-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Materials and Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2166-5346 e-ISSN: 2166-5354
2012; 2(5): 205-207
doi:10.5923/j.ijmc.20120205.04
Effects of Colour-filtering Solar Beam on Reaction Product from d-group Transition Metals in N2 Gas Environment under Heating with Concentrated Solar Beam
Nobumitsu Shohoji
LEN - Laboratório Nacional de Energia, LNEG - Laboratório Nacional de Energia e Geologia, Estrada do Paço do Lumiar, 22, 1649-038, Lisboa, Portugal
Correspondence to: Nobumitsu Shohoji , LEN - Laboratório Nacional de Energia, LNEG - Laboratório Nacional de Energia e Geologia, Estrada do Paço do Lumiar, 22, 1649-038, Lisboa, Portugal.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Recently, Noda and collaborators at Kyoto University reported possible enhancement of photo-voltaic cell (PVC) energy conversion efficiency by allowing penetration of preferential range of wavelength components alone to PVC by filtering the solar beam through a special semiconductor thin film developed at their laboratory. During the course of our recent experimental attempts ofnitridingd-group transition metals in N2 gas environment, we detected intriguing effects of colour-filtering on reaction product. In the present report, these effects of colour-filtering are reviewed under new light of recently reported evidence by Noda and co-workers. It appears that, by colour-filtering the selected wavelength range in solar beam, undesirable secondary reactions might be suppressed to result in promotion of a target reaction under heating using concentrated solar beam as the source of reaction heat.
Keywords: Colour-filtering Solar Beam, Solar-induced Fluorescence (SIF) of C2 Radical, Morphology of Carbo-nitride of d-group Transition Metals
Cite this paper: Nobumitsu Shohoji , Effects of Colour-filtering Solar Beam on Reaction Product from d-group Transition Metals in N2 Gas Environment under Heating with Concentrated Solar Beam, International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, Vol. 2 No. 5, 2012, pp. 205-207. doi: 10.5923/j.ijmc.20120205.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In a recent issue of Nature Photonics[1], an interesting report by collaborators of Noda at Kyoto University suggesting possible enhancement of photo-voltaic cell (PVC) energy conversion efficiency by allowing penetration of preferential range of wavelength components alone to PVC by filtering solar beam using special semiconductor thin film developed at their laboratory. Very essence of this significant information was published immediately in some Japanese newspaper[2]. During the course of recent attempts of nitride synthesis using a solar furnace at PROMES-CNRS (Laboratoire Procédés Materiaux et Energie Solaire) in Odeillo (France) undertaken in July 2010, the authors[3-5] detected also some intriguing effects of colour filtering of solar beam on reaction products. In a standard experimental setup at PROMES-CNRS, graphite crucible is used as sample holder. In an earlier report from Flamant and co-workers at PROMES-CNRS[6], solar-induced fluorescence (SIF) of C2 radical plume was reported to yield from graphite under concentrated solar beam irradiation. This does not do any harm for synthesis of carbides of d-group transition metals. However, in our experimental campaign at PROMES-CNRS during July 2010, objective was nitride formation by using concentrated solar beam as the reaction heat source for which presence of C2 radical in gas phase was definitely not favourable. According to Badie et al.[6], C2 Swan band emission was detected at around 517 nm. Thus, Sky blue filter (Ref.#068) supplied from Lee Filters (Andover, UK)[7] showing low transmittance of wavelength range 600 ± 100 nm was tried to be inserted for suppression of C2 radical emission from graphite crucible (see Fig. 1). The consequence was significant suggesting satisfactory extent of suppression of carburizing for MC1-xNx type carbo-nitrides for IVa-group element (Ti) and Va-group elements (V, Nb and Ta)[3]. For VIa-group elements (Mo and W)[4], starting material M remained in metallic state after 30 min heating at 2000ºC in N2 gas environment without showing no evidence of carburization. Mo and W are known to be very difficult to be converted to nitride with N2[8,9] but relatively easy to be carburized. Thus, the acquired experimental results were interpreted as the evidence of effective C2 radical yield suppression by insertion of the Sky blue filter.As the supplemental experiment, we undertook filtering experiment using Medium yellow (Ref.#010) filter of Lee[10] which cut wavelength component shorter than 450 nm almost completely. The effect of this filter on C2 plume emission did not seem very significant unlike the Sky blue filter. However, we detected unmistakable evidences of surface morphological modification for carbo-nitrides of Ti, V, Nb and Ta by insertion of the Medium yellow filter.In this report, the results so-far-acquired during the course of colour-filtering experiments[3-5] are interpreted under new light of recently reported evidence by Noda and co-workers[1,2].
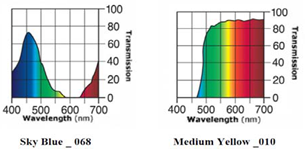 | Figure 1. Wave transmission performances of the Lee Colour Filters. Sky blue (Ref.# 068) filter; cited atRef.[7]. Medium yellow (Ref.# 010) filter; cited at Ref.[10] |
2. Detected Effects of Colour-filtering
2.1. Implications of the Published Work by de Zoysa et al.[1]
- Detailed contents of the published work by de Zoysa et al.[1] were quite physical and not at all easy to understand straightforwardly the pragmatic significance by readers like myself who are not familiar with proper physics but digested newspaper introduction of this article[2] concisely demonstrated the essence of the reported work. According to de Zoysa et al.[1], Al0.3Ga0.7As/GaAs quantum well (QW) inter-sub-band transistors (ISB-T) of ISB absorption wavelength λ = 9.7 μm was synthesized with GaAs QW layer of thickness 6.8 nm and Al0.3Ga0.7As barrier layer of thickness 13 nm. By filtering the solar beam through the developed QW ISB-T to allow penetration of only limited range of wavelength component with certain extent of intensity enhancementby converting the other wavelength components into the preferred wavelength onto PVC surface, PVC energy conversion efficiency was enhanced up to remarkable 40% from conventional 20% gained using non-filtered white spectrum solar beam[2].This appears to be a quite significant achievement with pragmatic convenience implying that PVC energy conversion efficiency was enhanced through suppressed side reactions taking place alongside the principal reaction contributing to the conversion of thermal energy to electricity.
2.2. Evidences Acquired during Heating of Compacted Meal Powder Samples in N2 Gas Environment under Colour-filtered Concentrated Solar Beam[3-5]
2.2.1. Suppressing C2 Plume Yield from Graphite Crucible by Inserting the Sky Blue Filter
- As reported in Ref.[3], N content x in the synthesized carbo-nitride MC1-xNx under concentrated solar beam colour-filtered through the Sky blue filter was appreciably higher than the counterpart synthesized under heating with concentrated solar beam with no insertion of the Sky blue filter for M = Ti, V, Nb and Ta. For the VIa-group elements, Mo and W which are known to be extremely difficult to be converted to nitride in N2 gas environment[8,9], reaction product remained in metallic M without being converted to neither carbide nor nitride by 30 min heating to 2000ºC using the Sky blue colour-filtered concentrated solar beam[4] implying that C2 plume yield was well suppressed to inhibit carburizing reaction while chemical activity a(N) of N2 gas molecules were too low to promote nitriding reaction.By the heating in N2 gas environment with the concentrated solar beam filtered through the Sky blue filter, certain extent of grain size refinement was detected for M = V (Fig. 3 in Ref.[5]) and for M = Ta (Fig. 5 in Ref.[5]).
2.2.2. Selective Promotion of Certain Reaction Route by Inserting the Medium Yellow Filter
- As reported in Ref.[5], intriguing consequence of inserting the Medium yellow filter was detected as the surface morphology modifications of the synthesized carbo-nitride by solar heating to 2000ºC for several transition metals of IVa- and Va-groups although the effect of the Medium yellow filter on C2 plume suppression was insignificant judging from the lattice parameters for the synthesized MC1-xNx evaluated by X-ray diffraction (XRD). On the contrary to the grain size refinement effect detected for M = V and Ta by the Sky blue filtered concentrated solar beam radiation in N2 gas environment as pointed out above in 2.2.1., certain extent of crystal grain coarsening appeared to take place by irradiation of concentrated solar beam filtered through the Medium yellow filter for M = Nb (Fig. 4 in Ref.[5].Although the detailed mechanisms leading to distinguishable surface morphologies among the reaction products MC1-xNx with and without the Medium yellow filter remained unknown, it seemed certain that, by inserting the Medium yellow filter, some routes of secondary reactions competing the principal reaction were retardedto result in promotion of the rate of the principal reaction which was, in some sense, analogous to the enhanced PVC energy conversion efficiency by allowing arrival of the intensified monochromatic solar beam alone to the PVC surface using the special quantum effect filter[1,2].
2.2.3. Temperature Drop Caused by Inserting the Colour Filter
- By insertion of either the Medium yellow or Sky blue colour filter, temperature drop was measured to be insignificant implying that the heating effect by concentrated solar beam was largely contributed by IR (infra-red) range of wave components not by UV (ultra-violet) and shorter wavelength components.By the special QW ISB-T thin film filter developed by Noda and collaborators[1,2], light component of ≈ 10 m alone is selectively transmitted to PVC surface. The light component of this wavelength range would not contribute to unfavourable heating of PVC element and this fact might also contribute favourably for enhancement of PVC energy conversion.
3. Discussion
- According to Noda and co-workers[1,2], energy conversion efficiency of PVC might be nearly doubled by allowing the transmission of intensified wave components favourable for the energy conversion process selectively by filtering the solar beam through the special QW ISB-T thin film filter. The cut wavelength component by the filter must have included the IR component that would contribute the heating of PVC element.The exclusion of the IR component might have contributed to certain extent the enhanced energy conversion efficiency of PCV through minimization of undesirable heat-up effect for the PVC element besides the retarded unfavourable secondary reactions taking place competitively alongside the principal photo-voltaic process of the PVC element under exposure to the solar beam.The QW ISB-T thin film developed by de Zoysaet al.[1,2] is not a simple filter but has capacity to convert thermal energy of solar beam with white spectrumto the narrow band spectrum at around the preferable frequency for theenergy conversion function of the PVC element and this must have also contributed to the enhanced PVC energy conversion efficiency.
4. Concluding Remarks
- The evidences so far acquired through colour-filtering experiments in our recent solar nitride synthesis[3-5] were still very scarce and thence further systematic investigation is definitely desirable. Anyway, as well as for PVC energy conversion efficiency enhancement, selective filtering of solar beam must be of pragmatic merit on usage of concentrated solar beam as the heat source for synthesis of refractory materials including nitride and carbide.In conventional presentation of equilibrium phase diagram for multi-component system, pressure P and temperature T are employed as the state variables to define the composition C. However, the recent experimental evidences acquired through heating using concentrated solar beam with deliberately cut wavelength components by colour-filtering seemed to suggest necessity for introduction of new state parameter, wavelength, for definition of phase relationship for some compounds synthesized at elevated temperatures.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML