-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Internet of Things
2022; 10(1): 22-31
doi:10.5923/j.ijit.20221001.02
Received: Apr. 14, 2022; Accepted: May 6, 2022; Published: May 12, 2022

A Combined Metric Objective Function for RPL Load Balancing in Internet of Things
Kala Venugopal , T. G. Basavaraju
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Government Engineering College, Hassan, Karnataka, India
Correspondence to: Kala Venugopal , Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Government Engineering College, Hassan, Karnataka, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In an IoT-oriented intelligent world, everything around us is interconnected and integrated. The IoT ecosystem comprises a network of constrained devices called Low-Power Lossy Networks, where RPL (IPv6 Routing Protocol over Low power lossy networks) is recognized as the standard routing protocol for these networks. Though RPL projects several distinctive features, Load Balancing is identified as one of the significant inadequacies unaddressed by this protocol. In this paper, a novel Combined Metric Objective Function (COM-OF) is proposed that considers a combination of significant metrics to design a load-balanced DODAG, that distributes the traffic load equally amongst the different nodes within the network and maximizes the network lifetime. The metrics of our interest incorporates the expected lifetime of the node, the child count, the energy consumption, and link reliability for the nodes. The performance of COM-OF is compared with the standard RPL objective functions OF0 and MRHOF using the Cooja simulator of Contiki OS. The results prove that COM-OF exhibits enhanced performance than OF0 and MRHOF with 33% reduction in power consumption, 97% packet delivery ratio, up to 45% improvement in network lifetime and 36% reduction in the average number of child nodes.
Keywords: Internet of Things, Load balancing, Low power Lossy Networks, Objective Function, RPL
Cite this paper: Kala Venugopal , T. G. Basavaraju , A Combined Metric Objective Function for RPL Load Balancing in Internet of Things, International Journal of Internet of Things, Vol. 10 No. 1, 2022, pp. 22-31. doi: 10.5923/j.ijit.20221001.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- IoT envisages the idea of worldwide connectivity. Here we can connect a network of dedicated devices or objects called “things” that are entrenched with sensors, actuators, software and, electronics to the Internet so that they can gather and exchange real-world data without human intervention. Post data collection, the sensors share their data through other IoT devices or the gateway, which is later analyzed locally or in the cloud. It is anticipated that the volume of data created by IoT will reach a massive total of 79.4 zettabytes, with around 75 billion devices connected by 2025 [1]. IoT has shaped multiple opportunities to link the natural world with computer-aided systems leading to automation in numerous fields and empowering innovative applications. When combined with the latest technologies like 5G, IoT helps improve the operational efficiency of organizations with minimal cost and enhanced decision-making and user experience.IoT typically deals with a distinct category of a network of embedded devices termed Low-power Lossy Networks (LLNs), where both the routers and interconnects are constrained [2]. The routers are constrained in resources like low memory, battery power, bandwidth, and processing power. The interconnects are constrained, providing low data rates, stability, and high loss rates. LLNs support point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and multipoint-to-point traffic flow between thousands of nodes.These constrained devices can be connected to the IPv6 network using the 6LoWPAN (IPv6 over Low-power Wireless Personal Area Network) standard. Here, an adaptation layer is compressed between the IP and 802.15.4 standard protocol layers in the protocol stack [3]. This adaptation layer compresses and fragments the IP protocol stack 1280 octets MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) into packets of 127 bytes, attuned to the 802.15.4 standard. It also lets routing protocols be implemented at the network layer to provide end-to-end connectivity for various applications [4]. Routing data for these heterogeneous low power lossy networks is a unique unresolved challenge due to the intrinsic properties of IoT like inadequate resources, fluctuating link quality, and regular topological changes. Therefore, routing protocols that can acclimate to these low-power lossy links play a vital role in reliable end-to-end data delivery. Here we look for reliable routing protocols that can handle critical and massive data generated by the tremendous traffic of numerous IoT applications. Unfortunately, with the evolution of the Internet and IoT, conventional routing protocols like OSPF, OLSR, AODV, or DSR cannot lodge in IoT, overcoming the limitations of LLNs. Therefore, IPv6 Routing Protocol for Low power and Lossy Networks (RPL) was developed as the routing protocol used in 6LoWPAN for LLNs and was standardized for IoT [2]. RPL is proposed to aid MultiPoint-to-Point (MP2P), Point-to-MultiPoint (P2MP), and Point-to-Point (P2P) traffic. MP2P traffic provides connectivity to the core private IP network or the Internet. A destination advertisement technique is used by P2MP traffic to provide paths toward the downward destinations. P2P traffic routes the packet from the root to the destination with the help of routing tables at the nodes [2].RPL has many incomparable features like nominal battery usage, quick topology creation, self-healing nature, and a loop-free structure. Still, one of the significant limitations of this protocol is that it cannot handle Load balancing, which is required for the fair dispersal of traffic in the network. RPL Objective Functions create volatile load traffic for the nodes significantly closer to the root. The preferred parent node through which most of the traffic is diverted becomes a fragile node serving all the traffic from the child nodes compared to other parent nodes. This drainage of energy from the preferred parent node causes network breakage, affecting network lifetime and reliability [5].This paper intends to equalize the network load and increase the network's lifetime. We present a novel Objective Function named Combined Metric Objective Function (COM-OF), which considers the ETX metric and energy consumption of the nodes and a combination of the Estimated Lifetime (ELT) metric and the Child count metric. We compare the COM-OF with the RPL’s default objective functions, Minimum Rank with Hysteresis OF (MRHOF) [6] and Objective Function Zero (OF0) [7]. The performance evaluation of COM-OF is done by conducting simulations using the Cooja simulator of Contiki OS, with a network of 10, 30, and 50 nodes, and the results are compared.The key features of the proposed objective function are as follows:• First, the Child Count metric is calculated based on the parent ID in the DIO message.• Then, the Estimated Lifetime (ELT) metric is calculated based on the total traffic generated, ETX, and energy consumption.• A Combined Metric Objective Function (COM-OF) is projected that uses a combination of metrics mentioned above to construct a load balancing DODAG. COM-OF minimizes the energy consumption, advances the network lifetime, and increases the network reliability in comparison to the standard objective functions.The paper's structuring takes the following layout: Section 2 outlines the RPL protocol functioning. Section 3 reviews the related works about load balancing. The proposed work is briefed in Section 4, and the performance evaluation is presented in Section 5. Ultimately, Section 6 concludes the research work.
2. Outline of RPL Protocol
- The IPv6 Routing Protocol over Low power lossy networks (RPL) is a Distance vector routing protocol based on source routing developed by IETF for LLNs and designed for IEEE 802.15.4 PHY and MAC layers [2].
2.1. Topology and Control Messages of RPL
- RPL is constructed based on Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) that calculates routes between LLN nodes. A node can have multiple parents in the DAG structure, unlike trees with only one parent. In RPL, nodes are organized as DODAGs, i.e., Destination-Oriented DAGs. The network's root node also referred to as the Sink or Border Routers (BR) or LLN Border Routers (LBR) or Gateways, connects the 6LoWPAN RPL network to the IPv6 Internet. Also, the RPL network can run multiple RPL instances, each instance identified by a unique RPLInstanceID and having single or several DODAGs in it.The Network topology in RPL is formed by exchanging four RPL control messages that are different types of ICMPv6 control messages [8]. These messages are identified by their code field• A DODAG Information Solicitation (DIS) message is issued by a new node trying to reach and attach to a network and explore the nodes nearby. • A DODAG Information Object (DIO) message is multicast by a node, usually the root node, in the network, to let the nearby nodes determine the RPL Instance and let them choose a parent based on the Rank and other design specifications. The rank of a node identifies the node's location in the network from the DODAG root. • A node replies with a Destination Advertisement Object (DAO) message to its parent, broadcasting the route information in the upward path and informing its participation. • A node receiving the DAO message responds by sending back a unicast Destination Advertisement Object Acknowledgement (DAO-ACK).
2.2. DODAG Construction
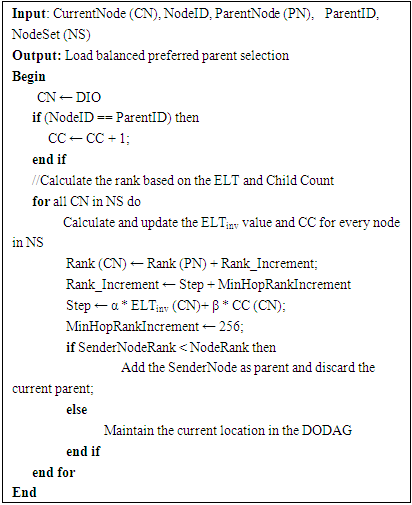
- DODAG formation is centered on the Neighbour Discovery process, where DIO messages are directed from the root to all the other nodes in the network, and DAO messages are sent from the other nodes to create a path towards the root [9]. A node issues a DIS message probing for the topology information from its neighbors to join a network. Based on the Trickle timer, DIO messages are broadcast from the root to the child nodes in the network. This DIO message is accepted by a node wanting to join the network or a node already existing in the network. The DIO message carries information regarding the RPLInstanceID, the details of the node’s rank, and the Objective function. The node, based on (1) and (2), calculates the Rank and updates the parent list with the sender of the DIO message [10].
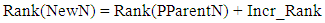 | (1) |
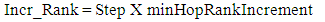 | (2) |
2.3. RPL Objective Functions
- RPL uses the Objective function (OF) to construct routes, defining how the nodes choose the best-optimized route in an RPL instance [2]. Here, the nodes support and advertise one or more metrics and constraints through their DIO messages used for the parent selection in DODAG. An Objective function specifies how these metrics or constraints are converted into a rank value, defining the location of a node from its DODAG root and specifying the parent selection mechanism for a node in DODAG. Thus, referring to the DAG container within the DIO messages, the objective function decides on the rules for using metrics and constraints, parent selection mechanism, load balancing, etc. [2].The two Objective Functions that are defined in the RPL protocol are Objective Function Zero (OF0) [7] and Minimum Rank with Hysteresis OF (MRHOF) [6].OF0 is proposed to find the closest Grounded root. The OF0 finds the shortest path to the sink node based on the hop count metric, where a node’s rank is calculated based on the least number of hops to the sink. Here, load balancing is not considered while routing the traffic towards the root through the preferred parent.The Minimum Rank with Hysteresis OF (MRHOF) discovers the routes with minimum path cost avoiding unnecessary churns in the network. The term ‘hysteresis’ confirms that the path with minimum rank or cost selected is less than the existing one by a threshold value. MRHOF utilizes the Expected Transmission Count (ETX) metric that computes the quality of the link, thereby considering the congestion at the link level rather than the node level.
3. Related Survey
- As already mentioned, Load balancing in RPL networks is one of the critical issues that need to be addressed. Researchers have proposed several methods to alleviate the load balancing issue and improve the network lifetime in recent years.Authors in [10] use an amalgamation of three metrics, ETX, Content, and Energy, to fulfill the needs of different IoT applications using the Cooja simulator of Contiki OS. They use the enhanced triggering technique to remove the trickle timer’s accumulative effect on the short-listen problem. It was observed that when compared to default OF, the results for PDR and Latency delay were better for Energy combined with Content (EC) and aggregation with Enhanced timer (EC_En_Timer) design, and the results for energy consumption was better for Residual Energy (RE) merged with ETX (EE) and combination with Enhanced timer (EE_En_Timer) design. To handle the energy imbalance problem and improve the network lifetime, the authors in [11] propose a Time OF (T-OF) where ETX, a weighted combination of energy, and the Number of Children and Siblings (NOCS) metrics is used. Compared to MRHOF, OF0, and Energy Objective Function (EN-OF), T-OF shows a PDR of 95%, an improvement in the lifetime of the network to 54 minutes, and an advancement in balancing of energy due to lesser latency of 11.35 seconds.In [12], the authors compare the diverse OFs where OF0, MRHOF (ETX), MRHOF (NONE), MRHOF (ETX + ENERGY), MRHOF (ENERGY) and is compared for enhanced RPL performance. It was observed that MRHOF(ETX) could be favored for bigger networks and that Hybrid OF is best suited for small networks compared to larger networks. Simulations with the Cooja simulator in Contiki OS show an increase of 24% in PDR, a decrease of 28% in power consumption, and a lesser inter-packet time of 39% compared to single metric RPL. Unfair traffic distribution due to a lack of load balancing in the network also leads to a decline in network efficiency. A new method based on cluster ranking called C-Balance is proposed in [13] to improve the network lifetime. Here, cluster heads are identified for clusters using a first rank that is calculated. Then, parents are determined for these cluster heads for packet forwarding using a second rank. The metrics ETX, hop count, the number of children, and the residual energy were used to calculate the Ranks. The C-balance functioning is equated with OF0, MRHOF, and QU-RPL using the Cooja simulator of Contiki OS with a network topology of 20, 40, and 60 nodes. It was observed that the energy consumption and network lifetime in C-Balance are improved by 30 to 40% and 28 to 48%, respectively, and the average number of child nodes is reduced by 15 to 23%. However, the end-to-end delay is more in comparison with OF0, MRHOF, and QU-RPL.To extend reliability, the lifetime of the network, and stability of the network, two novel objective functions called the weighted combined metrics objective function (WCM-OF) along with non-weighted combined metrics objective function (NWCM-OF) is projected in [14]. They are centered on the ETX, the quality of the link, the node energy consumption, and the additive combination with equal and non-equal weights. Simulations on the Cooja emulator of Contiki OS show that the network performance based on the proposed objective function is improved compared to the default OFs. A new enhancement of the RPL protocol called Energy and Load aware RPL (EL-RPL) protocol is projected in [15] to maximize the network lifetime. The rank of DODAG is calculated based on a composite metric based on Load and battery depletion index and ETX for route selection. The performance of EL-RPL is approximated to RER(BDI) RPL and fuzzy logic-based RPL (OF-FL RPL) protocols using the Cooja simulator. EL-RPL shows improved performance in network lifetime and PDR by 8-12% and 2-4%, respectively.To balance the Load in terms of traffic in the network and extend the lifetime of overburdened nodes, the authors in [5] propose the Load balanced objective function (LB-OF) that considers the child count for each candidate parent node. The different steps put forward include amending the DIO message, including a new utilization technique for this DIO, and finally balancing the nodes using a new RPL metric. The simulations were conducted using the Cooja simulator and Contiki OS for up to 100 nodes and compared with MRHOF and OF0 OFs. It is observed that LB-OF displays better performance for power consumption, PDR, and network lifetime.Authors in [16] propose the Parent Aware Objective Function (PAOF) for RPL, where the ETX metric and parent count metric are used to calculate the optimal route to the sink. Here, a more significant number of intermediate nodes are preferred parents to route the packets to the destination. The Contiki OS and the Cooja simulator are used to compare the performance of PAOF with MRHOF. It was observed that PAOF showed improvements in parent diversity and load density ensuring better load balancing and network lifetime.To enhance the reliability and power consumption of RPL, LBSR, which is a new Load Balancing Objective Function, is projected in [17]. Here, a new routing primitive to calculate the number of children, a new load balancing mechanism to fairly distribute energy among the nodes, a new path selection mechanism to eliminate instability issues, and a new routing propagation mechanism is developed. Cooja simulator and Contiki OS are used to simulate the network, demonstrating improvements in energy consumption, PDR, and load distribution compared to RPL.To detect and correct the load imbalance, bottleneck, and network congestion in large networks at the different levels in DODAG, a new child count method called Child Count based Load Balancing in RPL (Ch-LBRPL) that enhances [5] [17] is proposed in [18]. The simulations were conducted for 31 nodes using the Cooja simulator of Contiki OS and compared to RPL and Load balanced RPL (LBRPL). The number of DIO messages were observed to be reduced with minimal parental switching. It also exhibited better control overhead and energy usage. The mathematical model proposed also suits well for scalable network size too. However, from the aforesaid review, it is observed that research works in [10-12] and [14–15] concentrate on the usage of one or more metrics that are quite complex but does not meet all the performance requirements of a network that include network lifetime, stability of the network, end-to-end delay, PDR, control overhead, reliability of the network, energy imbalance issues, power consumption etc. It is therefore quite evident that a single objective function may not be able to achieve all the needs and requirements of the different IoT applications. In [16], though the objective function confirms better load balancing and network lifetime, it also leads to several DIO and DAO messages. While research work in [5] is yet to consider a greater number of metrics for their future work, resource-based load balancing is the future deliberation in [18]. Also, validation of the efficiency of the different approaches on real test beds [17] is still an anticipated work for most of the current research works.
4. The Proposed Work
4.1. RPL Load Balancing Problems
- Unequal traffic or load affects the connectivity of LLNs, leading to various issues like congestion in the network, excessive utilization of the energy of the nodes, reduced network lifetime, reliability, and stability of the network. As RPL is conceived for heterogeneous networks of heterogeneous devices, it must deal with unequal and heavy traffic. RPL objective functions and metrics lead to congestion as it does not consider Load Balancing. Several reasons can induce load imbalance in a network. One such instance is the Hotspot problem [19], where a preferred parent node is overloaded with traffic during congestion in the network and increases the data relay to manage the traffic. Such a node becomes a hotspot in a network, leading to energy depletion and reduced network lifetime. Another instance is the Bottleneck problem [20], where the hotspots are the first-hop node to the root called the bottleneck nodes. As most of the traffic is directed through the bottleneck nodes, the energy depletion of such nodes occurs must faster. The Thundering herd or herding effect problem [21] [17] is another reason for load imbalance in a network during congestion. Here, a set of nodes keeps switching between the preferred parent nodes in a pointless attempt to balance the load. A similar problem is the Instability problem [22], where the nodes keep changing their preferred parent based on the updated rank value and link metric value of the parent node leading to instability of the network. Another reason to cause load imbalance, totally by chance, is the “Randomly unbalanced network” problem [23]. Here, a parent node can be repeatedly and randomly selected between two parent nodes having the same rank.
4.2. RPL Load Balancing Metrics
- The selection of a path is based on the metric of an objective function and is measured as the path cost [24]. Metrics could be node-based or link-based, dependant on where it was developed in a network. Metrics like Energy and hop count are examples of node-based metrics, whereas metrics concerned with link quality like ETX, throughput, latency, etc., are link-based metrics [25]. We can also use a single metric or multiple metrics for routing in a network. The metrics of interest deliberated for our proposed work are given below.1) Expected Lifetime Metric: A node's Expected Lifetime (ELT) is the residual time until a node gets exhausted of its energy [26]. In our work, we not only consider the link quality variations and maximization of reliable energy-efficient routes but also reducing the consumption of energy by the most energy-consuming nodes or bottleneck nodes. We take into consideration a node’s Expected lifetime for parent selection. ELT metric is used to maximize the lifetime of bottleneck nodes in a network. It calculates the time for a node to die if it keeps forwarding traffic at a given rate. The ELT calculation for a Node (NN) is done as follows [26].• Total traffic to transmit T(NN) for a given new node NN is calculated as the traffic generated by the node TG(NN) along with the traffic generated from its child nodes TC(NN) as given in (3).
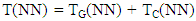 | (3) |
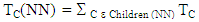 • Initially, The Average number of retransmissions RTavg is calculated using (4).
• Initially, The Average number of retransmissions RTavg is calculated using (4).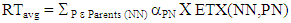 | (4) |
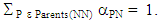 ETX metric is explained further in the forthcoming subtopic. Then, the Average number of MAC transmissions (TMACavg) is determined by (5), where T(NN) is the total traffic transmitted and RTavg is an average of the number of retransmissions.
ETX metric is explained further in the forthcoming subtopic. Then, the Average number of MAC transmissions (TMACavg) is determined by (5), where T(NN) is the total traffic transmitted and RTavg is an average of the number of retransmissions.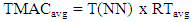 | (5) |
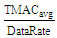 | (6) |
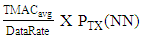 | (7) |
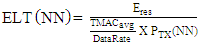 | (8) |
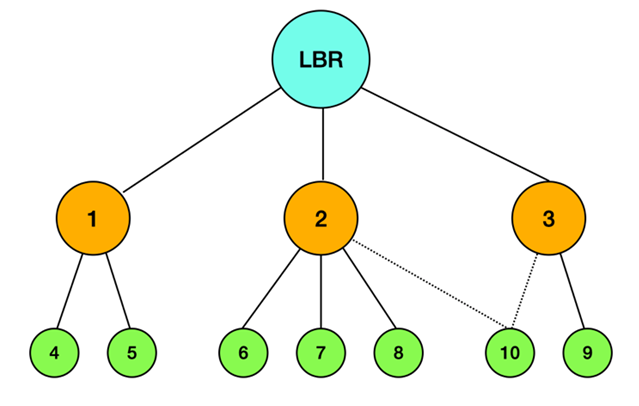 | Figure 1. Parent selection using child count metric for load balancing |
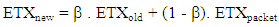 | (9) |
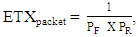 which is the probability that the packet is sent in the forward direction and reached the receiver (PF) and the acknowledgment has reached back to the sender in the reverse direction (PR) [25] and
which is the probability that the packet is sent in the forward direction and reached the receiver (PF) and the acknowledgment has reached back to the sender in the reverse direction (PR) [25] and  represents the learning ratio which in ContikiRPL is given a value of 0.9 [5].In RPL, the OF uses the ETX metric to calculate the rank. During DODAG construction, on the reception of the DIO message, the node uses the rank value with minimum ETX value to choose the parent node. Though ETX may provide a reliable network, it may not provide an optimal path considering the load in the network. 4) Residual Energy Metric: The residual energy of the nodes in a network plays a substantial role in balancing the load, increasing the network lifetime, and calculating an optimal path in LLNs. As shown in (8), the Residual Energy metric is used to calculate a node's Expected lifetime (ELT) and eventually improve the network lifetime. The Residual Energy (Eres) of a node N is calculated using (10).
represents the learning ratio which in ContikiRPL is given a value of 0.9 [5].In RPL, the OF uses the ETX metric to calculate the rank. During DODAG construction, on the reception of the DIO message, the node uses the rank value with minimum ETX value to choose the parent node. Though ETX may provide a reliable network, it may not provide an optimal path considering the load in the network. 4) Residual Energy Metric: The residual energy of the nodes in a network plays a substantial role in balancing the load, increasing the network lifetime, and calculating an optimal path in LLNs. As shown in (8), the Residual Energy metric is used to calculate a node's Expected lifetime (ELT) and eventually improve the network lifetime. The Residual Energy (Eres) of a node N is calculated using (10).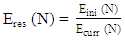 | (10) |
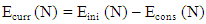 | (11) |
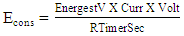 | (12) |
4.3. The Proposed Combined Metric Objective Function
- The projected Combined Metric Objective Function (COM-OF) provides a holistic approach towards network load balancing by considering significant metrics like the number of child nodes and the Expected lifetime of the nodes in addition to the ETX and residual energy of the nodes in the network. During DODAG construction, the DIO message is amended with the parent ID. Once a node accepts the DIO message, it compares the parent ID with its own ID to keep track of the child count if the message is from its child node. The traffic to and from the node is calculated using the throughput metric [26]. The ELT value for the node is calculated based on the traffic estimated, ETX value, and residual energy of the node, as explained in the earlier sections. The ELT and the child count values are used to calculate the new rank of the node. Here, the objective function selects a preferred parent with a minimal number of children, a maximum network lifetime with minimal energy usage, and a reliable link to the node. This preferred parent selection helps equalize the load in the network.We understand that the metric ELT is maximizable, whereas the metric CC is minimizable. To transform the derived metrics in our proposed work (ELT and CC) to the same domain [27], we express the network lifetime maximization metric as inverse lifetime minimization [28]. Therefore, to make the ELT metric minimizable, we use the inverse lifetime value of the node N, ELTinv (N) given as
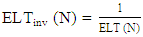 to calculate the rank. Also, we use two constant parameters,
to calculate the rank. Also, we use two constant parameters, 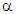 = 0.5 and
= 0.5 and 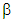 = 0.5, whose values should be between 0 and 1, with a total value of 1. These parameters are used to balance each metric’s influence on the network and are given by (13).
= 0.5, whose values should be between 0 and 1, with a total value of 1. These parameters are used to balance each metric’s influence on the network and are given by (13). 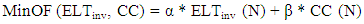 | (13) |
|
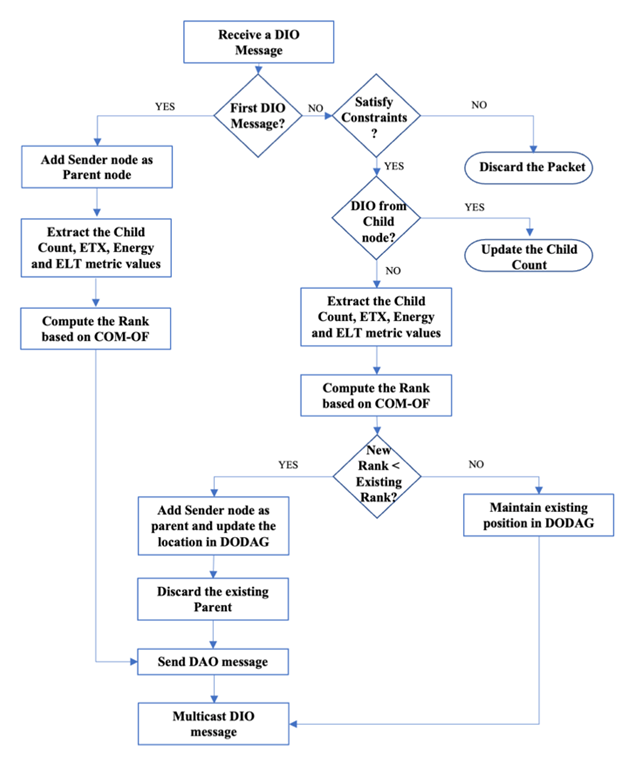 | Figure 2. Flowchart for the parent selection process |
5. Performance Evaluation
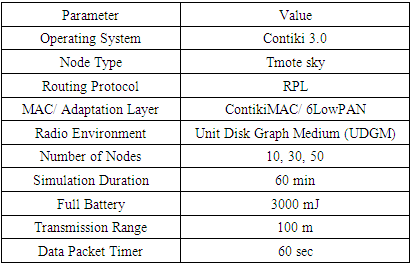
- To gauge the performance of our proposed objective function, we have carried out our simulation experiments using the Cooja simulator of the Contiki Operating system [29]. Contiki is a prevalent, accessible, and open-source operating system specially designed for IoT, targeting small, constrained devices with insufficient memory, bandwidth, battery power, and processing power. It is compatible with the IP network stack where the existing protocols like UDP, TCP, and HTTP coexist with protocols designed explicitly for constrained networks like CoAP, 6LowPAN, and RPL. Cooja is a powerful network simulation software tool developed by Contiki-OS developers to simulate Contiki-based applications. Contiki motes of small and huge networks can be simulated or emulated using the simulator. We use the Tmote sky motes for our simulation, which are low-power, high data rate wireless sensor module that supports interoperability with IEEE 802.15.4 devices [30].The simulation is carried out with 10, 30, and 50 nodes spread over an area of 100 X 100 meters for one hour each. In all the scenarios, the proposed COM-OF is compared with the standard RPL Objective Functions, OF0 and MRHOF. The performance parameters considered for the comparison include Power consumption, Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR), Network Lifetime, and the average number of child nodes. The simulations are carried out multiple times, and the average of the performance parameters is considered. The simulation parameters considered for the evaluation are given in Table 1.
|
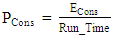 | (14) |
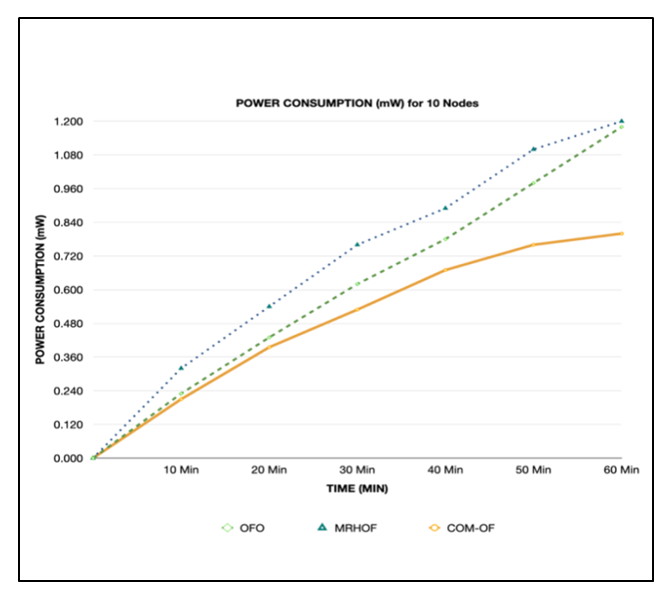 | Figure 3. Power consumption for 10 nodes |
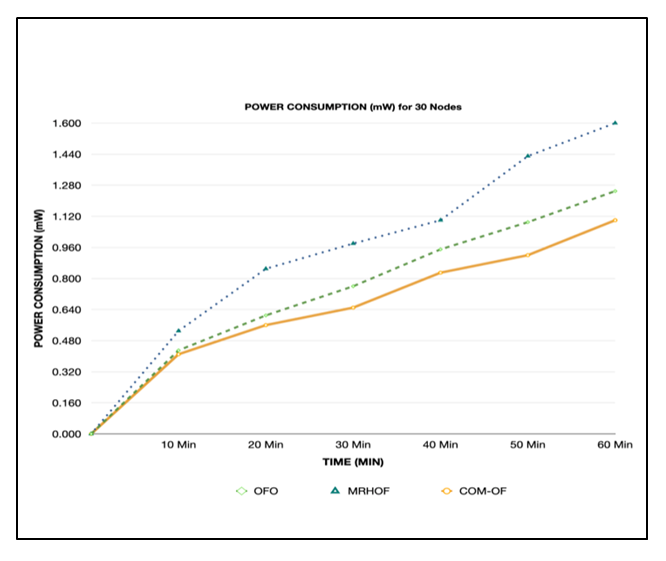 | Figure 4. Power consumption for 30 nodes |
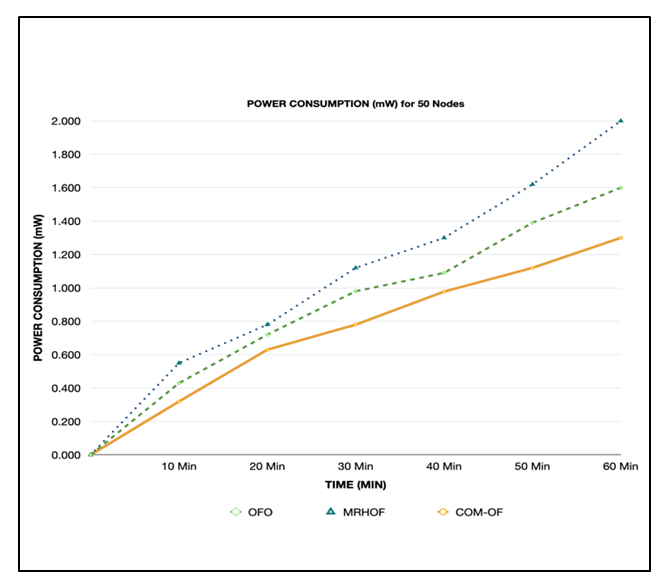 | Figure 5. Power consumption for 50 nodes |
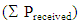 by the total number of packets sent by the sender nodes
by the total number of packets sent by the sender nodes 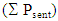 as given in (15).
as given in (15).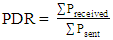 | (15) |
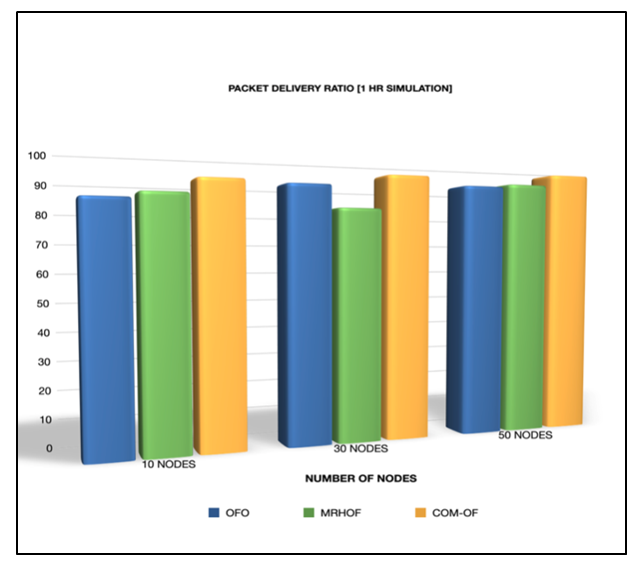 | Figure 6. PDR comparison of OFs for 10, 30, and 50 nodes |
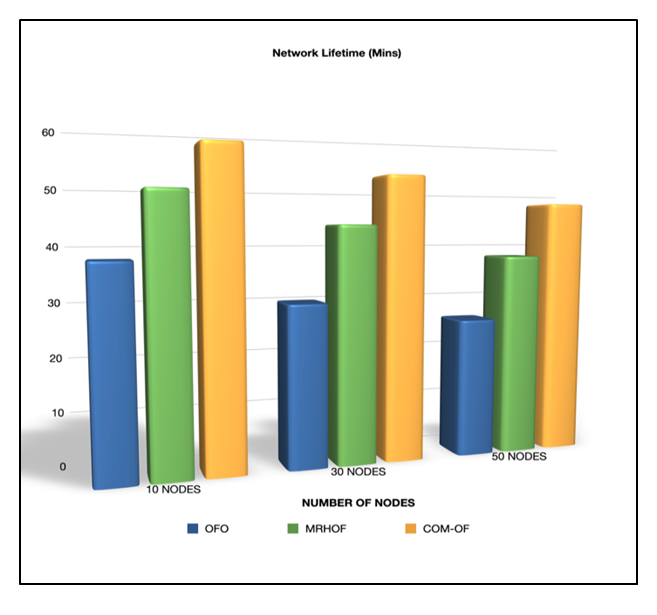 | Figure 7. Network Lifetime comparison of OFs for 10, 30, and 50 nodes |
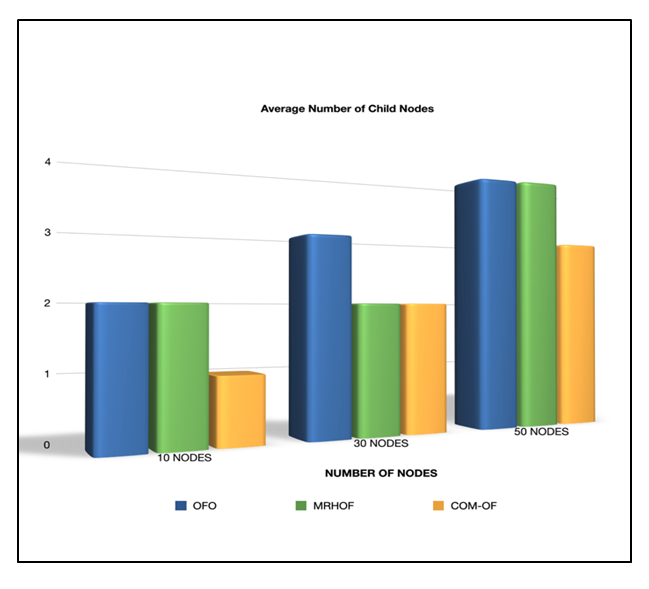 | Figure 8. Comparison of Average number of child nodes for 10, 30, and 50 nodes |
6. Conclusions
- In this paper, a novel Combined Metric Objective Function (COM-OF) is recommended to address one of the prime issues in RPL called Load balancing. COM-OF balances the load in a network by considering the Child count, the Estimated lifetime, the energy consumption of the nodes, and the reliability of the links in the network. Our projected objective function was simulated using the Cooja simulator of Contiki OS for small and medium-sized networks, and the performance was compared with the standard RPL objective functions OF0 and MRHOF. COM-OF exhibits better performance when compared to the single metric objective functions OFO and MRHOF in terms of power consumption, PDR, network Lifetime, and the average number of child nodes. On average, COM-OF exhibits a 10 to 33% reduction in power consumption, 36% reduction in the average number of child nodes, 18 to 33% improvement in network lifetime, and around 8% improvement in the packet delivery ratio. In our future work, we plan to consider other composite metrics and methods that also assess the stability and scalability of the network.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML