| [1] | Albee, F., assisted by Morrison, H., Studies in bone growth. Ann. Surg. 1920, 71, 32-38 |
| [2] | Haldeman, K., and Moore, J., Influence of a local excess of calcium and phosphorus on the healing of fractures. Arch. Surg. 1934, 29, 385-396 |
| [3] | Ray, R., Degge, J., Gloyd, P., and Mooney, G., Bone regeneration. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1952, 34A, 638-647 |
| [4] | Getter, L., Bhaskar, S., Cutright, D., Perez, B., Brady, J., Driskell, T., and O’Hara, M., Three biodegradable calcium orthophosphate slurry implants in bone. J. Oral Surg. 1972, 30, 263-268 |
| [5] | Roy, D., and Linnehan, S., Hydroxyapatite formed from coral skeletal carbonate by hydrothermal exchange. Nature 1974, 247, 220-222 |
| [6] | Koster, K., Karbe, E., Kramer, H., Heide, H., and Konig, R., Experimenteller Knochenersatz durch resorbierbare Calciumphosphat-Keramik. Langenbecks Arch. Chir. 1976, 341, 77-86 |
| [7] | Peelen, J., Rejda, B., Vermeiden, J., and de Groot, K., Sintered tri-calcium orthophosphate as bioceramic. Sci. Ceram. 1977, 9, 226-236 |
| [8] | Jarcho, M., Kay, J., Gumaer, K., Doremus, R., and Drobeck, H., Tissue, cellular and subcellular events at a bone-ceramic hydroxyapatite interface. J. Bioeng. 1977, 1, 79-92 |
| [9] | Jarcho, M., Calcium phosphate ceramics as hard tissue prosthetics. Clin. Orthop. 1981, 157, 259-278 |
| [10] | LeGeros, R. Z., Calcium phosphates in oral biology and medicine, Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1991; 210 pp |
| [11] | Dorozhkin, S. V., Calcium orthophosphates in nature, biology and medicine. Materials 2009, 2, 399-498 |
| [12] | LeGeros, R. Z., Chohayeb, A., and Shulman, A., Apatitic calcium phosphates: possible dental restorative materials. J. Dent. Res. 1982, 61, Spec. Iss., 343 |
| [13] | Brown, W. E., and Chow, L. C., A new calcium phosphate setting cement. J. Dent. Res. 1983, 62, Spec. Iss., 672 |
| [14] | Brown, W. E., and Chow, L. C., A new calcium phosphate water setting cement. In: Cements Research Progress, Brown, P. W., Ed., Westerville, OH, American Ceramic Society, 1986, pp. 352-379 |
| [15] | Brown, W. E., and Chow, L. C., Dental restorative cement pastes. US Patent No. 4518430. May 21, 1985 |
| [16] | Gruninger, S. E., Siew, C., Chow, L. C., O’Young, A., Tsao N, K., and Brown, W, E., Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a new calcium phosphate setting cement. J. Dent. Res. 1984, 63, Spec. Iss., 200 |
| [17] | Tas, A. C., Porous, biphasic CaCO3-calcium phosphate biomedical cement scaffolds from calcite (CaCO3) powder. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2007, 4, 152-163 |
| [18] | Driskell, T. D., Heller, A. L., and Koenigs, J. F., Dental treatments. US Patent No. 3913229. October 21, 1975 |
| [19] | Kingery, W. D., II. Cold setting properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1950, 33, 242-246 |
| [20] | Driessens, F. C. M., Planell, J. A., and Gil, F. J., Calcium phosphate bone cements. In: Encyclopedic Handbook of Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Part B, Applications, Wise, D. L., Trantolo, D. J., Altobelli. D. E., Yaszemski, M. J., Gresser, J. D., Schwarz, E. R. Eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, USA, 1995; Vol. 2, pp. 855-877 |
| [21] | Bolarinwa, A., Gbureck, U., Purnell, P., Bold, M., and Grover, L. M., Cement casting of calcium pyrophosphate based bioceramics. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2010, 109, 291-295 |
| [22] | Schmitz, J. P., Hollinger, J. O., and Milan, S. B., Reconstruction of bone using calcium phosphate bone cements: a critical review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 57, 1122-1126 |
| [23] | Gbureck, U., Barralet, J. E., Spatz, K., Grover, L. M., and Thull, R., Ionic modification of calcium phosphate cement viscosity. Part I: Hypodermic injection and strength improvement of apatite cement. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2187-2195 |
| [24] | Generosi, A., Rau, J. V., Komlev, V. S., Albertini, V. R., Fedotov, A. Y., and Barinov, S., M. Anomalous hardening behavior of a calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 973-979 |
| [25] | Rau, J. V., Generosi, A., Komlev, V. S., Fosca, M., Barinov, S. M,, and Albertini, V. R., Real-time monitoring of the mechanism of poorly crystalline apatite cement conversion in the presence of chitosan, simulated body fluid and human blood. Dalton Trans. 2010, 21, 11412-11423 |
| [26] | Smirnov, V. V., Rau, J. V., Generosi, A., Albertini, V. R., Ferro, D., and Barinov, S. M., Elucidation of real-time hardening mechanisms of two novel high-strength calcium phosphate bone cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 93B, 74-83 |
| [27] | Tagaya, M., Goto, H., Iinuma, M., Wakamatsu, N., Tamura Y., and Doi, Y., Development of self-setting Te-Cp/alpha-TCP cement for pulpotomy. Dent. Mater. J. 2005, 24, 555-561 |
| [28] | Driessens, F. C. M., Boltong, M. G., Khairoun, I., de Maeyer, E. A. P., Ginebra, M. P., Wenz, R., Planell, J. A., and Verbeeck, R. M. H., Applied aspects of calcium phosphate bone cement. In: Biomaterials Engineering and Devices: Human Applications, Wise, D. L., Trantolo, D. J., Lewandrowski, K. U., Gresser, J. D., Cattaneo, M. V. Eds., Orthopedic, Dental and Bone Graft Applications. Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; Vol. 2, pp. 253-260. |
| [29] | Driessens, F. C. M., Planell, J. A., Boltong, M. G., Khairoun, I., and Ginebra, M. P., Osteotransductive bone cements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H: J. Eng. Med. 1998, 212, 427-435 |
| [30] | Frankenburg, E. P., Goldstein, S. A., Bauer, T. W., Harris, S. A., and Poser, R. D., Biomechanical and histological evaluation of a calcium phosphate cement. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1998, 80A, 1112-1124 |
| [31] | Frayssinet, P., Gineste, L., Conte, P., Fages, J., and Rouquet, N., Short-term implantation effects of a DCPD-based calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 971-977 |
| [32] | Rey, C., Tofighi, A., Mounic, S., Combes, C., and Lee, D., Biomimetism and calcium phosphate cements, In: Actualités en Biomatériaux, Mainard, D., Louis, J. P. Eds. Editions Romillat: Paris, France, 2002; Vol. 6, pp. 27-37 |
| [33] | Combes, C., Bareille, R., and Rey, C., Calcium carbonate-calcium phosphate mixed cement compositions for bone reconstruction. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 79A, 318-328 |
| [34] | Bohner, M., Gbureck, U., and Barralet, J. E., Technological issues for the development of more efficient calcium phosphate bone cements: a critical assessment. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6423-6429 |
| [35] | Ikenaga, M., Hardouin, P., Lemaître, J., Andrianjatovo, H., and Flautre, B., Biomechanical characterization of a biodegradable calcium phosphate hydraulic cement: a comparison with porous biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 40, 139-144 |
| [36] | Ginebra, M. P., Traykova, T., and Planell, J. A., Calcium phosphate cements: competitive drug carriers for the musculoskeletal system? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2171-2177 |
| [37] | Ginebra, M. P., Traykova, T., and Planell, J. A., Calcium phosphate cements as bone drug delivery systems: a review. J. Control. Release 2006, 113, 102-110 |
| [38] | It is interesting to note that calcium sulfate (gypsum or plaster of Paris) has been implanted into fracture gaps and voids of bones for more than 100 years[39-41] |
| [39] | Dreesmann, H., Knochenplombierung bei Hohlenforigen Defekten des Knochens. Beitr. Klin. Chir. 1892, 9, 804-810 |
| [40] | Peltier, L. F., The use of plaster of Paris to fill defects in bone. Clin. Orthop. 1961, 21, 1-29 |
| [41] | Kelly, C. M., Wilkins, R. M., Gitelis, S., Hartjen, C., Watson, J. T., and Kim, P. T., The use of a surgical grade calcium sulfate as a bone graft substitute: results of a multicenter trial. Clin. Orthop. 2001, 382, 42-50 |
| [42] | Bohner, M., New hydraulic cements based on α-tricalcium phosphate – calcium sulfate dihydrate mixtures. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 741-749 |
| [43] | Fernández, E., Vlad, M. D., Gel, M, M., Lopez, J., Torres, R., Cauich, J. V., and Bohner, M., Modulation of porosity in apatitic cements by the use of α-tricalcium phosphate – calcium sulphate dihydrate mixtures. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3395-3404 |
| [44] | Hu, G., Xiao, L., Fu, H., Bi, D., Ma, H., and Tong, P., Degradable and bioactive scaffold of calcium phosphate and calcium sulphate from self-setting cement for bone regeneration. J. Porous Mater. 2010, 17, 605-613 |
| [45] | Hu, G., Xiao, L., Fu, H., Bi, D., Ma, H., and Tong, P., Study on injectable and degradable cement of calcium sulphate and calcium phosphate for bone repair. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 627-634 |
| [46] | Nilsson, M., Fernández, E., Sarda, S., Lidgren, L., and Planell, J. A., Characterization of a novel calcium phosphate/sulphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 600-607 |
| [47] | Vlad, M. D., Şindilar, E. V., Mariñoso, M. L., Poeatǎ, I., Torres, R., López, J., Barracó, M., and Fernández, E., Osteogenic biphasic calcium sulphate dihydrate/iron-modified α-tricalcium phosphate bone cement for spinal applications: in vivo study. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 607-616 |
| [48] | Grover, L. M., Gbureck, U., Wright, A. J., Tremaynec, M., and Barralet, J. E., Biologically mediated resorption of brushite cement in vitro. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2178-2185 |
| [49] | Grover, L. M., Gbureck, U., Wright, A. J., and Barralet, J. E., Cement formulations in the calcium phosphate H2O – H3PO4 – H4P2O7 system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 3096-3103 |
| [50] | Grover, L. M., Gbureck, U., Young, A. M., Wright, A. J., and Barralet, J. E., Temperature dependent setting kinetics and mechanical properties of β-TCP – pyrophosphoric acid bone cement. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 46, 4955-4962 |
| [51] | Oh, K. S., Jeong, Y. K., Yu, J. P., Chae, S. K., Kim, H. Y., Lee, H. Y., and Jeun, S. S., Preparation and in vivo studies of β-TCP based bone cement containing polyphosphate. Key Eng. Mater. 2005, 284-286, 93-96 |
| [52] | Lilley, K. J., Gbureck, U., Wright, A. J., Knowles, J. C., Farrar, D. F., and Barralet, J. E., Brushite cements from polyphosphoric acid, calcium phosphate systems. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 1892-1898 |
| [53] | Fernández, E., Planell, J. A., and Best, S. M., Precipitation of carbonated apatite in the cement system α-Ca3(PO4)2 – Ca(H2PO4)2 – CaCO3. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 47, 466-471 |
| [54] | Calafiori, A. R., di Marco, G., Martino, G., and Marotta, M., Preparation and characterization of calcium phosphate biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 2331-2338 |
| [55] | Kon, M., Hirakata, L. M., Miyamoto, Y., Kasahara, H., and Asaoka, K., Strengthening of calcium phosphate cement by compounding calcium carbonate whiskers. Dent. Mater. J. 2005, 24, 104-110 |
| [56] | Serraj, S., Michailesco, P., Margerit, J., Bernard, B., and Boudeville, P., Study of a hydraulic calcium phosphate cement for dental applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 125-131 |
| [57] | Nurit, L., Margerit, J., Terol, A., and Boudeville, P., pH- metric study of the setting reaction of monocalcium phosphate monohydrate/calcium oxide-based cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 1007-1014 |
| [58] | Boudeville, P., Serraj, S., Leloup, J. M., Margerit, J., Pauvert, B., and Terol, A., Physical properties and self-setting mechanism of calcium phosphate cements from calcium bis-dihydrogenophosphate monohydrate and calcium oxide. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 99-109 |
| [59] | Michaïlesco, P., Kouassi, M., Briak, H. E., Armynot, A., and Boudeville, P., Antimicrobial activity and tightness of a DCPD – CaO-based hydraulic calcium phosphate cement for root canal filling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 74B, 760-767 |
| [60] | Briak, H. E., Durand, D., Nurit, J., Munier, S., Pauvert, B., and Boudeville, P., Study of a hydraulic dicalcium phosphate dihydrate/calcium oxide-based cement for dental applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 2002, 63, 447-453 |
| [61] | Briak, H. E., Durand, D., and Boudeville, P., Study of a hydraulic DCPA/CaO-based cement for dental applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 737-744 |
| [62] | Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., and Ishikawa, K., Formation of hydroxyapatite in new calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1593-1599 |
| [63] | Yang, Q., Troczynski, T., and Liu, D. M., Influence of apatite seeds on the synthesis of calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2751-2760 |
| [64] | Hsu, H. C., Chiu, C. Y., Tuan, W. H., and Lee, H. Y., Structural stability of calcium phosphate cement during aging in water. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 429-433 |
| [65] | Roemhildt, M. L., McGee, T. D., and Wagner, S. D., Novel calcium phosphate composite bone cement, strength and bonding properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 137-141 |
| [66] | Roemhildt, M. L., Wagner, S. D., and McGee, T. D., Characterization of a novel calcium phosphate composite bone cement: flow, setting, and aging properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 1127-1132 |
| [67] | Wang, X., Ye, J., Wang, Y., and Chen, L., Self-setting properties of a β-dicalcium silicate reinforced calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 82B, 93-99 |
| [68] | Huan, Z., and Chang, J., Novel tricalcium silicate/ monocalcium phosphate monohydrate composite bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 82B, 352-359 |
| [69] | Huan, Z., and Chang, J., Calcium-phosphate-silicate composite bone cement, self-setting properties and in vitro bioactivity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 833-841 |
| [70] | Huan, Z., and Chang, J., Novel bioactive composite bone cements based on the β-tricalcium phosphate – monocalcium phosphate monohydrate composite cement system. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1253-1264 |
| [71] | Shen, Q., Sun, J., Wu, J., Liu, C., and Chen, F., An in vitro investigation of the mechanical-chemical and biological properties of calcium phosphate/calcium silicate/bismutite cement for dental pulp capping. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94, 141-148 |
| [72] | Guo, D., Xu, K., Zhao, X., and Han, Y., Development of a strontium-containing hydroxyapatite bone cement. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4073-4083 |
| [73] | Wang, X., and Ye, J., Variation of crystal structure of hydroxyapatite in calcium phosphate cement by the substitution of strontium ions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1183-1186 |
| [74] | Pina, S., Torres, P. M. C., and Ferreira, J. M. F., Injectability of brushite-forming Mg-substituted and Sr-substituted α-TCP bone cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 431-438 |
| [75] | Wu, F., Su, J. C., Wei, J., Guo, H., and Liu, C. S., Injectable bioactive calcium-magnesium phosphate cement for bone regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 044105 (7 pages) |
| [76] | Wu, F., Wei, J., Guo, H., Chen, F. P., Hong, H., and Liu, C. S., Self-setting bioactive calcium-magnesium phosphate cement with high strength and degradability for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1873-1884 |
| [77] | Pina, S., Olhero, S. M., Gheduzzi, S., Miles A. W., and Ferreira, J. M. F., Influence of setting liquid composition and liquid-to-powder ratio on properties of a Mg-substituted calcium phosphate cement. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1233-1240 |
| [78] | Klammert, U., Reuther, T., Blank, M., Reske, I., Barralet, J. E., Grover, L. M., Kübler, A. C., and Gbureck, U., Phase composition, mechanical performance and in vitro biocompatibility of hydraulic setting calcium magnesium phosphate cement. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1529-1535 |
| [79] | Jia, J., Zhou, H., Wei, J., Jiang, X., Hua, H., Chen, F., Wei, S., Shin, J. W., and Liu, C., Development of magnesium calcium phosphate biocement for bone regeneration. J. Royal Soc. Interf. 2010, 7, 1171-1180 |
| [80] | Pina, S., Vieira, S. I., Torres, P. M. C., Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F., Neubauer, J., da Cruz E. Silva, O. A. B., da Cruz E. Silva, E. F., and Ferreira, J. M. F., In vitro performance assessment of new brushite-forming Zn- and ZnSr-substituted β-TCP bone cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94B, 414-420 |
| [81] | Gbureck, U., Knappe, O., Grover, L. M., and Barralet, J. E., Antimicrobial potency of alkali ion substituted calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6880-6886 |
| [82] | Driessens, F. C. M., Boltong, M. G., de Mayer, E. A. P., Wenz, R., Nies, B., and Planell, J. A., The Ca/P range of nanoapatitic calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4011- 4017 |
| [83] | Gbureck, U., Thull, R., and Barralet, J. E., Alkali ion substituted calcium phosphate cement formation from mechanically activated reactants. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 423-427 |
| [84] | Doi, Y., Shimizu, Y., Moriwaki, Y., Aga, M., Iwanaga, H., Shibutani, T., Yamamoto, K., and Iwayama, Y., Development of a new calcium phosphate cement that contains sodium calcium phosphate. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 847-854 |
| [85] | Lilley, J., Gbureck, U., Knowles, J. C., Farrar, D. F., and Barralet, J. E., Cement from magnesium substituted hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 455-460 |
| [86] | Ni, G. X., Lu, W. W., Tang, B., Ngan, A. H. W., Chiu, K. Y., Cheung, K. M. C., Li, Z. Y., and Luk, K. D. K., Effect of weight-bearing on bone-bonding behavior of strontium-containing hydroxyapatite bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 83A, 570-576 |
| [87] | Alkhraisat, M. H., Mariño, F. T., Rodríguez, C. R., Jerez, L. B., and Cabarcos, E. L., Combined effect of strontium and pyrophosphate on the properties of brushite cements. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 664-670 |
| [88] | Yao, Z. P., Liu, W, G., and Ni, G. X., Biology characteristics and clinical application of strontium substituted hydroxyapatite bone cement. J. Clin. Rehabil. Tissue Eng. Res. 2008, 12, 7151-7154 |
| [89] | Li, S., Liu, B., Cheng, J., and Hu, J., Composite cement of magnesium-bearing phosphoaluminate-hydroxyapatite reinforced by treated raw silk fiber. Cement and Concrete Composites 2008, 30, 347-352 |
| [90] | Ni, G. X., Lin, J. H., Chiu, P. K. Y., Li, Z. Y., and Lu, W. W., Effect of strontium-containing hydroxyapatite bone cement on bone remodeling following hip replacement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 377-384 |
| [91] | Fadeeva, I. V., Barinov, S. M., Komlev, V. S., Fedotov, D. A., Durisin, J., and Medvecky, L., Apatite formation in the reaction-setting mixture of Ca(OH)2 – KH2PO4 system. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 70A, 303-308 |
| [92] | Tas, A. C., Use of vaterite and calcite in forming calcium phosphate cement scaffolds. Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 2008, 28, 135-150 |
| [93] | Fernández, E., Vlad, M. D., Hamcerencu, M., Darie, A., Torres, R., and Lopez, J., Effect of iron on the setting properties of α-TCP bone cements. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 3677-3682 |
| [94] | Vlad, M. D., del Valle, L. J., Poeata, I., Barracó, M., López, J., Torres, R., and Fernández, E., Injectable iron-modified apatitic bone cement intended for kyphoplasty, cytocompatibility study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 3575-3583 |
| [95] | http://en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Cement (accessed in November 2011) |
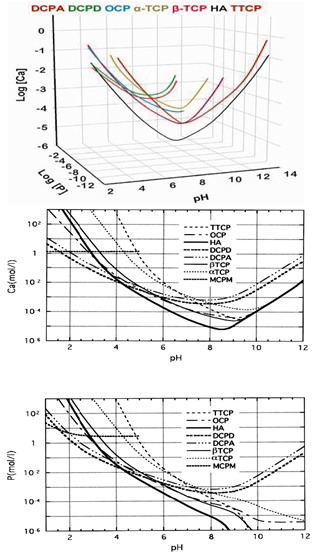
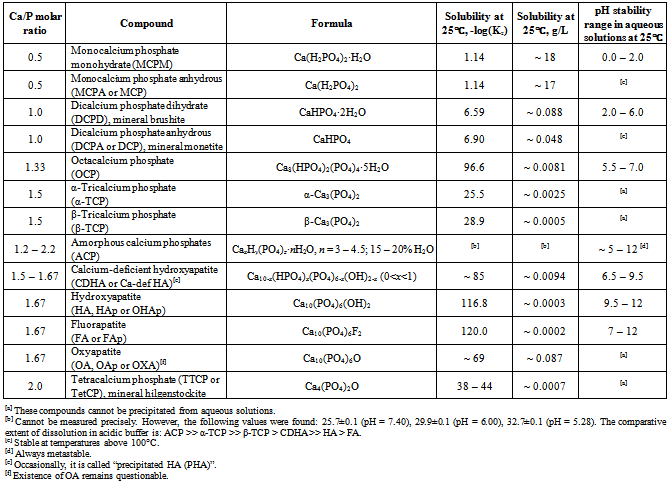
| [96] | There are some differences between TTCP + DCPD and TTCP + DCPA cements. Due to a higher solubility of DCPD (Table 1 and Fig. 1), a TTCP + DCPD cement sets faster than a TTCP + DCPA cement. Besides, injectability of a TTCP + DCPD cement is better[97,98] |
| [97] | Burguera, E. F., Xu, H. H. K., and Weir, M. D., Injectable and rapid-setting calcium phosphate bone cement with dicalcium phosphate dihydrate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 77B, 126-134 |
| [98] | Burguera, E. F., Guitian, F., and Chow, L. C., A water setting tetracalcium phosphate – dicalcium phosphate dihydrate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 71A, 275-282 |
| [99] | Driessens, F. C. M., Boltong, M. G., Bermudez, O., and Planell, J. A., Formulation and setting times of some calcium orthophosphate cements, a pilot study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1993, 4, 503-508 |
| [100] | Chow, L. C., Markovic, M., and Takagi, S., Calcium phosphate cements. In: Cements research progress, Struble, L. J., Ed. Chapter 7. American Ceramic Society: Westerville, OH, USA, 1998; pp. 215-238 |
| [101] | Driessens, F. C. M., Boltong, M. G., Bermudez, O., Planell, J. A., Ginebra, M. P., and Fernández, E., Effective formulations for the preparation of calcium phosphate bone cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1994, 5, 164-170 |
| [102] | Kurashina, K., Hirano, M., Kotani, A., Klein, C. P. A. T., and de Groot, K., In vivo study of calcium phosphate cements, implantation of an α-tricalcium phosphate/dicalcium phosphate dibasic/tetracalcium phosphate monoxide cement paste. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 539-543 |
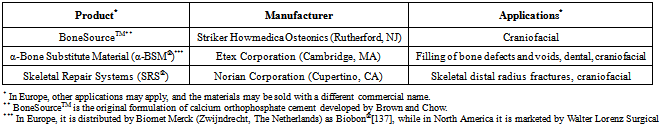
| [103] | Friedman, C. D., Costantino, P. D., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., BoneSourceTM hydroxyapatite cement, a novel biomaterial for craniofacial skeletal tissue engineering and reconstruction. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 43, 428-432 |
| [104] | Khairoun, I., Boltong, M. G., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell J. A., Effect of calcium carbonate on the compliance of apatitic calcium phosphate bone cement. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 1535-1539 |
| [105] | Fernández, E., Gil, F. J., Best, S. M., Ginebra, M. P., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Improvement of the mechanical properties of new calcium phosphate bone cements in the CaHPO4 – α-Ca3(PO4)2 system, compressive strength and microstructural development. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 41, 560-567 |
| [106] | Fukase, Y., Eanes, E. D., Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., and Brown, W. E., Setting reactions and compressive strengths of calcium phosphate cements. J. Dent. Res. 1990, 69, 1852-1856 |
| [107] | Xie, L., and Monroe, E. A., Calcium phosphate dental cements. Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1991, 179, 25-39 |
| [108] | Ishikawa, K., Miyamoto, Y., Kon, M., Nagayama, M., and Asaoka, K., Non-decay type fast-setting calcium orthophosphate cement composite with sodium alginate. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 527-532 |
| [109] | Xu, H. H. K., Quinn, J. B., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Processing and properties of strong and non-rigid calcium phosphate cement. J. Dent. Res. 2002, 81, 219-224 |
| [110] | Lee, Y. K., Lim, B. S., and Kim, C. W., Mechanical properties of calcium phosphate based dental filling and regeneration materials. J. Oral Rehabil. 2003, 30, 418-425 |
| [111] | Ginebra, M. P., Fernández, E., de Mayer, E. A. P., Verbeeck, R. M. H., Boltong, M. G., Ginebra, J., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Setting reaction and hardening of an apatitic calcium phosphate cement. J. Dent. Res. 1997, 76, 905-912 |
| [112] | Liu, C., Shen, W., Gu, Y., and Hu, L., Mechanism of the hardening process for a hydroxyapatite cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 35, 75-80 |
| [113] | Driessens, F. C. M., de Mayer, E. A. P., Fernández, E., Boltong, M. G., Berger G., Verbeeck, R. M. H., Ginebra, M. P., and Planell, J. A., Amorphous calcium phosphate cements and their transformation into calcium deficient hydroxyapatite. Bioceramics 1996, 9, 231-234 |
| [114] | Driessens, F. C. M., Planell, J. A., and Gil, F., Calcium phosphate bone cements. In: Encyclopedic handbook of biomaterials and bioengineering, Wise, D. L., Trantolo, D. J., Altobelli, D. E., Yaszemski, M. J., Cresser, J. D., and Schwartz, E. R., Eds. Part B, Applications. Marcel Dekker: New York, USA, 1995; Vol. 2, pp. 855-877 |
| [115] | Lemaître, J., Injectable calcium phosphate hydraulic cements: new developments and potential applications. Inn. Tech. Biol. Med. 1995, 16, 109-120 |
| [116] | Neira, I. S., Kolen’ko, Y. V., Lebedev, O. I., van Tendeloo, G., Gupta, H. S., Matsushita, N., Yoshimura, M., and Guitián, F., Rational synthesis of a nanocrystalline calcium phosphate cement exhibiting rapid conversion to hydroxyapatite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 2124-2132 |
| [117] | Tañag, M. A., Yano, K., and Hosokawa, K., Orbital floor reconstruction using calcium phosphate cement paste: an animal study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 1826-1831 |
| [118] | Hatoko, M., Tada, H., Tanaka, A., Yurugi, S., Niitsuma, K., and Iioka, H., The use of calcium phosphate cement paste for the correction of the depressed nose deformity. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2005, 16, 327-331 |
| [119] | Tañag, M. A., Madura, T., Yano, K., and Hosokawa, K., Use of calcium phosphate cement paste in orbital volume augmentation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 1186-1193 |
| [120] | Meng, D., Xie, Q. F., and Xiao, J. J., Effects of two calcium phosphate cement pastes on osteoblasts during solidification. J. Clin. Rehabilit. Tiss. Eng. Res. 2009, 13, 471-474 |
| [121] | According to Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia: “Putty is a generic term for a plastic material similar in texture to clay or dough typically used in domestic construction and repair as a sealant or filler. ” http://en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Putty (accessed in November 2011) |
| [122] | Ishikawa, K., Miyamoto, Y., Takechi, M., Toh, T., Kon, M., Nagayama, M., and Asaoka, K., Non-decay type fast-setting calcium phosphate cement: hydroxyapatite putty containing an increased amount of sodium alginate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 36, 393-399 |
| [123] | Ishikawa, K., Miyamoto, Y., Takechi, M., Ueyama, Y., Suzuki, K., Nagayama, M., and Matsumura, T., Effects of neutral sodium hydrogen phosphate on setting reaction and mechanical strength of hydroxyapatite putty. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 44, 322-329 |
| [124] | Momota, Y., Miyamoto, Y., Ishikawa, K., Takechi, M., Yuasa, T., Tatehara, S., and Nagayama, M., Effects of neutral sodium hydrogen phosphate on the setting property and hemostatic ability of hydroxyapatite putty as a local hemostatic agent for bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 69B, 99-103 |
| [125] | Bohner, M., Design of ceramic-based cements and putties for bone graft substitution. Eur. Cell Mater. 2010, 20, 1-12 |
| [126] | In the vast majority cases, a precipitated poorly crystalline HA and CDHA are undistinguishable and might be considered as synonyms[11] |
| [127] | To honor Prof. George Jarvis Brush (1831 – 1912), an American mineralogist, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, USA |
| [128] | Xia, Z., Grover, L. M., Huang, Y., Adamopoulos, I. E., Gbureck, U., Triffitt, J. T., Shelton, R. M., and Barralet, J. E., In vitro biodegradation of three brushite calcium phosphate cements by a macrophage cell-line. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4557-4565 |
| [129] | Monma, H., Makishima, A., Mitomo, M., and Ikegami, T., Hydraulic properties of the tricalcium phosphate – dicalcium phosphate mixture. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 1988, 96, 878-880 |
| [130] | Bermudez, O., Boltong, M. G., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Development of an octacalcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1994, 5, 144-146 |
| [131] | Sena, M., Yamashita, Y., Nakano, Y., Ohgaki, M., Nakamura, S., Yamashita, K., and Takagi, Y., Octacalcium phosphate-based cement as a pulp-capping agent in rats. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2004, 97, 749-755 |
| [132] | Markovic, M., and Chow, L. C., An octacalcium phosphate forming cement. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2010, 115, 257-265 |
| [133] | In early 1990-s, depending on the type of calcium orthophosphate formed after the setting, five groups of the cement formulations were thought to exist: DCPD, CDHA, HA, ACP and OCP[101, 134], while currently only two cement groups remain |
| [134] | Khairoun, I., Boltong, M. G., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Limited compliance of some apatitic calcium phosphate bone cements with clinical requirements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 667-671 |
| [135] | Lacout, J., Mejdoubi, E., and Hamad, M., Crystallization mechanisms of calcium orthophosphate cement for biological uses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1996, 7, 371-374 |
| [136] | Song, Y., Feng, Z., and Wang, T., In situ study on the curing process of calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1185-1193 |
| [137] | Weiss, D. D., Sachs, M. A., and Woodard, C. R., Calcium phosphate bone cements: a comprehensive review. J. Long Term Eff. Med. Implants 2003, 13, 41-47 |
| [138] | Fernández, E., Gil, F. J., Ginebra, M. P., Driessens, F. C. M., Planell, J. A., and Best, S. M., Calcium phosphate bone cements for clinical applications. Part I: Solution chemistry. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 169-176 |
| [139] | Brown, W. E., and Chow, L. C., A new calcium phosphate water-setting cement. In: Cements Research Progress, Brown, P. W., Ed., American Ceramic Society: Westerville, OH, USA, 1986; pp. 351-379 |
| [140] | Hatim, Z., Freche, M., Keribech, A., and Lacout, J. L., The setting mechanism of a phosphocalcium biological cement. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 1998, 23, 65-68 |
| [141] | Ishikawa, K., and Asaoka, K., Estimation of ideal mechanical strength and critical porosity of calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 1537-1543 |
| [142] | Chow, L. C., Development of self-setting calcium phosphate cements. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 1991, 99, 954-964 |
| [143] | Chow, L. C., Calcium phosphate cements: chemistry, properties and applications. Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2000, 599, 27-37 |
| [144] | Chow, L. C., Calcium phosphate cements. In: Octacalcium Phosphate, Chow, L. C., Eanes, E. D., Eds., Monographs in Oral Science. Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2001; Vol. 18, pp. 148-163 |
| [145] | Brown, P. W., and Fulmer, M. T., Kinetics of hydroxyapatite formation at low temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 934-940 |
| [146] | TenHuisen, K. S., and Brown, P. W., The formation of hydroxyapatite-ionomer cements at 38 °C. J. Dent. Res. 1994, 3, 598-606 |
| [147] | Ishikawa, K., Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., and Suzuki, K., Reaction of calcium phosphate cements with different amounts of tetracalcium phosphate and dicalcium phosphate anhydrous. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 46, 504-510 |
| [148] | Matsuya, S., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Effect of mixing ratio and pH on the reaction between Ca4(PO4)2O and CaHPO4. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 305-311 |
| [149] | Burguera, E. F., Guitian, F., and Chow, L. C., Effect of the calcium to phosphate ratio of tetracalcium phosphate on the properties of calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85A, 674-683 |
| [150] | Lemaître, J., Mirtchi, A. A., and Mortier, A., Calcium phosphate cements for medical use: state of the art and perspectives of development. Silic. Ind. 1987, 9-10, 141-146 |
| [151] | Bajpai, P., Fuchs, C., and McCullum, D., Development of tricalcium orthophosphate ceramic cement. In: Quantitative characterization and performance of porous implants for hard tissue applications, Lemons, J., Ed., ASTM STP 953. Am. Soc. Test. Mater. : Philadelphia, 1987; pp. 377-388 |
| [152] | Mirtchi, A. A., Lemaître, J., and Terao, N., Calcium phosphate cements: study of the β-tricalcium phosphate – monocalcium phosphate system. Biomaterials 1989, 10, 475-480 |
| [153] | Bohner, M., van Landuyt, P., Merkle, H. P., and Lemaître, J., Composition effects on the pH of a hydraulic calcium orthophosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1997, 8, 675-681 |
| [154] | Bohner, M., Lemaître, J., and Ring, T. A., Effects of sulfate, pyrophosphate and citrate ions on the physiochemical properties of cements made of β-tricalcium phosphate – phosphoric acid – water mixtures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 1427-1434 |
| [155] | Grover, L. M., Hofmann M. P., Gbureck, U., Kumarasami B., and Barralet, J. E., Frozen delivery of brushite calcium phosphate cements. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1916-1923 |
| [156] | Fernández, E., Gil, F. J., Best, S. M., Ginebra, M. P., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., The cement setting reaction in the CaHPO4 – α-Ca3(PO4)2 system: an X-ray diffraction study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 42, 403-406 |
| [157] | Fernández, E., Gil, F. J., Ginebra, M. P., Driessens, F. C. M., Planell, J. A., and Best, S. M., Production and characterisation of new calcium phosphate bone cements in the CaHPO4 – α-Ca3(PO4)2 system: pH, workability and setting times. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 223-230 |
| [158] | Barralet, J. E., Lilley, K. J., Grover, L. M., Farrar, D. F., Ansell, C., and Gbureck, U., Cements from nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 407-411 |
| [159] | Lilley, K. J., Gbureck, U., Wright, A. J., Farrar, D. F., and Barralet, J. E., Cement from nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite: effect of calcium phosphate ratio. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 1185-1190 |
| [160] | Alge, D. L., Cruz, G. S., Goebel, W. S., and Chu, T. M. G., Characterization of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate cements prepared using a novel hydroxyapatite-based formulation. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 025016 |
| [161] | Wang, X., Ye, J., Wang, Y., Wu, X., and Bai, B., Control of crystallinity of hydrated products in a calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 81A, 781-790 |
| [162] | Wang, X., Ye, J., and Wang, H., Effects of additives on the rheological properties and injectability of a calcium phosphate bone substitute material. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 78B, 259-264 |
| [163] | Tofighi, A., Schaffer, K., and Palazzolo, R., Calcium phosphate cement (CPC): a critical development path. Key Eng. Mater. 2008, 361-363, 303-306 |
| [164] | de Maeyer, E. A. P., Verbeeck, R. M. H., and Vercruysse, C. W. J., Conversion of octacalcium phosphate in calcium phosphate cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 95-106 |
| [165] | Nakano, Y., Ohgaki, M., Nakamura, S., Takagi, Y., and Yamashita, K., In vitro and in vivo characterization and mechanical properties of α-TCP/OCP settings. Bioceramics 1999, 12, 315-318 |
| [166] | Nakano, Y., Preparation and characterization of porous octacalcium phosphate setting improved by α-tricalcium phosphate additive. J. Dent. Mater. 2000, 19, 65-76 |
| [167] | Wang, X., Ye, J., and Wang, Y., Hydration mechanism of a novel PCCP + DCPA cement system. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 813-816 |
| [168] | Zoulgami, M., Lucas, A., Briard, P., and Gaudé, J., A self-setting single-component calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1933-1937 |
| [169] | Knaack, D., Goad, M. E., Aiolova, M., Rey, C., Tofighi, A., Chakravarthy, P., and Lee, D. D., Resorbable calcium phosphate bone substitute. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 43, 399-409 |
| [170] | Tofighi, A., Mounic, S., Chakravarthy, P., Rey, C., and Lee, D., Setting reactions involved in injectable cements based on amorphous calcium phosphate. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 192-195, 769-772 |
| [171] | Monma, H., and Kanazawa, T., Hydration of α-tricalcium phosphate. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 108, 575-580 |
| [172] | Fernández, E., Ginebra, M. P., Boltong, M. G., Driessens, F. C. M., Ginebra, J., de Maeyer, E. A. P., Verbeeck, R. M. H., and Planell, J. A., Kinetic study of the setting reaction of a calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 32, 367-374 |
| [173] | Gbureck, U., Barralet, J. E., Radu L., Klinger, H. G., and Thull, R., Amorphous α-tricalcium phosphate, preparation and aqueous setting reaction. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 1126-1132 |
| [174] | Bohner, M. Malsy, A. K., Camire, C. L., and Gbureck, U., Combining particle size distribution and isothermal calorimetry data to determine the reaction kinetics of α-tricalcium phosphate – water mixtures. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 343-348 |
| [175] | Brunner, T. J., Grass, R. N., Bohner, M., and Stark, W. J., Effect of particle size, crystal phase and crystallinity on the reactivity of tricalcium phosphate cements for bone reconstruction. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 38, 4072-4078 |
| [176] | Alves, H. L. R., dos Santos, L. A., and Bergmann, C. P., Injectability evaluation of tricalcium phosphate bone cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 2241-2246 |
| [177] | Jack, V., Buchanan, F. J., and Dunne, N. J., Particle attrition of α-tricalcium phosphate, effect on mechanical, handling, and injectability properties of calcium phosphate cements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H: J. Eng. Med. 2008, 222, 19-28 |
| [178] | Oh, S. A., Lee, G. S., Park, J. H., and Kim, H. W., Osteoclastic cell behaviors affected by the α-tricalcium phosphate based bone cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 3019-3027 |
| [179] | Gbureck, U., Grolms, O., Barralet, J. E., Grover, L. M., and Thull, R., Mechanical activation and cement formation of β-tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4123-4131 |
| [180] | Gbureck, U., Barralet, J. E., Hofmann, M. P., and Thull, R., Nanocrystalline tetracalcium phosphate cement. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 425-428 |
| [181] | Gbureck, U., Barralet, J. E., Hofmann, M. P., and Thull, R., Mechanical activation of tetracalcium phosphate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 311-313 |
| [182] | Tsai, C. H., Ju, C. P., and Lin, J. H. C., Morphology and mechanical behavior of TTCP-derived calcium phosphate cement subcutaneously implanted in rats. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 2407-2415 |
| [183] | Tsai, C. H., Lin, R. M., Ju, C. P., and Lin, J. H. C., Bioresorption behavior of tetracalcium phosphate-derived calcium phosphate cement implanted in femur of rabbits. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 984-993 |
| [184] | Tsai, C. H., Lin, J. H. C., and Ju, C. P., γ-radiation-induced changes in structure and properties of tetracalcium phosphate and its derived calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 80B, 244-252 |
| [185] | Chow, L. C., Markovic, M., Frukhtbeyn, S. A., and Takagi, S., Hydrolysis of tetracalcium phosphate under a near-constant composition condition – effects of pH and particle size. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 393-401 |
| [186] | TenHuisen, K. S., and Brown, P. W., Formation of calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite from α-tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 2209-2217 |
| [187] | Ginebra, M. P., Fernández, E., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Modeling of the hydrolysis of α-TCP. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 2808-2812 |
| [188] | Durucan, C., and Brown, P. W., α-tricalcium phosphate hydrolysis to hydroxyapatite at and near physiological temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 365-371 |
| [189] | Durucan, C., and Brown, P. W., Kinetic model for α-tricalcium phosphate hydrolysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 2013-2018 |
| [190] | Fulmer, M. T., and Brown, P. W., Hydrolysis of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate to hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 197-202 |
| [191] | Ginebra, M. P., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Effect of the particle size on the micro and nanostructural features of a calcium phosphate cement: a kinetic analysis. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3453-3462 |
| [192] | Koshino, T., Kubota, W., and Morii, T., Bone formation as a reaction to hydraulic hydroxyapatite thermal decomposition product used as bone cement in rabbits. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 125-128 |
| [193] | Liu, C., Huang, Y., and Chen, J., The physicochemical properties of the solidification of calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 69B, 73-78 |
| [194] | Liu, C., Gai, W., Pan, S., and Liu, Z., The exothermal behavior in the hydration process of calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2995-3003 |
| [195] | Charrière, E., Terrazzoni, S., Pittet, C., Mordasini, P., Dutoit, M., Lemaître, J., and Zysset, P., Mechanical characterization of brushite and hydroxyapatite cements. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2937-2945 |
| [196] | Morgan, H., and Dauskardt, R. H., Notch strength insensitivity of self-setting hydroxyapatite bone cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 647-653 |
| [197] | Bohner, M., Calcium orthophosphates in medicine: from ceramics to calcium phosphate cements. Injury 2000, 31, Suppl. 4, S-D37-S-D47 |
| [198] | Bohner, M., Physical and chemical aspects of calcium phosphates used in spinal surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2001, 10, S114-S121 |
| [199] | von Gonten, A. S., Kelly, J. R., and Antonucci, J. M., Load-bearing behavior of a simulated craniofacial structure fabricated from a hydroxyapatite cement and bioresorbable fiber-mesh. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 95-100 |
| [200] | Gisep, A., Kugler, S., Wahl, D., and Rahn, B., The mechanical characterization of a bone defect model filled with ceramic cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 1065-107 |
| [201] | Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., Markovic, M., Friedman, C. D., and Costantino, P. D., Morphological and phase characterizations of retrieved calcium phosphate cement implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 2001, 58, 36-41 |
| [202] | Ambard, A. J., and Mueninghoff, L., Calcium phosphate cement: review of mechanical and biological properties. J. Prosthodont. 2006, 15, 321-328 |
| [203] | Lewis, G., Injectable bone cements for use in vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, state-of-the-art review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 76B, 456-468 |
| [204] | Kenny, S. M., and Buggy, M., Bone cements and fillers: a review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 923-938 |
| [205] | Takagi, S., Frukhtbeyn, S., Chow, L. C., Sugawara, A., Fujikawa, K., Ogata, H., Hayashi, M., and Ogiso, B., In vitro and in vivo characteristics of fluorapatite-forming calcium phosphate cements. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2010, 115, 267-276 |
| [206] | Constantz, B. R., Ison, I. C., Fulmer, M. T., Poser, R. D., Smith, S. T., van Wagoner, M., Ross, J., Goldstein, S. A., Jupiter, J. B., and Rosenthal, D. I., Skeletal repair by in situ formation of the mineral phase of bone. Science 1995, 267, 1796-1799 |
| [207] | Bohner, M., Reactivity of calcium phosphate cements. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 38, 3980-3986 |
| [208] | Bohner, M., Brunner, T. J., and Stark, W. J., Controlling the reactivity of calcium phosphate cements. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5669-5675 |
| [209] | Yuan, H., Li, Y., de Bruijn, J. D., de Groot, K., and Zhang, X., Tissue responses of calcium phosphate cement, a study in dogs. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1283-1290 |
| [210] | Takechi, M., Miyamoto, Y., Ishikawa, K., Toh, T., Yuasa, T., Nagayama, M., and Suzuki, K., Initial histological evaluation of anti-washout type fast-setting calcium phosphate cement following subcutaneous implantation. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 2057-2063 |
| [211] | Fulmer, M. T., and Brown, P. W., Effects of Na2HPO4 and NaH2PO4 on hydroxyapatite formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1993, 27, 1095-1102 |
| [212] | Otsuka, M., Matsuda, Y., Suwa, Y., Fox, J. L., and Higuchi, W. I., Effect of particle size of metastable calcium phosphates on mechanical strength of a novel self-setting bioactive calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 25-32 |
| [213] | Liu, C., Shao, H., Chen, F., and Zheng, H., Effects of granularity of raw materials on the hydration and hardening process of calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4103-4113 |
| [214] | Chen, W. C., Lin, J. H. C., and Ju, C. P., Transmission electron microscopic study on setting mechanism of tetracalcium phosphate/dicalcium phosphate anhydrous-based calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 64, 664-671 |
| [215] | Fernández, E., Gil, F. J., Ginebra, M. P., Driessens, F. C. M., Planell, J. A., and Best, S. M., Calcium phosphate bone cements for clinical applications. Part II: Precipitate formation during setting reactions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 177-183 |
| [216] | Brown, W. E., Crystal growth of bone mineral. Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 1966, 44, 205-220 |
| [217] | Tung, M. S., and Brown, W. E., An intermediate state in hydrolysis of amorphous calcium phosphate. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1983, 35, 783-790 |
| [218] | Brown, W. E., Eidelman, N., and Tomazic, B. B., Octacalcium phosphate as a precursor in biomineral formation. Adv. Dent. Res. 1987, 1, 306-313 |
| [219] | Constantz, B. R., Barr, B. M., Ison, I. C., Fulmer, M. T., Baker, J., McKinney L. A., Goodman S. B., Gunasekaren, S., Delaney, D. C., Ross, J., and Poser, R. D., Histological, chemical and crystallographic analysis of four calcium phosphate cements in different rabbit osseous sites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 1998, 43, 451-461 |
| [220] | Elliott, J. C., Structure and chemistry of the apatites and other calcium orthophosphates, Elsevier: Amsterdam, Holland, 1994; 404 pp |
| [221] | Legrand, A. P., Sfihi, H., Lequeux, N., and Lemaître, J., 31P solid-state NMR study of the chemical setting process of a dual-paste injectable brushite cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 91B, 46-54 |
| [222] | Bohner, M., Merkle, H. P., van Landuyt, P., Trophardy, G., and Lemaître, J., Effect of several additives and their admixtures on the physico-chemical properties of a calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 111-116 |
| [223] | Vereecke, G., and Lemaître, J., Calculation of the solubility diagrams in the system Ca(OH)2 – H3PO4 – KOH – HNO3 – CO2 – H2O. J. Cryst. Growth 1990, 104, 820-832 |
| [224] | Klein, C. P., de Groot, K., Driessen, A. A., and van der Lubbe, H. B., Interaction of biodegradable β-whitlockite ceramics with bone tissue, an in vivo study. Biomaterials 1985, 6, 189-192 |
| [225] | Liu, C., Shen, W., and Chen, J., Solution property of calcium phosphate cement hardening body. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1999, 58, 78-83 |
| [226] | Apelt, D., Theiss, F., El-Warrak, A. O., Zlinszky, K., Bettschart-Wolfisberger, R., Bohner, M., Matter, S., Auer, J. A., and von Rechenberg, B., In vivo behavior of three different injectable hydraulic calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1439-1451 |
| [227] | Barralet, J. E., Grover, L. M., and Gbureck, U., Ionic modification of calcium phosphate cement viscosity. Part II: Hypodermic injection and strength improvement of brushite cement. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2197-2203 |
| [228] | Sarda, S., Fernández, E., Nilsson, M., Balcells, M., and Planell, J. A., Kinetic study of citric acid influence on calcium phosphate bone cements as water-reducing agent. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 653-659 |
| [229] | Qi, X., Ye, J., and Wang, Y., Improved injectability and in vitro degradation of a calcium phosphate cement containing poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1837-1845 |
| [230] | Grover, L. M., Knowles, J. C., Fleming, G. J. P., and Barralet, J. E., In vitro ageing of brushite calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4133-4141 |
| [231] | Mariño, F. T., Mastio, J., Rueda, C., Blanco, L., and Cabarcos, E. L., Increase of the final setting time of brushite cements by using chondroitin 4-sulfate and silica gel. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1195-1201 |
| [232] | Mariño, F. T., Torres, J., Hamdan, M., Rodríguez, C. R., and Cabarcos, E. L., Advantages of using glycolic acid as a retardant in a brushite forming cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 83B, 571-579 |
| [233] | Flautre, B., Delecourt, C., Blary, M., van Landuyt, P., Lemaître, J., and Hardouin, P., Volume effect on biological properties of a calcium phosphate hydraulic cement, experimental study on sheep. Bone 1999, 25, S35-S39 |
| [234] | Bohner, M., pH variations of a solution after injecting brushite cements. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 192-195, 813-816 |
| [235] | Xie, J., Riley, C., and Chittur, K., Effect of albumin on brushite transformation to hydroxyapatite. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 57, 357-365 |
| [236] | Frayssinet, P., Roudier, M., Lerch, A., Ceolin, J. L., Depres, E., and Rouquet, N., Tissue reaction against a self-setting calcium phosphate cement set in bone or outside the organism. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 811-815 |
| [237] | Ohura, K., Bohner, M., Hardouin, P., Lemaître, J., Pasquier, G., and Flautre, B., Resorption of and bone formation from new β-tricalcium phosphate – monocalcium phosphate cements: an in vivo study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 30, 193-200 |
| [238] | Flautre, B., Maynou, C., Lemaître, J., van Landuyt, P., and Hardouin, P., Bone colonization of β-TCP granules incorporated in brushite cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 2002, 63, 413-417 |
| [239] | Standard test method for time of setting of hydraulic cement paste by Gillmore needles. ASTM C266-89. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, Vol. 04. 01: Cement, Lime, Gypsum. American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, USA, 1993; pp. 189-191 |
| [240] | Standard test method for time of setting of hydraulic cement paste by Vicat needle. ASTM C191-92. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, Vol. 04. 01: Cement, Lime, Gypsum. American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, USA, 1993; pp. 158-160 |
| [241] | Nilsson, M., Carlson, J., Fernández, E., Planell, J. A. Monitoring the setting of calcium-based bone cements using pulse-echo ultrasound. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 1135-1141 |
| [242] | Carlson, J., Nilsson, M., Fernández, E., and Planell, J. A., An ultrasonic pulse-echo technique for monitoring the setting of CaSO4-based bone cement. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 71-77 |
| [243] | Hofmann, M. P., Nazhat, S. N., Gbureck, U., and Barralet, J. E., Real-time monitoring of the setting reaction of brushite-forming cement using isothermal differential scanning calorimetry. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 79B, 360-364 |
| [244] | Martin, R. I., and Brown, P. W., The effects of magnesium on hydroxyapatite formation in vitro from CaHPO4 and Ca4(PO4)2O at 37. 4 °C. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1997, 60, 538-546 |
| [245] | Brunner, T. J., Bohner, M., Dora, C., Gerber, C., and Stark, W. J., Comparison of amorphous TCP nanoparticles to micron-sized α-TCP as starting materials for calcium phosphate cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 83B, 400-407 |
| [246] | Gao, W. Y., Wang, Y. W., Dong, L. M., and Yu, Z. W., Thermokinetic analysis of the hydration process of calcium phosphate cement. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 85, 785-789 |
| [247] | Bohner, M., and Gbureck, U., Thermal reactions of brushite cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 84B, 375-385. |
| [248] | Hofmann, M. P., Young, A. M., Nazhat, S. N., Gbureck, U., and Barralet, J. E., Setting kinetics observation of a brushite cement by FTIR and DSC. Key Eng. Mater. 2006, 309-311, 837-840 |
| [249] | Liu, C., Huang, Y., and Zheng, H., Study of the hydration process of calcium phosphate cement by AC impedance spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 1052-1057 |
| [250] | Hofmann, M. P., Young, A. M., Gbureck, U., Nazhat, S. N., and Barralet, J. E., FTIR-monitoring of a fast setting brushite bone cement: effect of intermediate phases. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 3199-3206 |
| [251] | Hsu, H. C., Tuan, W. H., and Lee, H. Y., In-situ observation on the transformation of calcium phosphate cement into hydroxyapatite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 950-954 |
| [252] | Rau, J. V., Generosi, A., Smirnov, V. V., Ferro, D., Rossi, A. V., and Barinov, S. M., Energy dispersive X-ray diffraction study of phase development during hardening of calcium phosphate bone cements with addition of chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1089-1094 |
| [253] | Generosi, A., Smirnov, V. V., Rau, J. V., Rossi, A. V., Ferro, D., and Barinov, S. M., Phase development in the hardening process of two calcium phosphate bone cements: an energy dispersive X-ray diffraction study. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 561-571 |
| [254] | Ginebra, M. P., Fernández, E., Driessens, F. C. M., Boltong, M. G., Muntasell, J., Font, J., and Planell, J. A., The effects of temperature on the behaviour of an apatitic calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 857-860 |
| [255] | Baroud, G., Bohner, M., Heini, P., and Steffen, T., Injection biomechanics of bone cements used in vertebroplasty. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2004, 14, 487-504 |
| [256] | Leung, K. S., Siu, W. S., Li, S. F., Qin, L., Cheung, W. H., Tam, K. F., Po, P., and Lui, Y., An in vitro optimized injectable calcium phosphate cement for augmenting screw fixation in osteopenic goats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 78B, 153-160 |
| [257] | Eames, W. B., Monroe, S. D., Roan, J. D., and Oneal, S. J., Proportioning and mixing of cements – comparison of working times. Oper. Dent. 1977, 2, 97-104 |
| [258] | Baroud, G., Matsushita, C., Samara, M., Beckman, L., and Steffen, T., Influence of oscillatory mixing on the injectability of three acrylic and two calcium phosphate bone cements for vertebroplasty. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 68B, 105-111 |
| [259] | Nomoto, T., Haraguchi, K., Yamaguchi, S., Sugano, N., Nakayama, H., Sekino, T., and Niihara, K., Hydrolyses of calcium phosphates-allografts composite in physiological solutions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 379-385 |
| [260] | Oda, M., Takeuchi, A., Lin, X., Matsuya, S., and Ishikawa, K., Effects of liquid phase on basic properties of α-tricalcium phosphate-based apatite cement. Dent. Mater. J. 2008, 27, 672-677 |
| [261] | Sarda, S., Fernández, E., Llorens, J., Martinez, S., Nilsson, M., and Planell, J. A., Rheological properties of an apatitic bone cement during initial setting. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 905-909 |
| [262] | Liu, C., Shao, H., Chen, F., and Zheng, H., Rheological properties of concentrated aqueous injectable calcium phosphate cement slurry. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5003-5013 |
| [263] | Bohner, M., and Baroud, G., Injectability of calcium phosphate pastes. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1553-1563 |
| [264] | Khairoun, I., Boltong, M. G., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Some factors controlling the injectability of calcium phosphate bone cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 425-428 |
| [265] | Burguera, E. F., Xu, H. H. K., and Sun, L., Injectable calcium phosphate cement: effects of powder-to-liquid ratio and needle size. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 84B, 493-502 |
| [266] | Habib, M., Baroud, G., Gitzhofer, F., and Bohner, M., Mechanisms underlying the limited injectability of hydraulic calcium phosphate paste. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1465-1471 |
| [267] | Baroud, G., Cayer, E., and Bohner, M., Rheological characterization of concentrated aqueous beta-tricalcium phosphate suspensions: the effect of liquid-to-powder ratio, milling time and additives. Acta Biomater. 2005, 1, 357-363 |
| [268] | Ishikawa, K., Effects of spherical tetracalcium phosphate on injectability and basic properties of apatitic cement. Key Eng. Mater. 2003, 240-242, 369-372 |
| [269] | Habib, M., Baroud, G., Gitzhofer, F., and Bohner, M., Mechanisms underlying the limited injectability of hydraulic calcium phosphate paste. Part ІІ: Particle separation study. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 250-256 |
| [270] | Bohner, M., Doebelin, N., and Baroud, G., Theoretical and experimental approach to test the cohesion of calcium phosphate pastes. Eur. Cell Mater. 2006, 12, 26-35 |
| [271] | Miyamoto, Y., Ishikawa, K., Takechi, M., Toh, T., Yuasa, T., Nagayama, M., and Suzuki, K., Histological and compositional evaluations of three types of calcium phosphate cements when implanted in subcutaneous tissue immediately after mixing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 1999, 48, 36-42 |
| [272] | Bermudez, O., Boltong, M. G., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Compressive strength and diametral tensile strength of some calcium-orthophosphate cements, a pilot study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1993, 4, 389-393 |
| [273] | del Valle, S., Miňo, N., Muňoz, F., González, A., Planell, J. A., and Ginebra, M. P., In vivo evaluation of an injectable macroporous calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 353-361 |
| [274] | Khairoun, I., Driessens, F. C. M., Boltong, M. G., Planell, J. A., and Wenz, R., Addition of cohesion promoters to calcium orthophosphate cements. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 393-398 |
| [275] | Alkhraisat, M. H., Rueda, C., Mariño, F. T., Torres, J., Jerez, L. B., Gbureck, U., and Cabarcos, E. L., The effect of hyaluronic acid on brushite cement cohesion. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3150-3156 |
| [276] | Alkhraisat, M. H., Rueda, C., Jerez, L. B., Mariño, F. T., Torres, J., Gbureck, U., and Cabarcos, E. L., Effect of silica gel on the cohesion, properties and biological performance of brushite cement. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 257-265 |
| [277] | Low, K. L., Tan, S. H., Zein, S. H. S., Roether, J. A., Mouriño, V., and Boccaccini, A. R., Calcium phosphate-based composites as injectable bone substitute materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94B, 273-286 |
| [278] | Bigi, A., Bracci, B., and Panzavolta, S., Effect of added gelatin on the properties of calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2893-2899 |
| [279] | Ishikawa, K., Matsuya, S., Nakagawa, M., Udoh, K., and Suzuki, K., Basic properties of apatite cement containing spherical tetracalcium phosphate made with plasma melting method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 13-17 |
| [280] | Wang, X., Ye, J., and Wang, Y., Effect of additives on the morphology of the hydrated product and physical properties of a calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 285-288 |
| [281] | Barralet, J. E., Hofmann, M., Grover, L. M., and Gbureck, U., High strength apatitic cement by modification with α-hydroxy acid salts. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 2091-2095 |
| [282] | Barralet, J. E., Duncan, C. O., Dover, M. S., Bassett, D. C., Nishikawa, H., Monaghan, A., and Gbureck, U., Cortical bone screw fixation in ionically modified apatite cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 73B, 238-243 |
| [283] | Ginebra, M. P., Boltong, M. G., Fernández, E., Planell, J. A., and Driessens, F. C. M., Effect of various additives and temperature on some properties of an apatitic calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 612-616 |
| [284] | Acarturk, O., Lehmicke, M., Aberman, H., Toms, D., Hollinger, J. O., and Fulmer, M. T., Bone healing response to an injectable calcium phosphate cement with enhanced radiopacity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 86B, 56-62 |
| [285] | Wang, X., Ye, J., and Wang, Y., Influence of a novel radiopacifier on the properties of an injectable calcium phosphate cement. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 757-763 |
| [286] | Chen, F., Liu, C., and Mao, Y., Bismuth-doped injectable calcium phosphate cement with improved radiopacity and potent antimicrobial activity for root canal filling. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3199-3207 |
| [287] | Romieu, G., Garric, X., Munier, S., Vert, M., and Boudeville, P., Calcium-strontium mixed phosphate as novel injectable and radio-opaque hydraulic cement. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3208-3215 |
| [288] | Watanabe, M., Tanaka, M., Sakurai, M., and Maeda, M., Development of calcium phosphate cement. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 549-552 |
| [289] | Bercier, A., Gonçalves, S., Lignon, O., and Fitremann, J., Calcium phosphate bone cements including sugar surfactants: part one – porosity, setting times and compressive strength. Materials 2010, 3, 4695-4709 |
| [290] | Sarda, S., Nilsson, M., Balcells, M., and Fernández, E., Influence of surfactant molecules as air-entraining agent for bone cement macroporosity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 65A, 215-221 |
| [291] | Friberg, J., Fernández, E., Sarda, S., Nilsson, M., Ginebra, M. P., Martinez, S., and Planell, J. A., An experimental approach to the study of the rheology behavior of synthetic bone calcium phosphate cements. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 192-195, 777-780 |
| [292] | Reinstorf, A., Hempel, U., Olgemöller, F., Domaschke, H., Schneiders, W., Mai, R., Stadlinger, B, Rösen-Wolff, A., Rammelt, S., Gelinsky, M., and Pompe W.,O-phospho-L-serine modified calcium phosphate cements – material properties, in vitro and in vivo investigations. Mat. -Wiss. u. Werkstofftech. 2006, 37, 491-503 |
| [293] | Lode, A., Reinstorf, A., Bernhardt, A., Wolf-Brandstetter, C., König, U., Gelinsky, M. Heparin modification of calcium phosphate bone cements for VEGF functionalization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 86A, 749-759 |
| [294] | Mai, R., Lux, R., Proff, P., Lauer, G., Pradel, W., Leonhardt, H., Reinstorf, A., Gelinsky, M., Jung, R., Eckelt, U., Gedrange, T., and Stadlinger, B., O-phospho-L-serine: a modulator of bone healing in calcium-phosphate cements. Biomed. Tech. 2008, 53, 229-233 |
| [295] | Vater, C., Lode, A., Bernhardt, A., Reinstorf, A., Nies, B., and Gelinsky, M., Modifications of a calcium phosphate cement with biomolecules – influence on nanostructure, material, and biological properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 95A, 912-923 |
| [296] | Markovic, M., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Formation of macropores in calcium phosphate cements through the use of mannitol crystals. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 192-195, 773-776 |
| [297] | Tajima, S., Kishi, Y., Oda, M., Maruta, M., Matsuya, S., and Ishikawa, K., Fabrication of biporous low-crystalline apatite based on mannitol dissolution from apatite cement. Dent. Mater. J. 2006, 25, 616-620 |
| [298] | Xu, H. H. K., Weir, M. D., Burguera, E. F., and Fraser, A. M., Injectable and macroporous calcium phosphate cement scaffold. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4279-4287 |
| [299] | Cama, G., Barberis, F., Botter, R., Cirillo, P., Capurro, M., Quarto, R., Scaglione, S., Finocchio, E., Mussi, V., and Valbusa, U., Preparation and properties of macroporous brushite bone cements. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2161-2168 |
| [300] | Vazquez, D., Takagi, S., Frukhtbeyn, S., and Chow, L. C., Effects of addition of mannitol crystals on the porosity and dissolution rates of a calcium phosphate cement. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2010, 115, 225-232 |
| [301] | Shimogoryo, R., Eguro, T., Kimura, E., Maruta, M., Matsuya, S., and Ishikawa, K., Effects of added mannitol on the setting reaction and mechanical strength of apatite cement. Dent. Mater. J. 2009, 28, 627-633 |
| [302] | Almirall, A., Larrecq, G., Delgado, J. A., Martínez, S., Planell, J. A., and Ginebra, M. P., Fabrication of low temperature macroporous hydroxyapatite scaffolds by foaming and hydrolysis of an α-TCP paste. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3671-3680 |
| [303] | Barralet, J. E., Grover, L., Gaunt, T., Wright, A. J., and Gibson, I. R., Preparation of macroporous calcium phosphate cement tissue engineering scaffold. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3063-3072 |
| [304] | Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Formation of macropores in calcium phosphate cement implants. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 135-139 |
| [305] | Simon, Jr. C. G., Khatri, C. A., Wight, S. A., and Wang, F. W., Preliminary report on the biocompatibility of a moldable, resorbable, composite bone graft consisting of calcium phosphate cement and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J. Orthop. Res. 2002, 20, 473-482 |
| [306] | Ruhe, P. Q., Hedberg, E. L., Padron, N. T., Spauwen, P. H. M., Jansen, J. A., and Mikos, A. G., Biocompatibility and degradation of poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid)/calcium phosphate cement composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2005, 74A, 533-544 |
| [307] | Habraken, W. J. E. M., Wolke, J. G. C., Mikos, A. G., and Jansen, J. A., Injectable PLGA microsphere/calcium phosphate cements, physical properties and degradation characteristics. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2006, 17, 1057-1074 |
| [308] | Habraken, W. J. E. M., Wolke, J. G. C., Mikos, A. G., and Jansen, J. A., PLGA microsphere/calcium phosphate cement composites for tissue engineering, in vitro release and degradation characteristics. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 1171-1188 |
| [309] | Link, D. P., van den Dolder, J., van den Beucken, J. J. J. P., Cuijpers, V. M., Wolke, J. G. C., Mikos, A. G., and Jansen, J. A., Evaluation of the biocompatibility of calcium phosphate cement/PLGA microparticle composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87A, 760-769 |
| [310] | Link, D. P., van den Dolder, J., Jurgens, W. J. F. M., Wolke, J. G. C., and Jansen, J. A., Mechanical evaluation of implanted calcium phosphate cement incorporated with PLGA microparticles. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4941-4947 |
| [311] | Fullana, S. G., Ternet, H., Freche, M., Lacout, J. L., and Rodriguez, F., Controlled release properties and final macroporosity of a pectin microspheres-calcium phosphate composite bone cement. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2294-2300 |
| [312] | Tas, A. C., Preparation of porous apatite granules from calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 2231-2239 |
| [313] | Tas, A. C., Preparation of self-setting cement-based micro- and macroporous granules of carbonated apatitic calcium phosphate. Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 2006, 27, 49-60 |
| [314] | Li, M., Liu, X., Liu, X., Ge, B. and Chen, K., Creation of macroporous calcium phosphate cements as bone substitutes by using genipin – crosslinked gelatin microspheres. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 925-934 |
| [315] | Habraken, W. J. E. M., de Jonge, L. T., Wolke, J. G. C., Yubao, L., Mikos, A. G., and Jansen, J. A., Introduction of gelatin microspheres into an injectable calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87A, 643-655 |
| [316] | Tang, P. F., Li, G., Wang, J. F., Zheng, Q. J., and Wang, Y., Development, characterization, and validation of porous carbonated hydroxyapatite bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90B, 886-893 |
| [317] | Wang, X. P., Ye, J. D., Li, X., and Dong H., Production of in-situ macropores in an injectable calcium phosphate cement by introduction of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 3221-3225 |
| [318] | Habraken, W. J. E. M., Zhang, Z., Wolke, J. G. C., Grijpma, D. W., Mikos, A. G., Feijen, J., and Jansen, J. A., Introduction of enzymatically degradable poly(trimethylene carbonate) microspheres into an injectable calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2464-2476 |
| [319] | Xu, H. H. K., and Simon, Jr. C. G., Self-hardening calcium phosphate composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 2004, 22, 535-543 |
| [320] | Burguera, E. F., Xu, H. H. K., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., High early strength calcium phosphate bone cement: effects of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate and absorbable fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2005, 75A, 966-975 |
| [321] | Xu, H. H. K., and Quinn, J. B., Calcium phosphate cement containing resorbable fibers for short-term reinforcement and macroporosity. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 193-202 |
| [322] | Gorst, N. J. S., Perrie, Y., Gbureck, U., Hutton, A. L., Hofmann, M. P., Grover, L. M., and Barralet, J. E., Effects of fiber reinforcement on the mechanical properties of brushite cement. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 95-102 |
| [323] | Zuo, Y., Yang, F., Wolke, J. G. C., Li, Y., and Jansen, J. A., Incorporation of biodegradable electrospun fibers into calcium phosphate cement for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1238-1247 |
| [324] | Xu, H. H. K., and Simon, Jr. C. G., Self-hardening calcium phosphate cement-mesh composite: reinforcement, macropores, and cell response. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 69A, 267-278 |
| [325] | Losee, J. E., Karmacharya, J., Gannon, F. H., Slemp, A. E., Ong, G., Hunenko, O., Gorden, A. D., Bartlett, S. P., and Kirschner, R. E., Reconstruction of the immature craniofacial skeleton with a carbonated calcium phosphate bone cement, interaction with bioresorbable mesh. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2003, 14, 117-124 |
| [326] | Xu, H. H. K., Carey, L. E., and Simon, Jr. C. G., Premixed macroporous calcium phosphate cement scaffold. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1345-1353 |
| [327] | Ginebra, M. P., Espanol, M., Montufar, E. B., Perez, R. A., and Mestres, G., New processing approaches in calcium phosphate cements and their applications in regenerative medicine. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2863-2873 |
| [328] | del Real, R. P., Wolke, J. G. C., Vallet-Regi, M., and Jansen, J. A., A new method to produce macropores in calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3673-3680 |
| [329] | del Real, R. P., Ooms, E., Wolke, J. G. C., Vallet-Regi, M., and Jansen, J. A., In vivo bone response to porous calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 65A, 30-36 |
| [330] | Hesaraki, S., Moztarzadeh, F., and Sharifi, D., Formation of interconnected macropores in apatitic calcium phosphate bone cement with the use of an effervescent additive. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 83A, 80-87 |
| [331] | Hesaraki, S., Zamanian, A., and Moztarzadeh, F., The influence of the acidic component of the gas-foaming porogen used in preparing an injectable porous calcium phosphate cement on its properties, acetic acid versus citric acid. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 86B, 208-216 |
| [332] | Hesaraki, S., Moztarzadeh, F., and Solati-Hashjin, M., Phase evaluation of an effervescent-added apatitic calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 79B, 203-209 |
| [333] | Ginebra, M. P., Delgado, J. A., Harr, I., Almirall, A., del Valle S., and Planell, J. A., Factors affecting the structure and properties of an injectable self-setting calcium phosphate foam. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 80A, 351-361 |
| [334] | Montufar, E. B., Aguirre, A., Gil, C., Engel, E., Traykova, T., Planell, J. A., and Ginebra, M. P., Foamed surfactant solution as a template for self-setting injectable hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 876-885 |
| [335] | Andrianjatovo, H., and Lemaître, J., Effects of polysaccharides on the cement properties in the monocalcium phosphate/β-tricalcium phosphate system. Innov. Tech. Biol. Med. 1995, 16, 140-147 |
| [336] | Cherng, A., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Effects of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and other gelling agents on the handling properties of calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 35, 273-277 |
| [337] | Yokoyama, A., Matsuno, H., Yamamoto, S., Kawasaki, T., Kohgo, T., Uo, M., Watari, F., and Nakasu, M., Tissue response to a newly developed calcium phosphate cement containing succinic acid and carboxymethyl-chitin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 64A, 491-501 |
| [338] | Jyoti, M. A., Thai, V. V., Min, Y. K., Lee, B. T., and Song, H. Y., In vitro bioactivity and biocompatibility of calcium phosphate cements using hydroxy-propyl-methyl-cellulose (HPMC). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 1533-1539 |
| [339] | Bigi, A., Torricelli, P., Fini, M., Bracci, B., Panzavolta, S., Sturba, L., and Giardino, R., A biomimetic gelatin-calcium phosphate bone cement. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2004, 27, 664-673 |
| [340] | Bigi, A., Panzavolta, S., Sturba, L., Torricelli, P., Fini, M., and Giardino, R., Normal and osteopenic bone-derived osteoblast response to a biomimetic gelatin – calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 78A, 739-745 |
| [341] | Fujishiro, Y., Takahashi, K., and Sato, T., Preparation and compressive strength of α-tricalcium phosphate/gelatin gel composite cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 54, 525-530 |
| [342] | Bigi, A., Panzavolta, S., and Rubini, K., Setting mechanism of a biomimetic bone cement. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3740 -3745 |
| [343] | Panzavolta, S., Torricelli, P., Sturba, L., Bracci, B., Giardino, R., and Bigi, A., Setting properties and in vitro bioactivity of strontium-enriched gelatin-calcium phosphate bone cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 84A, 965-972 |
| [344] | Xu, L. X., Shi, X. T., Wang, Y. P., and Shi, Z. L., Performance of calcium phosphate bone cement using chitosan and gelatin as well as citric acid as hardening liquid. J. Clin. Rehabil. Tissue Eng. Res. 2008, 12, 6381-6384 |
| [345] | Shie, M. Y., Chen, D. C. H., Wang, C. Y., Chiang, T. Y., and Ding, S. J., Immersion behavior of gelatin-containing calcium phosphate cement. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 646-655 |
| [346] | Majekodunmi, A. O., Deb, S., and Nicholson, J. W., Effect of molecular weight and concentration of poly(acrylic acid) on the formation of a polymeric calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 747-752 |
| [347] | Majekodunmi, A.O., and Deb, S., Poly(acrylic acid) modified calcium phosphate cements, the effect of the composition of the cement powder and of the molecular weight and concentration of the polymeric acid. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1883-1888 |
| [348] | Chen, W. C., Ju, C. P., Wang, J. C., Hung, C. C., and Lin, J. H. C., Brittle and ductile adjustable cement derived from calcium phosphate cement/polyacrylic acid composites. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 1616-1622 |
| [349] | Komath, M., and Varma, H. K., Development of a fully injectable calcium phosphate cement for orthopedic and dental applications. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2003, 26, 415-422 |
| [350] | Bohner, M., Theiss, F., Apelt, D., Hirsiger, W., Houriet, R., Rizzoli, G., Gnos, E., Frei, C., Auer, J. A., and von Rechenberg, B., Compositional changes of a dicalcium phosphate dihydrate cement after implantation in sheep. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3463-3474 |
| [351] | Leroux, L., Hatim, Z., Freche, M., and Lacout, J. L., Effects of various adjuvants (lactic acid, glycerol and chitosan) on the injectability of a calcium phosphate cement. Bone 1999, 25, S31-S34 |
| [352] | Barralet, J. E., Tremayne, M. J., Lilley, K. J., and Gbureck, U., Chemical modification of calcium phosphate cements with α-hydroxy acids and their salts. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 1313-1319 |
| [353] | Driessens, F. C. M., Boltong, M. G., de Maeyer, E. A. P., Verbeeck, R. M. H., and Wenz, R., Effect of temperature and immersion on the setting of some calcium phosphate cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 453-457 |
| [354] | Gbureck, U., Dembski, S., Thull, R., and Barralet, J. E., Factors influencing calcium phosphate cement shelf life. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3691-3697 |
| [355] | Ishikawa, K., Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., and Ishikawa, Y., Properties and mechanisms of fast-setting calcium phosphate cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 528-533 |
| [356] | Miyamoto, Y., Ishikawa, K., Fukao, K., Sawada, M., Nagayama, M., Kon, M., and Asaoka, K., In vivo setting behavior of fast-setting calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 855-860 |
| [357] | Kawai, T., Fujisawa, N., Suzuki, I., Ohtsuki, C., Matsushima, Y., and Unuma, H., Control of setting behavior of calcium phosphate paste using gelatinized starch. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 118, 421-424 |
| [358] | Bohner, M., Luginbühl, R., Reber, C., Doebelin, N., Baroud, G., and Conforto, E., A physical approach to modify the hydraulic reactivity of α-tricalcium phosphate powder. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3524-3535 |
| [359] | Takechi, M., Miyamoto, Y., Momota, Y., Yuasa, T., Tatehara, S., Nagayama, M., are Ishikawa, K., Effects of various sterilization methods on the setting and mechanical properties of apatite cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 69B, 58-63 |
| [360] | Schneider, G., Blechschmidt, K., Linde, D., Litschko, P., Körbs, T., and Beleites, E., Bone regeneration with glass ceramic implants and calcium phosphate cements in a rabbit cranial defect model. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2853-2859 |
| [361] | Johal, H. S., Buckley, R. E., Le, I. L. D., and Leighton, R. K., A prospective randomized controlled trial of a bioresorbable calcium phosphate paste (α-BSM) in treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J. Trauma - Injury, Infect. Crit. Care 2009, 67, 875-882 |
| [362] | Yuasa, T., Miyamoto, Y., Ishikawa, K., Takechi, M., Nagayama, M., and Suzuki, K., In vitro resorption of three apatite cements with osteoclasts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 54, 344-350 |
| [363] | Puricelli, E., Corsetti, A., Ponzoni, D., Martins, G. L., Leite, M. G., and Santos, L. A., Characterization of bone repair in rat femur after treatment with calcium phosphate cement and autogenous bone graft. Head and Face Medicine 2010, 6, art. no. 10 |
| [364] | Zhaoa, X., Lib, F., and Lic, S., Degradation characteristic of strontium-containing calcium phosphate cement in vivo. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 105-106, 553-556 |
| [365] | Khairoun, I., Magne, D., Gauthier, O. Bouler, J. M., Aguado, E., Daculsi, G., and Weiss, P., In vitro characterization and in vivo properties of a carbonated apatite bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 633-642 |
| [366] | Mao, K., Yang, Y., Li, J., Hao, L., Tang, P., Wang, Z., Wen, N., Du, M., Wang, J., and Wang, Y., Investigation of the histology and interfacial bonding between carbonated hydroxyapatite cement and bone. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 045003 |
| [367] | Sanzana, E. S., Navarro, M., Macule, F., Suso, S., Planell, J. A., and Ginebra, M. P., Of the in vivo behavior of calcium phosphate cements and glasses as bone substitutes. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1924-1933 |
| [368] | Bodde, E. W. H., Cammaert, C. T. R., Wolke, J. G. C., Spauwen, P. H. M., and Jansen, J. A., Investigation as to the osteoinductivity of macroporous calcium phosphate cement in goats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 83B, 161-168 |
| [369] | Miyamoto, Y., Ishikawa, K., Takeshi, M., Toh, T., Yoshida, Y., Nagayama, M., Kon, M., and Asaoka, K., Tissue response to fast-setting calcium phosphate cement in bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 37, 457-464 |
| [370] | Young, S., Holde, M., Gunasekaran, S., Poser, R., and Constantz, B. R., The correlation of radiographic, MRI and histological evaluations over two years of a carbonated apatite cement in a rabbit model. In: Proceedings of the 44th Annual Meeting, Orthopedic Research Society, New Orleans, USA, March 16-19, 1998; p. 846 |
| [371] | Feng, B., Guolin, M., Yuan, Y., Changshen, L., Zhen, W., and Jian, L., Role of macropore size in the mechanical properties and in vitro degradation of porous calcium phosphate cements. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2028-2031 |
| [372] | Kroese-Deutman, H. C., Wolke, J. G. C., Spauwen, P. H, M., and Jansen, J. A., Closing capacity of cranial bone defects using porous calcium phosphate cement implants in a rabbit animal model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 79A, 503-511 |
| [373] | Bourgeois, B., Laboux, O., Obadia, L., Gauthier, O., Betti, E., Aguado, E., Daculsi, G., and Bouler, J. M., Calcium-deficient apatite: a first in vivo study concerning bone ingrowth. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 65A, 402-408 |
| [374] | Lu, J., Descamps, M., Dejou, J., Koubi, G., Hardouin, P., Lemaître, J., and Proust, J. P., The biodegradation mechanism of calcium phosphate biomaterials in bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 2002, 63, 408-412 |
| [375] | Wenisch, S., Stahl, J. P., Horas, U., Heiss, C., Kilian, O., Trinkaus, K., Hild, A., and Schnettler, R., In vivo mechanisms of hydroxyapatite ceramic degradation by osteoclasts, fine structural microscopy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 67A, 713-718 |
| [376] | Ooms, E. M., Wolke, J. G. C., van der Waerden, J. P., and Jansen, J. A., Trabecular bone response to injectable calcium phosphate (Ca-P) cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 9-18 |
| [377] | Theiss, F., Apelt, D., Brand, B., Kutter, A., Zlinszky, K., Bohner, M., Matter, S., Frei, C., Auer, J. A., and von Rechenberg, B., Biocompatibility and resorption of a brushite calcium phosphate cement. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4383-4394 |
| [378] | Heymann, D., Pradal, G., and Benahmad, M., Cellular mechanisms of calcium phosphate degradation. Histol. Histopathol. 1999, 14, 871-877 |
| [379] | Penel, G., Leroy, N., van Landuyt, P., Flautre, B., Hardouin, P., Lemaître, J., and Leroy, G., Raman microspectrometry studies of brushite cement: in vivo evolution in a sheep model. Bone 1999, 25, Suppl. 2, 81S-84S |
| [380] | Dorozhkin, S. V., Inorganic chemistry of the dissolution phenomenon, the dissolution mechanism of calcium apatites at the atomic (ionic) level. Comment Inorg. Chem. 1999, 20, 285-299 |
| [381] | Dorozhkin, S. V., A review on the dissolution models of calcium apatites. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. 2002, 44, 45-61 |
| [382] | Knabe, C., Driessens, F. C. M., Planell, J. A., Gildenhaar, R., Berger, G., Reif, D., Fitzner, R., Radlanski, R. J., and Gross, U., Evaluation of calcium phosphates and experimental calcium phosphate bone cements using osteogenic cultures. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 498-508 |
| [383] | Teitelbaum, S. L., Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science 2000, 289, 1504-1508 |
| [384] | Mostov, K., and Werb, Z., Journey across the osteoclast. Science 1997, 276, 219-220 |
| [385] | Rodan, G. A., and Martin, T. J., Therapeutic approaches to bone diseases. Science 2000, 289, 1508-1514 |
| [386] | Midy, V., Hollande, E., Rey, C., Dard, M., and Plouët, J., Adsorption of vascular endothelial growth factor to two different apatitic materials and its release. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 293-298 |
| [387] | Hossain, M., Irwin, R., Baumann, M. J., and McCabe, L. R., Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) adsorption kinetics and enhancement of osteoblast differentiation on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2595-2602 |
| [388] | Sun, L., Berndt, C. C., Gross, K. A., and Kucuk, A., Material fundamentals and clinical performance of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings, a review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2001, 58, 570-592 |
| [389] | Renault, F., Chabriere, E., Andrieu, JP., Dublet, B., Masson, P., and Rochu, D., Tandem purification of two HDL-associated partner proteins in human plasma., paraoxonase (PON1) and phosphate binding protein (HPBP) using hydroxyapatite chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 836, 15-21 |
| [390] | Yoshitake, T., Kobayashi, S., Ogawa, T., and Okuyama, T., Hydroxyapatite chromatography of guanidine denatured proteins: 1. guanidine containing phosphate buffer system. Chromatography 2006, 27, 19-26 |
| [391] | Ooms, E. M., Egglezos, E. A., Wolke, J. G. C., and Jansen, J. A., Soft-tissue response to injectable calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 749-757 |
| [392] | Ooms, E. M., Wolke, J. G. C., van de Heuvel, MT., Jeschke, B., and Jansen, J. A., Histological evaluation of the bone response to calcium phosphate cement implanted in cortical bone. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 989-1000 |
| [393] | Kobayashi, N., Ong, K., Villarraga, M., Schwardt, J., Wenz, R., Togawa, D., Fujishiro, T., Turner, A. S., Seim, III H. B., and Bauer, T. W., Histological and mechanical evaluation of self-setting calcium phosphate cements in a sheep vertebral bone void model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 81A, 838-846 |
| [394] | Wen, C. Y., Qin, L., Lee, K. M., and Chan, K. M., The use of brushite calcium phosphate cement for enhancement of bone-tendon integration in an anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction rabbit model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 89B, 466-474 |
| [395] | Musha, Y., Umeda, T., Yoshizawa, S., Shigemitsu, T., Mizutani, K., and Itatani, K., Effects of blood on bone cement made of calcium phosphate: problems and advantages. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92B, 95-101 |
| [396] | Fernández, E., Ginebra, M. P., Bermudez, O., Boltong, M. G., Driessens, F. C. M., and Planell, J. A., Dimensional and thermal behaviour of calcium phosphate cements during setting compared to PMMA bone cements. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1995, 14, 4-5 |
| [397] | Andrianjatovo, H., Jose, F., and Lemaître, J., Effect of β-TCP granulometry on setting time and strength of calcium orthophosphate hydraulic cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1996, 7, 34-39 |
| [398] | Ishikawa, K., Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., Ishikawa Y., Eanes, E. D., and Asaoka, K., Behavior of a calcium orthophosphate cement in simulated blood plasma in vitro. Dent. Mater. 1994, 10, 26-32 |
| [399] | Driessens, F. C. M., Chemistry and applied aspects of calcium orthophosphate bone cements. In: Concepts and clinical applications of ionic cements, 15th European Conference on Biomaterials. Arcachon, Bordeaux, France. Sept. 8, 1999 |
| [400] | Yamamoto, H., Niwa, S., Hori, M., Hattori, T., Sawai, K., Aoki, S., Hirano, M., and Takeuchi, H., Mechanical strength of calcium phosphate cement in vivo and in vitro. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1587-1591 |
| [401] | Pittet, C., and Lemaître, J., Mechanical characterization of brushite cements: a Mohr circles approach. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 2000, 53, 769-780 |
| [402] | Morgan, E. F., Yetkinler, D. N., Constantz, B. R., and Dauskardt, R. H., Mechanical properties of carbonated apatite bone mineral substitute: strength, fracture and fatigue behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1997, 8, 559-570 |
| [403] | Miyazaki, K., Horibe, T., Antonucci, J. M., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Polymeric calcium phosphate cements, analysis of reaction products and properties. Dent. Mater. 1993, 9, 41-45 |
| [404] | Miyazaki, K., Horibe, T., Antonucci, J. M., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Polymeric calcium phosphate cements: setting reaction modifiers. Dent. Mater. 1993, 9, 46-50 |
| [405] | dos Santos, L. A., de Oliveira, L. C., Rigo, E. C. S., Carrodeguas, R. G., Boschi, A. O., and de Arruda, A. C. F., Influence of polymeric additives on the mechanical properties of α-tricalcium phosphate cement. Bone 1999, 25, 99S-102S |
| [406] | Mickiewicz, R. A., Mayes, A. M., and Knaack, D., Polymer – calcium phosphate cement composites for bone substitutes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 581-592 |
| [407] | Fernández, E., Sarda, S., Hamcerencu, M., Vlad, M. D., Gel, M., Valls, S., Torres, R., and López, J., High-strength apatitic cement by modification with superplasticizers. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2289-2296 |
| [408] | Takahashi, T., Yamamoto, M., Ioku, K., and Goto, S., Relationship between compressive strength and pore structure of hardened cement pastes. Adv. Cement Res. 1997, 9, 25-30 |
| [409] | Costantino, P. D., Friedman, C. D., Jones, K., Chow, L. C., and Sisson, G. A., Experimental hydroxyapatite cement cranioplasty. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1992, 90, 174-185 |
| [410] | Chow, L. C., Hirayama, S., Takagi, S., and Parry, E., Diametral tensile strength and compressive strength of a calcium phosphate cement, effect of applied pressure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 2000, 53, 511-517 |
| [411] | Barralet, J. E., Gaunt, T., Wright, A. J., Gibson I. R., and Knowles, J. C., Effect of porosity reduction by compaction on compressive strength and microstructure of calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Appl. Biomater. 2002, 63, 1-9 |
| [412] | Zhang, Y., Xu, H. H. K., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., In situ hardening hydroxyapatite-based scaffold for bone repair. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 437-445 |
| [413] | Khairoun, I., LeGeros, R. Z., Daculsi, G., Bouler, J. M., Guicheux, J., and Gauthier, O., Macroporous, resorbable and injectable calcium phosphate-based cements (MCPC) for bone repair: augmentation, regeneration and osteoporosis treatment. US patent No. 7351280. April 1, 2008 |
| [414] | Speirs, A. D., Oxland, T. R., Masri, B. A., Poursartip, A., and Duncan, C. P., Calcium phosphate cement composites in revision hip arthroplasty. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7310-7318 |
| [415] | dos Santos, L. A., Carrodeguas, R. G., Boschi, A. O., and de Arruda, A. C. F., Fiber-enriched double-setting calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 65A, 244-250 |
| [416] | Gbureck, U., Spatz, K., and Thull, R., Improvement of mechanical properties of self-setting calcium phosphate bone cements mixed with different metal oxides. Mat. -Wiss. u. Werkstofftech. 2003, 34, 1036-1040 |
| [417] | Zhang, Y., and Xu, H. H. K., Effects of synergistic reinforcement and absorbable fiber strength on hydroxyapatite bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2005, 75A, 832-840 |
| [418] | Buchanan, F., Gallagher, L., Jack, V., and Dunne, N., Short-fibre reinforcement of calcium phosphate bone cement. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H: J. Eng. Med. 2007, 221, 203-212 |
| [419] | Wang, X., Ye, J., Wang, Y., and Chen, L., Reinforcement of calcium phosphate cement by bio-mineralized carbon nanotube. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 962-964 |
| [420] | Vélez, D., Arita, I. H., García-Garduño, M. V., and Castaño, V. M., Synthesis and characterization of a hydroxyapatite-zinc oxide-polyacrylic acid concrete. Mater. Lett. 1994, 19, 309-315 |
| [421] | According to Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia: “Concrete is a construction material that consists of a cement (commonly Portland cement), aggregates (generally gravel and sand) and water. It solidifies and hardens after mixing and placement due to a chemical process known as hydration. The water reacts with the cement, which bonds the other components together, eventually creating a stone-like material. ” http://en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Concrete (accessed in November 2011) |
| [422] | Dickens-Venz, S. H., Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., Bowen, R. L., Johnston, A. D., and Dickens, B., Physical and chemical properties of resin-reinforced calcium phosphate cements. Dent. Mater. 1994, 10, 100-106 |
| [423] | Xu, H. H. K., Eichmiller, F. C., and Barndt, P. R., Effects of fiber length and volume fraction on the reinforcement of calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 57-65 |
| [424] | Xu, H. H. K., Quinn, J. B., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Synergistic reinforcement of in situ hardening calcium phosphate composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1029-1037 |
| [425] | Yokoyama, A., Yamamoto, S., Kawasaki, T., Kohgo, T., and Nakasu, M., Development of calcium phosphate cement using chitosan and citric acid for bone substitute materials. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1091-1101 |
| [426] | Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., Hirayama, S., and Eichmiller, F. C., Properties of elastomeric calcium phosphate cement-chitosan composites. Dent. Mater. 2003, 19, 797-804 |
| [427] | Xu, H. H. K., and Simon Jr., C. G., Fast setting calcium phosphate-chitosan scaffold: mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1337-1348 |
| [428] | Sun, L., Xu, H. H. K., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Fast setting calcium phosphate cement – chitosan composite, mechanical properties and dissolution rates. J. Biomater. Appl. 2007, 21, 299-316 |
| [429] | Pan, Z. H., Jiang, P. P., Fan, Q. Y., Ma, B., and Cai, H. P., Mechanical and biocompatible influences of chitosan fiber and gelatin on calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 82B, 246-252 |
| [430] | Liu, H., Li, H., Cheng, W., Yang, Y., Zhu, M., and Zhou, C., Novel injectable calcium phosphate/chitosan composites for bone substitute materials. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 557-565 |
| [431] | Pan, Z. H., Cai, H. P., Jiang, P. P., and Fan, Q. Y., Properties of a calcium phosphate cement synergistically reinforced by chitosan fiber and gelatin. J. Polymer Res. 2006, 13, 323-327 |
| [432] | Weir, M. D., and Xu, H. H. K., High-strength, in situ-setting calcium phosphate composite with protein release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85A, 388-396 |
| [433] | Lian, Q., Li, D. C., He, J. K., and Wang, Z., Mechanical properties and in-vivo performance of calcium phosphate cement – chitosan fibre composite. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H: J. Eng. Med. 2008, 222, 347-353 |
| [434] | Wang, X., Chen, L., Xiang, H., and Ye, J., Influence of anti-washout agents on the rheological properties and injectability of a calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 81B, 410-418 |
| [435] | Tanaka, S., Kishi, T., Shimogoryo, R., Matsuya, S., and Ishikawa, K., Biopex acquires anti-washout properties by adding sodium alginate into its liquid phase. Dent. Mater. J. 2003, 22, 301-312 |
| [436] | Lin, J., Zhang, S., Chen, T., Liu, C., Lin, S., and Tian, X., Calcium phosphate cement reinforced by polypeptide copolymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 76B, 432-439 |
| [437] | Miyamoto, Y., Ishikawa, K., Takechi, M., Toh, T., Yuasa, T., Nagayama, M., and Suzuki, K., Basic properties of calcium phosphate cement containing atelocollagen in its liquid or powder phases. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 707-715 |
| [438] | Knepper-Nicolai, B., Reinstorf, A., Hofinger, I., Flade, K., Wenz, R., and Pompe, W., Influence of osteocalcin and collagen I on the mechanical and biological properties of Biocement D®. Biomol. Eng. 2002, 19, 227-231 |
| [439] | Hempel, U., Reinstorf, A., Poppe, M., Fischer, U., Gelinsky, M., Pompe, W., and Wenzel, K. W., Proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts on Biocement D® modified with collagen type I and citric acid. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 71B, 130-143 |
| [440] | Reinstorf, A., Ruhnow, M., Gelinsky, M., Pompe, W., Hempel, U., Wenzel, K. W., and Simon, P., Phosphoserine – a convenient compound for modification of calcium phosphate bone cement collagen composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 451-455 |
| [441] | Otsuka, M., Kuninaga, T., Otsuka, K., and Higuchi, W. I., Effect of nanostructure on biodegradation behaviors of self-setting apatite/collagen composite cements containing vitamin K2 in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 79B, 176-184 |
| [442] | Moreau, J. L., Weir, M. D., and Xu, H. H. K., Self-setting collagen – calcium phosphate bone cement: mechanical and cellular properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 91A, 605-613 |
| [443] | Otsuka, M., Nakagawa, H., Ito, A., and Higuchi, W. I., Effect of geometrical structure on drug release rate of a three-dimensionally perforated porous apatite/collagen composite cement. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 286-292 |
| [444] | Gbureck, U., Spatz, K., Thull, R., and Barralet, J. E., Rheological enhancement of mechanically activated α-tricalcium phosphate cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 73B, 1-6 |
| [445] | Xu, H. H. K., Eichmiller, F. C., and Giuseppetti, A. A., Reinforcement of a self-setting calcium phosphate cement with different fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 107-114 |
| [446] | Xu, H. H. K., Quinn, J. B., Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., and Eichmiller, F. C., Strong and macroporous calcium phosphate cement: effects of porosity and fiber reinforcement on mechanical properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 57, 457-466 |
| [447] | dos Santos, L. A., Carrodeguas, R. G., Boschi, A. O., and de Arruda, A. C. F., Dual-setting calcium phosphate cement modified with ammonium polyacrylate. Artif. Organs 2003, 27, 412-418 |
| [448] | dos Santos, L. A., de Oliveira, L. C., da Silva Rigo, E. C., Carrodéguas, R. G., Boschi, A. O., and de Arruda, A. C. F., Fiber reinforced calcium phosphate cement. Artif. Organs 2000, 24, 212-216 |
| [449] | Liu, C. S., Chen, C. W., and Ducheyne, P., In vitro surface reaction layer formation and dissolution of calcium phosphate cement – bioactive glass composites. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 034111 (11 pages) |
| [450] | Alge, D. L., and Chu, T. M. G., Calcium phosphate cement reinforcement by polymer infiltration and in situ curing: a method for 3D scaffold reinforcement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 94A, 547-555 |
| [451] | Julien, M., Khairoun, I., LeGeros, R. Z., Delplace, S., Pilet, P., Weiss, P., Daculsi, G., Bouler, J. M., and Guicheux, J., Physico-chemical-mechanical and in vitro biological properties of calcium phosphate cements with doped amorphous calcium phosphates. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 956-965 |
| [452] | Lemaître, J., Munting, E., and Mirtchi, A. A., Setting, hardening and resorption of calcium phosphate hydraulic cements. Rev. Stomatol. Chir. Maxillofac. 1992, 93, 163-165 |
| [453] | Müller, F. A., Gbureck, U., Kasuga, T., Mizutani, Y., Barralet, J. E., and Lohbauer, U., Whisker-reinforced calcium phosphate cements. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 3694-3697 |
| [454] | Nakagawa, A., Matsuya, S., Takeuchi, A., and Ishikawa, K., Comparison of the effects of added α- and β-tricalcium phosphate on the basic properties of apatite cement. Dent. Mater. J. 2007, 26, 342-347 |
| [455] | Gisep, A., Wieling, R., Bohner, M., Matter, S., Schneider, E., and Rahn, B., Resorption patterns of calcium-phosphate cements in bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 66A, 532-540 |
| [456] | Ion-substituted ACPs contained other ions (carbonates, Mg, Zn, F) were used in that study[451] |
| [457] | van den Vreken, N. M. F., Pieters, I. Y., Declercq, H. A., Cornelissen, M. J., and Verbeeck, R. M. H., Characterization of calcium phosphate cements modified by addition of amorphous calcium phosphate. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 617-625 |
| [458] | Zhou, L., Yan, J. L., and Hu, C. J., Degradation of bone repairing composite of calcium polyphosphate fiber, calcium phospate cement and micromorselized bone in vitro. J. Clin. Rehabilit. Tiss. Eng. Res. 2007, 11, 33-36 |
| [459] | Xu, L. X., Shi, X. T., Wang, Y. P., and Shi, Z. L., Mechanical effect of calcium polyphosphate fiber on reinforcing calcium phosphate bone cement composites. J. Clin. Rehabilit. Tiss. Eng. Res. 2009, 13, 7474-7476 |
| [460] | Castaldini, A., and Cavallini, A., Setting properties of bone cement with added synthetic hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials 1985, 6, 55-60 |
| [461] | Sogal, A., and Hulbert, S. F., Mechanical properties of a composite bone cement, polymethylmethacrylate and hydroxyapatite. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Ceramics in Medicine, Bioceramics 1992, Vol. 5, pp. 213-224 |
| [462] | Harper, E. J., Behiri, J. C., and Bonfield, W., Flexural and fatigue properties of a bone cement based upon polyethylmethacrylate and hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 799-803 |
| [463] | Harper, E. J., Bioactive bone cements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H: J. Eng. Med. 1998, 212, 113-120 |
| [464] | Shinzato, S., Kobayashi, M., Mousa, W. F., Kamimura, M., Neo, M., Kitamura, Y., Kokubo, T., and Nakamura, T., Bioactive polymethylmethacrylate-based bone cement: comparison of glass beads, apatite- and wollastonite-containing glass-ceramic, and hydroxyapatite fillers on mechanical and biological properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 51, 258-272 |
| [465] | Harper, E. J., Braden, M., and Bonfield, W., Mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite reinforced poly(ethylmethacrylate) bone cement after immersion in a physiological solution, Influence of a silane coupling agent. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 491-497 |
| [466] | Espigares, I., Elvira, C., Mano, J. F., Vázquez, B., san Román, J., and Reis, R. L., New partially degradable and bioactive acrylic bone cements based on starch blends and ceramic fillers. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1883-1895 |
| [467] | Pek, Y. S., Kurisawa, M., Gao, S., Chung, J. E., and Ying, J. Y., The development of a nanocrystalline apatite reinforced crosslinked hyaluronic acid-tyramine composite as an injectable bone cement. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 822-828 |
| [468] | Xu, H. H. K., and Quinn, J. B., Whisker-reinforced bioactive composites containing calcium phosphate cement fillers, Effects of filler ratio and surface treatments on mechanical properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 57, 165-174 |
| [469] | Claes L., Höllen, I., and Ignatius, A., Resorbable bone cements. Orthopäde 1997, 26, 459-462 |
| [470] | Jansen, J. A., de Ruijter, J. E., Schaeken, H. G., van der Waerden, J. P. C., Planell, J. A., and Driessens, F. C. M., Evaluation of tricalciumphosphate/hydroxyapatite cement for tooth replacement, an experimental animal study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 653-657 |
| [471] | Larsson. S., and Bauer, T. W., Use of injectable calcium phosphate cement for fracture fixation: a review. Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 2002, 395, 23-32 |
| [472] | Oshtory, R., Lindsey, D. P., Giori, N. J., and Mirza, F. M., Bioabsorbable tricalcium phosphate bone cement strengthens fixation of suture anchors. Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 2010, 468, 3406-3412 |
| [473] | Gbureck, U., Knappe, O., Hofmann, N., and Barralet, J. E., Antimicrobial properties of nanocrystalline tetracalcium phosphate cements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 83B, 132-137 |
| [474] | Sethuraman, S., Nair, L. S., El-Amin, S., Nguyen, M. T. N., Greish, Y. E., Bender, J. D., Brown, P. W., Allcock, H. R., and Laurencin, C. T., Novel low temperature setting nanocrystalline calcium phosphate cements for bone repair: osteoblast cellular response and gene expression studies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 82A, 884-891 |
| [475] | Link, D. P., van den Dolder, J., Wolke, J. G. C., and Jansen, J. A., The cytocompatibility and early osteogenic characteristics of an injectable calcium phosphate cement. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 493-500 |
| [476] | Oda, H., Nakamura, K., Matsushita, T., Yamamoto, S., Ishibashi, H., Yamazaki, T., and Morimoto, S., Clinical use of a newly developed calcium phosphate cement (XSB-671D). J. Orthop. Sci. 2006, 11, 167-174 |
| [477] | Braun, C., Rahn, B., Fulmer, M. T., Steiner, A., and Gisep, A., Intra-articular calcium phosphate cement, its fate and impact on joint tissues in a rabbit model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 79B, 151-158 |
| [478] | Costantino, P., Friedman, C., Jones, K., Chow, L. C., Pelzer, H., and Sisson, G., Hydroxyapatite cement. I. Basic chemistry and histologic properties. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1991, 117, 379-384 |
| [479] | Hong, Y. C., Wang, J. T., Hong, C. Y., Brown, W. E., and Chow, C. Y., The periapical tissue reactions to a calcium phosphate cement in the teeth of monkeys. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 485-498 |
| [480] | Sugawara, A., Fujikawa, K., Kusama, K., Nishiyama, M., Murai, S., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Histopathologic reaction of calcium phosphate cement for alveolar ridge augmentation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 47-52 |
| [481] | Fujikawa, K., Sugawara, A., Kusama, K., Nishiyama, M., Murai, S., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Fluorescent labeling analysis and electron probe microanalysis for alveolar ridge augmentation using calcium phosphate cement. Dent. Mater. J. 2002, 21, 296-305 |
| [482] | Sugawara, A., Chow, L. C., Takagi, S., and Chohayeb, H., In vitro evaluation of the sealing ability of a calcium phosphate cement when used as a root canal sealer-filler. J. Endod. 1990, 16, 162-165 |
| [483] | Noetzel, J., Özer, K., Reisshauer, B. H., Anil, A., Rössler, R., Neumann, K., and Kielbassa, A. M., Tissue responses to an experimental calcium phosphate cement and mineral trioxide aggregate as materials for furcation perforation repair, a histological study in dogs. Clin. Oral Invest. 2006, 10, 77-83 |
| [484] | Zhang, W., Walboomers, X. F., and Jansen, J. A., The formation of tertiary dentin after pulp capping with a calcium phosphate cement, loaded with PLGA microparticles containing TGF-β1. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85A, 439-444 |
| [485] | Comuzzi, L., Ooms, E., and Jansen, J. A., Injectable calcium phosphate cement as a filler for bone defects around oral implants, an experimental study in goats. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2002, 13, 304-311 |
| [486] | Shirakata, Y., Oda, S., Kinoshita, A., Kikuchi, S., Tsuchioka, H., and Ishikawa, I., Histocompatible healing of periodontal defects after application of injectable calcium phosphate bone cement. A preliminary study in dogs. J. Periodontol. 2002, 73, 1043-1053 |
| [487] | Lee, S. K., Lee, S. K., Lee, S. I., Park, J. H., Jang, J. H., Kim, H. W., and Kim, E. C., Effect of calcium phosphate cements on growth and odontoblastic differentiation in human dental pulp cells. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1537-1542 |
| [488] | Chaung, H. M., Hong, C. H., Chiang, C. P., Lin, S. K., Kuo, Y. S., Lan, W. H., and Hsieh, C. C., Comparison of calcium phosphate cement mixture and pure calcium hydroxide as direct pulp-capping agents. J. Formos Med. Assoc. 1996, 95, 545-550 |
| [489] | Arisan, V., Anil, A., Wolke, J. G., and Özer, K., The effect of injectable calcium phosphate cement on bone anchorage of titanium implants: an experimental feasibility study in dogs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 463-468 |
| [490] | Aral, A., Yalçn, S., Karabuda, Z. C., Anιl, A., Jansen, J. A., and Mutlu, Z., Injectable calcium phosphate cement as a graft material for maxillary sinus augmentation: an experimental pilot study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 612-617 |
| [491] | Sliindo, M. L., Costantino, P. D., Friedman, C. D., and Chow, L. C., Facial skeletal augmentation using hydroxyapatite cement cranioplasty. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1993, 119, 185-190 |
| [492] | Bifano, C. A., Edgin, W. A., Colleton, C., Bifano, S. L., and Constantino, P. D., Preliminary evaluation of hydroxyapatite cement as an augmentation device in the edentulous atrophic canine mandible. Oral Surg. 1998, 85, 512-516 |
| [493] | Friedman, C. D., Constantino, P. D., Jones, K., Chow, L. C., Pelzer, H., and Sisson, G., Hydroxyapatite cement. II. Obliteration and reconstruction of the cat frontal sinus. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1991, 117, 385-389 |
| [494] | Sinikovic, B., Kramer, F. J., Swennen, G., Lubbers, H. T., and Dempf, R., Reconstruction of orbital wall defects with calcium phosphate cement: clinical and histological findings in a sheep model. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 36, 54-61 |
| [495] | Smartt, J. M., Karmacharya, J., Gannon, F. H., Ong, G., Jackson, O., Bartlett. S. P., Poser, R. D., and Kirschner, R. E., Repair of the immature and mature craniofacial skeleton with a carbonated calcium phosphate cement: assessment of biocompatibility, osteoconductivity and remodeling capacity. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 115, 1642-1650 |
| [496] | Reddi, S. P., Stevens, M. R., Kline, S. N., and Villanueva, P., Hydroxyapatite cement in craniofacial trauma surgery, indications and early experience. J. Cran. Maxillofac. Trauma 1999, 5, 7-12 |
| [497] | Friedman, C. D., Costantino, P. D., Synderman, C. H., Chow, L. C., and Takagi, S., Reconstruction of the frontal sinus and frontofacial skeleton with hydroxyapatite cement. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2000, 2, 124-129 |
| [498] | Kuemmerle, J. M., Oberle, A., Oechslin, C., Bohner, M., Frei, C., Boecken, I., and von Rechenberg, B., Assessment of the suitability of a new brushite calcium phosphate cement for cranioplasty – an experimental study in sheep. J. Cran. Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 33, 37-44 |
| [499] | Luaces-Rey, R., García-Rozado, A., Crespo-Escudero, J. L., Seijas, B. P., Arenaz-Búa, J., and López-Cedrún, J. L., Use of carbonated calcium phosphate bone cement and resorbable plates for the treatment of frontal sinus fractures: two case reports. J. Plastic Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2009, 62, 272-273 |
| [500] | Tamimi, F., Torres, J., Cabarcos, E. L., Bassett, D. C., Habibovic, P., Luceron, E., and Barralet, J. E., Minimally invasive maxillofacial vertical bone augmentation using brushite based cements. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 208-216 |
| [501] | Lee, D. W., Kim, J. Y., and Lew, D. H., Use of rapidly hardening hydroxyapatite cement for facial contouring surgery. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2010, 21, 1084-1088 |
| [502] | Singh, K. A., Burstein, F. D., and Williams, J. K., Use of hydroxyapatite cement in pediatric craniofacial reconstructive surgery: strategies for avoiding complications. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2010, 21, 1130-1135 |
| [503] | Bambakidis, N. C., Munyon, C., Ko, A., Selman, W. R., and Megerian, C. A., A novel method of translabyrinthine cranioplasty using hydroxyapatite cement and titanium mesh: a technical report. Skull Base 2010, 20, 157-161 |
| [504] | Abe, T., Anan, M., Kamida, T., and Fujiki, M., Surgical technique for anterior skull base reconstruction using hydroxyapatite cement and titanium mesh. Acta Neurochirur. 2009, 151, 1337-1338 |
| [505] | Sanada, Y., Fujinaka, T., Yoshimine, T., and Kato, A., Optimal reconstruction of the bony defect after frontotemporal craniotomy with hydroxyapatite cement. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 280-282 |
| [506] | Benson, A. G., and Djalilian, H. R., Complications of hydroxyapatite bone cement reconstruction of retrosigmoid craniotomy: two cases. Ear, Nose and Throat J. 2009, 88, E1 |
| [507] | Liverneaux, P., Osteoporotic distal radius curettage-filling with an injectable calcium phosphate cement. A cadaveric study. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2005, 15, 1-6 |
| [508] | Liverneaux, P., Vernet, P., Robert, C., and Diacono, P., Cement pinning of osteoporotic distal radius fractures with an injectable calcium phosphate bone substitute, report of 6 cases. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2006, 16, 10-16 |
| [509] | Thordarson, D., Hedman, T., Yetkinler, D., Eskander, E., Lawrence, T., and Poser, R., Superior compressive strength of a calcaneal fracture construct augmented with remodelable cancellous bone cement. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1999, 81A, 239-246 |
| [510] | Stankewich, C. J., Swiontkowski, M. F., Tencer, A. F., Yetkinler, D. N., and Poser, R. D., Augmentation of femoral neck fracture fixation with an injectable calcium-phosphate bone mineral cement. J. Orthop. Res. 1996, 14, 786-793 |
| [511] | Goodman, S., Bauer, T., Carter, D., Casteleyn, P. P., Goldstein, S. A., Kyle, R. F., Larsson, S., Stankewich, C. J., Swiontkowski, M. F., Tencer, A. F., Yetkinler, D. N., and Poser, R. D., Norian SRS® cement augmentation in hip fracture treatment. Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 1998, 348, 42-50 |
| [512] | Bai, B., Jazrawi, L., Kummer, F., and Spivak, J., The use of an injectable, biodegradable calcium orthophosphate bone substitute for the prophylactic augmentation of osteoporotic vertebrae and the management of vertebral compression fractures. Spine 1999, 24, 1521-1526 |
| [513] | Ryf, C., Goldhahn, S., Radziejowski, M., Blauth, M., and Hanson, B., A new injectable brushite cement: first results in distal radius and proximal tibia fractures. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2009, 35, 389-396 |
| [514] | Horstmann, W. G., Verheyen, C. C. P. M., and Leemans, R., An injectable calcium phosphate cement as a bone-graft substitute in the treatment of displaced lateral tibial plateau fractures. Injury 2003, 34, 141-144 |
| [515] | Simpson, D., and Keating, J. F., Outcome of tibial plateau fractures managed with calcium phosphate cement. Injury 2004, 35, 913-918 |
| [516] | Welch, R. D., Zhang, H., and Bronson, D. G., Experimental tibial plateau fractures augmented with calcium phosphate cement or autologous bone graft. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2003, 85A, 222-231 |
| [517] | Keating, J. F., Hajducka, C. L., and Harper, J., Minimal internal fixation and calcium-phosphate cement in the treatment of fractures of the tibial plateau. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2003, 85B, 68-73 |
| [518] | Moore, D., Maitra, R., Farjo, L., Graziano, G., and Goldstein, S., Restoration of pedicle screw fixation with an in situ setting calcium orthophosphate cement. Spine 1997, 22, 1696-1705 |
| [519] | Cho, W., Wu, C., Erkan, S., Kang, M. M., Mehbod, A. A., and Transfeldt, E. E., The effect on the pullout strength by the timing of pedicle screw insertion after calcium phosphate cement injection. J. Spinal Disorders and Techniques 2011, 24, 116-120 |
| [520] | Mermelstein, L. E., McLain, R. F., and Yerby, S. A., Reinforcement of thoracolumbar burst fractures with calcium phosphate cement. Spine 1998, 23, 664-671 |
| [521] | Mermelstein, L. E., Chow, L. C., Friedman, C., and Crisco, J., The reinforcement of cancellous bone screws with calcium orthophosphate cement. J. Orthop. Trauma 1996, 10, 15-20 |
| [522] | Stadelmann, V. A., Bretton, E., Terrier, A., Procter, P., and Pioletti, D. P., Calcium phosphate cement augmentation of cancellous bone screws can compensate for the absence of cortical fixation. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 2869-2874 |
| [523] | Liverneaux, P., and Khallouk, R., Calcium phosphate cement in wrist arthrodesis: three cases. J. Orthop. Sci. 2006, 11, 289-293 |
| [524] | Ooms, E. M., Wolke, J. G. C., van der Waerden, J. P. C. M., and Jansen, J. A., Use of injectable calcium phosphate cement for the fixation of titanium implants: an experimental study in goats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2003, 66B, 447-456 |
| [525] | Strauss, E. J., Pahk, B., Kummer, F. J., and Egol, K., Calcium phosphate cement augmentation of the femoral neck defect created after dynamic hip screw removal. J. Orthop. Trauma 2007, 21, 295-300 |
| [526] | Schildhauer, T. A., Bennett, A. P., Wright, T. M., Lane, J. M., and O’Leary, P. F., Intravertebral body reconstruction with an injectable in situ-setting carbonated apatite: biomechanical evaluation of a minimally invasive technique. J. Orthop. Res. 1999, 17, 67-72 |
| [527] | Jansen, J. A., Ooms, E., Verdonschot, N., and Wolke, J. G. C., Injectable calcium phosphate cement for bone repair and implant fixation. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 2005, 36, 89-95 |
| [528] | Maestretti, G., Cremer, C., Otten, P., and Jakob, R. P., Prospective study of standalone balloon kyphoplasty with calcium phosphate cement augmentation in traumatic fractures. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16, 601-610 |
| [529] | Hisatome, T., Yasunaga, Y., Ikuta, Y., and Fujimoto, Y., Effects on articular cartilage of subchondral replacement with polymethylmethacrylate and calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 59, 490-498 |
| [530] | Lim, T. H., Brebach, G. T., Renner, S. M., Kim, W. J., Kim, J. G., Lee, R. E., Andersson, G. B., and An, H. S., Biomechanical evaluation of an injectable calcium phosphate cement for vertebroplasty. Spine 2002, 27, 1297-1302 |
| [531] | Belkoff, S. M., Mathis, J. M., Jasper, L. E., and Deramond, H., An ex vivo biomechanical evaluation of a hydroxyapatite cement for use with vertebroplasty. Spine 2001, 26, 1542-1546 |
| [532] | Heini, P. F., Berlemann, U., Kaufmann, M., Lippuner, K., Fankhauser, C., and van Landuyt, P., Augmentation of mechanical properties in osteoporotic vertebral bones – a biomechanical investigation of vertebroplasty efficacy with different bone cements. Eur. Spine J. 2001, 10, 164-171 |
| [533] | Tomita, S., Kin, A., Yazu, M., and Abe, M., Biomechanical evaluation of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty with calcium phosphate cement in a simulated osteoporotic compression fracture. J. Orthop. Sci. 2003, 8, 192-197 |
| [534] | Libicher, M., Hillmeier, J., Liegibel, U., Sommer, U., Pyerin, W., Vetter, M., Meinzer, H. P., Grafe, I., Meeder, P., Nöldge, G., Nawroth, P., and Kasperk, C., Osseous integration of calcium phosphate in osteoporotic vertebral fractures after kyphoplasty: initial results from a clinical and experimental pilot study. Osteoporos. Int. 2006, 17, 1208-1215 |
| [535] | Khanna, A. J., Lee, S., Villarraga, M., Gimbel, J., Steffey, D., and Schwardt, J., Biomechanical evaluation of kyphoplasty with calcium phosphate cement in a 2-functional spinal unit vertebral compression fracture model. Spine J. 2008, 8, 770-777 |
| [536] | Zhu, X. S., Zhang, Z. M., Mao, H. Q., Geng, D. C., Wang, G. L., Gan, M. F., and Yang, H. L., Biomechanics of calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty. J. Clin. Rehabil. Tissue Eng. Res. 2008, 12, 8071-8074 |
| [537] | Otsuka, M., Matsuda, Y., Suwa, Y., Fox, J. L., and Higuchi, W. I., A novel skeletal drug-delivery system using a self-setting calcium orthophosphate cement. 3. Physicochemical properties and drug-release rate of bovine insulin and bovine albumin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 255-258 |
| [538] | Yu, D., Wong, J., Matsuda, Y., Fox, J. L., Higuchi, W. I., and Otsuka, M., Self-setting hydroxyapatite cement: a novel skeletal drug-delivery system for antibiotics. J. Pharm. Sci. 1992, 81, 529-531 |
| [539] | Bohner, M., Lemaître, J., van Landuyt, P., Zambelli, P., Merkle, H. P., and Gander, B., Gentamicin-loaded hydraulic calcium orthophosphate bone cement as antibiotic delivery system. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 565-572 |
| [540] | Bohner, M., Lemaître, J., Merkle, H. P., and Gander, B., Control of gentamicin release from a calcium phosphate cement by admixed poly(acrylic acid). J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1262-1270 |
| [541] | Ratier, A., Freche, M., Locout, J. L., and Rodriguez, F., Behaviour of an injectable calcium phosphate cement with added tetracycline. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 274, 261-268 |
| [542] | Kisanuki, O., Yajima, H., Umeda, T., and Takakura, Y., Experimental study of calcium phosphate cement impregnated with dideoxy-kanamycin B. J. Orthop. Sci. 2007, 12, 281-288 |
| [543] | McNally, A., Sly, K., Lin, S., Bourges, X., and Daculsi, G., Release of antibiotics from macroporous injectable calcium phosphate cement. Key Eng. Mater. 2008, 361-363, 359-362 |
| [544] | Hofmann, M. P., Mohammed, A. R., Perrie, Y., Gbureck, U., and Barralet, J. E., High-strength resorbable brushite bone cement with controlled drug-releasing capabilities. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 43-49 |
| [545] | Tamimi, F., Torres, J., Bettini, R., Ruggera, F., Rueda, C., López-Ponce, M., and Cabarcos, E. L., Doxycycline sustained release from brushite cements for the treatment of periodontal diseases. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85A, 707-714 |
| [546] | Young, A. M., Ng, P. Y. J., Gbureck, U., Nazhat, S. N., Barralet, J. E., and Hofmann, M. P., Characterization of chlorhexidine-releasing, fast-setting, brushite bone cements. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1081-1088 |
| [547] | Hesaraki, S., and Nemati, R., Cephalexin-loaded injectable macroporous calcium phosphate bone cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 89B, 342-352 |
| [548] | Otsuka, M., Matsuda, Y., Suwa, Y., Fox, J. L., and Higuchi, W. I., A novel skeletal drug delivery system using a self-setting calcium orthophosphate cement. 5. Drug release behavior from a heterogeneous drug-loaded cement containing an anticancer drug. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 1565-1568 |
| [549] | Otsuka, M., Matsuda, Y., Suwa, Y., Fox, J. L., and Higuchi, W. I., A novel skeletal drug delivery system using a self-setting calcium orthophosphate cement. 2. Physicochemical properties and drug release rate of the cement-containing indomethacin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 611-615 |
| [550] | Panzavolta, S., Torricelli, P., Bracci, B., Fini, M., and Bigi, A., Alendronate and pamidronate calcium phosphate bone cements, setting properties and in vitro response of osteoblast and osteoclast cells. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 101-106 |
| [551] | le Nihouannen, D., Hacking, SA., Gbureck, U., Komarova, S. V., and Barralet, J. E., The use of RANKL-coated brushite cement to stimulate bone remodeling. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3253-3259 |
| [552] | Li, D. X., Fan, H. S., Zhu, X. D., Tan, Y. F., Xiao, W. Q., Lu, J., Xiao, Y. M., Chen, J. Y., and Zhang, X. D., Controllable release of salmon-calcitonin in injectable calcium phosphate cement modified by chitosan oligosaccharide and collagen polypeptide. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 2225-2231 |
| [553] | Kamegai, A., Shimamura, N., Naitou, K., Nagahara, K., Kanematsu, N., and Mori, M., Bone formation under the influence of bone morphogenetic protein/self-setting apatite cement composite as delivery system. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 1994, 4, 291-307 |
| [554] | Fei, Z., Hu, Y., Wu, D., Wu, H., Lu, R., Bai, J., and Song, H., Preparation and property of a novel bone graft composite consisting of rhBMP-2 loaded PLGA microspheres and calcium phosphate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1109-1116 |
| [555] | Ruhé, P. Q., Kroese-Deutman, H. C., Wolke, J. G. C., Spauwen, P. H. M., and Jansen, J. A., Bone inductive properties of rhBMP-2 loaded porous calcium phosphate cement implants in cranial defects in rabbits. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2123-2132 |
| [556] | Bodde, E. W. H., Boerman, O. C., Russel, F. G. M., Mikos, A. G., Spauwen, P. H. M., and Jansen, J. A., The kinetic and biological activity of different loaded rhBMP-2 calcium phosphate cement implants in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87A, 780-791 |
| [557] | Perrier, M., Lu, Y., Nemke, B., Kobayashi, H., Peterson, A., and Markel, M., Acceleration of second and fourth metatarsal fracture healing with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/calcium phosphate cement in horses. Vet. Surg. 2008, 37, 648-655 |
| [558] | Meraw, S. J., Reeve, C. M., Lohse, C. M., and Sioussat, T. M., Treatment of perimplant defects with combination growth factor cement. J. Periodont. 2000, 71, 8-13 |
| [559] | Liu, H., Zang, X. F., Zhao, Z. P., Wang, J. L., and Mi, L., Co-transplantation of exogenous nerve growth factor and calcium phosphate cement composite for repairing rabbit radial bone defects. J. Clin. Rehabil. Tissue Eng. Res. 2008, 12, 8037-8041 |
| [560] | Qu, X. Y., Jiang, D. M., Li, M., Zhang, D. W., Qin, J. Q., and Liu, C. K., Deproteinized osteoarticular allografts integrated with calcium phosphate cement and recombinant human vascular endothelial cell growth factor plus recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2, an immunological study. J. Clin. Rehabil. Tissue Eng. Res. 2008, 12, 8067-8070 |
| [561] | Yu, T., Ye, J., Gao, C., Yu, L., and Wang, Y., Synthesis and drug delivery property of calcium phosphate cement with special crystal morphology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 1241-1244 |
| [562] | Stallmann, H. P., de Roo, R., Faber, C., Amerongen, A. V, N., and Wuisman, P. I. J. M., In vivo release of the antimicrobial peptide hLFi-11 from calcium phosphate cement. J. Orthop. Res. 2008, 26, 531-538 |
| [563] | Sasaki, T., Ishibashi, Y., Katano, H., Nagumo, A., and Toh, S., In vitro elution of vancomycin from calcium phosphate cement. J. Arthroplasty 2005, 20, 1055-1059 |
| [564] | Blom, E. J., Klein-Nulend, J., Wolke, J. G. C., van Waas, M. A. J., Driessens, F. C. M., and Burger, E. H., Transforming growth factor-β1 incorporation in a calcium phosphate bone cement, Material properties and release characteristics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 59, 265-272 |
| [565] | Blom, E. J., Klein-Nulend, J., Yin, L., van Waas, M. A. J., and Burger, E. H., Transforming growth factor-β1 incorporated in calcium phosphate cement stimulates osteotransductivity in rat calvarial bone defects. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2001, 12, 609-616 |
| [566] | Link, D. P., van den Dolder, J., van den Beucken, J. J., Wolke, J. G. C., Mikos, A. G., and Jansen, J. A., Bone response and mechanical strength of rabbit femoral defects filled with injectable CaP cements containing TGF-β1 loaded gelatin microparticles. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 675-682 |
| [567] | Habraken, W. J. E. M., Boerman, O. C., Wolke, J. G. C., Mikos, A. G., and Jansen, J. A., In vitro growth factor release from injectable calcium phosphate cements containing gelatin microspheres. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 91A, 614-622 |
| [568] | Ruhé, P. Q., Boerman, O. C., Russel, F. G. M., Mikos, A. G., Spauwen, P. H. M., and Jansen, J. A., In vivo release of rhBMP-2 loaded porous calcium phosphate cement pretreated with albumin. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 919-927 |
| [569] | Naito, K., Obayashi, O., Mogami, A., Itoi, A., and Kaneko, K., Fracture of the calcium phosphate bone cement which used to enchondroma of the hand, a case report. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2008, 18, 405-408 |
| [570] | Blattert, T. R., Delling, G., and Weckbach, A., Evaluation of an injectable calcium phosphate cement as an autograft substitute for transpedicular lumbar interbody fusion: a controlled, prospective study in the sheep model. Eur. Spine J. 2003, 12, 216 -223 |
| [571] | Cavalcanti, S. C., Santos, S. C., Pereira, C. L., Mazzonetto, R., de Moraes, M., and Moreira, R. W. F., Histological and histomorphometric analyses of calcium phosphate cement in rabbit calvaria. J. Cran. Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 36, 354-359 |
| [572] | Sanchez-Sotelo, J., Munuera, L., and Madero, R., Treatment of fractures of the distal radius with a remodellable bone cement: a prospective, randomised study using Norian SRS®. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2000, 82B, 856-863 |
| [573] | Lobenhoffer, P., Gerich, T., Witte, F., and Tscherne, H., Use of an injectable calcium phosphate bone cement in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures: a prospective study of twenty-six cases with twenty-month mean follow-up. J. Orthop. Trauma 2002, 16, 143-149 |
| [574] | Cassidy, C., Jupiter, J. B., Cohen, M., Delli-Santi, M., Fennell, C., Leinberry, C., Husband, J., Ladd, A., Seitz, W. R., and Constantz, B. R., Norian SRS® cement compared with conventional fixation in distal radial fractures, a randomized study. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2003, 85A, 2127-2137 |
| [575] | Schmidt, R., Cakir, B., Mattes, T., Wegener, M., Puhl, W., and Richter, M., Cement leakage during vertebroplasty, an underestimated problem? Eur. Spine J. 2005, 14, 466-473 |
| [576] | Vlad, M. D., Torres, R., López, J., Barracó, M., Moreno, J. A., and Fernández, E., Does mixing affect the setting of injectable bone cement? An ultrasound study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 347-352 |
| [577] | Krebs, J., Aebli, N., Goss, B. G., Sugiyama, S., Bardyn, T., Boecken, I., Leamy, P. J., and Ferguson, S. J., Cardiovascular changes after pulmonary embolism from injecting calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 82B, 526-532 |
| [578] | Russell, T. A., and Leighton, R. K., Comparison of autogenous bone graft and endothermic calcium phosphate cement for defect augmentation in tibial plateau fractures. A multicenter, prospective, randomized study. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2008, 90A, 2057-2061 |
| [579] | Dickson, K. F., Friedman, J., Buchholz, J. G., and Flandry, F. D., The use of BoneSourceTM hydroxyapatite cement for traumatic metaphyseal bone void filling. J. Trauma 2002, 53, 1103-1108 |
| [580] | Jungbluth, P., Hakimi, M., Grassmann, J. P., Schneppendahl, J., Kessner, A., Sager, M., Hakimi, A. R., Becker, J., Windolf, J., and Wild, M., The progress of early phase bone healing using porous granules produced from calcium phosphate cement. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2010, 15, 196-203 |
| [581] | Yoshikawa, T., Suwa, Y., Ohgushi, H., Tamai, S., and Ichijima, K., Self-setting hydroxyapatite cement as a carrier for bone-forming cells. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 1996, 6, 345-351 |
| [582] | Simon, Jr. C. G., Guthrie, W. F., and Wang, F. W., Cell seeding into calcium phosphate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 68A, 628-639 |
| [583] | Xu, H. H. K., Weir, M. D., and Simon, Jr. C. G., Injectable and strong nano-apatite scaffolds for cell/growth factor delivery and bone regeneration. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 1212-1222 |
| [584] | Takagi, S., Chow, L. C., Hirayama, S., and Sugawara, A., Premixed calcium phosphate cement pastes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2003, 67B, 689-696 |
| [585] | Carey, L. E., Xu, H. H. K., Simon, Jr. C. G., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Premixed rapid-setting calcium phosphate composites for bone repair. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5002-5014 |
| [586] | Xu, H. H. K., Carey, L. E., Simon, Jr. C. G., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Premixed calcium phosphate cements: synthesis, physical properties, and cell cytotoxicity. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 433-441 |
| [587] | Shimada, Y., Chow, L. C., Takagi, S., and Tagami, J., Properties of injectable apatite-forming premixed cements. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2010, 115, 233-241 |
| [588] | Sugawara, A., Fujikawa, K., Hirayama, S., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., In vivo characteristics of premixed calcium phosphate cements when implanted in subcutaneous tissues and periodontal bone defects. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2010, 115, 277-290 |
| [589] | Rajzer, I., Castaño, O., Engel, E., and Planell, J. A., Injectable and fast resorbable calcium phosphate cement for body-setting bone grafts. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2049-2056 |
| [590] | Han, B., Ma, P. W., Zhang, L. L., Yin, Y. J., Yao, K. D., Zhang, F. J., Zhang. Y. D., Li, X. L., and Nie, W., β-TCP/MCPM-based premixed calcium phosphate cements. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3165-3177 |
| [591] | Chow, L.C., and Takagi, S., Premixed self-hardening bone graft pastes. US Patent Application No. 20060263443, November 23, 2006 |
| [592] | Aberg, J., Brisby, H., Henriksson, H. B., Lindahl, A., Thomsen, P., and Engqvist, H., Premixed acidic calcium phosphate cement: characterization of strength and microstructure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 93, 436-441 |
| [593] | Lemaître, J., Pittet, C., and Brendlen, D., Pasty or liquid multiple constituent compositions for injectable calcium phosphate cements. US Patent No. 7407542, May 8, 2008 |
| [594] | Chow, L. C., and Takagi, S., Dual-phase cement precursor systems for bone repair. US Patent Application No. 20070092580, April 26, 2007 |
| [595] | Bohner, M., Calcium phosphate emulsions: possible applications. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 192-195, 765-768 |
| [596] | Troczynski, T., A concrete solution. Nature Mater. 2004, 3, 13-14 |
| [597] | Xu, H. H. K., Burguera, E. F., and Carey, L. E., Strong, macroporous and in situ-setting calcium phosphate cement-layered structures. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3786-3796 |
| [598] | Xu, H. H. K., Takagi, S., Quinn, J. B., and Chow, L. C., Fast-setting calcium phosphate scaffolds with tailored macropore formation rates for bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 68A, 725-734 |
| [599] | Ginebra, M. P., Rilliard, A., Fernández, E., Elvira, C., san Roman, J., and Planell, J. A., Mechanical and rheological improvement of a calcium phosphate cement by the addition of a polymeric drug. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 57, 113-118 |
| [600] | García-Fernández, L., Halstenberg, S., Unger, R. E., Aguilar, M. R., Kirkpatrick, C. J., and san Román, J., Anti-angiogenic activity of heparin-like polysulfonated polymeric drugs in 3D human cell culture. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7863-7872 |
| [601] | Andriotis, O., Katsamenis, O. L., Mouzakis, D. E., and Bouropoulos, N., Preparation and characterization of bioceramics produced from calcium phosphate cements. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2010, 45, 239-243 |
| [602] | Steffen, T., Stoll, T., Arvinte, T., and Schenk, R. K., Porous tricalcium phosphate and transforming growth factor used for anterior spine surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2001, 10, S132-S140 |
| [603] | Guo, H., Su, J., Wei, J., Kong, H., and Liu, C., Biocompatibility and osteogenicity of degradable Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite scaffolds from calcium phosphate cement for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 268-278 |
| [604] | Guo, H., Wei, J., Kong, H., Liu, C., and Pan, K., Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of calcium phosphate cement scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 47-50, 1383-1386 |
| [605] | Weir, M. D., Xu, H. H. K., and Simon, Jr. C. G., Strong calcium phosphate cement-chitosan-mesh construct containing cell-encapsulating hydrogel beads for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 77A, 487-496 |
| [606] | Xu, J. H., Tan, W. Q., and Lin, J., Repair of madibular bone defect by combining calcium phosphate cement with bone morphogenetic protein composite as a bone graft material. Chinese J. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 26, 153-156 |
| [607] | Niikura, T., Tsujimoto, K., Yoshiya, S., Tadokoro, K., Kurosaka, M., and Shiba, R., Vancomycin-impregnated calcium phosphate cement for methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus femoral osteomyelitis. Orthopedics 2007, 30, 320-321 |
| [608] | Lode, A., Wolf-Brandstetter, C., Reinstorf, A., Bernhardt, A., König, U. Pompe, W., and Gelinsky, M., Calcium phosphate bone cements, functionalized with VEGF: release kinetics and biological activity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 81A, 474-483 |
| [609] | Yoshikawa, M., and Toda, T., In vivo estimation of periapical bone reconstruction by chondroitin sulfate in calcium phosphate cement. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 521-531 |
| [610] | Wang, J. L., Mi, L., Hou, G. H., and Zheng, Z., Repair of radial defects using calcium phosphate cements/poly lactic-co-glycolic acid materials combined with mesenchymal stem cells in rabbits. J. Clin. Rehabil. Tissue Eng. Res. 2008, 12, 8001-8005 |
| [611] | Zhao, L., Weir, M. D., and Xu, H. H. K., Human umbilical cord stem cell encapsulation in calcium phosphate scaffolds for bone engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3848-3857 |
| [612] | Ding, T., Yang, H., Maltenfort, M., and Xie, R., Silk fibroin added to calcium phosphate cement to prevent severe cardiovascular complications. Case Reports Clin. Pract. Rev. 2010, 16, 23-26 |
| [613] | Panzavolta, S., Torricelli, P., Bracci, B., Fini, M., and Bigi, A., Functionalization of biomimetic calcium phosphate bone cements with alendronate. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 1099-1106 |
| [614] | Xu, H. H. K., Zhao, L., Detamore, M. S., Takagi, S., and Chow, L. C., Umbilical cord stem cell seeding on fast-resorbable calcium phosphate bone cement. Tiss. Eng. A 2010, 16, 2743-2753 |
| [615] | Li, M., Liu, X., Liu, X., and Ge, B., Calcium phosphate cement with BMP-2-loaded gelatin microspheres enhances bone healing in osteoporosis: a pilot study. Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 2010, 468, 1978-1985 |
| [616] | Weir, M. D., and Xu, H. H. K., Human bone marrow stem cell-encapsulating calcium phosphate scaffolds for bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4118-4126 |
| [617] | Zhao, L., Weir, M. D., and Xu, H. H. K., An injectable calcium phosphate-alginate hydrogel-umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell paste for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6502-6510 |
| [618] | dos Santos, L. A., Carrodéguas, R. G., Rogero, S. O., Higa, O. Z., Boschi, A. O., and de Arruda, A. C., Alpha-tricalcium phosphate cement: “in vitro” cytotoxicity. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2035-2042 |
| [619] | Baroud, G., and Steffen, T., A new cannula to ease cement injection during vertebroplasty. Eur. Spine J. 2005, 14, 474-479 |
| [620] | Anderson, J. M., The future of biomedical materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 1025-1028 |
| [621] | Chow, L. C., Next generation calcium phosphate-based biomaterials. Dent. Mater. J. 2009, 28, 1-10 |
| [622] | Ishikawa, K., Bone substitute fabrication based on dissolution-precipitation reactions. Materials 2010, 3, 1138-1155 |
| [623] | Bohner, M., Resorbable biomaterials as bone graft substitutes. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 24-30 |
| [624] | Dorozhkin, S. V., Calcium orthophosphate cements and concretes. Materials 2009, 2, 221-291 |

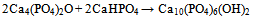
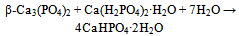
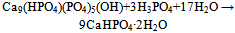
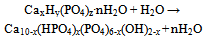
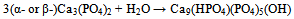
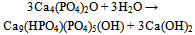
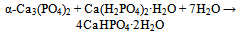
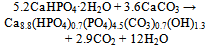
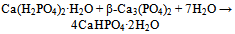
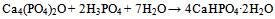
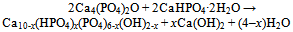
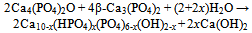
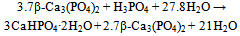
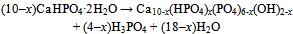
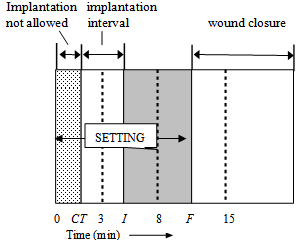
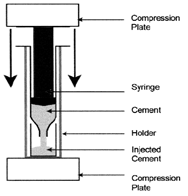
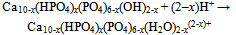
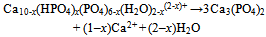
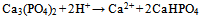
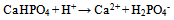
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML