-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1948 e-ISSN: 2163-1956
2015; 5(6): 216-219
doi:10.5923/j.ijpbs.20150506.03

Effect of Memory Load on Visual Search
Ryotaro Saito 1, 2, Hideyuki Okuzumi 3, Mitsuru Kokubun 3
1Division on Education and Development Science for Individuals with Special Needs, Tokyo Gakugei University, Japan
2Research Fellow of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Japan
3Department of Special Needs Education, Tokyo Gakugei University, Japan
Correspondence to: Ryotaro Saito , Division on Education and Development Science for Individuals with Special Needs, Tokyo Gakugei University, Japan.
| Email: | 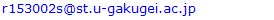 |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Visual search functions require visual attention for the detection of particular stimuli from large amounts of information. In a state of storing a target stimulus, visual search is performed to determine whether the stimulus in front of the eye is a target stimulus. Therefore, the number of stimuli to remember is believed to affect performance of the task. This study examined the effects of memory load on visual search using the cancellation task. Participants were 28 healthy adults. Participants performed six type cancellation tasks consisting of the number of target types: 1–6. Results showed that canceling efficiency became lower as the error increased and that the time to completion is prolonged by an increase in the number of target types. The effects of increasing the memory load on the visual search showed strong correlation in the logarithmic function, which suggests that when the target types are few, the effect of the number of target types on the task performance is strong, but for numerous target types, the effect of the number of target types on the task performance is weak.
Keywords: Visual search, Cancellation task, Memory load
Cite this paper: Ryotaro Saito , Hideyuki Okuzumi , Mitsuru Kokubun , Effect of Memory Load on Visual Search, International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 5 No. 6, 2015, pp. 216-219. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpbs.20150506.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Visual search is a function that requires visual attention to find a specific target stimulus (target) among other interference stimuli (distractors). Using this function, humans process the selection of specific information from much information.Several tasks are used to measure visual search. One is a cancellation task, which is a paper-and-pencil test that requires the placement of a mark through each occurrence of a specific target that is displayed on the sheet of paper among distractors. Some cognition and motor skills such as sustained and selective attention, visual search, psychomotor speed, and fine motor coordination are needed for the cancellation task (Byrd, Touradji, Tang, & Manly, 2004). This task was used originally as an assessment tool for visual neglect patients, Alzheimer-related diseases and developmental disabilities (Amieva, Lafont, Dartigues, & Fabrigoule, 1999; Sandson, Bachna, & Morin, 2000; Solfrizzi et al., 2002; Bottini, & Toraldo, 2003; Jones, Lemley, & Barrett, 2008; Huang, & Wang, 2009; Huang, & Wang, 2012). However, in recent years, it is also being used to investigate the visual search characteristics of healthy people (Lowery, Ragland, Gur, Gur, & Moberg, 2004; Pradhan & Nagendra, 2008).Performance is evaluated in terms of accuracy and speed in the cancellation task. Many studies used number of errors and time to completion as such evaluations. The performance score (PS), which was first introduced by Geldmacher (1996), is also frequently used as an index of cancelling efficiency that evaluates both accuracy and speed of the performance at the same time (Geldmacher, 1998; Huang, & Wang, 2008, 2009).Cancellation tasks are influenced by the stimulus type, arrangement, and target-to-distractor ratio (T/D ratio). Effects of these factors have been examined in many studies. For instance, when shapes are used as stimuli, cancellation tasks are more difficult for healthy adults and persons with unilateral spatial neglect than when letters are used (Weintraub & Mesulam, 1988). Such tasks are also more difficult for children when letters are used as stimuli and when complex stimuli are used than when simple geometric shapes are used (Marra et al., 2013). Reportedly, the tasks are easier when using shapes that pop out (Geldmacher, 1998). For the stimulus array, some results of studies have suggested that it is easier to perform the task in an structured array than in a random array (Wang, Huang, & Huang, 2006; Weintraub, & Mesulam, 1988), but results of other studies suggest that a structured array is difficult (Huang & Wang, 2008). For the T/D ratio, some studies have demonstrated that the search efficiency is increased when the distractors are fewer (Geldmacher, 1996; Nakajima, Ikeda, & Okuzumi, 2013).A cancellation task is necessary when seeking many targets in a state of storing the target stimulus (Woodman, Vogel, & Luck, 2001). Therefore, fewer target types for stored performance are assumed to give better task performance. Some studies have revealed that execution of two target tasks requires a longer time to completion, with more errors, than a single target task (Caplan, 1985; Curran, Brignell, Fletcher, Middleten, & Henry, 2002; Curran, Kleckham, Bearn, Strang, & Wanigaratne, 2001; Hatta, Yoshizaki, Ito, Mase, & Kabasawa, 2012). However, the time and errors cannot be considered separately. Moreover, they have not been considered for the effects of applying an additional memory load, so those study results remain controversial.This study was conducted to examine the effect of a memory load such as an increased number of target types to be memorized for the visual search using the cancellation task. Previous studies mostly use one or two target types, but no linear relation has been clarified. In this study, up to six target types are used to assess details of the effects of memory load.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
- Participants were 28 Japanese university student volunteers (11 men, 17 women; M = 22.3 yr, SD = 1.49, range= 20–27) from a university in Tokyo, Japan. All participants were right-handed with 1.0 or better vision. They self-reported that they were free of physical illness, visual or motor problems, and perceptual or cognitive disorders.
2.2. Stimuli and Experimental Design
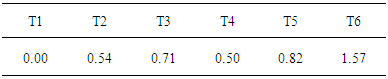
- Stimuli were 35 types consisting of concrete pictures (e.g. animal, vehicle, stationery) used on license from Memory Cards (Kogumakai Corp.). This task used 12 targets and 48 distractors. In all, 60 stimuli were arranged on standard white A4 paper (21×29.7 cm). Stimuli were arranged in 10 columns and 6 rows.Participants performed six cancellation tasks consisting of target types 1–6 (T1 task, T2 task, T3 task, T4 task, T5 task, T6 task). Distractors were of 14 types except the 21 types used in the target among 35 stimuli types as whole tasks (Table 1).
|
2.3. Procedure
- The participants were seated at a desk, where they performed a practice trial in a cancellation task involving only one line. After the practice trial, they began the experiment trials. Experimental trial was divided in the memory phase and the perform phase. First, in memory phase, participants tried to store the stimuli that are the target and stimuli were hidden at the end of memory phase. And participants were immediately transition to the perform phase. For perform phase, the task paper was flipped first. Participants turned over the paper at the time of the start signal and began checking. Participants were required to seek stimuli presented as targets as accurately and quickly as possible. Using a stopwatch, the time was measured from a participant’s first mark until the pen was put down. The order of the six cancellation tasks was randomized.
2.4. Analysis
- The numbers of incorrect responses, the numbers of correct responses, the time to completion, and the performance score (PS) were calculated. PS was obtained using the following formula (Geldmacher, 1996). Higher PS represents that the number of correct responses per unit time is larger and that the canceling efficiency is higher.
 CR stands for correct responses, TTa denotes total targets, and TTi represents total times.For time to completion and PS, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) of the number of target types (six levels) was conducted using software (SPSS22.0 for Windows; SPSS Inc.).
CR stands for correct responses, TTa denotes total targets, and TTi represents total times.For time to completion and PS, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) of the number of target types (six levels) was conducted using software (SPSS22.0 for Windows; SPSS Inc.).2.5. Ethical Approval
- Our experimental protocol was administered in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional review board. Informed consent was obtained from all participants in advance.
3. Results
- Table 2 shows means of the number of errors for each task. Results show that the number of errors is greater for the T6 task than for the T1 task. In the T1 task, no one committed a single error; in the T6 task, more than one error was observed on average.
|
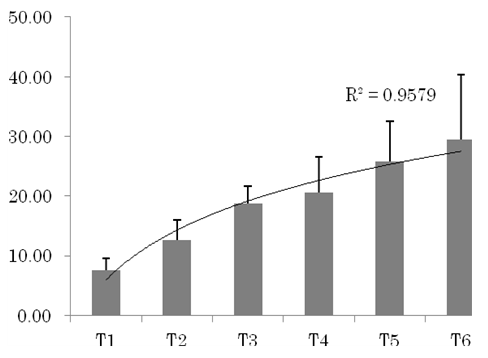 | Figure 1. Means and standard deviations of time to completion in each task and logarithmic approximation curve and the R2 value by the logarithmic function |
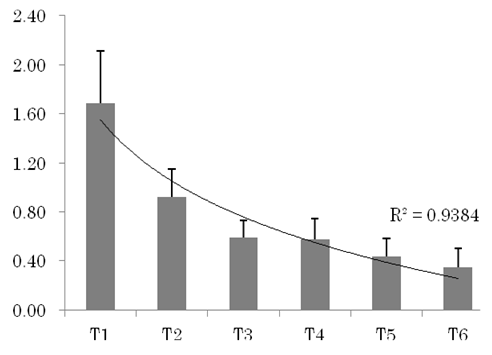 | Figure 2. Means and standard deviations of performance scores in respective tasks, with a logarithmic approximation curve and the R2 value by the logarithmic function |
4. Discussion
- This study examined the effect of memory load amount in visual search using cancellation tasks. As results, the following were found.The number of errors tended to increase as the number of target types to remember increased, which supports earlier findings (Caplan, 1985; Hatta et al., 2012) and which suggests that the load on storage and processing increases with the number of stimuli that must be remembered, which leads to errors and oversights. Regarding the time to completion, the time increased along with the number of target types remembered. A study of working memory found that the task time increased concomitantly with the number of stimuli remembered (Ozonoff & Strayer, 2001). In the visual search context, an increase in the number of targets to remember is associated with the increased number of times a person must check a stimulus against whether or not to match it with any target. When specifically examining the memory load, no difference between 3 and 4 or 5 and 6 target types was observed, which suggests that an irregularity exists in the memory load that affects the processing speed in visual search. For PS, the canceling efficiency began to decline: the number of targets increased, which suggests that the search entailed increased difficult according to the greater memory load. However, no difference was found between task performances results obtained using three target types and four target types.For the time to completion and PS, strong correlation was found with a logarithmic function, which suggests that when the target types are few, effects on the time to completion and PS by the number of target types are strong. When the target types are numerous, effects on the time to completion and PS by the number of target types are weak.Limitations of this study were the following. First, we did not study memory and search strategies. It is possible that a participant’s search strategy changed according to the number of stimuli to be remembered. Furthermore, the number of stimuli against one target differed among conditions. In contrast, each distractor stimulus was arranged by equal numbers. Therefore, it is likely that a difference in the degree of pop-out occurred in this study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I would like to give heartful thanks to Mr. Ikeda whose comments and suggestions were innumerably valuable throughout the course of my study. This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows Grant Number 15J11313 & JSPS Kakenhi Grant Number 26381309.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML