-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Materials and Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2166-5346 e-ISSN: 2166-5354
2012; 2(4): 128-131
doi: 10.5923/j.ijmc.20120204.02
Synthesis of 1, 3, 5-Triarylbenzenes, Using CuCl2 as a New Catalyst
Sohrab Abdollahi , Fatemeh Mostaghni
Chemistry department, Payame Noor University, I. R. of Iran, PO BOX 19395-3697 Tehran , Iran
Correspondence to: Sohrab Abdollahi , Chemistry department, Payame Noor University, I. R. of Iran, PO BOX 19395-3697 Tehran , Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Among the aromatic ketones, aceto phenone and its various substituted derivatives have been studied since early 20th century. This ketone can perform the self condensation reaction and produces trimmer having an aromatic ring of 1,3,5-triphenyl benzene (T.P.B) with general formula of C24H18. In this research, the compounds 1,3,5-triphenyl benzene and 1,3,5-tris (2-naphthyl) benzene are synthesized via self condensation of acetophenone and 2-aceto naphthalene respectively, using Cu2+(CuCl2) as a new catalyst. Catalyst of copper(II) chloride is a very suitable catalyst and comparing to the other ones is cheaper, abundant and very facile to use in these condensation reactions for the synthesis of trimmers. Since Cu2+ has empty p and d orbitals, therefore, CuCl2 acts as a good Lewis acid. Further, the catalyst is a good electron transfer oxidative reagent, therefore it is very useful catalyst for self-condensation of ketones. This method seems to be general for the synthesis of other derivatives of 1,3,5-triarylbenzene using various ketone derivatives. These trigonal molecules may be converted to flexible clathrates or nano cage molecules, which are highly promising for the separation and chemical transformation.
Keywords: Trimerization, Tri Aryl Benzene, Clathrate Inclusion Compounds
Cite this paper: Sohrab Abdollahi , Fatemeh Mostaghni , "Synthesis of 1, 3, 5-Triarylbenzenes, Using CuCl2 as a New Catalyst", International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, Vol. 2 No. 4, 2012, pp. 128-131. doi: 10.5923/j.ijmc.20120204.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The synthesis of 1,3,5-tris arylbenzene compounds due to self-condensation of acetophenone were reported for the first time in 1874[1]. The years later, these compounds with different substituted phenolic rings using various reagents were prepared. In 1991, the synthesis of different derivatives of this compound were conducted with high yield, using catalyst of tetrachloro silane in ethanol as a solvent at room temperature and molar ratio of 1:1 (acetophenone:catalyst) [2]. In these reactions, the central benzene ring is created by condensation of three molecules of ketones via releasing three molecules of water to produce expected trimer[3-8]. Bishop and Dance, for the first time, show that 1,3,5-triarylbenzene compound reacts with water and benzene to produce solvated crystalline molecules[9]. Later on, Weber et al. prepared these inclusion compounds with a number of molecules of different sizes from methanol to morpholine having properties of alicyclic, aromatic, heterocyclic and dipolar molecules with and without proton[10]. X-ray studies on the single crystal of inclusion compounds such as 1,3,5-Tris (4-carboxyl phenyl) benzene- dimethyl formamide (1:3) show that the host molecule has a propeller conformation with complete three-fold symmetry providing hydrogen bond as a donor to three DMF molecules[3]. Therefore, in the crystalline structure the units of host-gust are arranged such as stack form in Figure 1.
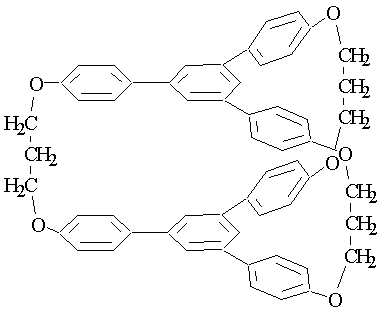 | Figure 1. Inclusion molecule made of two triarylbenzene planes connected by hydrocarbon bridge and having cavity to hold different molecules |
 -alumina with CuCl (4-8 wt% Cu) following the incipient wetness method. Other chlorides, (mainly alkaline or alkaline earth chlorides) in a variable concentration are also added in order to improve the catalytic performance; making the catalyst more suitable for use in the industrial reactors[34,35]. A type of polymer- supported CuCl2 catalyst for synthesis of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) was obtained by using
-alumina with CuCl (4-8 wt% Cu) following the incipient wetness method. Other chlorides, (mainly alkaline or alkaline earth chlorides) in a variable concentration are also added in order to improve the catalytic performance; making the catalyst more suitable for use in the industrial reactors[34,35]. A type of polymer- supported CuCl2 catalyst for synthesis of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) was obtained by using  - conjugated poly (2,2'-bipyriding-5,5-diyl) as the supporting ligand. The high catalytic activity is associated with the
- conjugated poly (2,2'-bipyriding-5,5-diyl) as the supporting ligand. The high catalytic activity is associated with the  -conjugated conductive properties of the supporting ligand, PBpy[32]. Another type of homogeneous catalyst for dimethyl carbonate synthesis by oxidative carbonylation of methanol in the liquid-phase reaction was investigated by Jun-cheng Hu et.al.[36]. The polymer-bond monometallic PVP-CuCl catalyst (PVP, poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrolidone) prepared by the combination of an alcoholic solution of PVP and CuCl2, exhibits excellent catalytic performance for the oxidative carbonylation of methanol with carbon monoxide and oxygen to DMC under 3.0 MPa pressure at temperature around 140-160℃ [36].
-conjugated conductive properties of the supporting ligand, PBpy[32]. Another type of homogeneous catalyst for dimethyl carbonate synthesis by oxidative carbonylation of methanol in the liquid-phase reaction was investigated by Jun-cheng Hu et.al.[36]. The polymer-bond monometallic PVP-CuCl catalyst (PVP, poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrolidone) prepared by the combination of an alcoholic solution of PVP and CuCl2, exhibits excellent catalytic performance for the oxidative carbonylation of methanol with carbon monoxide and oxygen to DMC under 3.0 MPa pressure at temperature around 140-160℃ [36].2. Experimental
- Yields refer to isolated pure center cut from column chromatography or to the main band scratched from preparative TLC plate. Products were characterized by comparison with authentic sample through IR, NMR,TLC, and mp methods. Due to the experimental limitation, the melting points are not fully accurate and determined by Metller FP5 melting point apparatus. IR spectra were obtained on a Shimadzu IR-470. 1HNMR data were recorded in CDCl3 on Brucker 80 MHz and 13CNMR on Brucker Advance 500-MHz spectrometer. All reagents were analytical grade and used without further purification.
2.1. Preparation of 1,3,5-tris(2-naphthyl) Benzene
- For the synthesis of 1,3,5-tris(2-naphthyl) benzene, 2-acetonaphthalene and CuCl2 are used with molar ratio of (1:15). CuCl2(0.03 gr, 0.19 mmole) was added to a mixture of 2-acetonaphthalene(0.4 gr 2.3 mmol) and toluene(5ml) in a 25 ml round bottom flask equipped by magnetic stirrer and reflux condenser. The mixture was refluxed in oil bath for 6 hours at temperature of 180-220℃. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was extracted by ether (3 x 10ml) and dried by magnesium sulfate. Then, the mixture components were separated by column chromatography (mp = 115-120℃). The structure of the product was analyzed by spectroscopic method such as IR, 1H NMR and 13C NMR. IR(KBr): 3050(W), 3250(m), 1418(m), 1180(s), 1145(m), 1120(s), 720(vs), 695(s) cm-1.1HNMR(CDCl3): δ; 6.8-7.7 (m,24H)ppm.13CNMR(CDCl3):δ;131.7(s),131.6 (s),128.1(s), 128 (s). Anal. Calcd For C36H24 (456.396):C, 94.7; H,5.3 Found:C,94.7; H,5.5.
2.2. Preparation of 1,3,5-triphenyl Benzene
- For the synthesis of 1,3,5-triphenylbenzene, CuCl2 and acetophenone are used with molar ratio of (1:15). CuCl2(0.03 gr, 0.19 mmole) was added to a mixture of acetophenone (0.34 gr 2.9 mmol) and toluene(5ml) in a 25 ml round bottom flask equipped by magnetic stirrer and reflux condenser. The mixture was refluxed in oil bath for 6 hours at temperature of 180-220℃. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was extracted by ether (3 x 10ml) and dried by magnesium sulfate. Then, the mixture components were separated by column chromatography (mp = 173-174℃). The structure of the product was analyzed by spectroscopic method such as 1H NMR and 13C NMR , as shown in the Figure 2 for 1H NMR and Figure 3 for 13C NMR . 1H NMR(CDCl3): δA = 7.77 ppm, δB = 7.68, δC = 7.46, δD = 7.37.
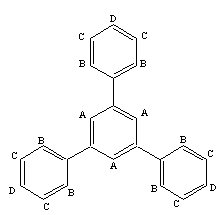 | Figure 2. 1H NMR of 1,3,5-triphenyl benzene molecule in which hydrogens are labled by letters of A, B, C and D |
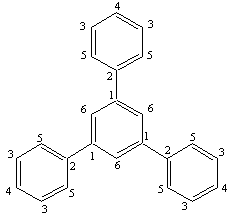 | Figure 3. 13C NMR of 1,3,5-triphenyl benzene molecule in which carbons are labeled with numbers 1,2,3,4,5,6 |
3. Results and Discussion
- The goal of this research is an investigation on the self condensation reaction of aromatic ketones via CuCl2 catalyst, considering the fact that the trisanulated benzenes, and 1,3,5-tris(2-thienyl) compound have been synthesized previously by our group using the same catalyst[37]. Now, in this paper, CuCl2 catalyst is used to conduct self condensation reaction of 2-aceto naphthalene to produce1,3,5-tris(2-naphthyl)benzene. this molecule is a new one with bulky structure and trigonal symmetry that can behave as a clatherat. Substituted benzene of 1,3,5-triaryl is considered as a rich source of porous crystalline host which can provide inclusion compounds[38]. Wide spread application, specific properties of these type of compounds and also the fact that the porosity of the compounds depends on the nature, type and position of these substituents linked to it, have caused an incentive for our group to prepare 1,3,5-tris(2-naphthyl)benzene, which is shown in Figure 4. Contrary to previous syntheses by other researcher that use ligand bonded CuCl2 catalysts, in this research the pure unhydrated powder of CuCl2 was used as a catalyst for condensation reaction. In condensation process, CuCl2 reduces to CuCl (Cu2+ to Cu1+). On the other hand the produced water during reaction can oxidize in acidic solution. This oxidation reaction in turn produces more H+ and helps the solution become more acidic. Cooper cation, Cu2+, contains empty orbitals such as p and d orbitals and therefore acts as a Lewis acid and attacks to free loan pairs of oxygen in carbonyl group; producing coordination bond. As a result, the oxygen of carbonyl group achieves positive charge. The positive charge at high temperature can be neutralized by
 hydrogen via chloride ion which acts as a bridge in this mechanism. In this case enolate is formed and immediately attaches to protonated carbonyl group of second molecule of 2-aceto naphthalene and produces keto alcohol. At the reflux temperature, the keto alcohol releases a molecule of water. At acidic condition this ketone is protonated and reacts with third molecule of 2-aceto naphthalene via releasing two molecules of water and forms a central aromatic ring.
hydrogen via chloride ion which acts as a bridge in this mechanism. In this case enolate is formed and immediately attaches to protonated carbonyl group of second molecule of 2-aceto naphthalene and produces keto alcohol. At the reflux temperature, the keto alcohol releases a molecule of water. At acidic condition this ketone is protonated and reacts with third molecule of 2-aceto naphthalene via releasing two molecules of water and forms a central aromatic ring. 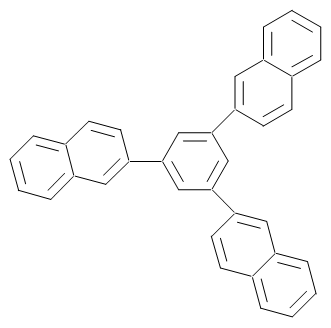 | Figure 4. Molecule of 1,3,5-tris(2-naphthyl)benzene precursor of inclusion compounds |
4. Conclusions
- This synthesis and related product, 1,3,5- tris(2-naphthyl) benzene, can provide extensive research for the future. For example, substitution of different kinds of functional group on naphthalene ring can obtain various kinds of inclusion compounds with different sizes and inclusion behavior which may be essentially useful for the various syntheses as shown in Figure 5.The synthesis of star like molecules such as 1,3,5-triaryl benzene ((1,3,5-triphenylebenzene and 1,3,5-tris(2-naphthyl) benzene) can be used for designing and synthesis of binary crystals via hydrogen bonds[39], halogen bonds[40],
 or van der Walls forces[42]. Even, the construction of ternary and higher-order cocrystals will be under considerations[43, 44].One possible challenge to make three-component solids is host-gust design in which the host is a crystalline lattice assembled using two molecular species[45]. Usually, inclusion compounds have been synthesized by crystallizing the host and guest compounds from a solution[46]. The choice of components available for the construction of such a system is limited by the solubility of the host and the guest compounds. This limitation become more serious in multicomponent systems that require balancing the solubility of several molecular species.By using these cyclization condensation reactions, via CuCl2 as catalyst, and using heteroaromatic rings such as thiophene, pyrole and furan, one may synthesis various molecules of star like structures with different physical and chemical properties. Many of hetero atoms such as oxygen and nitrogen that contain free loan pairs of electrons can provide an inclusion compounds with interesting electrical properties in addition to separation abilities. These kinds of properties make star like molecules a good precursor for making nano cage-like compounds. By selecting proper derivatives of ketones, the cavity of the inclusion compounds can be controlled for the separation of specific molecule.
or van der Walls forces[42]. Even, the construction of ternary and higher-order cocrystals will be under considerations[43, 44].One possible challenge to make three-component solids is host-gust design in which the host is a crystalline lattice assembled using two molecular species[45]. Usually, inclusion compounds have been synthesized by crystallizing the host and guest compounds from a solution[46]. The choice of components available for the construction of such a system is limited by the solubility of the host and the guest compounds. This limitation become more serious in multicomponent systems that require balancing the solubility of several molecular species.By using these cyclization condensation reactions, via CuCl2 as catalyst, and using heteroaromatic rings such as thiophene, pyrole and furan, one may synthesis various molecules of star like structures with different physical and chemical properties. Many of hetero atoms such as oxygen and nitrogen that contain free loan pairs of electrons can provide an inclusion compounds with interesting electrical properties in addition to separation abilities. These kinds of properties make star like molecules a good precursor for making nano cage-like compounds. By selecting proper derivatives of ketones, the cavity of the inclusion compounds can be controlled for the separation of specific molecule. | Figure 5. Proposed stack form of two molecules of 1,3,5-tris(2-naphthyl) benzene which can be used to make an inclusion compound |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I would like to acknowledge the Gilan University and University of Payame Noor of lamerd, for their financial support and the opportunities that were provided for our research. I sincerely thank Homa Shafikhani and Saeid Zahmatkesh for correction and editing this paper.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML