-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1948 e-ISSN: 2163-1956
2016; 6(3): 119-127
doi:10.5923/j.ijpbs.20160603.04

Personality, Social Anxiety and Excessive Use of Facebook
Arooj Zahra Rizvi
Beaconhouse National University, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Arooj Zahra Rizvi , Beaconhouse National University, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of the present study was to investigate the relation between Personality, Social anxiety and excessive use of Facebook. The research method is a quantitative approach, by using a questionnaire 150 participants were used, 75 females and 75 males between ages 17 to 27 was approached. Instruments included demographic and related to facebook use questionnaire, International Personality Item Pool (Goldberg, 2002) and Social Avoidant and Distress Scale (Watson, 1969). Pearson’s- Product Moment correlation was used to analyze the relation between personality, social anxiety and use of facebook and T- test independent was used to analysis gender differences. The results indicated that the both gender male and female use facebook equally, and no significance difference was found with high level of social anxiety. Whereas, no significant difference was found between how often participant log in to facebook with social anxiety. On other hand result as shows no significance difference between Neuroticism, Agreeableness, Openness & Consciousness with social anxiety, where as extroversion is negatively correlated with social anxiety. However, there is no significant relationship between how often participant log into facebook with Extroversion, Neuroticism, Openness, Consciousness and Agreeableness. In conclusion, the findings shows that personality traits and social anxiety didn’t linked with excessive use of facebook.
Keywords: Personality traits, Social anxiety, Facebook
Cite this paper: Arooj Zahra Rizvi , Personality, Social Anxiety and Excessive Use of Facebook, International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 6 No. 3, 2016, pp. 119-127. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpbs.20160603.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The recent growth of Facebook to over one billion users has given people a massive virtual stage on which they can perform. Facebook is easily accessible with more than half of the users using it on their mobile devices. Facebook’s mission statement is “to give people the power to share and make the world more open and connected” (Facebook.com, 2012). Facebook users can add friends, update their status, share opinions, exchange messages both publically and privately, share photographs and their location and whomever they are with a that location. Facebook notifies the user if they have received any updates, this can be by email or a phone notification. Almost half of the population of Pakistan is Facebook users, with the majority between eighteen and forty four, 47% are male and 53% female (Mehdiali, 2011). Sheldon et al. (2011) found people are using facebook to avoid feelings of disconnection; from real world problems and their own problems. Some people use facebook to get information about their relatives, and friends (Bonds et.al. 2010). Facebook provides the ideal environment for a “hoped for possible self” (Mehidizadeh, 2010, p358), this statement emphasizes on the individual social desire and identities to establish the right circumstances. (Mehdizadeh, 2010).This research build on the psychological aspects of Facebook use most of which has been centered on personality traits and convenience sample of the student population. This research focus on the relationship of excessive use of facebook with social anxiety which have had less investigation in terms of its role in the lives of users of Facebook. Facebook can fulfill curiosity and enhance social bond’s, it can also cause stress and negative feelings. The question whether Facebook member’s are socially anxious people or which personality trait they are belonged.The phenomena of using internet are determining people to use facebook as it is socially influenced by other. Teo et al. (2009) conducted a research among Singaporean in which he tried to find out how the people of Singapore are effected by facebook use in related to having numbers of friends in use of social online sites. As he belief that facebook is the only one site which is mostly used by Singaporean and other country members. He predicted that people use website by the connection they have in real world to connect them by online too. The predictions of his questions concluded that peer is affected by online sites as it play an important role in their life to be connected with others. His findings are also confirmed by Cheung and Lee (2010) study as he also find the relation of facebook use in peer generation. Cheung and Lee (2010) developed his research on the basis of theoretical model which is developed by Kelman (1974; quoted by Cheung and Lee, 2010, p.25), in which he presents three modes of social influence. One is subjective norm of compliance and the process by which individual start using internet or specific sites by influenced of friends and family members. Secondly mode on social influence of group norm which represent individual decision of values e.g. interest of groups or communities. Third is the social identity the individuals emotional and feeling of being evaluative his place in group of community. Around 389 students were taken by Cheung and Lee (2010) in which 54% were males and 46% were females. He found most of the student used facebook to maintain the subjective norms and social identity. As social norms have meaningful impact on a person to adopt internet things as where family members and friends are represented their opinion and suggestions. On other hand social identity relates to recognition of self by others as it occur by joining communities to share own feelings and interest of self and finding outs to be part of social acceptance. Survey was conducted by Stern and Taylor (2007) on initiate relationship among facebook using. 364 university students were taken to find the relation of facebook and its link to their personal life. He found less number of facebook users meet new people on facebook to develop initiate relationship and most of them have already relationship which they try to maintain via facebook. He also find that people mostly use facebook to connect with others who are far away from them like out of country (Golder et al., 2007; Sheldon, 2008; Dong, 2008). Bryant and Marmo (2009) carried out study in which he tried to find out what kind of relationship college students had with their facebook friends and what are the behaviors they adopted to maintain the relationship and how they used the strategies to changed the type of relationship. He found that facebook does not allow developing a close relationship to maintain it. According to them, he also founded that people only use facebook to communicate with new people and send private messages to share information on confidentially. He also founded that facebook is cheap and easily connect to other for maintain the new relationship with other country members. In contrast to Stern and Taylor study he also founded similar results that students most use facebook to in touch with distance friends and family members rather than making romantic relationships (Stern and Taylor, 2007, p.17). The clarification of both studies shows that Stern and Taylor’s results show less cheap suggestions regarding use of facebook and developing initiating relationship and maintain it then Bryant and Marmo’s study. In fact, private messages send by any sites like hotmail or facebook does not function exclusively between the sender and the receiver to maintain romantic relationships with their partners to be public.Many of studies done on personality and it traits. Through which we get to know that personality is most important part of our life. If any individual is in trouble or in tension automatically its personality is affected by their behavior. Personality is made up of thoughts, feeling and behavior (Mayer, 2005). Different researchers evaluate the relation between facebook use and their personality. Recently at Boston Medical Centre researcher published a review that all over the world people are conducting research related to facebook and personality that how they both variable interact with each other ( Nadkarni and Hofman 2012). After analyzing the data from the world its shows that facebook usage confirms the gratifies its users and deal them by their individual characteristics. Many of the researchers conduct study on personality and its traits that how it interact with different activities in daily life and how user engage on facebook rather than spend less time on facebook. From many decades researchers have studied personality traits and how it shape the modern lives of person in the time of Facebook.A paper-based survey was conducted by Ross et al. (2009) in northeast US private university. In which he take around 400 level class students with all majors subject. Student are voluntarily participate in survey. To measuring the personality factor the items were selected from the FFM. Then self reported answers were concluded by student how much time they spend on facebook each day.In conclusion of this survey he found those who are high on extraversion are likely to be in facebook groups. High on neuroticism are always be on wall post as it is there favorite part on facebook. Further openness individual reported that facebook is the source to be sociable. More over the author find few findings in relation to personality variable. On the other hand the survey was conducted by Amichai- Hamburger and Vinitsky (2010) he found those who are high on extroversion had big list of friends and they are not associated with number of group’s friend. Both Ross et al. (2009) and Amichai-Hamburger and Vinitsky (2010) didn’t find any relationship between personality traits and the intensity of use of facebook.Further, different studies also mentioned that extraverted users are more facebook user than the introverted users (Ryan. et.al. 2011). Different types of personality traits are related with facebook use. As mentioned in many studies extraverts have large connection with internet sites, conscientious people are less user of facebook and other net worksites, agreeableness people used facebook wall as they focus on themselves and want other too look them. On other hand neuroticism link with the time spent on facebook (Moore. et.al. 2010). Other studies also conclude that people who are more likely to be social and want to be in contact with social world they are always high on neuroticism and they seek social contact via any social sites. No significant relationship was found with Extraversion, openness and conscientiousness related to facebook use (Hughes et al. 2012). Further, Muscanell and Guadagno (2012) conduct research in which he measured neuroticism and found no relationship with any of the specific social networking activities and other personality traits are also not link with any social sites.Ross et al. surveyed undergraduate and graduate students and found that personality variables were associated with some aspects of Facebook use (Ross et.al. 2009). They found that individuals high on the trait of extraversion were more likely to belong to Facebook groups than introverted individuals. Those high on the trait of neuroticism reported that the Wall was their favorite Facebook component. Openness to experience was found to be related to higher levels of being sociable through Facebook. More generally, the authors commented that “one of the most surprising outcomes from the present study was the relatively few significant findings in relation to the personality variables.” Amichai- Hamburger and Vinitsky (2010) found that students who were high on extroversion had a greater number of Facebook friends but contrary to Ross et al. (2009), extraversion was not associated with the use of Facebook groups. Both Ross et al. (2009) and Amichai-Hamburger and Vinitsky (2010) were not able to find a relationship between personality variables and the intensity of Facebook use. Ryan and Xenos (2011) found that extraverted Facebook users would be more likely to use Facebook than introverted users. Moore and McElroy (2010) found that personality variables are significantly related to different types of Facebook use. Extraverts tended to have a significantly wider social network than introverts. Conscientious people tended to use the Facebook wall function significantly less than other individuals and individuals high in agreeableness were more likely to post wall content about themselves. However, only neuroticism was significantly related to the time spent on Facebook. Hughes et al. (2012) found that Individuals who were more socially oriented and high on neuroticism tended to be more likely to seek social contact via Facebook. Extraversion, openness and conscientiousness were found to have no significant relationship with Facebook use. Muscanell and Guadagno (2012) on the other hand, found that neuroticism was not significantly related to any of the specific social networking activities that they measured. They did find that extraversion, agreeableness, openness and conscientiousness did predict specific types of social networking use. One of the study was conducted by Fernandez (2013) in which he explores the relationship between social anxiety, internet use and Facebook use. The finding shows the individual with higher social anxiety reported increased internet use, to avoid face to face interactions. These individuals also reported higher Facebook importance but not higher Facebook use (Fernandez et.al. 2013).In UK, nonprofit Anxiety unit conduct a study in which they used polling system to get the answer about social media uses i.e. facebook. They founded that 51% of people are saying that social networking sites changes their life as, they feel hesitant while interacting with others. But facebook change their life and make it easy for them to interact with those people whom they are unable to connect. On other hand, 45 percent people said they feel uncomfortable and worried when they are unable to connect with facebook or there emails, while 60% people said they are tired and feel fed up with facebook or other sites used so they need to power off all the connections to rid off and secure self from un predictable technology. (www.anxeityuk.org.uk)Further, from different researches some data was revealed that two third of people had difficulty while using social media in sense to continuously connected with other. 25% people reported that they feel insecure to maintain relationship on online as in real world they are unable to interact easily with other. In UK Salford Business School conduct a small survey of 228 participants for Anxiety UK's research. Small sample size was used, but the results shows the participants are addictive of social media to overcome their anxiety by use of social sites. So its showed people mostly use facebook or other social media sites to overcome their social anxiety in real world life. On other hand mobile mindset company also conduct a survey to found that how lost mobile panic for internet addictives. In study they found 73% people would panic when they lost their mobiles and 54% people reported that they constantly checking their mobiles while sleeping. However, social media may cause some anxiety, and people suffer from higher fever of it. As Katherine bindley, (2013) reported that amount of time spent on facebook reduce the anxiety as people feel pleasant while having good conversation with love one. She also found anxious people use more facebook to control their physiological problems and reduce the sign of depression. (www.huffingtonpost.com)From the institute of social anxiety Richards (2012) highlights about the symptoms of social anxiety that it is negatively judged by other people which leading to fear of them and situation where they felt about it. He also said that it is factor which lead to depression. Social anxiety also termed as social phobia which is much more common in people. Around the world millions of people are suffering from social phobia on every day bases. Epidemiological studies publish the statistical rank of social anxiety disorder in united state as the third largest psychological disorder after depression and alcoholism in the country. Related to facebook use many websites explain the relation with social anxiety as they say facebook is more favorable for those people who are in relationship rather than who are not or beginning the close relationship (Ellison et al., 2007). On other hand Forest (2012) also explain that those who are low on self esteem automatically have negative remarks related to facebook use and likely don’t make friends as they avoid to interact with anyone (Forest & Wood, 2012).There have been several studies looking at the relationship between online networks and social anxiety. These studies give us mixed answers. One study concluded, “Although the Internet does not change a person’s actual level of social anxiety, it may decrease their perception of social anxiety when interacting online.” (Kimberlee et.al. 2010). Other research has shown that those with social anxiety may find “it easier to interact online where anonymity can be maintained rather than engage in face to face interaction where being observed by others might induce a fear.” (Robin et.al 2005).Statement of the ProblemThe impetus of current study to find the relationship between the level of social anxiety of facebook users and their personality traits. The basic concept in this study to evaluate the behavior of an individual which is affected by facebook use. As in this study the most important predictors are highlighted which affect the behavior of an individual. As personality play an important role in individual life which raises the characteristics and traits of the person. Those people who started using facebook excessively their personality changes because of the culture, environment and social values. The researches show that people use facebook to interact with other peoples. In this study main focus is on the participant and why they use facebook excessively and what its outcome. Facebook is used in areas of maintaining the relationship, constructing the identity and developing self satisfaction for psychological and emotional well being. Many of studies shows that online sites are for maintaining the relations and developing friendship for the well being (Duff 2012).Aims and Objectives of the StudyThe aim and objectives of this study are:1. To identify the level of social anxiousness in facebook users.2. To identify the personality traits of facebook users.3. To identify the level of social anxiety in personality traits.HypothesesŸ H1: Females uses more facebook as compared to males.Ÿ H2: Females have high level of social anxiety as compared to males.Ÿ H3: There is significant negative correlation between the social anxiety and how often the participants log into Facebook.Ÿ H4: There is significant negative correlation between high level of social anxiety and Neuroticism personality.Ÿ H5: There is significant Positive correlation between low level of social anxiety and Extroversion, Openness, Agreeableness and Conscientiousness personality. Ÿ H6: There is significant positive relationship between the extrovert personality and how often the participants log in to Facebook.Ÿ H7: There is significant negative relationship between the agreeableness personality and how often the participants log in to Facebook.Ÿ H8: There is significant negative relationship between the conscientiousness personality and how often the participants log onto Facebook.Ÿ H9: There is significant negative relationship between the neurotic personality and how often the participants log in to Facebook.Ÿ H10: There is significant negative relationship between the openness personality and how often the participants log in to Facebook.
2. Method
- SampleThe sample consists of 150 (75 boys and 75 girls) from different educational institution of Lahore. The inclusion criteria for the participant is to have a Facebook profile. Ages ranged from 18-27. The sample was selected conveniently from the different Institution of Lahore. Participation in the study was totally voluntary and participants were assured of the confidentiality of information was provided.MeasuresThe questionnaire contained two sections. First section, contained Facebook Use and the second section contained scales measuring Personality (International Personality Item Pool (IPIP; Goldberg, 1999) and Social Avoidant Distress Scale (Watson & Friend, 1969).Facebook UseQuestions was constructed.Do you have a facebook account? How often do you log in to Facebook? How long do you spend on Facebook on each log in? How many friends do you have on Facebook? Do you have Facebook on your mobile?International Personality Item Pool (IPIP)The IPIP was used to assess the ‘Big Five’ personality traits. The scale developed by Goldberg (1999). The IPIP contains 50 items which measure the following domains of personality: Emotional Stability (ES), Extraversion (E), Intellect (I), Agreeableness (A) and Conscientiousness (C). Each participant rated how accurately the statements described them on a Likert scale ranging from 1 ‘Very inaccurate’ to 5 ‘Very accurate’. There is general consensus among personality researchers that the ‘Big Five’ summaries the common variance across personality traits and provides a ‘comprehensive account of human personality differences’ (Matthews et al, 2003). The IPIP consists of 10 items for each personality domain. Scores for each item in each domain were added together to give an overall score for that domain. The reliability is as follows: Extraversion 0.90, Conscientiousness 0.85, Agreeableness 0.85, Neuroticism 0.88, and Openness 0.84. Negative items were reverse scored.Social Avoidant and Distress Scale (SADS)The SADS was used to assess the level of Social Anxiety in Facebook user. The scale was developed by Watson and Friend (1969). Questionnaire including 28 true & false items. It measured the two aspects of anxiety which including 4 experiencing forms: fear, discomfort, avoidance and distress situations. The SADS uses social situations in the questioning such as “I feel relaxed even in unfamiliar social situations” and “I find it easy to relax with other people”. Participants respond about how they feel in those situations by indicating if this statement is true or false. The high reliability with its internal consistency is .94 and the test reliability ranging from .68.
3. Procedure
- The data was collected from different institutions of Lahore. The questionnaires were distribute during lectures and throughout other social connections with friends and colleagues within the Colleges and were filled out during the individual’s own time. A brief verbal explanation was given to each subject and an information sheet was provided with each questionnaire explaining that the study was researching the relationships between facebook use and its relationship with personality and social anxiety. Each participant will filled a consent respond on two measuring instruments International Personality Item Pool (IPIP; Goldberg, 1999) and Social Avoidant and Distress Scale (Watson & Friend, 1969).The scores on each item will be entered in Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 18.0 for Windows. Where a significant difference was displayed (p<0.05 or p<0.01).
4. Results
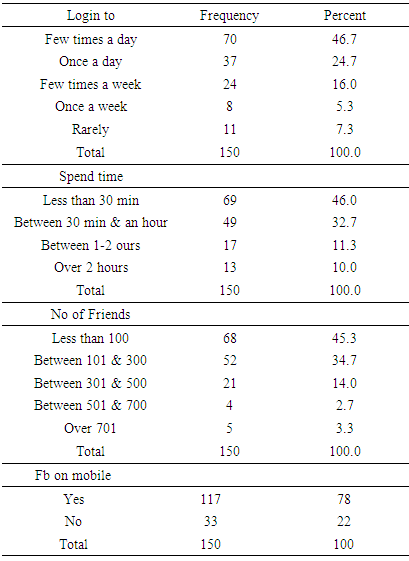
- The data collected was analyzed through Statistical Package of Social Sciences (SPSS) 22 version. All data was carefully entered and was screed for any missing value. First the frequency and percentage of the responses on facebook usage was computed. Then descriptive statistics of sample was calculated. The Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation was computed between the sub scales of Personality (IPIP), Social Avoidance and Distress Scale (SAD) and Facebook usage responses. Then independent t sample was used to find the gender differences and ANOVA was used to analyze the difference between gender group means and their associated procedures with social anxiety and personality traits.Frequencies and Percentages A series of questions were asked to participant related to facebook usage. The responses to the questions are listed below with it frequencies and percentages.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. Discussion
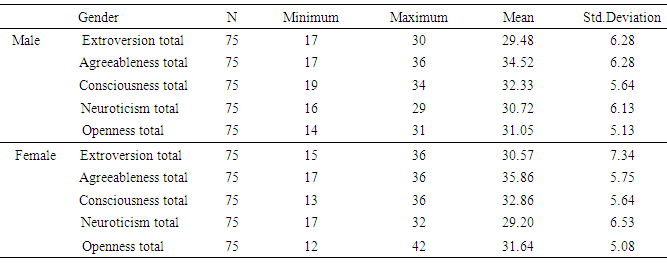
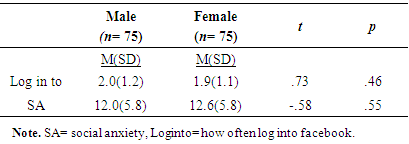
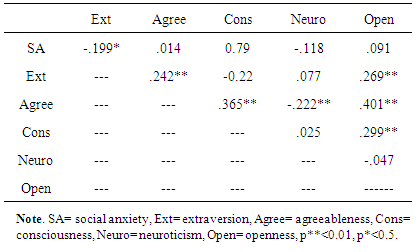
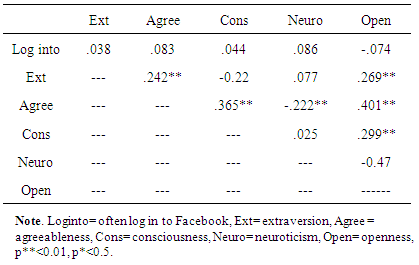
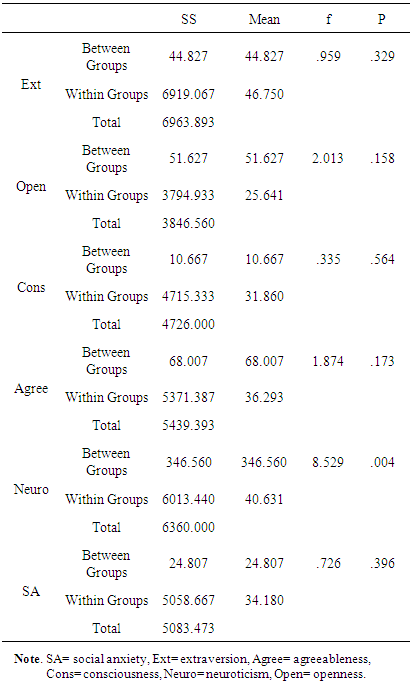
- Analysis regarding gender differences on use of facebook revealed that both male and female have equally use facebook, no significant difference was found. According to Sheryl (2013) CO of Facebook said social network is the biggest site in the world which is dominated by women and man. In the world of social network women used more social sites than male. On the other hand the time news analyst found decrease in use of facebook in women especially younger teens. As they found that now a day’s women are not interested to use facebook as it is wasted of time. Pakistani ads manager citied in paper that use of facebook in Pakistan is around10.6-11.8 million of which 7.4-8.2 million are men and 3.0-3.4 million are women (Saqib, 2013). As facebook is most popular site for interaction between friends and other people. If we review from the last year ratio of using facebook in Pakistan are decreased in women and there are many reasons to stop using it. Pakistani female are more concern about their privacy on facebook as compare to western female. In Pakistan last year lots of incidence occurs like male hack the facebook account and steal the pictures to black mail females. On other hand in Pakistan relatives are so concerned about their females. Women felt less secure by having the relationship partner who shares photos of friends and events of family and other. As in society of Pakistan those female who make friends on facebook and provide their pictures and share it with others they are judged negatively as here it consider sin.Further, no significant difference was found between high level of social anxiety in both genders male and female. In the broadest sense, it is difficult to determine girls exhibit more anxiety than boys. Taken in a general context, adolescents are highly vulnerable to anxiety due to the developmental stage they are in and the accompanying relational obstacles. But when cultural and social elements are factored in, subtle differences seem to exist in levels of self-esteem and anxiety between girls and boys. In this research the both gender are educated to understand the cultural values of their societies so that why the result seem to be not significant so the hypothesis was rejected.Moreover, it was also hypothesized that there was a relationship between social anxiety and how often the user log in to facebook. The results were not significant, a reason for this may be the participants were educated and may experience less social anxiety than younger respondents in previous studies. As the new generation don’t feel more anxious regarding getting online on facebook as they are more concern about their friends, studies, relatives in real life rather than wasting time on facebook. Further, the research was to find the positive relationship between social anxiety and extrovert personality trait and negative relationship between social anxiety and neuroticism, agreeableness, consciousness and openness personality trait. So the result finds negative relationship between extrovert personality traits. There is no research has examined relation between social anxiety and personality traits. Hence results show no significance difference in openness, agreeableness, and conscientiousness. Whereas, the neuroticism personality trait shows negative relation in this study. In 2010 Stefan et. al (2010) examine the cultural aspects related to social anxiety, he reviewed many literatures and then conclude social anxiety may occur due to different aspects like may be culturally or environmentally. As we all are human being and we belong from different society and living standers. So he said that cultures, social norms, gender roles and gender identification matter a lot. He suggests that the prevalence rate of having social anxiety is depend on the culture of people they belong. In Asia he find the lowest rate of having social anxiety than the US and Russian culture. Further, in Pakistan the norms of living standard and cultures are strong’s so might be in high living standard social anxiety didn’t follows as in rural areas of Pakistan. Thus, it is possible that cultural norms are contributing to social anxiety and other emotional feelings or disorder in contrast to cultural orientation of a person. Further, no significant relationship was found between agreeableness personality and users log in to Facebook. This finding follow the Wilson et al (2010) results in which he found no impact between facebook use and agreeableness. The result also support the Landers and Lounsbury (2004) study in which he also didn’t found any relationship between agreeableness and facebook, as he find disagreeable people spend more time on facebook. No significant relationship was found between conscientiousness personality and users log into Facebook. These findings support Wilson et al (2010) study where he found low on conscientiousness people spent more time on facebook as they are suspicious to interact with others. On other hand high on conscientiousness only concern about their living standers so it’s doesn’t matter for them to use social sites or not. In contrast, to Wilson et al (2010) study Marcus et al (2006) study was not accepted in this research as he found that conscientiousness was positively correlated to social network to get social approval. Hence hypothesis was not accepted as the finding of this study is not significant.Next, no significant relationship was found between the neuroticism personality and users log in to Facebook. However in this research male are high in neuroticism than female. These finding support Marcus et al (2006) findings as he find no relation between neuroticism and social networking. He said those who are high on neuroticism gain social approval and show lack in changing behavior as in this study male are high on neuroticism trait. Positive relationship of neuroticism with female indicates that they easily get social approval and they change their behavior to be more supportive. Wilson et al (2010) founded neuroticism has no impact on facebook use as it correspond to male finding because the results were not significant this cannot be proven. On the other hand, Muscanell and Guadagno (2012) result showed that neuroticism didn’t link with any social network activities. Hence, no significant relationship was found between openness personality trait and users log in to Facebook. Wilson et al (2010) study support this hypothesis as he found no relationship between facebook use and openness. As he believed that social network is no longer new creation so the person with openness trait had no interest in it. So far, the same result was found in present study as facebook had not been on market too long to constantly use. So the hypothesis was not accepted.Well in this present study the results seem like there is no proper relationship between excessive use of facebook and the personality traits extraversion, neuroticism, openness and conscientiousness. As the same results was shown in Hughes research as he think facebook develop and change the personality of a single person. (Hughes et al. 2012). On the other hand, Muscanell and Guadagno (2012) result showed that neuroticism didn’t link with any social network activities. He just focused on neuroticism trait in link with social network, he didn’t measure other personality traits.Evidence and results of present study has suggested that personality traits have no influence on Facebook use. However both females and males result was not significant. The reason of it may the cultural differences and the participant was educated to understand the social norms and there values. As this present study is support by Vasalou et al. (2010) study as he conduct research on different five countries to find whether culture is a prenominal for facebook use. As in his result he founded that culture aspect are mostly link by country to country. Using the social media or network is depending on every country culture that how they perceives and think about it. Well it is important to find out how and what is basic reason of changing behavior of personality trait towards facebook use. However, in this year the use of facebook decreased around 2.5% which shows people are no more interested in use of facebook (Facebook Press, 2013).
6. Conclusions
- In this study we discussed about personality traits and social anxiety in context to influence on social network i.e. facebook. The findings and material were taken from literature review. The findings of this study uncovered the reality and emphasize on the role and implications regarding use of social network and tell how its effect on people’s lives. Finally, it is clear that results of the present study show that there is no link between personality trait and social anxiety with Facebook usage. Present findings give new idea and results as other researcher said that women are more addicted to use social network than males, so far in this research both gender use facebook equally and have no significant relationship between facebook use. Further, researcher discussed the need of privacy of facebook use as they think it is not relevant theme among the users. They feel that people use social network sites to present their emotions, feelings and beliefs but in this study we find that both genders are worried about the privacy of facebook. Further the social anxiety is pent up due to the feelings and emotions toward others and specially the privacy and safeguarded phenomenon of social network sites.
7. Limitations of Study
- The present study included 75 males and 75females and focused mainly on which personality trait used more facebook and how they act toward social anxiety. There are certain weakness were founded in methodology of all studies when concluding the findings of research. So, one of the limitation of present study is correlation design was used which is not sufficient for the related finding of current study. Cross cultural and longitudinal studies should be beneficial to find the aspects and factors of personality traits in contract to feeling of social anxiety for a long period of time. Unlikely, co relational study just explores the current relation between variables and excessive use of facebook. In this study, small amount of information given on personality traits of social anxious people. So further more research was needed to explore the relationship between personality traits and social anxiety.Another limitation was the sample size was small, finding in this study are just guideline not a worldwide indictor that personality traits don’t link with facebook use. Social anxiety and personality traits should be studied more detailed to know which trait are more anxious. Research in this area is not much detailed to uncover the essential feature of it to conduct future research. Finally the direct assessment of social anxiety is not sufficient in current study. As the real pathology of it is different so it needs to be more excessive and use it for specifically to assessed the level of social anxiety to established the status for clinically purpose for social network.
References
| [1] | Amichai-Hamburger, Y., and Vinitzky, G. (2010). Social Network use and personality. Computers in Human Behavior, 26 1289-1295. |
| [2] | Cheung, C. M. K., & Lee, M. K. O. (2010). A theoretical model of intentional social action in online social networks. Decision Support Systems, 49, 24-30. |
| [3] | Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C. & Lampe, C. (2007). The benefits of Facebook “friends”: Social capital and college students’ use of online social network sites. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 12, 1143–1168. |
| [4] | Facebook. (2006). Retrieved May 31, 2012, from www.facebook.com. |
| [5] | Fernandez KC, Levinson CA, Rodebaugh TL. Profiling: predicting social anxiety from Facebook profiles. Social Psychological and Personality Science. in press <http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1948550611434967>. |
| [6] | Forest, A. L. & Wood, J.V. (2011). When social networking is not working: Individuals with low self-esteem recognize but do not reap the benefits of self-disclosure on Facebook. Psychological Science, 23, 295–302. |
| [7] | Hughes, D. J., Rowe, M., Batey, M. and Lee. A. (2012), A tale of two sites: Twitter vs. Facebook and the personality predictors of social media usage. Computers in Human Behavior, 28 561-569. |
| [8] | Mayer, J. D. (2005). A tale of two visions: Can a new view of personality help integrate psychology? American Psychologist, 60, 294-307. |
| [9] | McCrae, R.R., and Costa, P.T. (1987) Validation of the five-factor model of personality across instruments and observers, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52 81-90. |
| [10] | Mehdizadeh, S. (2010). Self-Presentation 2.0: Narcissism and Self-Esteem on Facebook. Cyberpsychology, Behavior & Social Networking, 13(4), 357-364.doi:10.1089/cyber.2009.0257. |
| [11] | Moore, K. and McElroy, J. C., (2012). The influence of personality on Facebook usage, wall postings, and regret. Computers in Human Behavior, 28 267-274. |
| [12] | Muscanell, N. L. and Guadagno, R. E. (2012). Make new friends or keep the old: Gender and personality differences in social networking use. Computers in Human Behavior 28 107-112. |
| [13] | Nadkarni, A., and Hofmann, S. (2012). Why do people use Facebook? Personality and Individual Differences. 52 (pp. 243- 249). |
| [14] | Richards, T. A. (2012, April 2). Comprehensive Cognitive- Behavioral Therapy. Social Anxiety Institute. Retrieved September 14, 2013, from www.socialanxietyinstitute.org. |
| [15] | Robin, M. S., and Robert, J. E. (2005), Reasons for Internet Use and Social Anxiety. Personality and Individual Differences, 27, 167-200. |
| [16] | Ross, C., Orr, E., Sisic, M., Arseneault, M., Simmering, M., and Orr, R. (2009), Personality and Motivations Associated with Facebook Use. Computers in Human Behavior 25.2: 578-586. |
| [17] | Ryan, T., and Xenos, S. (2011). Who uses Facebook? An Investigation into the relationship between the Big-Five, shyness, narcissism, loneliness and Facebook usage. Computers in Himan Behaviors, 27, 1658-1664. |
| [18] | Sheldon, K. M., Abad, N., & Hinsch, C. (2011). A two-process view of Facebook use and relatedness need-satisfaction: Disconnection drives use, and connection rewards it. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 100, 766-775. doi:10.1037/a0022407. |
| [19] | Stern, L. A., & Taylor, K. (2007). Social networking on Facebook. Journal of the Communication, Speech & Theatre Association of North Dakota, 20, 9-20. |
| [20] | Teo, J., Seng, S., & Fu, W. (2009). Network effect in adoption and use of online social network sites: the case of Facebook. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication, Boston, MA. |
| [21] | Vasalou, A., Joinson, A.N., & Courvoisier, D. (2010). Cultural differences, experience with social networks and the nature of “true commitment” on Facebook. International Journal of Human- Computer Studies, 68, 719-728. |
| [22] | Wilson, K, Fornasier, S., & White, K.M (2010). Psychological Predictors of Young Adults’ Use of Social Networking Sites. Cyberpsychology, Behavior & Social Networking, 132), 173-177. |
| [23] | https://www.anxietyuk.org.uk/news/for-some-with-anxiety-technology-can-increase-anxiety/. |
| [24] | http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/07/10/social-media-anxiety_n_1662224.html. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML