-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Genetic Engineering
p-ISSN: 2167-7239 e-ISSN: 2167-7220
2025; 13(4): 62-65
doi:10.5923/j.ijge.20251304.02
Received: Mar. 26, 2025; Accepted: Apr. 20, 2025; Published: Apr. 26, 2025

The Effect of Insulin on Carbohydrate Metabolism in Experimental Alzheimer's Model Animals
Ikromov S. A. 1, Saatov T. S. 1, Mustafakulov M. A. 1, Yalalova I. R. 1, Kosimova Z. T. 2
1Institute of Biophysics and Biochemistry, Uzbekistan
2Impuls Medical Institute, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Ikromov S. A. , Institute of Biophysics and Biochemistry, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article investigates the effect of insulin on carbohydrate metabolism in experimental Alzheimer's model animals. The study analyzes how insulin influences metabolic changes associated with Alzheimer's disease, particularly in glucose levels and carbohydrate metabolism. Experimental trials on animal models observed insulin balance and changes in carbohydrate metabolism. The results helped identify the connection between insulin sensitivity and metabolic disruptions in Alzheimer's disease development.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease, Insulin, Carbohydrate metabolism, Experimental animal model, Glucose, Metabolic changes
Cite this paper: Ikromov S. A. , Saatov T. S. , Mustafakulov M. A. , Yalalova I. R. , Kosimova Z. T. , The Effect of Insulin on Carbohydrate Metabolism in Experimental Alzheimer's Model Animals, International Journal of Genetic Engineering, Vol. 13 No. 4, 2025, pp. 62-65. doi: 10.5923/j.ijge.20251304.02.
1. Introduction
- For many years, the brain was considered incapable of glucose uptake without insulin. However, recent findings show that insulin not only regulates glucose transport and metabolism but also plays a role in neuronal excitability, proliferation, progenitor cell differentiation, synaptic plasticity, memory formation, neurotransmitter secretion, and apoptosis [1,25]. The effect of insulin on the brain's progenitor cells is especially noteworthy. It has been demonstrated that neuroblast reactivation occurs along with active signaling through insulin receptors, which is essential for the transition of progenitor cells from an inactive stage to active proliferation. Additionally, insulin is synthesized directly in the brain. This hypothesis is based on the discovery of insulin-specific mRNA in the hypothalamus, hippocampus, and neuronal cultures [22,23]. Insulin plays a critical role in neuronal survival and brain function. Its influence on synaptic plasticity and memory consolidation in neurons is vital [15,12,30]. Insulin is also crucial for neuronal circuit formation, neural stem cell activation, neuronal growth, recovery, neuroprotection, energy metabolism regulation, and protection against oxidative stress [4,13]. Consequently, disruptions in insulin signaling in the central nervous system (CNS) may lead to various neurological diseases. Recent research has highlighted a link between Alzheimer's disease (AD) and disruptions in insulin signaling in the CNS [5,19]. Insulin resistance and reduced insulin action may play significant roles in the pathogenesis of these diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
- The sporadic form of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NDH) with Alzheimer's symptoms is typically induced in animal models through intraventricular administration of streptozotocin at doses ranging from 1 mg to 3 mg per kilogram of body weight [6,29]. In this study, rats were fed a special high-calorie diet, which included 0.2% cholesterol and 4-6 mg of margarine per rat, along with 2% total dietary fat. The rats also received 3% sweet water with 0.04-0.06 mg of Merkazalol daily for 21 days. The rats' weight was measured weekly, and behavioral tests (Open Field, Morris Test) and glucose measurements were conducted. Blood and tissue samples were collected to measure insulin, lipids, and cholesterol levels.The sporadic form of NDH with Alzheimer's symptoms is usually induced by administering streptozotocin intraventricularly in doses ranging from 1 mg to 3 mg per kilogram of body weight, either as a single injection or over three days [6,16,17]. In our experiments, to induce sporadic NDH with Alzheimer's symptoms, the animals were fed a special high-calorie diet for three months, which included a standard diet supplemented with an additional 0.2% cholesterol. Each rat received 4-6 mg of margarine, and 2% of the total food intake consisted of fat. To slightly slow down the metabolism in the rats, they were given 3% sweetened water with 0.04-0.06 mg of Merkazalol per rat daily for 21 days. During the preparation of the experimental model, the rats' weight was measured weekly, and behavioral tests (Open Field [OM], ShRPH, ShRFH, Morris Test), along with individual biochemical indicators, were monitored. 100 µl of blood was periodically taken from the tail to measure glucose levels. Blood and tissue samples were collected to measure insulin, lipids, and cholesterol. In the final stage of preparing the experimental model, the glucose level in the animals' blood had risen to 7-8 mmol/l. In the study, the experimental group of animals received streptozotocin at a dose of 3 mg per kilogram of body weight, administered intranasally via liposomes over the course of one week [8,21,25].
3. Discussion
- Before starting the experiments to induce a sporadic NDH experimental model with signs of encephalopathy (NDHE), the animals were kept in quarantine for 10 days to adapt to vivarium conditions. Then, the animals were selected according to the criteria defined by neurological NSS scale indicators of behavior. The animals were divided into general groups. Out of the 80 animals examined, 40 rats were selected for experiments. The experimental NDH model was created by long-term feeding of animals with an atherogenic high-calorie diet consisting of a standard diet supplemented with 0.2% cholesterol (CS) of the general diet: for each animal selected for the study, 4-6 mg of cholesterol, a total of 20% margarine and pork fat, (40% of calories) sweetened drinking water with fructose/sucrose (3% solution), and the thyroid hormone inhibitor mercazolil, in a dosage of 0.04-0.06 mg per rat, were added to the diet. The animals were fed a high-calorie diet for 12 weeks, and after feeding the experimental animals high-calorie foods until the 13th week, the weight of each animal was measured, and after reaching the required weight, each animal was administered streptozotocin solution intranasally at a dosage of 3 mg/kg through the nasal cavity over a period of 3 days. This is considered the first stage of the model preparation in animals. The induction of the NDHE model was monitored through periodic behavioral tests and biochemical blood tests of the animals.
4. Result
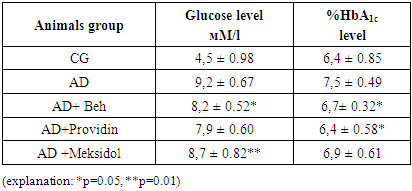
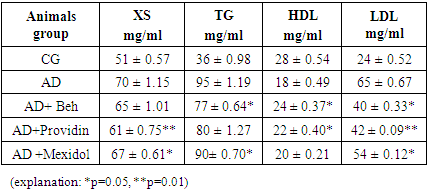
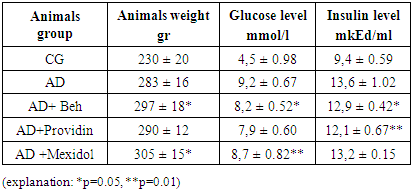
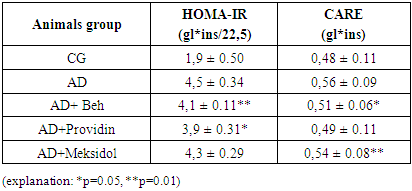
- The analysis of the obtained results is presented below. The results of blood tests of the animals after inducing the NDHE model showed the following (see Table 1).
|
|
|
|
5. Conclusions
- In the hippocampus of experimental animals, insulin stimulates neurogenesis by lowering the activation threshold for long-term potentiation and plays a key role in maintaining nerve cells by binding to insulin receptors (InsRs). It was found that insulin plays an important role in glucose uptake by neurons, in glucose uptake by the hypothalamus, and in the formation of spatial memory in the hippocampus.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML