-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Materials and Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2166-5346 e-ISSN: 2166-5354
2015; 5(4): 85-90
doi:10.5923/j.ijmc.20150504.01
Composites of Sulfonated Polystyrene-block-Poly (ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-Polystyrene and Graphite-Polyoxometalate: Preparation, Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Ayesha Kausar
Nanosciences and Catalysis Division, National Centre For Physics, Quaid-i-Azam University Campus, Islamabad, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Ayesha Kausar, Nanosciences and Catalysis Division, National Centre For Physics, Quaid-i-Azam University Campus, Islamabad, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In the present work novel nanocomposites have been prepared using sulfonated polystyrene-block-poly (ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-polystyrene (SPSPB) as matrix material. Two types of nanofiller were used i.e. neat graphite (G) and nanobifiller of graphite-polyoxometalate (G-POM). The series of SPSPB/G and SPSPB/G-POM nanocomposites were developed using simple solution method. The nanocomposites were incorporated with various filler content (0.01-0.5 wt. %). The SPSPB/G revealed flake-like morphology while SPSPB/G-POM nanocomposite depicted uniform dispersion of G-POM particles in the matrix. The tensile strength of sulfonated polystyrene-based matrix nanocomposites increased from 60.9 to 93.2 MPa with the nanobifiller addition of 0.01 to 0.5 wt. %. Thermal conductivity of SPSPB/G-POM 0.01-0.5 was higher (1.9-2.7 W/mK) than the SPSPB/G series. Higher electrical conductivity of 0.68 Scm-1 was also achieved with the 0.5 wt. % loading of G-POM.
Keywords: Sulfonated polystyrene-based matrix, Graphite-polyoxometalate, Tensile strength, Thermal conductivity, Electrical conductivity
Cite this paper: Ayesha Kausar, Composites of Sulfonated Polystyrene-block-Poly (ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-Polystyrene and Graphite-Polyoxometalate: Preparation, Thermal and Electrical Conductivity, International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, Vol. 5 No. 4, 2015, pp. 85-90. doi: 10.5923/j.ijmc.20150504.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Carbon is sixth element in the periodic table. Owed to its exceptional ability of catenation (with itself or other chemical elements) it is certainly remarkable. It forms foundation of life and organic chemistry. In nature, coal and natural graphite exist in profusion and diamond is found in lesser amount. Well-recognized allotropes of carbon are graphite (sp2 hybridization) and diamond (sp3 hybridization) [1, 2]. Graphite has hexagonal layers of carbon sheets (Fig. 1). Metallic and covalent bonding is present within each sheet. The sheets of carbon in graphite are recognized as graphene layers. Because of in plane metallic bonding within the sheets, graphite shows a good thermal and electrical conductivity. Likewise, owed to weak vander Waals forces between the sheets, it acts as poor thermal and electrical conductor perpendicular to the sheets. Graphite has anisotropic nature, by reason of which the sheets of carbon can slide over each other rather easily, accordingly making the graphite worthy lubricant and a pencil resource [3, 4]. Polymers are lightweight and flexible material that can be fabricated at low expense. In comparison to ceramics and metals, numerous polymers have weak electrical, thermal, and mechanical features. The continuum of requisitions of polymeric resources can be broadened by regulating the specific features such as heat resistance, modulus, fire resistance, and strength. Such polymeric materials propose hindrance to their prospective applications that can be overcome through the incorporation of nanofillers as a second phase. For compositing, polymers have been reported as worthy candidate for hosting matrices owing to their flexile nature. Henceforth, they can be feasibly tailored to accomplish bulk enhancement in physical behavior. Polymer-based nanocomposites have grown into a well-known purview of in-progress research among different polymeric materials [5]. Over former years, the development of new polymer nanocomposites has been of research emphasis world wide. Polymeric nanocomposites are described by the filler size which is in a lesser amount of 100 nm. Such polymeric nanocomposites are much advantageous than traditional ones without losing their inherent mechanical features during processability. Most imperative characteristics, which performs significant role, are the properties and size of nanofiller plus the interface between nanofiller and matrix [6]. Polymer-based composites showed some adversity compared to other materials and are utilized as alternative materials [7, 8]. The formation of polymer/graphite nanocomposites has attracted more consideration due to their latent requisition in high technology spectrum. There is requirement of thermoplastic matrix particularly styrene-based matrices in microelectronics industry because of higher insulating material resources with low dielectric loss and low conductivity. The design and requisition of polystyrene (PS)/graphite nanocomposites in electromagnetic interference shielding and electrostatic charge dissipation made them an alternative and novel field of investigation [9]. The variation in electrical conductivity of graphite-doped polystyrene with different graphite concentrations have been studied [10]. High electrical conductivity of 0.6 ×10-2 S/cm was perceived at a concentration of 1.5% graphite. The composite system of polystyrene and graphite has also been formed in the cationic grafting polymerization manner [11]. An upsurge in conductivity with 2.6-7.3 wt.% graphite composites has been obtained. The composite conductivity augmented from 10-16 S cm-1 (clean PS) to 10-2 S cm-1 with 13.4 wt.% graphite content. Styrene and potassium intercalated graphite was used to prepare polystyrene/graphite composites [12]. In-situ polymerization was employed to achieve electrically conductive composites. It was testified that the composites having 10% graphite could generate an electrical conductivity of 1.3 × 10−1 S/cm [13]. The reduction in the volume resistivity of composite system has been obtained with an enhancement of graphite load. The composites presented a percolation threshold of lower than 8.2 wt.%, which was 16 orders of magnitude lesser than clean PS. A sharp enhancement in the dielectric constant has been observed with an increased amount of graphite load. Polyoxometalates (POMs) is a class of molecularly determined inorganic metal oxide groups that have achieved specific interest because of their demand in numerous technological areas such as catalysis, medicine, biology, and materials due to their structural, chemical, and electronic versatility [14]. In correspondence, the development of POM-containing functional nanomaterials and nanodevices has been continuously increasing [15]. Additionally, their functional properties have also been investigated which provide motivation to the combined arrangement of nanoscience and polyoxometalates chemistry. On the basis of exceptional redox characteristics and enhanced protonic conductivity of polyoxometalates, both Keggin and Dawson-type hetero polyanions have been extensively applied as highly selective and long-time stable redox catalysts [16]. In this effort, novel nanocomposites of sulfonatedpolystyrene-block-poly(ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-polystyrene (SPSPB) have been prepared. Two series of nanocomposites were developed using (i) graphite alone as filler and (ii) nanobifiller of graphite-polyoxometalate (G-POM). The SPSPB/G-POM nanocomposites were obtained using solution route and incorporating various filler content. To the best of our knowledge these composites are novel and have never been produced or reported before. The electrical and thermal conductivity and mechanical studies revealed interesting results for original system developed.
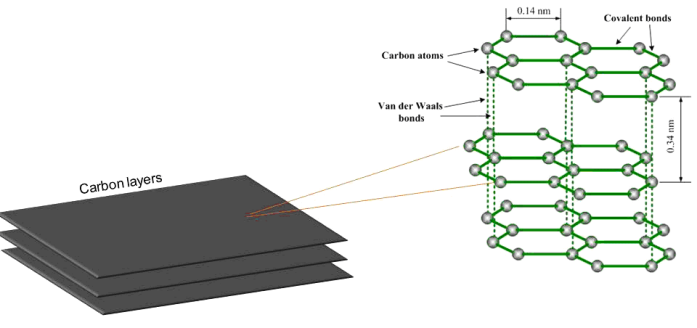 | Figure 1. Structure of graphite |
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
- Polystrene-block-poly(ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-polystyrene (sulfonated, cross-linkable solution, conductivity 0.1078 S/cm, density ~0.800 g/mL at 25°C), graphite (nanofibers, O.D.×I.D.×L 200-500 nm×1-10 nm × 10-40 μm), and tetrahydrofuran (anhydrous, ≥99.9%) were supplied by Aldrich. H3PMo12O40 (POM) was purchased from Alfa Aesar.
2.2. Characterization Techniques
- IR spectra were taken at room temperature with a resolution of 4 cm-1 using Excalibur Series FTIR Spectrometer, Model No. FTSW 300 MX manufactured by BIO-RAD. The scanning electron microscopic (SEM) images were obtained by Scanning Electron Microscope S-4700 (Japan Hitachi Co. Ltd.). Tensile testing was carried out using WP 310 universal material tester. Thermal conductivity of the samples were measured using a HotDisk Transient Plane Source TPS 2500 S (HotDisk AB). Electrical conductivity of the nancomposites was measured using Zetasizer Nano (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK).
2.3. Preparation of Graphite-Polyoxometalate (G-POM)
- Prior to ball milling, impurities from the balls were removed with a mixture of NaCl/H2O solution and distilled water. The 10 g of graphite-POM (1:1 wt. ratio) was placed in ball milling machine. The process was carried out for 24 h [9]. After the required time of milling, the crushed powder was extracted (Fig. 2). FTIR (cm-1): 3406 (O–H), 3001 (Ar C–H stretching vibration), 1021 (M–O–M asymmetric stretching), 921 (M–OH), 809 (M–O–M symmetric stretching), 465 (M–O–M bending mode).
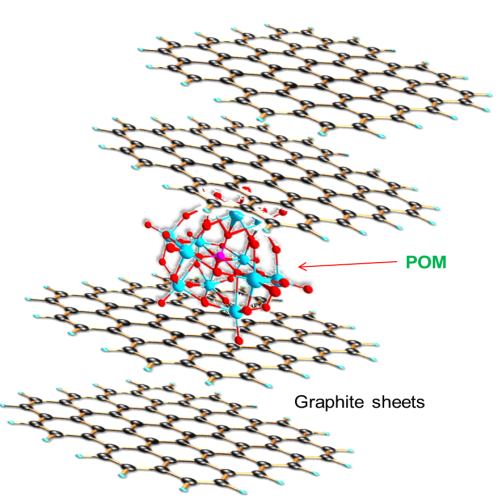 | Figure 2. Structure of graphite-POM |
2.4. Preparation of SPSPB/G-POM Nanocomposite
- Different mixtures of SPSPB (1g) and nanobifiller (0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5 wt. %) was prepared by mechanical stirring using THF as solvent. The solution obtained by mixing filler and matrix was heated at 60°C for 2 h [17]. After 2 h, the solution was allowed to cool to a temperature of 35°C. The viscous solution obtained was poured into moulds for sample preparation for various tests. Similar procedure was adopted for the preparation of SPSPB and graphite loaded films. FTIR (cm-1): 3406 (O–H), 3006 (Ar C–H stretching vibrations), 2908 (C–H stretching vibrations), 1332 and 1190 (S=O stretch), 1031 (M–O–M asymmetric stretching), 931 (M–OH), 825 (C−S), 811 (M–O–M symmetric stretching), 470 (M–O–M bending mode).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology Study of Nanocomposite
- FESEM studies of the fractured surfaces of two composites SPSPB/G-POM 0.01 and SPSPB/G-POM 0.1 were carried out. Fig. 3A & B show the morphology of SPSPB/G-POM 0.01 composite with 0.01 wt. % G-POM loading. At lower resolution, SPSPB/G-POM 0.01 was found to have scattered islands on the surface (Fig. 3A). The scattered islands were found to appear due to the dispersed and embedded POM modified graphite sheets in the matrix. Fig. 3 B shows the orderly dispersion and arrangement of graphite flakes in polystyrene-based matrix. Few evenly dispersed flakes were more visible at the fractured surface. Fig. 3 C & D show the dispersion of 0.1 wt. % bifiller in the matrix. The SPSPB/G-POM 0.1 revealed different morphology compared with SPSPB/G-POM 0.01. The change in morphology was due to the permutation of graphite and POM structure at higher loading. Fig. 3C depict uniform dispersion of G-POM. At higher resolution in Fig. 3 D, the filler dispersion was consistent but some dispersed spherical particles were also observed. These particles might have appeared because of some aggregation of G-POM bifiller in matrix at higher loading. With the increasing G-POM content, the graphite and polyoxometalate layers were found to be closely stacked. The aggregated filler particles were dispersed homogeneously and were found to be entirely covered with the matrix.
 | Figure 3. FESEM images of (A) SPSPB/G-POM 0.01 (5µm); (B) SPSPB/G-POM 0.01 (2µm); (C) SPSPB/G-POM 0.1 (5µm); and (D) SPSPB/G-POM 0.1 (2µm) |
3.2. Mechanical Study
- In this attempt, nanocomposite samples with various nanobifiller addition (0.01-0.5 wt.%) were prepared by solution route. Fig. 4 shows the tensile strength of SPSPB/G-POM nanocomposite. According to the results, the tensile strength of the composites gradually increased with the filler addition. The tensile stress of SPSPB/G-POM 0.01 nanocomposite was found as 60.9 MPa. The tensile stress was increased to 72.1 MPa with 0.05 wt. % filler addition in SPSPB/G-POM 0.05.
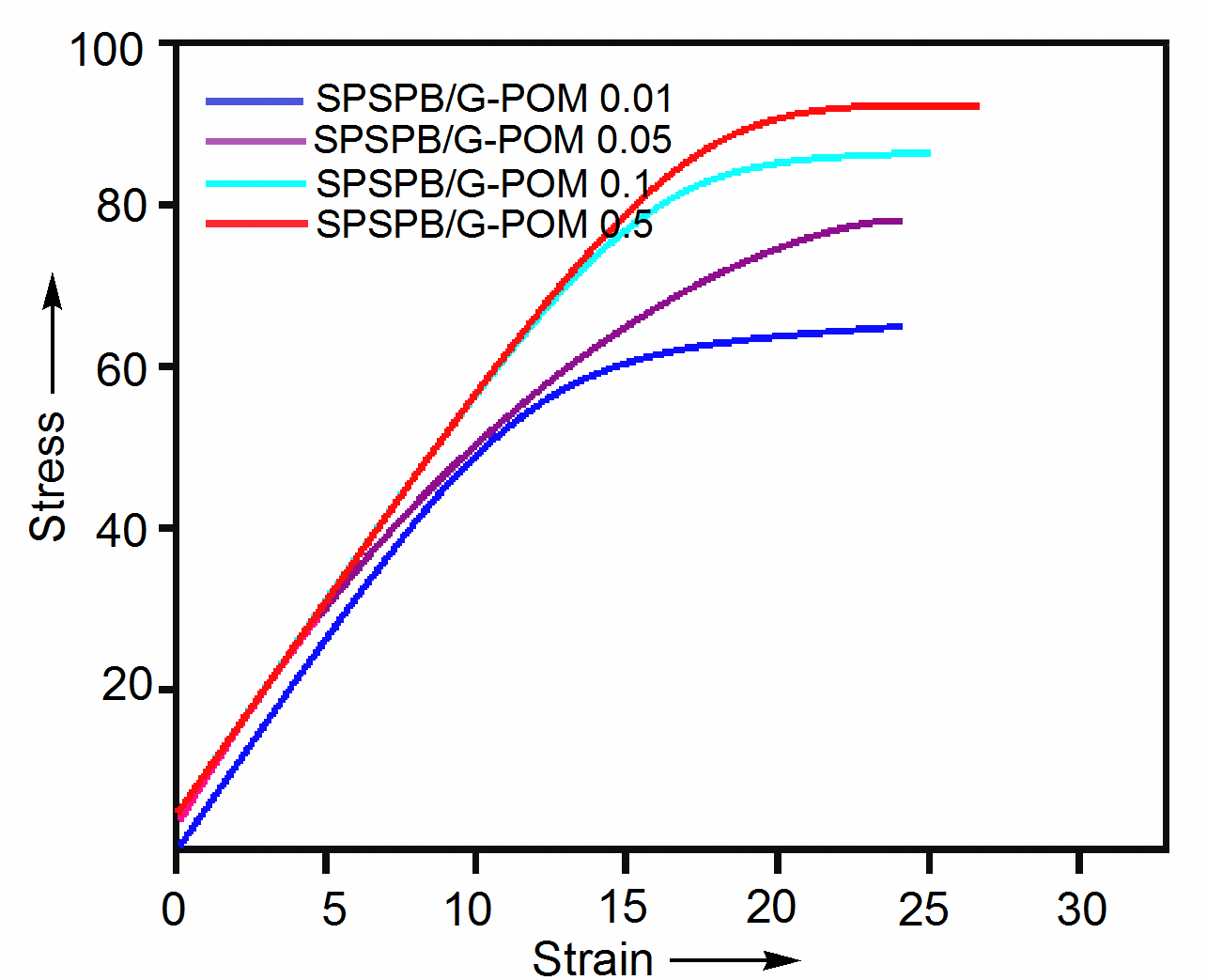 | Figure 4. Tensile strength of SPSPB/G-POM nanocomposite |
3.3. Thermal Conductivity Measurement
- Table 1 shows the influence of graphite and G-POM on the thermal conductivity of polystyrene-based matrix. The coefficient of thermal transport was studied by independent Hot-Disk method. For SPSPB/G-POM 0.5 material, the thermal conductivity (2.7 W/mK) was orders of magnitude higher than 0.01 wt. % filler loaded sample (1.9 W/mK). On the other hand the SPSPB/G 0.01-0.5 had thermal conductivities 1.5–2.1 W/mK depending on the exact morphology of the composites [18, 19]. As the matrix was poorly thermal conductive material, graphite-based filler was added to improve the thermal conductivity. Graphite is intrinsically thermally conducing, so its various loading increased the thermal conductivity of the final composites. The results revealed that the SPSPB/G-POM possess better thermal conductivity relative to SPSPB/G nanocomposites (Fig. 5). Efforts to improve the thermal conductivity have been made through three successful models (i) dispersing thermal-conductive nanoparticles within polymer [20]; (ii) inserting a metallic matrix [21]; and (iii) compositing with graphite structures [22, 23]. Compared with the first two methods, compositing of polymers with graphite or its derivatives significantly enhanced the thermal conductivity with a small change in phase change enthalpy.
|
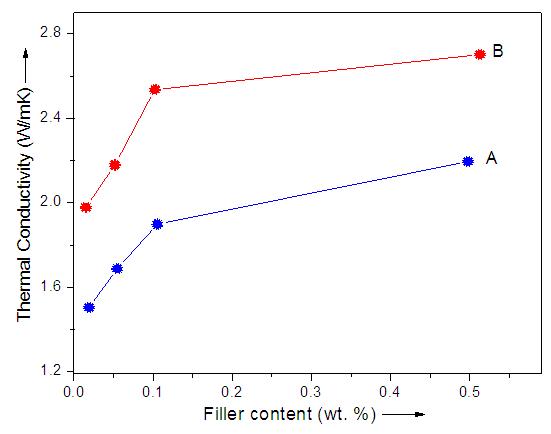 | Figure 5. Thermal conductivity of (A) SPSPB/G and (B) SPSPB/G-POM nanocomposite |
3.4. Electrical Conductivity Measurement
- The electrical conductivity of the samples prepared was also measured (Fig. 6). The neat sulfonated polymer has very low electrical conductivity of 0.11 Scm-1. The inclusion of graphite obtained through various routes increased the conductivity considerably compared with the neat matrix. The SPSPB/G 0.01 showed the conductivity of 0.15 Scm-1. The conductivity was increased with the graphite loading and reached 0.57 Scm-1 for SPSPB/G 0.05. The second series of SPSPB/G-POM showed better electrical conductivity. The SPSPB/G-POM 0.01 with lower filler loading showed the conductivity of 0.16 Scm-1. The SPSPB/G-POM 0.05 revealed the conductivity value of 0.40 Scm-1, higher relative to the pristine matrix and graphite composites. Higher electrical conductivity was achieved with the 0.5 wt. % loading of 0.68 Scm-1. The conductivity of novel series was found to be improved than several literature composites [2, 9]. Increase in the electrical conductivity was primarily due to the formation of internal conductive network of graphite-based particles within the polymer matrix and the material became electro conductive. There were several contributing factors involved in the formation of conductive networks in these composites such as the filler distribution, filler shape, filler/matrix interaction and the processing technique.
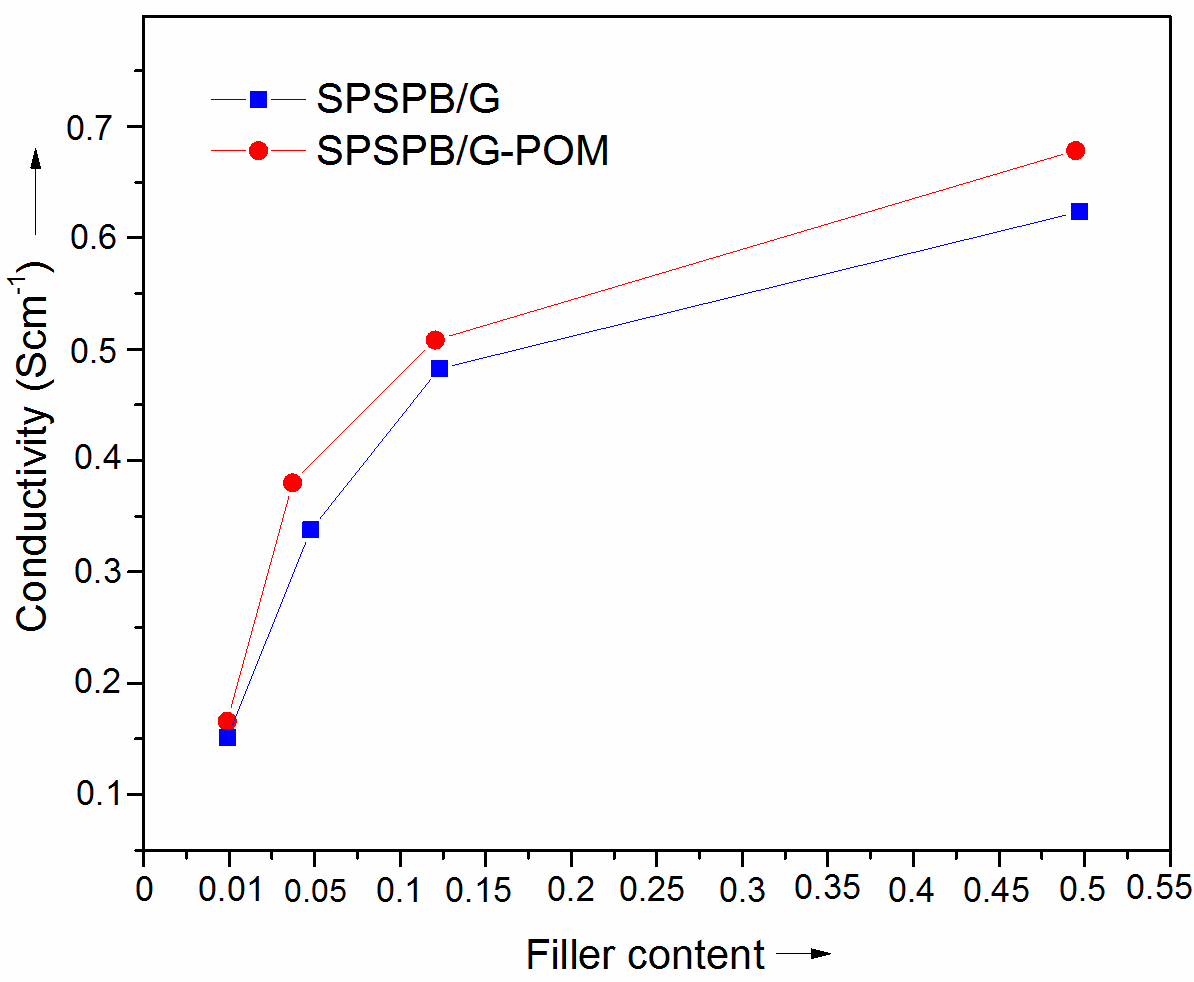 | Figure 6. Electrical conductivity of SPSPB/G and SPSPB/G-POM nanocomposite |
4. Conclusions
- Sulfonated polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene-ranbutyl- ene) -block-polystyrene have been prepared using solution route. In this work, two series of nanocomposites were developed using graphite and nanobifiller of graphite-polyoxometalate. The SPSPB/G-POM nanocomposites were obtained incorporating various filler content 0.01 to 0.5. Due to the interfacial interaction between the graphite nanolayers and the SPSPB, thermally and electrically conducting nanocomposites were formed. Both the thermal and electrical conductivities of SPSPB/G and SPSPB/G-POM were found to increase with filler loading. Obviously there is huge difference between the measurement of electrical conductivity and that of thermal conductivity. The relationship holds only for materials with freely moving electrons. The graphite-based nanofiller loading seemed to be responsible for increasing conductivity in both the cases. An increase in the tensile strength of the hybrid films was also observed with an increase in nanobifiller content, indicating significant reinforcement of the matrix in the presence of nanoparticles. SEM showed that the SPSPB/G-POM has better filler dispersion with scattered spherical particles. It is worth mentioning that the nanocomposites based on polystyrene-based matrix and graphite filler have commercial potential.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML