-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Networks and Communications
p-ISSN: 2168-4936 e-ISSN: 2168-4944
2021; 11(1): 17-25
doi:10.5923/j.ijnc.20211101.02
Received: Jun. 18, 2021; Accepted: Jun. 28, 2021; Published: Jul. 26, 2021

Performance of Coherent Optical Networks Incorporating Kramers-Kronig Direct-Detection Receivers Part II: Single-Sideband Transmission
Zainab H. Hasan, Raad S. Fyath
Department of Computer Engineering, Al-Nahrain University, Baghdad, Iraq
Correspondence to: Raad S. Fyath, .
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

A single-sideband (SSB) transmission has been adopted in modern coherent optical networks to increase the bit rate capacity and maximum reach. Recently, direct-detection (DD) technique, which does not use a local laser, has been proposed to retrieve the phase of the complex optical signal from the photocurrent at the receiver side. This technique uses Hilbert transform-based Kramers-Kronig (KK) algorithm and has been mostly investigated for less than 100 Gbps optical networks. The aim of this paper is to design and performance investigate KK-based coherent optical networks operating with 200 Gbps and beyond data rates under SSB transmission. A virtual carrier-assisted coherent optical network configuration supported by KK-based DD technique is designed using VPIphotonics ver.11 software. The configuration uses only one laser where the information is embedded in its field using a SSB modulation. A virtual assisted-optical carrier is generated by making the message modulates a radio frequency (RF) subcarrier before using optical modulation. The configuration is designed to support 16-QAM single-polarization (SP) signaling with 200 and 400 Gbps bit rates and dual-polarization (DP) multiplexing to support 400 and 800 Gbps networks. The effect of various design and system parameters on the transmission and bit error rate characteristics are investigated. Simulation results show the SSB configuration can support maximum reach of 360 and 180 km for SP 200 and 400 Gbps, respectively.
Keywords: Single-sideband (SSB), Direct-detection (DD), Single-polarization (SP), Dual-polarization (DP)
Cite this paper: Zainab H. Hasan, Raad S. Fyath, Performance of Coherent Optical Networks Incorporating Kramers-Kronig Direct-Detection Receivers Part II: Single-Sideband Transmission, International Journal of Networks and Communications, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 17-25. doi: 10.5923/j.ijnc.20211101.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction and Related Work
1.1. Introduction
- Advanced high-bit rate optical networks faces two main challenges [1]. The first one is related to the limited available bandwidth of the electrical/optical and optical/electrical devices to support the high bit rate. Note that it is important to use low-order modulation formats to avoid sensitivity penalties due to system impairments. The second challenge is the increased effect of fiber chromatic dispersion as the bandwidth of the modulated carrier increases. To solve these challenges simultaneously, SSB transmission has been proposed in the literature since it reduces the bandwidth of modulated optical signal to the half [2,3]. One of the techniques used to generate an optical SSB modulation is to generate a SSB-modulated RF subcarrier which is used to modulate the output of the CW laser. This type of optical modulation is called SSB subcarrier modulation (SCM) which offers low cost implementation [4]. Direct detection (DD) scheme has been investigated to recover the message at the receiver side bit. The performance is limited by SSBI generated after the single-PD detection. Recently, KK-based DD receiver has been proposed to reduce the effect of SSBI [5,6].The aim of this paper is to design high-bit rate (200 Gbps and beyond) SSB coherent optical networks incorporating direct-detection optical receivers. Optical signal processing is used at the transmitter side to produce high-order coherent modulation format and Kramers-Kronig (KK) algorithm is to implemented using DSP after photodetection in the receiver side. The goal is achieved through the following steps(i) Design and performance investigation of single-polarization 200 and 400 Gbps SSB coherent optical networks supported by KK-DD receivers. The effect of various design and system parameters on the bit error rate (BER) and transmission performance are to be addressed in details.(ii) Applying polarization-multiplexing technique to double the transmission bite rate for the networks designed in step (i).
1.2. Related Works
- In 2017, Li et al. [7] assessed the performance of DD transceivers employing electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) combined with digital DSP-based receiver linearization techniques. Experiments were performed on a 4 × 112 Gb/s WDM DD SSB QAM Nyquist-subcarrier- modulation (SCM) system operating at a net optical information spectral density of 2.8 b/s/Hz in transmission over up to 240 km of standard single-mode fiber (SSMF) links. The experimental study was focused on the effectiveness of performing EDC either at the transmitter (Tx-EDC) or at the receiver (Rx-EDC) in DD-SCM transceivers combined with different receiver linearization techniques. The experimental results indicate that the performance difference of Tx and Rx-EDC depends on the effectiveness of the linearization scheme that is used, and that they can achieve similar performance if the beating interference is effectively suppressed. Therefore, it becomes possible to perform the EDC at the receiver rather than at the transmitter, which simplifies the system operation since knowledge of link dispersion is not required at the transmitter. In 2018, Li et al. [8] experimentally demonstrated a bidirectional-passive optical network (PON) based on the KK receiver and 50 km 7-core fiber. The middle core was used to deliver the seed light to optical network unit (ONU) for colorless upstream transmission. The upstream and downstream signals were transmitted simultaneously over the same outer core for each ONU. The design simultaneously coped with the induced signal-signal beating interference (SSBI) and Rayleigh backscattering noises. A low-cost self-homodyne detection using only one PD was used at both optical line terminal (OLT) and ONU. By this means, the signals and local oscillator for upstream and downstream transmission all originate from the same laser which was located at OLT. The results show that SSBI could be effectively eliminated and the fiber dispersion can also be digitally compensated due to the reconstruction of the complex field of the received signal in the KK-based receiver. In the experiment, the carrier-to-signal power ratio (CSPR) and the frequency gap between the upstream and downstream signals were investigated. Furthermore, bidirectional transmission of 60 Gbps SSB-Nyquist-16-QAM signals over 50 km 7-core fiber was successfully achieved, and the frequency gap between the upstream and downstream signals was only 3 GHz. In 2018, Li et al. [5] used KK scheme to achieve 4 ×168 Gbps WDM DD SSB 64-QAM Nyquist-SCM signal transmission over 80 km of uncompensated SSMF. The joint optimization of the optical carrier-to-signal power ratio (CSPR) and the sampling rate used for the KK algorithm was experimentally studied. The sensitivity of the KK scheme’s performance to the sampling rate was compared with alternative recently proposed single-stage and two-stage linearization filters. Both the back-to-back and transmission evaluations indicate that, of the three schemes, the best performance was achieved using the KK scheme (provided a sampling rate corresponding to at least 2.75 sample per symbol was used for the KK algorithm). The optimum performance being achieved at 6 samples per symbol. This experimental analysis quantified the trade-off between the linearization performance and the DSP sampling rate in high spectral efficiency 64-QAM DD receivers. In 2019, Zhu et al. [9] presented a comparative study of equalization-enhanced phase noise (EEPN) and phase-to-amplitude (P2A) noise with CD pre- and post-compensation in SSB transmission and KK-DD systems, respectively. The interplay of laser phase noise and fiber dispersion on an optical SSB Nyquist shaped four-level pulse amplitude modulation (4-PAM) signal in KK receiver was investigated numerically. The main results show that the EEPN in a DD-KK receiver dominates the system noise with the relaxed signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Further, the P2A noise in CD post-compensation scheme is relaxed due to the complex filed recovery with KK receiver. These conclusions were drawn from simulation of 56-GBaud 4-PAM signal over 100-km SSMF transmission. In 2020, Wang et al. [4] proposed new optical modulator configuration for KK receiver-based optical SSB DD systems to cope with SSBI for long-reach optical interconnect and 400 GZR. They analyzed the principle of dual-drive Mach-Zehnder modulator (DD-MZM)-based SSB modulation due to its low cost compared with in-phase quadrature (IQ) modulator. The results indicate that SSBI does not exist in back-to-back after square-law DD, and EDC cannot be realized at the transmitter due to the nonlinear modulation of DD-MZM. Simulation results were reported for both 25 GHz SSB conventional DD-MZM-based scheme and new proposed scheme incorporating discrete Fourier transform spread discrete multi-tone (DFT-S DMT). The BERs of the proposed and conventional schemes with optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) of 26 dB were 1.2 × 10−3 and 1.7 × 10−2, respectively, after 80 km SSMF transmission with pre-EDC. In 2020, Al-Qadi et al. [2] experimentally demonstrated the simultaneous generation and transmission of 12 channels SSB 16-QAM signals at 18 GBaud per channel using a single mode locked laser (MLL). This laser acts as an optical comb with 25 GHz line spacing. A total net data rate of >800 Gbps was achieved over 78 km of SSMF. Direct detection with a single PD is used at the receiver and optical field reconstruction was performed based on the KK algorithm to provide SSBI cancellation and allow for EDC. A BER of less than 2x10-3 was reported after transmission which was lower than the threshold of hard-decision (HD) forward error correction (FEC) with 7% overhead (BER threshold = 3.8x10-3 was assumed). Numerical simulations were also performed to assess the impact of noises from the laser source and the receiver front-end on the system performance. Receiver noise was found to be the most important limiting factor for the BER of this system. A linear PD capable of accepting high signal optical power with large dynamic range and high responsivity is critically important to improve the optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) performance in these systems.It is clear from this literature survey that most of the work was reported for a single-polarization (SP) KK receiver-based optical networks with less than 100 Gbps data rate per single channel. It is interesting to address the performance of such networks for higher-bite rate SP transmission (for example, 200 and 40Gbps). Further, one can redesign the system using DP multiplexing to double the transmission bit rate. The effect of system parameters needs to be investigated for these advanced systems. These issues are considered in this work.
2. Single-Sideband/Direct Detection Transmission
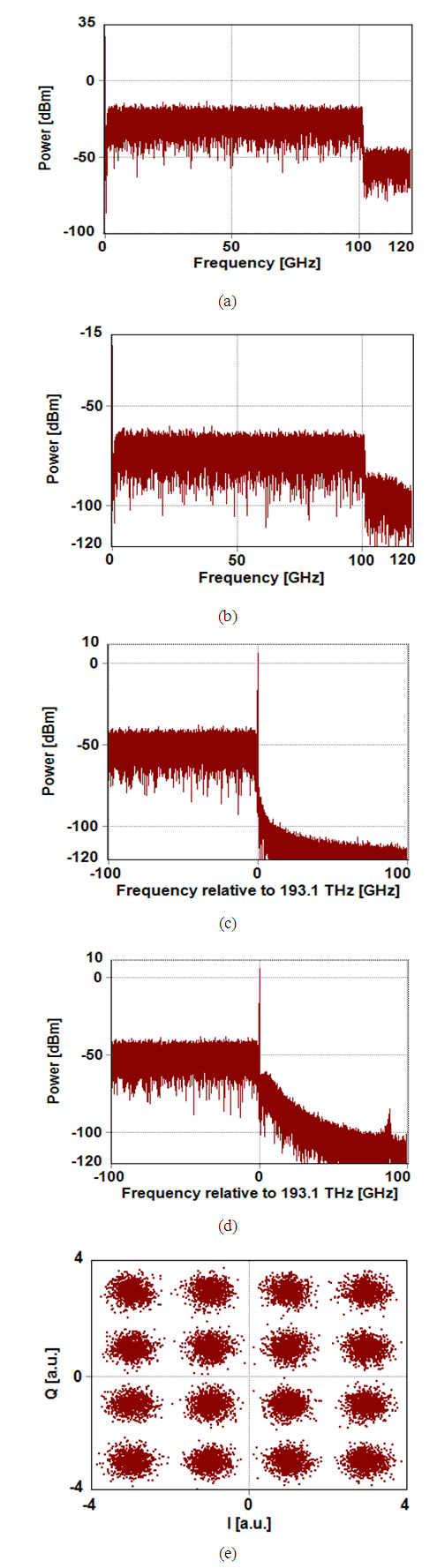
- Figure 1 shows a simplified block diagram of the optical SSB-SCM transmitter. The RF SSB M-QAM signal is used to modulate the CW laser (optical carrier) through IQ optical modulator. The RF subcarrier frequency 𝑓sc is set to ≥ (1+r)Rs/2 where r is the roll-off factor of the root-raised cosine filter used for pulse shaping the M-QAM electrical pulse and Rs is the symbol rate. A unmodulated carrier component is added during the electrical-to-optical conversion achieved by the IQ modulator [6].
 | Figure 1. Schematic of a SSB-SCM Transmitter |
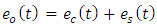 | (1a) |
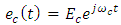 is the carrier component with Ec is a constant and represents the amplitude of the optical carrier. Further the es(t) is the modulated carrier component
is the carrier component with Ec is a constant and represents the amplitude of the optical carrier. Further the es(t) is the modulated carrier component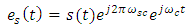 | (1b) |
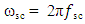 is radian subcarrier frequency. Combining eqns. (1a) and (1b) yields
is radian subcarrier frequency. Combining eqns. (1a) and (1b) yields 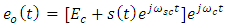 | (2) |
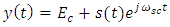 is a minimum phase signal when
is a minimum phase signal when 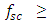 electrical message bandwidth Bme and Ec is large enough compared the peak of |s(t)| [10]. In this case KK receiver can be used to detect the message with negligible SSBI.
electrical message bandwidth Bme and Ec is large enough compared the peak of |s(t)| [10]. In this case KK receiver can be used to detect the message with negligible SSBI.3. Performance Investigation of SSB KK-based DD Optical Networks
- Two SP SSB/DD point-to-point networks are implemented in VPIphotonics environment to deliver 200 and 400 Gbps data rates in the C band (λ ≃ 1550 nm). 16-QAM signaling is used for the electrical SSB QAM modulator. The KK algorithm is implemented in the receiver side to retrieve the complex data phase from the photocurrent. The main system parameters are listed in Table 1.
|
3.1. Performance of 200 Gbps SSB SCM 16-QAM System
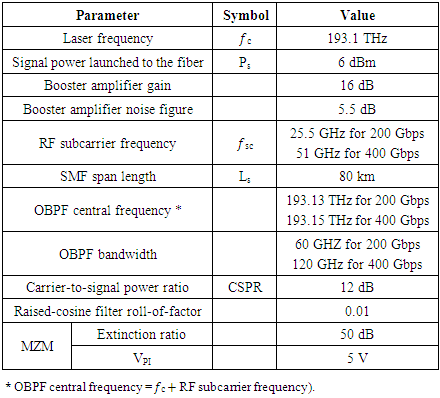
- Figures 2a-d show signal spectra at different points of the system. The corresponding received constellation diagram is depicted in Fig. 2e. The system is simulated for a single-span transmission link (i.e., L = 80 km) using Ps = 6 dBm, r = 0.01, CSPR = 12 dBm, 𝑓sc = 25.5, and OBPF bandwidth = 60 GHz. Figure 2a shows the spectrum of the generated electrical SSB QAM signal and the figure indicates that this signal has 50 GHz-bandwidth (≃ (1+r)Rs). Note further that the constellation diagram is clear which ensures a low BER (BER=3.1X10-5).
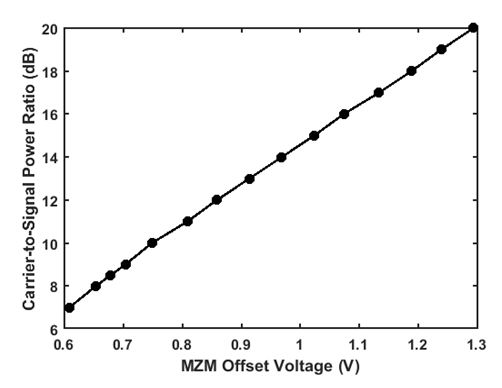 | Figure 3. Variation of carrier-to-signal power ratio with MZM voltage |
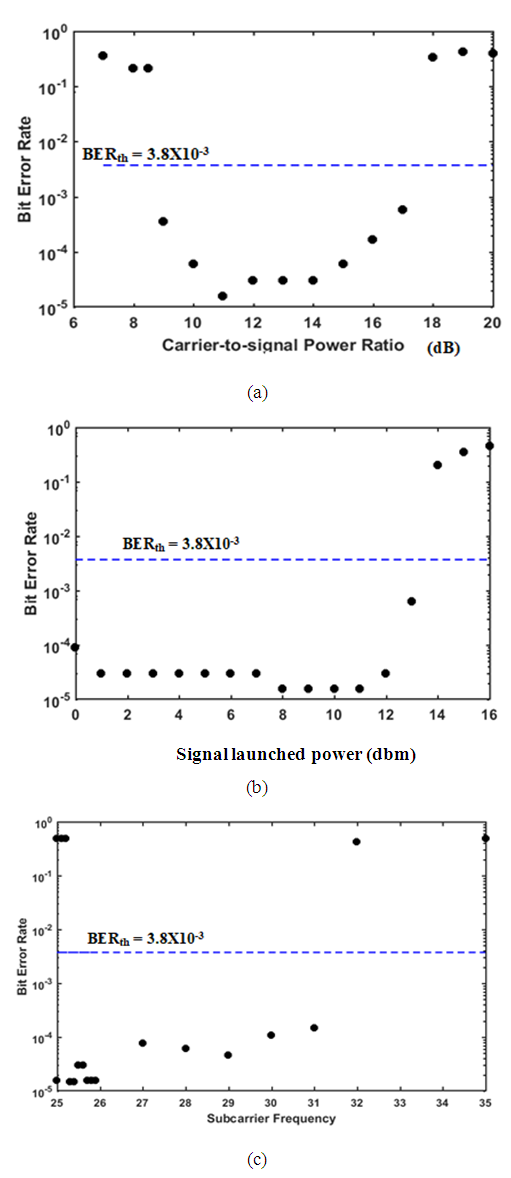 | Figure 4. Variation of BER of SP 200 Gbps SSB SCM 16-QAM system with (a) Carrier-to-signal power ratio. (b) Signal launched power. (c) Subcarrier frequency |
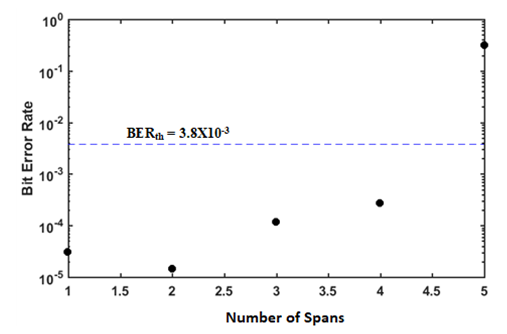 | Figure 5. Variation of BER of SP 200 Gbps SSB SCM 16-QAM with transmission distance measured by numbers of 80 km SMF span |
3.2. Performance of 400 Gbps SSB SCM 16-QAM System
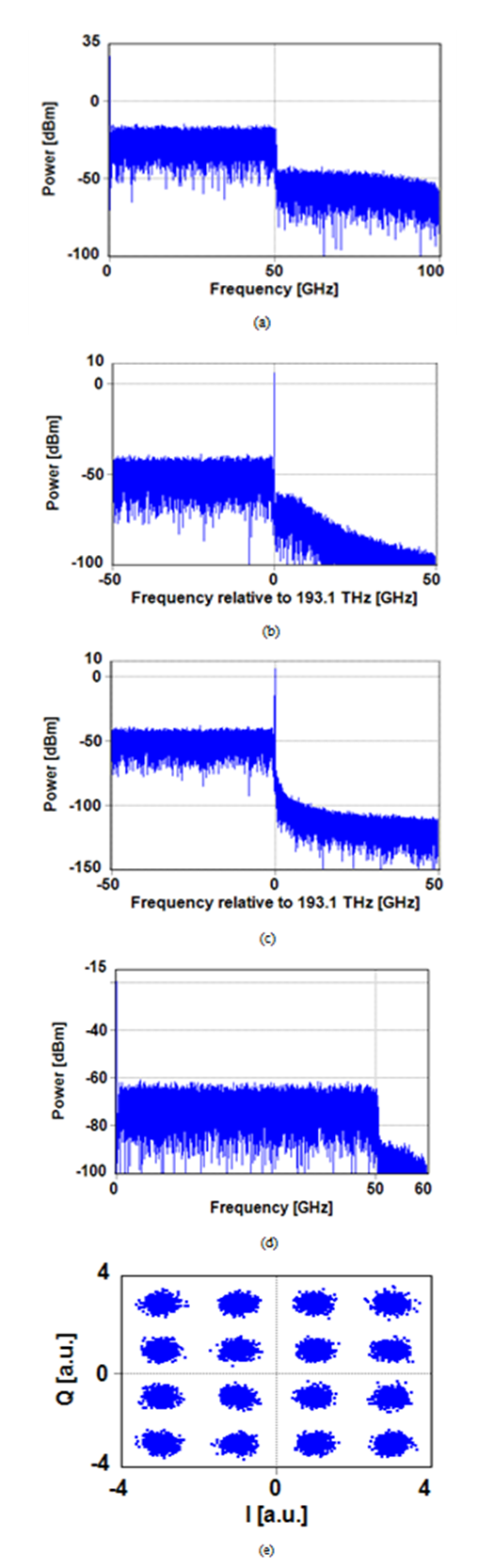
- This subsection addresses the transmission performance of 400 Gbps 16-QAM system designed with SSB modulator and KK algorithm-based DD receiver. The system is implemented in VPIphotonics environment using the following parameters: Ps = 6 dBm, r = 0.01, CSPR = 12 dB, and 𝑓sc = 51 GHz. For comparison purposes, the values of Ps, r, and CSPR are kept as in the 200 Gbps counterpart. Figures 6a-e show the spectra of the signals at different points of communication system in addition to the received constellation diagram. A single 80 km-SMF span is used to construct the transmission link. Figure 6a shows the spectrum of the generated the electrical SSB signal. The bandwidth of this signal is 100 GHz and it is in accord with the expected value of (1+r)Rs where Rs=100 Gsps for the 400 Gbps 16-QAM signaling. The received constellation diagram (Fig. 6e) is clear and leads to a BER of 1.1X10-4 (< BERth = 3.8X10-3).
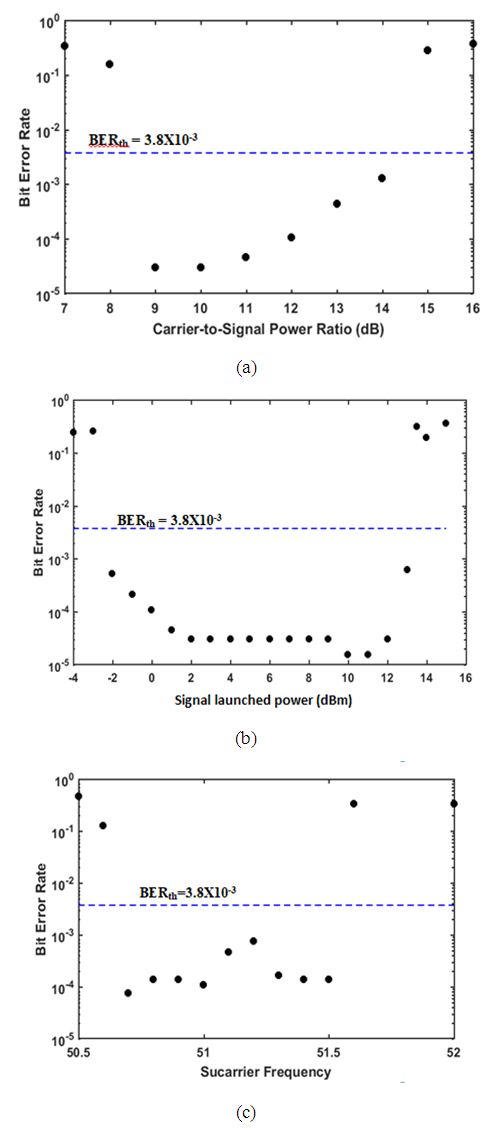 | Figure 7. Variation of BER of SP 400 Gbps SSB SCM 16-QAM system with (a) Carrier-to-signal power ratio. (b) Signal launched power. (c) Subcarrier frequency |
3.3. Design and performance Evaluation of Dual-Polarization SSB/DD Systems
- The results reported in subsections 3.1 and 3.2 are used as a guideline to design DP counterparts carrying 400 and 800 Gbps, respectively. The DP system is designed using two identical subsystems sharing the same transmission link. Each of the two subsystems is designed for one of two perpendicular states of polarization. A single laser with 45° polarization angle to deliver two equal power-polarization components TE and TM (or X and Y). Figure 8 shows the DP simulation results corresponding to the DP 400 Gbps system operating with L = 80 km. Note that both polarization systems offer almost identical results. The same conclusion can be drawn for the DP 800 Gbps system as shown in Fig. 9.
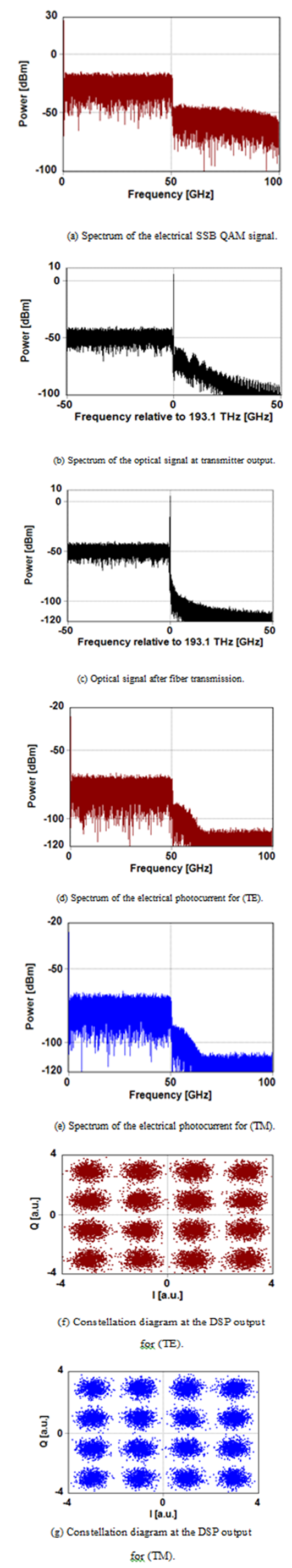 | Figure 8. Spectra and constellation diagrams of DP 400 Gbps SSB SCM 16-QAM system |
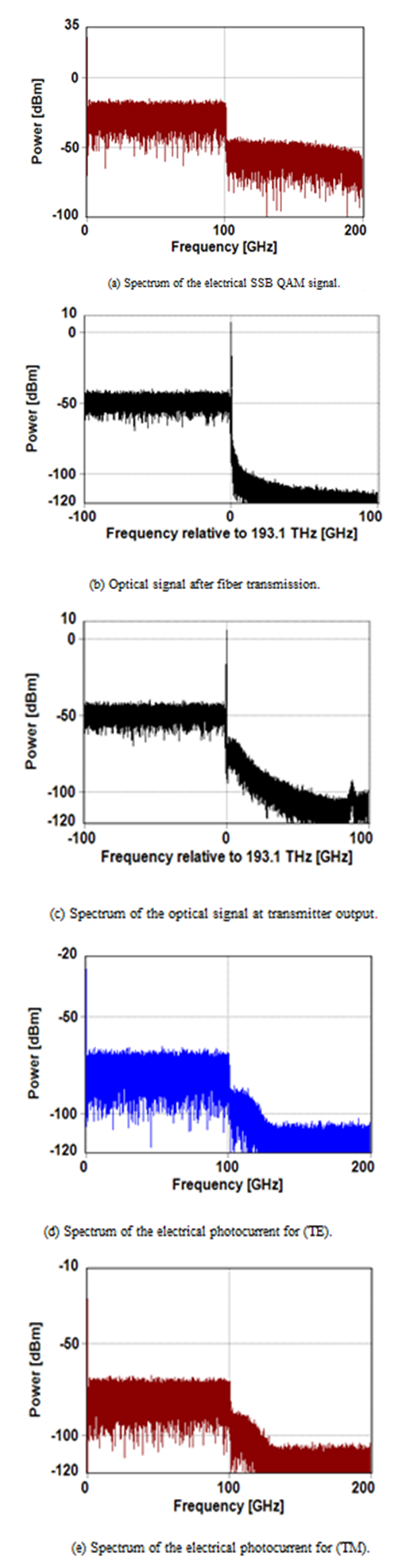 | Figure 9. Spectra of DP 800 Gbps SSB SCM 16-QAM system |
4. Conclusions
- A point-to-point optical network configuration has been designed using single-sideband (SSB) coherent modulation/KK direct detection schemes to support single-polarization (SP) 200 and 400 Gbps 16-QAM signaling. The design has been modified to double the transmission bit rates (400 and 800 Gbps) using dual-polarization (DP) multiplexing technique. The configuration uses a single laser at transmitter side and Kramers-Kronig algorithm to retrieve the complex phase of the received optical signal data from the photocurrent using Hilbert transform. In addition, DSP-based electronic chromatic dispersion is implemented at the receiver side. The main conclusions drawn for this study are (i) The configuration supports the transmission of SP 400 Gbps 16-QAM (DP 800 Gbps 16-QAM) signal over more than 100 km SSMF.(ii) The configuration is relatively less cost and more robust than configuration that uses two lasers since it uses a single laser at the transmitter.(iii) The KK-based receiver offers efficient direct-detection process for a single-sideband coherent-modulated optical signals operating at these high-bit rates.(iv) The configuration offers 360 and 180 km, maximum reach for SP 16-QAM signals operating with 200 and 400 Gbps data rates, respectively, when the second configuration is used. (v) There is an optimum value for the carrier-to-signal power ratio, CSPRopt, of 12 and 12 dB when 200 and 400 Gbps SP 16-QAM signals are transmitted over a single span (80 km) of SSMF, respectively.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML