-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Inspiration & Resilience Economy
2019; 3(2): 50-57
doi:10.5923/j.ijire.20190302.03

Quality of Life and Welfare Economy (A Case on Algeria)
Benzair Abdelouahab, Hicham Guendouz
Professor at the University of Taheri Mohamed -Bechar, Faculty of Economic Sciences, Member of the Economic Studies and Local Development Studies in Southern Algeria
Correspondence to: Benzair Abdelouahab, Professor at the University of Taheri Mohamed -Bechar, Faculty of Economic Sciences, Member of the Economic Studies and Local Development Studies in Southern Algeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Although the main objective of any economic activity is to meet the infinite needs of human beings through the optimal utilisation of various resources available, this activity remains social, and the results of the economics evolution constrain it. However, this paper debates that the development in the world no longer seeks to meet only the physical needs of individuals, but looks for meeting even their sensory needs. This is called the ‘Welfare Economy’ which will certainly contribute to solving many of the social problems, and to the advancement of the daily life of the members of the community to reach an advanced stage of the quality of life. Within this framework, the purpose of this paper is to try to link the concept of ‘quality of life’ and ‘welfare economy’ concerning the case of Algeria.
Keywords: Welfare Economy, Quality of life, Local Development, Algeria
Cite this paper: Benzair Abdelouahab, Hicham Guendouz, Quality of Life and Welfare Economy (A Case on Algeria), International Journal of Inspiration & Resilience Economy, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2019, pp. 50-57. doi: 10.5923/j.ijire.20190302.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The main objective of economics is to address the economic problem that ensures that increasing human's needs, stay within the limited resources available. However, the significant development of human societies at present has led to multiple aspects of this goal, and the improved the mechanisms to achieve it also. Today, human societies no longer seek to solve their economic problems only; they also seek to achieve the so-called ‘welfare economy’, which A. Marshall said in his book Principles of Political Economy that it is achieved by achieving an optimal situation of production and distribution and the search for the complex welfare as a whole. Thus it seems that the achievement of economic well-being goes beyond the side Guetsada towards more the social side, through equitable distribution of local development and the output per capita. This intersects with the quality of life.Therefore, this paper seeks to link the concept of the economy of welfare and quality of life concerning the case of Algeria.
2. The Problem of Study
- This paper focuses on the following problem: ‘To what extent can the welfare economy contribute to the quality of life in Algeria?’The basic objective of this paper seeks to link between the concept of the welfare economy and the concept of quality of life, with reference to the situation in Algeria, by taking into account the concept of the welfare economy and mechanisms to achieve it and to what extent this will contribute to the quality of life with reference to the case of Algeria.
3. The Importance of Study and Its Methodology
- Modern development plans in various countries of the world seek to achieve advanced levels of quality of life and economic well-being of various segments of society, and this concept is of great interest in academic research which is trying to determine the best ways to achieve this goal, especially in developing countries such as Algeria, accordingly this study is of great importance where the Algerian economy is undergoing significant changes in order to cope with the changes taking place in the international economic arena add to that and the result of common points between the Algerian economy and the rest of the Arab economies that the Algerian experience with regard to the subject of the study and its findings is a model that can be circulated to other Arab economies.In this study, we will review the backwardness of data and statistics that contribute to drawing a clear picture on the subject in general and in Algeria in particular, through three main axes:Ÿ The first axis: quality of life.Ÿ The second axis: a theoretical approach to the life economy.Ÿ The third axis: the economy of welfare and its contribution to the quality of life - the case of Algeria.
4. Literature Review
4.1. The First Axis: Quality of Life
- Humanity today has achieved significant development in terms of improving and developing lifestyles, and most of the countries of the world seek to promote the various economic, social and even psychological aspects of their peoples. In this context, the concept of quality of life is the general framework that combines these concepts.The word "life" expresses the general situation in which a person lives, and the word "quality" often expresses excellence and achieves an advanced level of positive characteristics. Hence, the quality of life is related to achieving a high level that encompasses various aspects of human life. The World Health Organization defined the quality of life as an individual's perception of his or her way of life in the context of the culture and values of the society in which he lives, and the relevance of this awareness to his goals, expectations and level of interest. The quality of life means improving the level of physical and social services Society, and the tendency towards lifestyle that is characterized by luxury, and this type of life can only be achieved by the society of abundance, a society that was able to solve all the living problems of the majority of the population and also means enjoying the physical conditions in the external environment and the sense of good, Life, and the individual's awareness of the forces and contents of his life and sense of life in addition to positive physical health and sense of happiness and to live a harmonious life compatible between the essence of human values prevailing in the community.It seems clear through the previous definitions that the concept of quality of life is very much related to the stability of the general situation of the individual, whether social, economic or even psychological, and the quality of life is achieved only by the individual satisfaction on all these aspects, which contributes to enhancing happiness in the general framework, This concept encompasses many dimensions defined by WHO in the field of physical area (pain, activity ...), psychological (positive thinking, education ...), level of independence (reliance on communication, ability to work ...) Social relations (personal relationships, social support. Environmental (household safety, water resources ...), and finally religiosity and personal beliefs. Hence, it is clear how overlapping the dimensions of the concept of quality of life are reflected in Figure (1).
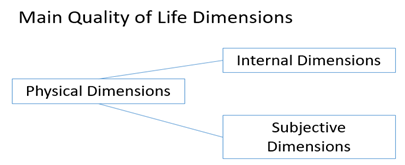 | Figure (1). Main Quality of Life Constraints |
4.2. Second Aaxis: Theoretical Approach to the Welfare Economy
- Achieving economic balance is an essential objective that economic supervisors seek to achieve. This is due to its positive advantages such as economic efficiency, growth and income distribution. This goal has been developed to interfere with social welfare and human concepts, and this concept is what is termed the welfare economy.The economies of the world today are striving to achieve advanced levels of well-being for their societies. The economy is the main tool for achieving this. It is linked to the concept of the welfare economy, and the welfare economy is defined as part of the social welfare that is governed by and influenced by economic factors in the light of economic potential. The maximum possible saturation of all goods and services to all members of the community, in the sense that there is an optimal allocation of resources, and the economy of prosperity and the development of the economy and looking at how to make the economic system the best possible is reflected in the creation of an optimal state of the economic system. Although the welfare economy addresses the macro issues, how these issues are addressed revolves around the microeconomics.In this regard, Bijou decides that there are two basic ideas to indicate the level of the overall economic well-being of society. These two ideas used by Bijou in his analysis are based on the idea of net social output. They involve the possibility of aggregating the satisfaction of individuals and the two ideas presented by Bijou:A. The size of national income: This idea means that increasing the national income of society leads to increased economic well-being, provided that the share of low-income is not less than it was before the increase, as Bejo stresses that increasing national income will lead to the economic well-being of society where The relationship between the level of national income and the level of economic prosperity is positive.B. The distribution of national income: Bejou urged that there be a redistribution of income for each period, so that this process will improve the economic situation of all members of society through the fair distribution of income, and that this distribution for the benefit of low incomes at the expense of the income High.The welfare economy is linked to economists pigou and Pareto, but A.Marshall is the first to address the welfare economy when he recognized the economy as a special role that was never discussed in his book Principles of Political Economy. He referred to the firm contribution of the economy to finding solutions to problems Social and social problems. It is implicit in the search for an optimal situation for the production, distribution and searches for the well-being of the society. This book also referred to national income when it realized that competition might not lead to an optimal situation or to raise what it called the "national divide" National income means Palm Talh current, it is known that we are currently intent on the national income to measure the extent of the economic prosperity and prosperity of different countries, but this does not deny touched by the predecessors A.Marshall to the economy of luxury, because the Muslims of the model of competition is to search for optimal situation for the market, Adam Smith, according to Samuelson, is the first theory to be exposed to the welfare economy. On the other hand, the concept of the welfare state refers to the state providing services, social insurance and aid to the members of society to achieve a high standard of living or guarantee a minimum. This concept is based on the right of every human being to a dignified life and a social and humane outlook based on a strong bond between the well-being of individuals and the well-being of society. Services and insurance in the welfare state include education, health, income, employment, disability insurance and old age, to name a few.
4.3. Measuring the Economy of Luxury
- The question of achieving advanced levels of the economic well-being of the members of society is a modern issue in the economic analysis. However, there are many approaches that have sought to identify mechanisms to achieve this goal,- Bariatric Analysis Practical AnalysisPareto is the first to present a recent analysis of welfare economies by interpreting the optimal state of well-being, which he defines as the highest attainable standard of living for all members of society without exception, so that any change at this optimal level leads to an increase in the standard of living of some Social groups, this change must result from harming other social groups and reduce their level of satisfaction from the optimal level, and therefore any difference that occurs from the optimal level of saturation will lead to failure to achieve prosperity In the area of allocation of production elements, Pareto's optimization is impossible if it is impossible to reorganize production in such a way as to increase the production of one or more goods without diminishing the production of other goods. In light of this, maximum economic welfare is achieved if the marginal conversion rate Production is equal to the marginal conversion rate of consumption per a couple of goods and per person consumes goods.- Analysis of Kaldor - HicksPerhaps the problem we face when trying to measure the welfare of society is the difference that may occur between the improvement in the standard of living of the individuals benefiting from those changes and the individuals involved. Hence the Hicks test set by default compensation for and create enough benefits, so that the winners can compensate the losers.Because the Kaldor and Hicks principle gave the decision-maker a flexible criterion for evaluating proposals that included the transfer of income from one social sector to another, it quickly replaced the Pareto principle as a yardstick for judging the proposed economic changes. Kaldor and Hicks based their formulation on "real output" and later circulated the idea to include cost and social return components. Thus, the Kaldor and Hicks principles were introduced into revenue and cost analysis as a preferred criterion for accepting or rejecting projects, It remains a source of great controversy in economic literature, since the Kaldor and Hicks standard does not require the beneficiaries of any policy change to compensate the losers in real terms, but the ability of these beneficiaries to assert that no The losers become because of this change in a worse situation, so the standard Kaldor and Hicks is primarily concerned with efficient investment of resources rather than distribution justice.- Analysis: I. Little and J. MirrleesThis analysis is based on the moral basis, that the winning individuals of the change compensate the losers by the low levels of satisfaction from the standard of living to achieve social justice and achieve the level of economic well-being of society, this model is the first attempt to combine the principles of economic welfare theory, Between the investment project evaluation accounts, by introducing the foundations of the welfare economics into the field of project analysis, which was limited to maximizing the material return from the projects to be established, focusing mainly on "See the accounting prices" without the introduction of many.Other considerations in the evaluation area, such as the distribution of benefits between different groups or regions and a pattern.The distribution of these benefits between consumption and savings and the authors revised and modified this approach.In a comprehensive manner.It is clear through Figure (1) that the concept of quality of life relates to objective dimensions based on what the society has the material possibilities of how to exploit them properly, in addition to this set of self-dimensions moreover, it expresses the satisfaction of the individual to believe about the life he lives in these two dimensions Which leads to the existential dimensions that reflect the depth of quality of life and the ideal size it can achieve. Within these dimensions, the social trend intersects with the psychological and medical direction of the quality of life. The social aspect relates to the quality of work, education, freedom of expression and belief. Self-perception of life satisfaction and psychological compatibility values, while the medical-oriented quality of life is related to public health for individuals and their quality.
4.4. Explanatory Theories of Quality of Life and Measuring Indicators
- - Explanatory theories of quality of lifeMany theories are explaining the concept of quality of life as a result of the breadth of this concept and the intersection of many areas in it, especially concerning sociology and economy, and despite the recent most theories on the quality of life, this term is considered to be an old one. Aristotle's book of ethics is one of the early sources of quality Life, where he said: Both the public or the riffraff and the upper class are aware of the good life in one way that they are happy, and Aristotle believes that good life is only a poetic state, and a kind of activity which corresponds to the modern concept of quality of life and hence Some theories explain the concept of quality of life, and return to the theories that tried to control this concept and identify its features we find:- Choice theoryWilliam Glaser is the founder of this theory that evolved from control theory, which explains both internal and external control. The theoretical basis was laid in 1894, but the term "control" changed to the term "choice." The importance of this theory is that it includes several dimensions in order to provide A good method of life management and treatment of various problems, and the idea of the theory mainly to avoid the common idea that calls for external control in the lives of others, and the external control is the sense of the individual control of others in his life, and deep in this theory to identify the main axes that can be implemented through the achievement of quality of life , Where it includes Gluttonous axes generally relate to the behaviour of an individual with a focus on the behaviour of this relationship with the rest of the community, has identified four basic needs Glaser contribute to enhancing the quality of life of the individual: the need for love and belonging, the need for power, the need for freedom of the need for fun.- The theory of six factorsAccording to Carroll Ryff, the concept of quality of life is characterized by mobility and pluralism as a result of the intersection of many dimensions within this concept, and despite the multiplicity of these dimensions between the psychological and social and even those related to general behavior, but can be summed up in self-acceptance, Which contributes significantly to the quality of life, in addition to the purpose of life and positive relationships This dimension focuses on the extent to which individuals recognize the meaning of their existence and the pursuit of their goals in addition to their ability to establish a positive relationship between them, and independence and personal maturity Independence includes all personal aspects of individuals, especially with respect to beliefs, while personal maturity is a function of the ability to self-determination.- The theory of Joseph SirgySatisfaction with the level of life that the individual lives according to this theory is based on the difference between the reality of the individual and the ideal picture of the standard of life. Hence, reducing the difference between the two images leads to a higher quality of life. Conversely, the large difference between the two images leads to dissatisfaction, Especially in terms of materiality. In his theory, Joseph Sirgy asserts that the satisfaction of society members is made in terms of income, wealth and material possessions. This theory is called the physical theory of Joseph Sirgy, and it may be added to this aspect some of the beliefs that individuals have in their minds and are associated with values such as relationships Profession and so on.- Veenhoven modelThis model is one of the latest models of quality of life and its components. According to Veenhoven, the quality of life consists of four dimensions:- Internal and external factors: The quality of life on a range of factors emanating from within the individual the extent of the development of its ability to address the problems and obstacles that prevent the raising of quality of life.- In addition to this must provide a range of external factors provided by the general environment of society, and the combination of these factors, internal and external, collectively represent opportunities for life.- The benefit provided by life: This indicates the extent to which individuals can exploit the benefits provided by the external environment to them.- The general view of life and estimated: This element is intended to a personal vision of individuals and judges the quality of the neighbourhood.
5. Comparative Study
5.1. Quality of Life and Welfare Economy in Algeria
- Economic development is the main objective that economic policy supervisors fail to achieve. The great changes in the concept of development have led to a great development in the indicators that can be used to measure the achievement of the objectives of economic development. As evidenced by the past two axes, it is clear how closely the quality of life and the welfare economy are interrelated. This is illustrated by the common points between the two concepts. The function of the indicator Economic development is no longer limited to describing the characteristics of the economic system, but also the social characteristics, and thus highlights the relationship between the quality of life and economic well-being, and it should be noted that there is an international trend vigorously by most countries of the world and many international bodies pour into this subject, Algeria is not Exceptions to these developments The following are some of the indicators related to the Algerian economy related to this subject.
5.2. The Development of Algerian Economic Growth as an Indicator of Economic Well-being and Quality of Life
- Economic growth is related to GDP, which is defined as all final goods and services produced in a country over a given period. This indicator focuses on the value of final goods and services to avoid double counting. There are many economists who consider it the best measure of economic behaviour. The index is one of the most important indicators of measuring economic well-being. Figure (2) represent this index in Algeria.
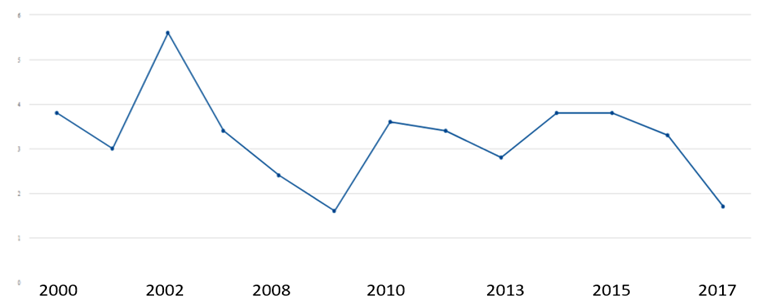 | Figure (2). The growth rates Development of the Algerian economy between (2000-2017) (Source: World Bank) |
5.3. Development of Per Capita GDP as an Indicator of Economic Well-being and Quality of Life
- Per capita GDP is one of the economic indicators that are related to the concept of income distribution to members of society or to the income/expenditure groups that make up this society. This study is of economic, social and political dimensions. It can investigate the impact of various economic policies adopted by the state Influence on the incomes of different social groups. This analysis has been fundamental in economics since classical school, which studied the distribution of income among the three strata of society: workers, capitalists and landowners. Adam Smith, Ricardo and Marx The second is the determinants of the income of each stratum. The second traces the effects of economic growth on the method of income distribution among the factors of production. At present, this indicator is one of the most important indicators of economic welfare. Figure (3) shows Algeria's per capita GDP growth as an indicator of well-being.
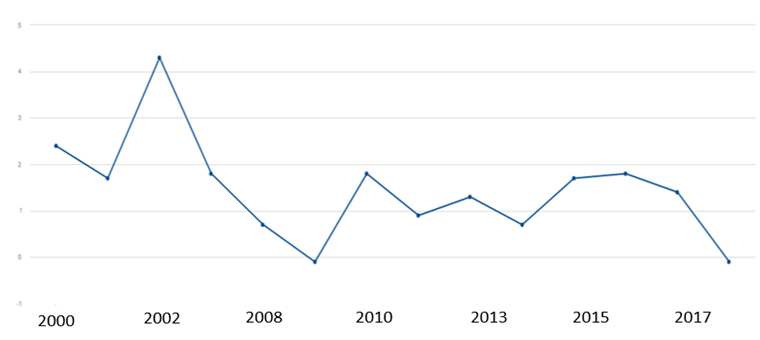 | Figure (3). Algeria's per capita GDP growth for 2000-2017 |
5.4. Local Development as an Instrument for Achieving a Welfare Economy and Achieving an Advanced Stage of Quality of Life
- Social promotion of development is based on reliance on local or local communities accredited by small networks of society. Therefore, the social proposal in local development aspects suggests that participatory democracy must be relied upon. It is believed that the economy is at the service of man rather than vice versa. Local development with a set of characteristics that are closely related to both the economy of well-being and quality of life, especially if we consider that local development is a kind of division of labour within the framework of the policy for the overall development of society as a whole, especially if the society is characterized by multi-geographical regions with different resources and capabilities, Through the perspective of a separate part of the development strategy of society in general, but the legitimacy of this development stems from their outstanding contribution in helping to cope with the problems of the large community as well as face the problems of regional or local, in addition to local development based on the cooperation and mutual influence between the activities of society and the elements of social life, whether governmental or non-governmental, should not be left to chance. Rather, the appropriate climate and organization must be created for constructive cooperation or positive interaction between these bodies. Each other, not negative to impede some of them, development strategies in the developing country should be based on state intervention in various economic, social and other affairs in order to achieve a higher level of well-being and development and in a fair manner for all citizens.With regard to local development in Algeria, the year 2000 has been the turning point in the development process in Algeria since independence. After the move towards a market economy and a series of structural adjustments to consolidate its principles, which were agreed with the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank, The scheduling and reduction of debt, the implementation of a series of required structural adjustments in the economy, the achievement of acceptable growth rates during the period from 1995 to 2000, the return of political stability, the improved security situation and the increase in financial revenues derived from the collection of debts Which was the result of the high prices of fuel in the world markets, Algeria has undertaken large development programs to achieve and support economic reforms, by allocating huge funds for investment spending for these various development programs, which had the share of local development a large part in various stages, starting with the economic recovery program 2001 - 2004 to the last Five-Year Program 2010-2014.There are programs that are supportive and supportive of economic reforms that have benefited local communities in the local development aspect, which are responsive to specific situations. They are designed to ensure that these situations are overcome.Economic Recovery Program (2001-2004): This program aims at reducing poverty, providing job opportunities, achieving regional balance and revitalizing the national space, and allowing the stability of the national economy and re-launching the path of economic growth which reached its peak in 2003, Which has been accompanied by a number of achievements for the population in the areas of health, water resources, rural development and in several other sectors.Five-Year Development Program (2010-2014): The Five-Year Development Program, approved by the Council of Ministers on 25 May 2010, is the base and engine for a specific development vision and policy by the public authorities. It is also considered as the second five-year development program in the period from 2010 To the year 2014. Algeria has allocated an extraordinary financial envelope to this program, which has not yet been allocated to the developing country, which is estimated at 21.214 billion dz (equivalent to 286 billion US dollars), including a current program (i.e., the remainder of the supplementary program to support growth 2005). 2009) at $ 9680 billion (equivalent to $ 130 billion) US $), a new program of $ 11534 billion (equivalent to 155 billion US dollars).The program has several objectives in terms of promoting local development in the country. It has worked through its financial envelope to consolidate economic growth within the dynamic of national reconstruction launched ten years ago. These goals included the support of human development, improving living conditions in the countryside Continuing to expand the housing base in its various forms, continue the agricultural and rural renewal and improve the food security of the country.South Development Program: The problem of development of the southern regions remains closely linked to the respect of the coastal ecosystems in the oases and deserts that characterise these areas and to preserve their scarce resources. In the light of various development plans and special programs, the regions of the South have benefited as other regions of the country have benefited from an investment effort A special fund was established for the development of the southern regions indicating the will of the state to pursue a policy aimed at reducing social and economic disparities between the regions, a national fund specifically for the development and promotion of the regions of the South, A part of the homeland to create a kind of regional balance between different regions of the country.Despite all these efforts, the development of local development in Algeria continues to face two main obstacles: the total area of more than 2.38 million km2, which is central to decision-making and management. Also, the southern and border states suffer from significant shortcomings compared to the northern states. The population of Algeria in the northern states is more than 70%.
6. Discussion & Conclusions
- In addition, the quality of life concept is highly intertwined with the concept of the welfare economy, especially in the social sphere. Besides, the implementation of the quality of life dimensions is highly supported by all relevant international bodies, especially in the economic aspect related to the fairness of the income stream and economic development in its comprehensive concept. Hence the long road for developing countries in general and Algeria in particular, where the latter suffers from significant imbalances in this regard. Certainly, the positive repercussions for the promotion of indicators of the welfare economy in Algeria and the quality of life N collection holds if the primary objective pursued by him since Algeria Alasagtlal, but it is out of the circle of economies rentier and diversify the sources of funding, in addition to the promotion of local development, and to achieve this proposal are the following points:1- The activation of the welfare economy in Algeria is certainly reflected positively on many areas, especially social ones, which will pave the way to develop the concept of quality of life and change the old view of economic policies.The fact that the absence of the social aspect in Algerian economic policies is unfair, but that the mechanisms envisaged in this framework must be carefully re-examined should be kept abreast of developments in the outside world since Algeria cannot remain isolated from it.2- Algeria urgently needs to diversify the sources of total income by optimizing and diversifying the available resources, especially the sectors of industry, agriculture and agriculture. These sectors are almost paralysed by the great control of the hydrocarbons sector in the Algerian economy.3- The key to the fairness of income distribution in Algeria is not only through the activation of local development, especially in the southern regions, which suffer from significant imbalances in this area, but this is also many attempts, such as the South Development Funds.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML