were provided with the study days by the research team to familiarize them with treatment. The entire participating physiotherapist was given 5 days training in procedures to be used in the treatment. After finishing questionnaire, all the subjects received a mechanical evaluation following McKenzie assessment methods.
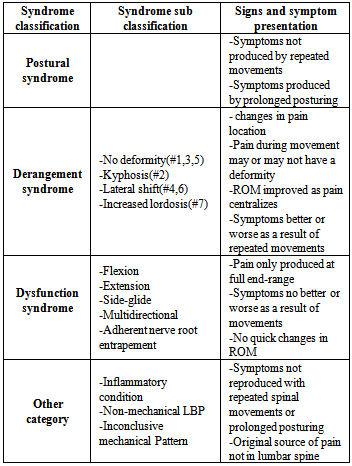
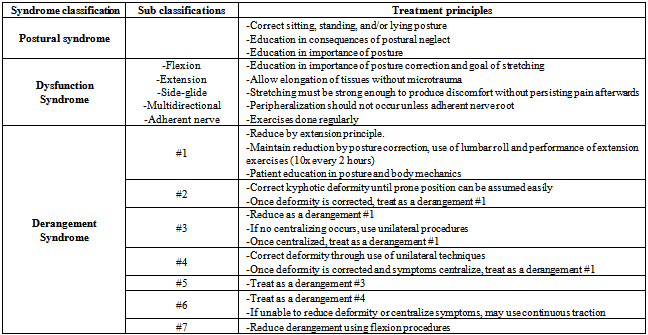
4.1. McKenzie Exercises Group (MEG)[11]
- Patient examination emphasizes repeated test movements. Precise changes in pain location in response to trunk movements were documented. Specific spinal movements, which abolish the symptoms or shift them centrally away from the peripheral parts of the body, are noted by therapist. i.e.Flexion, extension or lateral displacement of spine. After finishing the examination, the subjects were assigned to any one of the four syndrome classifications(Table 1). Depending on the classification, a treatment program was prescribed that may have included posture correction, performance of end-range repeated movements of the spine, or the use of manual techniques designed to reduce or abolish the patient's signs and symptoms. All types of extension / flexion exercises will be performed with 10 reps each, each Session will last about 50 – 60 min and treatment will be provided twice a week for a period of six weeks. (Table 2) All exercises were modified so that they are performed at three levels of difficulty: basic, intermediate, and advanced.
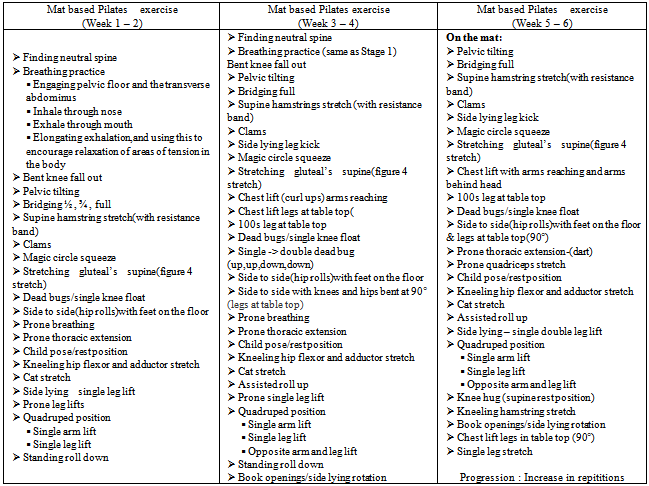
4.2. Mat Based Pilates Exercise Group (MBPE)
- This core strength activation is also known as “powerhouse”[5, 11, 12 and17]. Sessions last up to 60min and provided twice a week for a period of six weeks. Exercises are performed 6 to 10 repetitions with progression if needed and stretches were held for between 30 seconds. All exercises can be performed at three levels of difficulty: basic (week1-2), intermediate (week3-4), and advanced (week5-6). All exercises were completed with emphasis on traditional Pilates principles; breathing; precision; core control; flowing and efficient movement.
|
|
5. Outcome Measures
5.1. To Evaluate the Subjects, Three Instruments were Used
- 1. Pain Intensity was measured by 11- point Numeric Pain Rating Scale (NPRS) The NPRS was used to measure low back pain intensity. The NPRS ranges from 0 being equal to no pain, 1-3 is mild, 4-6 moderate, 7-10 being the most severe pain imaginable[19]. Participants were asked to rate how ‘bothersome’ their pain had been in the past week by circling a number on the scale of 0-10[29].2. Functional Disability associated with back pain was measured by Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ).RMDQ was used to assess disability related to low back pain. It consists of 24 items that used to describe functional activities in subjects having low back pain. The greater number of questions positive, the greater the disability. Instructions were given to complete the items that describe them over the last 24 hours[12].3. Trunk Flexion and extension ROM were measured by Modified Schober’s index.The Modified Schober’s Index is used to indicate flexibility of forward being of the lumbar spine. A mark is made in the midline 5cm below the level of the posterior inferior iliac spine (PSIS) and another 10cm above the level of the PSIS. The subject is then instructed to flex forward as if to touch one's toes, and the distance between the marks is measured. Normal is considered to be 20cm when in full lumbar spine flexion, less than this is an indication of decreased range of motion or stiffness in the lumbar spine[17]. Fifteen centimeters (the original distance of the marks) are subtracted from the distance between the two marks when in full flexion, to give a value for flexion of the lumbar spine in centimeters[18], while the final length of trunk extension was subtracted from the initial length (15cm) to obtain the extent of trunk extension.
6. Statistical Analysis
- For statistical analysis SPSS 20.0 program was used. The mean and standard deviation of data obtained from both groups were identified. In both groups the difference between pre and post treatment was evaluated by Wilcoxon test and the difference between groups was evaluated by Mann-Whitney U test. The significance level was accepted as p<0.05.
7. Results
- All the 30 subjects who were selected by inclusion criteria took part in the study; all the participants received the intervention in two groups. The Table 4 shows the gender distribution of the study. The McKenzie group had 10 males and 5 females, whereas Pilates group had 9 males and 6 females. There was no significant predominance of sex.
|
|
|
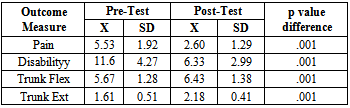
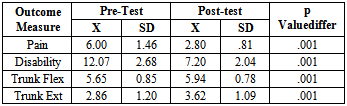
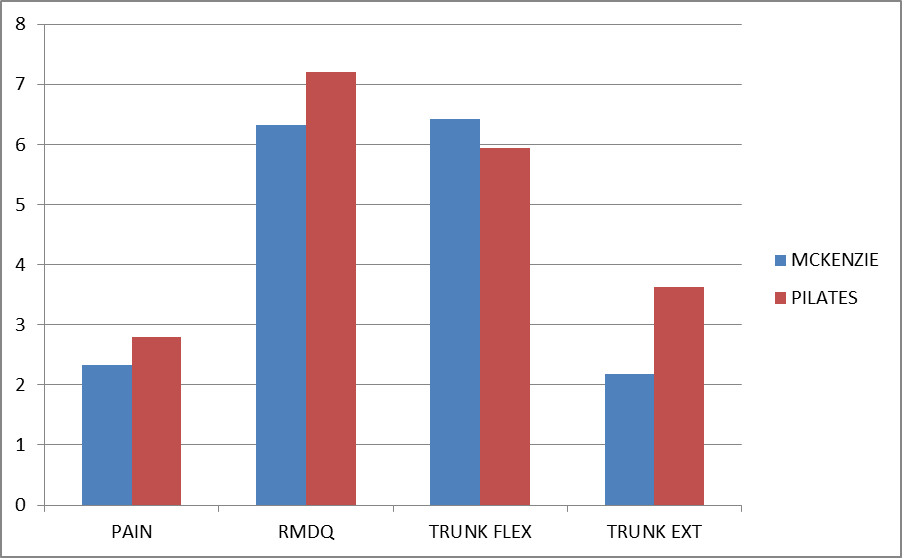 | Figure 2. Scores for Pre-Posttest Analysis: Mckenzie vs. Pilates exercise group |
|
|
8. Discussion
- The purpose of the study was to compare the effectiveness of two treatment programs for CNLBP. The results of this study did not support the initial hypothesis that the McKenzie exercises would more positively affect pain levels, functional disability and trunk ROM of individuals with CNLBP as compared to mat based Pilates exercise. Improvements were noted in all variables that were assessed in both groups. However pain, disability, ROM measurements of the trunk revealed no significant statistical differences between the groups treated with a McKenzie exercise programme and mat based spinal exercise programme. No previous study has been published comparing McKenzie treatment with mat based Pilates exercises for CNLBP subjects. The McKenzie group demonstrated improvements in all dependent variables that were assessed. Little evidence present to use of repeated end range active and passive movements for the management of the population with CNLBP. However, these findings are supported by studies of sport et al[38]. While the McKenzie concept of displacement of the nucleus pulposus with repeated movement to reduce abnormal disc pressures remains controversial, several studies have shown nucleus migration anterior or posterior away from the compressive forces of flexion and extension movements in the sagittal plane[27-29]. Schenebel, Watkins and dillin[39] demonstrated the relief of pain because of the pain control theory of gating mechanism. Derosa and Porterfield[40] proposed that the increased afferent input result pain modulation because of stimulation of arterial, venous and lymphatic or mechanoreceptor stimulation. While the McKenzie group demonstrated positive changes in all of the measured variables, only present pain index was found to be statistically significant. In systematic review[36] when McKenzie compared to other therapies and strengthening exercises, the results shows short term relief of pain and disability, skikic and suad[34] observed differences in the improvement of trunk mobility statistically. Similarly, toscando and egypto[35] found that the relief of symptoms are related to improvements in trunk ROM. However, subjects were more satisfied with McKenzie than Pilates exercises because, a more “hands-on”’ approach such as McKenzie programme has been found previously to be related to higher patient satisfaction[37].Although using of pilatesfor CNLBP has steadily increased, but its effectiveness is still supported by a low number of studies. Rydeard R et al,[33] proves treatment with a modified Pilates-based approach was more efficacious in reducing pain and functional disability than usual care in a population with CNLBP. The Randomized control trials in this review demonstrated that Pilates method, develops core muscle strength to assist in the structural imbalances, so is effective for the treatment of LBP. La touché et al[32] pointed out that it would be important to determine if Pilates performed on mats is more effective or adequate than Pilates performed using machines. Ryder et al[33]study shows that outcomes measures of pain (p=0. 002) and disability (p=0. 023) were considered significant. The current study demonstrates that apilates and mckenzie training approach similarly addressing neuromuscular control mechanisms is effective in decreasing pain and improving function in an identified group with CNLBP. The subjects in the O’Sullivan et al[31] study were trained in stabilization exercises designed to improve local muscular stability of the intervertebral segment. The transverse abdominal muscles, the lumbar multifidus, diaphragm, and pelvic floor muscles have all been shown to be important for localized stabilization. Activation of the gluteal muscles were also given importance in this study to assist with global stability of the lumbopelvic region during movement. However, more research needed to determine Pilates ability to maintain improvements in low back pain over longer periods of time. The drawback is that Pilates is often seen as a progressive therapy. The McKenzie group and pilates group demonstrated positive changes in all of the measured values, but McKenzie has shown to have more patient satisfaction, however it was not statistically significant. Therefore, on the basis of this data, it appears that in managing subjectswith CNLBP for 6 weeks of McKenzie exercises and mat based exercises are equally effective.
9. Limitations
- The current study consists of subjects who were referred to an outpatient physiotherapy department by the physicians. Thus, the sample may not be having all the representation of CNLBP, thereby limiting generalization of results. The results are further affected by the sample size limiting statistical methods. Furthermore, the trail was pragmatic with no true control (non-intervention).
10. Conclusions
- The results of the study support the basic use of McKenzie and mat based Pilates method was efficacious in the treatment of a group of individuals with nonspecific chronic Low back pain. However, no statistical difference in outcomes was noted between the groups. The results of the current study support the use of McKenzie for the management of CNLBP. A 6-week Pilate’s intervention was able to decrease the amount of functional disability, low back pain intensity, and LBP troublesomeness in adults with non-specific CLBPB. Both the two interventions did positive effect on pain, disability and trunk mobility. Future investigations of these same treatment approaches may provide more efficient results for the physiotherapists. Studies involve in CNLBP with a more specific diagnosis of disc degeneration, disc prolapse, or spinal stenosis is recommended for future research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author would like to thankthe people who contributed to the successful completion of the study, particularly the orthopaedicians,post graduate students and physiotherapy colleagues.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML