-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1948 e-ISSN: 2163-1956
2019; 9(2): 31-34
doi:10.5923/j.ijpbs.20190902.03

Relationship between the Selected Significant Others and English Language Achievement among Secondary School Students in Kenya
Hawa A. Rabongo1, Peter J. O. Aloka2, Janet Odhiambo3
1Masters Student in Educational Psychology, Jaramogi Oginga Odinga University of Science & Technology, Bondo, Kenya
2Department of Psychology & Educational Foundations, Jaramogi Oginga Odinga University of Science & Technology, Bondo, Kenya
3Department of Special Needs Education, Jaramogi Oginga Odinga University of Science & Technology, Bondo, Kenya
Correspondence to: Peter J. O. Aloka, Department of Psychology & Educational Foundations, Jaramogi Oginga Odinga University of Science & Technology, Bondo, Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

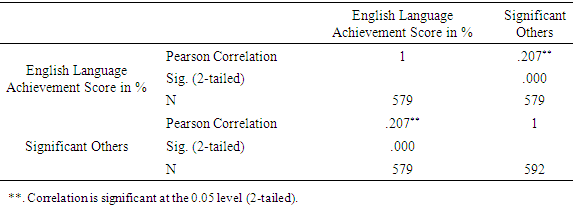
There has been relatively low level of achievement in English language among secondary school students. The present study examined the relationship between the selected significant others and English language achievement among secondary school students in Kisumu East Sub-County. The study was guided by Lev Vygotsky’s Social Development Theory. The study employed sequential explanatory design. The target population comprised 6000 form three students drawn from the 19 secondary schools in Kisumu East Sub-County. The study sample included 600 form 3 students drawn from the 19 sampled schools from Kisumu East Sub-County. Stratified Random sampling and simple random techniques were used to draw the samples. Quantitative data collection was done using questionnaires and English Language Achievement Test while qualitative data was collected using Focused Group Discussions. The instruments were validated by engaging the research supervisors to check and assess the frequency of error and accuracy. Split- half method was used to check the reliability of the questionnaire. The collected data was analyzed using the SPSS computer software version 22. Quantitative data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and inferential statistics such as Pearson Correlation Coefficient r. The qualitative data was transcribed, coded and analyzed thematically. There was a positive correlation (n=579; r =.207; p <.05) between selected significant others and English Language Achievement among secondary school students in Kisumu East Sub County, it was statistically significant. The study recommended that both the administration and the teachers, especially the Heads of guidance and Counselling (HODs) and the teachers of English put in place comprehensive programs to help the students develop positive attitude towards the learning of English language.
Keywords: Selected significant others, English language achievement, Secondary school, Students, Kenya
Cite this paper: Hawa A. Rabongo, Peter J. O. Aloka, Janet Odhiambo, Relationship between the Selected Significant Others and English Language Achievement among Secondary School Students in Kenya, International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 31-34. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpbs.20190902.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Students’ performance in English has been an issue of great concern since the beginning of modern education. In the heart of educational process are students. Further, it has been noted that all the innovations being seen in education without good performance are destined for failure (Glewwe, 2013). Globally, the main objective of education in any democratic society is to provide learners with quality education that enlightens them to be productive members of the society (Kundu & Tutoo, 2014). With globalization, English has been the language used in the world of science, commerce, trade, politics, history, education, media and technology (Kagan, 2012).Low academic performance has been a problem faced by students with low proficiency in English as literature has reported through many researches that have been carried out at school as well as college level, in several countries around the world. In the United States of America, for example, it is recorded that schools comprehensively focus on the various tasks involved in learning English for students with low proficiency in English (Pardeep, 2014). The author points out that the transition and preparation of students academically in moving to a new culture is often lost on the wayside. In the US, students who have low proficiency in English are placed in low track classes and are considered to be low level learners. They are instructed using lecture as well as paper and pencil method (Pardeep, 2014). Scholars have demonstrated that learners of English become poor performers not as a result of low proficiency in English, but as a result of the method used in instructing them (Pardeep, 2014).The question remains, however, about the way measures of academic achievement are applied in regard to the English Language Learners (ELLs) population. Measures of academic achievement in different states around the country use standardized tests (US Department of Education, 2008). These tests are used to determine all students’ college and career readiness. This is done without taking into consideration that standardized tests do not account for ELLs diverse levels of English language proficiency when measuring subject area content (Tsang et al., 2011). Ardasheva, Tretter, and Kinny (2012) asserted that it is unclear, however, what level of language proficiency ELLs need before achievement tests are able to accurately measure academic development. Therefore, the effectiveness of the new standardized test to determine the academic achievement of Mississippi students, including the ELL population, may be subject to future discussions in the field of education if additional measures, besides the utilization of standardized test scores are not included in the state accountability model. According to (Fortuny & Chaudry, 2011), In US, the learning of English is neither the sole nor the primary determinant of the academic achievement of learners of English. Availability of trained as well as prepared teachers also brings all the difference in improving the performance (Fortuny & Chaudry, 2011).This study was guided by Lev Vygotsky’s Social Development Theory. Vygotsky proposed scaffolding which is a method that helps children to learn more by working with the More Knowledgeable Other (Feldman, 2010). In educational process, it could be defined as a teaching method that helps students learn more by working with a teacher or a more advanced student to achieve their learning goals. The More Knowledgeable Other (MKO) refers to someone who has a better understanding or higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process or concept. The MKO need not be a person at all. Electronic tutors have also been used in educational setting to facilitate and guide students through the learning process. The key to MKO is that they must have (or be programmed with) more knowledge about the topic learned than the learner does. The concept of the More Knowledgeable Other is integrally related to the second important principle of Vygotsky’s work, the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD). This is an important concept that relates the difference between what a child can achieve independently and what a child can achieve with guidance and encouragement from a skilled partner.Literature on the influence of significant others and academic achievement exists. Abbott (2012) investigated the relationship between family factors and adolescent academic achievement. Secondary data was used from the Iowa Youth and Family Project data set. In this sample, parental alcohol use did not have a significant relationship with achievement, but income per capita, target sex and father marital happiness did. Wang M, (2013) the study investigates the role of significant other in shaping the academic self – concept of Chinese college students with a questionnaire research. Aspelin J, (2012) explored the influence of relationships on student achievement by examining empirical evidence and by adopting a social psychological theory. According to the analysis, relationships play an essential role in a student’s achievement. Diaz (2013) established relationships between personal, family and academic factors that account for school failure as well as determine how these factors influence each other. The result of the survey made clear the direct influence of variables such as parents’ academic level, gender, motivation, relationships between peers. Caldas, Bankston (2012) examined the relationship between the socioeconomic status (SES) of peers and individual academic achievements. Peer family social status in particular does have a significant and substantive independent effect on individual academic achievement, only slightly less than an individual’s own family social status.According to Prah (2013), other than specific courses, the language of instruction in most African countries are the European languages, such as English, French and Portuguese. Africa, therefore, stands out as one of the few developing countries where children are mainly educated through foreign languages. This is believed to be among the many reasons for the high failure and drop-out rate of African learners in the course of their school careers (Heugh, 2011). English language plays a fundamental role in Nigerian schools right from primary to tertiary level. The knowledge of the contents of school subjects is transmitted to students in all levels of education using English language as the main medium of communication, and it is presumed that students’ academic achievement is dependent to a large extent on their level of proficiency in English language (Orgunsiji, 2012).Orgunsiji (2010), indicated that English language proficiency significantly impacted on the students’ overall academic achievement. Furthermore, they found a positive significant relationship between English language proficiency of the students and their overall academic achievement. According to Yohana (2012), students’ English language performance in National Examinations has been poor for a long period of time. The author continues to point out that nearly half of the students obtained between divisions four and zero in rural as well as urban secondary schools. That sadly meant that the students graduated and left school with little proficiencies in English. As such, Tanzania, just like other multilingual communities globally, has not been able to eradicate the problem of poor language performance in education (Yohana, 2012). The secondary school English language performance is relatively below average in Kisumu East Sub-County. The information gathered in this section reveals that a lot of research has been done on the possible causes of the decline in the English language performance, such as the integration of English language and Literature in English, instructional techniques, amongst others. However, there’s scanty information on the influence of the significant others as possible factors that may also influence performance in English language. In social psychology according to (Haller 1972), a significant other is an ‘insulating person,’ uncle or aunt, grandparent, guardian or teacher- the person who guides and takes care of a child during primary socialization. The significant other protects, rewards, and punishes the child as a way of aiding the child’s development.
2. Research Methodology
- The study employed sequential explanatory design. The target population comprised 6000 form three students drawn from the 19 secondary schools in Kisumu East Sub-County. The study sample included 600 form 3 students drawn from the 19 sampled schools from Kisumu East Sub-County. Stratified Random sampling and simple random techniques were used to draw the samples. Data collection was done using questionnaires, Focused Group Discussion and English Language Achievement Test. The instruments were validated by engaging the research supervisors to check and assess the frequency of error and accuracy. Split- half method was used to check the reliability of the questionnaire. The collected data was analyzed using the SPSS computer software version 22. Quantitative data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and inferential statistics such as Pearson Correlation Coefficient r. The qualitative data was transcribed, coded and analyzed thematically.
3. Findings & Discussions
- To establish whether there was any statistical relationship between selected Significant others and English language achievement among secondary school students in Kisumu East Sub-County, a bivariate Pearson’s Product-Moment Coefficient of Correlation analysis between the scores of the two variables was conducted. The SPSS output Table 1 shows the correlation results.
|
4. Conclusions & Recommendations
- The correlation analysis indicated a statistically significant positive relationship between selected significant other and achievement in English language among secondary school students in Kisumu East Sub – County. This implies that teachers’ commitment and availability of teaching and learning resources help enhance students’ performance in English. Holding group discussions and consultations with peers also help to enhance performance. However, this study concluded that students don’t embrace this and, therefore, should be encouraged to do so. The teachers of English should device methods to help learners embrace group discussions and peer consultations. This is necessary because learners are likely to retain any information shared by the peers.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML