-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Networks and Communications
p-ISSN: 2168-4936 e-ISSN: 2168-4944
2018; 8(2): 29-33
doi:10.5923/j.ijnc.20180802.01

Comparison of Routing Protocols in Wireless Mesh Network on the Basis of Performance
Waqas Ahmad, Awais Salman Qazi
Department of Computer Science, Lahore Garrison University, Lahore, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Waqas Ahmad, Department of Computer Science, Lahore Garrison University, Lahore, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Wireless Mesh Networks (WMNs) are acquiring tremendous change and moving on a fast pace in the field of telecommunications and internet systems. They are having rapid progress and many scintillating deployments. WMN is a reliable technology that is used to remove the limitations and to increase the performance of ad-hoc networks, wireless local area networks, wireless personal area networks and wireless metropolitan area networks. WMNs are consisted of mesh routers, mesh clients and gateways, where mesh routers are the backbone. WMN is an extraordinary type of wireless ad-hoc networks. One of the core issues in WMNs is resource management, which includes routing, which is not possible without routing protocols. There are specific protocols that gives better execution/performance when tested under certain parameters. Protocols are the set of rules that govern data communication. There can be many parameters in WMN, some of them are end to end delay, hop-count, jitter, latency, packet loss, capacity, handover speed, re-convergence, piggybacking, throughput, mobility rate and network load. Three routing protocols named Advanced on Demand Vector (AODV), Dynamic Source Routing (DSR) and Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR) have been tested in WMN under certain parameters which are end to end delay, throughput and network load. The testing of these routing protocols has been performed in the Riverbed modeler 14.5. The captured outcomes from Riverbed modeler have been displayed in this research paper in the form of graphs.
Keywords: Riverbed, ad-hoc, Protocols, Parameters, Routing
Cite this paper: Waqas Ahmad, Awais Salman Qazi, Comparison of Routing Protocols in Wireless Mesh Network on the Basis of Performance, International Journal of Networks and Communications, Vol. 8 No. 2, 2018, pp. 29-33. doi: 10.5923/j.ijnc.20180802.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Recently, Wireless mobile communication has gained colossal importance with its ever rising utilization demand. The technological needs emerging from different tablets, iPads, cellphones, Smart TV, have pressed for more data rate requirement and the cost effective solution to develop it fast. Wireless communication employs a two tiered strategy to occur between hubs which is; firstly, if an existing system is allowed to transmit information in any shape whether it's an audio or an image and secondly a special system is invoked so that the hubs can communication without any hurdle [1]. Wireless Mesh Networks (WMN) are a sort of ad hoc system that are also known as Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Most of the Establishments are moving towards wireless mesh networks for large scale development of wireless neighborhood because of its salient features like scalability, versatility, adaptability and robustness. WMN is the new innovation that has a few things in the same manner as MANET. WMN is the new advancement that has taken MANET a little further. By convention, WMNs have wireless nodes in which each node sends its own packet to other nodes to interface and communicate. A technique is evolved in MANETs where every node goes around as a workstation and is involved in switching. In WMNs, clients use interfaces mainly Ethernet 802.11 and Bluetooth to interconnect with the switches. In the absence of any notable network interface, any sort of communication is not realizable. WMN implies networking interfaces show its own particular significance in communication network. At some point in time, the router of WMN is accessible inside the network card, when a client needs to communicate with the router, it can utilize other network interfaces like peripheral component interconnect (PCI) or PCMCIA bus. The nodes in mesh network that can provide web accessibility are known as gateways. Gateways are the basic piece of network communication whether it is wireless or wired communication. Gateways are also known as protocol convertor and it can work on any open system interconnect (OSI) layer. Notwithstanding of this adaptability, the exercises of gateways are somewhat more mind boggling as contrasted with routers and switches, on the grounds that gateways utilize more than one routing convention to make communication conceivable. Router and switch have its own particular unique routing protocol. There are many advantages of WMNs over other traditional topologies like for example minimum deployment time, dependability, adaptability, strength, robustness, simple, less expensive and maximum market scope [2]. Many organizations like Nokia, Motorola, Ericson, Samsung, Huawei, Siemens and so forth have indicated extraordinary trust in WMNs innovation in view of its adaptability and efficient administrations like giving full IP solution for the organizations [3]. On account of the relentless advancements in the field of wireless communication (tablets, Smart-Phones, IPads, PDAs) the interest for getting 24x7 web network from anywhere is expanding on a high rate. Wireless stations are the gadgets that utilize the 802.11 protocol that can give web network to wireless devices by making a path between them. These wireless stations are Wi-Fi phones, access points, tablets, desktop PC or PDA. Network is made by these wireless stations for wireless devices and gives a bridge between internet and network. Access points have some coverage zone; this coverage territory can be stretched out by enabling wireless devices to pass packets towards access points. This sort of multi-hop wireless access networks are known as WMNs [4]. Routing protocols are continually being critical and significant for a wide range of mobile networks. Routing protocols are the set of rules and regulations that govern data communication. Without routing protocols WMN is incomplete, because for a proper network it is necessary that all nodes are connected with each other and they all can communicate with each other. Routing protocols help routers to speak with each other and for every routing protocol there is a unique arrangement of principles and rules. They forestall routing loops and select preferred routes [5]. Each routing protocol during communication procedure can experience certain parameters, for example, delay; jitter, throughput, latency, hop-count, congestion, overhead, mobility rate, packet loss, transfer speed, reliability and network load in WMN. Specialists and computer scientists have been taking a shot at this issue since quite a while and they are as yet unfit to locate an appropriate and proficient routing protocol that can give sublime execution under every single conceivable condition.Our main motivation in this research paper is to make a performance wise observation of different routing protocols under certain parameters and suggest a protocol that has better adaptability record under any kind of changes.
2. Types of Routing Protocols
- Routing protocols for WMNs can be arranged into various types i.e. reactive protocols, proactive protocols, hybrid routing protocols and hierarchical protocols. Every one of these types are different with each other to some degree. In proactive routing, every node of a network keeps up at least one table that speak to the overall network. In reactive routing, route can be built up at whatever point there is a request and whatever sort of interest, it can be satisfied. In the event that a node needs to convey to some other node and if there is no route accessible, at that point reactive routing protocol will endeavor to build up the route to make communication conceivable. Hybrid routing implies that it consolidates the properties of reactive and proactive routing protocols, its other name is balanced hybrid routing (BHR). In hybrid routing, a protocol is mindful to locate optimal destination. It has another advantage too, as if there is any topology adjustment occurs in a network, this HRP will create a report. In hierarchical routing, the decision of reactive or proactive routing relies upon the hierarchic in which the node is in current condition. At first proactive calculation has been picked and afterward responsive calculation. In any case, hierarchical routing has a few hindrances that is the reason it is stayed away to use in WMNs. Protocols like OLSR, BABEL, DREAM, BATMAN and DSDV are proactive while protocols like AODV, ABR, DSR and FSDR are reactive. Whereas hybrid routing protocols are ZRP and ZHLS [6].
3. Routing Protocols in WMN
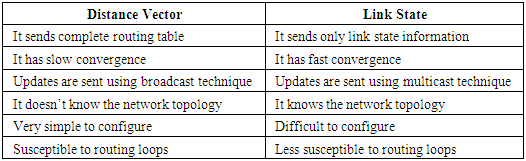
- There are more than 70 routing protocols that can be used in wireless mesh networks [7]. It can be said that more than 70 protocols have been tried in wireless mesh networks already and researchers are finding the new techniques to improve the performance of communication network. Some of the names of those routing protocols are Associativity Based Routing, Ad-hoc on Demand Distance Vector, Better Approach to Mobile Ad-hoc Networking, Destination Sequenced Distance Vector Routing, Dynamic State Routing, Hazy Sighted Link State, Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol, Optimized Link State Routing Protocol, Order One Routing Protocol, Open Shortest Path First Routing, Predictive Wireless Routing Protocol, Zone Routing Protocol, Temporarily Ordered Routing Protocol and BABEL Protocol. Like all other routing protocols, protocols of WMN also specify how routers can communicate and exchange information with each other. All routing protocols are made up from different algorithms that determine the right choice of the respective route. All above routing protocols can be classified into two major types i.e. distance vector and link state. Difference between these two protocols can be summarized in the form of table which is shown below [7].
|
4. Advantages of WMN
- Wireless Mesh Network is a progressive innovation in the field of wireless communication. WMN has turned the fantasy of associating every nodes of a network consistently into seamless connection. WMN is distinctive when contrasted with the conventional wireless networks on the grounds that traditional networks depend on the wireless hotspots. As compared with traditional wireless, WMN is expandable which implies as the need of more nodes/hosts happen, we can without much of a stress make them as a piece of that system. By and large, WMN has the accompanying focal points over traditional systems. These points are the main features of wireless mesh network which are written below [8].1. Versatility2. Extensibility3. Commodious4. Economical5. Fast Thoroughpaced6. Reliability7. Trustworthy8. High Speed Mobility9. High Quality Video Surveillance10. Redundant
5. Introduction to Opnet/Riverbed
- Simulation intends to see the conduct of a true world procedure, behavior or system over time. To reenact anything, as a matter of first importance its model is created. The created model has the attributes and elements of real world framework or process. Opnet is a simulation tool that is flexible in nature than the other tools, for instance it is greatly easy to use having excellent graphical user interface that encourages users to play out the reenactment of any sort of system. The OPNET word recommends that it is utilized for assessing any sort of system, OPNET remains for advanced system assessment. Presently this name OPNET has been changed into RIVERBED Modeler. Opnet Modeler Suite was the old name, and new name is Riverbed Modeler. One might say that Opnet modeler is currently a piece of riverbed modeler. This riverbed suite encourages us to configuration, dissect and show diverse sorts of communication networks [9].
6. Simulation Results
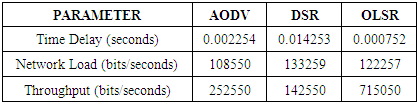
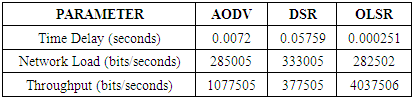
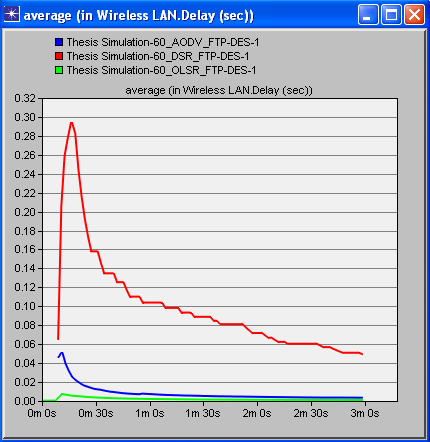
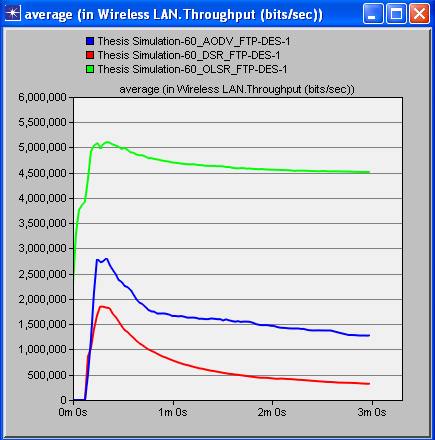
- Simulation of three protocols (AODV, DSR and OLSR) have been carried out in the Riverbed or Opnet Modeler under the parameters of postponement (delay), organize network load and throughput. A decent routing protocol is viewed as great just on the off chance that it gives super execution whatever the situation is. These chose protocols are tried in different cases like for instance we have made a little WMN when we have less number of interconnected hubs/nodes i.e. 15 hubs/nodes, later we have made 30 hubs/nodes network and then we have made 60 hubs/nodes WMN. This expanding measure of hubs/nodes in WMN helped us to demonstrate that just a single of these three protocols is the best. The results of simulation when we have 30 and 60 nodes/hubs of WMN are shown here just for comprehension. The diagrams appeared underneath unmistakably demonstrates that OLSR is the only protocol that outflanks other two protocols as far as execution and effectiveness, when we have certain parameters like postponement (delay), arrange network load and throughput. These results after simulation don't ensure that OLSR will always be dependably protocol of decision in WMN. The choice of protocol can vary with the parameters. Since there are numerous parameters that a protocol can confront in a communication network. So under various types of network, each protocol has its own advantages and disadvantages. Most importantly, reproduction aftereffects of 30 nodes wireless mesh network are as per the following figures. Figure 1 shows delay, figure 2 shows network load and figure 3 shows throughput.
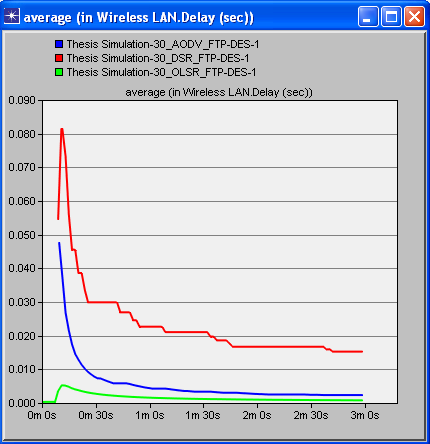 | Figure 1. Delay of all protocols (30 nodes) |
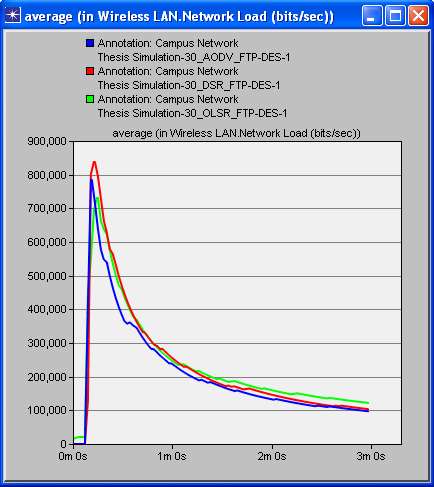 | Figure 2. Network Load in all protocols (30 nodes) |
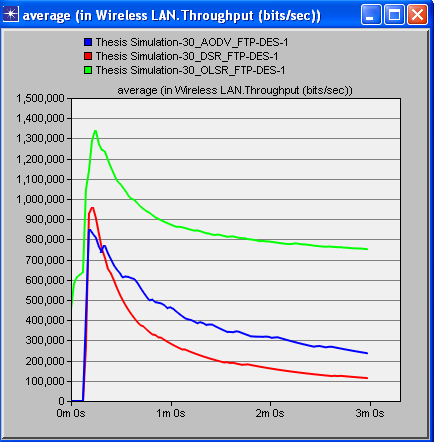 | Figure 3. Throughput in all protocols (30 nodes) |
 | Figure 4. Delay of all protocols (60 nodes) |
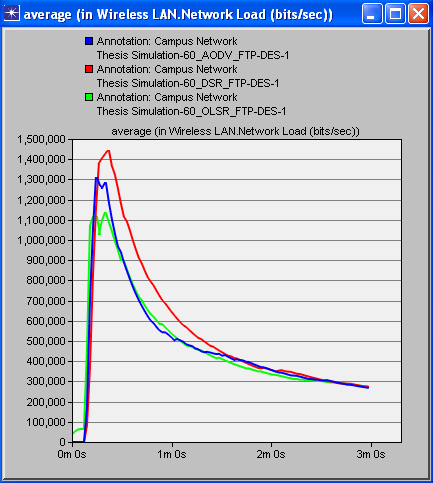 | Figure 5. Network Load in all protocols (60 nodes) |
 | Figure 6. Throughput in all protocols (60 nodes) |
7. Analysis on Simulation Results
- On the off chance that we examine every one of the diagrams separately we concoct the better comprehension of the execution of different protocols. Beginning from the figure 1, red line speaks to DSR, blue line speaks to AODV and green line speaks to OLSR. It can be seen obviously that DSR protocol is giving the most extreme time delay which is not adequate in any communication network. AODV has a marginally less time delay as compared with DSR while OLSR is giving exceptionally minor time delay. Correspondingly, in the second figure, in wording network load it is being watched that after couple of moments DSR handles the network load marginally superior to the others yet as the time goes on, the execution of all protocols regarding network load continues as before. In the third figure, of 30 hubs/nodes condition, OLSR unmistakably beats staying two other protocols when throughput is required. Better throughput clearly implies superb effectiveness. In the fourth, fifth and 6th figures the outcomes are being seen in 60 hubs/nodes condition. Furthermore, these figures likewise demonstrate an indistinguishable sort of conduct of all protocols from it has been seen in less number of hubs/nodes condition. The general investigation tells that optimized link state protocol is the best decision/protocol when there is delay, arrange network load and throughput as parameters.
8. Demographic Analysis
- For more exact and precise perspective of these routing protocols execution, a factual information has been organized as table. This measurable information is taken straight forwardly from the figures given above. Beneath table shows factual information of all conventions in 30 nodes and 60 nodes conditions in table 2 and table 3 respectively.
|
|
9. Conclusions
- From our research we have concluded that there is no such a routing protocol existed which includes each and every strength. In other words, there is no routing protocol available which shows ideal attitude under any kind of situation. However, there is a diehard need of such routing protocol which addresses all the reservations of wireless mesh network. Clearly, WMN has been considered marvelous as compared to other wireless topologies. Therefore, we have performed the simulation in wireless mesh network and got the conclusion that OLSR is the routing protocol that outperforms remaining two routing protocols in terms of better performance. Selection of more routing protocols and testing them under many parameters can lead towards different results and outcomes.
Future Work/Research
- Network arranged in mesh topology has many advantages over conventional wireless systems which have been talked about in this research paper already. There will always dependably be a request of a perfect routing protocol in wireless mesh organization, on the grounds there is no such a protocol accessible for WMN that gives 100% ideal performance. Analysts/scientists should endeavor to make a routing protocol that is ideal under all parameters. The protocols of WMN that are accessible right now don't bargain precisely with the congestion issue. To defeat congestion or clog, there must be a synchronization amongst network and routing protocol. Aside from this, mobility management is the real worry in wireless mesh work systems. There ought to be no trade off on the mobility management of any system. Routing protocols that help finish mobility management issues are elusive nowadays. Mobility rate ought to be expanded as much as possible in any system, and there must be a perfect routing protocol for this reason. Mobility rate is the capacity to interface diverse clients and successfully conveying administrations to the wireless devices while they are in motion. Mobility management is the most stretched out territory of degree as it permits meandering for worldwide clients. A successful calculation to build up another routing protocol is required which can offer close to perfect execution whatever parameters can be. The quality oriented routing protocol must be created by the scientists that will bolster nature of administration and offer quality of service. Various endeavors have been made by the scientists to finish this errand, yet all futile. What's more, they are as yet chipping away at it. In the wake of building up the Quality of service protocol, if essential, it can be tried on numerous simulation tools to check their discrepancies. In addition, future work should be possible on making new simulation environments/tools too that will incorporate increasingly and propelled highlights, and that will defeat the deficiencies and disparities of past system recreation devices (simulation tools) [10].
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML