-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Information Science
p-ISSN: 2163-1921 e-ISSN: 2163-193X
2020; 10(2): 45-49
doi:10.5923/j.ijis.20201002.01
Received: Oct. 13, 2020; Accepted: Oct. 23, 2020; Published: Oct. 28, 2020

Porter’s Competitive Forces Model and SWOT Analysis to Payments
Deepak Tomar
Northwest Missouri State University, Maryville, USA. Visa Inc, USA
Correspondence to: Deepak Tomar, Northwest Missouri State University, Maryville, USA. Visa Inc, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article aims to apply Porter’s forces model and the SWOT analysis to the Payment Industry and the Technology so that Organization can improve Technology infrastructure considering all five forces and improve strategy using SWOT models that provides strengths, weakness, opportunities and threat. This paper focuses on different quadrants involved in the Payments and considers analyzing these stakeholder and factor these from time to time in order to improve and thrive in business. This analysis of the data that we can collect from these models can drive major shifts in the strategy.
Keywords: Porter Analysis, SWOT analysis, Payment Industry, Payment Processor, Buyer, Supplier, Cryptocurrency
Cite this paper: Deepak Tomar, Porter’s Competitive Forces Model and SWOT Analysis to Payments, International Journal of Information Science, Vol. 10 No. 2, 2020, pp. 45-49. doi: 10.5923/j.ijis.20201002.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- This article will focus on the forces which have strong influence on the organization and provide the competitive advantage in the market. The main idea behind this is to earn a return on investment which is better than the average. These models Porter and SWOT use IT as a supportive resource and means to achieve competitive strategies. (Thurlby, B. 1998). By Providing a combined understanding of these models and the Payments together, this article and the research focuses on the analysis of these models into the Payment Industry. This analysis also adequately demonstrates thorough process descriptions and the actual business outcomes.
2. What is Porter’s Competitive Forces Model
- Porter was given in 1980 by Michael porter, a strategy professor at Harvard business school. The original competitive forces model identifies five factors which have strong impact on organization behaviour. (Thurlby, B. 1998) The five forces are a framework for analysing the competition between existing sellers. It is to notice what our competitor will do in future, where do we have competitive advantage and how will the relation among seller change. This happens because of price competition and staging advertising battles. It brings a firm in pressure. (Michael, Hitt, 2000) Next is power exerted by customer. The customer demands high quality in less value and it bringing a higher competition for companies. The third factor is the impact of suppliers, the supply vendors with the product and service after the product is sold. Fourth factor is associated with the threats of a new seller which comes up with a lot of pressure and high competition to the existing company. The Last factor is threat of substitute products which are available in the market at fewer prices and are of the similar quality. These are five porter factors affecting organization position in the market. (Thurlby, B. 1998) All these factors combine and make up the environment. This model is to be applied to an entire industry. (Michael, H, 2000)
3. What is SWOT
- SWOT helps in practicing strategic information management. It provides an understanding of core competencies of the business units within the organization and also of the organization itself. (Orndoff, Keith, 2002) It is a tool to minimize the weaknesses, looking for the market opportunities, planning against threats and identifying strengths. The new opportunity may come in a form of a competitor going out of business or merging with the company itself (Kyle, Bobette). There are some possible opportunities like a new customer needs quality which a company is capable of producing and satisfying customer and thus expansion of market. (Lexisnexis, 2003) The possible threats can be a new competitor entry, changing of location of the company, a new technology invasion which is not cheap for already established organization and regulatory requirements. Looking at these features, the companies can create defensive measures to build a strategy against competitive market. (Michael, Hitt, 2000). First, it was used in complex business environment for the purpose of building business strategies (Xiaomin, 2000). Now, it has gained success as a management tool for analysis. It increases the productivity for any business (Backman and Butler, 2003). SWOT analysis can be used in many ways like building a team or business planning (Pearce, C, 2003). There are ten ways to implement SWOT. The first step is to consider use of SWOT. It will help in analysis if it is known beforehand the way and place where it is going to be implemented. The next step is to prepare a model that is having four sections for strength, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. When studying SWOT, SW can be seen as external and OT as internal factor. It can also be viewed as TOWS but both views SWOT and TOWS are same. (Pearce, C, 2003)
4. What are the Similarities
- Both the models help in developing strategies against online and as well as offline competitive environment. Both concepts help in competing in market. Porter and SWOT are frameworks that help an organization to build strategies and moves towards success. If viewed in detail, SWOT and Porter identify an organization’s strengths, weaknesses as well as their environment opportunities. When studying SWOT, SW as seen as internal and OT as external. (Kyle, Bobette)
5. What are the Differences
- Porter does not recognize the factors which are changing and are highly IT dependent. (Thurlby, B. 1998) The porter also does not balance operational and strategic issues. (Finlay, 1988) According to Porter, Porter model is not considered as strategy but as a way to deal with the failure of past strategies. (Finlay, 1988) Porter is an industry analysis and it is for environmental forces whereas SWOT is a situation analysis. (Kyle, Bobette) SWOT is not an analysis but a tool which helps in analysis. (Amundson) SWOT gives an overview of a company’s strategy situation (Michael, Hitt. 2000) It is used for external and internal analysis. (Michael, H, 2000) SWOT can also be used to perform an analysis of the competitor. SWOT can be used for personal career development whereas Porter model is used for industries. (Amundson)
6. What is Payment
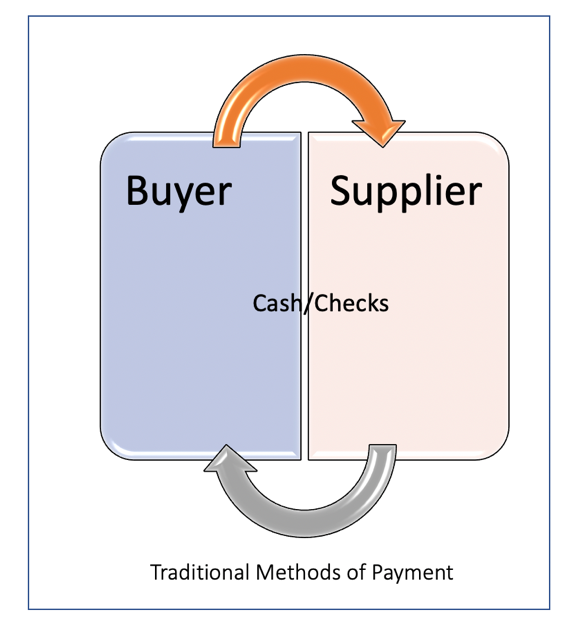
- It is very crucial to understand the concepts and workflows of the Payments before diving into Porter and SWOT analysis into Payment Industry. Payment is a complex ecosystem that enables Buyer buy goods and services from a Supplier (Merchant) and it involves multiple stakeholders. It essentially enables money movement in order to exchange good and services. All stakeholders rely upon set of services provided by the payment network. The below figure 1 describes a simple traditional method of Payments.
6.1. Traditional Method of Payment
6.2. Key Players
- I call this as Many-Party model because depending on if we are looking at the traditional methods of payments or the newer versions of Payment Processes, it can have 3-party model to x-Party model. The simplest way to describe the stakeholders in the Payments and how each of these are depending on each other is outlined as in Figure 2. This can be as detailed as depending on the various use cases involved in the Payment Technology.
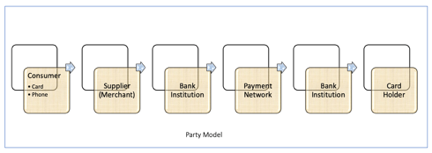 | Figure 2. Multi-party Model |
6.3. Definitions of Each Party Involved
- 6.3.1. Consumer: Beneficiary of the services, a cardholder, Buyer.6.3.2. Payment network: who provides payments rails, network of network, process transactions.6.3.3. Consumer Processor/Bank entity: An entity who bears the risk of providing extended line of credit to the consumer, services to consumer that are used for making payments.6.3.4. Supplier/Merchant: An entity that also pays for the services provided by the Payment network, processing entities but there is a high uptake for Supplier as their products can be sold more because of the consumer being able to use multiple method of payments as supported by Merchant.
7. Porter’s Analysis into Payments
- As this article focusses on the Porter five forces analysis of the Payments, it does determine the portion of Buyer, Supplier, other stakeholders and helps companies identify their strategic positions in the industry. This comparison also helps create or revise strategies for the Organization given that in a x-party model of payments there are players that corresponds to the different factors in the Porter’s model. This article mainly focuses on applying the Porter five forces factors to a payment industry and perform analysis. The below outlined Figure 3 draws the Porter five forces and also the various stakeholders in the Payment industry.
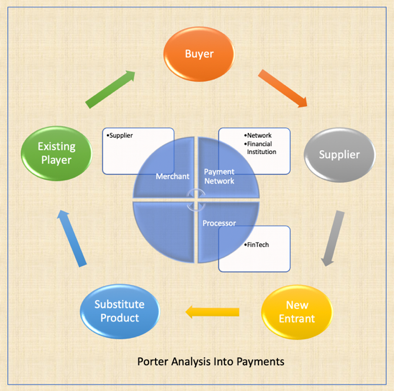 | Figure 3. Porter’s Analysis into Payment |
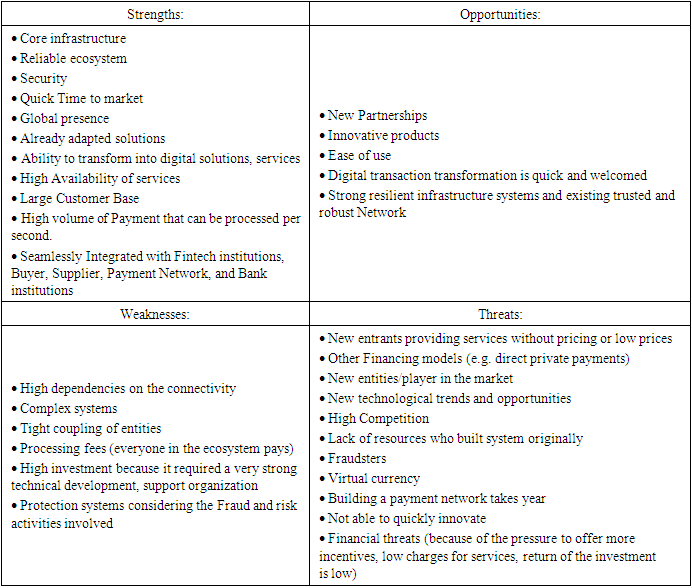
8. SWOT Analysis into Payments
- SWOT is a tool to analyse Strength, Weakness, Opportunities, and Threats. It is tool to be able to use to draw strategies. Its main purpose is to identify the strategies that a firm can utilize and thrive in the business and be successful. SWOT analysis of the payment industry can identify some important aspects of a business. The table below contains four quadrants each containing one part of SWOT analysis: Strength, weakness, opportunities and threats. This table highlights some key findings from each part of the SWOT analysis that can be performed for a payment industry and help business to be successful.
|
9. Conclusions
- As mentioned in the introduction, this article primarily focuses looking at the Porter factors to help build strong strategy for the organization. On other hand, SWOT helps to identify strengths and weaknesses. These 2 models can go hand-in hand by developing the strategy map and certainly fully understand strategy mapping. As we are building the forces, strategy and map, keep in mind there should be a natural alignment with the Business and goals. The strategy must map and if needed, it must be revised to meet the Organization goals and needs to reflect that. When we get to the process that stage the strategy mapping, activities can be set based on the strengths and those helps determine if there is any improvement needed. Payment Industry is a very complex system unlike many other industries and applying, implementing Porter/SWOT analysis can produce thriving results in this industry. Also, the outcome varies by industry, the organization and the implementation of these models but typically results can be very promising.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML