-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Information Science
p-ISSN: 2163-1921 e-ISSN: 2163-193X
2020; 10(1): 15-28
doi:10.5923/j.ijis.20201001.03

E-Government Readiness in the Civil Service: A Case of Zambian Ministries
Shadrick Sikaonga1, Simon Tembo2
1Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Zambia, Lusaka, Zambia
2Assistant Dean, School of Engineering, University of Zambia, Great East Road Campus, Lusaka, Zambia
Correspondence to: Shadrick Sikaonga, Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Zambia, Lusaka, Zambia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

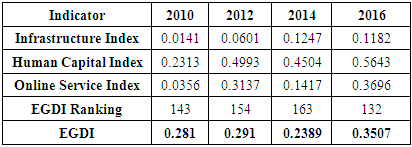
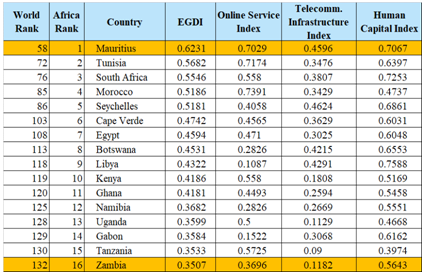
E-Government is identified as one of the key pillars for economic and social development in Zambia’s National ICT Policy of 2006. Coupled with Zambia’s vision 2030 agenda of transforming the nation into a middle-income country, the goal of the SMART Zambia Agenda is to achieve social and economic transformation by adopting a paradigm shift from traditional paper and file format approaches to that of electronic service delivery. Though Zambia’s e-Government implementation is still in its infancy, various e-Government initiatives have been introduced in the civil service especially in the last decade. However, there is a mismatch between Zambia’s e-Government implementation performance at local and regional levels. For example, Zambia ranks lowly on the United Nations E-Government Survey Development Index (EGDI) compared to other UN Member States. Out of 193 Member States of the United Nations (UN), Zambia trails at 132 on the E-Government Development Index (EGDI) with a score of 0.3507 compared to other regional countries such as Mauritius, Tunisia, South Africa and Morocco with over 0.5000. Literature review shows that the Telecommunication Infrastructure Index (TII) is the lowest performing component on EGDI marginally rising from 0.0141 in 2010 to 0.1182 in 2016 compared to the World marginal rise of 0.4406 to 0.4922 during the same period. This however is compensated by the Online Service Index (OSI) that rose from 0.0356 in 2010 to 0.3696 in 2016 and the Human Capital Index (HCI) rising from 0.2313 in 2010 to 0.5643 to 2016 respectively though lower than the regional average scores. Similarly, the World Internet Statistics reports of 2016 indicated 40.2% internet penetration an implication that the majority Zambian had no access to e-Services that are provided over the Internet. Therefore, a case study of all Zambian government Ministries was examined to understand e-Government readiness in the Civil Services as regards e-Government implementation. From the study, results indicated that the civil services in endowed with a vibrant workforce of less than 50 years with the majority being university graduates and eager to embrace electronic government while some Ministries where already in full gear delivering e-Government services. However, it was also discovered that there are a number of challenges that ought to be addressed for e-Government to attain its maturity and these included lack of publicity of e-Government services, none existence of dedicated e-Government funding at Ministerial level, mismatch between policy pronouncements especially on ICT training with what was obtaining on the ground, cost of Internet and perceived inertial by a clique of civil servants to switch to electronic service delivery. Therefore, understanding the status core of e-Government readiness in the civil service provided an opportunity to cypher salient unaddressed challenges that could shape the road map for both policy makers and implementers in their decisions making.
Keywords: E-Government, Telecommunication infrastructure, Human capital, Online services, ICT, Civil Service
Cite this paper: Shadrick Sikaonga, Simon Tembo, E-Government Readiness in the Civil Service: A Case of Zambian Ministries, International Journal of Information Science, Vol. 10 No. 1, 2020, pp. 15-28. doi: 10.5923/j.ijis.20201001.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The emergence of Information Communication Technologies (ICTs) has in the recent past brought a lot of changes to the way things are done world over. Unlike the early twentieth century where public administration was characterized by bureaucratic structures built on rationale principles that failed to respond to the changing requirements of the present times [1] modern governance systems are slowly shifting from the traditional paper and file types of administrative processes that dominated most government Ministries and Agencies. The disadvantage of such systems was that it called for the physical presence of citizens before business transactions could take place. The era created moments of apprehension resulting in delays in implementing government policies for societal development. However, in recent times both the private and government sectors have realised that ICTs are enablers of economic and social development. They have revolutionised the way the private sector conducts its businesses within and outside its own environment, and the way government sectors provides and interacts with stakeholders in service delivery [2].E-Government implementation in Zambia is linked to the enactment of National ICT Policy of 2006 [3]. Within the framework of the Policy, e-Government is identified as one of the thirteen pillars necessary to transform government service delivery using ICTs [3]. Though the process is still in its infancy stages, there are several electronic government services that the Zambian government has undertaken. Examples include, the implementation of the Online Tax Systems, Zambia Immigration Management Systems (ZIMS) or e-Visa System, Government Service Bus (GSB), establishment of the Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS), e-Cab Memorandum, Management Monitoring System, and the decentralized Payroll Management and Establishment Control (PMEC) among others. Technically, all these systems are anchored on ICTs thus emphasizing thae fact that e-Government cannot thrive without the application of ICTs [1] [2]. Statistics show that countries that perform extremely well in the area of e-Government globally are also ranked highly on ICT Developed Indices. For example, South Korea, Denmark, Iceland, and the United Kingdom (UK) are among the top 10 ranked countries on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) ICT Development Index [4]. Equally all these countries make up the top 10 on the E-Government Development Index [4]. Similarly, at regional level, Mauritius, Tunisia, South Africa, Morocco, and Seychelles are among the top 10 performing countries both on ICT Development Index and the EGDI.Despite government’s effort in introducing various e-Government initiatives, the electronic government in Zambia presents several weaknesses especially in the area of telecommunication infrastructure, human capital, government online presence, systems integration, political will, financing, security and trust among others as cited by previous researchers. At global level, Zambia ranks lowly on the EGDI according to the UN E-Government Survey of 2016. Out of 193 Member States of the United Nations (UN), Zambia trails at 132 with EGDI of 0.3507 compared to other regional countries such as Mauritius, Tunisia, South Africa and Morocco with over 0.5000 [6]. The Telecommunication Infrastructure Index (TII) is cited as the lowest performing EGDI component for Zambia dropping marginally from 0.1247 in 2014 to 0.1182 in 2016 compared to the World marginal rise of 0.3650 to 0.3711 during the same period. Telecommunication Infrastructure evidently is a major hindrance to the country’s e-Government implementation [7] [8] and the TII index on EGDI. On the contrary, Online Service Index (OSI) rose from 0.0356 in 2010 to 0.3696 in 2016 and the Human Capital Index (HCI) rising from 0.2313 in 2010 to 0.5643 to 2016 respectively [6].Based on these composite indicators, this paper therefore attempts to assess civil service readiness in implementing e-Government as a tool of service delivery. Previous studies by institutions such as the United Nations, ZICTA, OECD, as well as individuals [7] [9-13] have mainly been focused on generalized e-Government adoption models, challenges and opportunities with very little research attention paid on the actual policy makers and implementers who is in this case are civil servants.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Overview of E-Government
- Like the early government systems, modern governments are arguably categorized by several factors as noted by different scholars. Previous studies reveal that some of the factors that frame up modern governments include the power structure of government; the source of power structure; government’s political ideologies; principles of authority; and acquisition and exercise of power. Ardently, the role of governments has always been that of maintaining good public order, providing national security, maintaining public safety, and providing material prosperity and economic stability [14]. Governments may either employ paper and file-based system or deploy services delivery mechanisms using Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) or may equally adopt both as is a common practice. [15] refers the deployment of ICTs and its associated applications as modern Electronic Government or ‘e-Government’. E-Government is a concept with a capacity to transform public administration using ICTs according to [16].Though there is no single universally accepted definition of e-Government [17] [18] states that the concept of e-Government is a relatively new area of study in the field of Information Systems (IS) that is concerned with the use of ICTs by government agencies to electronically deliver its services. Based on this presupposition, [19], defines e-Government as the use of ICTs that aims to promote efficient and cost-effective government, facilitates more convenient government services and allows greater public access to information. Effectiveness and efficiency can only be achieved where there is a two-way communication channel and to this effect [15] argues that e-Government is anchored on a two-way communication cycle that deploys the use of ICT by governments, civil societies and political institutions to engage citizens through dialogue. Any form of government service delivery model affects every human activity in one way or another and requires a combination of different development stages before attaining maturity.
2.2. E-Government Maturity Models
- Implementing e-Government is a continuous process, and most often the e-Government maturity models are often conceptualised in stages [20]. These stages are often prescribed as sequential and are usually difficult to generalize. E-Government maturity models as categorised by [21] include three common categories.1. The governmental models: developed by governments, consultants and academicians to help agencies identify and improve their level of e-Government maturity. 2. The holistic approach models: designed to be applied in public services development projects to help agencies identify if an e-Government project will be successful or not. 3. The evolutionary e-Government maturity models focus on the evolution of e-Government using sequential steps, from immature to mature e-Government with improved quality. From an academic perspective, the most famous maturity models are the Layne and Lee model, Gartner Group of e-Government, and the United Nations Five-Stage Model. The model depicted in this study is that developed by Layne and Lee.
2.2.1. Layne and Lee Four Stage E-Government Model
- E-Government projects [22] evolve through four stages of development as their integration, technological and organizational complexity increases. The model advances through four sequential development stages [23]. It is developed based on observations of e-Government initiatives normally at country level hence the selection of this model given the Zambian scenario. The sequence of implementation stages are;Catalogue stage: governments establish an online presence of presentation. The initial efforts of the government are focused on establishing an on-line presence for the government interaction. At this stage, only one-way communication between the government and the public is possible.Transaction stage: services are made available for online use and databases are readied for the support of such transactions. All e-Government initiatives are focused on connecting the internal government system to on-line interfaces and allowing citizens to transact with government electronically. This creates a two-communication between the government and the public.Vertical integration stage: government operations within functional areas are integrated at local, state, and federal systems in all three branches of government namely the legislative, executive, and judiciary. Departments working in the same functional area integrate their online operations. Horizontal integration phase: electronic systems are all government levels and branches with different functions and services are linked through a central portal. Different levels within similar functionality is posited to precede the horizontal integration across different functions [22].Based on the Layne and Lee maturity model, literature shows that Zambia’s position is assumed to be anchored between transaction and vertical interaction. This is because some form of manual interventions still exists such as application for various licenses where forms are downloaded and completed manually before submitting to relevant institutions while at interaction level services that include electronic submission of annual tax returns, payments for application for Visas are among those that have been achieved so far. See the Figure 1 below.
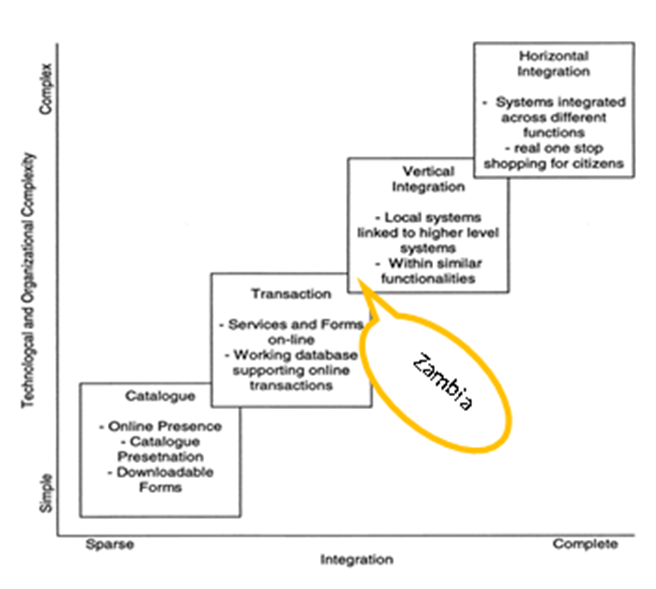 | Figure 1. Zambia e-Government current position on Layne and Lee maturity model. (Adapted from International Journal for Infornomics, January 2006) |
2.3. Of E-Government
- Primarily there are three different types of e-Governments implementation models namely Government-to-Citizen (G2C), Government-to-Government (G2G), Government-to-Business (G2B). Though Government-to-Employees (G2E) to some extent is considered as one of the categories, [15] argues that it is simply an extension of G2G. The following paragraphs discusses the basic e-Government categories and some typical Zambian initiatives Zambia in each category.
2.3.1. Government-to-Citizens (G2C)
- Government-to-Citizens commonly referred to as G2C allows citizens to participate in government driven initiatives electronically. As noted by [24], the basic idea of G2C is to facilitate citizens’ interaction with the government. A typical example of G2C platform is the Zambia Revenue Authority (ZRA) e-Tax Online System that allows businesses to electronically register their businesses, file tax returns and make payments and has received accolade from the business world especially the Small Medium Enterprises [25].
2.3.2. Government-to-Business (G2B)
- Though like G2C, Government-to-Business (G2B) is a domain that focuses on the interaction between government agencies and the private businesses sector via online mediated environments. It basically involves electronic transactions with business entities and other institutions that may include non-profit making organizations. The electronic-Government Procurement (e-GP) System implemented by the Zambia Public Procurement Authority (ZPPA) is a typical example of a G2B initiative. The e-GP platform is a web-based, collaborative system that facilitates the full lifecycle of a tendering process, for both buyers and suppliers [26].
2.3.3. Government-to-Government (G2G)
- Government-to-Government (G2G) category as posits by [27] involves transactions done between the central, national or local governments, other government agencies and departments as well as attached agencies and bureaus while [28] notes that services provided through this dimension take place at two levels; at the local or domestic level and at the international level. The Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS) is an example of a G2G category that enables all levels of government to work cohesively in an efficient and effective manner thereby reducing on the fragmented government processes that demotes sharing of information timely [29].
2.3.4. Government-to-Employees (G2E)
- Though most researchers and academicians recognise only the first three categories of e-Government, Government-to-Employees (G2E) to some extent can be considered as one of the delivery modes of e-Government though [15] argues that it is simply an extension of G2G. Government-to-Employees refers to the relationship between government and its employees. The focus of G2E is on strategy and tactical mechanisms that are used for encouraging the implementation of government goals and programs as well as human resource management, budgeting and accounting [30]. The decentralized Payroll Management and Establishment Control (PMEC) program is an example of a Government-to-Employee model in Zambia.In the context of e-Government, [10] ICT is viewed as a portal for information exchange or a platform through which decisions can be made. It facilitates interactions between government on the internal side and other stakeholders on the external side [31]. See Figure 2 below.
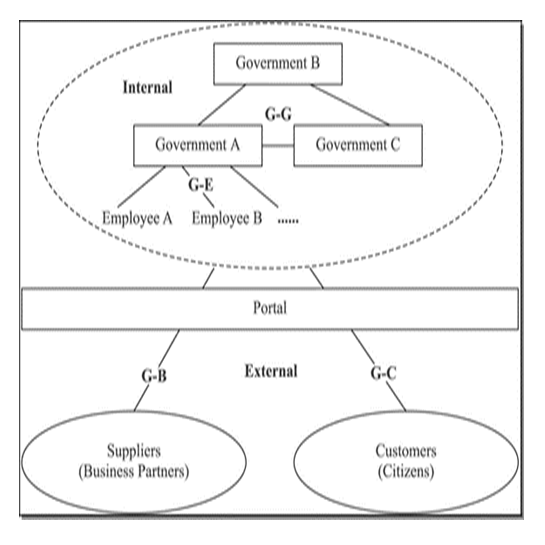 | Figure 2. E-Government interaction dimensions. (Source: Siau and Long, 2005) |
2.4. Benefits of E-Governments
- In their e-Government study of ‘Harnessing e-Government Adoption in the SADC Region’, [32] observed that e-Government is a potential democracy tool, which promotes inclusive governance (e-inclusion) by allowing people to use ICTs to engage with government structures. The focus of e-Government [33] is largely on improving administrative efficiency and reducing administrative corruption while [1] views e-Government as a subset of governance. The advantages and benefits of e-Government implementation are more less the same for both developed and developing countries [15].Other authors such as [34], note that the implementation of e-Government reduces cost and levels of organizational processes by streamlining and re-organizing operating procedures. E-Government has the capacity to transform old ways of running government and has the possibility of creating unprecedented possibilities for sustainable economic development, just as it has done for businesses in the industrial world according to [3]. Every governments wish is to deliver its services effectively and efficiently and this assumption is echoed by [35] who state that using of e-Government systems improves the performance of government agencies thus enabling them to deliver public services effectively and efficiently for all customers. Other benefits as outline by various researchers include;1. potential to contribute to efficiency gains and cost reductions [36].2. increased transparency of decision-making processes [15].3. potential democracy tool, which promotes inclusive governance (e-inclusion) by allowing people to use ICTs to engage with government structures [32].4. Increased employee responsibility [28].5. eliminates some manual processes of tendering, bidding and notification of stakeholders [26].6. Improves accountability, transparency, anti-bureaucratic tendencies as well as eliminating corruption [10].7. Promotes the use of ICT in other sectors of society as transactions become electronic [7].Summing up, [10], outlines e-Government benefits as that of time saving, reduced corruption resulting in facilitating transparency and accountability of different resources. And critical to all these is the component of ICTs as the main portal for distribution of services.
2.5. Challenges of E-Government
- Now that ICT has become an integrated part of everyday life, the implementation of e-Government will continue to improve public sector performance notwithstanding certain factors that may impede its effectiveness. Factors may range from the initial implementation strategies and frameworks, aims and objectives of introducing e-Government initiatives to structural organization and citizens perceptions and adoptions. Critical to all these is the Telecommunication infrastructure which has been cited by [7] [15] [10] [37] [38] as one major impediments to e-Government adoption. Lack of leadership qualities and failure in appreciating e-Government by top level policy makers is another cited majority barrier around e-Government implementation [7] [9] [15] [37] [38] [39]. Other common challenges in developing countries [25] [40] [41] include social economic conditions, lack of appropriate content, language barriers, digital divide, low ICT literacy levels, human resources, and skills to effectively implement e-Government projects. Summing up [42] concludes that these factors affect the willingness of businesses and citizens to use, or take-up electronic services and have an impact on the success or failure of e-Government. Failure or success of e-Government largely depends of the reality gap that is created between ‘where we are now’ and 'where want to be’ according to [43] analysis of ‘why most e-Government initiatives fail’.
2.6. Overview of E-Government in Zambia
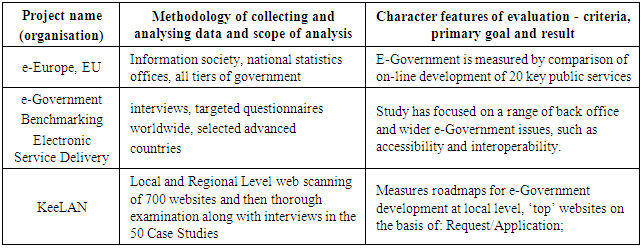
- Assessing current e-Government readiness in the civil service in Zambia [45] call for reliable and relevant e-Government measurements. The researcher stresses that well-crafted measurements can lead to crucial signposts for policy makers and practitioners. Some important common threads highlighted [45] include a country’s economic strength, technological development, and aggregate level of education. Others include infrastructure, human capital, government leadership, IT strategies and policies and many more. Based on the aforementioned, the ITU e-Government Implementation toolkit recommends four core dimensions of the e-Government environment; Infrastructure, Policy, Governance and Outreach [31] whereas the EU assesses e-Government services that covers the priority areas of the eGovernment Action Plan. Each priority area is measured by one or more indicators, included in the so-called top-level benchmarks: User-centric Government, Transparent Government, Cross-border Mobility, and Key Enablers [6]. The e-Government evaluation in this study however, focus on the UN methodology of assessing e-Government development using a set of globally comparative e-Government core dimensions that include infrastructure, human capital and availability of online presence [44] using the E-Government Development Index (EGDI).The EGDI in principle, is a weighted average of three normalized indices; Telecommunications Infrastructure Index (TII) data provided by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU), Human Capital Index (HCI) generated by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), Online Service Index (OSI) data collected from independent surveys conducted biennially by the UN [6]. Though UN agrees that methodological work on UN e-Government surveys has helped elucidate some of the issues in e-Government measurement, there is however, no formal agreement on a common framework of measurement [46]. Various diverse measurement techniques exist, yet some common threads emerge. According to [47], there are various approaches to measure the development of e-Government apart from those employed by the ITU and UN. Table 1 below shows some selected approaches applied in e-Government evaluation or benchmarking.
|
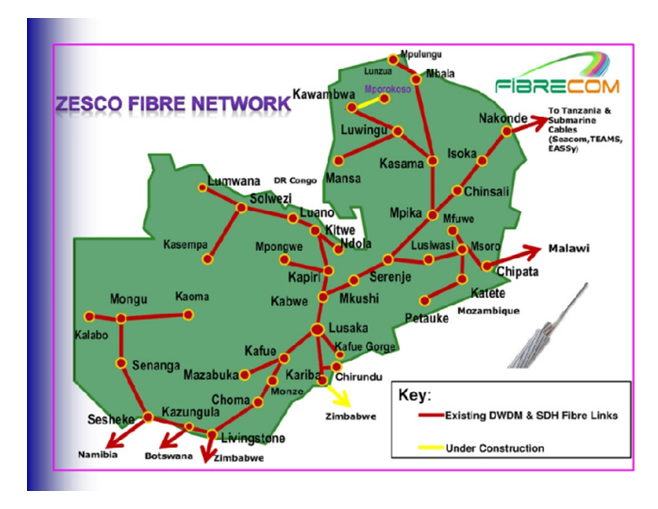 | Figure 3. ZESCO Fibre Network Coverage. (Source: SMART Zambia e-Government Master Plan 2016-2020) |
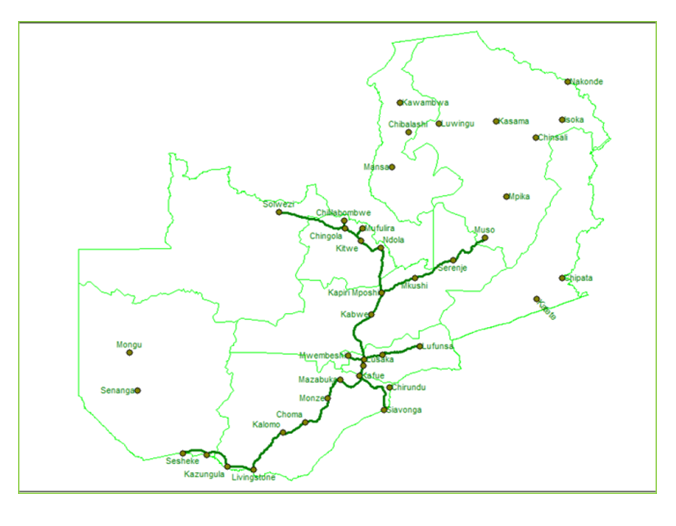 | Figure 4. ZAMTEL Fibre Network Coverage. (Source: SMART Zambia e-Government Master Plan 2016-2020) |
|
|
|
3. Methodology
- The research methodology applied in this study was a combination of both qualitative and quantitative approaches. The motivation for utilizing both qualitative and quantitative methods stems from high precision analytical results obtained in various studies that have used this approach before. Secondary data was collected from case studies, student’s thesis, paper presentation, journal articles, policy documents as well as data from public service workers. Primary data was collected using survey questionnaires which were physically administered at all government Ministries’ Headquarters. Questionnaires included both structured and semi-structured questions as well as open-ended questionnaires with reference to understanding the readiness of the civil service on e-Government implementation. During the research, certain ethical issues were considered including participants’ rights to privacy, dignity, self-determination, and the researcher’s right to know. The study population was purposefully drawn from those government departments that are exposed to ICTs in their execution of duties such as the planning department, Finance, IT, Procurement, Human Resource, and the e-Government division under the Office of the President. The targeted study sample size of 373 respondents from a total population of 13698 was selected based on the 2016 government payroll for Ministry Headquarters. The rationale behind confining the study to Lusaka District was that all government Ministry headquarters are based in Lusaka District and that time and financial resource was a constraint allow for extended coverage area.It is the view of this researcher that future studies in this area may further be extended to cover the entire civil service across the country.
4. Research Findings and Discussion
4.1. Sample Size
- The targeted sample size was 373 from a total of 27 government Ministries and one e-Government Division. Below is a table showing percentage distribution of participating Ministries.
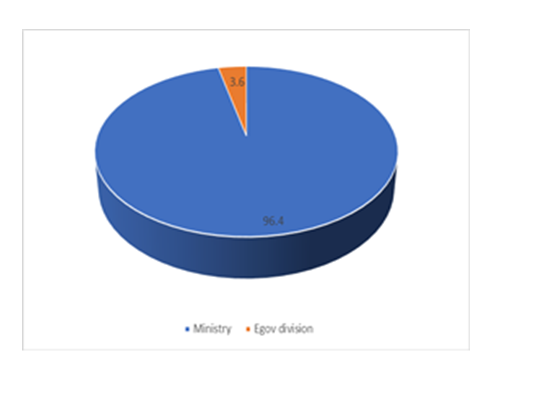 | Figure 5. Percentage distribution of participating Ministries and e-Government Division |
4.2. Demographic Information
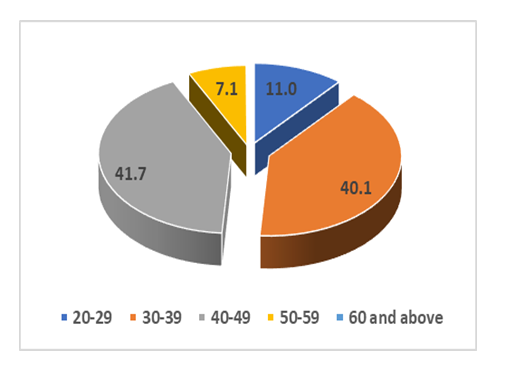
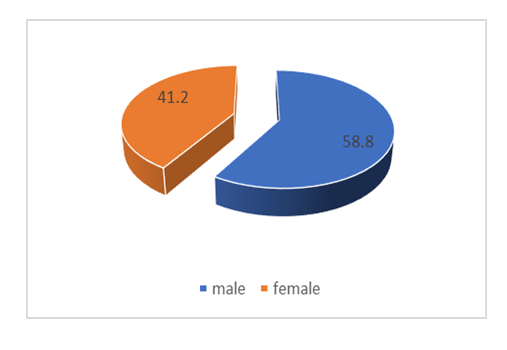
- Out of a total sample size of 373 respondents interviewed, 59% constituted males whilst 41% accounted for female. The higher numbers of participating males are attributed to the proportional employment figures in the civil service. Key to this presentation is that the majority in the civil service are university graduates in the age range of 20 – 49 years with competent ICT skills. See Figure 6 below.
 | Figure 6. Gender distribution |
 | Figure 7. Age distribution |
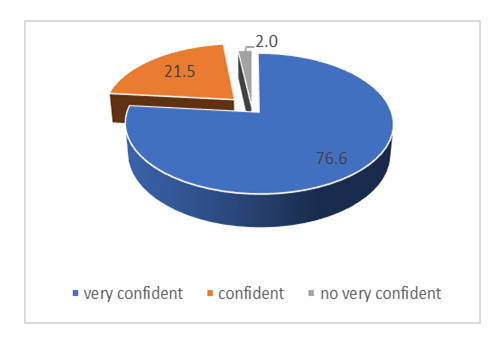 | Figure 8. ICT competence levels |
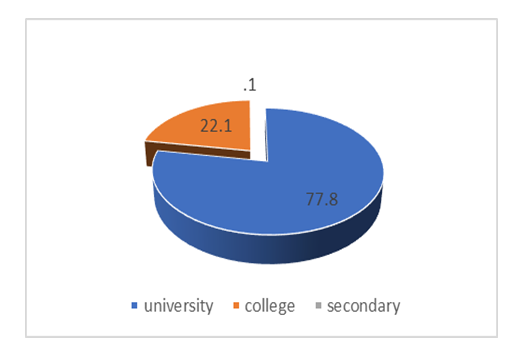 | Figure 9. Highest of Level of education |
4.3. E-Government Publicity
- From literature reviewed, it is evident that the Zambian government has been on top of things in ensuring that e-Government initiatives are accelerated in service delivery. From the data collected, there was a slight difference in perceptions. Those that said e-Government had enough publicity accounted for 51% while 49% said otherwise. Though the difference may seem insignificant, attention should be directed at understanding the issues raised by this group that suggested otherwise.See diagram below.
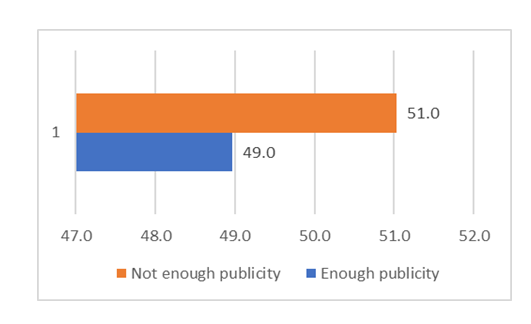 | Figure 10. E-Government publicity |
4.4. E-Government Maturity Cycle
- Critical to successful e-Government is the element of time lapse. Time to mature is one of the key factors that governments must endure with. In the case of Zambia, percentage distribution showed that over 80% of respondents agreed that the time taken for e-Government to mature had a significant impact on e-Government implementation while 11.1% disagreed with the assumption. Cost of Internet was another factor identified while Cultural and tradition had a relative impact on e-Government attracting a 50.4% and 49.6% yes and no responses respectively. See Figure 11 below.
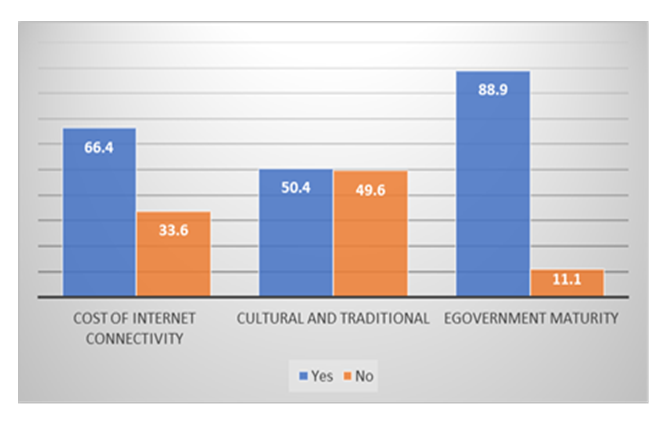 | Figure 11. Factors affecting e-Government in the civil service |
4.5. Telecommunication Infrastructure
- Taking into consideration the three core dimensions applied by the UN in assessing e-Government implementation, literature shows that IT infrastructure is the driving force for all e-Government activities. Zambia has continued to demonstrate its commitment by way of introducing various interventions or initiatives as attested both by literature and study findings. The introduction of a Government Wide Area Network coupled with rolling-out of a combined Zesco and Zamtel fibre network of over 9300 km across the country with 69.8% riding on this network. See Figure 12 below.
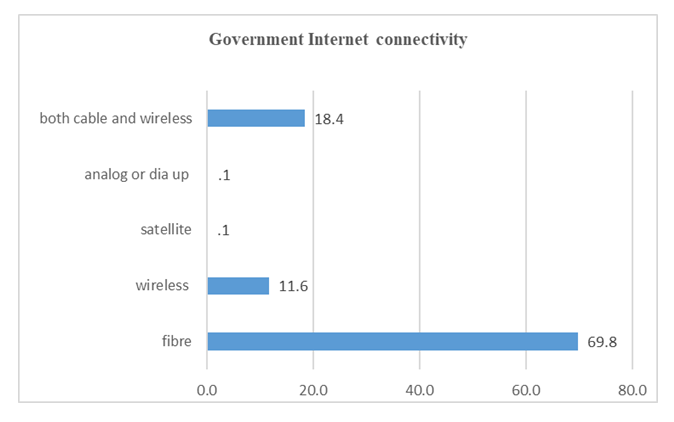 | Figure 12. Ministries with different Internet connectivity |
4.6. ICT Budget Allocation
- Literature shows that countries that have successfully implemented e-Government have deliberately set aside budget lines specifically for ICT development and implementation in line with policy pronouncements. From the literature reviewed, successful e-Government implementing countries have budget lines specifically set aside for ICT development and implementation under which e-Government is a component. On whether there is a separate budget line for e-Government implementation in Zambia, the results showed that 36% said yes, 45% where not sure, and 19% said no. Having the majority in the category of “not sure” and “no” is a clear indication that very little is being done in this area. Results in Figure 13 below show the levels of participant’s awareness or knowledge on budget lines directed at e-Government service provision.
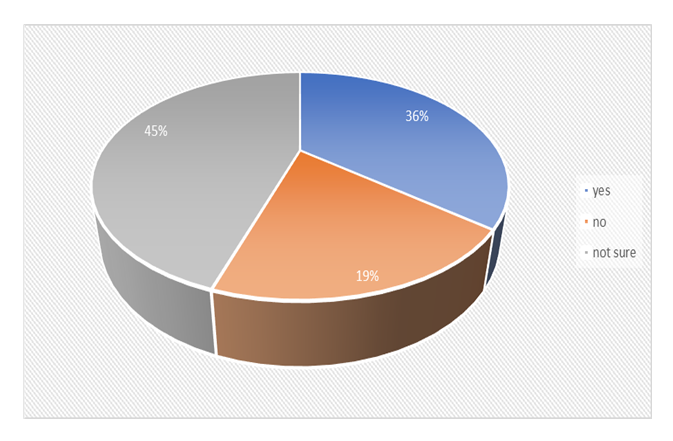 | Figure 13. ICT budget allocation to government Ministries |
4.7. ICT Training Policies
- The Human Capital Index (HCI) is another key component considered in measuring e-Government for UN Member States. Successful nations in e-Government have invested heavily in human resource capacity building. From the figure given below, 69.8% of the respondents indicated that most government Ministries lacked deliberate ICT training policies at workplace while 30.2% said otherwise. To assess strides made by government in championing the e-Government agenda, data on ICT training policies was inevitable. This provided the basis to assess whether the civil service had the capacity to embrace e-Government agenda. From the findings, we can conclude that there is a mismatch between political pronouncements and actual implementation of ICT training policies. See Figure 14 below.
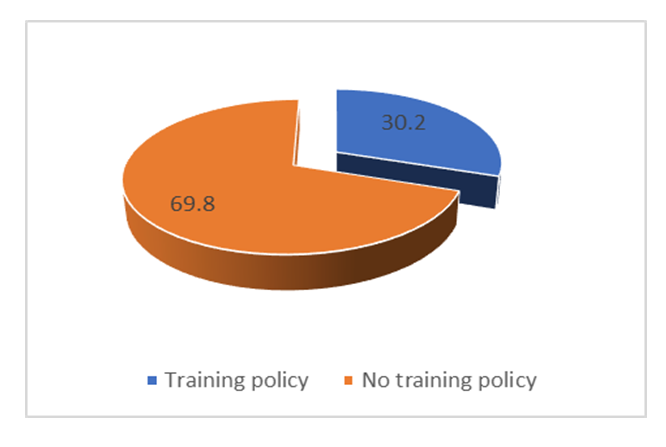 | Figure 14. Availability of ICT training policies in Ministries |
4.8. Government Online Services
- The presence of e-Government services is one indicator within the confine of Online Service Index that helps assess the status on individual country’s performance. From the results obtained, all Zambian Ministries now have Internet connectivity with some able to offer online. Respondent were asked whether they were aware of any transactions done online and the bar chart below shows the percentage distribution of responses.
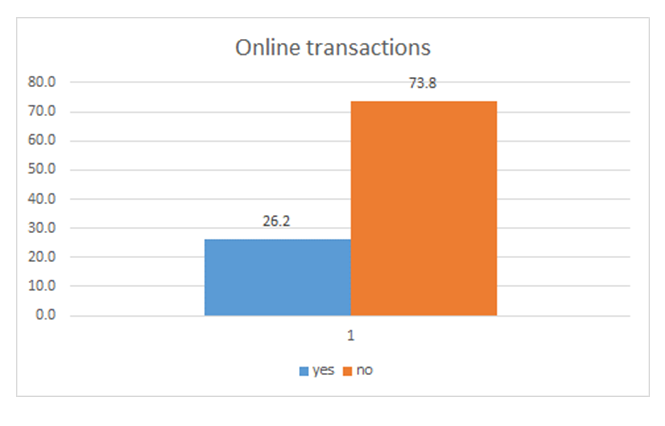 | Figure 15. Online transaction awareness |
4.9. E-Government Services
- The presence of e-Government services is one indicator within the confine of Online Service Index that helps assess the status on individual country’s performance. From the results obtained, all Zambian Ministries now have Internet connectivity with some able to offer online services such as immigration services, taxes and other online payments for government services. As indicated above, limited publicity of e-Government services has an implication on the preference of mode of e-Government service delivery. Most citizens currently would rather transact with the government manually rather than electronically. See graph below.
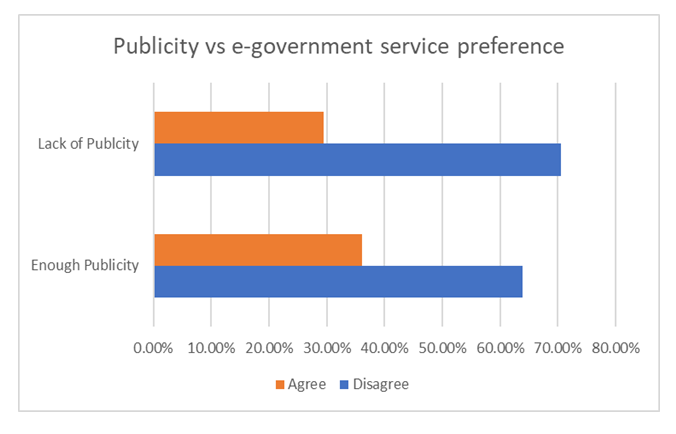 | Figure 16. E-Government publicity against mode of service delivery |
4.10. Mode of Service Delivery
- Respondents were asked to choose which mode of service delivery was better between electronic or manual means. Figure 17 below shows respective responses.
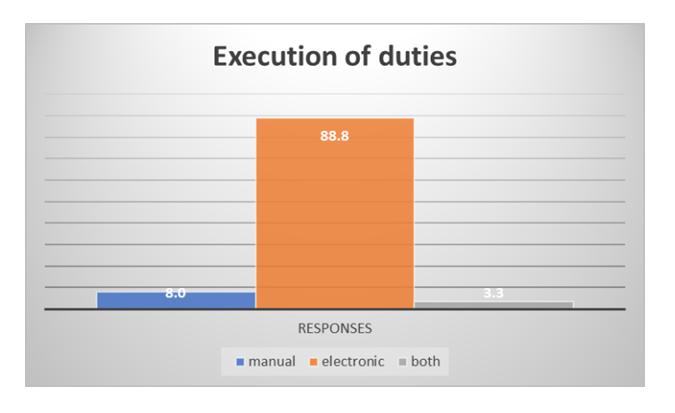 | Figure 17. Perception on mode of executing duties |
4.11. Implication of Age on E-Government Implementation
- Age is an important demographic variable that has a significant impact on behavioral intention and acceptance of technology according to [53]. Age was explored in the context of using and adopting of electronic services. Normally, it is expected that older citizens will have less skill and motivation to acquire and use of new technology. On the contrary, this hypothesis proved otherwise in this case study. Results analysed showed that over 70% of civil servant aged 40 and above were equally ready to accept the electronic way of doing business unlike the old times when paper and file was the norm for this group. See graph below.
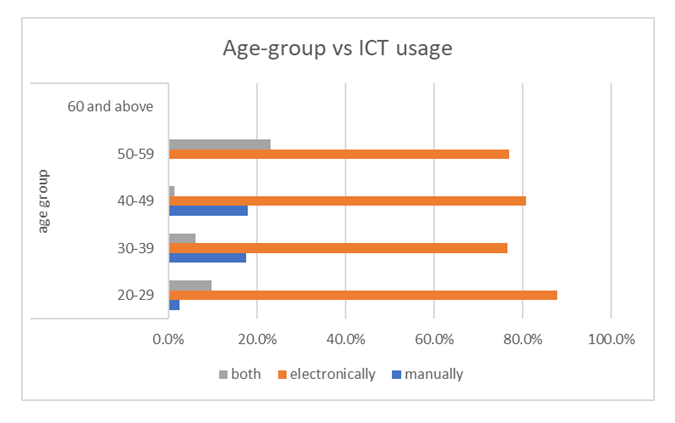 | Figure 18. Perception on the choice of service delivery |
4.12. Perception on the Choice of Service Delivery
- For e-Government to succeed there is need to understand how current government services are delivered and whether these meet the aspiration of clients. In this regard, respondents were asked to state whether services delivered electronically were more convenient than those delivered manually. Figure 19 shows the results.
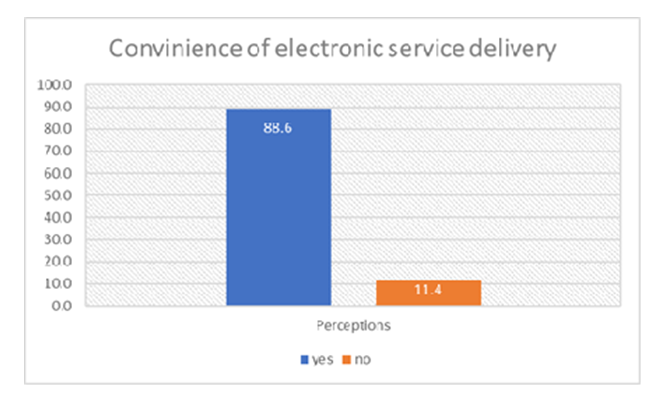 | Figure 19. Preferred mode of service deliver |
5. Conclusions
- The results presented from several Ministries indicated that Zambia still has a long way before its e-Government can reach maturity in the civil service. The paper presented several key factors that could be viewed as as opportunities and impediments to a fully functional e-Government within government Ministries. The availability of well-educated workforce was discovered as on of the opportunities that government can leverage on. On the flip side, limited publicity of e-Government services, inadequate e-Government services, lack of ICT training opportunities, non-existence of budget lines for ICTs, the slow and parallel pace at with ICT infrastructure network is rolled out across the country marks some of the key factors that have implications on the successful implementation of e-Government in the civil service. In view of the above electronic government readiness in the Civil Service and specifically in Zambia should call prioritised and committed public administration of ICTs. The following are therefore recommended.1. detach all ICT related functional areas from other departments in the civil service and make ICT units them autonomous with independent funding. 2. bring on board various stakeholders especially the private sector involved in e-Services to help deliver e-Governments services across the country. E-Government services are only useful if people know about them [54]. 3. marry policy pronounced with actual implementation plans especially in the area of basic computing skills.4. In order to progressively move “catalogue and transaction stage” (current Zambia’s position) to “horizontal transaction” (maturity), government should expedite and link all government electronic systems through a central portal. This once created will act as a one-stop-entry point for all e-Government services. 5. expedite the planned proposes of coming up with a coordinated telecommunication infrastructure development where all institutions be it private or public with fibre networks are built on a common infrastructure to reduce redundancies.Given the limited resources and time constraint, only government Ministry headquarters were target. However, it is worth noting that most of these Ministries have presence at District level and it is the researcher’s view that future studies on this subjected should be extended to these areas. Other future studies in this particular area should also endeavor to analyse internal systems within Ministries and what other factors decelerate the implementation e-Government in the civil service. It goes without saying “a vision without substance is a vision that is vague, misrepresentative of institutions, current position and time” [55].
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- First and foremost, I would like to acknowledge the abundant grace and love that the Almighty God has bestowed on me and my family. It has not been a kids journey to see the fruition of this project but credit goes to the favour from God and kind understanding of my peers and advisors for keeping me in good health throughout the rigors and demanding tasks of this research study. My sincere heartfelt gratitude goes to Dr. Simon Tembo for the relentless guidance and encouragement he gave me during the process of working on this research. At a time when all hopes were lost, Dr Banda raised me up and encouraged me to finish that which I had started. Thanks Doc.Lastly, I pay gratitude to my beloved children, my parents, and brothers and only sister Janet for providing me with unfailing financially and moral support. To Niza Nakaonga, this one if for you.
Disclosure
- This section is ONLY for those who requested disclosure. The name of the experts that reviewed your paper, in case they accepted selling disclosure to you, will appear here. Each reviewer is allowed to make their own price for that, since that is a public endorsement of your findings and may be used for varied purposes.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML