| [1] | Dodge, K. A., & Price, J. M. (1994). On the relation between social information processing and socially competent behavior in early school-aged children. Child Development, 65(5), 1385-1397. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1994.tb00823.x. |
| [2] | Eron, L.D. & Huesmann, L.R. (1984). The relation on prosocial behavior to the development of agression and psychopathology. Agressive Behavior, 10, 201-211. |
| [3] | Hindley, P., Hill, P., McGuigan, S. & Kitson, N. (1994). Psychiartric disorder in deaf and hearing-impaired children and young people:A prevalence study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 35(59), 917-934. |
| [4] | Van Eldik, T., Treffers, P., Veerman, J. & Verhulst, F. (2004). Mental health problems of deaf Ducth children as indicated by parents' responses to the child behaviour checklist. American Annals of the Deaf, 148(5), 390-394. http://muse.jhu.edu/journals/american_annalsy_of the deaf. |
| [5] | Feelinger, J., Holzinger, D., Sattel, H. & Laucht, M. (2008). Mental health and quality of life in deaf pupils. Eurapean Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 17(7), 414-423. doi:10.1007/s00787-008-0683-y. |
| [6] | Barker, D. H., Quittner, A. L., Fink, N. E., Eisenberg, L. S., Tobey, E. A. & Niparko, J. K. (2009). Predicting behavior problems in deaf and hearing children: The influences of language, attention, and parent-child communication. Development and Psychopatology, 21, 373-392, doi: 10.1017/S0954579409000212. |
| [7] | Dammeyer, J. (2010). Psychosocial development in Danish population of children with cochlear implants and deaf and hard-of hearing children. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 15(1), 50-58. doi: 10.1093/deafed/enp024. |
| [8] | Harvey, H. & Kentish, R. (2010). Factors related to emotional and behavioural difficulties in children with hearing impairments. Educational & Child Psychology, 27(2), 23-32. |
| [9] | Stevenson, J., McCann, D., Watkin, P., Worsfold, S. & Kennedy, C. (2010). The relationship between language development and behaviour problems in children with hearing loss. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 51(1), 77-83, doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02124. |
| [10] | Hooper, S. R., Swartz, C. W., Wakely, M. B., deKruif, R. E. L. & Montgomery, J. W. (2002). Executive functions in elementary school children with and without problems in written expression. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 35(1), 57- 68. doi:10.1177/0022219402035000105. |
| [11] | Howley, M. & Howe, C. (2004). Social interaction and cognitive growth: An examination through the role-taking skills of deaf and hearing children. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 22(2), 219 243. doi: 10.1348/026151004323044582. |
| [12] | Hintermair, M. (2013). Executive functions and behavioral problems in deaf and hard-of- hearing students at general and special schools. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 18(3), 344-359; doi: 10.1093/deafed/ent003. |
| [13] | Buss, A. (1961). The Psychology of Aggression. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. |
| [14] | Felson, R. B. (2000). A social psychological approach to interpersonal aggression. In V B. Van Hasselt & M. Hersen (Ed.), Aggression and violence: An introductory text.(pp. 9-23). USA: Allyn and Bacon. |
| [15] | Marschark, N. & Wauters, I. (2011). Cognitive functioning in deaf adults and children. In M. Marschark & P.E. Spencer(Eds.). Oxford handbook of deaf studies, language and education. Vol. I, Second Edition (pp, 486-499).Oxford. Oxford Universitiy Press. |
| [16] | Cuhadaroglu, H. (1993). Adolesanlarda depresyon ve anksiyetenin birlikte görülmesi: Gözden geçirme. Türk Psikiyatri Dergisi, 4(3), 183-188. |
| [17] | Most, T., Shinga-August, E. & Meilijson, S. (2010). Pragmatic abilities of children with hearing loss using cochlear implants and hearing aids compared to hearing children. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 15, 422-437. Doi:10.1093/deafed/eng032 |
| [18] | Buss, A.H., & Perry, M. (1992). The Aggression Questionnaire. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63(3), 452-459. |
| [19] | Archer, J., Kilpatrick, G. & Bramwell, R. (1995). Comparison of two aggression inventories. Aggressive Behavior, 21(5), 371-380.doi:10.1002/1098-2337(1995)21:5<371::AID-AB2480210506>3.0.CO-2-p. |
| [20] | Harris, J.A. (1995). Confirmatory factor analysis of the Aggression Questionnaire. Behavior Research & Therapy, 33(8), 991-993. |
| [21] | Meesters, C., Muris, P., Bosma, H., Schouten E. & Beuving, S. (1996). Psychometric evaluation of the Dutch version of the Aggression Questionnaire. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 34(10), 839-843.doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0005-7967(96)00065-4. |
| [22] | Archer, J. & Haigh, A.M. (1997). Do beliefs about aggressive feelings and actions predict reported levels of aggression? British Journal of Social Psychology, 36(1), 83–105. doi:10.1111/j.2044-8309-1997.tb01120.x. |
| [23] | O’Connor, D.B., Archer, J. & Wu, F. (2001). Measuring aggression: Self-reports, partner reports, and responses to provocation situations. Aggressive Behavior, 27(2), 79–101. Article first published online: March 30, 2001.doi: 10.1002/ab.2. |
| [24] | Ireland, J.L. & Archer, J. (2004) .The association between measures of aggression and bullying among juvenile and young offenders. Aggressive Behavior, 30(1), 29–42. Article first published online: January 27, 2004. doi: 10.1002/ab.20007. |
| [25] | Can, S. (2002). “Aggression questionnaire” adlı ölçeğin Türk popülasyonunda geçerlilik ve güvenilirlik çalışması. (Unpublished master’s thesis). Genel Kurmay Başkanlığı, Gülhane Askeri Tıp Akademisi Haydarpaşa Eğitim Hastanesi Ruh Sağlığı ve Hastalıkları Servis Şefliği, İstanbul. |
| [26] | Björkqvist, K., Lagerspetz, K. M. J., & Kaukiainen, A. (1992). Do girls manipulate and boys fight? developmental trends in regard to direct and indirect aggression. Aggressive Behavior, 18(2), 117-127. doi:10.1002/1098-2337(1992)18:2<117::AID-AB2480180205>3.0.C0; 2-3. |
| [27] | Piskin, M. (2002). Okul zorbalığı: Tanımı, türleri, ilişkili olduğu faktörler ve alınabilecek önlemler. Kuram ve Uygulamada Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi, 2(2), 531-562. |
| [28] | Yamasaki, K. & Nishida, N. (2009). The relationship between three types of aggression and peer relations in elementary school children. International Journal of Psychology, 44(3), 179-186.doi: 10.1080/00207590701656770. |
| [29] | Derman-Taner, M. (2013). Determining the relationship between aggressiveness and hopelessness levels of 10-11 years of children. International Journal of Social Science, 6(2), 879-889. |
| [30] | Paatsch, L.E. & Toe, D.M. (2013). A comparison of pragmatic abilities of children who are deaf or hard of hearing and their hearing peers. Journal of Deaf Studies and Education, 19(1), 1-19. doi:10.1093/deafed/ent030. |
| [31] | Günhan, Ö., Palandöken, M. & Ege, Y. (1980). Sağır dilsizlikte anaokulunun önemi. 11. Otarinolaringoloji Kongre Tutanakları, İstanbul. |
| [32] | Downs, M.P. (1982). Early identification of hearing loss, speech, language and hearing. Lass, Mc Reynolds & Northern, Yoder(Ed.), (pp. 982-999). Philadelphia, W.B Saunders Company. |
| [33] | Northern, J. L. & Downs, MP. (1984). Education for hearing handicapped children. (pp. 245-264). Baltimore. William's and Wilkins. |
| [34] | Aktas, F., Belgin, E. & Derinsu, U. (1985). İşitme kayıplı çocukların odyoloji ünitelerine havalesinde gecikme. 18. Türk OtoRinoLaringoloji Ulusal Kongresi, Bursa. |
| [35] | Ozsoy, Y., Enç, M. & Çağlar, D. (1987). Özel eğitime giriş. Ankara, AÜEBF Yayınları, No: 156. |
| [36] | Ozsoy, Y. & Ozyürek, M. (1989). İşitsel özürlüler, özel eğitime muhtaç çocuklar, özel eğitime giriş. Ankara, Karatepe Yayınları, Yeniçağ Matbaası. |
| [37] | Tuncer, O. (1989). Sağır çocukların somatik-nörolojik ve psikoentellektüel bakıları. Psikoloji Dergisi, 7, 7-16. |
| [38] | Kargın, T. (1990). Eğitsel yaklaşımlı aile rehberliğinin işitme engelli çocukların sözel becerilerine etkisi. (Unpublished master’s thesis). Ankara Üniversitesi, Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü, Ankara. |
| [39] | Ersoy, E. (1995). The evaluation of hearing impaired children’s auditory perception. (Unpublished master’s thesis). Hacettepe Üniversitesity, Institute of Health Sciences, Ankara. |
| [40] | Andersson, G., Olsson, E., Rydell, A.M. & Larsen, H.C. (2000). Social competence and behavioral problems in children with hearing impairment. Audiology, 39(2), 88-92. |
| [41] | Moeller, M. P., & Schick, B. (2006). Relations between maternal input and theory of mind understanding in deaf children. Child Development, 77(3), 751-766. doi:10.1111/ j.1467-8624.2006.00901.x. |
| [42] | Sipal, F. R. (2010). Assessing the link between executive functions and aggressive behaviors of children who are deaf: impact of early special education. Electronic Journal of Research in Educational Psyhchology, 8(3), 991-1014- ISSN:1696-2095. |
| [43] | Peterson, C. C. (2004). Theory-of-mind development in oral deaf children with cochlear implants or conventional hearing aids. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45(6), 1096-1106. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.t01-1-00302.x. |
| [44] | Leigh, I. W., Maxwell-McCaw, D., Bat-Chava, Y., & Christiansen, J. B. (2009). Correlates of psychosocial adjustment in deaf adolescents with and without cochlear implants: A preliminary investigation. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 14(2), 244-259. doi:10.1093/ deafed/enn038. |
| [45] | Sarıkardasoglu, A. (2010). The relationship between the social cognitive understanding and aggressive behaviors in children with hearing loss (Unpublished masters’s thesis). Middle East Technical University, Department of Psychology, Ankara. |
| [46] | Sipal, F.R. (2002). A Comparison of 7-11 years old normally developing and hearing impaired children in terms of their social adaptation levels. (Unpublished master’s thesis). Hacettepe Üniversitesity, Institute of Health Sciences, Ankara. |
| [47] | Coll, K. M., Cutler, M. M., Thobro, P., Haas, R., & Powell, S. (2009). An exploratory study of psychosocial risk behaviors of adolescents who are deaf or hard of hearing: Comparisons and recommendations. American Annals of the Deaf, 154(1), 30-35. doi: 10.1353/aad.0.0074. |
| [48] | McCroskey, R.L. & Kasten, R.G. (1980). Assessment of central auditory processing. In R. R Rupp & K. G Stockdell(Ed.), Speech protocols in audiology (pp.339-389). New York. Grune & Stratton. |
| [49] | Belgin, E. (1984). Çocuklarda işitme kayıplarının etyolojisi: Tanı, tedavi ve rehabilitasyon prensipleri. Katkı, 5: 1402-1405. |
| [50] | Sunal, S. & Cam, O. (2005). The research on the psychological adaptation level of the hearing impaired children in preschool period. Turkish Journal of Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 12(1), 11-18. |
| [51] | Arıcak, O. T. (1995). Üniversite öğrencilerinde saldırganlık, benlik saygısı ve denetim odağı ilişkisi. (Unpublished master’s thesis). Marmara Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü, İstanbul. |
| [52] | Tuzgöl, M. (1998). Examining aggressiveness levels of high school students whose parents have different attitudes in terms of variousvariables (Unpublished master’s Thesis). Hacettepe Üniversitesity, Institute of Social Sciences, Ankara. |
| [53] | Brubaker, R.G. & Szakowski, A. (2000). Parenting practices and behavior problems among deaf children. Child & Family Behavior Therapy, 22(4), 13-28, doi:10. 1300/J019v22n04-02. |
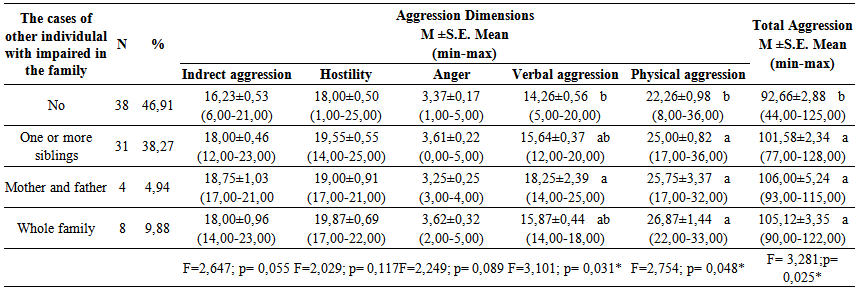
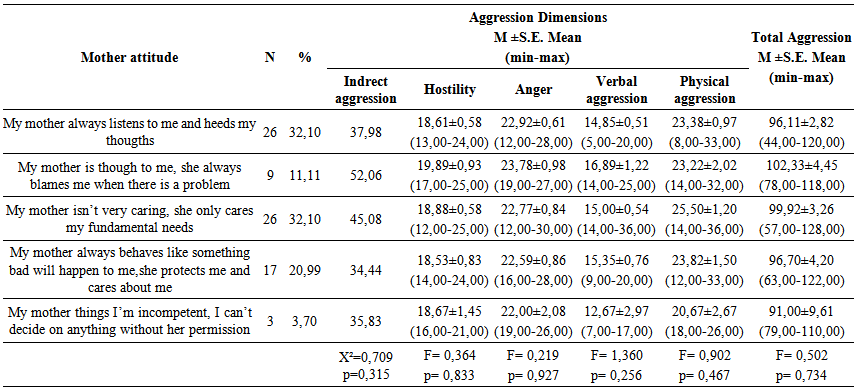
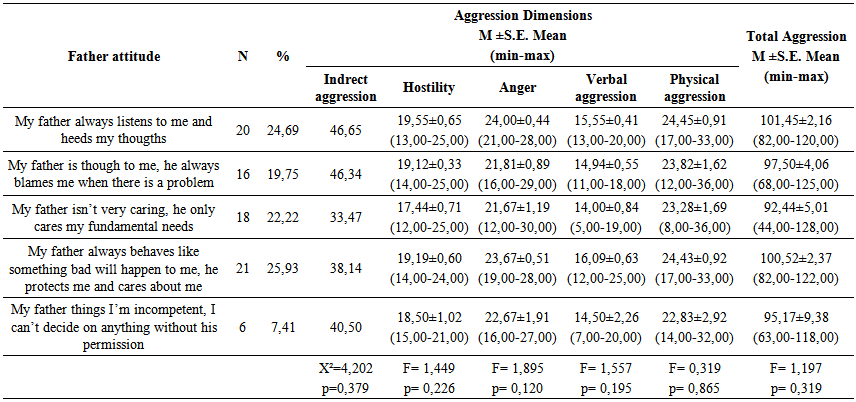
 according to the factor analysis.
according to the factor analysis.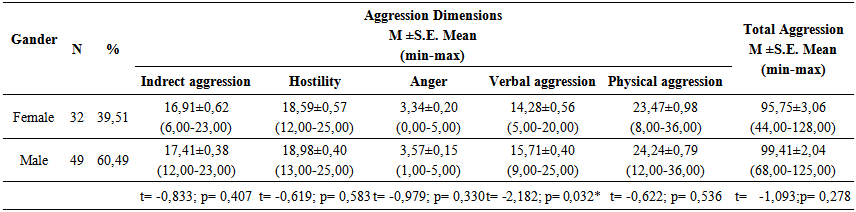
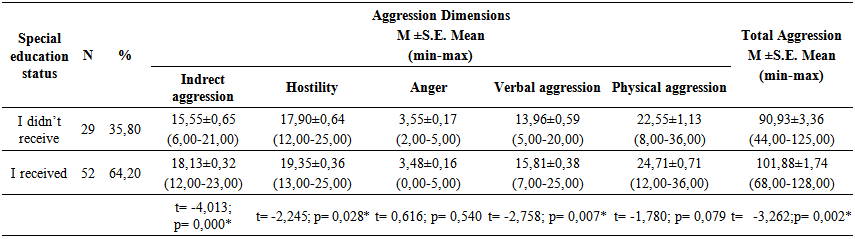
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML