-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Materials and Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2166-5346 e-ISSN: 2166-5354
2024; 14(2): 13-18
doi:10.5923/j.ijmc.20241402.01
Received: Feb. 19, 2024; Accepted: Mar. 4, 2024; Published: Mar. 6, 2024

Study of Biologically Active Substances in Gel Obtained on the Basis of Local Plant Raw Materials
D. R. Gulyamova1, N. A. Yunuskhodjayeva2, X. O. Tursunov3, N. E. Yunuskhojiyeva4
1Assistant of the Tashkent Pharmaceutical Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2DSc of the Tashkent Pharmaceutical Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3PhD, State Agency for the Development of the Pharmaceutical Industry under the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan "State Center for Expertise and Standardization of Medicines, Medical Devices and Medical Equipment", Tashkent, Uzbekistan
4Student of the Tashkent Pharmaceutical Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: D. R. Gulyamova, Assistant of the Tashkent Pharmaceutical Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this article, a quantitative analysis of biologically active substances in a gel obtained from local plant materials was carried out. The aerial part of plants (Urtica dioica U.), (Polygonum hydropiper L.) and (Polygonum aviculare L.) were used as local plant materials. Studies of literature data showed that these medicinal plants contain valuable biologically active substances that have a healing effect on the human body. The article deals with the development of gel technology based on the liquid extract Hemostat. The choice of the base and excipients, the specifics of the technology. Special attention is paid to the choice of base concentration. Using technological methods of analysis, the composition and technology of a dental gel based on the liquid extract Hemostat FSP 42 Uz-22477731-3757-2019 was experimentally substantiated and developed. A promising and fundamental method for the treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa is the use of rational dosage forms - a transdermal system - a gel with good absorption based on active medicinal substances. Using high performance liquid chromatography, the qualitative and quantitative content of flavonoids and vitamin К1 was studied.
Keywords: Gel, Base, Urtica dioica, Polygonum hydropiper, Polygonum aviculare, High performance liquid chromatography, Quantitative determination of flavonoids, Rutin, Quercetin, Vitamin К1
Cite this paper: D. R. Gulyamova, N. A. Yunuskhodjayeva, X. O. Tursunov, N. E. Yunuskhojiyeva, Study of Biologically Active Substances in Gel Obtained on the Basis of Local Plant Raw Materials, International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, Vol. 14 No. 2, 2024, pp. 13-18. doi: 10.5923/j.ijmc.20241402.01.
1. Introduction
- Despite the rich range of drugs of synthetic origin, plant-based drugs do not lose their popularity. In dental practice, for the treatment of inflammation in the mouth and gums, more and more preference is given to the use of herbal medicine [1-8]. Phytotherapy is a method of treatment based on the use of medicinal plants and complex preparations based on them. Plants synthesize aromatic substances, most of which are phenols and their oxygen-substituting derivatives, such as tannins, useful for maintaining human and animal health. [8-15] Many of them, in particular alkaloids, are defense mechanisms of plants against microorganisms, insects and herbivores [16]. Therefore, phytopreparations, as a rule, have a pronounced immunostimulating effect (effect). Stinging Urtica dioica L., family Urticaceae-nettles is one of the most popular medicinal plants in traditional and folk medicine. Preparations from Urtica dioicas are used as a hemostatic, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and choleretic agent. [17-19] Medications based on stinging nettle "Prostaforton" and "Bazoton" are used to treat prostate adenoma and prostatitis, which are among the most common diseases in men [19-25]. The beneficial properties of medicinal plants depend on the content of so-called active substances in them, such as macro- and microelements, vitamins К1, B, flavonoids, saponins, alkaloids, essential oils, organic substances [26-30]. Infusion, liquid extract, powder and juice of Urtica dioica are used for acute and chronic enterocolitis with intestinal, uterine bleeding and as a multivitamin and diuretic [30-32].The pharmacological action of drugs based on the herb of Polygonum hydropiper L., Buckwheat family - Polygonaceae is due to a number of substances, including flavonoids, vitamin К1, terpenoids, carotenoids, however, literary data regarding their component composition are quite contradictory [1-3]. So, in the domestic literature it is reported that the herb of Polygonum hydropiper contains quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, myricetin, isorhamnetin, rhamnasin, quercitrin, hyperoside, persicarin 7-methyl ether, rutin. According to foreign scientists, the herb of this plant, along with quercetin and quercitrin, contains taxifolin, quercetin-3-sulfate. [1-5]The herb Polygonum aviculare L. is used as a source of flavonoids that have anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictive effects. [8]. Infusions of herb Polygonum aviculare are effective in bleeding, sexual disorders. Knotweed has antibacterial and antiviral (anti-HIV) activity, is part of medicinal preparations (phytolysin, tussiflorin, Zdrenko collection). Herbal preparations of P. aviculare are used for urolithiasis, uric acid diathesis, and skin diseases [12-15]. They are also effective in functional insufficiency of the liver and kidneys, inhibit the development of liver fibrosis. Glycosylated quercetin derivatives are used in cancer prevention [16-18].The aim of the work is to study the qualitative and quantitative content of flavonoids, carotenoids, and vitamin К1 in the gel obtained from local plant materials using high performance liquid chromatography [20].
2. Materials and Methods
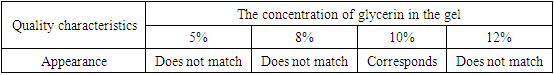
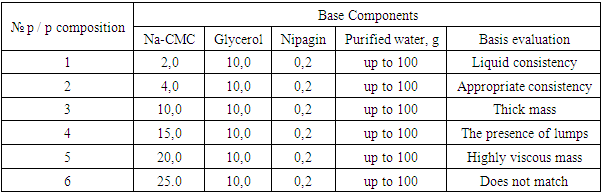
- To obtain the gel, we chose as an active pharmaceutical ingredient: liquid extract "Hemostat", with a pronounced anti-inflammatory and hemostatic effect, which helps wound healing and bleeding of the gums [9].The following were used as excipients: sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (NaCMC - the basis of the gel), nipagin (preservative), purified water (solvent, pharmacologically indifferent, is a universal solvent for a number of biologically active substances), glycerin (plasticizer, is a viscous transparent, colorless liquid, unlimitedly soluble in water. Sweet in taste, which is why it got its name, it dissolves many substances well). Hydrophilic pressure-sensitive bases can provide high adhesion to both dry substances and liquid extracts, and are also suitable for use in the development of the composition of dental gels [9]. To increase the plasticity of the gel, glycerol was introduced at a concentration of 3-15%. The results of the experiment are presented in Table 1.
|
|
|
|
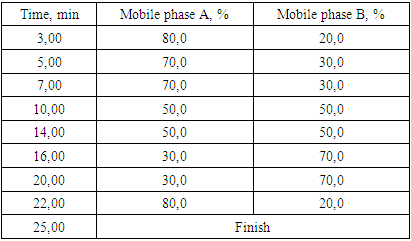
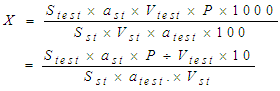 where:Sst – the area of the main peaks in the chromatogram of solutions of RSO of rutin and quercetia, mAU;Stast – peak area of rutin and quercetin on the chromatogram of the test sample, mAU;ast – weighed RSO of rutin and quercetin, g;P – the content of rutin and quercetin in the standard sample, %.Determination of vitamin К1. Liquid chromatograph with isocratic pump and variable wavelength spectrophotometric detector, type Agilent 1200 series or equivalent. Chromatographic column with a size of 3.0x150 mm, filled with Zorbax Eclipse XDB C-18 sorbent, with a particle size of 3.5 μm or similar; mobile phase: methanol: acetonitrile (55:45%/%) filtered and degassed in any convenient way; detection wavelength - 262 nm; mobile phase flow rate - 1.0 ml/min; temperature - room; the volume of the injected sample - 20 µl; the analysis time should be at least 3 times the retention time of the main peak (vitamin К1). Alternately injected into the chromatograph injector, 20 μl of solution A, B each, and chromatograms were obtained. The content of related compounds was evaluated by comparing the peak areas in the chromatograms obtained with solutions A and B. The limits of the content of related compounds:- the area of the vitamin К1 peak on the chromatogram of solution A should not exceed the sum of the areas of all peaks on the chromatogram of solution B by more than 2 times (no more than 10.0%);- the peak area of the related compound A in the chromatogram of solution A should not exceed the sum of the areas of all peaks in the chromatogram of solution B (not more than 5.0%);- the area of the peaks of individual impurities in the chromatogram of solution A should not exceed the sum of the areas of all peaks in the chromatogram of solution B by more than 0.4 times (no more than 2.0%); the sum of the peak areas of unidentified impurities in the chromatogram of solution A should not exceed the sum of the areas of all peaks in the chromatogram of solution B by more than 1.4 times (no more than 7.0%); do not take into account peaks with areas less than 0.04 of the sum of the areas of all peaks in the chromatogram of solution B (0.2%).Preparation of a solution of RSO rutin. 0.0055 g of rutin (FS 42 Uz-0137-2013) was dissolved in methanol in a pycnometer with a capacity of 10 ml and the volume was adjusted to the mark with the same solvent.Preparation of a solution of RSO quercetin. 0.0054 g of quercetin (No. UA/0119/0101 23.08.2013) was dissolved in methanol in a pycnometer with a capacity of 10 ml and the volume was adjusted to the mark with the same solvent.Preparation of the test solution. About 1 g (accurately weighed) of the gel was placed in a 100 ml flask, and 10 ml of 70% ethanol was added. After complete dissolution, it was filtered through a Millipore brand filter.Preparation of a solution of RSO vitamin К1. About 0.50 g (accurately weighed) vitamin К1 was transferred into a 100 ml volumetric flask, dissolved in the mobile phase and the solution volume was brought up to the mark. 2.5 ml of solution A was transferred into a 50 ml volumetric flask and the solution volume was adjusted to the mark. B).Preparation of the test solution (vitamin К1). About 2.5 g (accurately weighed) of the drug was transferred into a volumetric flask with a capacity of 100 ml, dissolved in the mobile phase and the volume of the solution was brought up to the mark. a solution of 2.5 ml of solution A was transferred into a volumetric flask with a capacity of 50 ml and the volume of the solution was brought up to the mark fast solution B).
where:Sst – the area of the main peaks in the chromatogram of solutions of RSO of rutin and quercetia, mAU;Stast – peak area of rutin and quercetin on the chromatogram of the test sample, mAU;ast – weighed RSO of rutin and quercetin, g;P – the content of rutin and quercetin in the standard sample, %.Determination of vitamin К1. Liquid chromatograph with isocratic pump and variable wavelength spectrophotometric detector, type Agilent 1200 series or equivalent. Chromatographic column with a size of 3.0x150 mm, filled with Zorbax Eclipse XDB C-18 sorbent, with a particle size of 3.5 μm or similar; mobile phase: methanol: acetonitrile (55:45%/%) filtered and degassed in any convenient way; detection wavelength - 262 nm; mobile phase flow rate - 1.0 ml/min; temperature - room; the volume of the injected sample - 20 µl; the analysis time should be at least 3 times the retention time of the main peak (vitamin К1). Alternately injected into the chromatograph injector, 20 μl of solution A, B each, and chromatograms were obtained. The content of related compounds was evaluated by comparing the peak areas in the chromatograms obtained with solutions A and B. The limits of the content of related compounds:- the area of the vitamin К1 peak on the chromatogram of solution A should not exceed the sum of the areas of all peaks on the chromatogram of solution B by more than 2 times (no more than 10.0%);- the peak area of the related compound A in the chromatogram of solution A should not exceed the sum of the areas of all peaks in the chromatogram of solution B (not more than 5.0%);- the area of the peaks of individual impurities in the chromatogram of solution A should not exceed the sum of the areas of all peaks in the chromatogram of solution B by more than 0.4 times (no more than 2.0%); the sum of the peak areas of unidentified impurities in the chromatogram of solution A should not exceed the sum of the areas of all peaks in the chromatogram of solution B by more than 1.4 times (no more than 7.0%); do not take into account peaks with areas less than 0.04 of the sum of the areas of all peaks in the chromatogram of solution B (0.2%).Preparation of a solution of RSO rutin. 0.0055 g of rutin (FS 42 Uz-0137-2013) was dissolved in methanol in a pycnometer with a capacity of 10 ml and the volume was adjusted to the mark with the same solvent.Preparation of a solution of RSO quercetin. 0.0054 g of quercetin (No. UA/0119/0101 23.08.2013) was dissolved in methanol in a pycnometer with a capacity of 10 ml and the volume was adjusted to the mark with the same solvent.Preparation of the test solution. About 1 g (accurately weighed) of the gel was placed in a 100 ml flask, and 10 ml of 70% ethanol was added. After complete dissolution, it was filtered through a Millipore brand filter.Preparation of a solution of RSO vitamin К1. About 0.50 g (accurately weighed) vitamin К1 was transferred into a 100 ml volumetric flask, dissolved in the mobile phase and the solution volume was brought up to the mark. 2.5 ml of solution A was transferred into a 50 ml volumetric flask and the solution volume was adjusted to the mark. B).Preparation of the test solution (vitamin К1). About 2.5 g (accurately weighed) of the drug was transferred into a volumetric flask with a capacity of 100 ml, dissolved in the mobile phase and the volume of the solution was brought up to the mark. a solution of 2.5 ml of solution A was transferred into a volumetric flask with a capacity of 50 ml and the volume of the solution was brought up to the mark fast solution B).3. Results and Its Discussion
- Chromatograms of the test sample are shown in Figures 1, 2. Chromatograms of working standard samples of vitamin К1, rutin.
 | Figure 1. Gel chromatogram (rutin, quercetin) |
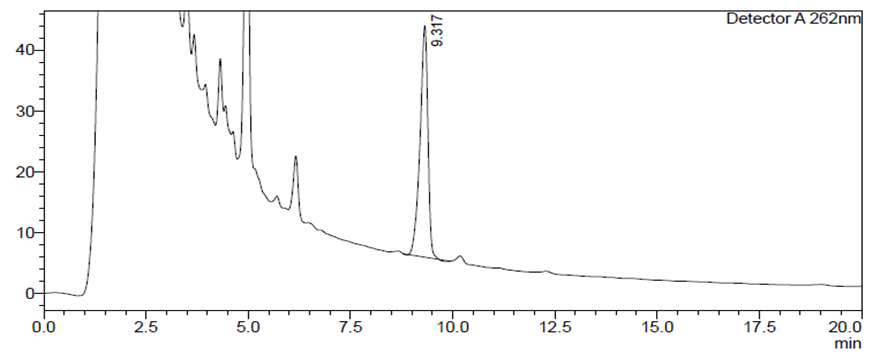 | Figure 2. Gel chromatogram. (vitamin К1) |
|
|
4. Conclusions
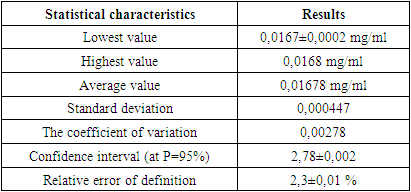
- A dental gel was developed based on local plant materials, and bases for the gel were also selected. As excipients selected: sodium carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC - the basis of the gel), nipagin as a preservative, purified water and glycerin.To study biologically active substances in the gel, HPLC methods have been developed for the quantitative determination of flavonoids and vitamin К1. The content of rutin was 0.051 mg/ml, and vitamin К1 was 0.0168 mg/ml. The relative error in the content of rutin was 3.68%, vitamin К1 2.3%.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML