Nurbek Kuchkarov
PhD., Associate Professor, National University of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Nurbek Kuchkarov, PhD., Associate Professor, National University of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2026 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
This article determines the water content and water deficit indicators in the leaves of Sedum spectabile, Sedum spurium, Kalanchoe laciniata, and Kalanchoe daigremontiana species during the season in the Tashkent hills, and provides information on the changes in these physiological indicators in relation to environmental factors and their adaptive characteristics in conditions of severe air and soil drought.
Keywords:
Sedum spectabile, Sedum spurium, Kalanchoe laciniata, Kalanchoe daigremontiana, Vegetation, Water content, Water deficit, Abiotic factor, Air temperature, Soil temperature, Soil moisture
Cite this paper: Nurbek Kuchkarov, Ecophysiological Properties of Some Species of the Crassulaceae Family Under the Influence of Abiotic Factors, International Journal of Genetic Engineering, Vol. 14 No. 1, 2026, pp. 28-32. doi: 10.5923/j.ijge.20261401.05.
1. Introduction
Abiotic factors (air temperature, relative humidity, soil temperature, soil moisture) play a significant role in the optimal course of plant life processes, and during vegetation, soil salinity and air drought conditions cause water shortages in various organs, which leads to morpho-physiological changes in the stages of growth and development. In determining the tolerance to such extreme conditions, it is of great importance to determine the maximum, minimum, and optimal ranges of leaf water content and water deficit indicators [1].
2. Literature Analysis and Methods
T.U. Rakhimova studied the bioecological, biomorphological, and physiological (water regime) properties of forage and food plants in the Fergana Hills and Kyzylkum Deserts, and determined the resistance of plants to drought in the desert ecosystem and their adaptation properties based on correlation analyses. O.N. Imomov studied the bioecology of some useful food plants in the Chust-Pop Hills, studied water deficit, water content, transpiration intensity, water holiding capacity, and determined the adaptation properties to the environment [3,4,5].Leaf water deficit was studied using the Catsky method and scientific results were obtained. The leaf water deficit (ST) relative to full saturation was calculated using the O. Stocker formula, and the water content was determined using the gravitational method [2].
3. Results
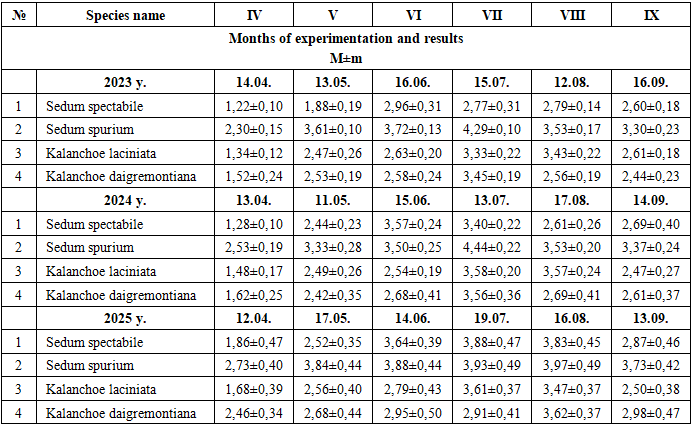
In the first year of the Kalanchoe laciniata vegetation (2023 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +24,5°C, the average soil temperature was +20,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 20,9±0,18%, the water content of the leaf plate was 95,4% when the average temperature was +22,5°C, and the water deficit in the leaf was 1,34±0,12%. In May, the air temperature is +29,7°C, the soil temperature is +28,0°C, the soil moisture is 20,0±0,64%, the leaf plate temperature is +27,5°C, the water content is 93,4%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,47±0,26%. In June, the air temperature is +36,5°C, the soil temperature is +37,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,1±0,60%, the leaf plate temperature is +34,3°C, the water content is 92,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,63±0,20%. In July, the air temperature is +38,2°C, the soil temperature is +38,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,5±0,39%, the leaf plate temperature is +35,9°C, the water content is 92,1%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,33±0,22%. In August, the air temperature is +34,4°C, the soil temperature is +33,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,3±0,53%, the leaf plate temperature is +32,2°C, the water content is 90,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,43±0,22%. In September, when the air temperature was +28,4°C, the soil temperature was +25,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,1±0,56%, and the leaf plate temperature was +26,4°C, the water content was 92,0%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,61±0,18% (Table 1).Table 1. Water deficit in plant leaves (in%) (2023-2025 years)
 |
| |
|
In the second year of the vegetation period (2024 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +22,6°C, the average soil temperature was +19,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 18,1±0,69%, the water content at the leaf plate temperature of +21,9°C was 95,4%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 1,48±0,17%. In May, the air temperature is +27,1°C, the soil temperature is +23,0°C, the soil moisture is 19,1±0,38%, the leaf plate temperature is +25,8°C, the water content is 93,4%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,49±0,26%. In June, the air temperature is +35,5°C, the soil temperature is +35,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,7±0,86%, the leaf plate temperature is +33,8°C, the water content is 92,7%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,54±0,19%. In July, the air temperature is +36,3°C, the soil temperature is +37,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,43%, the leaf plate temperature is +34,7°C, the water content is 91,3%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,58±0,20%. In August, the air temperature is +35,6°C, the soil temperature is +34,0°C, the soil moisture is 11,8±0,55%, the leaf plate temperature is +33,4°C, the water content is 90,7%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,57±0,24%. In September, when the air temperature was +28,8°C, the soil temperature was +24,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,0±0,87%, and the leaf plate temperature was +26,4°C, the water content was 91,0%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,47±0,27%.In the third year of the vegetation period (2025 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +23,0°C, the average soil temperature was +21,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 19,5±0,56%, the water content at the leaf plate temperature of +20,0°C was 94,8%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 1,68±0,39%. In May, the air temperature is +29,0°C, the soil temperature is +24,0°C, the soil moisture is 19,8±0,39%, the leaf plate temperature is +23,5°C, the water content is 93,0%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,56±0,40%. In June, the air temperature is +32,0°C, the soil temperature is +34,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,0±0,45%, the leaf plate temperature is +31,0°C, the water content is 91,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,79±0,43%. In July, the air temperature is +40,0°C, the soil temperature is +42,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,43%, the leaf plate temperature is +32,2°C, the water content is 91,3%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,61±0,37%. In August, the air temperature is +34,6°C, the soil temperature is +35,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,53%, the leaf plate temperature is +30,0°C, the water content is 90,7%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,47±0,37%. In September, when the air temperature was +27,8°C, the soil temperature was +24,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,9±0,69%, and the leaf plate temperature was +24,2°C, the water content was 92,6%, and the leaf water deficit was 2,50±0,38%.In the first year of the Kalanchoe daigremontiana vegetation (2023 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +24,5°C, the average soil temperature was +20,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 20,9±0,18%, the water content of the leaf plate was 96,3%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 1,52±0,24%. In May, the air temperature is +29,7°C, the soil temperature is +28,0°C, the soil moisture is 20,0±0,64%, the leaf plate temperature is +28,3°C, the water content is 95,3%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,53±0,19%. In June, the air temperature is +36,5°C, the soil temperature is +37,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,1±0,60%, the leaf plate temperature is +35,2°C, the water content is 94,9%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,58±0,24%. In July, the air temperature is +38,2°C, the soil temperature is +38,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,5±0,39%, the leaf plate temperature is +36,5°C, the water content is 94,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,45±0,19%. In August, the air temperature is +34,4°C, the soil temperature is +33,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,3±0,53%, the water content of the leaf plate is 95,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,56±0,19%. In September, when the air temperature was +28,4°C, the soil temperature was +25,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,1±0,56%, and the leaf plate temperature was +27,6°C, the water content was 96,0%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,44±0,23%.In the second year of the vegetation period (2024 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +22,6°C, the average soil temperature was +19,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 18,1±0,69%, the water content of the leaf plate at temperature of +22,6°C was 95,6%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 1,62±0,25%. In May, the air temperature is +27,1°C, the soil temperature is +23,0°C, the soil moisture is 19,1±0,38%, the leaf plate temperature is +26,3°C, the water content is 94,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,42±0,35%. In June, the air temperature is +35,5°C, the soil temperature is +35,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,7±0,86%, the leaf plate temperature is +34,5°C, the water content is 94,1%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,68±0,41%. In July, the air temperature is +36,3°C, the soil temperature is +37,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,43%, the leaf plate temperature is +35,2°C, the water content is 94,1%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,56±0,36%. In August, the air temperature is +35,6°C, the soil temperature is +34,0°C, the soil moisture is 11,8±0,55%, the leaf plate temperature is +34,3°C, the water content is 95,0%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,69±0,41%. It was determined that in September the air temperature was +28,8°C, the soil temperature was +24,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,0±0,87%, the water content of the leaf plate at temperature of +27,2°C was 95,5%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,61±0,37%.In the third year of the vegetation period (2025), the maximum air temperature in April was +23,0°C, the average soil temperature was +21,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 19,5±0,56%, the water content at the leaf plate temperature of +21,3°C was 96,4%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,46±0,34%. In May, the air temperature is +29,0°C, the soil temperature is +24,0°C, the soil moisture is 19,8±0,39%, the leaf plate temperature is +24,6°C, the water content is 95,5%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,68±0,44%. In June, the air temperature is +32,0°C, the soil temperature is +34,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,0±0,45%, the leaf plate temperature is +32,5°C, the water content is 94,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,95±0,50%. In July, the air temperature is +40,0°C, the soil temperature is +42,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,43%, the leaf plate temperature is +33,5°C, the water content is 93,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,91±0,41%. In August, the air temperature is +34,6°C, the soil temperature is +35,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,53%, the leaf plate temperature is +31,3°C, the water content is 95,2%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,62±0,37%. In September, when the air temperature was +27,8°C, the soil temperature was +24,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,9±0,69%, and the leaf plate temperature was +25,3°C, the water content was 96,0%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,98±0,47%.The daily average water content in the leaf of Sedum spurium in the first year of the growing season (2023 year) was: in April, the maximum air temperature was +24,5°C, the average soil temperature was +20,0°C, the average soil moisture content (0-60 cm.) was 20,9±0,18%, the average leaf plate temperature was +22,5°C, the water content was 94,9%, the leaf water deficit was 2,30±0,15%. In May, the air temperature is +29,7°C, the soil temperature is +28,0°C, the soil moisture is 20,0±0,64%, the leaf plate temperature is +27,5°C, the water content is 94,0%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,61±0,10%. In June, the air temperature is +36,5°C, the soil temperature is +37,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,1±0,60%, the leaf plate temperature is +34,3°C, the water content is 93,3%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,72±0,13%. In July, the air temperature is +38,2°C, the soil temperature is +38,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,5±0,39%, the leaf plate temperature is +35,9°C, the water content is 92,5%, the water deficit in the leaf is 4,29±0,10%. In August, the air temperature is +34,4°C, the soil temperature is +33,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,3±0,53%, the leaf plate temperature is +32,2°C, the water content is 93,1%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,53±0,17%. In September, when the air temperature was +28,4°C, the soil temperature was +25,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,1±0,56%, and the leaf plate temperature was +26,4°C, the water content was 93,3%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 3,30±0,23%.In the second year of the vegetation period (2024 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +22,6°C, the average soil temperature was +19,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 18,1±0,69%, the water content at the leaf plate temperature of +21,9°C was 95,7%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,53±0,19%. In May, the air temperature is +27,1°C, the soil temperature is +23,0°C, the soil moisture is 19,1±0,38%, the leaf plate temperature is +25,8°C, the water content is 95,2%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,33±0,28%. In June, the air temperature is +35,5°C, the soil temperature is +35,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,7±0,86%, the leaf plate temperature is +33,8°C, the water content is 94,5%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,50±0,15%. In July, the air temperature is +36,3°C, the soil temperature is +37,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,43%, the leaf plate temperature is +34,7°C, the water content is 92,5%, the water deficit in the leaf is 4,44±0,22%. In August, the air temperature is +35,6°C, the soil temperature is +34,0°C, the soil moisture is 11,8±0,55%, the leaf plate temperature is +33,4°C, the water content is 94,0%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,53±0,20%. In September, when the air temperature was +28,8°C, the soil temperature was +24,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,0±0,87%, and the leaf plate temperature was +26,4°C, the water content was 94,3%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 3,37±0,24%.In the third year of the vegetation period (2025 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +23,0°C, the average soil temperature was +21,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 19,5±0,56%, the water content at the leaf plate temperature of +20,0°C was 94,3%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,73±0,40%. In May, the air temperature is +29,0°C, the soil temperature is +24,0°C, the soil moisture is 19,8±0,39%, the leaf plate temperature is +23,5°C, the water content is 93,6%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,84±0,44%. In June, the air temperature is +32,0°C, the soil temperature is +34,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,0±0,45%, the leaf plate temperature is +31,0°C, the water content is 93,4%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,88±0,44%. In July, the air temperature is +40,0°C, the soil temperature is +42,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,43%, the leaf plate temperature is +32,2°C, the water content is 92,6%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,93±0,49%. In August, the air temperature is +34,6°C, the soil temperature is +35,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,53%, the leaf plate temperature is +30,0°C, the water content is 93,0%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,97±0,49%. In September, it was determined that the air temperature was +27,8°C, the soil temperature was +24,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,9±0,69%, and the leaf plate temperature was +24,2°C, the water content was 94,2%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 3,73±0,42%.The daily average water content in the leaf of Sedum spectabile during the growing season (2023 year), when the maximum air temperature in April was +24,5°C, the average soil temperature was +20,0°C, the average soil moisture content (0-60 cm.) was 20,9±0,18%, the water content in the leaf plate was 95,4%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 1,22±0,10%. In May, the air temperature is +29,7°C, the soil temperature is +28,0°C, the soil moisture is 20,0±0,64%, the leaf plate temperature is +29,5°C, the water content is 94,6%, the water deficit in the leaf is 1,88±0,19%. In June, the air temperature is +36,5°C, the soil temperature is +37,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,1±0,60%, the leaf plate temperature is +36,3°C, the water content is 93,8%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,96±0,31%. In July, the air temperature is +38,2°C, the soil temperature is +38,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,5±0,39%, the leaf plate temperature is +37,9°C, the water content is 93,9%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,77±0,31%. In August, the air temperature is +34,4°C, the soil temperature is +33,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,3±0,53%, the leaf plate temperature is +34,2°C, the water content is 94,4%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,79±0,14%. It was determined that in September, the air temperature was +28,4°C, the soil temperature was +25,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,1±0,56%, the leaf plate temperature was +28,4°C, the water content was 95,6%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,60±0,18%.In the second year of the vegetation period (2024 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +22,6°C, the average soil temperature was +19,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 18,1±0,69%, the water content at the leaf plate temperature of +23,9°C was 95,7%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 1,28±0,10%. In May, the air temperature is +27,1°C, the soil temperature is +23,0°C, the soil moisture is 19,1±0,38%, the leaf plate temperature is +27,8°C, the water content is 94,9%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,44±0,23%. In June, the air temperature is +35,5°C, the soil temperature is +35,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,7±0,86%, the leaf plate temperature is +35,8°C, the water content is 93,9%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,57±0,24%. In July, the air temperature is +36,3°C, the soil temperature is +37,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,43%, the leaf plate temperature is +36,7°C, the water content is 93,9%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,40±0,22%. In August, the air temperature is +35,6°C, the soil temperature is +34,0°C, the soil moisture is 11,8±0,55%, the leaf plate temperature is +35,4°C, the water content is 94,2%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,61±0,26%. In September, when the air temperature was +28,8°C, the soil temperature was +24,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,0±0,87%, and the leaf plate temperature was +28,4°C, the water content was 95,7%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,69±0,40%.In the third year of the vegetation period (2025 year), the maximum air temperature in April was +23,0°C, the average soil temperature was +21,0°C, the average soil moisture index (0-60 cm.) was 19,5±0,56%, the water content at the leaf plate temperature of +22,0°C was 95,4%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 1,86±0,47%. In May, the air temperature is +29,0°C, the soil temperature is +24,0°C, the soil moisture is 19,8±0,39%, the leaf plate temperature is +25,5°C, the water content is 93,5%, the water deficit in the leaf is 2,52±0,35%. In June, the air temperature is +32,0°C, the soil temperature is +34,0°C, the soil moisture is 14,0±0,45%, the leaf plate temperature is +33,0°C, the water content is 93,2%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,64±0,39%. In July, the air temperature is +40,0°C, the soil temperature is +42,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,43%, the leaf plate temperature is +34,2°C, the water content is 92,5%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,88±0,47%. In August, the air temperature is +34,6°C, the soil temperature is +35,0°C, the soil moisture is 13,2±0,53%, the leaf plate temperature is +32,0°C, the water content is 93,6%, the water deficit in the leaf is 3,83±0,45%. In September, when the air temperature was +27,8°C, the soil temperature was +24,0°C, the soil moisture was 13,9±0,69%, and the leaf plate temperature was +26,2°C, the water content was 95,1%, and the water deficit in the leaf was 2,87±0,46%.
4. Discussion
Changes in water content and water deficit were noted with the onset of the summer. According to research results, water content decreases slightly, and as a result, when analyzed across species, the water deficit in the leaf was found to be slightly higher in the Sedum spurium species. Studies have shown that the water deficit index is lower than that of plants belonging to the xerophyte and mesophyte groups.
5. Conclusions
In general, the water regime indicators of the studied plants can be explained by their ability to adapt to harsh conditions and the optimal course of physiological processes.
References
| [1] | Kuchkarov N.Y. Bioecology of Inula helenium L. and Inula salicina L. species under introduced conditions: Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Biological Sciences. Dissertation. – Tashkent: 2021. – P. 3-108. |
| [2] | Rakhimova T.T. Methodological manual on plant ecology and phytocenology. – Tashkent, 2009. – P. 3-70. |
| [3] | Rakhimova T.U. Plant ecology of the adyr zone of Uzbekistan. Part I. – Tashkent: University, 1997. – P. 46-203. |
| [4] | Rakhimova T.U. Plant ecology of the adyr zone of Uzbekistan. Part II. – Tashkent: University, 1997. – P. 3-187. |
| [5] | Imomov O.N. Bioecology of some useful food plants in the conditions of the Chust-Pop hills. Namangan – 2020. P. 3-110. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML