-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Modern Botany
p-ISSN: 2166-5206 e-ISSN: 2166-5214
2014; 4(2): 61-74
doi:10.5923/j.ijmb.20140402.04

Physiological and Biochemical Responses in Cucurbita pepo Leaves Associated with Some Elicitors-Induced Systemic Resistance against Zucchhini yellow mosaic virus
Mahmoud R. Sofy, Abd El-Monem M.A. Sharaf, Mohamed Noufl, Ahmed R. Sofy
Botany and Microbiology Department, Faculty of Science, Al-Azhar University, 11884 Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Ahmed R. Sofy, Botany and Microbiology Department, Faculty of Science, Al-Azhar University, 11884 Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In a greenhouse experiment, four treatments (Salix alba water extract, Mannitol solution, Pomegranate peel water extract andSpirulina sp. filtrate), were tested as seeds soaking for induction systemic resistance in Cucurbita pepo cv. Eskandarani plants against Zucchhini yellow mosaic virus (ZYMV). The results demonstrated that ZYMV challenged plants emerged from Salix-soaked seeds and Spirulina-soaked seeds not only showed a pronounced and significant reduction in percent disease severity (DS) but also a significant reduction in the virus concentration (ELISA), compared to challenged control plants. Results from analysis of physiological parameters indicated that viral infection and seeds soaked treatments affected metabolism. Viral infection decreased photosynthetic pigments, carbohydrate and protein levels. An alleviation of ZYMV severe infection effects was evidenced by alteration in the photosynthetic pigments, the carbohydrate and protein contents in challenged treatments (Salix+V, Mannitol+V, Pomegranate peel+V and Spirulina+V). Moreover, the other biochemical parameters showed variable alterations, where the proline content and antioxidant enzymes activities were induced by both viral infection and treatments compared to absolute control plants. On the other hand, IAA and GA3 were significantly decreased, while ABA, JA and SA contents were significantly increased due to the viral infection. Significantly, higher IAA GA3, JA and SA, levels were observed in leaves of non-challenged treatments (Salix and Spirulina) and challenging treatments (Salix+V and Spirulina+V), while the ABA content was significantly decreased compared to absolute control (AC) and challenged control (ChC). In addition, protein patterns using SDS-PAGE represent two newly synthesized polypeptides (46 and 41 KDa) which reflect formation of pathogenesis related proteins in challenged treatments (Salix+V and Spirulina+V), respectively. Also, Salix and Spirulina increased the density and number of peroxidase and polyphenoloxidase isozymes. It can be concluded thatSalix and Spirulina treatments increase the Cucurbita pepo cv. Eskandarani plants resistance against ZYMV.
Keywords: Cucurbita pepo cv. Eskandarani, ZYMV, Salix alba, Mannitol, Pomegranate peel, Spirulina sp., SAR, Antioxidant enzyme, Endogenous horomones, ELISA
Cite this paper: Mahmoud R. Sofy, Abd El-Monem M.A. Sharaf, Mohamed Noufl, Ahmed R. Sofy, Physiological and Biochemical Responses in Cucurbita pepo Leaves Associated with Some Elicitors-Induced Systemic Resistance against Zucchhini yellow mosaic virus, International Journal of Modern Botany, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 61-74. doi: 10.5923/j.ijmb.20140402.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Stress factors (a biotic and biotic) reflect and specify the plant morphology and called as "stress" and have negative effect(s) on growth, development, quality, quantity and can reduce average plant productivity by 65 to 87%, depending on the plants and stage(s) and also give various permanent or temporary damage(s) according to length of exposed period, violence/density, developmental stage, age, etc. [1]. Plants are under constant assault by biotic agents, including viral, bacterial and fungal pathogens, parasitic plants and insect herbivores, with economic and ecological impact [2].Viruses are among the most important kinds of plant pathogens causing severe economic losses in many crops. Viruses do not have self-movement or entry mechanisms like many fungi and bacteria do. They require a wound and direct delivery into that wound in order to infect a plant. Only once inside a plant cell, can the virus begin to multiply, high jacking the host machinery for its own uses, thus causing a variety of disruptions to normal plant physiology [3]. Certain biochemical and physiological changes associated with virus infection include the oxidative burst [4], growth inhibition, changes in pigment content, chlorophyll synthesis and antioxidant enzyme systems [5]. Altered active oxygen species (AOS) formation occurs under biotic and abiotic stress. This alteration causes direct or indirect damage to plants, leading to the appearance of epidemiological symptoms [6].Cucurbita pepo L., of the family Cucurbitaceae is commonly known as zucchini or summer squash when immature and pumpkin or winter squash when mature. Squash is considered as one of the most important crops in Egypt and worldwide. It is native of America, but cultivated worldwide with an annual production of 17.7 million tonnes from 1.4 million hectares [7].Viruses are the most important pathogens of cucurbits (pumpkins, cucumber, watermelon and melon) belonging to the Cucurbitaceae family. More than 30 infectious viruses causing destructive symptoms and considerable economic losses were reported on these plants [8]. Zucchini yellow mosaic virus (ZYMV) is one of the most important viruses affecting cucurbit production globally. It causes destructive diseases on a large variety of economically important cucurbits including zucchini squash (Cucurbita pepo), where it can completely destroy the crop under favorable conditions leading to yield loss [9, 10]. Plant viruses affect physiological processes such as photosynthesis [11] by decreasing the photosynthesis rate, pigment contents [5], soluble sugar contents and reducing starch accumulation [12]. Peroxidase is the first to show changes in its activity during viral infection stages, where it shows an increase in its activity in Cucurbita pepo plants infected with viruses such as CMV [12]. Systemic acquired resistance (SAR) is considered a form of resistance induced in plants against subsequent infection and attack by a broad spectrum of organisms [13]. Plants exhibiting systemic acquired resistance (SAR) show a decreased level of susceptibility to many types of pathogen [14]. Several chemicals have been reported as systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in plants [15]. Among these chemicals, salicylic acid (SA) is considered one of the key components of defense signal transduction, inducing the full set of systemic acquired resistance genes [16]. Radwan et al. [17] reported that spraying pumpkin leaves with SA increases the plant resistance against ZYMV. Also, induction of SAR was observed in tobacco plants treated with 0.01 mM 1-hexadecene, where hexadecene is a hydrocarbon commonly reported in seaweeds [18] and it was observed in the crude extract of Spirulina [19]. On the other hand, twelve algal species were screened for their antiphytoviral activity against Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) infected cucumber plants, where acquired resistance against CMV was observed as the cucumber seeds were soaked in algal extracts at different periods [20]. Mannitol, an important osmolyte, is normally synthesized in large amount in many plant species. Although mannitol plays an important role in osmotic adjustment, it acts as an antioxidant to scavenge of hydroxyl radicals (OH-) [21].The growing cost of pesticides and consumer demand for pesticide-free food have led to a search for substitutes for these chemical products. There are also a number of fastidious diseases, i.e., virus and viroid diseases, for which chemical solutions are few, ineffective, or non-existent [22]. So, the aim of this study is to investigate the effect of viral infection on growth and metabolism of squash plants and also the use of some elicitors hopping to abolishing the detrimental effects of viruses on these plants.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
- Seeds of Cucurbita pepo cv. Eskandarani were obtained from Agriculture Research Centre, Ministry of Agriculture, Giza, Egypt, and germinated in seeds trays containing perlite.
2.2. Spirulina sp.
- Spirulina sp. culture was kindly provided by Biofertelizer production unit, Soil, Water and Environment Research institute, Agriculture Research Center (ARC) Giza Egypt. It was filtered through a filter paper and the filtrate was obtained.
2.3. Preparation of the Plant Extract
- Dried leaves and bark of the Salix alba plant as well as pomegranate peel were obtained from Botanical garden, Agriculture Research Centre (ARC) Giza Egypt. The dry leaves and bark of the Salix plant as well as pomegranate peel were crushed into powder. 0.5 gm of the powder was put in 50°C boiled water and left for 1 hour, then filtered into a conical flask. The aqueous infusion was serialized by bacterial filter. An equivalent of 10 mg dried material per ml of aqueous infusion was obtained [23].
2.4. Zucchhini yellow mosaic virus (ZYMV) inoculation
- A ZYMV isolate was obtained from Virology Laboratory, Faculty of Agriculture, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, where it was maintained on Cucurpita pepo cv. Eskandrani plants. The virus was checked on Chenopodium amaranticolor L. and reisolated from a single lesion. The extraction of resulted local lesions was inoculated on the healthy Cucurbita pepo cv. Eskandrani plants as a ZYMV propagative host. Inoculum of the virus was prepared by grinding fresh leaves showing severe symptoms in 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) using sterilized pestle and mortar. The pulp was squeezed through two layers of cheesecloth and the filtrate was centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min. The first two leaves of three leaves-old squash plants were lightly dusted with carborundum (600 mesh). The supernatant containing virus was used after dilution 10-1 with the same buffer as a virus inoculum.
2.5. Methods of Planting, Treatments and Collection of Samples
- A pot experiment was carried out in the greenhouse of Botany and Microbiology Department, Faculty of Science, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt to evaluate Salix alba water extract, mannitol solution (100 ppm), pomegranate peel water extract and algal filtrate of Spirulina sp. for inducing systemic resistance in squash plants against ZYMV. Surface sterilized seeds were soaked in the following treatments for 2 hrs before planting. Randomized complete block design was used with 8 treatments and 2 controls, where each consisted of eight replicate pots and two plants per pot. Treatments included sterilized seeds were soaked in Salix alba water extract (T1), T1 + ZYMV (T2), sterilized seeds were soaked in mannitol solution (100 ppm) (T3), T3 + ZYMV (T4), sterilized seeds were soaked in pomegranate peel water extract (T5), T5 + ZYMV (T6), sterilized seeds were soaked in algal filtrate of Spirulina sp. (T7) and T7 + ZYMV (T8) in addition to a virus challenged control (ChC, water soaked seeds) and an absolute control (AC, water soaked seeds and no virus). Seedlings were cultivated under natural lighting, day/night temperature of approx. 22/20°C and 60% mean relative humidity in the greenhouse. One week old seedlings were potted in soil and grown under the same conditions. After two weeks of growth, the 2 true-leaf seedling of the plants with treatments T2, T4, T6 and T8 in addition to the challenged control (ChC) were challenged inoculated mechanically with ZYMV inoculum. The plant samples were collected for analysis when the plants were 45 days old.
2.6. DAS-ELISA
- Serological examination for the presence of ZYMV was carried out using double antibody sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (DAS-ELISA) according to Clark and Adams [24]. Five infected plants from each treatment were taken and six symptomatic leaves from each plant were used as replicates to carry out ELISA determination. In case of absolute control plants, a randomly selected leaf samples was used. Absorbance values were recorded using a Dynatech MR700 plate reader at 405 nm. Leaf samples were considered positive for the presence of ZYMV if the absorbance value exceeded a threshold value equal to the mean of the absorbance value of healthy control samples + (3) (standard deviation of the mean) [25].
2.7. Disease Severity (DS)
- The disease severity induced by ZYMV was recorded after 15 days of inoculation, where the severity of symptoms was examined using the following rating scale: 0= no symptoms; 1= mild mosaic; 2= mottling 3= mild mosaic, mottling and blisters; 4= severe mosaic, green blisters and vein banding and 5= severe mosaic, green blisters, vein banding and filiform. Disease severity values were calculated using the following formula according to Yang et al. [26]:
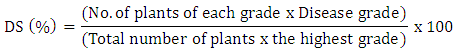
2.8. Physiological and Metabolic Changes
2.8.1. Determination of Chlorophyll and Carotenoids
- After 15 days of inoculation with a virus, the leaves with similar age were taken to extract the pigments. The method used for the quantitative determination of chlorophyll was that of Vernon and Selly [27]. Carotenoids were carried according to Lichtentahler [28] equation:
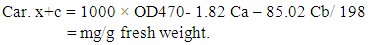
2.8.2. Determination of Soluble Carbohydrates and Soluble Proteins Content
- Total soluble carbohydrates and total soluble protein content were estimated according to the methods of Umbriet et al. [29] and Lowery et al. [30], respectively.
2.8.3. Determination of Proline Content
- The leaves were hand-homogenized in 3% of sulfosalicylic acid and centrifuged at 3000g at 4°C for 10 min. The supernatants were used for proline estimation according to Bates et al. [31].
2.8.4. Antioxidant Enzymes Activities
- Antioxidant enzymes were extracted according to the method of Mukherjee and Choudhuri [32]. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD) and polyphenoloxidase (PPO) activities were measured according to the methods of Dhindsa et al. [33], Bergmeyer [34] and Kar and Mishra [35], respectively.
2.8.5. Determination of Endogenous Hormone
- Levels of endogenous indole acetic acid (IAA), gibberellic acid (GA3), abscisic acid (ABA), salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) were determined for all treatments and the controls using HPLC according to the method of Lee et al. [36].
2.9. Electrophoretic Analysis of Protein by SDS-PAGE
- SDS-PAGE was done according to Laemmli [37] as modified by Studier [38]. In this protocol, electrophoresis is in a vertical slap gel between glass plates. Two gels consisted of two parts, the upper stacking gel (5%) and the lower resolving gel (15%). 80 µl of leaf samples containing 1 mg/ml protein were denatured at 100ºC for 3 min in 1% SDS containing 100 mM β-mercaptoethanol and Tris-glycine buffer at pH 6.8. Electrophoresis was conducted at 25 mA for 6-7 h. The two gels were stained with solution (10% v/v methanol, 10% v/v acetic acid, 0.0125% w/v Coommassie Brilliant Blue R-250) and shaken gently for 24 h. The gels were viewed by transilluminator (Uvitec, UK) and the position of the bands was recorded by photographing the gel.
2.10. Detection of Isozyme Markers
2.10.1. Peroxidase (POD) isozymes analysis
- Peroxidase isozymes were analyzed according to Stegmann et al. [39]. The enzyme extract was prepared by homogenizing one gram of leaf sample in 5 ml of 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 in a chilled pestle and mortar. The homogenate was centrifuged in a refrigerated centrifuge at 12,000 x g at 4°C for 20 min and the supernatant so obtained was used for POD isozymes analysis. Samples (50 μg) were mixed with sample buffer (150 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 3% bromophenol blue and 30% glycerol) and separated by nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) using a 12% acrylamide gel. Electrophoresis of protein samples was carried out in a Mighty Small II gel electrophoresis unit (Hoefer Scientific Instruments, San Francisco, CA, USA) at a constant current of 20 mA for 2h. After electrophoresis the gel was equilibrated for 30 min in 50 ml of 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0. Peroxidase isoforms were then visualized by incubating the gel in the dark with a freshly prepared diaminobenzidine solution (10 mg in 20 ml 0.05 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0) for 5-10 min, washing twice with water and then incubating with 10 μl 30% H2O2 in 20 ml of 0.05 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0.
2.10.2. Polyphenoloxidase (PPO) Isozymes Analysis
- The enzyme extract prepared for peroxidase isozymes analysis was used in polyphenoloxidase isozymes analysis. Separation of proteins (50 μg) was achieved by non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) of samples using a 12% acrylamide gel as described above. Following electrophoresis, the gel was equilibrated for 30 min in 50 ml of 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0. Polyphenol oxidase isoforms were then visualized by incubating the gel in the dark with freshly prepared p-phenylene diamine solution (10 mg in 20 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0) for 5-10 min, washing twice with water and then incubating with 0.2 M catechol in the same buffer. The addition of catechol was followed by a gentle shaking which resulted in the appearance of dark brown discrete protein bands [40].Relative band mobility was measured in relation to the dye front and indicated by Rf values. The gel analysis was applied by AlphaEaseFCTM ver. 4 software.
2.11. Statistical Analyses
- All statistical calculations were done using SPSS (statistical package for the social science version 20.00) statistical program at the 0.05 level of probability [41]. Quantitative data with parametric distribution were done using analysis of variance the one-way ANOVA and Post hoc-LSD tests (the least significant difference). The confidence interval was set to 95% and the margin of error accepted was set to 5%. The p-value was considered non significant (NS) at the level of > 0.05,* significant at the level of < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Confirmation of ZYMV
- Zucchini yellow mosaic virus Egyptian isolate was obtained from Virology Laboratory, Agricultural Microbiology Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Ain Shams University, Egypt. It was maintained on Cucurpita pepo. The ZYMV was confirmed biologically with local infection on Ch. amaranticolor which gave chlorotic local lesion (12-15 days, O.D. of DAS-ELISA at 405 nm = 0.380).
3.2. Disease Severity
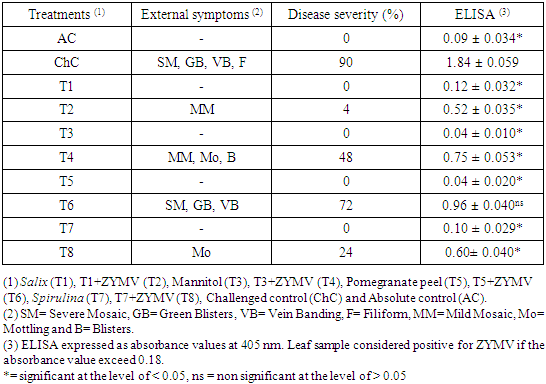
- ZYMV infected leaves of Cucurbita pepo cv. Eskandarani showed severe symptoms on the new leaves 15 days post inoculation with disease severity 90% (Table 1). These symptoms include severe mosaic, green blisters, vein banding and filiform (Fig. 1). The response of squash plants emerged from seeds soaked with Salix alba extract, mannitol solution, pomegranate peel extract and Spirulina sp. filtrate to challenge with ZYMV is quantified in the table (1). As shown in the table (1) and Fig. (1), challenged plants emerged from Salix-soaked seeds (T2) showed pronounced and significant reduction in percent disease severity (DS: 4%), followed by these emerged from Spirulina-soaked seeds (T8) (24%), mannitol-soaked seeds (T4) (48%) and pomegranate peel-soaked seeds (T6) (72%) compared with 90% for the challenged control plants (ChC). Also, soaking of the seeds with Salix extract (T2), Spirulina filtrate (T8) or mannitol (T4) significantly reduced virus concentration in the symptomatic leaves of the challenged plants, as these treatments showed ELISA values of 0.52, 0.60 and 0.75, respectively, while the challenged control (ChC) showed an ELISA value of 1.84. On the other hand, soaking of the seeds with pomegranate peel extract (T6) not significantly reduced virus concentration in the symptomatic leaves of the challenged plants, as this treatment showed an ELISA value of 0.96.
|
3.3. Physiological and Metabolic Changes
3.3.1. Photosynthetic Pigment Contents
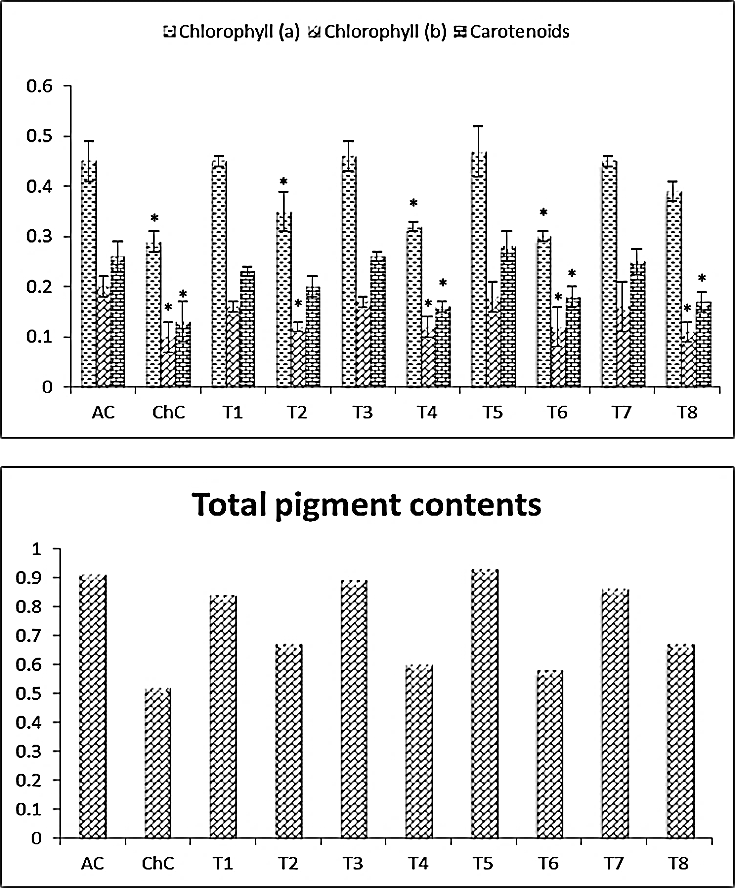
- Squash leaves infected with ZYMV showed a significant reduction in the photosynthetic pigment contents (Chl a, Chl b and carotenoids) (Fig. 2). The reduction in photosynthetic pigment contents of challenged control (ChC), clearly appeared as the development of leaf mosaic, and disease symptoms which was confirmed by the chemical analysis of the chlorophyll a & b and carotenoids were reduced by 35.55%, 50% and 50%, respectively, in comparison to corresponding absolute control (AC). Also, ZYMV infection causes a decrease in the total pigment content by 42.85% in comparison to the absolute control (AC). An alleviation of ZYMV severe infection effects was evidenced by alteration in chlorophyll content (a & b), carotenoids and total pigment content in challenging treatments [Salix+V (T2), Mannitol+V (T4), Pomegranate peel+V (T6) and Spirulina+V (T8)] (Fig. 2).
3.3.2. Soluble Carbohydrate and Protein Contents
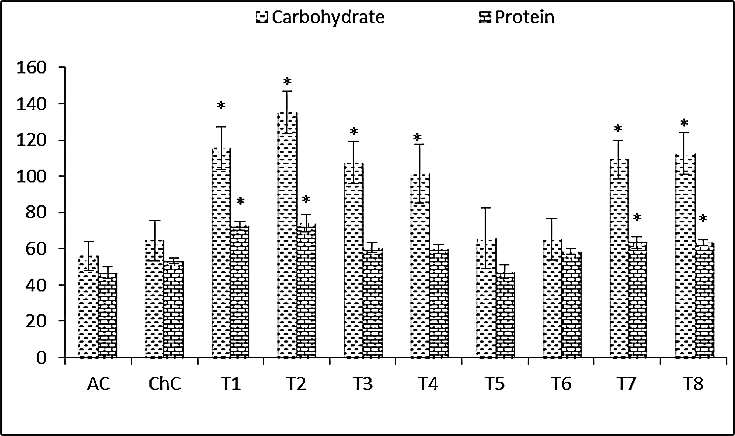
- Data illustrated graphically in Fig. (3) revealed that, soluble carbohydrate and soluble protein contents in leaves of squash plants were a slight significantly increased about 15.36% and 13.71%, respectively due to ZYMV infection. Also, in challenged treatments, significantly increasing in soluble carbohydrate and soluble protein contents was observed in leaves of squash plants, where Salix+V (T2) was 141.59% and 57.78%, Mannitol+V (T4) was 81.93 and 28.08, Pomegranate peel+V (T6) was 16.49 and 25.03% as well as Spirulina+V (T8) was 101.04 and 35.28%, respectively compared to absolute control (AC).
3.3.3. Proline Content as Osmolyte Indicator
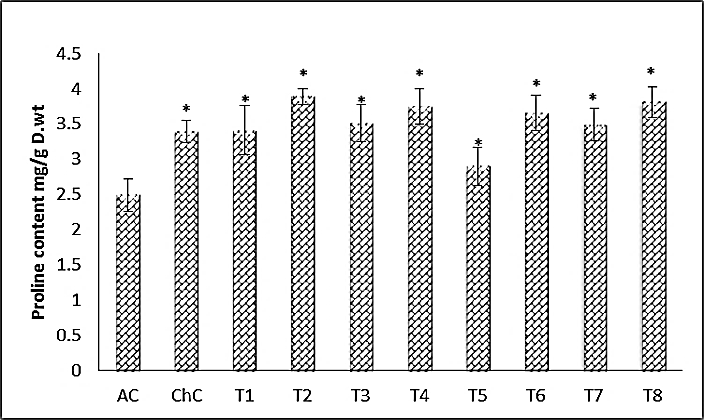
- The most obvious results illustrated graphically in Fig. (4) are the significant increase in proline content in challenged control (ChC) with 36.14% and challenged treatments (T2, T4, T6 and T8) with 56.22%, 50.60%, 46.99% and 53.01%, respectively compared to absolute control (AC).
3.3.4. Antioxidant Enzymes Activities
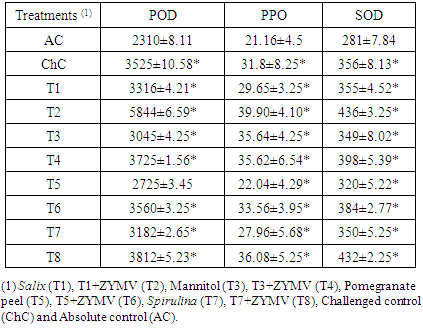
- The effect of viral infection and treatment with Salix, mannitol, Spirulina and pomegranate peel on the activities of peroxidase (POD), polyphenoloxidase (PPO) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) is shown in table (2). In virus inoculated leaves (ChC), the antioxidant enzymes activities (POD, PPO & SOD) increase significantly by 52.60%, 50.28% and 26.69%, respectively, when compared to that of the absolute control (AC). Also, the increase reached the highest value at challenged treatment [Salix+V (T2)] with 152.99%, 88.56% and 55.16%, respectively, compared to that of the absolute control (AC) and then the activities declined at challenged treatments [Mannitol+V (T4), Pomegranate peel+V (T6) and Spirulina+V (T8)]. Since, Spirulina+V (T8) with 65.02, 70.51 & 53.74, followed by Mannitol+V (T4) with 61.25%, 68.34% & 41.64%, respectively, and then Pomegranate peel+V (T6) with 54.11%, 58.60% & 36.65%, respectively, compared to that of the absolute control (AC).
|
3.3.5. Endogenous Hormones
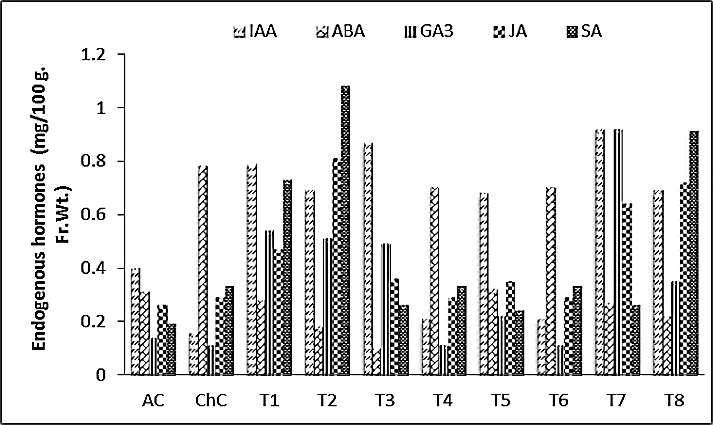
- Results of the present work Fig. (5) revealed that, activities of IAA and GA3 were significantly decreased, while ABA, JA and SA contents were significantly increased in squash plants due to the infection with ZYMV. Significantly higher IAA GA3, JA and SA, levels were observed in leaves of non-challenging treatments [Salix (T1) and Spirulina (T7)] and challenging treatments [Salix+V (T2) and Spirulina+V (T8)], while the ABA content was significantly decreased compared to absolute control (AC) and challenged control (ChC).
3.4. Electrophoretic Analysis of Protein by SDS-PAGE
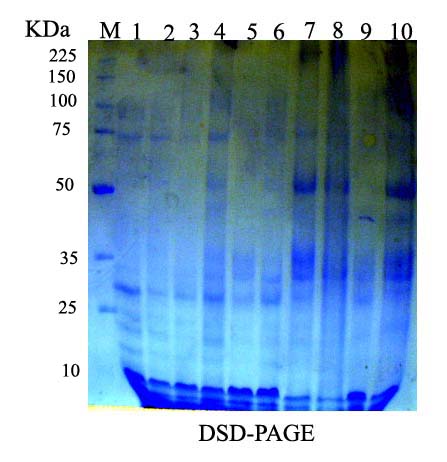
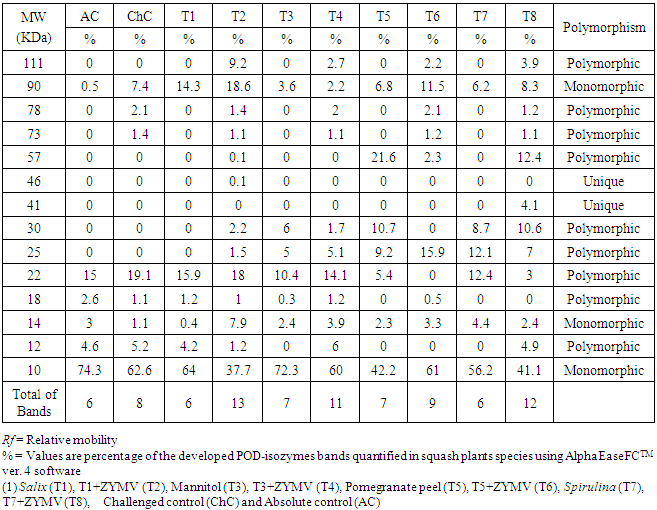
- The changes in protein patterns of pumpkin (C. pepo cv. Eskandarani) leaves challenged with ZYMV or not were analysed by SDS-PAGE. The results shown in Fig. (6) indicated that all challenged treatments varied greatly when compared to the control. The variance analysis, among four inducers (Salix, Spirulina, Mannitol and Pomegranate peel) appeared 14 protein bands. The molecular weight of polypeptides was determined relating to protein markers ranged from 111 to 10 KDa. The polypeptide number of polymorphism was 9 with percentage 64.28%. Inoculation with virus (ChC, T2, T4, T6 and T8) caused appearance of two new polypeptides of about 78 and 73 KDa (Table 3). In response to Sailx and Spirulina-challenged plants (T2 & T8), two newly synthesized bands (unique bands) of about 46 and 41 KDa, respectively were detected. Also, challenged treatments [Salix+V (T2), Mannitol+V (T4), Pomegranate peel+V (T6) and Spirulina+V (T8)] showed one newly synthesized band of about 111 KDa with intensity 9.2%, 2.7%, 2.2% and 3.9%, respectively. Furthermore, it was noticed that all lanes concerning challenged treatments (T2, T4, T6 and T8) showed a higher number of protein bands (13, 11, 9 and 12 bands, respectively) in comparison with control (6 bands) and challenged control (8 bands) lanes (Table 3).
|
3.5. Detection of Isozymes Markers
3.5.1. Peroxidase (POD) Isozymes Analysis
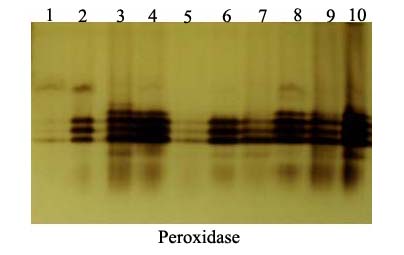
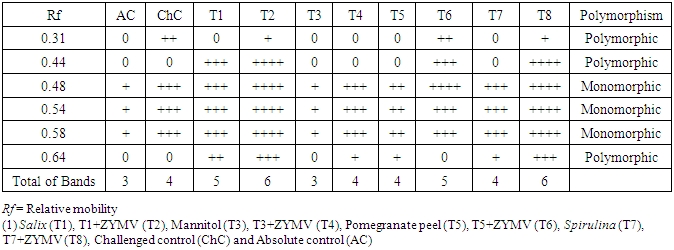
- The peroxidase and polyphenoloxidase isozymes analysis on the basis of the number, intensity and reproducibility of POD and PPO bands among challenged plants with ZYMV or not. POD-isozymes analysis displayed a total 6 bands as shown in Fig. (7) and table (4) where 3 polymorphic bands with Rf of 0.31, 0.44 and 0.64 with percentage of 50%. In addition, 3 monomorphic bands with Rf of 0.48, 0.54 and 0.58 with percentage of 50%. The challenged treatments [Salix+V (T2), Mannitol+V (T4), Pomegranate peel+V (T6) and Spirulina+V (T8)] showed variation in number, relative mobility and density polypeptide bands compared with control and challenged control. Sailx and Spirulina-challenged plants (T2 & T8), increased the density and number of isozymes (6 isozymes), while mannitol (T4) gave 5 isozymes. On the other hand, pomegranate peel-challenged plants (T6) gave 4 isozymes, equal to that in plants of challenged control (ChC) (Table 4).
|
3.5.2. Polyphenoloxidase (PPO) Isozymes Analysis
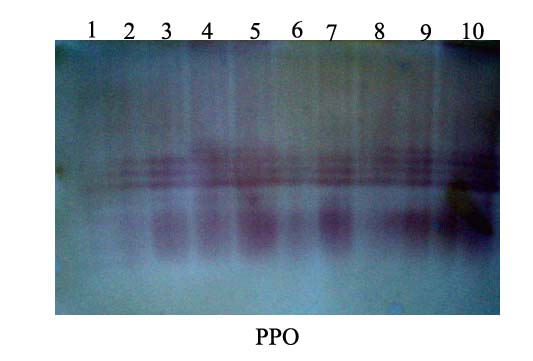
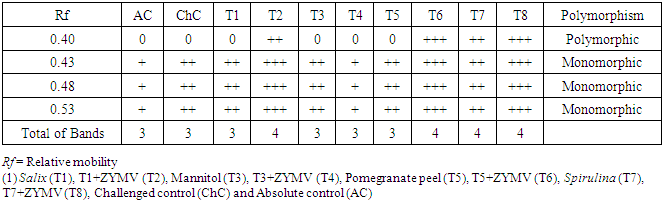
- The total numbers of polyphenoloxidase isozymes were 4 bands as shown in Fig. (8) and table (5). The isozymes bands of treatments showed variation in number, relative mobility and density polypeptide bands. Salix, Mannitol and Spirulina-challenged plants (T2, T6 & T8) increased the density and number of isozymes (4 isozymes) in comparison with pomegranate peel-challenged plants (T6), absolute control (AC) and challenged control (ChC) (3 isozymes, Table 5).
|
4. Discussion
- The objectives of this study were induction systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in Cucurbita pepo cv. Eskandarani plants against virus infection with ZYMV upon priming with treatments and subsequent challenge inoculation of the plant with the virus. No strategies are currently available to completely protect these plants against the virus, but a common feature of induced resistance to the disease is the priming of plant tissues by elicitors that allows rapid deployment of active defense mechanisms against invading pathogen [42]. We try to realize this purpose; many experiments were successively to deduce if induction of systemic acquired resistance was successfully achieved could also protect Cucurbita pepo cv. Eskandarani plants against infection by ZYMV. During the present work four inducer seeds soaked treatments (Salix alba extract, Mannitol solution, Pomegranate peel extract and Spirulina filtrate) were tested for their potentiality as resistance inducers in the treated plants.Disease severity percentage and virus concentration using DAS-ELISA were different in challenged control and challenged plants emerged from four treatments-soaked seeds where challenged plants emerged from Salix-soaked seeds showed pronounced and significant reduction in percent disease severity and virus concentration, followed by these emerged from Spirulina-soaked seeds, mannitol-soaked seeds and pomegranate peel-soaked seeds compared with the challenged control plants. The same results were obtained by many authors [17, 43-46]. They have been suggested, induced resistance is a state of enhanced defensive capacity developed by a plant when appropriately stimulated.Virus infection leads to many alterations of physiological and biochemical processes within the plant where the appearance of severe symptoms on virus-infected leaves in a form of severe mosaic and, the new leaves showed deformation of leaf morphology (filiform) occurs due to changes in metabolism, alteration of some enzyme activities, photosynthetic capacity and accumulation or reduction in certain metabolites such as carotenoids [12, 17, 44]. In the present investigation, results clearly reveal a reduction in the photosynthetic pigment levels (chlorophyll a, b and carotenoids) in squash plant leaves due to ZYMV infection where Tecsi et al. [12] reported that the appearance of systemic chlorosis due to virus infection is accompanied by a decrease in photosynthesis. There are various theories about how Chl a and Chl b contents in infected leaves were decreased. According to Lucas [47] decreases of chlorophyll were the result of the blocking Chl synthesis. On the other hand, Roca and Minguez-Mosquera [48] thought that it could be due to increased chlorophyllase activity. The decrease in chlorophyll is considered to be a symptom of oxidative stress condition, this decrease after virus infection might be due to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) causing damage to chlorophyll a that is mean the plant failed to capture the light and so photosynthesis will decrease or stopped [49]. Similar results for numerous host plants infected with different viruses were published by Radwan et al. [17] and Kyseláková et al. [50]. In our results, an alleviation of ZYMV severe infection effects was evidenced by alteration in chlorophyll content (a & b), carotenoids and total pigment content in challenging treatments (Salix+V, Mannitol+V, Pomegranate peel+V and Spirulina+V). Leslie and Romani [51] reported that salicylic acid lead to improve the carotenoid molecules from degradation to prevent breakdown of other pigment constituents. It proved to decrease ethylene production and activated the synthesis of carotenoids which protect chlorophyll from oxidation and finally increased chlorophyll content as reported in this study.The results of the present work showed that total soluble carbohydrate and protein contents in leaves of squash plants were a slight significantly increased about 15.36% and 13.71%, respectively due to ZYMV infection. Also, in challenged treatments, significantly increasing in soluble carbohydrate and soluble protein contents was observed in leaves of squash plants, where Salix+V was 141.59% and 57.78%, Mannitol+V was 81.93 and 28.08, Pomegranate peel+V was 16.49 and 25.03% as well as Spirulina+V was 101.04 and 35.28%, respectively compared to absolute control (AC). It has been known that the virus infection leads to increased sugar levels in plant tissues, where the plants have the ability to modulate their sugar pools to act either as a source of carbon and energy or to use as signals and perhaps as putative priming agents to intensify immune reactions [52, 53]. Similar results were recorded by Radwan et al. [17] who reported that in response to viral inoculation, the soluble, insoluble and total protein contents increased significantly as well as a slight increase in soluble carbohydrate in comparison to uninoculated control. Also, reported that salicylic acid (SA) enhances the synthesis of sugar even if applied, followed by viral infection where SA seems to be the factor causing an increase of soluble and total carbohydrates. The high protein content in virus infected plants is possibly due to the synthesis of virus coat protein and other virus associated non-structural proteins. Also, plants develop a complex variety of events involving synthesis and accumulation of new soluble proteins that have a direct or indirect role in inducing plant resistance [54], where the newly-induced proteins may help to limit virus spread or multiplication [55].Proline accumulation is a common metabolic response to both abiotic and biotic stress and when higher plants are exposed to stress; many plants accumulate high amounts of proline in tissues [56]. Stress-susceptible plants are characterized by the accumulation of proline where, when plants are exposed to microbial pathogens, they produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) that induce programmed cell death in the plant cells surrounding the infection site to effectively wall off the pathogen and terminate the disease process [57, 58]. The amino acid proline may act as a potent scavenger of ROS and this property of proline might prevent the induction of programmed cell death by ROS [59]. Our results showed that the proline content increased significantly in challenged control plants with 36.14% and challenged treatments (Salix+V, Mannitol+V, Pomegranate peel+V and Spirulina+V) with 56.22%, 50.60%, 46.99% and 53.01%, respectively compared to absolute control. Radwan et al. [17] noticed that the exogenous application of salicylic acid (SA) on pumpkin plants infected with ZYMV increases the plant resistance against ZYMV where the proline content was induced by viral infection and SA treatment.A large number of defense enzymes that have been associated with SAR include, peroxidase (POD), polyphenol oxidase (PPO), superoxide dismutase (SOD) [60]. These enzymes also bring about liberation of molecules that elicit the initial steps in induction of resistance, phytoalexins and phenolic compounds [61]. Peroxidase was considered to be one of the antioxidant enzymes involved in the plant defense response to pathogen attack, it was reported to be the first enzyme to show changes in its activity under stress [17]. Also, the enhancement of peroxidase activity has been reported in many plants exposed to external biotic and abiotic stresses [62]. Our results showed that antioxidant enzymes activities increased significantly in plants infected with ZYMV. To obtain a more clear indication on some defense-responsible enzymes, mean activities of peroxidase, polyphenoloxidase and superoxide dismutase of the tested squash plants were determined in this study. The POD, PPO and SOD activities were greater in both infected and uninfected plants treated with Salix extract followed by Spirulina, mannitol and pomegranate peel compared to their control ones. Our results are in agreement with Riedle-Bauer [63] who found that a highly significant increase in POD and SOD in both Cucumis sativus and Cucurbita pepo infected by ZYMV. The level of phenol metabolizing enzymes, phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), peroxidase (POD), and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) are induced upon treatment with chemical and/or biological elicitors that influences the levels of phenolic compounds in the metabolic pool [64]. Similar results were recorded by Radwan et al. [17] who reported an increase in POD activity of pumpkin leaves infected with ZYMV. Virus infection appears to stimulate POD activity in all hosts in which necrotic or chlorotic symptoms are induced, the degree of stimulation correlating with the severity of symptoms [65]. In our work, the results of severity of symptom index are in accordance with the POD, PPO and SOD activity data, where the higher the severity of symptoms, the higher POD, PPO and SOD activities. Formation of H2O2 in the cells during disease development is controlled by the activities of antioxidant enzymes, which are directly or indirectly controlled by hormones such as salicylic acid [66]. There is no clear relationship between POD activity and the chlorophyll content because the site of peroxidase action is within the apoplast, where we found the chlorophyll content decreases, while the POD activity increases for the same treatment. The POD is known to be involved in the produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) where the ROS accumulation causes oxidative damage through actions such as lipid peroxidation and membrane destruction. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are imposed to be responsible for chlorophyll degradation and POD levels increase during senescence [67]. So, there is a correlation between the decrease in chlorophyll content and the increase in POD activity in the green leaves infected with a virus [5]. Also, POD is known to catalyze the final polymerization step of lignin synthesis and is directly associated with the increased ability of systemically protected tissues to lignify [68]. Therefore, this is a way to interpret the higher activity of POD during virus infection and SA treatments that lignification process is considered as a pathogen resistance mechanism [17].Our results demonstrated that, amounts of IAA and GA3 were significantly decreased while ABA, JA and SA contents were significantly increased in squash plants due to the infection with ZYMV. Pennazio and Roggero [69] reported that virus infection reduces both auxin activity and concentration. Also, Zhang et al. [70] reported a decrease in both cytokinin and GA and an increase in ABA in virus-infected banana leaves, where gibberellins are biosynthesized from the isoprenoid metabolic pathway and share common intermediates with both cytokinin and ABA. Fraser et al. [71] postulated that while changes in ABA concentration alone could account for the correlation between symptom severity and growth in tobacco, It is apparent that intracellular localization of ABA is important in the development of symptoms following virus infection. Whether the increased cytoplasmic ABA is due to virus-induced damage to the chloroplastic envelop and/or ABA synthesis external to the chloroplast is not known [72].On the other hand, our results demonstrated that, significantly higher IAA, GA3, JA and SA, levels were observed in leaves of non-challenged treatments (Salix and Spirulina) and challenged treatments (Salix+V and Spirulina+V), while the ABA content was significantly decreased compared to absolute control (AC) and challenged control (ChC). Thus, a type of protection might be activated by treatment with these elicitors, where the first hormones to be marked as central players in defense against plant pathogens were salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and ethylene (ET) [73]. Clarke et al. [74] suggest that the action of higher concentrations of IAA on the inhibition of virus may be due to auxin-induced ethylene production. Also, exogenous GA3 reduced/inhibited virus replication [75]. Studies have demonstrated that JA is the major defense-signaling molecule associated with the wound response, where Ravnikar et al. [76] reported that the reduction of potato virus M content in potato meristems was correlated with an increased JA concentration.The natural resistance of plants to pathogens and parasitic weeds is based on the combined effects induced mechanisms among which the systemic acquired resistance (SAR) that controlled by signaling pathway and depends on the endogenous accumulation of salicylic acid, which activates many defense compounds, including phenolic acids, coumarins, flavonoids and lignin [77]. Salicylic acid, its glucose conjugate, and methyl ester have been shown to increase markedly following virus infection [78], where SA is synthesized from trans-cinnamic acid via benzoic acid, a reaction catalyzed by benzoic acid 2-hydroxylase. This enzyme is expressed constitutively in tobacco but is highly induced by inoculation with TMV or the application of benzoic acid, indicating de novo biosynthesis of SA in response to virus infection [79]. By monitoring endogenous SA levels in virus-inoculated and uninoculated leaves, using mutants over- or under expressing SA, and the nahG gene to hydrolyze and inactivate SA, there is strong evidence for a role for SA in the activation of cell death, in pathogen localization, in defense gene activation, and in the induction of SAR [80].Our results concerning the protein content and antioxidant enzymes activities (POD & PPO) are parallel with those describing protein and isozymes (POD & PPO) patterns investigation by SDS-PAGE and native-PAGE, respectively. Inoculation with ZYMV caused appearance of two new polypeptides of about 78 and 73 KDa in challenged control and challenged treatments (Salix+V, Mannitol+V, Pomegranate peel+V and Spirulina+V). Also, we found two newly synthesized polypeptides of about 46 and 41 KDa in response to Sailx and Spirulina-challenged plants, respectively. Also, challenged treatments (Salix+V, Mannitol+V, Pomegranate peel+V and Spirulina+V) showed one newly synthesized band of about 111 KDa with intensity 9.2%, 2.7%, 2.2% and 3.9%, respectively. Furthermore, it was noticed that all lanes concerning challenged treatments showed a higher number of protein bands (13, 11, 9 and 12 bands, respectively) in comparison with control (6 bands) and challenged control (8 bands) lanes. It is possibly due to the synthesis of virus coat protein and other virus associated non-structural proteins. Also, plants develop a complex variety of events involving synthesis and accumulation of new soluble proteins that have a direct or indirect role in inducing plant resistance [54], where the newly-induced proteins may help to limit virus spread or multiplication [55]. Formation of new proteins and protein accumulation is considered a way and an indicator of resistance towards ZYMV infection. Salicilic acid plays an important role in induction of resistance in pumpkin against ZYMV through the formation of the new polypeptides or pathogenesis related proteins [17]. Also, the SA-induced protein kinases identified by Zhang and Klessig [81] are thought to regulate PR protein expression and the expression of several genes (R genes) involved in bacterial, fungal, nematode, and virus resistance [82].Variation in isozymes reveals the information in the biochemistry entity of resistant genes to physiological changes, genetic characteristics and development of different organisms [83, 84]. Moreover, their relative contents and activities could be used as a biochemical indicator to identify whether a strain had resistant ability to an external stress [84]. In this study, clear differences existed not only in enzymatic activity but also in enzymatic composition among challenged plants with elicitors or no. In general, Sailx and Spirulina-challenged plants, increased the density and number of POD isozymes (6 isozymes), while mannitol-challenged plants (5 isozymes). On the other hand, pomegranate peel-challenged plants gave 4 isozymes, equal to that in plants of challenged control. While, in case of PPO isozymes mannitol as well as Salix and Spirulina-challenged plants increased the density and number of PPO isozymes (4 isozymes) in comparison with pomegranate peel-challenged plants, absolute control and challenged control (3 isozymes). Since, mannitol plays an important role in osmotic adjustment, it acts as an antioxidant to scavenge of hydroxyl radicals (OH-) [21]. Walter et al. [85] reported that SAR results from the expression of several parameters, including changes in cell wall composition and de novo synthesis of phytoalexins and PR (pathogenesis related) proteins. Moreover, the local de novo synthesis of phytoalexins is often related to the induced resistance stage.
5. Conclusion
- The objective of this study was evaluated biochemical markers in response to viral infection and evaluation of some inducers to systemic acquired resistance in squash plants against ZYMV. Some inducers like Salix alba extract and Spirulina sp. filtrate as seeds soaked lead to more resistance to viral infection, while others like mannitol solution and pomegranate peel extract lead to less resistance to viral infection.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML