-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Information Science
p-ISSN: 2163-1921 e-ISSN: 2163-193X
2021; 11(1): 1-11
doi:10.5923/j.ijis.20211101.01
Received: Nov. 15, 2021; Accepted: Dec. 16, 2021; Published: Dec. 24, 2021

The Willingness of Citizens to Use E-government - The Jamaican Context
Alex Lewis , Denrick Williams , Damith Wickramanayake
School of Computing and Information Technology, University of Technology, Jamaica, Kingston, Jamaica
Correspondence to: Alex Lewis , School of Computing and Information Technology, University of Technology, Jamaica, Kingston, Jamaica.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study’s purpose was to investigate the willingness of Jamaican Citizens to use e-government services, specifically transactional e-government (online payments) at the Tax Administration of Jamaica (TAJ), using a quantitative methodology. Consequent to the study’s findings, appropriate measures were identified that will guide the government on the successful adoption of e-government. The Decomposed Theory of Planned Behaviour (DTPB) theoretical framework was used to identify the factors that would prevent the adoption of e-government services. Key findings revealed that 68.7% of respondents are willing to use e-government services. Moreover, this study revealed a significant correlation between perceived usefulness, ease of use, compatibility, and the attitude of Jamaicans to use e-government services. Also there is a significant correlation between peer influence, superior influence and the subjective norms of Jamaicans to use e-government services. Further there is a significant correlation between self-efficacy, resource facilitating conditions, technology facilitating conditions and Jamaicans’ perceived behavioural control to use e-government services. Additionally there is a significant correlation between attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioural control and the behavioural intention of Jamaicans to use e-government services.
Keywords: E-government, Decomposed Theory of Planned Behaviour, Tax Administration of Jamaica (TAJ)
Cite this paper: Alex Lewis , Denrick Williams , Damith Wickramanayake , The Willingness of Citizens to Use E-government - The Jamaican Context, International Journal of Information Science, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 1-11. doi: 10.5923/j.ijis.20211101.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Introduced in the 21st century as a replica of e-commerce [1], e-government has provided a new approach for government in both developed and developing countries. Almarabeh & Abuali (2010) [2] argues that E-government is more than websites, e-mail and processing transactions over the internet. It is more than automating government systems; it uses technology to enhance different government areas, transforming politics and the relationship between governments and citizens [3]. In addition, E-government has introduced the concepts of transparency, accountability, and citizen participation [2]. While seeking a definition for e-government, the literature revealed several descriptions. For example, Alasem (2015) [4] described e-government as “the use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to promote access to government information and services via the internet. This is achieved by offering government information and services through an agency’s website or, in a more advanced method, through a one-stop access e-government portal”. Alshehri et al. (2013) [5] stipulated that e-government is typically adopted to enhance the service delivery provided by the government to its citizens. Further to this, Alshehri et al. (2013) [5] posit that e-government services systems seek to offer a multitude of benefits. For example, it enhances the operations and processes of government services and facilitates information sharing between the government and the public. Carter & Bélanger (2005) [6] defined e-government as the utilisation of information technology to permit and revamp government services productivity as it concerns service efficiency to employees, citizens, agencies and businesses.Conversely, Fang (2002) [7] emphasised that e-government is the process by which government uses technological innovations, specifically web-based Internet applications, to offer its citizens and businesses opportune access to government services and information. Moreover, the author states that e-government improves service quality and offer opportunities to partake in democratic institutions and processes. On the other hand, Mensah (2019) [8] stated that e-government is “the application of information and communication technologies (ICTs) such as the Internet in the public administration processes.” The author further explained that “e-government is also considered as the combination of e-administration and e-democracy to achieve the objective of good governance.” Thus, based on the current use of e-government worldwide [7] has the most comprehensive description. It speaks to all the significant elements of e-government clearly and concisely.E-government services are fast becoming an integral part of government services around the world. As a result, leaders have made considerable efforts to adopt current government services into new e-government services. The purpose is to improve the services delivery provided by the government to its citizens [5]. In Jamaica, however, there has been some resistance to these e-government services. According to a senior member of the Communications Department, (personal communication, May 2021), they currently offer sixteen (16) e-government services; however, these services are underutilised by the public. The services available to taxpayers on the Tax Administration Jamaica’s (TAJ’s) online platform include online tax filing, online payments (taxes and fees), web messages, trade license application, application for General Consumption Tax (GCT) registration, and zero-rating application.According to a senior member of the Taxpayer Service & Education Programmes Department, (personal communication, August 2021), the first service offered online by the TAJ was the ability to pay traffic tickets online in 2008. Since then, the Tax Administration of Jamaica (TAJ) has expanded its list of services and increased the number of online payments, but the latest data show that only 21.47% of citizens opt to make their payments online, indicating that there is significant room for improvement. Currently, there is a wide variety of literature looking into the acceptance of government services using various theoretical models, but there has been no research done within Jamaica.This study’s purpose will be to use a quantitative methodology to investigate the willingness of Jamaican Citizens to use e-government services. In addition, this study will have a theoretical contribution to the existing body of literature on e-government.Additionally, it will have practical implications for governments as they will use this study to guide the successful adoption of e-government. This study will use the Decomposed Theory of Planned Behaviour (DTPB) theoretical framework to identify the factors that would prevent the adoption of e-government. From the theoretical framework, eleven (11) different hypotheses were derived.
2. Related Work
- A crucial component of e-government is the building of partnerships among citizens, businesses and government. Thus, e-government introduces several essential benefits to several sectors: government, citizens, businesses, employees, nonprofit organisations, political and social organisations. Consequently, e-government can be classified into eight types namely Government-to-Citizen (G2C), Citizen-to-Government (C2G), Government-to-Business (G2B), Business-to-Government (B2G), Government-to-Government (G2G), Government-to-Nonprofit (G2N), Nonprofit-to-Government (N2G), Government-to-Employee (G2E) [7].
2.1. Opportunities from E-government
- The principal opportunities realised from e-government include cost reduction, efficiency, improved quality of service, transparency, anti-corruption, accountability, and improved quality of decision-making. Other opportunities include increased capacity, fostering community development, and promoting information and communications technology in other sectors of society [9].
2.2. Challenges with E-government
- Numerous challenges can hinder the exploitation of e-government, especially in developing countries: inadequate information technology infrastructure, lack of knowledge, lack of security and privacy of information, absence of qualified personnel, and training courses. In addition, the support of leaders and management, culture differences, the non-existence of policies and regulations for e-usage, lack of partnership and collaboration, a strategic plan, resistance to change to e-systems and shortage of financial resources could prevent government entities from implementing e-government services [9].
2.3. Failures in E-government
- Based on Heeks’s (2003, as cited in Dada, 2006) extensive research carried out in e-government implementations in developing countries, 35% completely fail, and 50% partly fail. Three design reality gaps were associated with the failures: hard-soft, private-public and country context gaps [3].
2.4. E-government in Jamaica
- Globally developing countries have identified information and communication technologies as an integral part of the public sector. Information and communication technologies have been seen as the driving force of wealth creation and growth in the private sector. Moreover, these technologies improve government efficiency, effectiveness and public service delivery. Nonetheless, there are barriers to the successful implementation of these technologies in developing countries globally. Many e-government initiatives in developing countries tend to fail to meet their objectives or fail to get started. E-government is not novel to Jamaica. The government of Jamaica commenced public sector improvement initiatives to enhance efficiency, effectiveness and service delivery in the mid-1990s. However, several impediments have been identified, including ICT infrastructure (hardware, software, power grid, networking and monitoring activities), privacy and security (issue of trust), digital divide (unequal access to technologies) and a lack of money. Solid leadership from both political parties has been attributed to the success of e-government in Jamaica; however, until the impediments are overcome, Jamaica will not enjoy improved efficiency, effectiveness, and service delivery [10]. The Jamaican government has made sure that the desired information and communications technology diffusion is one of the main priorities for the new millennium. The information and communications technology diffusion has been amplified through workshops and seminars organised by private and public sector entities [11]. Jamaican researchers have looked at the challenges to implementing e-government initiatives. According to Waller & Genius (2015), [10] the factors that undermine Jamaica’s ability to implement Jamaican e-government solutions successfully are technical issues such as the required ICT infrastructure, including the hardware, software, and network to operate the services. Another major factor the paper pointed out was privacy and security concerns. Generally, governments store a large quantity of private data about their citizens; if this information is used in an e-government service, Jamaican citizens expect that their data will be safe and secure and that their privacy is protected. Additionally, social issues were identified as another factor; however, out of the two elements of social barriers, culture and the digital divide, the digital divide was highlighted as the main barrier. The digital divide is considered the gap between individuals who have access to and the availability of ICTs/ICT infrastructure and those who do not. While the research paper did mention the digital divide as one reason why users may not use these services, Waller & Genius (2015) [10] did not take a detailed look at the user acceptance of these services once these services have been developed. Another research from Jamaica has looked at the possibility of using e-government services to fix voter apathy among Jamaican youths [12]. The research suggested that internet voting could be used to overcome challenges to political participation. While the research suggests that internet voting may not substantially reduce apathy, it could help with perceptions of political efficacy, which would ultimately lead to improved voter turnout.
2.5. E-government in Developing Countries
- Developing countries around the world have recognised the importance of e-government services. Large developing countries such as China to smaller countries such as Tunisia, Kuwait, Rwanda, Saudi Arabia, Kyrgyzstan, Morocco, Malaysia, Nigeria, Philippines have made considerable efforts to develop simple e-government services such as websites to more complex transactional e-government services such as tax filing systems. Each country has used these services as solutions to address different problems.Citizens’ low continuous use has hampered the evolution of e-government in China. Citizens will not be encouraged to use e-government services if the service quality is inadequate; citizens will view the service inferior. The study seeks to identify the relationship among e-government website service quality, perceived value and continuous use intention. The study results disclose that service quality comprises eight associated factors: system quality, reliability, security, accessibility, information quality, service capability, interactivity, and responsiveness. Perceive service value is the intermediary between service quality and continuous use intention. The resultant of intention to use are service quality, service value and satisfaction [13].Tunisia is aware of the vital role of ICT and has started to invest in this field in an effort to develop e-government. Mellouli et al. (2016) [14] said the country’s government has aimed to strengthen the use of Information and Communication Technology to improve the relationship between the government and citizens. One of the initiatives of the Tunisian government to do this is a Tax filing system. The tax filing system aimed to enhance government performance, provide more efficient and better-quality service, create greater transparency, and fight against corruption. Mellouli et al. (2016) [14] looked at the e-government acceptance in Tunisia in the case of its online tax filing service and found that trust is the strongest determinant that affects the acceptance of the online tax filing. The paper also found that a negative experience caused by service unavailability, incorrect information, or technical error may have a negative effect on a user’s intention to use. Additionally, users’ trust in government and technology, their personal innovativeness, the compatibility and quality of the information, and the system are also significant factors of citizens’ intention to use e-government services. However, this paper did not consider research by taking into account cultural, demographic, and social variables.Rwanda created a one-stop e-government platform to include most of the government services. However, implementing a one-stop e-government service similar to the solution implemented in Rwanda can be challenging. Implementing this type of government solution requires typically addressing several organisational issues with the government. The issues are generally related to integrating government information systems of different departments, which traditionally function as silos. Tackling these organisational issues can be difficult due to the nature of the public sector. Twizeyimana et al. (2018) [15] reviewed the ongoing initiative by the Government of Rwanda to digitalise all G2C and G2B into this one-stop single-window e-government platform. The e-government service created is called IREMBO; this project was envisioned to digitalise all G2C and G2B in Rwanda. The results of the study showed six main challenges to the successful implementation of the e-government solution. These challenges were information infrastructure, management, governance, social inclusion, trust in the new system, and languages. Twizeyimana et al. (2018) [15] added that these challenges are influenced by various contextual factors, including political support, nature of the e-government project, implementation strategies, human and socio-economic development, existing information infrastructure, and operational capabilities. Bakunzibake et al. (2019), [16] in their study a year later, looked at the organisational challenges of the implementation of the same Rwandan ‘one-stop’ e-government service and noted that four critical organisational challenges were identified. These are inadequate planning of ‘to-be’ service processes, unclear change management strategy, lack of systematic organisational learning, and unclear operational goals of the local governments concerning the one-stop initiative.The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) instituted a programme in 2005 to create and combine several e-government services in a solution called ‘Yesser’. The solution interacts with over 170 organisations whose aim is to deliver a national e-government programme as part of the country’s national government strategy in support of the country’s 2030 Vision. A study by Aljarallah et al. (2020) [17] indicated that critical characteristics that were likely to influence citizens’ utilisation of sustainable e-government services were most significantly usability, security, performance, transparency, and flexibility. Their study also revealed that respondents were relatively unconcerned with the social, environmental and economic dimensions of the impact of the e-government solution.There have been several e-government initiatives in Kuwait. Therefore, a study by Alenezi et al. (2017) [18] was created to understand the factors that may influence or hinder Kuwait’s enabling e-government strategic benefits. The team collected data from three Kuwaiti e-government agencies, namely, the Ministry of Justice, the Ministry of Finance, and the Public Authority for Civil Communication. The study revealed that three main themes were affecting the adoption of e-government. The themes include Information Quality, Strategic Benefits and Institutional Values. Information Quality refers to how sound, useful, dependable, and valuable the information used within the service is. Strategic Benefits describe factors such as the costs benefits and the quality of the service. Finally, Institutional Values refer to the factor of the credibility of an image of the institution offering the service. Khalil et al. (2014) [19] specifically looked at one of Kuwait’s e-government services, the Traffic Violation E-payment System (TVEPS). The study main focal point was the factors affecting the adoption of the service by Kuwaiti citizens. They found that effort expectancy and social influence were found to influence the use intention, and users’ internet experience moderated such a relationship. However, performance expectancy did not influence the intention to use the service.Brimkulov & Baryktabasov (2014) [20] reviewed Web Sites in Kyrgyzstan looking at the Public Transactional e-Services offered by each the official website of the Kyrgyz Government ministries and agencies. The study found that while the Kyrgyz Republic is trying to develop e-government initiatives and some state organisation’s websites do provide some online transactional services and are trying to use the web technologies to involve citizens, generally, these activities can be characterised as of weak nature. In Malaysia, e-government is used as a method of mitigating procurement fraud. An e-procurement system was created to handle government procurements. Azmi (2015) [21] findings suggest that e-procurement can be used as a ‘gatekeeper’ for all bidders in ensuring that they follow the ‘rules as stipulated in the system. E-procurement helps to safeguard many public officials through its transparent and efficient system. Furthermore, it can be used as a ‘barrier’ to avoid unnecessary demands and interference from people with a vested interest. Finally, the system e-procurement is also valuable for dealing with intertwined relationships between public and private organisations.
2.6. E-government in Developed Countries
- Developed countries such as Sweden, Australia and several European countries have recognised the importance of e-government services and have implemented such a service.Bernhard et al. (2018) [22] conducted a study focusing on the relationship between government and citizens. First, the researchers investigated whether there was a relationship between the degree of e-government in Swedish municipalities and perceived satisfaction among citizens generally. The results confirmed this relationship with all three dimensions of citizen satisfaction: living in the municipality, the performance of government activities/services, and the transparency of citizens’ influence on their local government. Furthermore, the study also indicated a relationship between citizen satisfaction and other crucial factors such as educational level and median income.Zada et al., (2016) [23] conducted a study looking at the perceptions of the Australian public towards mobile internet e-voting. In the study, researchers noted that there had been little change to Australia’s voting system since the development of the Australian Secret Ballot in 1855. Before the new voting system, there were no viable alternatives to how eligible voters could choose to vote. This is in contrast to other areas like health care, where the government has deployed a wide range of new channels to deliver e-government services to citizens. The Australian government has combined the use of the internet and e-commerce technologies to create e-government services for health and welfare in the country. Australian citizens can now access services such as their personal medical records online and control information pertaining to these records through the Australian eHealth service website (http://www.ehealth.gov.au/). Australia first used the iVote Remote Electronic Voting system in the country’s March 2011 State General Elections and later used it in its 2015 NSW State General Election on 28th March 2015. The service allowed eligible voters to cast their ballots online. According to Zada et al., (2016), [23] Australian voters favored using mobile internet e-voting (75.25%). Respondents to the survey said they were more likely to request more information about the technology (15.93%) instead of being against its use (8.82%).Significant investments have been made in e-government service throughout the last decade; nonetheless, the major challenge remains citizens’ limited use of the service. The study of 27 countries in Europe between 2010 and 2018 revealed that e-government services were impacted by supply-side e-government evaluation, trust in government by citizens, and the digital divide relating to income and education [24].
2.7. Theoretical Frameworks
- Several theoretical frameworks were examined, namely Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA), Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB), Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), and Technology Acceptance Model 2 (TAM 2), to identify an apt theoretical framework for this study. The other frameworks examined were Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), Diffusion of Innovation (DOI) and Decomposed Theory of Planned Behaviour (DTPB). Out of these frameworks, the Decomposed Theory of Planned Behaviour (DTPB) was selected as the preferred theoretical framework.DTPB is an enhanced model, which is an amalgamation of Innovation of Diffusion Theory (IDT), TPB and TAM. The model is used to look at the factors that influence technology adoption and can assist managers and operators understand the factors that influence human behaviour [25]. DTPB incorporates three key elements: attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioural control [26]. Figure 1 illustrates the Decomposed Theory of Planned Behaviour.
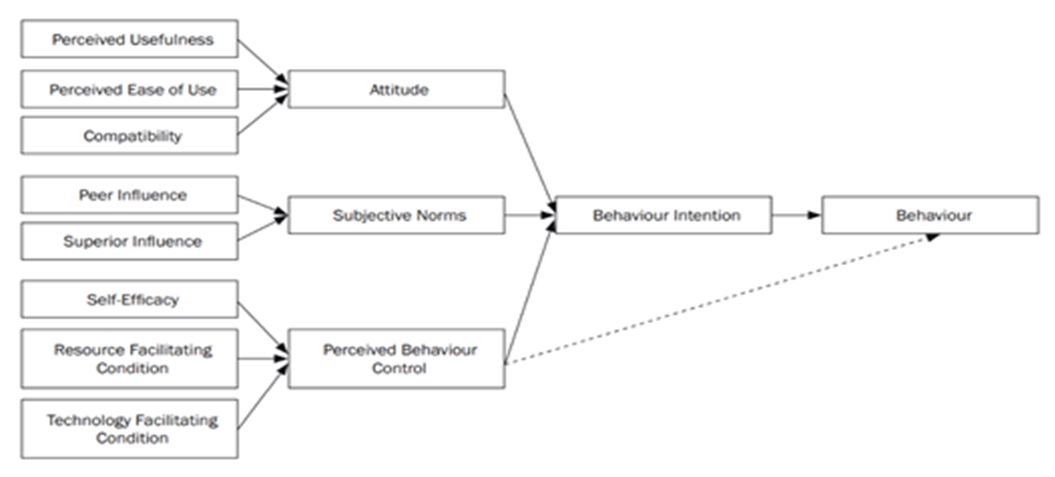 | Figure 1. Proposed Model |
2.8. Future Studies
- Several studies have been carried out in the area of e-government adoption in developing countries. These studies however, did not address the adoption of e-government or transactional e-government (online payment) in other Caribbean countries. To fill the gap in knowledge, this study will identify the factors that affect the adoption of transactional e-government (online payments) in the Caribbean. Future studies could examine the successful adoption of e-government by Governments. Another interesting avenue for future studies could look at the comparison between the factors that affect e-commerce adoption in private sector organisations and the factors that affect the adoption of e-government in the public sector. Another area of further studies is to investigate the feasibility of implementing a one-stop for e-government service in Jamaica.
3. Methodology
- This study’s purpose is to determine the willingness of Jamaicans to use the transactional e-government services, primarily the transactional e-government services offered by the Tax Administration of Jamaica (TAJ). The Decomposed Theory of Planned Behaviour (DTPB) model was used to identify the factors that hinder the adoption of e-government services. A quantitative approach was employed to answer the five research questions. The study identified 13 independent variables and five dependent variables. The study is guided by 13 hypotheses based on the Decomposed Theory of Planned Behaviour (DTPB) theoretical framework. The instrument used to conduct the survey is a questionnaire which was created after reviewing similar questionnaires used in other studies. Convenience sampling was utilised by the researcher to select the sample. The following assumptions were made regarding this study: the instrument that was used elicited reliable responses, and the answers from the participants were honest.The target sample size of 385 was derived from a population size of 2,024,687, a confidence level of 95%, and a margin of error of 5%. Due to the constraints of time, resources and the covid-19 global pandemic, we could not reach the targeted population size; however, we were able to collect information from 192 participants. A pilot survey was conducted in which the questionnaire was disseminated via Google Forms and WhatsApp to 67 participants, of which 44 responded. After which, the revised questionnaires were disseminated using the Google Forms. The participants received the questionnaire via email and WhatsApp.The statistical analysis of the responses was done using IBM SPSS Statistics. Bivariate Correlation Analysis and Linear Regression were the statistical techniques that were used to analyse the data. The primary constraints identified in this study were time and resources. As a result, the study was to be restricted to transactional e-government (online payments) offered by the Tax Administration of Jamaica (TAJ). Furthermore, the University of Technology, Jamaica Research Ethics Committee approved this study. The information collected for use in this study is confidential and accessible to and by the researchers.
4. Results
- The first research question is, “To what extent are Jamaican citizens willing to use e-government services?”. Using the Likert 5-point scale, the respondents were asked to rate the extent they agree that they had plans to use an e-government service on the next opportunity. As shown in Figure 2, approximately 51% agreed that they would use e-government services on the next opportunity, 17.7% strongly agree that they will use it, 26.6% were undecided, 4.2% disagree, and 0.5% strongly disagree. Based on the results as shown in Figure 2, 68.7% of respondents are willing to use e-government services. If these findings were to be applied to the wider population of Jamaica and to answer the first research question, it would suggest that Jamaican citizens are willing to use e-government services.
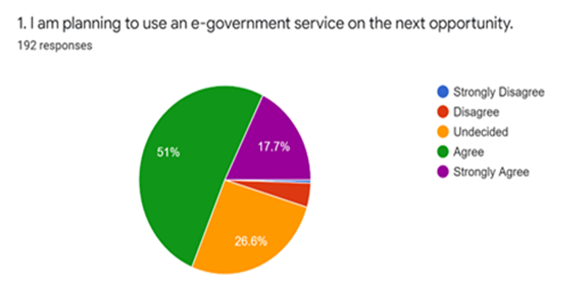 | Figure 2. Willingness to use e-government services |
5. Conclusions
- This study aimed to use a quantitative methodology to investigate and study the willingness of Jamaican Citizens to use e-government. Consequently, the aim of this study was to answer the following research questions:• RQ 1: To what extent are Jamaican citizens willing to use e-government services?• RQ 2: What is the association between perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, compatibility, and the attitude of Jamaicans to use e-government services?• RQ 3: What is the association between peer influence, superior influence and the subjective norms of Jamaicans to use e-government services?• RQ 4: What is the association between self-efficacy, resource facilitating conditions, technology facilitating conditions and the perceived behavioural control of Jamaicans to use e-government services?• RQ 5: What is the association between a user’s attitude, subjective norms or perceived behavioural control, and a user’s behavioural intention to use e-government?Results of this study show that 68.7% of respondents are willing to use e-government services. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and compatibility were found to be significantly correlated with the attitude of Jamaicans to use e-government services. Peer influence and superior influence were found to be significantly correlated with the subjective norms of Jamaicans to use e-government services. Self-efficacy, resource facilitating conditions, and technology facilitating conditions were significantly correlated with Jamaicans’ perceived behavioural control to use e-government services. Attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioural control were found to be significantly correlated with behavioural intention.
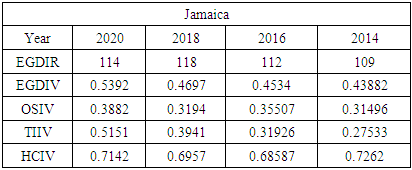
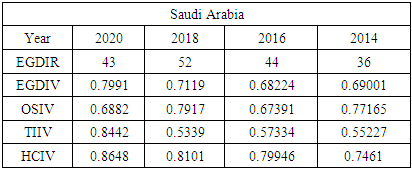
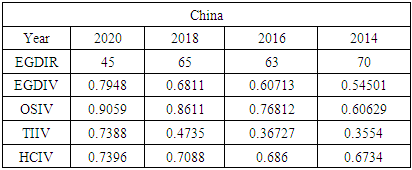
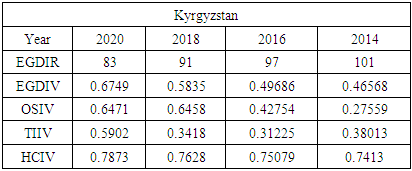
5.1. Comparing Jamaica to Other Developing Countries
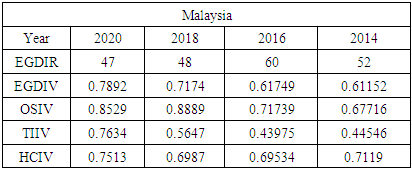
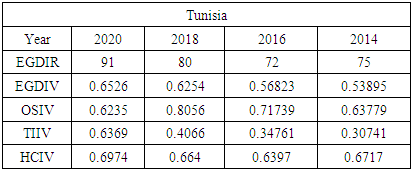
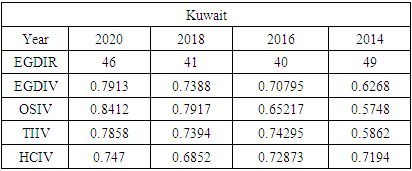
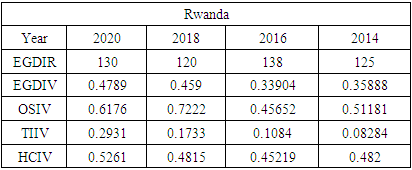
- To compare Jamaica’s e-government progress with other developing countries, the United Nations (UN) E-Government Development Index was reviewed from 2014 - 2020. Chipeta (2018), in his paper “A Review of E-government Development in Africa: A case of Zambia,” defined the E-Government Development Index and its three most important elements of e-government as follows:E-Government Development Index rank (EGDIR): The e-government development index rank is the numerical position of a country in a list based on that country’s E-Government Development Index value. The rank is used to compare all the countries featured on the United Nations E-Government Development survey [30].E-Government Development Index value (EGDIV): The e-government development index value is a mathematically weighted average of normalized scores on the three most important elements of e-government. The EGDI value is based on an expert survey used by the United Nations to measure the adoption of ICT in governments across the world for the delivery of essential public services. The three elements used to compute the value of the EGDI are Telecommunication Infrastructure, Online Services, and Human Capital. The survey results also list E-participation value and rank as sub-indicators [30].Online Service Index value (OSIV): The Online Service Index value of the e-government development index assesses the features of government websites. It measures the use of ICT by the government to distribute basic public services to citizens using the internet. The index also evaluates the policies and strategies used by the country’s government to support the delivery of its e-services [30].Telecommunication Infrastructure Index value (TIIV): The Telecommunication Infrastructure Index value is computed by evaluating the number of users using key parts of the country’s telecommunication infrastructure. It measures five key indicators; these are the number of wireless broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants, the number of fixed telephone lines in the country per 100 inhabitants, number of fixed broadband facilities in the country per 100 inhabitants, the number of mobile subscribers in the country per 100 inhabitants and the number of internet users in the country per 100 inhabitants.Human Capital Index value (HCIV): Human capital index value looks at four indicators. These indicators are adult literacy rate; combined primary, secondary, and tertiary enrolment ratio. The value of HCIV is computed from a weighted average composite of the indicators. HCIV is one of the most critical indicators used in the calculation of the EGDIV [30].
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.2. Recommendations for Government
- Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, compatibility, peer influence, superior influence, self-efficacy, resource facilitating conditions, technology facilitating conditions, attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioural control were found to be significant factors that influence the willingness of Jamaican to use e-government. As a result, special attention should be paid to the above factors to ensure the successful implementation of e-government.Moreover, the internet, a critical component in e-government, ensures that citizens from all socio-economic backgrounds are connected to requisite e-government services. Consequently, the government must ensure that the digital divide is bridged. The digital divide refers to persons who have access to the internet and those who do not have access. Internet access has become increasingly important. While many persons in Jamaica have gained access to the internet, many rural communities have not benefited from the service. According to Stocker & Whalley (2019), [29] the UK has experienced a similar situation. As a result, the UK government announced a broadband universal service obligation (USO). The initiative attempts to connect rural homes and businesses with a 10 Mbps connection at an affordable cost with the help of the UK government. Therefore, it is recommended that the Jamaican government support high-speed wireless home services that are affordable and easily installed. These services can connect rural areas to the internet, allowing students to learn online and adults to work from home. The government should also make every effort to subsidize these services’ installation and monthly fees, allowing them to expand through rural areas quickly.Another recommendation is that rather than having various user interfaces for e-government services, the government must ensure that there is a standard user interface. The interfaces should be redesigned to be similar for all e-services used across multiple e-government entities, making it easier for citizens to learn and use without any difficulties. The government consists of several ministries, departments, agencies, each hosting its group of services. Rather than having a separate portal for each area of a government entity, it is recommended that a virtual government organizational structure be implemented. This virtual government organizational structure should be a well-designed portal that will facilitate access to all online government services using one system/application. This will encourage citizen participation.Bakunzibake et al. (2019) [16] referred to a similar service offered in Rwanda as a one-stop e-government platform. The service, IREMBO, aimed to include most of the government services provided by the Rwandan government. Implementing an inclusive e-government service similar to the example in Rwanda can be challenging as it involves integrating several government information systems of different departments, units and agencies, which traditionally function as silos. The Jamaican government should consult with Rwandan officials to learn how to develop a similar service here in Jamaica. This one-stop e-government service should be able to run on all major platforms, android iOS and web. It would require a dedicated team of administrators and developers or a government ICT authority to examine each existing government service, create a plan for development, execute these plans and maintain all services offered by the platform. The platform should be modular, allowing each service to be activated in modules upon completion, expanding the platform over time. It should be scalable, allowing the developers to add new services or replace outdated services as the government attempts to improve its service to Jamaican citizens.
5.3. Limitations of the Study
- The limitations of the study were as follows:• The targeted sample size for this study was 385 participants; however, owing to time and resource constraints, the study was restricted to 192 participants.• The Government of Jamaica has several ministries, departments, and agencies (MDAs). However, given the constraints of time and resources, the study was restricted to a single government agency, the Tax Administration of Jamaica (TAJ).• The Government of Jamaica offers several services to its citizens; however, this study was restricted to a single service, transactional e-government service (online payment).• The global pandemic forced the researchers to disseminate the survey using only online means (email and WhatsApp) without visiting the offices of the single agency that was studied. Visiting the ministries, departments and agencies to solicit participation in the study would increase the number of participants.• Due to the constraints of time and resources, the sample size was not a representation of the population of Jamaica.• This study utilised only one instrument, a questionnaire.
5.4. Recommendations for Further Studies
- Based on the above limitations of the study, the researchers recommended that the targeted sample size or a sample size that represents the population of Jamaica. This study only focused on the clientele of e-government services; therefore, expanding the participant pool to include employees of the government ministries, departments, and agencies will improve the representation of the findings.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML