-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Networks and Communications
p-ISSN: 2168-4936 e-ISSN: 2168-4944
2014; 4(2): 33-38
doi:10.5923/j.ijnc.20140402.02
Research on Returned Logistics and Its Models for Wasted Electrocution Product
Zhang Qian, Shen Zhongming
School of Business, Hua Qiao University P. R. China
Correspondence to: Zhang Qian, School of Business, Hua Qiao University P. R. China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Operational models for waste recycle is established based on the theory of closed loop supply chains. And an analysis was centralized on to decentralize decision making in the process of waste recycle with game theory adopted. The present situation and existing problems are subsequently discussed before an accumulate data process of the data of 9 experimental provinces and 19 other provinces on which an empirical study is performed on the effects that selling price and recycling price respectively have on sales volume and recycle volume. The results revealed that the implementation of “old-for-new” service has considerably promoted the sales of household appliances, not only bringing benefits to manufacturers, retailers and consumers, but also reducing the harm to environment by boosting the recycle and reuse of waste.
Keywords: Closed loop supply chains, Game theory, Returned logistics, Pricing model
Cite this paper: Zhang Qian, Shen Zhongming, Research on Returned Logistics and Its Models for Wasted Electrocution Product, International Journal of Networks and Communications, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 33-38. doi: 10.5923/j.ijnc.20140402.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Since the closed-loop supply chain is not only able to achieve the protection of the environment and efficient use of resources, but also to achieve the sustainable development of enterprises, so a lot of literature has the qualitative and quantitative research on the closed-loop supply chain. Karl Inderfurth, Ruud H. Teunter pointed out that the closed-loop supply chain a significant feature is the recovery of product recovery and re-manufacturing. The recyclables from the consumer may also come from the supply chain of various joints, such as the existence of producing defective products, or damaged products, etc. in the distribution channel. Bloemhof-Ruwaard deem that the closed-loop supply chain in reverse logistics process consists of three activities: (1) waste products from the final consumer to return to the manufacturer's physical activities; (2) The manufacturer transform the waste products into the activities of the supplies; (3) re-use of waste products, product design activities. May be found in the first two activities is a waste product recycling activities, activities of the latter is to ensure that the waste products can take advantage of lower costs and efficiency. Specific logistics activities included in the above activities are: (1) recycling of waste materials; (2) test of waste materials; (3) reprocessing of waste materials; (4) landfill or incineration of waste materials; (5) re-distribution, waste product after this process can continue to circulate in the market, the product is about distribution to the needs of market. Krikke pointed out that the goal of implementing of the closed-loop supply chain is the cycle use of renewable waste and to reduce waste emissions relate with reduce the impact on the environment, to provide customers with services at a lower cost. Geyer and Jackson also thought that economic goals and environmental goals is the supply chain of the closed-loop two goals. Roland Clift and Lucy Wright, using a large number of data in mobile phone industry, the conclusions to draw the value of the supply chain at every stage of proliferation is out of proportion to impact on the environment. The article summed up with the extension of the supply chain, the impact of each stage on the environment and the ratio of the value added is getting smaller and smaller, which shows that the extended supply chain and reverse logistics, thereby achieve the goods re-use and recycling, then this will be good promotional sense for build a resource-saving and environment-friendly society. At present, in many countries, producer responsibility extends to the production of the entire product life cycle, it can be through the entire product life cycle management to achieve environmental protection requirements.
2. The Mode Analysis of Recycling Waste Electronic Products in Our Country
- Waste electrical and electronic product recycling regulations have passed on August 20, 2008 with the State Council executive meeting, effective January 1, 2011. Therefore, the purpose of investigate the implementation of the closed-loop supply chain management is for conserve resources, reduce waste of resources and improve the cycle of resource use efficiency, achieve resource - production - consumption - renewable resources "closed loop cycle so as to achieve the protective effect on the environment . This article describes the reverse recovery process of waste electronic products use a specific use case of the closed-loop supply chain management, combination of the above analysis of the recycling of waste electronic products in Japan and China's current situation, summed up for our country's waste electronics recycling mode as follows:
2.1. Members of the Supply Chain Specialization
- (1) Manufacturers. Manufacturers is a key figure in the entire supply chain, without his presence there would be no production, distribution, sale, consumption, waste, there is no possibility of the existence of other members, and no need study for closed-loop supply. Mainly from the point of view to consider the role manufacturers division: ① EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility), It is the meaning of the various forms of legal obligation to assume the producer have responsibility for recycle use the waste product. In 1975, this concept first proposed on the Swedish government in 1988, this concept first appeared in a Swedish-UNEP report, proposed by Thomas, a Swedish environmental economist. Taiwan was among the first areas of legislation to establish this system in China .Around the world there are more than 28 countries and regions put to use producer responsibility in different areas of production. ② Advocate the clean and green production. Cleaner production is based on the production process and take the preventive environmental strategy to reduce the harm to environment and human purpose, it is a kind of creative concept, through its implementation we can not only meet the development needs of our own, but also the reasonable protection and utilization of natural resources, is a efficient production methods and ways to protect environment. ③ Professional technology and equipment of recycling. This paper argues that the product can be recovered in manufacturer, mainly focused on recovery processing stage of the product, because the company more familiar to the process design of raw material and the functional characteristics, recycling of waste products is more handy, and make recycle cost internalization, conducive to the realization of cost management. The enterprise will be reused components added to the production and manufacturing process, some product can be transported back to the suppliers of raw materials. (2) Retailer. The retailer is the key link between the upstream products’ provider (manufacturer) and the downstream customer. It can play a product’s marketing role in the forward supply chains, meanwhile it is the recovery party for used products’ recycling in the reverse supply chains. It could provide customers many fast selling services for its wide distribution network and a good service delivery system. Because it can master the function, production time, selling time, useful life, customers distribution and the other information for selling products in time, thus we enable to use these features of retailer to deal with the used product recycle. Besides, the “old for new service” of retailer stimulates customer’s returning for more used electronic products.(3)The third recovery party. It includes professional recycle firms and a number of personal units. Many personal recovery party only deal with the precious metal of the used products, and treat other parts as litter to bury and burn, pour the waste gas and water. Of course, the firms are more professional than persons. But they cannot do technical treatment and take most of the resource reusing. Moreover, as the personal units participant, the number of used products for the firms is reducing. (4) The third-party forwarders. There is a saying that, “the forward is the third profit spring”. That is the reason why so many companies outsource their forward business. We should develop the advantages for the third-party forwarders in conducting the closed-loop supply chain management. All in all, the operation efficiency for whole supply chains will be improved.(5) Customers. They are the key factor for reverse recycle in the closed-loop supply chain. They decide to return the used products or not, their action would impact the final result of the closed-loop supply chains. So everyone should start from me, and from the side of the small start, set up the environmental protection consciousness, develop recycling consumption concept, change the unreasonable consumption idea, but as far as possible environmental friendly products. Classify the used products first, then disposed by the professional recycling department to deal. In the same time, excepting take part in the recycling of used products, customers shall play their supervision ability.
2.2. Closed Loop Supply Chain Information Platform Construction
- To make the closed-loop supply chain each link can effective implementation and operation, building a based on closed loop supply chain is the key for members of the platform of information system. based on the Internet, each member of the information systems to link up, and using the data exchange interface (EDI), geographic information system (GIS), Global Positioning System (GPS), tuners data interface techniques of the system data fusion, to construct an open channels of information to achieve the information is accurate, in time, fully sharing. Information for system model as shown in Figure 1.
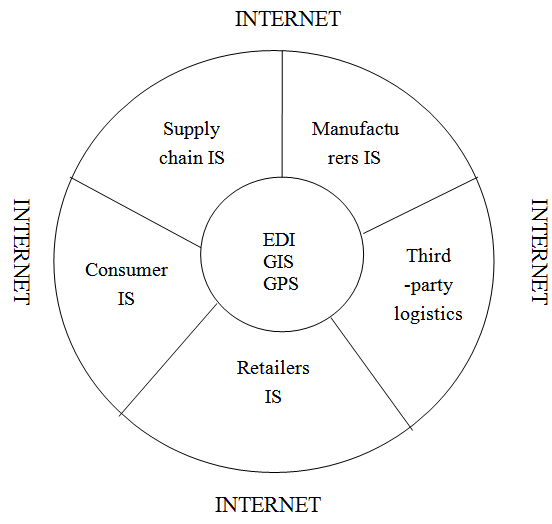 | Figure 1. Information for System model |
2.3. Government’s Role in Closed-loop Supply Chain Management
- Each member on the supply chain is the main part to implement supply chain management, so government which is in the leading level plays a guiding role towards the whole supply chain. The government can implement the Closed-loop Supply Chain Management as below:(1) Develop and improve relevant laws and regulations in recycling of waste. On 28 February, 2006, Electronic Information Products Pollution Control and Management Methods,was released to the public which is the first law about the abandoned electronic products in China and it came into effect on o1 March,2007. Its main purpose was to limit the use of poisoned materials (Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Hexavalent Chromium, PBB, PBDE) in the electronic products. Decreasing the use of these materials in the production and designing part to reduce damages to environment pollution and human body. Abandoned Household Appliances and Electronic Products Pollution's Control Technological Policies, was issued and practiced on 27 April, 2006 and its aim was to realize the E-waste reduction, resource and harmless. Reduction means reducing the emissions of abandoned electronic products; resource means realizing the recycling for the abandoned electronic products resources; harmless means decreasing the environment pollution which abandoned electronic products bring in the recycling link. It follows the principles of “polluter responsible” and each member on the supply chain legally shares the responsibility in a process during abandoned electronic products are being recycled.People’s Republic of China Circulation Economy Promotion Law,which was passed on 29 August,2008 and implemented on 01 January, 2009 stressed circulation economy and sustainable development concept to protect and improve environment by increasing the efficiency of resource consumption. Abandoned Appliances Electronic Products Recycling Control Ordinance, was issued formally on 25 February, 2009 and implemented on 01 January, 2011. This regulation was just for the abandoned electronic products recycling stage. Its aim was decreasing waste released and eliminating the hazardous materials via extracting recycle materials during dismounting and changing their physical or chemical characterization. It didn’t include the repair & reconditioning works against abandoned electronic products. Some other laws as,Solid Waste Pollution Prevention and Treatment Law, Clean Production Promotes Law, Product Quality Law etc. were also made by China. These rules purposes were providing some due legal grounds for electronic products recycling. But some operable, targeted, specific laws and regulations were still lacked. So strengthening work on this is necessary as law is the foundation and security to do every piece of work and has some certain compulsion and standard. (2) Carrying out tax incentives policy and promoting development of Closed-loop Supply Chain. At present, some manufacturing companies lack of strength, resources, technology equipment and they don’t have extra strength to manage the reverse supply chain, let alone combining the positive supply chain and the reverse one. So the government can provide some preferential policies like some subsidy and tax policy; Providing some certain financial rewards or preferential taxation policies to the companies who implement reverse logistics; encouraging the companies to conduct abandoned material reverse logistics activities. While for some companies with serious resource waste and environment pollution, can be imposed Peruvian tax to discipline them during production stimulating companies to do production technical innovation and industrial upgrading.(3) Adjusting upgrade of the property structure, prioritizing the development of renewable energy industry. China’s natural resources per capital is very low in the world and recycling rate for the resources is also very low. Data shows that developed countries recycling rate is 90% for the abandoned steel, copper and rubber while china’s are 45%, 30%, 40%. China could have had little resources and if the resource ratio continue to be so low, it will surely lead to the lack of product raw materials, and then will restrain economic growth. Thus it can be seen that it's very necessary to adjust upgrade of the property structure, to priorities the development of renewable energy industry and promote the reuse of resources. The government should strengthen these policies introductory, adjust to industrial policy in time, make a reasonable plan industry layout, focus on cooperation and exchange foreign developed counties, introduce foreign advanced technology and management experience and foster and develop recycle resource industries.(4) Government should strengthen avocation to raise all citizens the environmental awareness. So the government should play the leading role to promote environmental-protection knowledge to the public and train them the environmental-protection consciousness, for instance, dispatching booklets to citizens, marking environmental protecting signs in public places, posting environmental protecting knowledge in metro, bus and railway stations etc., also can introduce the environmental protecting into class, thus can realize the effect with the resources saving and environment protection.
3. The Development of Discarded Electronic Products Market in China and the Design of Recovery Mode
- As the improvement of our resident income level, the consumer’s demand of the electronic products is increasing .Meanwhile, the electronic products have the feature of vastly newest period. There are some useful resource in the abandoned electronic products, such as Copper, Aluminum, Iron and some kinds of rare metal, glass, paste etc. which have highly recycle value. The cost of get resource from the rebirth is more less than directly smelt and process form the mineral, raw material. Enhance the recycle of the abandoned electronic products have very important reality meaning on the development of recycle economy and overcome the resource shortage’s restrict to Chinese economy ‘s development. China as a big country of electronic production and consumption, regulate the abandoned electronic products reclamation and treatment will benefit on prevent and reduce environment pollution, boost resource general use, develop recycle economy, found conservation-oriented society.
3.1. The Development Status of Our Abandoned Electronic Products Market
- At present, the trend of our abandoned electronic products: First, from consume terminal recycle or through factory, retailer use the service of “old for new service” to recycle and then enter second-hand market and sell to low end consumers. Second, unwed, deal with or collect rare metal resource. Third, the final consumer directly abandon it. And nowadays the environment pollution problem are focus on the first and second trend: due to there are some unwed abandoned electronic products handwork workshop. They go for short-term profit, use open burning, acid soaking and other primitive methods to collect precious metal, then discharge waste gas, liquid, residue at their will. Those are very harmful to atmosphere, soil and water, also to people’s health. Though the government pay much attention to the environment and health problem which is triggered by electronic used products, the cooperation among different departments is not very good, then produce the regulatory gap. Thus, it is essential to strength law-based control for treatment of used electronic products to maintain sustainable development. The two issues reflected by now used electronic market are: the routine for recycle of the e-waste is not norm, the low-level for treatment cause environmental pollution and waste of resources; second, a new economic pattern exits in the back of the recycling for e-wastes. Once the issue is solved, the e-waste’s pollution will be good. So a norm recycle system is presented quite important. As a whole, the small veneers are the essential part of recycling for e-wastes. In the process, they cannot satisfy environmental requirements. In spite of the government Promulgated Electronic products recycling waste management regulations, but only the efforts of the government and manufacturer is not enough, it need supports from all of us.
3.2. Product Recycling System in China of Fuji Xerox
- The system of Fuji Xerox is conducted via the integration of resources circulation system. It is the first one for used electronic products and Se drum, reuse the new resources come from the e-wastes. The collected used products are divided into 70 parts, as iron, aluminum, glass, lens and so on. These parts will be reused or reproduced into raw material. These raw materials would passed on to partners to manufacture different kinds of products. During this process, no waste, no bury, no pollution. At present, Fuji Xerox do not benefit from this system, that is the reason why domestic firms pay a negative attitude to recycling system of e-waste. See the practice world widely, “manufacture-recycle” duty of factory is very clear. To companies, the obstacle is cost and benefit problem for investing this system. Besides, domestic firms lack of the power for self-construction resource recycling, the reason is that it is difficult to reclaim used products. Consequently, we need to build a close-loop supply chain to encourage every part to join in. Only in this way, can minimize the social cost.
3.3. The Design of the Recovery Mode
- For the large electronics manufacturers, through their own sound channels and platforms to achieve the recycling of discarded electronic products. Most of the small manufacturers lack the resources and funding to implement the recycling of waste electronic products. Therefore, the government departments should be preferential policies on third-party recycle. Through tax breaks and special subsidies to support the growth of third-party recycle. In China, Japan, South Korea and other Asian countries, it is generally rich in lithium, titanium, gold, indium, silver, cobalt and palladium and other precious metal waste electrical and electronic products called "urban mines". Third-party recycle and local government should cooperative use of "urban mines". Related research shows that in 2010, the retirement of home appliances in Chinese society to reach 50 million units, more than 1.5 million tons. In addition, computer ownership in China nearly 20 million units, about 190 million mobile phones, there are about 5 million computers, tens of millions of mobile phones into disuse. Improper handling of this e-waste will be cause serious pollution to the atmosphere, water and soil .the impact of e-waste on human health has become a prominent social problem. The city mine accumulation trend corresponds to the urgent needs of our mineral resources, the annual consumption of mineral resources in China has surpassed the U.S. as the world's resource consumption superpower. Large number of foreign raw ore to be imported annually to meet domestic market demand, China's "urban mines" of the recovery rate is significantly lower, such as cobalt and nickel resource recovery rate of only about 20% or even less than 10% in some provinces and municipalities. Due to domestic potential for this market, it is necessary to support third-party recovery, the establishment of collection points and acquisition of multi-channel point, motivate the main positive. to market participants.
4. Electronic Product Analysis-Based on Home Appliance Product
- The electronics industry is a rapidly growing industry, product updates upgrade, scrap electronic products will be more and more, China's electronic product growth rate of 3% -5% per year, this rate is three times the growth of municipal solid waste speed. Electronic products are convenience for human life, it also brings a lot of waste electronic products at the same time .On one hand, they contain harmful chemicals on the environment caused by pollution, on the one hand, which contains a lot of re-use a variety of precious metals, etc. , with high economic value and use value. This section will combine the electronic products in the appliance market, to provide a basis for exploration and research. This section of the country's leads to its recovery. As already mentioned the “New for Old " policy began in June 2009, involving mainly five categories of televisions, refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, computers in household electrical appliances, first in Shanghai, Beijing, Tianjin, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Guangdong, Shandong, Changsha, Fuzhou, nine pilot provinces and cities, and gradually extended to 19 provinces and cities to June 2010. Trade-in policy is aim to the urban and rural residents, the Government is also increase investment, and financial subsidies to consumers. This policy central financial subsidies accounted for 80% subsidy which accounted for 20% of the local financial. Consumers in the replacement of old home appliance in addition obtains the recycling price ,what is more, still can be obtained the purchase price of 10% of the price subsidies in buy new appliances, consumers have benefited, which greatly stimulated the consumers' purchasing desire that the policy is fairly obvious leading role. In short, the "New for Old" policy may implement to greatly enhance the consumption of appliances, which not only bring profits to the manufacturers and retailers, but also consumers gain the benefits. However, it also brought a large number of waste household electrical appliances, which requires us to enjoy concessions, think of how scientific reprocessing and reuse of the waste products at the same time, to reduce its impact on the environment.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- This paper was supported in part by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University under grant number NCET-10-0118, in part by 2013 year Ministry of Culture art of Scientific Research Project under grant number 13DH50, in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant number 71040009.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML