Alfiya Oserbaeva1, Nafisa Ismailova2, Makset Ayimbetov2
1Tashkent Chemical-Technological Institute, Navoiy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Karakalpak State University, Ch. Abridov, Nukus, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Alfiya Oserbaeva, Tashkent Chemical-Technological Institute, Navoiy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
In this research work, Langmuir isotherms, equilibrium constant of the process, thermodynamic quantities, temperature dependence of ∆G of the adsorption process and the mechanism of corrosion of metal samples in various acidic and hydrogen sulphide solution environments with the help of composite inhibitors containing nitrogen, amide and phosphorus were studied. If H2S participates in the environment where a metal sample is being corroded, it can form sulfides with a complex composition in the form of HS- or S-2 ions on the surface of iron in the form of FexSy, as well as HS- anions adsorbed on iron, and iron in the solution environment with H2S It was found that the corrosion process is gradual and H2S is adsorbed on the metal surface at the first stage, then corrosion starts in the cathodic and anode processes and the adsorption rate of S2- ion depends on the temperature and the concentration of H2S. When the IKA-8 inhibitor is introduced into the system, the equilibrium constant value of the adsorption-desorption process is large, and the negative value of ∆Gads determines that the adsorption of the inhibitor on the metal surface is irreversible.
Keywords:
Inhibition, Steels, Industrial metals, Acidic and hydrogen sulfide, Solutions, Composite inhibitors, Adsorption isotherms, Equilibrium constant, Thermodynamic quantities
Cite this paper: Alfiya Oserbaeva, Nafisa Ismailova, Makset Ayimbetov, Isotherms of Adsorption Process in Hydrogen Sulfide Medium, International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, Vol. 13 No. 3, 2023, pp. 42-45. doi: 10.5923/j.ijmc.20231303.02.
1. Introduction
Corrosion is a common problem for industrial metals and directly impacts their cost and safety. Presently, there are many ways to retard metal corrosion, such as the optimization of the metal constituents and smelting process, organic/inorganic coating technology, and the addition of corrosion inhibitors, among which the addition of corrosion inhibitors is the most economical and commonly used [1-4]. Most of the organic inhibitors have the ability to adsorb on the metal surface and form hydrophobic film layers, limiting the transmission of aggressive particles. The adsorption capacity of this type of inhibitor is related to the presence of heteroatoms such as N, O, P and S in the molecular structure [5,6].
2. Research Methods
Considering the above, the thermodynamics of adsorption and the physico-chemical basis of the inhibition process were studied based on Langmuir's molecular-kinetic theories. In order to calculate the value of the degree of saturation of the surface with an inhibitor (θ), the following equation was also used based on the values of the dissolution rate when the inhibitor was introduced into the corrosion process (Kinh) and without (K0)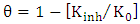 | (1) |
Corrosion of St.3 and St.12 steel samples in acidic and hydrogen sulphide environments with composite IKA-8 additives was studied according to the Langmuir isotherm equation: | (2) |
here, 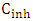 – inhibitor concentration,
– inhibitor concentration, 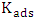 – adsorption and desorption equilibrium constant.
– adsorption and desorption equilibrium constant.
3. Results and Discussion
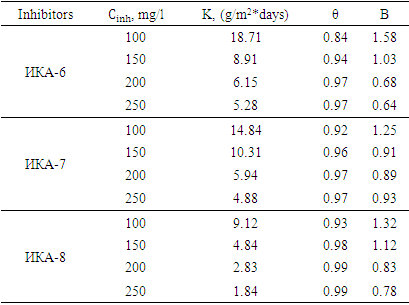
The dependence of the level of surface filling on the concentration of IKA-6, IKA-7, and IKA-8 inhibitors on the corrosion protection of St.3 steel sample in 3.0% H2SO4 acidic environment is shown by Langmuir isotherms given above according to the equation (2) with 3.0% H2SO4 and studied in the media of 5.0% H2S solutions (Table 1).Table 1. Values of surface filling level (θ) and adsorption equilibrium constant (B) of different inhibitors in 3.0% H2SO4 environment (Ст.3 – steel sample, Т=323К)
 |
| |
|
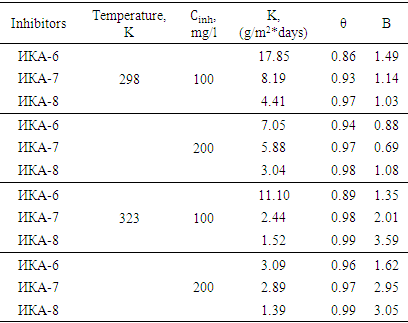
It was found that the correlation coefficient and thermodynamic values are different in the temperature range of 298÷343°C by the method of correlation through determined isotherm curves (straight line lying on the curve). This situation indicates that the IKA-8 inhibitor has different protection efficiency at different temperatures. [5,6].At the same time, it was found that the adsorption properties of the IKA-8 inhibitor depend on the number of electron-donating heteroatoms included in its composition, and how much heteroatoms are present ensures chemical sorption on the surface of the metal sample. Based on the results of the experiments, it was found that the inhibition of the IKA-8 composite inhibitor on the surface of the metal sample in acidic and H2S environments is very high.In the presence of the inhibitor, the protection of the St.3 steel sample from corrosion in 5.0% H2S atmosphere as a function of the concentration and temperature of the IKA-6, IKA-7 and IKA-8 inhibitors is presented in Table 2.Table 2. Values of surface filling level (θ) and adsorption equilibrium constant (B) of different inhibitors in 5.0% H2S environment (Ст.3 – steel sample)
 |
| |
|
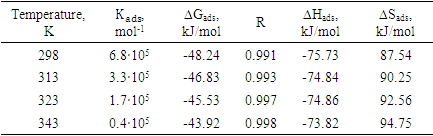
Based on the results of the experiments, it was found that during the adsorption process in the presence of IKA-6, IKA-7 and IKA-8 multi-component composite inhibitors, the high filling of the surface of the metal sample depends on the concentration of the inhibitors in the solution and the temperature is well explained by Langmuir isotherms.Also, the rate of dissolution of metal samples (K) depends on the content of the inhibitor, and even when the inhibitor has a low concentration, the degree of protection of metal samples from corrosion is 96-99.6%.The degree of filling of the surface of the metal sample with a coating layer (initial mono-molecular layer) is very high, which indicates that the adsorption equilibrium constant depends on the content of inhibitors. Thus, it is confirmed that IKA-6, IKA-7 and IKA-8 inhibitors are able to protect the above metal sample in various aggressive environments.The results of the calculation of thermodynamic quantities are presented in tables 3 and 4. Experiments show that the adsorption-desorption process of the adsorption-desorption process, which takes place in the system, has a large equilibrium constant value, and this condition shows that the IKA-8 composite inhibitor protects metal samples from corrosion in acidic and hydrogen sulphide environments. showed that it is of high value. According to tables 3 and 4, the negative value of the process ∆Gads indicates that the adsorption of the inhibitor on the metal surface is self-irreversible.Table 3. Thermodynamic parameters of the process of adsorption of IKA-8 composite inhibitor in of 3% H2SO4 environment (Ст.3 – steel sample, Cinh = 100mg/l)
 |
| |
|
Table 4. Thermodynamic parameters of the process of adsorption of IKA-8 composite inhibitor in of 5% H2S environment (Ст.3 – steel sample, Cinh = 100mg/l)
 |
| |
|
When the St.3 steel sample was added to the environment of 3.0% H2SO4 solution with the IKA-8 composition inhibitor, the value of ∆Gads changed from -48.24 kJ/mol-1 to -43.92 kJ/mol-1 in the temperature range of 298÷343K. This inhibitor St. 3 indicates that the surface of the steel sample is affected by mixed adsorption, that is, the inhibitor is adsorbed as a result of physical and chemical sorption processes.Adsorption of IKA-8 inhibitor in 3.0% H2SO4 environment of St.3 steel sample ∆Hads value was found to be between 75.73 and 73.82 kJ/mol, and 77.44 and 74.29 kJ/mol in 5.0% H2S environment. The negative value of ∆Hads, indicates that the adsorption of IKA-8 inhibitor on the surface of the metal sample is an exothermic process. Based on the data presented in the literature, it is determined that ∆Hads>0 in the process of endothermic adsorption. If adsorption occurs exothermicly, then ∆ Hads >0<0, and in such conditions physical or mixed type sorption takes place.It was found that the values of ∆Sads and ∆Hads, calculated by the relationship between ∆Gads and process temperature, calculated according to the results of experiments, are equivalent (Fig. 1). The value of ∆Gads was found to change in a linear relationship with increasing process temperature. It was found that the effectiveness of the IKA-8 composite inhibitor in protecting the metal sample from corrosion in acidic and hydrogen sulphide environments does not change significantly with increasing temperature, and during the adsorption process, physical sorption occurs more and chemical sorption occurs relatively less.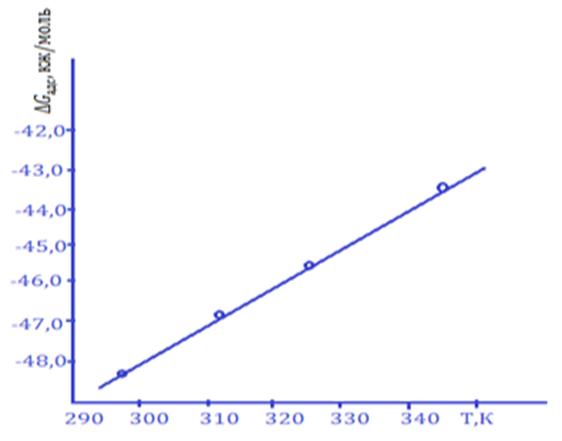 | Figure 1. Temperature dependence of the ∆Gads value of the adsorption process (Ст.3 – steel sample, Cinh=100mg/l) |
The obtained results showed that the adsorption of the IKA-8 composite inhibitor on the St.3 steel sample was carried out in the temperature range of 298÷343, and it was found that the inhibitor is effective in protecting the metal from corrosion even in these aggressive environments, because the adsorption of the IKA-8 inhibitor at a temperature of 298K ∆Hads -78.85 kJ/mol is equal to Therefore, the IKA-8 inhibitor can be adsorbed by strongly binding to the surface of the metal sample even in alkaline-saline environments. Langmuir adsorption isotherm curves of IKA-8 composite inhibitor in alkaline-saline environment were studied (Figures 2-3).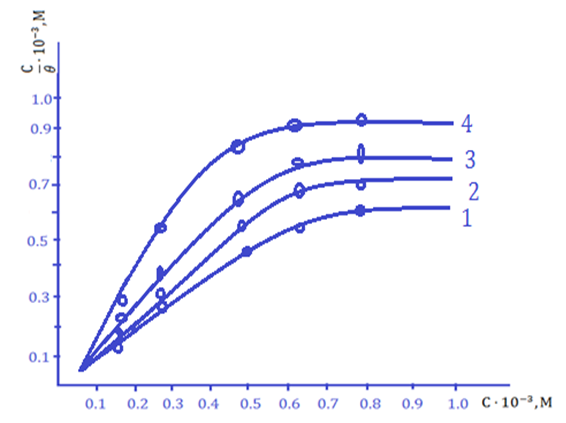 | Figure 2. Langmuir adsorption isotherm of IKA-8 inhibitor in alkaline-saline medium (Ст.3 – steel sample, Cinh=100mg/l) |
 | Figure 3. IKA-8 inhibitor adsorption ∆Gads value as a function of temperature (St.3 – steel sample, in 3.0% NaOH + 3.0% NaCl environment, Cinh=100mg/l) |
It was found that the ∆Gads value of the IKA-8 inhibitor metal sample adsorbed in an alkaline-saline environment decreases with increasing process temperature (Fig. 3). In this case, the protective layer created by the inhibitor on the surface of the metal sample in alkaline-saline environment does not dissolve in this environment, that is, it is solid.
4. Conclusions
With the use of composite inhibitors, the activation energy and thermodynamic calculations of St.3 and St.12 steel samples in various environments were shown to have a high negative value of ∆Geff. IKA-6, IKA-7, and IKA-8 filled the surface of the metal sample in the process of adsorption in the presence of multicomponent composite inhibitors. The dependence of inhibitors on concentration in solution and temperature was well explained by Langmuir isotherms.It was shown that the rate of deposition of additional reagents with surface-active properties of phosphate ions on the surface of the steel sample is uniform according to Langmuir's law, and the formation of a mono-molecular layer that prevents metal corrosion is shown.
References
| [1] | Семенова И.В., Флорианович Г. М., Хорошилов А.В. Коррозия и защита от коррозии. –М., 2002, С.336. |
| [2] | Килимник А.Б., Гладышева И.В. Химическое сопротивление материалов и защита от коррозии // Учебное пособие. –Тамбов, 2008, С.80. |
| [3] | Reyes-Dorantes, E.; Zuniga-Diaz, J.; Quinto-Hernandez, A.; Porcayo-Calderón, J.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, JG; Martinez-Gomez, L.J. Chem. 2017. doi: 10.1155/2017/2871034. |
| [4] | Porcayo-Calderón, J.; Martinez de la Escalera, LM; Canto, J.; Casales Diaz M. Intern. J. Electrochem. scientific 2015, 10, 3160-3176. |
| [5] | Осербаева А.К., Нуруллаев Ш.П. Изучение защитных свойств новых ингибиторов коррозии сталей. Журнал «Точная наука». Сборник сталей международной естественнонаучной конференции, Кемерово, 2018, С. 3-8. |
| [6] | Осербаева А.К., Нуруллаев Ш.П. Защита действия азот и фосфорсодержащих соединений при кислотной и сероводородной коррозии металлов // Сборник трудов Международной научно-практической конференции “Общество-наука-инновации”, Часть2, г. Оренбург, 2019, С.33-36. |



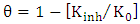

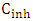 – inhibitor concentration,
– inhibitor concentration, 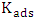 – adsorption and desorption equilibrium constant.
– adsorption and desorption equilibrium constant.


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML


