-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Materials and Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2166-5346 e-ISSN: 2166-5354
2016; 6(1): 12-18
doi:10.5923/j.ijmc.20160601.03

Aqueous Extracts of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham Roots as Eco-Friendly Corrosion Inhibition for Mild Steel in 0.5 M KOH Medium
Lebe Nnanna1, George Nnanna2, Justus Nnakaife2, Nneka Ekekwe3, Peter Eti4
1Materials Science Group, Department of Physics/Electronics, Abia State Polytechnic, Aba, Nigeria
2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University, Calumet, Indiana, USA
3Department of Chemistry, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand
4Department of Mechanical Engineering, Abia State Polytechnic, Aba, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Lebe Nnanna, Materials Science Group, Department of Physics/Electronics, Abia State Polytechnic, Aba, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This work is devoted to examine the effectiveness of the aqueous extracts of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root on corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M KOH solution using the weight loss measurement at room temperature and concentration effects. Potentiodynamic polarization method was employed to evaluate corrosion rate and inhibition efficiency. Corrosion inhibition efficiency of 84.02% was achieved at 0.3 g/L in 0.5 M KOH of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extract. It was found that the root extracts acted as a good inhibitor for the tested environment. The inhibitive action of the extract is discussed with a view to adsorption of its components onto the mild steel surface which made a barrier to mass and charge transfer. The adsorption of extract components onto the steel surface was found to be a spontaneous process and increases the activation energy of the corrosion process. The inhibition efficiency is greatly reduced as the temperature increased. Experimental results show that corrosion inhibition efficiency increases with concentration of the sample extract. Furthermore, the extract and corroded metals were characterized by Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and Scanning electron micrograph techniques. Adsorption behavior of the extract was also studied, which suggest Langmuir isotherm model as a most suitable adsorption mechanism. The data derived from the Potentiodynamic polarization confirmed the fact that corrosion inhibition mechanism was affected by the studied root extracts.
Keywords: Corrosion inhibition, Adsorption, Mild steel, Inhibition efficiency, Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham
Cite this paper: Lebe Nnanna, George Nnanna, Justus Nnakaife, Nneka Ekekwe, Peter Eti, Aqueous Extracts of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham Roots as Eco-Friendly Corrosion Inhibition for Mild Steel in 0.5 M KOH Medium, International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, Vol. 6 No. 1, 2016, pp. 12-18. doi: 10.5923/j.ijmc.20160601.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The environmental toxicity of organic corrosion inhibitors has prompted the search for green corrosion inhibitors as they are biodegradable, do not contain heavy metals or other toxic compounds. In addition to being environmentally friendly and ecologically acceptable, plant products are inexpensive, readily available and renewable. Investigations of corrosion inhibiting abilities of tannins, alkaloids, organic, amino acids, and organic dyes of plant origin are of interest [1].Corrosion inhibitors are one of the practical and cost effective methods of controlling metallic corrosion. They may be inorganic or organic substances. Inorganic substances suitable as metal corrosion inhibitor must easily oxidize the metal to form an impervious layer which prevent direct ions-metal interaction and hence retard the rate of metal dissolution in the medium. The organic counterpart, on the other hand, must possess features including presence of heteroatoms and/or double bonds, large surface area, active centre, etc. which upon adsorption on the metal surface will blanket a large area of the metal and thus isolate it from the aggressive ions present in the environment. The use of inorganic (silicates, nitrates, nitrites, molybates, phosphates, and borates) and organic (predominantly, those with O, N, S, and P heteroatoms) compounds have been reported in the literature as metal corrosion inhibitors in different corrosive environments [2-6]. However, the toxic nature of most inorganic metal corrosion inhibitors and the exorbitant prices of the organic counterparts are the major setbacks for their continuous use. The search for an efficient inhibitor for metal inhibitor for metal corrosion in different aggressive media has, in recent times, taken a new dimension owing to the clarion call for green chemistry. Moreover, since the whole idea of metal protection is anchored on economic gain and environmental sustainability, the substance to be used as metal corrosion inhibitor must be cheap, readily available, and environmentally friendly. Hence, research activities are geared towards finding a replacement for inorganic and organic metal corrosion inhibitors. Plant is one of the sources of cheap, readily available, and non-toxic green metal corrosion inhibitors. Plant products are organic in nature, and contain certain photochemical including tannins, flavonoids, saponins, organic and amino acids, alkaloids, and pigments which could be extracted by simple less expensive procedures. Extracts from different parts of plant have been widely reported as effective and good metal corrosion inhibitors in various corrosive environments [7-11]. To enhance the efficiency of metal corrosion inhibitors, extensive studies have been undertaken to identify the synergistic effect of other additives. [12] noted that synergism provides a way of improving the inhibitive force of inhibitor, decreasing the quantity of inhibitor usage, and diversifying the application of the inhibitor in an aggressive environment. The present work reports on the inhibitive effect of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extracts for mild steel in hydrochloric acid.Inhibitors are commonly used to prevent metal dissolution as well as acid consumption and retard the corrosive attack on metallic materials. Corrosion inhibitors are chemical compounds used in small concentrations in industry to reduce the corrosion rate of metals and alloys in contact with aggressive environment, and therefore, retard the corrosion process and keeps its rate to a minimum and thus prevents economic losses due to metallic corrosion. The mechanism action of inhibitors is of great importance and depends on their formulation as well as on their rational use in various environments. The electronic characteristic of the adsorbate molecules, the solution chemical composition, the nature of metallic surface, the temperature of the reaction, the immersion time and the electrochemical potential at the metal–solution interface determine the adsorption degree and hence the inhibition efficiency [13]. Corrosion inhibitors synthetic chemicals are widely used to protect metals against corrosion, but, Most of them are not environment friendly due to their toxicity levels, bioaccumulation and/or biodegradability [14]. Hence, the research of new corrosion inhibitors non-toxic, eco-friendly, natural, at low or ‘‘zero’’ environmental impact are desired [15]. Plant extract is rich source of naturally synthesized chemical compounds, readily available low-cost and eco-friendly, and can be obtained through simple extraction process with low cost as well as biodegradable [16].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
- A flat sheet of mild steel 0.05 cm in thickness with the following composition: C = 0.05%; Mn = 1.13%; Si = 0.05%; P = 0.91%; S = 0.85%; Cu = 0.09%; Pb = 0.15%; Ve 0.13%; Mo = 0.08%; and the balance Fe was used in the study. The mild steel was mechanically press-cut into coupons of 2 cm × 2 cm dimensions for weight loss measurements and 1 cm × 1 cm for electrochemical measurements. The coupons were polished with different grades (# 400, 600, 800 and 1000) silicon carbide paper, degreased in absolute ethanol, dried in warm air and stored in moisture-free desiccators prior to use. The aggressive medium was 0.5 M KOH prepared from 98% analytical grade supplied by Sigma-Aldrich. Deionised water was used for the preparation of all reagents. The Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root was obtained from the suburb of Owerri, Nigeria, air dried and ground to fine powder. 10 g of the ground roots was extracted using reflux apparatus for 3 h. The extracts were made into various concentrations. All chemicals used for preparing the test solutions were of analytical grade and the experiments were carried out at room temperature, 30±1°C.
2.2. Weight Loss Measurements
- Weight loss measurements were performed using 250 ml capacity beakers containing 200 ml test solution under total immersion in stagnant aerated condition at 30-45°C maintained in a thermostat water bath. The pre-cleaned and weighed mild steel coupons were suspended in beakers with the help of rods and hooks. The coupons were withdrawn at 2 h interval progressively for 24 h, cleaned as previously reported and reweighed. The weight loss in grams was taken as the difference in the weight of the mild steel coupons before and after immersion in different test solutions. Tests were performed for the blank solution (0.5 M KOH), Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extract concentrations of 0.1 – 0.5 g/l at ambient temperature. The experiments were done in triplicate to ensure reproducibility. The standard deviation values among parallel triplicate experiments were found to be less than 5%, indicating good reproducibility. From the weight loss values, corrosion rates were computed using the expression:
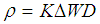 | (1) |
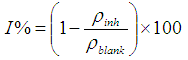 | (2) |
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
- The electrochemical experiments were performed using a VERSASTAT 400 complete dc voltammetry and corrosion system, with V3 Studio software. A conventional three-electrode Pyrex glass cell was used for the experiments. Test coupons with 1 cm2 exposed areas were used as working electrode and a graphite rod as counter electrode. The reference electrode was a saturated calomel electrode (SCE), which was connected via a Luggin’s capillary. The test electrolyte was 0.5 M solution of KOH. All experiments were undertaken in stagnant aerated solutions at 30 ± 1°C. The working electrode was immersed in a test solution for one hour until a stable open circuit potential was attained. The linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) tests were made at corrosion potential (Ecorr) over a frequency range of 100 kHz to 100 MHz, with a signal amplitude perturbation of 2 mV. The potentiodynamic polarization study was from cathodic potential of -250 mV to anodic potential of +250 mV with respect to the corrosion potential at a sweep rate of 1 mV/s. The linear Tafel segments of the anodic and cathodic curves were extrapolated to corrosion potential to obtain the corrosion current densities (icorr). Each experiment was carried out three times to estimate reproducibility and average values of the electrochemical parameters are reported.
2.4. EDS and SEM Surface Morphology
- The analysis of the morphology of the mild steel surface was carried out using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), operated in the contact mode under ambient conditions using JSM-6010LA analytical scanning electron microscope (JOEL Technologies, USA). Images of the specimens were recorded after 12 h exposure time in 0.5 M KOH without and with various concentrations of the extract inhibitor. The EDS of the extract inhibitor was performed so as to ascertain the compound composition. The result of the EDS micrograph confirmed the presence of the heteroatom of oxygen and phosphate which authenticates the root extract to be a good and efficient inhibitor.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Phytochemical Screening
- The phytochemical analysis of the leaves and seed extracts of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham has the followings; tannins, saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids and phenols [17, 18]. The presence of these active phytoconstituents in the extracts may have great influence on their corrosion inhibition property. This suggests that the root extracts Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham (Ugba root) is a good and efficient inhibitor of corrosion of mild steel within the environment.
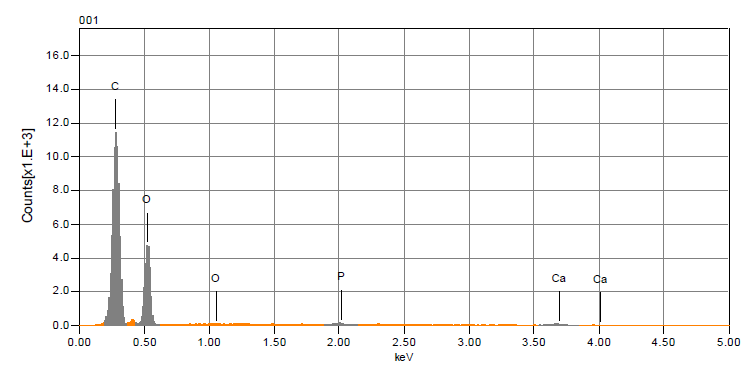 | Figure 1. EDS Micrograph of Ground Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham |
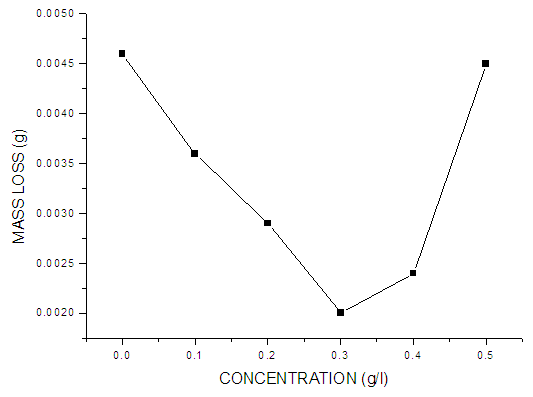 | Figure 2. Mass loss values of mild steel in 0.5 M KOH in the absence and different concentrations of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham |
3.2. Weight Loss Measurements
- Fig. 3 shows the plot of corrosion rate versus extract concentration for Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extracts. Inspection of the figures revealed that the corrosion rate of mild steel in 0.5 M KOH solution was reduced upon the introduction of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extracts into the corrosive medium. The extent of reduction in corrosion rate is seen to increase with increase in the concentration of the Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extracts except for the fifth concentration which showed slightly higher corrosion rate.
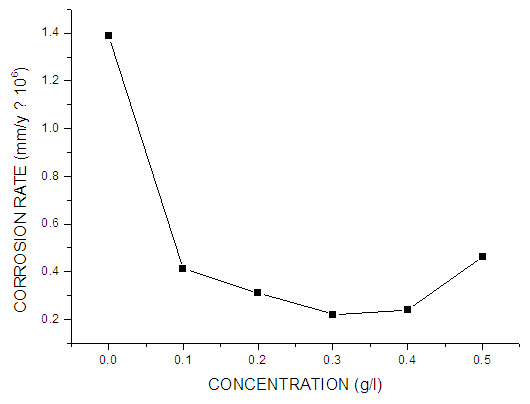 | Figure 3. Corrosion rate values of mild steel in 0.5 M KOH in the absence and different concentrations of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham |
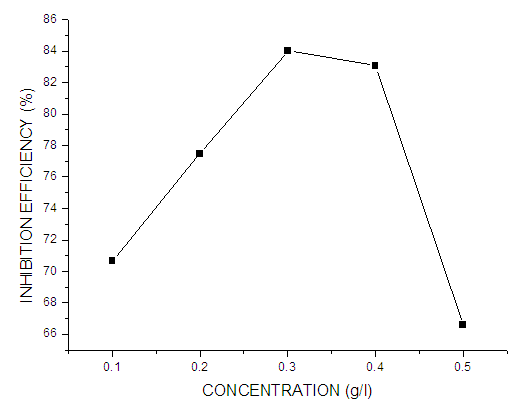 | Figure 4. Corrosion rate values of mild steel in 0.5 M KOH in the absence and different concentrations of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham |
3.3. Adsorption Considerations
- Adsorption at the metal-solution interface has been considered as the primary step in the action of most organic corrosion inhibitors in acidic environment. Langmuir adsorption isotherm was used to deduce whether there is formation of layer of insoluble complex of the metal on the surface which acts as a barrier between the metal surface and the corrosive medium - usually termed physisorption. The Langmuir plot describes the relationship between the surface coverage and inhibition concentration of a material as:
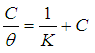 | (3) |
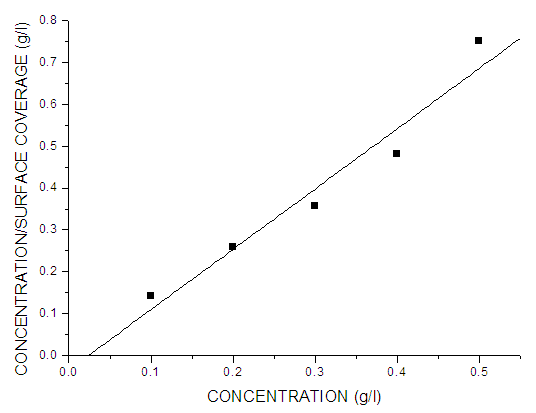 | Figure 5. Langmuir isotherm plots of corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M KOH in the presence of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extract after 12 h exposure time |
3.4. Potentiodynamic Polarization Curve
- The curves showed that the introduction of the extracts to the blank solution has modest influence appeared more pronounced. The potentiodynamic parameters obtained by extrapolation of the linear Tafel segments of the anodic and cathodic curves are presented in Table 1. The results in the table indicate that the introduction of the various concentrations of PMB root extracts remarkably shift Ecorr/SCE. For instance, the difference between the Ecorr/SCE of the blank solution and that of the highest concentration of PMB root extract is 162.4mV. It could be inferred that the extracts acted as a mixed-type inhibitor and the inhibition is due to simple geometric blocking mechanism [21].
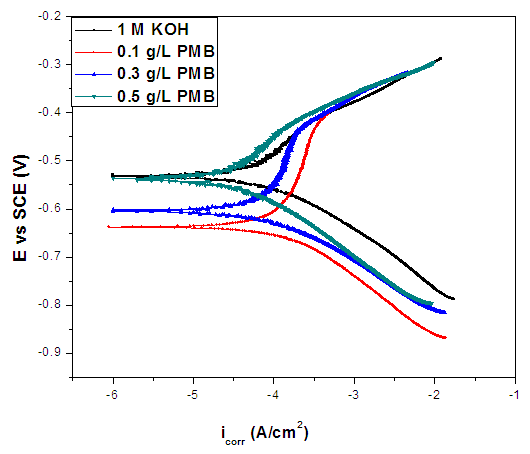 | Figure 6. Potentiodynamic Polarization Curve of the Corroded Mild Steel in 0.5 M KOH in the absence and Different Concentration of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham Root Extract |
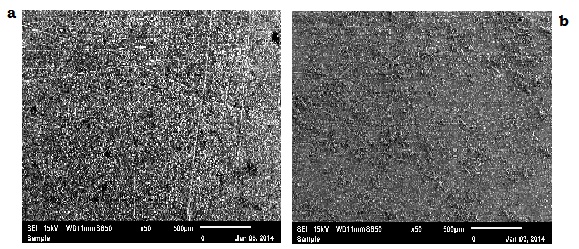 | Figure 7. EDS-SEM Characteristics of the corroded Mild Steel in 0.5 M KOH in (a) the absence of inhibitor and (b) the presence of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extract |
|
3.5. Micrograph of the Corroded Metals
- The EDS-SEM image clearly shows that the corrosion reaction does not take place homogenously over the surface of mild steel in 0.5 M KOH solution. However, the surface is remarkably protected by Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extracts, in comparison to the inhibitor-free solution.
3.6. Explanation for Inhibition
- The steel surface charges negative in base solution, so it is difficult for these protonated compounds to approach the negatively charged steel surface due to the electrostatic repulsion. Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extracts are composed of numerous naturally occurring organic compounds contain many O and N atoms in functional groups (O-H, C=O, C-O, N-H) and O-heterocyclic rings and they act as reaction centres leading to formation of films on the surface of the alloy. These compounds could be protonated in base solution; accordingly, the inhibitive action could be attributed to the adsorption of its components on the steel surface [22]. The corrosion inhibition property of plant/root extract is normally due to the presence of complex organic species such as tannins, alkaloids and nitrogen bases, carbohydrates, amino acids and proteins as well as hydrolysis products. These organic compounds contain polar functions with N, S and O atoms as well as conjugated double bonds or aromatic rings in their molecular structures, which are the major adsorption centres [23]. Also, the anticorrosion activity is attributed to the presence of heterocyclic constituents such as alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, cellulose, and others which form adsorbed films on the metal surface [24]. The root extracts of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham are a mixture of various components, which results in the complex inhibitive mechanism. It is rather difficult to determine what components present in plant extracts contribute to inhibit corrosion [22]. Those properties of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham are mostly attributed to their polyphenols which are classified as secondary metabolites having redox potential that are reducing agents, hydrogen donators, metal chelators and singlet oxygen quenchers [25]. The synergistic effects of various major and minor components present in raw root/plant extracts should be considered to account for their inhibitory activity of the phenomenon of corrosion of metals in alkaline media such as KOH [26].
4. Conclusions
- Based on the results obtained from the weight loss technique and electrochemical measurements, the following conclusions are drawn:● Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham root extracts act as good corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 0.5 M KOH solution.● Inhibition efficiency increases with increasing inhibitor concentration, and the maximum IE % of 84.02% was obtained at 0.3 g/L concentration of the root extracts of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham. ● The presence of the extracts of Pentaclethra macrophylla Bentham increases the activation energy of the corrosion process and decreases the charge density in the trans-passive region.● The introduction of the extracts into KOH solution results in the formation of films on the mild steel surface, which effectively protects the steel from corrosion.● The inhibition efficiency decreases with increasing temperature.● Test results obtained from various corrosion techniques point out that the corrosion rate of mild steel increases with high temperatures, which indicates that the adsorption of the extract on the metal surface is of physisorption type.● The inhibition action of the extract was attributed to the physical adsorption of its compounds onto the steel surface. Therefore, Langmuir adsorption isotherm is obeyed.However, neither the molecular mechanism of the anti-corrosive nor the specific compound or mixture compounds responsible for this bioactivity is well known.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors extend their sincere appreciation to the Tertiary Education Trust Fund (TETFUND) of Nigeria for funding the work through research grant, 2015. We acknowledge the assistance of Purdue Water Institute, Calumet, USA where the work was characterized.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML