Diana Laila Ramatillah1, Syed Azhar Syed Sulaiman1, Amer Hayat Khan1, Dato’ DR Ong Loke Meng2, Markum3
1Descpline of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia
2Physician and Consultanta in Nephrology and Hemodialysis Ward at General Hospital Penang, Malaysia
3Physician and Consultant in Nephrology and Hemodialysis Ward at Cempaka Putih Islamic Hospital Jakarta, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Diana Laila Ramatillah, Descpline of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Background: Almost, all of the countries in the world have a problem in increasing the prevalence of hemodialysis patients and it is followed by mortality cases. The quality of life is one of the indicators to reduce mortality cases, while physician’s knowledge on hemodialysis ward can give impact to quality of life and clinical outcome patients. Objective: To assess validity and reliability of a pilot study for the physician's knowledge questionnaire. Method: A cross-sectional study was carried out a pilot study of physicians knowledge on hemodialysis ward in Cempaka Putih Islamic Hospital Jakarta, Indonesia, using a new questionnaire that is not validated yet. Reliability was evaluated by intraclass correlation coefficients for test reliability and validity assessment with face to face interview and Cronbach’s alpha for internal consistency. Statistical analysis included descriptive statistics and Cronbach’s alpha. Results:There had 4 topics in this questionnaire. Before checking the validity of question’s item, there had 25 questions but only 12 questions were valid. Among 12 questions, there had five questions for topic 1 (laboratory value check), two questions for topic 2 (physical check), four questions for topic 3 (therapeutic drug monitoring) and one question for topic 4 (nutrition / keeping protein intake). Among 4 topics, topic 4 looked easy for physicians, while nine physicians had 75-100% right answer. This pilot study had included 15 physicians, 11 physicians among them were female. The average of physician’s age was 30-49 years old. Conclusions: The questionnaire of physician’s knowledge is valid and reliable and Cronbach's alpha for 12 items of questions is 0,842.
Keywords:
Physician’s knowledge, Pilot Study, Hemodialysis, Reliability, Cronbach’s Alpha
Cite this paper: Diana Laila Ramatillah, Syed Azhar Syed Sulaiman, Amer Hayat Khan, Dato’ DR Ong Loke Meng, Markum, Validity and Reliability of Pilot Study for Physician’s Knowledge Questionnaire on Hemodialysis Ward in Cempaka Putih Islamic Hospital Jakarta, Indonesia, International Journal of Internal Medicine, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2016, pp. 8-13. doi: 10.5923/j.ijim.20160501.02.
1. Introduction
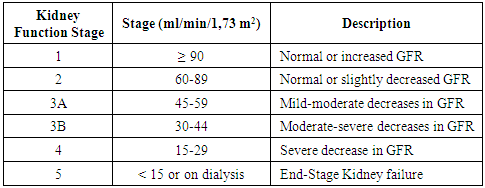
Hemodialysis is one of the processes in replacing kidney fungsion [1]. Patients who are doing hemodialysis will be engaged with this treatment for a long time or may be as long as their life [2]. Patients will come two or three times in a week for running this treatment [3]. Before and after running hemodialysis, patients condition have to be good such as their electrolyte, vital sign, blood sugar, clearance creatinine and blood urea nitrogen. During hemodialysis process, loss of electrolyte will be possible because of reducing of the fluid in their body. To avoid side effect after hemodialysis, checking it is necessary. Compliance patient is the first concern in hemodialysis including in medication, consumption of water, and food. Now, physician knowledge about hemodialysis treatment also being a great attention to improving the quality of life hemodialysis patients. There is some knowledge that physicians in the hemodialysis ward have to know.A. Laboratory Value Check To check the level of GFR (glomerular filtration rate) patients, Usually, the physician will use Cockroft-Gault Formula [4]. For this formula, clearance creatinine, serum creatinine, body weight, and age have to be known [4].Creatinine is produced in the muscles by the changing of non-enzymatic from creatinine and phosphocreatinine [6]. The normal serum creatinine level is 0,5 to 1,0 mg/dl according to diurnal and menstrual variations, pursuit and diet [6]. Increasing Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is also one of the indicators for decreasing of kidney function. One of the symptoms of increasing BUN is nausea. Sometimes, patients think, cause is from gastric ulcer so,they will take gastric ulcer medication otherwise it is from kidney problems (increasing of BUN). Table 1. Level of Kidney Function Based on GFR [5]
 |
| |
|
For electrolytes, usually, sodium, potassium, phosphate and calcium level will be checked. Rising of sodium level can give an indication that patient’s blood pressure is also increased. Increasing potassium level is caused by the resistance of water fluid in the body. Decreasing of kidney function will impede water fluid body excretion. Renal failure also causes increasing of phosphate elimination, therefore, calcium level will be low [2].Albumin is one of the types of protein in the body. Protein is not normally filtered at the glomerulus and is present only in trace amounts in the urine [2]. Proteinuria as an indicator of damaging in glomerular [2]. Proteinuria may cause elevations in serum creatinine and should be considered as an early marker of kidney damage [2]. Physicians should give their attention to the hypoalbuminemia condition due to it can give dangerous situation to the patients moreover if the patients get medication with normal doses [7]. In pharmacokinetics, in the body, drugs will be divided into two types. First, free drugs and the second the binding drugs of albumin. Effect of medication will be achieved when the free drugs bind to receptors in the body. In this case, patients with hypoalbuminemia will be easy to get toxicity. Therefore, this condition has to be the first attention for physicians before giving medications to the patients.For patients who are doing hemodialysis, usually, hemodialysis process will reduce blood glucose. Sometimes, patients will be hypoglycemia if patients did not take any meals before hemodialysis. Hemoglobin is one of the most important things that must be checked in hemodialysis patients. Patients with renal failure have less erythropoietin in their body, while erythropoietin is one of the hormones in the body that help bone marrow to produce erythrocyte. If erythrocyte less, it will give impact to hemoglobin level. Physicians will order to give a blood transfusion to the patients if hemoglobin level below 8 mg/dl [2]. To maintain their hemoglobin, usually, physicians will prescribe anemia medication. Anemia is a condition that hemoglobin level below normal value (below 12 mg/dl) [2].B. Physical Check (Blood Pressure before, during and after Hemodialysis)Almost all patients with renal failure will have problems with blood pressure. Decreasing of kidney function will activate renin-angiotensinogen system (RAS) while, angiotensin I activate angiotensin II by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) [2]. Angiotensin II will cause high blood pressure (hypertension) [2]. Usually, patients will get antihypertensive drugs. Some of them will be hypotension during or after hemodialysis if they did not take any antihypertensive drugs before hemodialysis. Physicians have to look to the blood pressure patients before doing hemodialysis (blood pressure patients must be normal or not too low). If it is too low, hemodialysis will be canceled at that time. C. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Varying the dose or dosing interval for a given agent may not be sufficient to guarantee therapeutic efficacy and avoid toxicity in patients with renal failure [8]. In prescribing, physicians should know the therapeutic drug concentration and level of toxicity. Drug level monitoring can greatly enhance individualized therapy, especially for patients with renal failure [8].Patients who undergoing dialysis treatment are required special attention to the schedule of dose and the supplemental dosing for agents substantially cleared by dialysis [8]. The molecular weight, water solubility and degree of protein binding for any given drug represent the major determinants of its pharmacologic agents which are removed by convective transport in hemofiltration procedures [8].D. Nutrition (Keeping Protein Intake) Usually, for hemodialysis patients, protein intake is quite strictly. One of the reasons for this is molecule weight9. Not only that, degradation result of protein is creatinine serum. Thus, the higher consumption of protein will increase more creatinine serum.
2. Methods
Study Design and SubjectsA cross-sectional study was carried out a pilot study of physicians knowledge on Hemodialysis Ward in Cempaka Putih Islamic Hospital Jakarta, Indonesia using a new questionnaire that is not validated yet. Fifteen medical internist specialist doctors at hemodialysis ward Cempaka Putih Islamic Hospital Jakarta were included in this pilot study since September till October 2015. They answered 25 questions of the questionnaire to assess their knowledge related to hemodialysis process and impact to the patient. Reliability was evaluated by intraclass correlation coefficients for test reliability and validity assessment with face to face interview and Cronbach’s alpha for internal consistency. Statistical analysis included descriptive statistics and Cronbach’s alpha.
3. Results
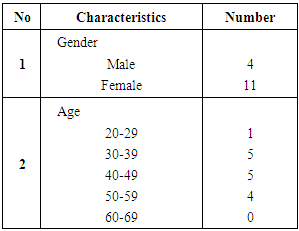
There were 4 topics in that physician’s knowledge questionnaire;1. Laboratory Value CheckSome of the laboratory value must be checked;a. Clearance creatinine, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) b. Electrolytes (Sodium, Potassium, Phosphate, Calcium)c. Albumin level (To avoid toxicity)d. Blood glucose e. Hemoglobin level2. Physical Check (Blood Pressure before, during and after Hemodialysis)3. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring4. Nutrition (keeping protein intake)There were 15 medical doctors that answered 25 questions. Among 25 questions, 12 questions were valid.Table 2. Sociodemography of Physicians
 |
| |
|
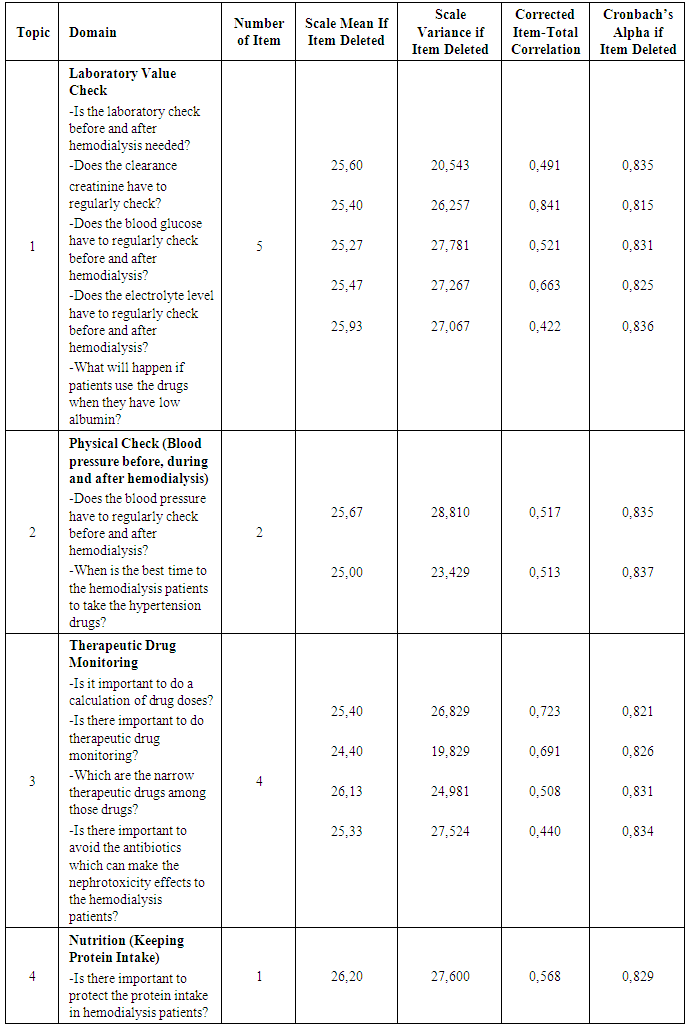
The number of female physicians is more than male physicians. Based on the age, the physicians who answered the questionnaire; 5 physicians were 30-39 years old, 5 physicians were 40-49 years old, 4 physicians were 50-59 and only 1 physician was 20-29 years old.Table 3. Internal Consistency Reliability
 |
| |
|
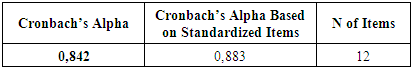
Table 4. Reliability Statistics
 |
| |
|
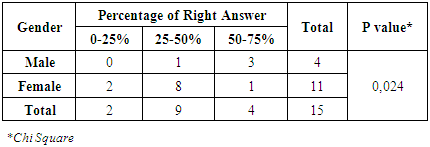
For 12 items of questions, Reliability of the physician’s knowledge is 0,842. Table 5. Correlation Between Gender and Percentage of Right Answer
 |
| |
|
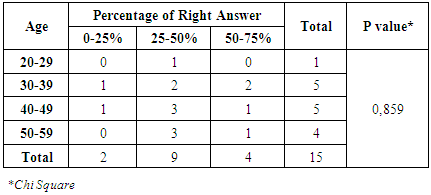
There had a significant relationship between gender and percentage of right answer (P-value = 0,024). Only for physicians had a 50-75% of right answer while, three of them were male physicians and two physicians had a 0-25% of right answer and they were female. From table 5, the number of physicians who had a 25-50% of the right answer were nine physicians. Eight of nine physicians were female.Table 6. Correlation Between Age and Percentage of Right Answer
 |
| |
|
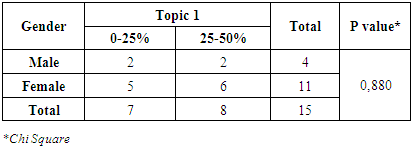
There had no significant correlation between age and percentage of right answer (P-value = 0,859). Three of nine physicians were 40-49 years old and also three of them were 50-59 years old. Only four physicians had a 50-59% right answer, while, two of them were 30-39 years old.Correlation between Each Topic of questionnaire with Gender and Age of PhysiciansTopic 1Table 7. Correlation Between Gender and Topic 1
 |
| |
|
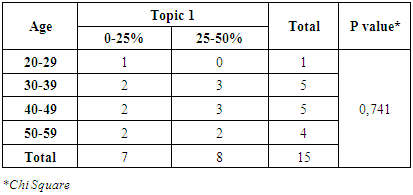
Table 8. Correlation Between Age and Topic 1
 |
| |
|
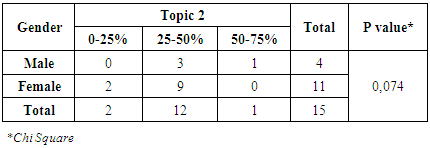
From table 8 and 9, it can be seen that no one among the physicians that had the right answer more than 50%. Despite, topic 1 was the important topic in that questionnaire. For correlation between gender-topic 1 and also age-topic 1, it had no significant relationship.Topic 2Table 9. Correlation Between Gender and Topic 2
 |
| |
|
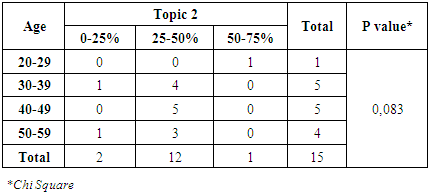
Table 10. Correlation Between Age and Topic 2
 |
| |
|
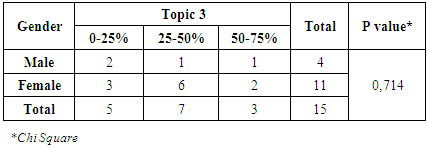
From table 9 and 10, it can be known that 12 physicians had a 25-50% right answer on the topic 2. It was still less than expectation. For physical check question’s such as blood pressure, physicians should know the answer properly because renal disease such as end-stage renal failure will give impact to the blood pressure. There had no significant relationship between gender, age and topic 2.Topic 3Table 11. Correlation Between Gender and Topic 3
 |
| |
|
Table 12. Correlation Between Age and Topic 3
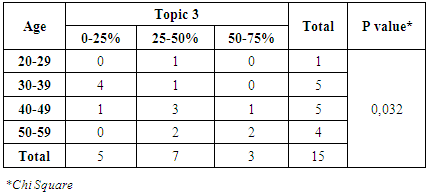 |
| |
|
From table 11 and 12, it can be known that 7 physicians had a 25-50% right answer on the topic 3. Only 3 physicians had a 50-75% right answer. It was still less than expectation but it was slightly better than topic 1 and 2. For therapeutic drug monitoring, physicians looks had more knowledge than previous topics. There had a significant relationship between age and topic three (P-value = 0,032) but it was not for the relationship between gender and topic 3.Topic 4Table 13. Correlation Between gender and Topic 4
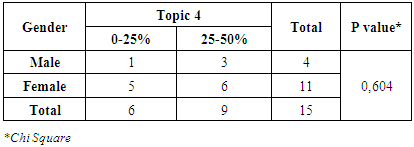 |
| |
|
Table 14. Correlation Between Age and Topic 4
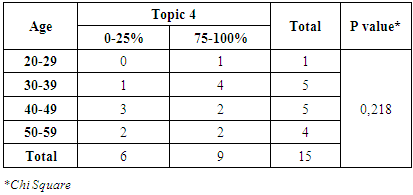 |
| |
|
From table 13 and 14, it can be seen that 9 physicians had a 25-50% right answer on the topic 4. Protein is one of the nutrition which has to be restricted for hemodialysis patient’s consumption. This knowledge is the common knowledge for the physicians because more than 50% of physicians had a 75-100% right answer. There had no significant c between correlation gender, age and topic 4.
4. Discussion
In the ward, usually, the physician is helped by nurses. Most of the time hemodialysis patients will be in the ward with nurses. Physicians will do check only for one time per day and they don’t follow hemodialysis process from beginning till the end. If the emergency situation happened in the hemodialysis ward, nurses will call the physicians to come and check the patients. To avoid the emergency situation in the hemodialysis ward especially for hemodialysis patients, physicians should know and apply the knowledge that related to the hemodialysis process, and medication.There had 4 topics in that questionnaire. For first topic (laboratory value check) has 5 questions. The first topic was very important knowledge which physicians should have. The good result of laboratory value like clearance creatinine, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) are the indicators that hemodialysis process well was done. Usually, before hemodialysis process, those values would be high and it will be low after hemodialysis. The electrolytes level check is one of the ways to avoid the side effects of hemodialysis. During hemodialysis, reducing of the fluid body is happening. When fluid remove from the body, electrolytes like sodium, potassium, phosphate and calcium will be decreased. Patients will be dehydration when sodium low. Low potassium will give harm effect to cardiac-like arrhythmias [2]. Low phosphate and calcium will give spasms or weakness to the patients [2]. Albumin level also including to the laboratory value check for the hemodialysis patients because it will give dangerous effect to the patients who take the normal doses of drugs if albumin level low. Not only that, for diabetic patients who are doing hemodialysis, blood glucose is also the important laboratory value check. Usually, hemodialysis process will make the blood glucose level become low [2]. Moreover, if patients don’t take any meals before doing hemodialysis process so after hemodialysis process patients will have dizzy, tired and pale because of low blood glucose. Hemoglobin level is also the primary laboratory value check because of the Erythropoietin hormone that is located in the kidney is reduce. Kidney failure will make the Erythropoietin hormone reduce otherwise this hormone is very important in helping bone marrow to produce erythrocytes [2]. Low erythrocytes will affect to the low hemoglobin [10]. The second topic (physical check) is also important. Mostly kidney failure will give effect to blood pressure. When patients get kidney failure, it means blood flow to the kidney is reduce then it will make the Renin-Angiotensinogen System (RAS) become active. Activating of RAS will produce angiotensin II then it will make blood pressure increase (hypertension) [11]. Physical checks such as blood pressure before, during and after hemodialysis process are needed. Hemodialysis process can not start if blood pressure is not normal, while, patients must get antihypertensive drugs before hemodialysis process if blood pressure too high.The third topic (therapeutic drug monitoring) is needed to know by physicians. Chronic heart failure (CHF) is one of the comorbidities that always happen in almost all hemodialysis patients. Digoxin is a primary drug for CHF and it is the narrow therapeutic drug. If the dose slightly increases, it can give toxicity to the patients [2]. Thus, physicians must aware to this treatment. Not only digoxin or narrow therapeutic drugs that must be checked but also nephrotoxicity drugs such as Aminoglycoside group. The adjusting dose of some drugs is needed for hemodialysis patients. The fourth topic is also needed to know. Keeping protein intake will help the patients condition [2]. When patients start doing hemodialysis, it means GFR less than 15 ml/minute then kidney can not do its function as normal as before [12].
5. Conclusions
This is the first study about physician’s knowledge that had been done in Indonesia especially about hemodialysis. Although this study is just a pilot study for new questionnaire of physician’s knowledge about hemodialysis, yet it can give a good impact for constructing of the new questionnaire. From this pilot study, it can be concluded that questionnaire is valid and reliable, while, Cronbach's alpha for 12 items of questions is 0,842.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to appreciate IPS Fellowship USM for their support in this publication.
References
| [1] | Sitprija V. Nephrology in South East Asia: fact and concept. Kidney Int Suppl. 2003; 63(83): S128-130. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12864891. |
| [2] | Koda-Kimble, Mary Anne, Young LY, Alldrege, BK, Corelli, RL, Guglielmo, BJ, Kradjan, WA, Williams B. Applied Therapeutics, The Clinical Use of Drugs Ninth Edition.; 2008. |
| [3] | Of OJOS, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013; 3(1): 4-4. doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.76. |
| [4] | Krishnaswamy R, Lukose S. EVALUATION OF THE THREE METHODS AVAILABLE FOR THE. Int J Clin Biochem Res. 2015; 2(June): 83-88. |
| [5] | Johnson D. Diagnosis, classification and staging of chronic kidney disease. Cari Guidel. 2012; (July): 1-31. |
| [6] | Amin N, Mahmood RT, Asad MJ, Zafar M, Raja AM. Evaluating Urea and Creatinine Levels in Chronic Renal Failure Pre and Post Dialysis: A Prospective Study. J cancer Surviv Res Pract. 2014; 2(2): 2-5. |
| [7] | Foundation NK. Kdoqi Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes and Ckd: 2012 Update Notice Section I: Use of the Clinical Practice Guideline. Yajkd. 2012; 60(5): 850-886. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.07.005. |
| [8] | Swan SK, Bennett WM. Conferences and Reviews Drug Dosing Guidelines in Patients With Renal Failure. West J Med. 1992. |
| [9] | Hess HD, Lascano CE, Flórez H. Blood and Milk Urea Nitrogen as a Tool to Monitor the Protein Nutrition of Cattle under Tropical Conditions. Deutcher Tropentag. 2000:1-6. |
| [10] | Dasari P, Venkateshwarlu K, Venisetty Rajk. Management of Comorbidities in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Prospective Observational Study. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014; 6(2): 2-6. |
| [11] | Chang B, Lau V, Ong KY, Yap CW, Vathsala A, How P. Predictors of anemia in a multi-ethnic chronic kidney disease population: a case – control study. Springerplus. 2015. doi:10.1186/s40064-015-1001-z. |
| [12] | Venkat KK. Proteinuria and Microalbuminuria in Adults; Significance, Evaluation, and Treatment. South Med J. 2004; 97(10): 969-980. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML












