-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1948 e-ISSN: 2163-1956
2016; 6(5): 219-224
doi:10.5923/j.ijpbs.20160605.04

Predicting Adjustment of Students to University Considering Positive and Negative Affects
Mikaeli Manee Farzaneh1, Isazadegan Ali1, Fekrat Reza2
1Ph.D of Psychology, Associate Professor of Urmia University, Iran
2Ph.D Student of Psychology, Urmia University, Iran
Correspondence to: Fekrat Reza, Ph.D Student of Psychology, Urmia University, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: This study aimed to predict adjustment of the students to university considering positive and negative affects in a case study of male and female students of Urmia University. Materials and Methods: This study is correlation using descriptive methods. The population included 6546 BA students of Urmia University. Using Cochran formula and simple randomization, the sample size of 486 students was achieved (d=0.5, p=0.5). To gather data, the positive and negative affects schedule (PANAS) and students' adjustment to the college questionnaire were used. Obtained data were analyzed using correlation and stepwise regression. Results: Statistical analyzes showed that there is a significant and positive correlation between all elements of the adjustment and positive affects. Results showed that positive and negative affects have significant roles in predicting the students' overall adjustment. In addition, results showed that positive and negative affects can explain and predict emotional, educational adjustment and attachment to university; but, positive and negative affects have no significant role in predicting the elements of social adjustment. Conclusions: Findings of this study showed that positive and negative affects had a significant role in predicting adjustment. Therefore, the causes of positive and negative affects in adjustment to university should get specific attention.
Keywords: Adjustment to university, Positive and negative affects
Cite this paper: Mikaeli Manee Farzaneh, Isazadegan Ali, Fekrat Reza, Predicting Adjustment of Students to University Considering Positive and Negative Affects, International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 6 No. 5, 2016, pp. 219-224. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpbs.20160605.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Universities are the centers which attract a considerable population of the youth. Attending university provides students with the experiences and opportunities for social and psychological evolution [16]. However, entering university is a stressful experience [11, 25] that may lead to the problems for the new-comers [29]. Without a successful adjustment to university, students may quit studying at university or reveal maladaptive responses. Attending university accompanies many changes in the students´ lives. Decreased parental control, more freedom, main changes in daily programs, increased expectations in the educational and social fields, prevalence of adjustment problems and anxiety increase are some of these changes [1]. This series of changes are considered serious and acute stress for some people so that 60% of the students leave university without finishing their courses in the first two years of their studies [3, 15]. Students’ adjustment is a process that should be considered by the researchers, experts and consultants. The term of adjustment refers to a person ´s attempts to get along with and survive in the social and physical environment [13]. In the notion of adjustment, there are two fundamental and personal factors. Adjustment of the students to the university is students´ experience about academic, social and personal-emotional compatibility with learning environment including the concepts of goal setting, goal commitment and attachment to the institute since their arrival there [6]. Adjustment to the university is adaptation to the prevalent norms and requirements of the university. From this perspective, the student needs to adjust to the laws and official rules of this environment and its unwritten rules [12].Paskarla and Terenzini [30] believe that adjustment to the university includes socialization and de-socialization. De-socialization requires changing or putting aside the values, qualities and believes that a person brings with him/her to the university which are not effective in the present situation. In contrast, socialization is reforming values, attitudes, and qualities that are necessary for succeeding in adjustment to the new environment. Baker and Siryk [8] stated four dimensions of university adjustment in which academic adjustment is associated with educational goals and main university requirements. If a student gains such an adjustment, he /she will easily handle the homework and educational requirements of the university. Interpersonal social requirements refer to the university experience in social adjustment. Social adjustment refers to the desire to engagement in the events and activities that enable and sustain relationships with other people. High levels of this adjustment refers to the student's satisfaction with the social dimensions of the university whose lower levels are associated with the student´s loneliness and perception from few opportunities of social interaction and support. Personal/emotional adjustment refers to the psychological and physical anxiety level of the student after entering university. Positive adjustment with the environment leads to the mental and physical health. Students who don’t adjust to the environment are more likely to experience anxiety and depression. From the other hand, affects are important aspects of human behavior with an important role in human life. Some scientists like Darwin assert that emotions are beneficial for human survival since they direct their activities toward a goal and make human do some things that are necessary for his survival, making him aware of harmful activities [27]. Affects can take the form of a state or quality. In the state form, positive affects are a person's enthusiasm for life, proactivity and astuteness. Negative affect refers to a general internal dimension and unpleasant employment, indicating undesirable affective states such as anger, hatred, disgust and fear. High positive affects in the form of an attribute or quality accompany high energy, full focus, and an enjoyable employment, active engagement and confrontation with the living environment and satisfaction with the social interactions. In contrast, when the positive affect is low, one will feel lethargy, sadness, and discouragement. While, people with negative affects tend more to dissatisfaction, have negative attitude towards themselves and are considered dissatisfied [9]. Different studies have shown that positive and negative affects influence satisfaction with the education and life [25, 32]. Shivy et al. [37] found that people with lower positive affects feel more problems associated with their life and work, expecting these limitations in the future. As a result, they have little hope for improving conditions and lower satisfaction levels. Positive affects can influence satisfaction with the life and work through achieving the goals [22]. Positive affects have an important role in creating happiness and general satisfaction with the life [21, 34]. Sanjuan [35] showed that satisfaction with life and other indices of positive adjustment are strong indicators of emotional maladjustments (depression and anxiety) in the men with coronary diseases. Slade [36] stresses using positive psychological approaches along with associated educational and medical services for the employed staff [36]. Arc et al. [4] showed that people with flexibility and adjustment show higher intention to express positive affects when confronting indefinite emotional experiences. In their belief, this may relate to the abilities of these people in dealing with different and difficult situations with an interpersonal nature. Results of Fredickson and Tavged [18] showed that proactive flexibility has a positive correlation with positive affects but it has a negative correlation with negative emotions of anger and sadness. Regarding the contradictory findings in this field and for the separation and psychological pressures many students confront in the first months of entering university, this study aimed to predict male and female students’ adjustment to the university and its correlation with the positive and negative affects of Urmia university.
2. Methodology
- This study is correlation using descriptive methods. Statistical population included all BA students of Urmia university (n=6546). Statistical sample of 486 students was obtained using simple randomization and Cochran formulation (d=0.5, p=0.5). 600 standard questionnaires whose descriptions come below were distributed among the participants from which 486 questionnaires were returned and analyzed.Positive and negative affects of students' schedule (PANAS). This measure was prepared by Watson et al, [5] including 10 questions scored by a five point Likert scale. Chronbach Alpha of this questionnaire was reported to be 0.76 in previous studies. This measure has been frequently used in Iran and its validity has been confirmed [26]. Mozaffari [42] reported positive Chronbach Alpha of 0.83 and negative Chronbach Alpha of 0.65.Students' adjustment to college questionnaire (SACQ). This questionnaire was provided with 67 self-report questions by Baker and Siryk (1984) consisting of four subscales of academic adjustment (24 questions), emotional-personal adjustment (15 questions), social adjustment (20 questions), and attachment to university (8 question). Every question was scored by a five point Likert scale (1 = it is not true for me at all, 5=it is completely true for me). Higher scores in this measure represent higher adjustment level and low scores indicate higher difficulty in adjustment to the university. Baker and Siryk (1984) reported Chronbach Alpha of 0.92-0.95 for this questionnaire and Alpha values of 0.81-0.90 for the academic adjustment, 0.77-0.86 for emotional-personal adjustment, 0.83-0.91 for social adjustment, and 0.85-0.91 for attachment to the university. Michaeli Manee (2009) reported Chronbach Alpha of 0.84, 0.69, 0.72, 0.9 for the academic adjustment, emotional-personal adjustment, social adjustment, and attachment to the university, respectively and general consistency value of 0.78.
3. Results
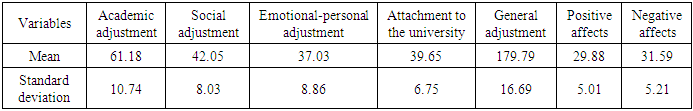
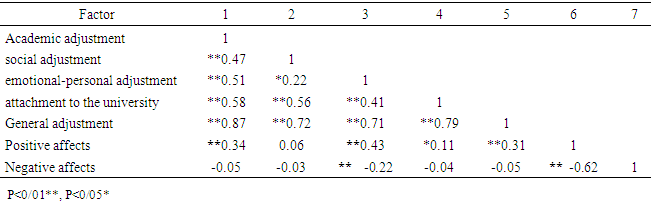
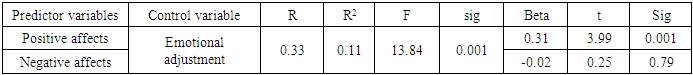
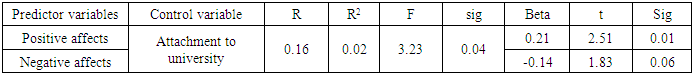
- After elementary investigations, data of 486 participants were analyzed. Mean and standard deviation of the age for the girls (n=284) was 21.71(5.36) and it was 21.47 (3.06) for the boys (n=202). 26 participants were married and 458 were single. 332 participants were local but 154 of them were not local. 70 participants were employed and 416 participants were unemployed. 44 students had failure history but 442 of them lacked that. Mean and standard deviation of the sample scores in the predictor and control variables are represented in Table 1.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion and Conclusions
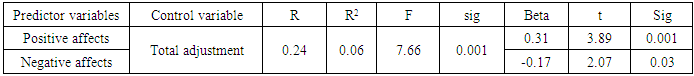
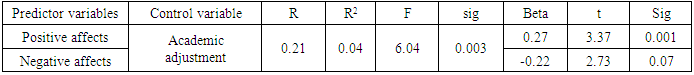
- Fast and great social changes may lead to incompatibility. The isolation and separation from friends, acquaintances and relatives and getting into an unfamiliar environment such as a university makes a person confront the risk of incompatibility difficulties. Thus, this study aimed to predict the adjustment of the students with the university and the predictive role of positive and negative affects in this regard in Urmia University.The first finding of this study showed that positive and negative affects had a significant role in predicting adjustment. The results regarding positive and negative affects´ correlation with the students’ adjustment is in line with the results of previous studies [8, 17]. WKCC and YT [41] reported that positive affects have a mediating role in the relationship of distress symptoms and psychological adjustment. Fredicson [17] believed that emotions and affects improve self-efficacy in humans, preparing them for facing life changes. In other words, positive affects lead to positive attitudes, facilitating life challenges and adjustment [8]. Positive attitude and optimism are the outcomes of having positive affects, improving psychological adjustment with increasing health and well-being level. Positive affects include joy, happiness, satisfaction, pride and negative affects include negative emotions such as guilt, shame, sadness, anxiety, anger and stress [14]. Positive affects play an important role in improving health through strengthening immune system. Positive affects lead to the engagement and confrontation with the social environments such as university. People with high positive affects enjoy the companion of others, having trust and satisfaction in their social interactions. From the other hand, people with low positive affects lack energy, enthusiasm and trust. They are cornered and introvert, avoid enthusiastic experiences and have doubts about active engagement with the environment. People with high negative affects tend to unhappiness and sadness, having negative attitudes towards themselves; while people with low negative affects are relatively calm and satisfied with themselves [2]. In this study, findings have showed negative and positive affects´ role in predicting the changes of academic adjustment. Findings showed that having positive affects really help people to be better and act more successfully, gaining good results [38] and higher academic adjustment. But, negative affects have inhibitive role in improving this adjustment. Because, people with negative affects are pessimistic and disappointed, not trying to improve their situations. Results of this study agree with Moosavi et al. [28]. They found that emotional hygiene is a predicting factor for the educational adjustment and academic success of the students. In fact, students with learning disabilities as a result of low levels of social and emotional adjustment face different problems in the field of communicative, interpersonal, discouragement, anxiety, and depression. These problems negatively influence academic adjustment of the students along with their social, academic and emotional achievements and educational and learning failure of the students. Another result of this study showed that predictor variables of positive and negative affects don’t have significant roles in predicting social adjustment. This finding disagrees with Forgas et al [19] who found that subjects with positive and happy spirits communicated more actively, used non-verbal signs and behaviors in their interactions, spoke more their friends about themselves, behaving more skillfully. In contrast, sad subjects with negative attitude faced lower friendly and confidant contacts. Using social skills, students can find their positions in social interactions with other students and gain social positions and this leads to the social adjustment. In fact, a person gets benefitted from adjustment when he or she can communicate effectively with his or her social environment and satisfy her or his motivations; otherwise, he or she is considered incompatible. This incompatibility may result from measurement tools and differences in the studied groups. The role of cultural differences should not be ignored. Analyses showed that positive affects have a significant role in predicting emotional adjustment elements. It must be mentioned that emotional adjustment can include good mental health, satisfaction with personal life, and the harmony of emotions, activities and thoughts. In other words, emotional adjustment includes mechanisms by which a person finds emotional stability [33]. Positive emotions may lead to the increased emotional adjustment. Tellegen [40] believes that positive and negative affects are correlated with depression and anxiety. Low positive affects and high negative affects are correlated with psychological disorders [2]. These mental disorders in the people with negative affects influence emotional adjustment. Emotional adjustment and its related elements like emotional intelligence about self-control provide more effective solutions for practical problems, helping the proper behaviors and reactions of the person Pankerato [31].Extremera et al. [43] found that the youth who have problems in self-identification and don’t have necessary abilities in controlling their emotions don’t have a good control over stressful conditions, understand stress nature with higher intensity and own lower psychological adjustment [43]. Analyses showed that positive affects have a significant role in predicting attachment to university. This finding agrees with Barzegar [7]. He found that positive affects are positively correlated with attachment to university. In other words, students with positive affects have higher attachment to university. A part of the study ´s limitations were as follows; statistical population of this study included university students. Thus, their generalization to other populations has some limitations. Therefore, it is suggested that similar studies should be conducted on other age groups. Second, data was obtained through self-measurement tools. Therefore, they can be combined with the evaluations of clinical experts to prevent from likely biases. Taking such measures indicate new patterns of correlations that can spread our theories effectively.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Authors appreciate all people who assisted them in conducting this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML