-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Information Science
p-ISSN: 2163-1921 e-ISSN: 2163-193X
2012; 2(6): 92-105
doi: 10.5923/j.ijis.20120206.05
An Application of UTAUT Model for Acceptance of Social Media in Egypt: A Statistical Study
Bashar Salim
Swedish Business School, Örebro University
Correspondence to: Bashar Salim , Swedish Business School, Örebro University.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Digital Social Media are now a part of daily human activities, and have opened a new era of informal communications in both private and public sectors. Platforms such as Facebook, twitter, YouTube and others, influence the spread of information more quickly and easily. This study investigates the influential factors for acceptance of social media in Egypt by inquiring whether the subscribers of Facebook’s ‘Khalid Saied page’ of the Arab spring accepted Facebook as an influential factor. This study uses the UTAUT model (Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology) representing performance expectancy, Effort expectancy, Social influence, Facilitating conditions and behavioral intention. A Survey methodology was used to gather data, whilst Spearman correlation technique has been used to analyze them. Statistically, the research finds they have significant correlation with behavioral intention so they accepted Facebook as influential factor. Also the research finds age and gender do not impact on performance expectancy and even experience has impacted on effort expectancy. Additional the experience factor affects social influence. Furthermore, older people have neither got impact of using Facebook nor motivate them to participate physically.
Keywords: Facebook, Social Media, UTAUT, Egypt
Cite this paper: Bashar Salim , "An Application of UTAUT Model for Acceptance of Social Media in Egypt: A Statistical Study", International Journal of Information Science, Vol. 2 No. 6, 2012, pp. 92-105. doi: 10.5923/j.ijis.20120206.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The new information technologies have an influence on human activities on all aspects. These technologies have revolutionized the global economy and human thoughts by forming the societies in different ways and changing the nature of human interaction.Wellman identified that when a computer network connects people, it is a social network.[40].The digital social networks and the Internet in general has had an impact on society. “Networks are becoming the nervous system of our society, and we can expect this infrastructure to have more influence on our entire social and personal lives than did the construction of roads for the transportation of goods and people in the past.”[7].There are growing demands of using these websites according to statistical graphs for the United Nations and other agencies[17]. Recently the statistical figures have shown that there is a major expansion of using social networks. For instance, the number of using Facebook exceeds 900 million subscribers in the world[30].People in the Middle Eastern countries have aspirations for more freedom of expression and exploiting all means to get their claims. In December 2010, The Arab Spring was an example of protest and uprising in several Arab countries. At that time the citizens started using digital social media (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube etc.) as additional channels to declare their rights.Then, it has been considered as a Twitter and Facebook revolution[27]. “Indeed some have been so bold as to label them as the ‘Twitter Revolutions’ or ‘Facebook Revolutions’ in recognition of the prominent part played by new social media, whether in the coordination of mass protests, communication of real-time images and up-to-date information, or processes of contagion across the Arab region”[4].Though, “the pattern of demand of use social media does not match with pattern of protests then come with result that social media sites provide the information to people not to revolt.”[9].However, new studies have found that social media had a mixed impact on the political culture. The analysis of outcome in 18 Arab countries has shown that the number of Facebook subscribers has been increased during that time “In most countries in the Arab world, Facebook is now one of the 10 most-visited Web sites, and in Egypt it ranks third, after Google and Yahoo. About one in nine Egyptians has Internet access, and around 9 percent of that group are on Facebook — a total of almost 800,000 members.”[31].The political system in Egypt is based on authoritarian rule, and military power is supporting regime more than the people. The situation in Egypt has worsened in the regime of President Hosni Mubarak. The emergency law had been continuously extended since 1981 and the president promised people to make reforms “frustration over economic issues like food inflation and high unemployment, as well as a lack of political freedoms like rights to free speech”[20], though all these endeavors of reforms were very suspicious[39].The people have realized that the government has not taken any serious action toward reforms so that the emergency law has been expired on 31 May 2012 and overcome the Mubarak regime.The development of ICT in Egypt has had a big role to increase Internet accessibility and made the information affordable to citizen by providing them new ways for communications (UN, 2011). The government had planned to improve the connectivity and increase PC penetration within private and academic sectors. It also planned to launch three more mobile operators’ licenses.The ratio of using mobile phones increased from 25 subscriptions per 100 inhabitants in 2006, to 90 in December 2010, and network infrastructure improved to reach Egyptian provinces and people started using the Internet through mobile and USB modems. The number of internet users had risen to 21,691,776 in 2010 while it was circa 8 million in 2005 according to World Bank figures (World Bank, 2012).The summer of 2010 saw the beginning of the Egyptian revolution. On June 6, 2010 Khalid Saied was at a cybercafé in Alexandria when he was taken by two detectives and beaten him to death in the street. His family said that Saied had videos showing the two police men dealing with drugs and the government feared that he would upload these videos on Facebook or YouTube, which were becoming popular in Egypt.[27]. The page “كلناخالدسعيد” (English: We are all Khalid Saied) on Facebook (Appendix B) “https://www.facebook.com/ElShaheeed” had massed more than 2 million subscribers. The people have started calling for protests through posting on “We are all Khalid Saied” page. On January25th, 2011 the revolution in Egypt was launched against Mubarak’s regime and managed to overthrow government. It was found that Khalid Saied page came in the fourth rank of using Facebook in Egypt, which it has registered 1 55836 as the PTA (the number of users who have interacted with a page in the past week by writing comments, like a page, post on page wall, share a post etc. ) and for fans about 2 074862.[33]After this event many pages have initiated by activists to encourage and influence people to disseminate the information that concerns Egyptians people around the world. It seems that comments on Facebook’s pages have created a wave of revealing the corruption in Egypt. Facebook provides a “news feed”, “answering questions”, “comments”, sharing different digital resources. In other hand, it is most actions on Facebook just a click away. In the case of Egypt, usually the revolutionists created groups or pages just to convey some political statement or to show solidarity with their followers.[11].The Facebook based communication was helpful to keep the motivation aroused, since the government banned uprisings in the street. At the same time the Egyptian regime undertook a campaign of delegitimization against Facebook, twitter and the internet in general[11]. The Egyptian regime shut down the Internet access for five days aims at frustration protests against the Mubarak regime in the first period of starting the revolution, at that time the social media such Facebook and Twitter became an increasingly important technique for organizers, activist and protesters while they have used the Internet to organize the demonstrations against Mubarak. During this event Hillary Clinton says “Both the American people and nations that censor the internet should understand that our government is committed to helping promote internet freedom”. Later Google Company cooperates with twitter it has invited a technique that can post messages to twitter by making telephone calls. The government restored the Internet when aware that they cannot stay against circulating the information among people.This study intends to complement the research of[29]to increase the scope of his work by taking a quantitative approach to clarify the type of relationship between performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence with behavioral intention, while his study devoted to examine the acceptance of social media in the Arab world and Egypt. This study applies the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model while this model works well with organizational environment.[37]By given such importance of using Facebook in that sense, this paper will investigate whether the participants “followers of Khalid Saied page” of the Arab spring accepted Facebook as an influential factor.The objective of the study is to analyze the relationship of participants intention “followers of Khalid Saied page” to accept Facebook with selected constructs such Performance expectancy, Effort Expectancy and, Social Influence. To give an overview about the attitudes of Egyptian people toward accepting social media through choosing Khalid Saied’s page on Facebook “in Egypt, a famous Facebook group named “We are all Khaled Said” was set up by activists to raise awareness “[29]Alsowhile this subject is quite new and scholars work out with this event, also determine the factors which have significant influence on accepting this technology.The theoretical analysis of constructs of performance expectancy PE, effort expectancy EP, social influence and facilitating conditions is presented in section 1.4in great detail.
1.1. Background Information
- Twitter, Facebook and other social networks are converting the political and social scene over the world example wiki leaks events, threat security of several countries whether they were democracy or dictatorship systems, “Political implications of ICT in a democracy it is the differences in access and control which lead to differences in ‘who benefits and who loses influence, who decides to participate in what decision.”. In other hand, in Islamic and Middle East countries, social media has made dramatic changes and revolutions in some countries.[27]With regard to academic system, shown that the students gaining social benefits of using those media (DeAndrea et al., 2012). Furthermore, those social sites have been using for a variety of educational purposes and support students in academic system. Karlin shown in her study that 60% of student debate online education-related themes. For instance discussion college meeting outside university or discuss something related to a particular subject or planning for picnic school or factory visiting and 50% talking about specific school work[18].With regard to public relation practices, Wang et al., 2010 concentrate it on benefits of social network in their study, they found that Facebook and social network playing role in preparing social relation, social interaction, marketing strategies, so they conclude that interaction with those sites will generate social relations with members.[38].With regard to business sectors, Bednorz found that Facebook has a high rank of visiting site comparing with others within the business domain “More business internet traffic goes to Facebook than to any other internet site, according to analysis by managed security company, Network Box”[3], this result has come from analysis of 13 billion URLs used by businesses in 2010 statistically found that 6.8 % all business internet traffic goes to Facebook. Bednorz has asked 250 IT managers for biggest security concern, and the answer was “‘employees using applications on social networks’ while at work, with 43 per cent of respondents saying this is a major concern” in contrast, there is 36% of respondents are concerned about malware passed via networks such as Twitter or LinkedIn. The top five websites visited by business according to Bednorz1.Facebook - 6.8 % of all traffic2.Google - 3.4 % of all traffic3.Yimg 2.8 % of all traffic4.Yahoo 2.4 % of all traffic5.Doubleclick 1.7 % of all trafficSimon Heron, says: “The figures show that IT managers are right to be concerned about the amount of social network use at work. There are two real concerns here: firstly those employees will be downloading applications from social networks and putting security at risk; and secondly the amount of corporate bandwidth that appears to be being used for non-corporate activity.”[16]
1.2. Literature Review
- The transformation of broadcasting traditional media into a network digital media has changed the way of information flow and nature of news work[20].The adoption of digital social networks was a result of a repression of traditional media by governments. Facebook, Twitter as an example of social networks playing a role of engaging with, and enlarging audiences while it altered the technique of receiving and republish daily news “As the world’s news media and new social networks communicated these dramatic images of mass opposition from across much of the Arab world”[4]. Shirky has discussed whether social media have impact to create demonstration by presenting news and information[32].User acceptance is defined as “the demonstrable willingness within a user group to employ information technology for the tasks it is designed to support”[1] . The purpose of using these social channels is to keep in touch with people with each other and transfer information more quickly “The advance of the use of social networking systems is rapid and compelling. People are continually connected to each other on their blackberries, i-phones, netbooks and computers.”[19]. Through using these social media, people may discuss their affairs publicly and privately. “Social networks exist because humans are societal and require relationships in order to survive.”[5]Most social networking websites allow users to create their profiles and share information and visiting another page and joining another group, also can cast a comment on a certain page, so the people feel free on expression of their thoughts without restrictions and share their opinions with others. This is why these media are considered as free communication channels between people.It is difficult to determine user acceptance of a system while there is no specific model describe and define acceptance, though, there are only studies suggests key factors in technology, user and the implementation process that impact acceptability.In order for the technology be accepted it must meet with basic usability requirements and perceived as helpful by society. Training and user experience are an influential factors to accept or reject technology, alsohow this technology is working in order to meet with users’ requirements, all these factors impact on the level of acceptance.[8]
1.3. The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) Model
- There are numbers of theoretical models helping to understand the influencing factors of acceptance information technology.[36]. Developed the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model to reinforce the TAM model (see figure 1).The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is one of the most powerful models in information technology and IT behavior acceptance and it has a role of understanding the influential factor of adopting information technology The main goal of the TAM model is to provide a basis for discovering the influence of external variables on internal belief, attitudes and intentions. The TAM model suggests the usefulness and ease of use which they have been the primary determinants of adoption of information technology in any organization. In TAM model, there are two determinants as a basis of relationship regarding of using the system, which are the ‘intention to use’, and then establish the ‘actual behavior or use’. Perceived usefulness refers to which degree that a person believes that use of the system would improve job performance. Perceived ease of use refers to which degree a person believes that using the system would be free mental effort[6]. The original TAM model has been created to study of IT/IS adoption in business companies. The UTAUT model used the performance expectancy and effort expectancy to integrate the structure of the perceived usefulness and ease of use in the original of TAM model. Also, the UTAUT model assumes that the Effort Expectancy can significance in determining user acceptance of information system technology.Regarding of ease of use, it did not become significant in use, it can expect ease of use is seen as more significant just in the early stages of use of new technologies, and it can have a positive impact on the perception of the usefulness of this technology.[22].
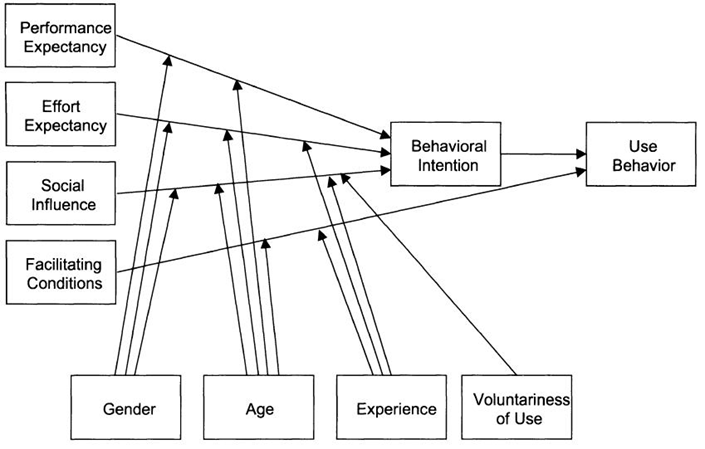 | Figure 1. The UTAUT model[37] |
1.4. The Theoretical Analysis of UTAUT Factors
- Performance Expectancy Factor Performance Expectancy has formulatedfrom five constructs from different model that are related to performance expectancy are (MPCU), relative advantage (IDT), perceived usefulness (TAM/TAM2 and C-TAM-TPB), job-fit,extrinsicmotivation (MM) and outcome expectations (SCT)[37]. It found that these constructs within each individualmodel is the strongest predictor of intension and have found significant in acceptance technology.[37]. However, from a theoretical point of view, there is reason to anticipate that the relationship between performance expectancy and intention to use social media among members of Khalid Saied page mediated by age and gender. Performance Expectancy concentrates on task accomplishment, are likely to be noticeable for men[37]. There has been some exploration of gender differences in social networking use. Hargittati has shown that women were more likely to use social networking site compared with men, and equal amount of men and women to use Facebook.[15]. Furthermore, it found that men were to be more likely to use social sites for dating and learning about new events compared with women.[28]. the age similar to gender, it is theorized to play a moderating role.[37]. Hall &Mansfeild propose that younger workers may place more importance on external reward[14] . The important to mention that this factor change significantly for working women between the time enter working life and time they reach child-rearing years[2].The study expect that the influence of performance expectancy will be moderated by both gender and age.“It appears then that gender differences found in online behavior may apply specifically to social networking sites, such that men and women use these sites, but for different reasons.”[25]. Effort Expectancy factorVenkatesh defined effort expectancy as “the degree of ease associated with the use of the system.”[37]. Effort Expectancyfactor formulatesfrom three constructs from different models to capture the concept of effort expectancy, perceived ease of use (TAM/TAM2), ease of use (IDT), and complexity (MPCU).[36](Morris &Venkatesh, 2000)[24] suggest that women have role in this context than men as it observed earlier, the gender differences are a key factor of performing desire job[21] .With regard to age, it is noticed that increased age has a relation with difficulty in job processing and allocation attention to information on particular conditions[26] .The processing information by person and attention to information are necessary when dealing with system information.[23] Conducted a survey and proposed that technical experience is a significant and it strongly influences on social attitudes. The study expects that the influence of effort expectancy will be moderated by experience and age and genderSocial Influence factor Social Influence factor is defined as “the degree to which an individual perceives that important others believe he or she should use the new system”[37]. The foundation of social influence represents by those constructs: subjective norm (TRA, TAM2, TPB/DTPB and C-TAM-TPB), image (IDT) and (MPCU) Thompson and his colleagues used in their study the term social norms in defining these constructs.[34]. the studies have found that social influence has been a strong impact of intention at early stage of adoption technology. The theory proposes that women were more sensitive to other opinions; therefore shown social influence has a role when forming an intention to use new technology.[24]. With regard to age, it suggests that the older workers have a more role to place on social influence than younger[37]. The study expects that facilitating conditions will moderated by experience and age. Facilitating Conditions factor Facilitatingconditions are defined as “the degree to which an individual believes that an organizational and technical infrastructureexists to support use of the system.”[37]. Thisfactor formulated from three different constructs: perceived behavioral control (TPBI DTPB, C-TAM-TPB), facilitating conditions (MPCU), and compatibility(IDT).[37]. each of these constructs based on technological aspects and the aim of formulating these constructs is to remove barriers of using technology. Facilitating conditions have direct influence on usage as it shown in the empirical results, the experience of using technology is important to help and support organizations to manage a particular event through using information technology system. Also it found that older workers need more help to know how use technology compared with younger workers.[14]. Table 1 gives a definition of each one of these factors which are used in this study and give an explanation of the questions which used in the Survey.
2. Method
- This research is aligned with positivistic approach. “The senses are used to accumulate data that are objective, discernible, and measurable, thus methods are chosen to obtain estimates of the truth”[10],which it dominates to quantitative data. “Quantitative approaches are associated with a positivist worldview and, thus, are compatible with the values embraced by the natural sciences.”[10]. A survey was used from subscribers in “followers of Khalid Saied page” of the Arab spring: Egypt as a target group. The survey which was presented to the respondents demonstrates the behavioral patterns of accepting Facebook during the revolution, and in turn the influence on the acceptance of Facebook.(UTAUT) model is used in this study to analyze behavioral patterns of Facebook in Egypt. The data were obtained from a target group who had participated in the events of the revolution. An anonymous web survey was used to collect data. The participants were contacted through “We are all Khalid Saied” Facebookpage and by asking to contact their friends in a snowball fashion. The questions are related to the UTAUT model constructs, the data are analyzed according to statistical tools which are mentioned in the Results section.This study uses the subscribers of Khalid Saied’s page to contact Egyptian Facebook users in analyzing Facebook influential factors for acceptance in Egypt. 16 questions in the survey were administrated and collected and they were generated based on 5 constructs (Performance expectancy, Effort expectancy, Social influence, Facilitating conditions, and Behavioral intention to use the system) as discussed in table 1, which they captured in UTAUT model. The data collected was run by SPSS version 14 to use regression analysis, this study want to verify the impact of four constructs of UTAUT (PE, EE, SI, and FC) towards acceptance of Facebook on the behavioral intention during the demonstration in Egypt. The Khalid Saied’s page was chosen for the study since this page has taken fourth rank and the participants are directly involved in this movement. The aim of using Survey is as base of this work by getting an opinion from members, because it reflects what they feel about acceptance technology (Facebook) by questioning them. The empirical data are as result of their experience with Facebook. An online survey was conducted based on the instrument designed by[37]There are (16 questions) questionnaire items extracted from an UTAUT model study of Venkatesh et al., (2003) for this work. Each participant was asked to complete the survey. Appendix A shows questions which used to measuring the behavioral intention of “followers of Khalid Saied page” via Facebook. In addition to editorial changes to fit with the theme of this study, the survey utilized seven-point scale, this scale used by[37]with same UTAUT model where 1 = completely disagree, 2 = moderately disagree, 3 = somewhat disagree, 4 = neutral (neither disagree nor agree), 5 = somewhat agree, 6 = moderately agree, and 7 = completely agree.Venkatesh, et al., (2003) hypothesized that performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence all of them have a significant impact on behavioral intention. They hypothesized that facilitating conditions would not have a significant effect on behavioral intention; however, it would affect usage behavior. Data were collected from April 4, 2012 to May 1, 2012 and 98 persons participated in this survey, where 11 of them have been ignored due to their responsiveness were part of questions not all, the total number is 87 participants. 63% were male, and 37% were female. Table 2 provides a summary of the participants’ ages.
|
|
3. Results
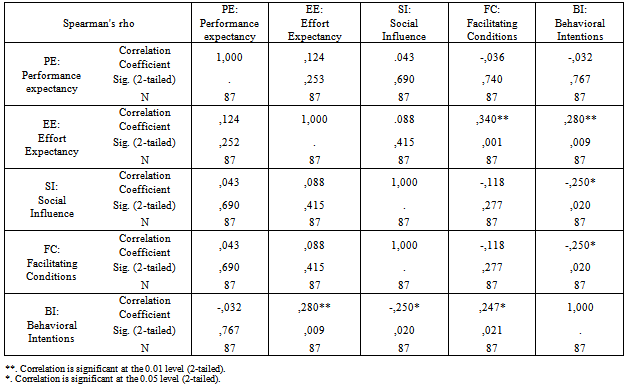
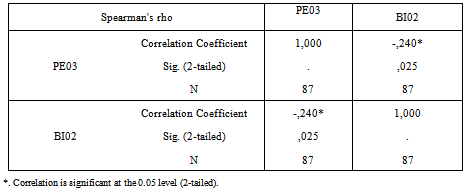
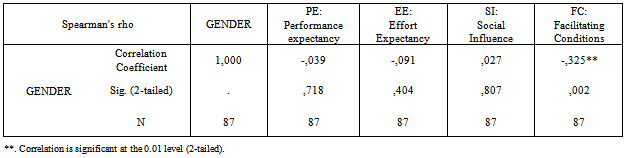
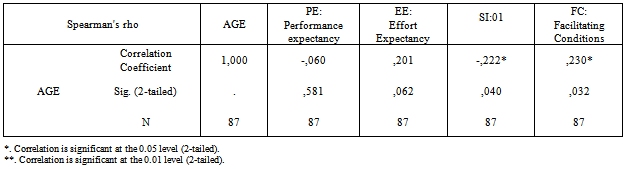
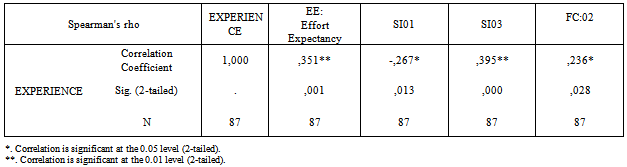
- Appendix C table 4 shows a summary of a Spearman correlation analysis by using SPSS14 software to examine the relationship among the UTAUT constructs, “A relatively simple technique that can be used for exploratory data analysis is the superman rank correlation coefficient”[12]. , those constructs represented the influential factors which let Khalid Said’s page members accept Facebook as an influential factor during demonstration. The outcome shows that Effort Expectancy, Social Influence and Facilitating Conditions have significant correlation with Behavioral Intention at 0.01 and 0.05 respectively.Also, it appears a significant correlation between PE03 and BI02 as shown in Appendix C table 5 at the .05 level of significance. These are the three main constructs (Performance Expectancy, Effort Expectancy and Social Influence) consider as influential factors and impact participants to accept Facebook according to UTAUT model. Unfortunately, no significant correlation can be found between gender with respect to their hypothesized relationships with Performance Expectancy, Effort Expectancy, and Social Influence, only it has found a significant relationship with Facilitating Conditions at 0.01 level. As shown in Appendix C table 6 Also it has found that Age has only significant correlation with social influence (SI01) at .05 level and with Facilitating Conditions at .01 level, as shown in Appendix C table 7The Experience variable has statistically significant correlation with Effort Expectancy, social influence (SI01, SI03, and Facilitating Conditions (FC02) due to the Sig.(2-tailed) less 0.01,0.05 respectively , as shown in Appendix C table 8Unfortunately, it has not found any relationships between Voluntariness of use and social influence as shown in Appendix C table 9 due to Sig.(2-tailed) is greater than 0.05.
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
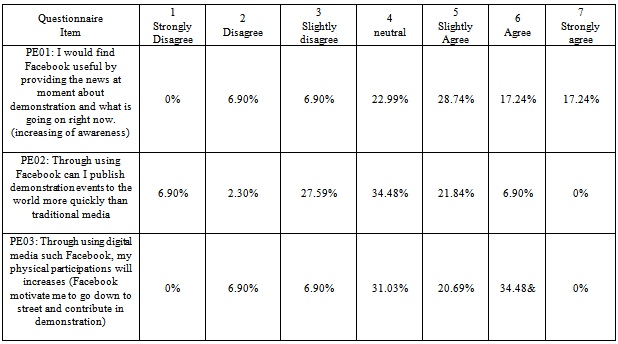
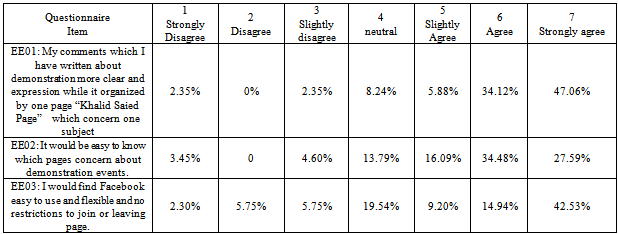
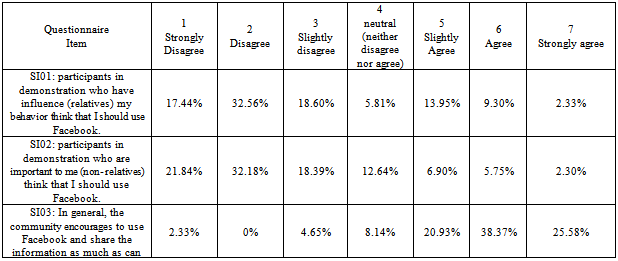
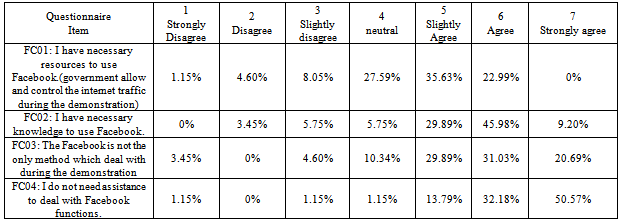
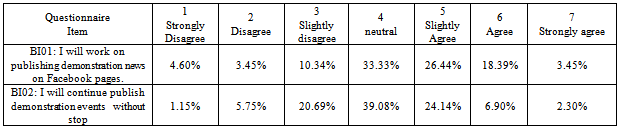
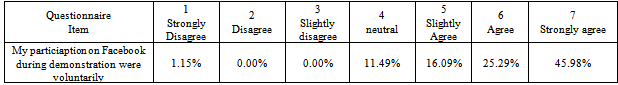
- Statistical analysis table builds up in order to give a full explanation of Egyptian peoples' perceptions. Appendix C table 10 shows the corresponding percentage of people with respect of performance Expectancy. The figures have shown that people slightly agree that find Facebook useful by providing the news about the demonstration at the moment and they agree that Facebook motivate them to go down to street and contribute in regulations, however, they tend to neutral in term of their perception that Through Facebook can publish demonstration events to the world more quickly than traditional media and accomplish tasks more quickly (uploading digital report, images, comments, spread information than traditional media).As can be seen in Appendix C table 11, people strongly agree that their interaction with the Facebook would be clear and understandable while it organized by one page “Khalid Saied Page” and which concern one subject; and there is no restriction to join or leaving the page. Descriptive analysis has shown that people agree that easy to find the desired page.Appendix C Table 12 descriptive analysis of peoples' perceptions regarding to social influence, it shows that people disagree or may not be influenced from somebody or someone important to them to use Facebook during the revolution, however, they tend to be agreed that the community encourages them to use Facebook.Descriptive analysis of facilitating conditions shows that, people strongly agree that they do not need assistance to deal with Facebook functions, and they agree that Facebook is not the only method which deal with during the revolution, and they have the necessary knowledge to use Facebook, however, they slightly agree that they have the necessary resources to use Facebook, as shown in Appendix C table 13. The people tend to be neutral in term of their perceptions that they intend to use Facebook, and work on publishing news on it, also they plan to use Facebook in the future, as it can see in Appendix C table 14. Interestingly, the descriptive analysis in Appendix C table 15 appears that the people strongly agree that are using Facebook during revaluation was voluntary.
4. Discussion
- There is a similarity between what this research has found and what Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg mentioned: “Facebook's role in the "Arab spring" revolutions has been overplayed”[35]. The result is matched with Mark Zuckerberg thoughts when he said of the uprisings in Egypt “I think that Facebook was neither necessary nor sufficient for any of those things to happen. I do think over time the internet is playing a role in making it so people can communicate more effectively and that probably does help to organize some of these things”[35]Performance expectancy expects to find relevant information and receive high contributions by using Facebook. The age and gender do not register any significant correlation on performance expectancy this is the inverse of Venkatesh’s finding, might because the majority of participants were between 30-34 years old and Venkatesh’s hypothesis concern for young people “The influence of performance expectancy on behavioral intention will be moderated by gender and age, such that the effect will be stronger for men and particularly for younger men.”[37] The gender impact by age issue “gender differences can be misleading without reference to age.”[37].Effort Expectancy concerns whether participants believe that it is worth the effort to use Facebook. Experience has registered as significant on effort expectancy, however, the age and gender do not have any effect, might because the male ratio of contributions were more than female ratio on this study, the percentage of adult higher than the percentage of youth, Venkateshs’ hypothesis based on women and youth “The influence of effort expectancy on behavioral intention will be moderated by gender, age, and experience, such that the effect will be stronger for women, particularly younger women, and particularly at early stages of experience.”[37]Social Influence identifies whether the participants expect others such relatives or neighbors, appreciate using Facebook. The experience variable has significant with social influence this match with Venkatesh’s hypothesis. Respectively the age, gender and Voluntariness of use do not have a significant impact on social influence. For voluntariness variable Venkatesh’s identified it as “Voluntariness was a dummy variable used to separate the situational contexts”[37]so it could be unnecessary as long as it has only one situational context that to overcome the political regime in Egypt.Facilitating Conditions factor is about whether people (participants) get enough support through Facebook existing, the experience has significant on facilitating conditions, however, age does not have a significant impact on it, might because the participants were not older worker as Venkatesh’s mentioned. Marchewka performed a similar study by using UTAUT and they have found neither age nor genders have a significant effect on their research.[22] The Statistical numbers have discovered that there are negative relationships between age and social influence; the older people will not get impacted of using Facebook. Also the young people (15-24 years old) have found Facebook useful during the demonstration which enabled them to publish their thoughts faster than traditional way. Older people think that social digital media like Facebook did not motivate them to participate physically during the revolution. The people who had experience of using Facebook have not been affected by anyone to use site as long as they know the functionality of Facebook.
5. Conclusions
- This research demonstrates Egyptian people’s perceptions of accepting Facebook by applying the UTAUT model. The aim of this study is to investigate whether the participants “followers of Khalid Saied page” of the Arab spring accepted Facebook as an influential factor. The influential factors take a part into Performance expectancy, Effort Expectancy and, Social Influence.It is found that social influence and effort expectancy have a significant impact on Behavioral Intention. Performance expectancy has a significant correlation with Behavioral Intention in regard to PE03 and BI02. The research indicated that the physical participation has a weak relationship with sharing comments on Facebook while the Correlation Coefficient value is close to zero, however, statistically this point has gotten significant impact on planning to use Facebook in the future. This research proved that facilitating conditions have a significant influence on behavioral intention, moderated by experience and age, inverse from what Venkatesh suggested. It might that UTAUT does not support this kind of social media technology in this context, or it needs maximizing the frequency of participators on the survey.Age has significant influence only on facilitating conditions and social influence SI: 01 (SI01: participants “followers of Khalid Saied page” who have influenced my behavior think that I should use Facebook.).There are some issues important behind using social media are quick, cheap, and popular used. To announce or show some comments can be done through putting it on these media and circulate by minutes to reach most of the citizens who they are using the internet, even among campaign people. Information distribution over the digital network including images or labels even text cheaper and take shorter process than print paper or posters. There is another issue also important, correction mistake; any mistake by campaign can correct it easily and faster than traditional ways.The technical issue is also an important aspect, it has to prepare a good context understandable and keep it easy to read, it is quite comfortable watching virtual images and video on computer screen. It is better to write simple language and organize context heading, points and headlight to make it clearer and easier to find information.The findings of research prove statistically that Facebook has been accepted as an influential factor by Khalid Saied’s page members, this what Sabadello confirmed in his research “It is wrong to say that social networks can start a revolution. It is equally wrong to say that they did not play a significant role during the Arab Spring.”[29].The limitation of this research is the sample size regarding to Egypt population 81 million 2010[41]. It was expected to participate more than this number in the survey, due to the situation in Egypt is still unstable and the people do not have a willing and time to perform this survey.Further research is needed to focus on governmental employees and find the similarities and differences between governmental people and Non-government employees in regard to influencing factors which UTAUT model suggested. This research raises interesting question, Doses the UTAUT model fit well with social digital service that deal with communities, if it does not, the question is what kind of modification should to do in order to fit with this kind of services
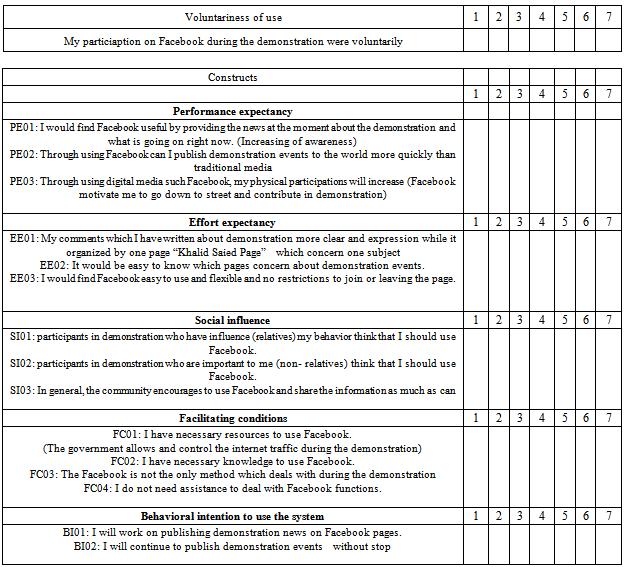
Appendix A: Questionnaire
- Survey on FacebookFacebook is one of powerful social media which played role in 25th Jan revaluation in Egypt, by showing recent news about revolutionists and government activities, also provide a free domain by allowing different kinds of people to share opinions and suggestions by online collaboration and communication. Please circle the appropriate number to indicate the level of your agreement or disagreement with the following statements on a scale of 1 to 7, where 1 = completely disagree, 2 = moderately disagree, 3 = somewhat disagree, 4 = neutral (neither disagree nor agree), 5 = somewhat agree, 6 = moderately agree, and 7 = completely agree.Participant InformationThe intent of this section is to obtain some information about individuals who respond to this survey. Information gathered about participants will be treated confidentially, and only group data will be reported as an outcome of this research Gender : FemaleMaleAgeAge: 15-1920-2425-2930-3435-3940-4445 and aboveExperienceHow long have you used Facebook?From 2011From 2010From 2009From 2008From 2007From 2006From 2005
Appendix B
Appendix C
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
References
| [1] | Andrew, D., & G., M. M. (1996). User acceptance of new information technology: theories and models. Information Science and Technology, 3-32. |
| [2] | Barnett, R. .., & Marshall, L. (1981). The Relationship between Women's Work and Family Roles and Their Subjective Well-Being and Psychological Distress " in Women, Work and Health:Stress and Opportunities M, . Frankenhaeuser,V. Lundberg, and M. A. Chesney (eds.),. New york:plenum press, 111-136. |
| [3] | Bednarz, A. (2009). Social networks take a bite out of corporate bandwidth: Facebook and YouTube usage dominates business networks. Communications--Computer Applications, Computers--Computer Networks. |
| [4] | Cottle, S. (2011). Media and the Arab uprisings of 2011: Research notes. SAGA, 647–659. |
| [5] | Coyle, C. L., & Vaughn, H. (2008). Social networking: Communication revolution or evolution? Bell Labs Technical Journal, 13-17. |
| [6] | Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Quarterly, 319 - 340. |
| [7] | Dijk, J. (2006). The Network Society. London: SAGE Publication Ltd. |
| [8] | Dillon, A. (2001). User acceptance of information technology. In W. Karwowski (ed). Encyclopedia of Human Factors and Ergonomics. London: Taylor and Francis, 1-6. |
| [9] | Ehrenberg, R. (2012). Social media didn't spur Arab Spring. Society for Science & the Public, 9. |
| [10] | Evely, A., Fazey, I., Pinard, M., & Lambin, X. (2008). The Influence of Philosophical Perspectives in Integrative Research: a Conservation Case Study in the Cairngorms National Park. Ecology and Society , 13. |
| [11] | Faris, D. (2008). Revolutions Without Revolutionaries? Network Theory, Facebook, and the Egyptian Blogosphere. Arab Media & Society, 1-11. |
| [12] | Gauthier, T. (2001). Detecting Trends using Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient. Environmental Forensics, 359-362. |
| [13] | Hagedoorn, J., & Cloodt, M. (2003). Measuring innovative performance: is there an advantage in using multiple indicators? Research Policy, 1365–1379. |
| [14] | Hall, D., & Mansfield, R. (1975). Relationship of age and seniority with career variables of engineers and scientists. Journal of Applied Psychology, 388-396. |
| [15] | Hargittai, E. (2008). Whose space? Differences among users and non-users of social network sites. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 276–297. |
| [16] | Heron, S. (2010, October 16). SC Magazine,Mobile enterprise security. Retrieved from Facebook and YouTube dominate workplace traffic and bandwidth: http://www.scmagazineuk.com/facebook-and-youtube-dominate-workplace-traffic-and-bandwidth/article/168082/ |
| [17] | ITU. (2011, 08 25). International Communication Unoin. Retrieved from ICT Data and Statistics (IDS): http://www.itu.int/ITU-D/ict/statistics/ |
| [18] | Karlin, S. (2007). Examining how youths interact online. School Board News, 6-9. |
| [19] | Lane, M., & Coleman, P. (2012). Technology ease of use through social networking media. Journal of Technology Research, 1-12. |
| [20] | Lotan, G., Graeff, E., Ananny, M., Gaffney, D., Pearce, I., & Boyd, D. (2011). The Revolutions Were Tweeted: Information Flows During the 2011 Tunisian and Egyptian Revolutions. International Journal of Communication 5 (2011), 1-32. |
| [21] | Lynott, P. P., & McCandless, N. J. (2000). The Impact of Age vs. Life Experiences on the Gender Role Attitudes of Women in Different Cohorts. Journal of Women andAging, 5-21. |
| [22] | Marchewka, J. T., Liu, C., & Kostiwa, K. (2007). An Application of the UTAUT Model for Understanding Student Perceptions Using Course Management Software. Communications of the IIMA, 93-104. |
| [23] | Marcus, A., Baumgarter, && Johanna, V. (2004). practical set of culture dimension for evaluating users interface design. Proceedings Sixth Asia-Pacific conference on computer-human interaction (APCHI 2004), (pp. 252-261). Rotoura, New Zealand. |
| [24] | Morris, M. G., & Venkatesh, V. (2000). Age Differences in Technology Adoption Decisions Implicationsf or a Changing Workforce. Personnel Psychology, 375-403. |
| [25] | Muscanel, N. L., & Guadagno, R. E. (2012). Make new friends or keep the old: Gender and personality differences in social networking use. Computers in Human Behavior, 107_112. |
| [26] | Plude, D., & Hoyer, W. (1985). Attentiona nd Performance: Identifyinga nd LocalizingA ge Deficits in Aging and Human Performance. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 47-99. |
| [27] | Pollock, J. (2010). How Egyption and Tunisian youth hacked the Arab spring:StreetBook. technology review, 70-82. |
| [28] | Raacke, J., & Bonds-Raacke, J. (2008). MySpace and Facebook: Applying the Uses and Gratifications Theory to Exploring Friend-Networking Sites. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 169-174. |
| [29] | Sabadello, M. (2011). The role of New Media for the Democratization processes in the Arab world. SAFRAN 09, Austrain Study Center for Peace and Conflict Resolutioin. Zsolt Sereghy,Sarah Bunk and Bert Preiss (eds)., 1-10. |
| [30] | Samuels, D., & Zucco, C. (2012). Using Facebook as a Subject Recruitment Tool for Survey-Experimental Research. Social Science Electronic Publishing, Inc, 1-34. |
| [31] | Santos, J. R. (1999). Cronbach's Alpha: A Tool for Assessing the Reliability of Scales. Journal of Extension, Volume 37 : Number 2. Retrieved from Extension Journal, Inc. ISSN 1077-5315. |
| [32] | shapiro, s. m. (den 22 Jan 2009). The New York Times. Hämtat från Revolution, Facebook-Style:http://www.nytimes.com/2009/01/25/magazine/25bloggers-t.html |
| [33] | Shirky, C. ( 2009 , DECEMBER 11). Prospect. Retrieved from The net advantage :http://www.prospectmagazine.co.uk/magazine/the-net-advantage/ |
| [34] | Socialbakers. (2012). Socialbakers. Retrieved from Facebook Page Statistics in Egypt:http://www.socialbakers.com/facebook-pages/egypt/page-1 |
| [35] | Thompson, R. L., Higgins, C. A., & and Howell, J. M. (1991). Personal Computing: Toward a Conceptual Model of Utilizatio. M IS Quarterly(, 124-143. |
| [36] | Tim, B. (2011, May 2). Financial Times. Retrieved from Facebook's uprising role played down: http://db.ub.oru.se/login?url=http://search.proquest.com.db.ub.oru.se/?url=http://search.proquest.com.db.ub.oru.se/docview/868720949?accountid=8028 |
| [37] | Venkatesh, & Davis. (2000). A Theoretical Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model Four Longitudinal Field Studies. Management Science, 186-204. |
| [38] | Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Quarterly, 425 - 478. |
| [39] | Wang, S. M. (2010). Face-off: Implications of visual cues on initiating friendship on Facebook. Computers in Human Behavior, 226-234. |
| [40] | Warschauer, M. (2003). Dissecting the “Digital Divide”: A Case Study in Egypt. The Information Society, 297–304. |
| [41] | Wellman, B. (1997). An Electronic Group is Virtually a Social Network. In S. Kiesler, (Ed.), Culture of the Internet, 179-205. |
| [42] | WordBank. (2012, march 30). Public Data. Retrieved from Population: http://www.google.com/publicdata/explore?ds=d5bncppjof8f9_&met_y=sp_pop_totl&idim=country:EGY&dl=en&hl=en&q=egypt+population |
| [43] | Wu, Y.-L., Tao, Y.-H., & Yang, P.-C. (2007). Using UTAUT to explore the behavior of 3G mobile communication users. Conference Publications (pp. 199- 203). Singapore: Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, 2007 IEEE International Conference on. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML