-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Probability and Statistics
p-ISSN: 2168-4871 e-ISSN: 2168-4863
2021; 10(1): 17-25
doi:10.5923/j.ijps.20211001.03
Received: Apr. 8, 2021; Accepted: May 12, 2021; Published: Jun. 15, 2021

Interval Estimation for Burr Type-XII Model Based on the Generalized Order Statistics
M. Maswadah, Seham M.
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Aswan University, Egypt
Correspondence to: Seham M., Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Aswan University, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this paper, the conditional inference was applied to study some statistical properties for the confidence intervals of the Burr type-XII distribution parameters based on generalized order statistics. To measure the performance of this approach compared to the Asymptotic maximum likelihood estimates, simulation studies were performed for different values of sample sizes and shape parameters. The simulation results indicated that the conditional intervals possess good statistical properties and can perform well even when the sample size is small compared to the classical intervals. Finally, real data sets are given to illustrate the confidence intervals that were developed in this paper.
Keywords: Asymptotic maximum likelihood estimates, Covering percentage, Conditional inference, Progressive type-II censored samples with binomial random removals
Cite this paper: M. Maswadah, Seham M., Interval Estimation for Burr Type-XII Model Based on the Generalized Order Statistics, International Journal of Probability and Statistics , Vol. 10 No. 1, 2021, pp. 17-25. doi: 10.5923/j.ijps.20211001.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The Burr type-XII distribution has been extensively studied in the literature as an appropriate and useful failure model for the applied statistics. Several studies were performed on Burr type-XII distribution, which includes Evans and Simon (1975) who discussed the Burr distribution as a failure model and derived the maximum likelihood estimators (MLEs) for the parametors. Evans and Ragab (1983) discussed the Bayesian estimotors for Burr distribution paramaeters based on type-II censored samples. Wu and Yu (2005) proposed some pivotal quantities to test shape parameters and established their confidence intervals based on the censored data. Soliman (2005) derived the MLE and Bayesian estimates of the parameters and some lifetime parameters. Xiuchun et al. (2007) derived the empirical Bayesian estimator for the reliability based on progressively type-II censored samples, and Liang and Yimin (2010) derived the empirical Bayesian estimators based on record values. For a comprehensive review of the Burr type-XII distribution, see Rodrignez (1977).However, in recent years, this distribution has been used in a variety of fields such as business, see Rodringuez and Taniguchi (1980). Economics and Finance see, McDonald and Richards (1987). Hydrology, see Mielke and Johanson (1974). Quality assurance, see Burr (1976). Medicine see Wingo (1983) and Mineralogy, see Cook and Johnson (1986). Wingo (1993) derived the MLEs of the parameters under type-II censoring. Wingo (1993) derived the MLEs for fitting the Burr type-XII model based on multiply censored data. Zimmer et al. (1998) studied the reliability analysis of the Burr typ-XII distribution. Wu and Yu (2005) proposed pivotal quantities to test the shape parameter and establish confidence interval of the shape parameter for the Burr type-XII distribution under the failure-censored plan. Malinawska et al. (2006) derived the estimation paramters of the Burr type-XII model using generalized order statistics. Lio et al. (2007) derived the paramter estimates based on the progressive type-II censoring. Li et al. (2007) proposed the epmirical Bayes estimators of reliability performances for the Burr type-XII model using LINEX loss function based on progressively type-II censored samples. Wu et al. (2007) derived the MLE estimates for the Burr type-XII distribution parameters. Asgharzadeh and Valiollahi (2008) derived the parameter estimates based on progressive type-II censored data. Wing (2008) studied the statistical inference of the Burr type-XII distribution. Lee et al. (2009) obtained Bayes and empirical Bayes estimators for reliability. Asgharzadeh and Abdi (2012) derived the confidence intervals of the Burr type-XII model parameters based on records. Soliman et al. (2012) studied the Bayesian statistical inference and prediction for the Burr type-XII model based on the progressive first inference censored samples. Kumar(2017) presented some statistical properties for this distribution. Amal et al. (2018) derived the Bayesian estimate of the reliability based on a new numerical loss function. Hakim et al. (2021) presented some characteristics of this distribution and its application to heavy tailed survival time data. Thus, many aspects of the distribution have been covered by the researchers, but there is still a lack of comprehensive statistical analysis of the distribution. In this paper, the conditional inference was applied to construct confidence intervals for the Burr type-XII model parameters based on generalized order statistics. However, the conditional inference as suggested by Sir Fisher (1934) has been applied to many lifetime distributions belonging to the location-scale family, see Lawless (1973-1982) or those that can be transferred to this family, see Maswadah (2003, 2005), and Maswadah and EL-Faheem (2018). Thus, as a new application of the conditional approach, the conditional confidence intervals were generated for the Burr Type-XII model parameters based on generalized order statistics.The Burr type-XII model was considered by Burr (1942), as a new lifetime distribution with the cumulative distribution function (cdf) and the probability density function (pdf), which are presented respectively by:
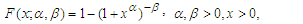 | (1.1) |
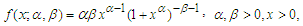 | (1.2) |
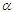 and
and 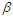 are two shape parameters.Thus, for the significance of this distribution, the confidence intervals were derived based on the conditional and the classical inferences based on generalized order statistics (GOS) that introduced by Kamps (1995) as a unified approach to ordinary OS, type-II progressive order statistics, record values and k-th record values.Definition.Let
are two shape parameters.Thus, for the significance of this distribution, the confidence intervals were derived based on the conditional and the classical inferences based on generalized order statistics (GOS) that introduced by Kamps (1995) as a unified approach to ordinary OS, type-II progressive order statistics, record values and k-th record values.Definition.Let 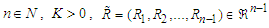 be parameters such that
be parameters such that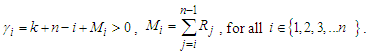 The random variables
The random variables 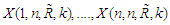 are called GOS, with noting that
are called GOS, with noting that 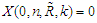 , if their joint pdf can be written in the form:
, if their joint pdf can be written in the form: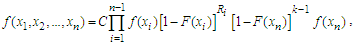 | (1.3) |
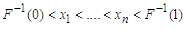 of
of 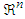 , where
, where 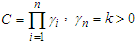 .
.2. Conditional Inference Methodology
- For the first time, in this section, we will provide an outline for the conditional inference to the Burr Type-XII distribution based on the generalized order statistics. Given a set of
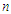 GOS
GOS 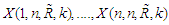 with sampling density function (1.3), thus by substituting (1.1) and (1.2) in (1.3) we can derive the joint pdf as follows:
with sampling density function (1.3), thus by substituting (1.1) and (1.2) in (1.3) we can derive the joint pdf as follows: 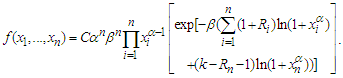 | (2.1) |
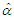 and
and 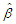 be any equivariant estimators such as the MLEs for
be any equivariant estimators such as the MLEs for 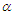 and
and 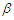 , then
, then 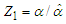 and
and 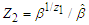 are pivotal quantities and
are pivotal quantities and 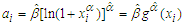 ,
, 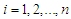 form a set of ancillary statistics. With noting that
form a set of ancillary statistics. With noting that 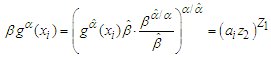 .Thus, based on the following theorem, we can derive the conditional densities of the pivotal quantities conditional on the ancillary statistics and the confidence intervals can be constructed and converted to
.Thus, based on the following theorem, we can derive the conditional densities of the pivotal quantities conditional on the ancillary statistics and the confidence intervals can be constructed and converted to 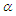 and
and 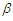 fiducially. Theorem:Let
fiducially. Theorem:Let 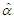 and
and 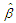 be any equivariant estimators of
be any equivariant estimators of 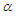 and
and 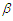 , based on the generalized order statistics
, based on the generalized order statistics 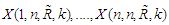 . Then the conditional pdf of
. Then the conditional pdf of 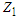 and
and 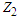 given
given 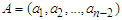 can be derived in the form
can be derived in the form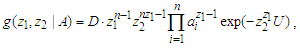 | (2.2) |
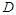 is a normalizing constant depends on
is a normalizing constant depends on 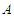 only, and
only, and 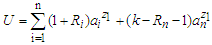 .Proof: see Maswadah (2003).
.Proof: see Maswadah (2003).3. Confidence Intervals Procedures
3.1. Conditional Confidence Intervals
- The marginal density of
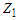 and the distribution function of
and the distribution function of 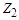 can be derived from (2.2) respectively as:
can be derived from (2.2) respectively as: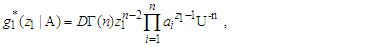 | (3.1) |
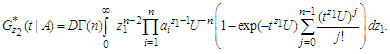 | (3.2) |
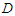 is a normalizing constant does not depend on
is a normalizing constant does not depend on 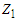 and
and 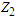 , that can be derived as:
, that can be derived as: 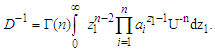 To obtain confidence intervals for
To obtain confidence intervals for 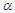 (say), from (3.1) the probability statement for
(say), from (3.1) the probability statement for 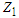 can be obtained as
can be obtained as 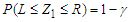 , which is the
, which is the 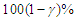 confidence interval for
confidence interval for 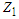 and then transformed fiducially to
and then transformed fiducially to 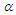 as
as 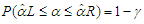 . This interval is not unique, and therefore using the tails of symmetric probability, the lower (
. This interval is not unique, and therefore using the tails of symmetric probability, the lower (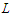 ) and upper (
) and upper (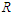 ) limits of such an interval are solutions of
) limits of such an interval are solutions of 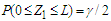 and
and 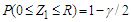 respectively. Similarly, the confidence interval for
respectively. Similarly, the confidence interval for 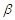 can be constructed from (3.2).
can be constructed from (3.2). 3.2. Asymptotic Confidence Intervals
- In this subsection, we obtained the Fisher information matrix to compute 95% asymptotic confidence intervals for the Burr type-XII distribution parameters based on maximum likelihood estimators (MLEs). The Fisher information matrix can be obtained by using loglikelihood function of (2.1). Thus, we have
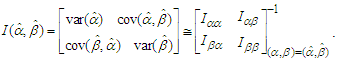 Where,
Where,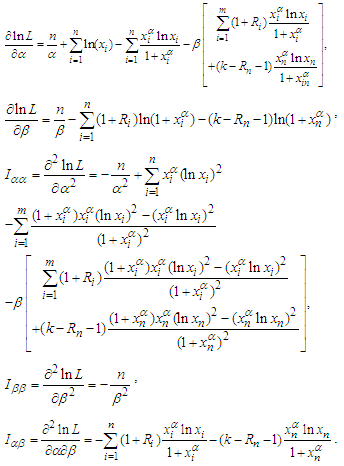 Thus, the approximate
Thus, the approximate 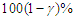 two sided confidence intervals for
two sided confidence intervals for 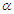 and
and 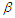 can be obtained respectively by
can be obtained respectively by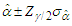 and
and 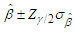 ,where
,where 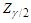 is the upper
is the upper 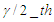 percentile of a standard normal distribution,
percentile of a standard normal distribution, 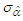 and
and 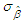 are the standard deviations of the MLEs of the parameters
are the standard deviations of the MLEs of the parameters 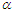 and
and 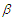 respectively, where they are elements of the following AVC matrix:
respectively, where they are elements of the following AVC matrix: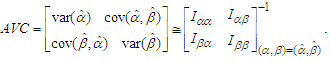
4. Simulation Studies
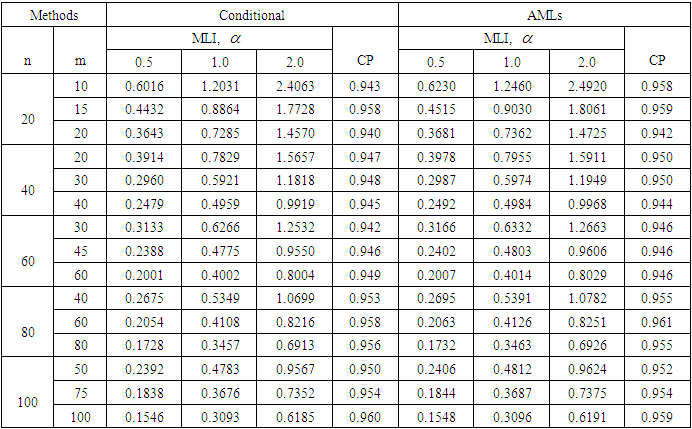
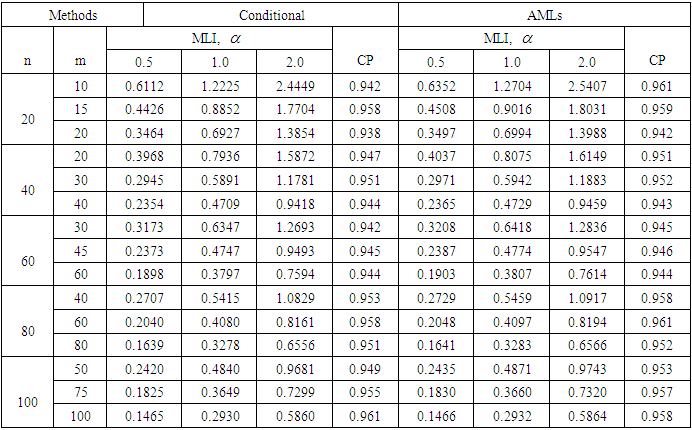
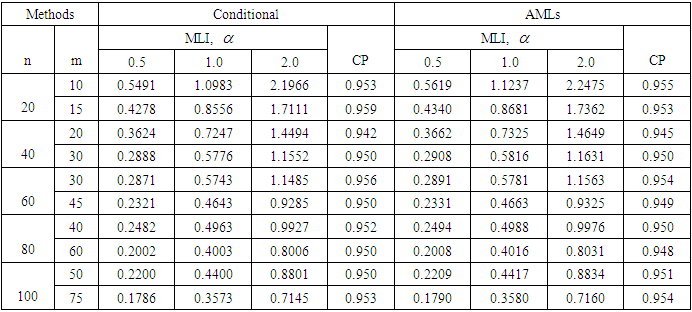
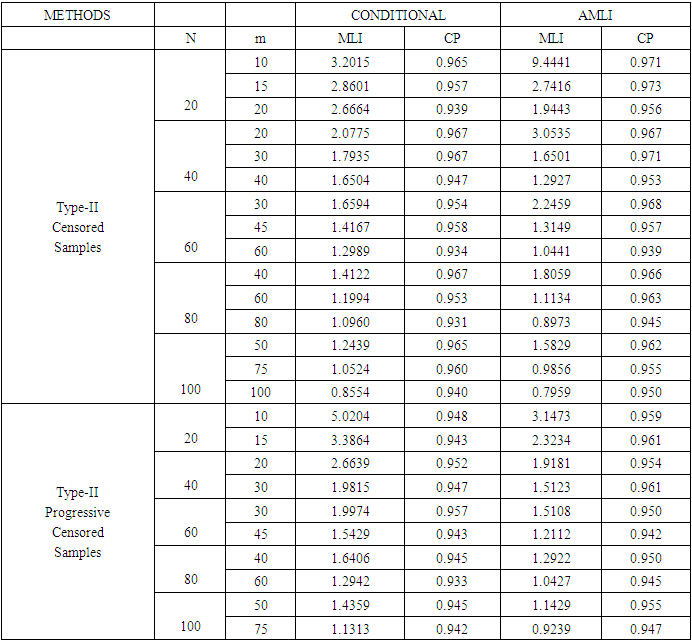
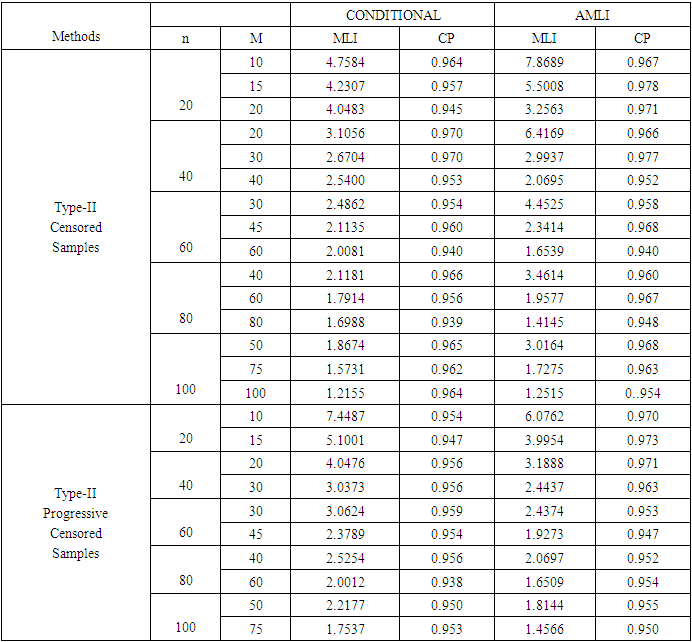
- In this section we mainly present some results based on the Monte Carlo simulation, to measure the performance of the conditional confidence intervals compared to the AMLE intervals in terms of the following criteria: 1- Covering percentage
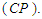 2- Mean length of intervals
2- Mean length of intervals 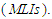 Comparative results, based on 1000 Monte Carlo simulation trials are given for sample sizes n =20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 with censoring levels 0.0%, 0.25% and 0.50%, that have been generated from the Burr type-XII model for shape parameter values
Comparative results, based on 1000 Monte Carlo simulation trials are given for sample sizes n =20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 with censoring levels 0.0%, 0.25% and 0.50%, that have been generated from the Burr type-XII model for shape parameter values 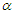 = 0.5, 1, 2 and the parameter
= 0.5, 1, 2 and the parameter 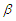 = 2 and 3. For the progressive type-II censoring sampling that are carried out with binomial random removals with probablity
= 2 and 3. For the progressive type-II censoring sampling that are carried out with binomial random removals with probablity 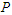 = 0.5, which means the number of units removed at each failure time follows a binomial distribution with probability
= 0.5, which means the number of units removed at each failure time follows a binomial distribution with probability 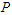 , where different values of
, where different values of 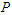 do not affect the calculations. From the simulation results that reported in Tables 2 to 7, we can summarize the following main points: i. It is worthwhile to note that for different values of
do not affect the calculations. From the simulation results that reported in Tables 2 to 7, we can summarize the following main points: i. It is worthwhile to note that for different values of 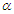 , the
, the 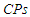 are the same for the pivotal
are the same for the pivotal 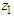 as expected because its distribution is independent from the parameter
as expected because its distribution is independent from the parameter 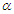 . However, the values of
. However, the values of 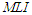 for the parameter
for the parameter 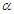 increases when
increases when 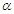 increases. On the contrary the values of the
increases. On the contrary the values of the 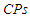 and
and 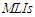 for the pivotal
for the pivotal 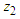 are the same for all values of
are the same for all values of 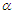 as expected. ii. Generally, the values of
as expected. ii. Generally, the values of 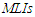 decrease, the
decrease, the 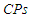 almost getting increase as the sample size increases for both parameters
almost getting increase as the sample size increases for both parameters 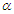 and
and 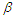 . iii. For the parameter
. iii. For the parameter 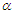 , the values of
, the values of 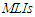 and
and 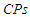 decrease and the values of
decrease and the values of 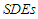 getting increase for increasing the value of
getting increase for increasing the value of 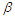 , but it is not the case for highly type-II censoring, where the values of
, but it is not the case for highly type-II censoring, where the values of 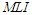 getting increase. On the contrary, for the parameter
getting increase. On the contrary, for the parameter 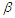 , the values of
, the values of 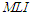 and
and 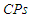 increase for increasing
increase for increasing 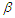 as expected.iv. The values of
as expected.iv. The values of 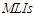 for
for 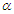 based on the conditional inference are smaller than those based on the AMLEs inference, in spite of they have almost higher
based on the conditional inference are smaller than those based on the AMLEs inference, in spite of they have almost higher 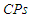 based on complete and censored samples. However the values of
based on complete and censored samples. However the values of 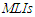 for
for 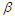 based on the AMLEs inference are almost equal for two decimal places to those based on the conditinal inference, but it is not the case for highly type-II censored samples and small sample sizes.v. Generally, the results based on the type-II progressive censored samples are better than those based on the type-II censored samples, in which they have smaller
based on the AMLEs inference are almost equal for two decimal places to those based on the conditinal inference, but it is not the case for highly type-II censored samples and small sample sizes.v. Generally, the results based on the type-II progressive censored samples are better than those based on the type-II censored samples, in which they have smaller 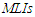 and higher
and higher 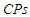 .Thus the simulation results indicated that the conditional confidence intervals possess good statistical properties and they can perform quite well even when the sample size is extremly small. However, the AMLE approach turns out to be impercise or even unreliable for small or highly type-II censored samples.
.Thus the simulation results indicated that the conditional confidence intervals possess good statistical properties and they can perform quite well even when the sample size is extremly small. However, the AMLE approach turns out to be impercise or even unreliable for small or highly type-II censored samples.5. Real Data Analysis
5.1. Application Data for Joint Patients
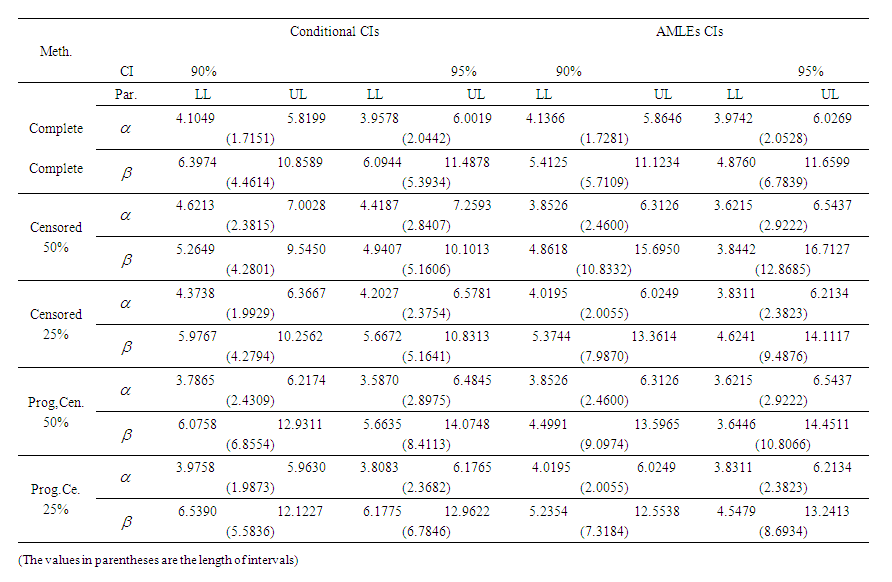
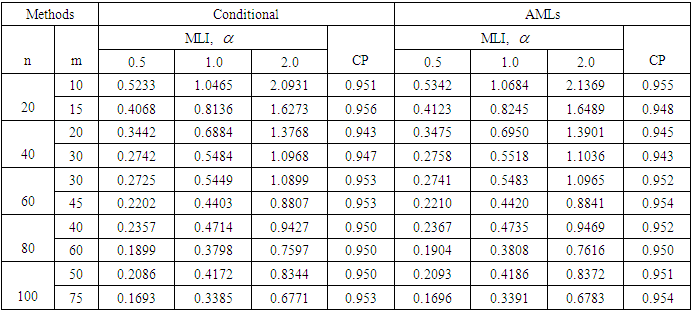
- Consider data in Wingo (1983) representing the relief times in hours of 50 arthritics patients receiving a fixed dose of analgesic, which fits the Burr type-XII distribution. 0.70, 0.84, 0.58, 0.50, 0.55, 0.82, 0.59, 0.71, 0.72, 0.61, 0.62, 0.49, 0.54, 0.72, 0.36, 0.71, 0.35, 0.64, 0.85, 0.55, 0.59, 0.29, 0.75, 0.53, 0.46, 0.60, 0.60, 0.36, 0.52, 0.68, 0.80, 0.55, 0.84, 0.70, 0.34, 0.70, 0.49, 0.56, 0.71, 0.61, 0.57, 0.73, 0.75, 0.58, 0.44, 0.81, 0.80, 0.87, 0.29, 0.50 Thus, for comparison purposes, the 90% and 95% confidence intervals for the parameters
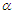 and
and 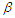 are derived based on the conditional and the AMLEs approaches. The results in Table 1 indicated that the length of intervals for the parameters
are derived based on the conditional and the AMLEs approaches. The results in Table 1 indicated that the length of intervals for the parameters 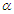 and
and 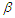 based on the conditional approach are smaller than those based on the AMLEs approach that ensures the simulation results.
based on the conditional approach are smaller than those based on the AMLEs approach that ensures the simulation results. 5.2. Application Data for Failure Components
- Consider the data in Wingo (1993) representing the failure times for 30 specific electronic components included in the life test, which are censored after 20 failures using type-II censoring. These failure times (in months) are: 0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 0.9, 1.2, 1.6, 1.8, 2.3, 2.5, 2.6, 2.9, 3.1The AMLEs for the parameters
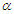 and
and 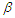 are 1.29118 and 0.63779 respectively. Wingo (1993) derived the 0.90% confidence intervals for the parameters based on the pivotal quantities.For
are 1.29118 and 0.63779 respectively. Wingo (1993) derived the 0.90% confidence intervals for the parameters based on the pivotal quantities.For 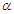 , the confidence interval is (0.8528, 1.7316) with a length of 0.8788. For
, the confidence interval is (0.8528, 1.7316) with a length of 0.8788. For 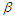 the 0.90% the confidence interval is (0.44221, 0.73692) with a length of 0.29471. For the purpose of comparison, the 90% the confidence intervals of the parameters
the 0.90% the confidence interval is (0.44221, 0.73692) with a length of 0.29471. For the purpose of comparison, the 90% the confidence intervals of the parameters 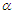 and
and 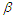 are derived based on the conditional approach as follows:For
are derived based on the conditional approach as follows:For 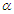 , the confidence interval is (0.8455, 1.7020) with length 0.8566, which is shorter than Wingo (1993) interval. For
, the confidence interval is (0.8455, 1.7020) with length 0.8566, which is shorter than Wingo (1993) interval. For 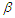 the confidence interval is (0.03089, 0.7468) with a length of 0.7159 which is longer than Wingo interval. The confidence intervals based on the AMLEs approach are: For
the confidence interval is (0.03089, 0.7468) with a length of 0.7159 which is longer than Wingo interval. The confidence intervals based on the AMLEs approach are: For 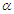 the CI is (0.8525, 1.7299) with a length of 0.8774, which is longer than the conditional ones and shorter than Wingo interval. For
the CI is (0.8525, 1.7299) with a length of 0.8774, which is longer than the conditional ones and shorter than Wingo interval. For 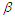 the confidence interval is (0.37895, 0.89663) with a length of 0.51768, which is longer than Wingo interval. The results of this data indicate that the confidence interval based on the conditional for
the confidence interval is (0.37895, 0.89663) with a length of 0.51768, which is longer than Wingo interval. The results of this data indicate that the confidence interval based on the conditional for 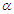 is shorter than Wingo (1993) and the AMLE confidence intervals. On the contrary, for Wingo (1993) the confidence interval for
is shorter than Wingo (1993) and the AMLE confidence intervals. On the contrary, for Wingo (1993) the confidence interval for 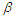 is very short because the data is not good fit for the Burr type-XII distribution based on the type-II censored sample.
is very short because the data is not good fit for the Burr type-XII distribution based on the type-II censored sample.
|
|
|
|
|
6. Conclusions
- In this paper, a new application for the conditional inference has been introduced to inference on Burr type-XII distribution based on generalized order statistics. Moreover, for purpose of comparison the asymptotic maximum likelihood estimate has been applied to measure the performance of the proposed approach based on the Monte Carlo simulations that indicated the conditional approach possess good statistical properties and it can perform quite well even when the sample size is extremly small. However, the AMLEs turn out to be impercise or even unreliable for small or highly type-II censored samples.
References
| [1] | Asgharzadeh A. and Valiollahi R. (2008). Estimation Based on Progressively Censored Data from the Burr Model. International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 3, No. 43, 2113-2121. |
| [2] | Asgharzadeh A. and Abdi M. (2012). Confidence Intervals for the Parameters of the Burr Type XII Distribution Based on Records. International Journal of Statistics and Economics. Vol. 8, No. S12. |
| [3] | Burr, I.W. (1942). Cumulative frequency functions. Annals of Mathematics. Vol. 13, 215-232. |
| [4] | Burr, I.W. (1976). The effect of non-normality on constants for  and R charts. Industrial Quality Control, 567-569. and R charts. Industrial Quality Control, 567-569. |
| [5] | Chen, Z. (2000). A new two-parameter lifetime distribution with bathtub-shape or increasing failure rate function. Statistics & Probability Letters . Vol. 49, 155-161. |
| [6] | Cook, D.R. and Johnson, E.S. (1986). Generalized Burr-Pareto-Logestic distributions with applications to a uranium exploration data set. Technometrics, Vol. 28,2, 123-131. |
| [7] | Evans, R.A. and Simons, G. (1975). Research on statistical procedures in reliability engineering, ARL, TR. 75-0154, AD A013687. |
| [8] | Evans, L.G. and Ragab, A.S. (1983). Bayesian Inferences Given a type-II Censored Sample from a BURR Distribution. Comm. in Statist. Theory Meth. A12, 1569-1580. |
| [9] | Fisher, R.A. (1934). Two New Properties of Mathematical Likelihood. Proc. R. Soc. A 144, 285-307. |
| [10] | Hakim, A.R., Fithriani, I., and Novita, M. (2021). Properties of Burr distribution and its application to heavy tailed survival time data. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 1725. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1725/1/012016. |
| [11] | Kamps, U. A. (1995). Concept of generalized order statistics. J. Statistical Planning & Inference, Vol. 48, 1-23. |
| [12] | Lai, C.D., Xie, M. and Murtly, D. N.P. (2003). Bathub-shaped failure rate life distribution. IN: Balakrishnan, N., Rao, C.R. eds. Handbokof Statistics: Advances in Reliability: Vol. 20. London: Elsevier, 69-104. |
| [13] | Lawless, J.F. (1972). Confidence interval estimation for the parameters of the Weibull distribution. Utilitas Mathematica, Vol. 2, 71- 87. |
| [14] | Lawless, J.F. (1973). Conditional versus Unconditional Confidence Intervals for the Parameters of the Weibull Distribution. J. Amer. Statist. Assoc., Vol. 68, 669-679. |
| [15] | Lawless, J.F. (1974). Approximations to Confidence Intervals in the Extreme Value and Weibull Distributions. Biometrika, Vol. 61, 123-129. |
| [16] | Lawless, J.F. (1975). Construction of Tolerance bounds for the Extreme Value and Weibull Distributions. Technometrics, Vol. 71, 255-261. |
| [17] | Lawless, J.F. (1978). Confidence interval Estimation for the Weibull and Extreme value Distributions. Technometrics, Vol. 20, 355-364. |
| [18] | Lawless, J. F. (1980). Inference in the Generalized Gamma and log Gamma Distributions. Technometrics, Vol. 22, 3, 409-419. |
| [19] | Lawless, J.F. (1982). Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data. John Wiley & Sons. New York. |
| [20] | Lee, W.C., Wu, J.W. and Hong, C.W. (2009). Assessing the lifetime performance index of products from progressively type-II censored data using Burr XII model, Mathematics and computers in simulations. Vol. 79, 2167-2179. |
| [21] | Li, X., Shi, Y., Wei, J. and Chai, J. (2007). Empirical Bayes estimators of reliability performances using LINEX loss under progressively type-II censored samples. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation. Vol.73 No. 5, 320-326. |
| [22] | Liang, W. and Yimin, S. (2010). Empirical Inference for the Burr Model based on Records. Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4, No. 34, 1663-1670. |
| [23] | Lio, Y. L., Tasi, Tzong-Ru and Chiang, Jyun-You. (2007). Parameter estimations for the Burr type-XII distribution under progressive type-II censoring. ICIC Express Letters. Vol. 1, No. 1, 1-6. |
| [24] | Kumar, D. (2017). The Burr type-XII distribution with some statistical properties. Journal of Data Science, Vol. 16, 509-534. |
| [25] | McDonald, J.B. and Richards, D.O. (1987). Model selection, some generalized distributions. Commun. Stat. Theory and Mthods, Vol. 16, 4, 1049-1047. |
| [26] | Malinowska I., Pawlas P. and Szynal D. (2006). Estimation of location and scale parameters for the Burr-XII distribution using generalized order statistics. Linear Algebra and its Applications. Vol. 417, 150–162. |
| [27] | Maswadah, M. (2003). Conditional Confidence Interval Estimation For The Inverse Weibull distribution Based on Censored Generalized Order Statistics. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, Vol. 73, No. 12, 887-898. |
| [28] | Maswadah, M.(2005). Conditional Confidence Interval Estimation For The Type-II Extreme Value Distribution Based on Censored Generalized Order Statistics Journal of Applied Statistical Science, Vol. 14, No. 1/2, 71-84. |
| [29] | Maswadah, M, and EL-Faheem, A.A. (2018). Conditional Inference for the Weibull Extension Model Based on the Generalized Order Statistics. Pak.j.stat.oper.res. Vol. XIV No.200 2, P. 119-214. |
| [30] | Mielke, P.W.Jr. and Johnson, E.S. (1974). Some generalized beta distributions of the second kind having desirable applications features in hydrology and meterology. Water resources Research, Vol. 10, 2, 223-226. |
| [31] | Amal A. Mohammed, A.A., Abraheem, S.K., and Al-Obedy, NJ.F. (2018). Bayesian Estimation of Reliability Burr Type-XII Under Al-Bayyatis' Suggest Loss Function with Numerical Solution. Journal of Physics: Conf. Series 1003. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1003/1/012041. |
| [32] | Rodiguez R.N. (1977). Aguide to the Burr type-XII distributions. Biometrika, Vol. 64, 129-134. |
| [33] | Soliman, A.S. (2002). Reliability Estimations in a Generalized Life-Model with application to the Burr-XII. IEEE Trans. On Reliab. Vol. 51, 3, 337-343. |
| [34] | Soliman, A. S., Abd Ellah, A.H., Abou-Elheggag, N.A. and Modhesh, A. A. (2012). Bayesian Inference and Prediction of Burr Type XII Distribution for Progressive First Failure Censored Sampling. Intelligent Information Management, 2011, 3, 175-185 |
| [35] | Wang, B. (2008). Statistical inference for the Burr type-XII distribution. Acta Mathematica Scientia (in Chinese), Vol. 28, 1103-1108. |
| [36] | Wu, J., Lu, H., Chen, C. and Wu, C. (2004). Statistical Inference about shape parameter of the new two-parameter Bathtub-shaped lifetime distribution. Quality and Reliability Engineering International. Vol. 20, 607-616. |
| [37] | Wu, J.W. and Yu, H.Y. (2005). Statistical Inference about shape parameter of the new two-parameter of the Burr XII distribution under the failure- censored sampling Plan. Applied Mathematics and Computation, Vol. 163, No. 1, 443-482. |
| [38] | Wu, S. J., Chen, Y. J. and Chang, C. T. (2007). Statistical inference based on progressively censored samples with random removals from the Burr type XII distribution, Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulations, Vol. 77, 19-27. |
| [39] | Wingo, D.R. (1983). Maximum likelihood methods for fitting the Burr type-XII distribution to life test data. Biometrical J. Vol. 25, 77-81. |
| [40] | Wingo, D.R. (1993). Maximum likelihood estimation of the Burr type-XII distribution parameters under type-II censoring. Microelectorn Reliab. Vol. 23, 1251-1257. |
| [41] | Wingo, D.R. (1993). Maximum likelihood methods for fitting the Burr type-XII distribution to multiply (progressively) censored life test data. Metrika, Vol. 40, 203-210. |
| [42] | Wu, J-W and Yu, H-Y. (2005). Statistical inference about the shape parameter of the Burr type XII distribution under the failure-censored sampling plan. Applied Mathematics and Computation. Vol. 163 No.1, 443-482. |
| [43] | Xiuchun, L., Yimin, S., Jieqiong, W. and Jian C. (2007). Empirical Bayes estimators of reliability performances using Linex loss under progressively Type-II censored samples. Mathematics and Computers in Simulations, Vol. 73, No. 5, 320-326. |
| [44] | Zimmer, W. J., Keats, J. B. and Wang, F. K. (1998). The Burr XII distribution in reliability analysis, Journal of Quality Technology, Vol. 30, 386-394. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML