-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Genetic Engineering
p-ISSN: 2167-7239 e-ISSN: 2167-7220
2025; 13(8): 147-151
doi:10.5923/j.ijge.20251308.01
Received: Jul. 21, 2025; Accepted: Aug. 16, 2025; Published: Aug. 19, 2025

Effect of Ferula foetida Extract on the Activity of Disaccharidases in the Small Intestine
Kuchkarova Lubov Salijanovna1, Qiyomova Nozigul Farxod qizi2, Qurbanov Shaniyaz Qurbanovich2, Eshbakova Kamila Alibekovna3, Kayumov Khasan Yusuf Ogli1
1National University of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Karshi State University, Karshi, Uzbekistan
3Institute of the Chemistry of Plant Substances, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Currently, much attention is paid to therapy using herbal medicines, as they have a smaller spectrum of side effects compared to artificial drugs. However, despite the wide range of pharmaceutical properties of widely used in folk and traditional medicine Ferula foetida, its effect on the ability to digest carbohydrates in the small intestine has not been studied. Meanwhile, when F. foetida or its derivatives enters the small intestine with food and spices, they directly encounter enzymes and can affect the activity of brush border disaccharidases. In this study, the effect of F. foetida stem extract on the activity of intestinal disaccharidases, which play a decisive role in regulating the glycemic status of the body, was studied. The results show that daily intragastric administration of F. foetida extract for 28 days leads to inhibition of disaccharide digestion in the small intestine of rats. This is manifested in the repression of maltase and sucrase activity against the background of unchanged lactase activity in rats treated with the extract. The inhibitory effect was significantly expressed in the proximal and medial parts of the small intestine, where the disaccharidase activity was highest. These results suggest that F. foetida-based spices may be used as an ingredient in products that help prevent hyperglycemia.
Keywords: Ferula foetida, Small intestine, Maltase, Sucrase, Lactase
Cite this paper: Kuchkarova Lubov Salijanovna, Qiyomova Nozigul Farxod qizi, Qurbanov Shaniyaz Qurbanovich, Eshbakova Kamila Alibekovna, Kayumov Khasan Yusuf Ogli, Effect of Ferula foetida Extract on the Activity of Disaccharidases in the Small Intestine, International Journal of Genetic Engineering, Vol. 13 No. 8, 2025, pp. 147-151. doi: 10.5923/j.ijge.20251308.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- It is known that herbal therapy has a smaller range of side effects compared to artificial drugs due to their natural origin and the presence of many useful components. A synergistic or buffering effect is often observed due to the presence of several compounds that potentially reduce the risk of side effects [1]. For example, Ferula foetida, widely used in Ayurveda and traditional medicine, as well as in Asian cuisine, has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, neuroprotective, anticancer, anthelmintic and other pharmacological properties [2,3]. However, not all pharmacological effects of this plant have been studied. Indeed, despite the fact that spices and pharmacological agents based on F. foetida enter the small intestine with food, their effect on the digestive capacity of the small intestine has been practically unstudied. Meanwhile, the substances of F. foetida, having direct contact with brush border digestive enzymes, including disaccharidases, can change their structure and activity.Mammalian intestinal disaccharidases catalyze the final step in the digestion of carbohydrates, which are abundant in the human diet. Small intestinal brush border disaccaridases cleave glycosidic bonds in oligosaccharides and glycoconjugates and play an essential role in carbohydrate digestion [4]. Possible changes in disaccharidase activity under the influence of F. foeida extract may play a significant role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis in the body, the disruption of which leads to serious diseases. Therefore, the purpose of the work was to study the effect of F. foeida extract on the activity of intestinal disaccharides.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
- The experiments were conducted on the outbred white male rats weighing 180–200 g, raised in the vivarium of the National University of Uzbekistan. Rats were kept in plastic cages of 50x30x28 cm in size 4 animals each under natural light and humidity and room temperature with unlimited access to water and standard vivarium feed.
2.2. F. foetida Extract Preparation and Dosage
- F. foetida was collected in the mountainous areas of the Dekhkonobad district of the Kashkadarya region, Uzbekistan. An alcoholic-aqueous extract of the plant stem was prepared as described by Tabassam et al. [5].Rats were divided into two experimental and one control groups. The rats of the first and second experimental group were administered F. foetida extract intragastrically daily for 28 days at a dose of 1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg respectively. The animals of the control group were similarly administered saline. It has been shown that chronic extract administration at doses of 3–22 mg/kg body weight reduced the mean arterial blood pressure [6] and high-dose administration of this preparation causes liver damage [7]. To prevent side effects of the extract, two relatively low doses that cause effect were used to treat animals.
2.3. Preparation of an Enzymatically Active Preparation and Determination of Disaccharidase Activity
- After decapitation of the rats, the small intestine was removed from the abdominal cavity, cleared of fatty tissue, divided into 3 sections (proximal, medial and distal) and each section was washed with Ringer's solution (pH 7.2) at a rate of 1 ml per 1 cm of intestinal length. The mucosа of each section was separated with a plastic spatula, weighed and diluted with Ringer's solution in a ratio of 1:9. The separated mucosa was homogenized, centrifuged, and the supernatant was analysed for disaccharidases activity. All operations were carried out in cold conditions. The activities of maltase (EC 3.2.1.20), sucrase (EC 3.2.1.48), and lactase (EC 3.2.1.23) were determined by the Dahlquist method [8]. Enzyme activity were expressed in μmol of glucose per minute per gram of wet weight of tissue.
2.4. Statistics
- Statistical analysis was performed using Student t-test, to compare the means of two groups. When P was less than 0.05, the differences between the values were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
- The activity of intestinal α-glucosidases (maltase, sucrase) and β-galactosidases (lactase) was studied in the proximal, medial and distal regions of the small intestine.
3.1. Maltase Activity
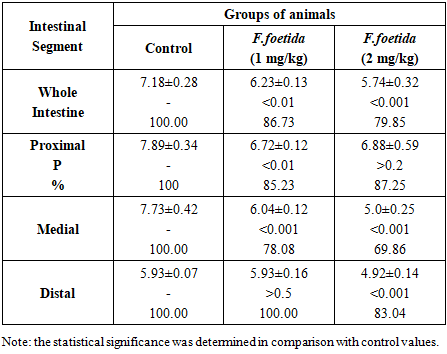
- Data reflecting the effect of F. foetida extract on the intestinal maltase activity are presented in Table 1.
|
3.2. Sucrase Activity
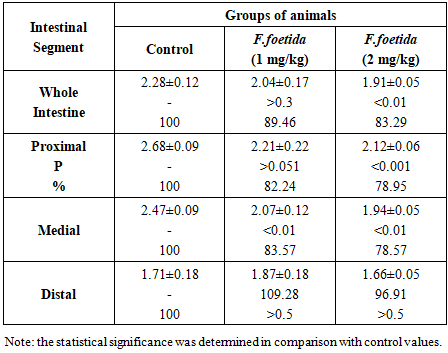
- The effect of F. foetida extract on sucrase activity in different segments of the small intestine is presented in Table 2.
|
3.3. Lactase Activity
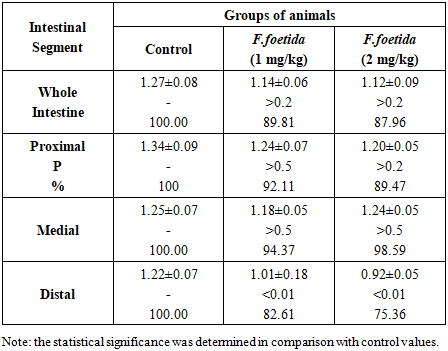
- Data on the changes in the activity of intestinal β-galactosidase – lactase under the influence of F. foetida extract are presented in Table 3.
|
4. Discussion
- The results have shown that the activity of maltase and sucrase in the small intestine of rats is more pronounced than the activity of lactase, which indicates a greater participation of α-glucosidases in glucose absorption compared to β-galactosidases. Maybe that's why inhibition of the activity of digestive α-glucosidases by herbal preparations is considered one of the advanced methods for the treatment of postprandial hyperglycemia and one of the accepted strategies for combating diabetes [9]. In the experiment, an inhibitory effect of F. foetida extract on the activity of digestive α-glucosidases, but not lactase, was found. This effect is confirmed by the fact that intragastric administration of F. foetida extract to rats reduces the hydrolytic capacity of the entire intestine for maltose and sucrose, but not for lactose. The same specificity of the effect on the activity of α-glucosidases and β-galactosidases was revealed for acarbose, a standard artificial inhibitor of the activity of digestive α-glucosidases [10]. Experiments have shown that the activity of α-glucosidases is concentrated in the proximal and medial sections of the rat intestine, but after treating rats with F. foetida extract, their specific activity lost its distribution gradient due to a decrease in the sections where it was highest. F. foetida is a traditional plant that has long been used in food and medicine. Millions of people use the plant daily as a spice, and its safety has been proven [11]. The plant contains many compounds (sulfur-containing compounds, terpenes, flavonoids, coumarins, phenolic acids, monosaccharides and other substances) with various pharmacological properties. [11-17]. Therefore, most likely, the inhibitory effect of F. foetida extract on the activity of intestinal α-glucosidases – maltase and sucrase, is the result of the synergistic action of many substances.The standard drug acarbose due to its high affinity for α-glucosidase, inhibits the activity of intestinal α-glucosidases in a competitive manner [10]. The competitive mechanism of inhibition of α-glucosidase activity is also evident for the flavonoids naringenin, taxifolin, and some sulfur-containing compounds present in the composition of F. foetida extraсt [17-19]. These substances bind to the same active site of the enzyme as the substrate, preventing its binding and cleavage. Taxifolin has been shown to have a dose-dependent inhibitory effect on alpha-glucosidase activity [19]. Other substances found in F. foetida, such as L-arabinose andferulic acid [13,20-22], inhibit the activity of intestinal α-glucosidases through an uncompetitive inhibition mechanism. L-arabinose binds to the sucrase-sucrose complex, and leads to a reduction in the rate of sucrose digestion [20]. This monosaccharide is not digested but accumulates in the intestine, which prolongs its inhibitory effect [21]. Ferulic acid alters the secondary structure of α-glucosidase and changes the microenvironment of certain amino acid residues. The interaction involves non-covalent bonds, including hydrogen bonds, and results in a moderate binding affinity [22].The third group of substances (coumarins, phenolic acids, terpenes and rutin) present in F. foetida can inhibit the activity of α-glucosidases by a mixed mechanism of action: competitive binding to the active center of the enzyme and non-competitive, causing protein aggregation [23-27]. The absence (maltase, lactase) or weak (sucrase) dose-dependence of the effect of the extract on the activity of brush border disaccharidases may be due to the fact that plant extracts, unlike pure compounds, contain multiple biologically active substances that can interact with each other in complex ways [28]. Therefore, it can be concluded that intestinal α-glucosidases are the target of many substances contained in the F. foetida extract. Inhibition of their-activity can occur through various pathways, including competitive mechanism, non-competitive inhibition, as well as both mechanisms simultaneously. Natural product-based α-glucosidase inhibitors are particularly attractive because their side effects are minimal, they also typically have other therapeutic properties, and therapy is well tolerated compared with other oral hypoglycemic agents currently available [1-3,28–32]. Many α-glucosides inhibitors not only help prevent and/or correct hyperglycemia, but also have a beneficial effect on a number of cardiovascular diseases, preventing obesity, hypertension and high glycemic variability [28-30]. So, the obtained data indicate the possibility of expanding the use of food products, spices and preparations based on F. foetida, considering them as suitable candidates for the prevention and/or correction of hyperglycemia and associated diseases.
5. Conclusions
- In general, chronic consumption of F. foeida extract reduces the ability of the small intestine to absorb carbohydrates, which is manifested in a decrease in the activity of brush border maltase and sucrase. This phenomena helps prevent excessive glucose from entering the bloodstream after eating carbohydrate-rich foods, i.e. preventing hyperglycemia. The use of food additives based on F. foeida extracts, through inhibition of the small intestinal enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion, will help prevent not only hyperglycaemia, but also diabetes, hypertension, some types of nephropathy and other associated diseases.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML