-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1948 e-ISSN: 2163-1956
2013; 3(5): 131-138
doi:10.5923/j.ijpbs.20130305.03
Relationship of Appraised Stress, Coping Strategies, and Negative Affect among College Students
Chris A. Eisenbarth1, Donna A. Champeau2, Rebecca J. Donatelle2
1Department of Health Promotion and Human Performance, Weber State University, Ogden, UT, 84408, USA
2College of Public Health and Human Sciences, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, 97331, USA
Correspondence to: Chris A. Eisenbarth, Department of Health Promotion and Human Performance, Weber State University, Ogden, UT, 84408, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Within a transactional model of stress framework, the high levels of depression, anxiety, and other forms of negative affect reported by college students suggests that many students are ill equipped to cope with stress. The aim of this study was to examine a structural model depicting multivariate relationships between self-report measures of students’ appraised stress (Perceived Stress Scale), dispositional coping strategies (Brief COPE), and negative affect (Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scales). Results derived from a cross-sectional sample of college students (573 females, 551 males) indicated that appraised stress, relative to dispositional coping, was the key predictor of negative affect. Overall, the structural model tested is a useful heuristic device to identify and target specific areas for stress intervention among college students.
Keywords: Psychological Stress, Dispositional Coping, Depression, Anxiety, College Students
Cite this paper: Chris A. Eisenbarth, Donna A. Champeau, Rebecca J. Donatelle, Relationship of Appraised Stress, Coping Strategies, and Negative Affect among College Students, International Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences, Vol. 3 No. 5, 2013, pp. 131-138. doi: 10.5923/j.ijpbs.20130305.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Research suggests that many college students are stressed by the demands of school[1-3], coping poorly with these demands[4-6], and experiencing symptoms of negative affect such as depression and anxiety[7,8]. According to the American College Health Association-National College Health Assessment (ACHA-NCHA) stress is the leading health impediment to students’ academic performance and nearly a third of student respondents feel stressed and overwhelmed by school[9,10]. A substantial literaturesuggests that symptoms of stress, including depression, anxiety, and other forms of negative affect, are chief concerns of students[7,9-11], and generally more common among students than in the general population[12,13]. Moreover, stress has been linked with a variety of negative coping behaviors in the college population, including behavioral disengagement, suicide ideation, and substance abuse[7,14]. Given such findings, it is not surprising that college student stress is a matter of growing concern for researchers and health professionals. As such, research is needed to examine appraisals of stress, methods used to combat stress, and the differential impact of such appraisals and methods on the experience of stress among college students—all objectives of this study. By garnering such knowledge, scientists and service providers will be more apt to assist students with stress and maximize the students’ educational experience.
1.1. Conceptual Overview of Stress
- There is no consensus on a definition of stress, but the most popular conceptualization is the transactional model forwarded by Lazarus and Folkman[15]. In short, the transactional model of stress posits the following: (a) an individual encounters stressful demands, either internal (e.g., esteem issues) or external (e.g., project deadlines),commonly referred to as stressors; (b) he or she evaluates these demands, a cognitive process called appraisal, to determine whether the demands tax or exceed his or her available resources to deal with the demands; (c) negative affect, or feelings of unpleasantness such as depression and anxiety, is assumed to be a characteristic adjunct of appraised stress; (d) the individual subsequently engages in cognitive and behavioural efforts both to manage the appraised demands, called problem - focused coping, and to regulate negative affect, called emotion-focused coping; and finally, (e) the implemented coping efforts are supposed to lead to some change in the individual’s well-being, such as a decrease in negative affect. Although there is disagreement about the causal directionality and the relative importance of the concepts of appraisal, coping, and affect, most researchers agree that these are fundamental elements of the stress phenomenon. Various taxonomies of coping also exist[16-19] but the dimensions of problem- and emotion-focused coping provide a simple, overarching theoretical framework that allows for the integration and simplification of a larger domain of coping strategies.
1.2. Empirical Overview of Stress
- A number of investigations with college students have provided support for the theoretical relationships between appraised stress with both coping and affective well-being. Research has revealed significant and positive associations between students’ levels of appraised stress, their use of emotion-focused coping strategies such as avoidance, detachment, and distancing from stress[20-24], and their reported negative affect[7,23,25,26]. Conversely, significant negative relationships have been found between the use of more problem-focused coping strategies, characterized by active attempts to address the stressor, with appraisedstress[5,23] and negative affect[25,26] among college students. The cumulative evidence tends to suggest that the use of problem - focused coping strategies, compared to emotion - focused strategies, is related to fewer self - reported symptoms of negative affect and less appraised stress.
1.3. Problem Statement and Purpose
- Evident from the preceding discussion, the concepts of appraised stress, coping, and negative affect appear to be related. Still, a paucity of research with college students [5,27,28] has examined the multivariate relationships among these variables within a theoretical framework, and many questions still remain. For instance, no consensus among researchers has been achieved as to the utility of problem- versus emotion-focused coping in predicting stress outcomes such as negative affect. As such, the purpose of this study was to test the goodness of fit of a model depicting the multivariate relationships between measures of appraised stress, coping strategies, and negative affect among college students.
1.4. Research Hypotheses
- Based on previous research with college students, the following model relationships were forwarded: (a) appraised stress was hypothesized to be positively and significantly related to negative affect[20,23,27], problem- and emotion - focused coping[22,23]; (b) emotion-focused coping was hypothesized to be positively and significantly related to negative affect[7,21,26]; and (c) problem-focused coping was hypothesized to be negatively and significantly related to negative affect[25,29].
2. Method
2.1. Participants
- Participants (N = 1124) consisted of male (n = 551) and female (n = 573) college students enrolled in large, baccalaureate core classes at a large university in the northwest United States. Eighty percent of the participants were 18 to 20 years old, with less than five percent being older than age 26. Approximately 70 percent of theparticipants identified themselves as White, European American, with no other ethnic group exceeding nine percent of the total sample. Most students were single (88 percent), did not work (63 percent), lived in residence halls (53 percent), and were enrolled in 15 to 17 term credits (46 percent). Prior to data collection, the project received institutional review board approval for the protection of human participants in research.
2.2. Measures
- A cross-sectional, self-report survey format was used to collect data. The participants completed a questionnaire that assessed demographic background information, appraised stress, coping styles, and negative affect.
2.2.1. Appraised Stress
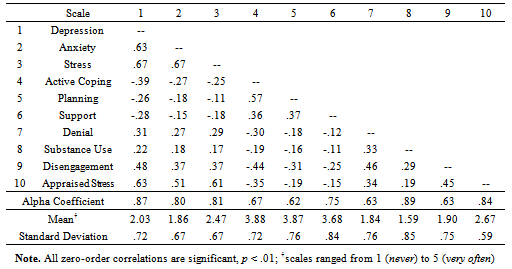
- The Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) was used to evaluate the nonspecific appraised stress of participants[30]. The PSS consists of 10 items that assess the degree to which respondents believe that life demands exceed their capabilities to cope. Respondents were asked to rate their extent of agreement with the PSS items across a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (never) to 5 (very often). The reliability and validity of the PSS have been demonstrated repeatedly[31-33]. In the present study, Cronbach’s coefficient alpha[34] for the PSS was .84, suggesting a high degree of internal consistency.
2.2.2. Coping Styles
- Carver’s[35] Brief COPE (not an acronym) was used to assess how respondents typically respond when under stress (i.e., dispositional coping styles). The Brief COPE is a Likert-type instrument that consists of 14 two-item scales measuring a variety of coping styles. Three scales measuring conceptually distinct aspects of problem-focused coping (i.e., active coping, planning, using instrumental support), and three scales measuring conceptually distinct aspects of maladaptive emotion-focused coping (i.e., substance use, denial, behavioural disengagement) were selected for this study. Respondents indicated what they generally do and feel when they experience stressful events, using a 5-point scale with anchors of 1 (never; i.e., I don’t do this at all) to 5 (very often; i.e., I usually do this a lot). Alpha coefficients ranged from .62 (planning) to .89 (substance use), and exceeded the minimum acceptable value of .50 forwarded by Nunnally[36] as adequate scale reliability (see Table 1).
2.2.3. Negative Affect
- To measure negative affect, Lovibond and Lovibond’s[37] Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scales (DASS) were administered. The depression scale measures symptoms of low positive affect, loss of self-esteem and incentive, and a sense of helplessness; the anxiety scale assesses symptoms of autonomic arousal (e.g., elevated heart rate) and fearfulness; and the stress scale taps into symptoms of irritability and a low threshold for becoming upset and frustrated[38]. Seven items corresponded to each subscale and respondents were asked to indicate how much each item had applied to them over the past few months using a 5-point response scale with anchors of 1 (never; i.e., item didn’t apply) to 5 (very often; i.e., item applied most of the time). Internal consistencies (i.e., coefficient alphas) were .87, .80, and .81, respectively, for the depression, anxiety, and stress subscales.
2.3. Data Analysis
- Prior to addressing the research hypotheses, variables were screened for accuracy and statistical assumptions using various SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) and AMOS (Analysis of Moment Structures) procedures. Next, structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to perform tests of the hypothesized relationships among appraised stress, coping, and negative affect. SEM allows researchers to conduct confirmatory analyses to determine the underlying structure of the data while controlling for measurement error. A particular strength of SEM is that it allows researchers to combine theoretically- and empirically-related variables (e.g., depression, anxiety) into larger super-ordinate variables (e.g., negative affect). This enhances the simplicity and the accessibility of research data, while not losing any valuable information.
2.3.1. Model Identification
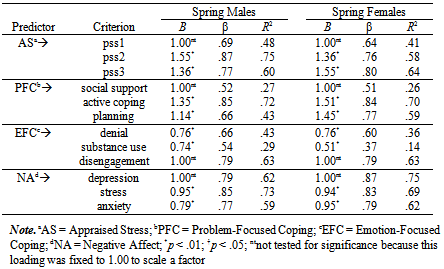
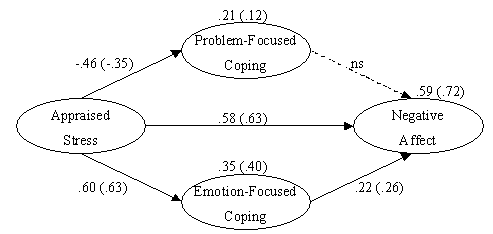
- The hypothesized model for the study is presented in Figure 1. The model is designed to identify basic concepts of stress, but does not include all possible variables or pathways. The model is simply a device to categorize key items within the stress universe, and to generate testable hypotheses of relationships among variables. The exclusion of variables and alternative pathways is not intended to reflect hypotheses about their existence. Negative affect, for example, may be conceptualized as either a manifestation or catalyst of appraised stress and coping[39].The ovals in Figure 1 represent unobservable, latent variables, and the unidirectional arrows indicate direct effects. The depression, anxiety, and stress scales from the DASS[37] were used to represent the latent construct of negative affect. The behavioural disengagement, denial, and substance use scales from the Brief COPE[35] were used to represent the latent construct of emotion-focused coping. The active coping, planning, and seeking instrumental support scales from the Brief COPE[35] were used to indicate the latent construct of problem-focused coping. To prevent model underidentification (i.e., insufficient information to calculate unique solutions for each model parameter), the 10 items of the PSS[30] were parceled randomly into three groups (e.g., pss1, pss2, pss3) to represent indicators of the latent factor of appraised stress. The error terms for problem- and emotion-focused coping were hypothesized to covary with one another (i.e., no implied direction of effect) because the indictors were derived from the same scale and likely contained shared error in responses.Given that the indicators across constructs consisted of different length scales (i.e., varying number of questions parceled together), mean values were used to create a common metric. The latent variables are unobserved and therefore have no definite metric scale; consequently, one factor loading per construct was set at 1.0 to give the latent variable the same metric as that indicator.
2.3.2. Model Estimation
- Model testing was performed using AMOS, and a maximum-likelihood estimation method to examine the fit of the model to the observed variance-covariances matrices. The following statistics were used to evaluate the goodness of fit of the hypothesized model: chi-square statistic (χ2), the ratio of χ2 to the degrees of freedom in the model (χ2/df), the goodness of fit index (GFI), the comparative fit index (CFI), and the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA). Good fit is indicated by a nonsignificant chi-square, χ2/df ratio less than 3.00, fit indexes (i.e., GFI, CFI) greater than .90, and a RMSEA of .05 or less[40,41].
|
3. Results
3.1. Data Screening
- To determine if cases could be combined for data screening, a global test of the equality of covariancestructures across groups (e.g., gender, ethnicity) was performed. Using listwise deletion, the analyses revealed no significant differences in variances and covariances between the groups of students, χ2(192, N = 1110) = 524.12, p < .001; ∆χ2(42) = 53.58, p > .05. As a result, the cases were combined for subsequent data screening. With missing data replaced and outliers subsequently deleted, 1088 cases (562 females, 526 males) remained and assumptions of normality, homogeneity of variance-covariance matrices, and linearity were satisfactory.To check for multicollinearity, zero-order correlations were computed among the variables utilized in thisinvestigation. An a priori level of less than .70 was established to determine whether the subscales measured relatively independent constructs[36,42]. Correlations ranged from |.11| to |.67|, suggesting that the scales tapped relatively independent constructs (see Table 1).
3.2. Group Differences
- To test mean differences among groups (e.g., gender, quarter in school, ethnicity, working status, etc.) a multivariate analysis of variance was conducted. No interactions were shown to be significant and only gender emerged as a significant main effect for the analysis, Wilks’ lambda = .98, F(10, 977) = 2.38, p < .05, η2= .02. The follow-up univariate F-test alpha levels were set at .005 (i.e., the apportionment of alpha across the 10 successiveANOVAS) to achieve an experimentwise error rate of five percent, however, leaving no significant mean differences between males and females on any of the measured variables.
3.3. Structural Equation Modeling
- To test the hypothesized model, structural equation modeling was performed using a multiple-group approach. The data was grouped by gender and school term: (a) to determine if males and females differed on any of the model parameters; and (b) to test the stability of the parameter estimates across samples from the Spring and Fall school terms. Specifically, the Spring sample of 519 participants (253 males, 266 females) was used to assess the initial fit of the hypothesized model, whereas the Fall sample of 569 participants (273 males, 296 females) was used to cross-validate the findings from the Spring sample.
3.3.1. Model Estimation
- Analysis of the Spring sample data revealed that the hypothesized model without cross-group constraintsexhibited good fit to the data, χ2(96, N = 519) = 230.76, p < .001; χ2/df = 2.40; GFI = .93; CFI = .95; RMSEA = .05. When all factor loadings and factor correlations were constrained to equality between the male and female groups the resulting fit was χ2(109, N = 519) = 246.74, p < .001; χ2/df = 2.26; GFI = .92; CFI = .94; RMSEA = .05. The change in the overall chi-square was not statistically significant (∆χ2 = 15.98, p > .05). This result implies that the model parameters as a set do not differ significantly across the male and female participants, and supports the use of a single model for both groups.
3.3.2. Measurement Model
- The parameter estimates and proportions of explained variance for the hypothesized measurement model, which specifies the relationships of the observed measures to their posited underlying constructs, are presented in Table 2. Unstandardized estimates are interpreted as regression coefficients (B) that estimate the direct effects of predictors on criterion variables. In other words, unstandardized estimates are coefficients that indicate the expected change in a criterion given a 1-point increase in the predictor, when controlling for the other variables in the model[43]. Standardized loadings are interpreted as correlations, or as beta regression coefficients (β), and their squared multiple correlation (SMC) as proportions of explained variance (R2).
|
3.3.3. Structural Model
- The links between the latent variables of the structural model are illustrated in Figure 1. Standardized path coefficients with absolute values less than .10 may indicate a “small” effect, values around .30 a “medium” effect, and those greater than .50 a “large” effect[43]. The following significant relationships were found between the latent constructs: large effects (p < .01) between appraised stress with both emotion-focused coping and negative affect; a medium effect (p < .01) between appraised stress and problem-focused coping; and a small effect (p < .05) between emotion-focused coping and negative affect.In Figure 1 the values printed above the latent constructs are squared multiple correlations (SMC). In this instance, the SMC value represents the proportion of variance (R2) that is explained by the predictors of the construct in question[41]. Accordingly, for females, 72 percent of the total variance in negative affect is accounted for by its three predictors: appraised stress, problem- and emotion-focused coping. A decomposition of effects across groups revealed that the direct effects of appraised stress on negative affect accounted for approximately 45 percent, and the indirect effects of appraised stress through coping another 20 percent, of the explained variance in negative affect. In comparison, emotion-focused coping contributed only about three percent, and problem-focused coping less than one percent, to the total proportion of explained variance in negative affect.
3.3.4. Model Cross Validation
- The Fall sample (N = 569) was then used to cross-validate the model derived from the Spring participants (N = 519). First, the Spring and Fall models were tested simultaneously with none of the parameters across samples constrained to be equal: χ2(192, N = 1088) = 496.09, p < .001; χ2/df = 2.58; GFI = .93; CFI = .94; RMSEA = .04. This unconstrained model then served as the baseline against which to judge a restricted model, where parameters were constrained to be equal to one another: χ2(231, N = 1088) = 537.70, p < .001; χ2/df = 2.33; GFI = .92; CFI = .93; RMSEA = .04. The change in the overall chi-square between models was not statistically significant (∆χ2 = 41.61, p > .05). This result implies that the model parameters as a set do not differ significantly across the Spring and Fall participants, and supports the use of a single model for both groups.
4. Discussion
- The purpose of this study was to examine the goodness of fit of a model specifying relationships between appraised stress, coping, and negative affect among college students. The hypothesized model exhibited good fit to the data and was cross validated across samples.
4.1. Multivariate Relationships
4.1.1. Appraised Stress and Negative Affect
- Consistent with previous research[23,44,45], a significant positive relationship was found between appraised stress and negative affect. This finding suggests that the more individuals judge their resources as insufficient to meet life demands, the greater their negative affect will be. The finding that appraised stress, relative to problem- and emotion-focused coping, is the most salient predictor of negative affect is consistent with other multivariate investigations with college students[5,28]. Still, other researchers have found that coping is a stronger predictor of negative affect than is appraised stress[46], and more research is needed to determine the relative importance of these variables in predicting negative affect among college students. Converging evidence in this area would assist practitioners to target the most appropriate concepts (i.e., appraisal versus coping) of college student stress for intervention.
4.1.2. Appraised Stress and Coping
- A significant positive relationship was found between respondents’ levels of appraised stress and emotion-focused coping, whereas a significant negative correlation was found between lower levels of appraised stress and the students’ use of more problem-focused coping strategies. Both of these findings are congruent with previous research[5,44,46] and suggest that the use of emotion-focused coping strategies characterized by avoidance may heighten appraised stress, whereas problem-focused coping may attenuate appraised stress among college students. Interventions designed to address these findings and to assist students to gain an appropriate repertoire of coping strategies are needed.
4.1.3. Coping and Negative Affect
- A pervasive assumption in the research literature is that problem-focused coping strategies are more adaptive and relate to better outcomes than the use of emotion-focused coping. Yet, in the present study, and studies similar to it[5,7,28], problem-focused coping did not have a unique association with negative affect, controlling for emotion - focused coping and appraised stress. The absence of a significant relation between problem-focused coping and negative affect may mean that (a) problem-focused coping is not predictive of feelings of depression, anxiety, and/or stress, or (b) the adaptiveness of problem-focused coping may be offset by students’ repeated use of emotion-focused coping. The practical implications of such findings are varied depending on whether a researcher chooses the former or latter explanation. As such, these findings should be interpreted cautiously and further replication is necessary to determine the efficacy of problem-focused coping in preventing or combating negative affect.The supposition in the research literature that certain types of emotion-focused coping are related to increases in negative affect[7,21,25,26,44] was supported in the current study. Although emotion-focused coping may provide temporary relief from situations appraised as stressful, the cumulative evidence of stress research suggests that emotion - focused coping strategies such as behaviouraldisengagement, denial and substance use typically work against students rather than to their advantage. The continued use of emotion-focused coping over time may represent a failure to confront demands directly (or, at the very least, a tendency to postpone dealing with demands) and add to or exacerbate negative affect. The literature suggests that, when controlling for the effects of other variables, emotion-focused coping is a better predictor of negative affect than is problem-focused coping[5,7,28]. Due to the maladaptive relationship of emotion-focused coping with negative affect, interventions targeted for college students should focus on increasing awareness and understanding of the potential influences these strategies have on students’ well-being. Past research has shown that college students prefer emotion-focused coping strategies over problem-focused strategies[47], and that students’ ability to regulate emotions reduces stress[48].
4.2. Implications and Applications
- The boarder implication of the findings from this study is a potential appeal to practitioners who require a scientific basis for interventions to promote well-being among college students. The model tested in this study is a useful heuristic device that can be used (a) to identify focal points for stress assessment and problem diagnosis, (b) to shape intervention designs and strategy selection, and (c) to distinguish reference points for program evaluation. In other words, the constructs of appraised stress, coping, and negative affect, respectively, can be used initially to make educational, behavioral, and epidemiological diagnoses to guide intervention development and implementation[49]. Next, the efficacy of interventions targeting appraised stress, coping, and negative affect can be estimated, respectively, with process, impact, and outcome evaluations. Such assessment and evaluation efforts are crucial for student affairs staff (a) to determine how best to develop effective intervention services, (b) to mobilize financial and institutional support for health programs, and (c) to provide data for intervention efficacy. Not only would programs assist students to combat the well-documented effects of college stress (e.g., depression, anxiety), but interventions also would assist students to develop coping skills and strategies to transfer to future endeavours and successes.
5. Conclusions
- The present study exhibited a number of theoretical, methodological, and practical strengths. First, the study was grounded in theory, and hypotheses were based on previous empirical research. Second, the selected instrumentation were reliable and demonstrated predictive validity. Third, the hypothesized model was tested and cross-validated with a large sample of students; this reduced sampling error, protected against Type I error, and improved generalizability. Fourth, structural equation modeling was used to combine empirically-related variables into larger constructs; this reduced measurement error, allowed for a truer examination of the relationships between constructs, and enhanced the simplicity and accessibility of the data. Finally, the model tested may provide practitioners with an empirically - validated framework to identify focal points for the assessment, design, and evaluation of stress interventions.Despite a number of strengths, several limitations were evident in this investigation. First, the results were based on cross-sectional, self-report data that are susceptible to response bias, and do not allow for statements of causality. Second, the study participants were mostly freshmen and Caucasian students drawn from a single university, and not necessarily representative of college students as a whole. Finally, a dispositional perspective was used to examine participants’ stress, and actual environmental differences in stress were not accounted for. Future research is needed to address these limitations and to bridge further theory and research to understand and improve stress, coping, and affect among college students.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML