-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1948 e-ISSN: 2163-1956
2017; 7(3): 72-78
doi:10.5923/j.ijpbs.20170703.02

Systematic Design Infrastructure Based on the Seven Elearning Content Information Literacy Benchmarking Approach
Ameneh Soleymanzade
M.A. in Education Management, Islamic Azad University, Sari, Iran
Correspondence to: Ameneh Soleymanzade, M.A. in Education Management, Islamic Azad University, Sari, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The main mission of teaching is training for the lifelong learning and assuming that individuals have the intellectual abilities of reasoning and critical thinking. The education system must during the period as a member of society as informed citizens learn how to learn. Information literacy is the key to lifelong learning. The need for information literacy is an education standards and indicators in the model curriculum and a system for benchmarking has been implemented. The survey-based study, providing a new model for the development of information literacy and at the end of said main characteristics of this model of development, how to operate it at different levels, effective for learners letter explained. An important feature of the proposed model is consistency with international models but it is endemic to the entire country. This typology provides wide range of proposals for educational philosophers, program planners, policy makers Training and mentoring to set the course for the development of new strategies of education. The application of this model and the document propose, under the framework of the development of information targeted to the educational system will be stable.
Keywords: E-learning, Seven models, Information literacy, Benchmarking approach, Electronic educational system learners
Cite this paper: Ameneh Soleymanzade, Systematic Design Infrastructure Based on the Seven Elearning Content Information Literacy Benchmarking Approach, International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 72-78. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpbs.20170703.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Growing needs of learners in today's rapidly changing world of digital communication and technical advances and technological 1, virtualized environments and e- learners, put huge pressure on the body of traditional structure of the education system on the third millennium. Design new learning programs and models to new ways of learning at all levels is necessary and the application of information literacy, flexible out of this challenge and a new tool for designing curricula and actively provide students and students in different levels of scientific and research. Baldridge, & Deal (1983) believe that to understand the opportunities for change in the structure, people should know that the external environment, these environments are considered the most powerful source for change. Also, according to Toffler (1985) developed strongly organizations change occurs when these conditions are met; First, external pressures are not strong enough. Second, people in the organization are strongly dissatisfied with the status of the organization and order. Third, a plan and framework, model or view are coherent. The first condition is certainly described the education system as a system and are applicable to many organizations. But the third term is an attempt to analyze models and views in the media is rapidly changing and very complex nowadays, this article seeks to explain the same thing we are all; That presents a systematic model-based electronic components and elements of information literacy to learners that article presents findings. The issues that are raised in this article and to seek clarification and accountability are as follows:- What are the skills needed to develop information literacy?- What we are in the field of information literacy acknowledged and experienced?- What is the influence of this knowledge and experience on designing e-learning curriculum document?- How can we engage learners with experiences related to information literacy?E-learningThe e-learning in general the use of electronic systems such as computers, the Internet, multimedia discs, electronic publications and virtual newsletters like this; Which aims to reduce traffic and save time and money, and it would be better and easier learning. Another definition of e-learning refers to learning through electronic means of communication which has Such as the Internet, intranet, extranet and hypertext offered (Govindasamy, 2002: 287).InformationThe word "information" is comes from the root word "notification" is. Latin word "Informer" means shaping the "formatting" (Introna, 2003). The term was coined in the late middle Ages and the second half of the twentieth century has been of fundamental importance. Bergman (1999) considers the structural information for describing the state. Interested basic structure of the relationship is between sign, something and the person.Information Literacy Stern (2002) that is a range of people with different perspectives. Then on the concept of literacy is looked after from different perspectives.Alphabetic literacy: that of writing his name for Office works and gets money.Functional literacy: the ability to read, write and count is the same.Social literacy: the power to communicate in a space and cultural context.Information Literacy: power of analysis and critical assessment and use of information.Digital literacy: the power and the ability to apply information literacy in a digital environment.According to Breivik (2000) information literacy instruction set of skills, but rather a process through which it flows better way of learning and cultural approaches, also Rader (2002), in conjunction with the question: What is information literacy? States that information literacy is the ability to access, evaluate, organize and use information in order to learn, problem solving, decision making on formal and informal learning environments, workplace, environment and educational series.Several definitions of the various authorities to provide information literacy are the most important are:A) selection of appropriate information behavior to obtain the data required by any method or possible medium and necessary awareness about the importance of wise and proper use of the information (Weber, 2002).B) The ability to access, evaluate and use information by using various sources (Steeve, 2003).C) When using the information to identify, locate, evaluate, effective use of information and transfer of information in different modes (Sirman, 2003).D) Skills - related information problem solving (Gupta, 2003).
2. Design E-learning Environment Approach
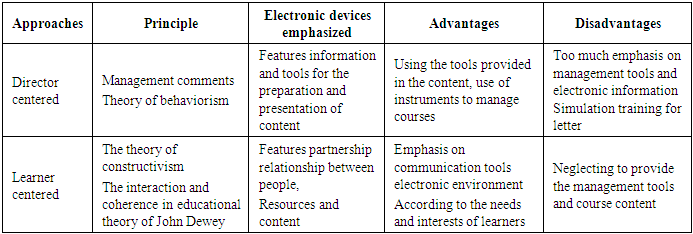
- The main issue is not access to information. We have access to more information than enough to be able to manage it. What is needed and providing it with e-learning is better methods for processing, receiving means and recreate the information. Current passive learning methods for data transfer, abilities and constructive interaction-oriented learning are in conflict. To take advantage of the potential of e-learning as a free system but coherent, it is necessary to revise the educational point of view too. Environmental design e-learning based on their knowledge of the characteristics of the environment, the design of the doors of the learning environment and learning environments are divided into two categories:A: principal axisB: learner-centeredA. Director-centered approachWith the development of a new generation of personal computers and the Internet in the late 1990s, using learning management system to provide e-Learning was common in organizations and universities. Learning management system software that measures and educational activities are recorded from beginning to end. In these systems, facilities, registration, how to access, produce and deliver content, access to materials and learning resources, learning guidance, evaluation, and save progress report is included. In the early years of designing e-learning environments, facilities and communication tools so developed often in these environments were not designed tools and information resources were used. The most important features of learning tools that are included in these learning environments include:- Key tools: signs of graft, Course Calendar, Search.- Tools provided content: presentation slides, text content and abstracts.- Tools write assignments and activity: online training and Web Quist.- Test and evaluation tools: tests, multiple choice, true false, short answers, fill – score book.- Help Tools: Tools for monitoring, follow-up conduct and evaluate the FAQ.- Communication tools: forums, share files, and internal e-mail bulletin board, whiteboard and Notes Online (Anderson & Garrison, 2003: 45).B) learner-centered approachFrom 2002 onwards, with the development of communication facilities, another approach in the design of learning environments letter introduced, according to which, e-learning opportunities should be designed so that learners according to their needs, learning style, interests and differences between their individual , personal learning tools to choose and apply. In this approach, the teacher's role as facilitator and adviser to become more nurturing learning are considered. Learning approach to the concept of educational strategies with specific goals that learner-centered approach as a specific kind of this approach to learning, this is no exception. Therefore, to implement a learner-centered learning opportunities in e-learning environment to set strategies or action are required. Each position of the e-learning dimension of learning to any learning situation shows thus its strategic objectives and positions should be known later. (Mahdavi-nasab & Pakpur, 2012) he Personal tools with learning facilities according to their own circumstances to choose, combine and apply. Development of social software has an important role in the formation of this approach. Social software is network tools that encourage learners to interact and learn from other sources and support communication between them. The tools available in this application, by helping to communicate, control and management of learning increases group interaction and the design process. E-learning system designer should be using social tools to engage learners and contribute to the formation of learning groups, exchange ideas and create networks that encourage learning. The following table shows a variety of approaches, principles and strengths and weaknesses of each are provided. (Saddlery, 2009; 108-111).
|
3. Information Literacy Models in the World
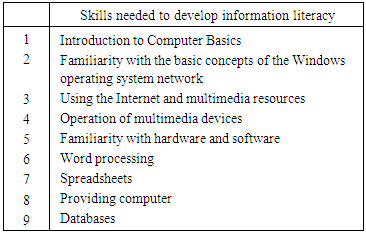
- The results of studies show the world the importance of the development of information literacy skills of staff in the development of the information society, For example, studies Ferguson in schools 900 area of Texas showed that about forty percent of the difference in the success of students in some subjects such as reading comprehension and mathematics from the expertise and information on teachers (Mirtu, 2003).New Zealand Department of Education assessment after reviewing the following steps to develop the country's schools Professional training and facilitate the use of information technology suggested by users.- Investigation and analysis of current ability of employees in information technology;- to predict Staff development capabilities on the future;- Plan to reach the planned objectives;- Preparations for coordinated staff training by providing the necessary hardware and software.In addition, the availability of computers for use by users in all parts of the organization, a computer network within the organization as well as, Possible for all students to access the Internet, including requirements for information technology development in organizational development as is. On the other hand, new research results show that in addition to the need to achieve a model for the development of information literacy, the model for each community and for the community of independently defined. On the other hand, the National Association of Information Technology in Malaysia according to the specific needs of its citizens My IUL standard for computer literacy and the development of Malaysian citizens has prepared. This Standard applies to all citizens, including workers and housewives, usable and holders of the certificate of basic knowledge and skills to use information and communication technology will have. The certificate is classified in two different levels of skills:The first level consists of skills (Quimm, 2003): Introduction to basic concepts of information and communication technology, computer applications and the Internet and Communications. The second level skills include word processing, spreadsheet, presentation and database computer (Steve, 2003). Brvnsky and colleagues in a study in 2004 among the countries of the Union of Europe concluded that despite the similarities relative culture of this country, because of the different languages, to benefit the community of IT applications and different applications each citizen in the field of IT, these communities are different models of information literacy and information literacy model, however, between 70 and 83 percent of these countries is similar, But the difference between these models result in more full effectiveness of each of the models in communities (Bronski, 2004).Shimoora in another study (2005) on this same point in the societies of Southeast Asia emphasized, saying that cultural differences between communities, the development of information technology, music, literacy and distribution of urban and rural populations have a serious impact on the development of information literacy in each of the countries there (Shimoora, 2005). Given the importance of the development of Information and Communication Technology, International Center for Technical and Vocational Training UNESCO, one of the missions important to reinforce the concepts and skills of information technology and the management of technical and vocational training based on information technology in several countries announced (Quimm, 2003). In this regard, the center of workshops on the use of ICT to improve the quality has held.
|
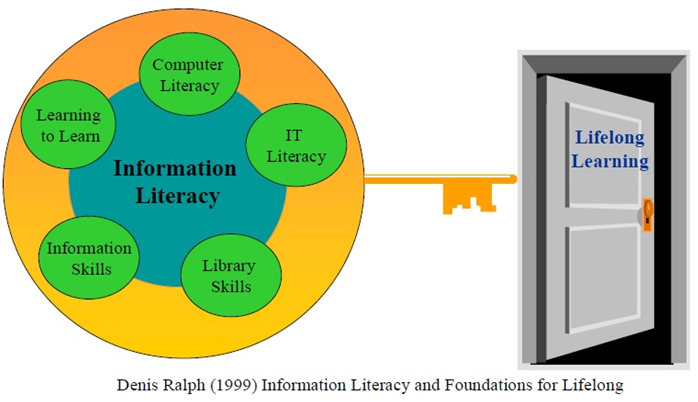 | Denis Ralph (1999) Information Literacy and Foundations for Lifelong |
4. Seven Models of Information Literacy
- Rational model or design the appropriate roles of the different ways to experience activities related to information literacy. This model reflects the experiences of the education system. In answer to the question why the model needs to be explained first: This model is consistent with theories of teaching and learning in the educational system and represents an attitude toward engagement with the world is information. Secondly: Helps us to point others in terms of our own design.First case: IT experienceAwareness and use of information technology in various disciplines has been used. This technology helps learners to communicate with each other and have good social experience.Second case: Assessment of Information resourceThis phase includes bibliographic indexing and organizing auditory information, text, image and multimedia information and the use of information technology is worth holding.Third: the experience of process information.At this stage, the process includes problem-solving and decision-making about information that involves discovering personal needs with the art of creativity and innovation. This ultimately leads to the use of information.For the fourth: control information.At this stage, learning to identify relevant information needed and information management deals and then using IT in addition to linking information, research, projects and users of the relationship between Information and a part of the project is created.Fifth place: Critical ThinkingThe following points should be considered at this stage.- Emphasis on learning.- developing a personal vision, using the knowledge gained.- Critical analysis and evaluation of the content.For the sixth: extension of knowledgeRequires the development of new mobile experiences to develop approaches, new solutions are commissioning tasks. This depends on the knowledge, creativity and innovation personal and private information learner.Seventh place: WisdomFinally, the last step leads to wisdom, insight and knowledge to be learners. At this stage the personal qualities of the individual increases, as of awareness and knowledge for the benefit of others, excellence and community uses and this knowledge, the knowledge that admiration societies with moral values and traits have been rich and fruitful.As a result of the use of information literacy, students will be able to use the information effectively in different tissues, scientific, and social and cultural and the social concept of education and its relevance to the understanding and data transmission to solve the problems on their own. By using the proposed model learners will be able to use information technology in their formal and informal communication, Control and manage their data, process information and use it in their day, based on the interests of their own making to create knowledge, A fresh perspective and provide new horizons, critical and creative thinking, and finally the conscious use of their knowledge and are effective for others.
5. E-learning Content Quality Indicators
- - Determine the nature and volume of information required and its efficiency- Critically evaluate information and resources relevant in terms of performance and value system- Goal setting, law and morality.- Organize and the right combination and the duties of learners and participants in the curriculum.- Problem-solving and creating new strategies (Bruce, 2003).Infrastructure for systematic design a curriculum that all elements of the model in that respect, and be able to effectively use information and conscious of the need to allow learners to:- Adopt a critical approach to knowledge construction.- Sensory capacity and creativity to gain insight into new cast.- When using information, not to forget ethics and values.- Information literacy should be aware of business opportunities.- The importance of information literacy in their economic development and recognize academic position (Bruce & Condi, 2000).The four basic elements in designing a document on the systematic terms:- to provide resources to facilitate the learning of these skills, continuing education courses, providing training packages Intuitive, Web-based skills and so on.- Design textbook based learning opportunities that these skills be included in it.- Learning opportunities upon which continuous interaction with the environment, science and information to learners in the curriculum is predicted.- Provide opportunities for reflection and learning documents that provide effective training intelligence activities, as well as systematic evaluation of learners with regard to elements of psychological, sociological and philosophical.
6. E-learning Design Models
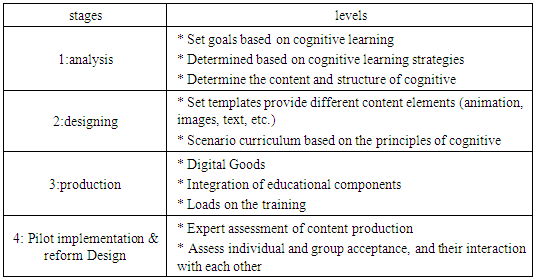
- Overall, the curriculum is defined as the basic design an educational activity (Vntlyng, 1993; 15). According to the traditional methods of eLearning, three models proposed to design and create the lesson. That include:Integrated or distributed training In this model, e-learning and related topics to be taught as a separate subject and independent and can be lower or higher levels of academic curriculum to be taught.Integrated extensive trainingIn this model, for different fields of study, a set core of information literacy skills offered and skills of information literacy in the educational field are added and consequently the students' understanding of the importance of information literacy in the field of study chosen deepens.Training in the form of extra-curricular programsIn this model, information literacy as one of the elements of e-learning and capabilities to enhance their skills in the field of career development, social and ... for extracurricular held by institutions and organizations.The design of the infrastructure for e-learning contentThe first approach means that separate training and fencing in coherent approach and flexibility training program is considered preferences; But according to the description of the case of seven information literacy education was provided according to the special atmosphere educational system, being new educational practices and evaluation of e-learning and the lack of teachers proficient in this field, in this study, the second approach, the design textbook e-learning as an integrated and broad curriculum in various training courses more efficient and more effective, and the results are far deeper and wider training provides learners letter were considered. Overall, the entire development process of a lesson in four main steps: analysis, design, production, repair trial run is planned (Mirzabeigi et al, 2009: 97). Each stage consists of different levels is to develop e-learning content. They can be summarized in the table below:
|
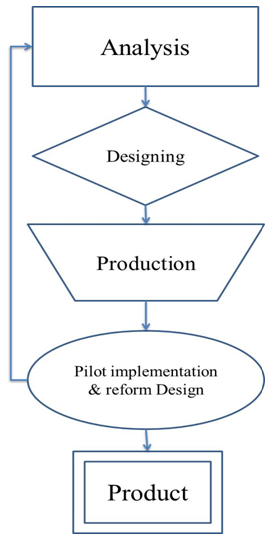 | Picture 1. Model of e-learning content development in the educational system |
7. Conclusions
- Learning and skills needed to survive in the information age to the information they need to identify, locate, and evaluate and effectively use information. Having this capability in the future for students who are in executive positions, teaching and research, put their role in society, a special place. IT as a branch of technology that uses hardware, software, thought application and network software allows you to study and application of data and processing it in various management and applications provides a significant impact also on all aspects of scientific, industrial, commercial, economic and political life is human. Grounding of the realization of the information society, human resources trained to recognize new framework governing the social relations and the characteristics of the era, the ability to obtain useful information, assess the quality and credibility, as well as how to implement them in order to produce new knowledge be. Therefore, the development of a model for the development of e-learning in the training of human resources as the most important step is literate e era of information need to identify and explain. Questions like that show information need be, adjust it. Sources of relevant information related to the information needs identified. Search strategies, tailored to the information needs of design. Information critical to the evaluation and analysis. Information obtained from a variety of sources of information and integrates with existing knowledge integration. Information obtained by maintaining intellectual property rights for the problem, need, or wants to be questioned; Based on what is learned, creates new questions.In addition to applying the proper content of e-learning in the educational system, the following recommendations may be provided for program planners, and education experts:Objectives, content and methods of implementation of information technology for social and cultural groups, each group is different, and even a closer look is unique for each student. This must be avoided in the design of the lessons from the global trends and our specific situation in education, social, cultural and consider. To achieve the educational goals of different groups, educational software must be designed to provide a learning process in different ways and knowledge be understood and be made by everyone. To achieve the goals of different social and cultural groups, as well as the necessary software design criteria such as race, class and gender, So that they can take advantage of a variety of ways to provide space for dialogue between students with different positions. It is hoped that the models and ideas expressed in this article can be curriculum planners in favor of efforts to create sustainable learning in the educational system and also to the benefit of future generations is in the new millennium.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML