-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Genetic Engineering
p-ISSN: 2167-7239 e-ISSN: 2167-7220
2024; 12(4): 39-47
doi:10.5923/j.ijge.20241204.01
Received: Apr. 28, 2024; Accepted: May 19, 2024; Published: May 21, 2024

Morphological Indicators of Self Organization of a Drop of Dehydrated Saliva at Various Vegetative Statuses and Health Levels
N. М. Gasanova1, E. A. Ergashev2
1Fergana Medical Institute of Public Health, Uzbekistan
2Fergana State University, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this article discusses the prospects for using the features of the morphology indicators of microcrystals of biological fluids, namely human saliva, as markers of prenosological diagnostics. Examination of 43 practically healthy students of both sexes and at the age of 18-22 years. showed that the values of morphology indices of microcrystals of their dehydrated saliva, depending on the level of health, have a value in the range from 2.0 to 4.0 conventional units. At the same time, 30% of them each have only 2.0 and 4.0 units, and the remaining 40% have variations in morphology indices in the range of 2.25 - 3.75 units, more than half of which have morphology indices of 3.0 and 3.25 units. Surveys found that 62.8% of them have a vegetative status of sympathicotonia, and 25.6% - parasympathicotonia and 11.6% - eutonia. It is shown that there are some tendencies in their interdependence, namely, with sympathicotonia, more crystalline structures are formed, and with parasympathicotonia, more amorphous formations, which, moreover, have gender characteristics, which indicates the peculiarities of changes in the composition of saliva, namely, different ratios of its organic and inorganic components when the initial vegetative status of the organism changes depending on gender. It was also revealed that the type of self regulation of blood circulation of the examined persons depended on their initial vegetative status. The factors established in the work are recommended to be used as diagnostic markers in the tasks of prenosological diagnostics.
Keywords: Saliva, Health levels, Indicators of microcrystal morphology, Vegetative status, Prenosological diagnostics, Type of self regulation of blood circulation
Cite this paper: N. М. Gasanova, E. A. Ergashev, Morphological Indicators of Self Organization of a Drop of Dehydrated Saliva at Various Vegetative Statuses and Health Levels, International Journal of Genetic Engineering, Vol. 12 No. 4, 2024, pp. 39-47. doi: 10.5923/j.ijge.20241204.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In accordance with the WHO strategy, monitoring of the functional reserves of the body, prenosological diagnostics at the early stages of development of the adaptation process and correction of the functional state are considered as the most optimal methodology for health protection. Achievement of this or that level of functioning of the organism or its certain systems is ensured through the activity of the mechanisms of regulation and control. The main task of the human nervous system is to create an apparatus that connects all organs and systems of the human body together, due to which it exists and functions. [11] It is a combination of two departments: somatic and vegetative. The first serves mainly to ensure that the human body can interact with the external environment. The second one regulates and coordinates the activity of internal organs, metabolism, smooth muscles, endocrine glands, constancy of the internal environment of the body and functional activity of tissues and innervates the entire body, all organs and tissues. The leading role in the processes of preservation and redistribution of functional resources is played by the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The mobilization of reserves occurs as a result of changes in the level of activity of regulatory systems, in particular, this is associated with an increase in the tone of the sympathetic division of the ANS. An indispensable and sometimes decisive influence is exerted by the autonomic system on the organization of adaptation processes, behavior and maintenance of internal homeostasis. [12] The ANS is divided into sympathetic (SNS), which is mainly mobilized during the implementation of the ergotropic function, and parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), which is more aimed at maintaining homeostatic equilibrium - trophotropic function. The balance between SNS and PNS determines the state of autonomic homeostasis. [14] The ANS plays an important integrative role at the central level, allowing the body to adapt to new conditions. Even small violations of the vegetative status, not always recorded in the form of a specific diagnosis, have a significant impact on the state of health in general, the course of concomitant pathology, its recovery from stressful situations, and adaptability to physical and psychological stress. [15] The above-mentioned features of the ANS indicators can be used to diagnose and predict various states of the body. Purposeful identification of autonomic disorders and their correction in the preclinical stage, i.e., their prenosological diagnosis can reduce the probability of developing somatic diseases. In this regard, studies of vegetative homeostasis in practically healthy students are of considerable scientific and clinical interest. [16]We have carried out studies to identify the features of the dependence of the morphological parameters of the solid phase of saliva on the vegetative status and functional state of the body in prenosological conditions, and on their basis to develop a non-invasive method for assessing the level of ANS and the health of healthy people. This is justified by the fact that the salivary glands perform not only specific functions, but also maintain the constancy of the internal environment of the body, play the role of the blood-salivary barrier of the body. With unfavorable metabolic changes in the body, the salivary glands are involved in the redistribution of biochemical substances between blood and saliva. Saliva is a complex filtrate of blood plasma, which reflects the state of dynamic constancy of the internal environment of the body. At the same time, it can change quite significantly in composition, physicochemical and biological properties when exposed to the body of various stimuli, that is, it is an indicator of the body's reactivity. The presence of certain correlations between the indicators of different physiological systems and the activity of the salivary glands gave researchers reason to call them "the mirror of diseases." There is every reason [1] to consider saliva (especially mixed saliva, which is the result of the activity of all salivary glands) as a "mirror" of the functional state of the body. It should be noted that the constancy of the content of organic and inorganic substances in saliva within the limits of individual fluctuations is maintained due to the normal functioning of the salivary glands. In turn, their function fully depends on the state of the body and is controlled by the activity of the nervous system and humoral factors, which depend largely on the type of autonomic regulation of the body. As you know, the salivary glands are richly innervated by the fibers of the autonomic nervous system. Therefore, it is natural that the nervous system is the main regulator of the functions of the salivary glands and, ultimately, the organic and inorganic components of saliva [2]. In a change in saliva indices in schoolchildren was found, depending on the established type of autonomic regulation, namely, in adolescents with vagotonic type of autonomic regulation, the rate of saliva secretion increases and the content of mineral components decreases, and in sympathotonics, the rate of saliva secretion and an increase in calcium content decrease. and phosphorus, in comparison with representatives of the normotonic type of autonomic regulation.A methodological approach to check this fact can be carried out using an extremely simple integrative method for assessing the properties of this liquid, which excludes the use of laborious and costly methods of its complex chemical analysis. As such a method, we have chosen the morphological analysis of the facies of the oral fluid (OF) - a crystallized plate after it has dried on a low-adhesive surface. This approach, based on the concepts of the morphology of biological fluids (BF) [3], implies that the self-organizing structure formation in the process of their dehydration reflects not only the chemical composition, but also the vital properties, as well as functional changes. In the BF of an organism, dissolved molecules and molecular complexes are relatively evenly distributed throughout their entire mass. In the case of wedge-shaped dehydration of BF, these molecules and their complexes, undergoing spatial displacements, form a corresponding concentration zone, which is localized in a strictly defined place of the formed dry film - facies. While, each zone represents the concentration gradient of a certain group of associated molecules, similar in their physicochemical parameters. As a result, during the transition of the BF drop to the solid phase, a facies with fixed morphological elements is formed, which is a structural macro-portrait of molecular interactions in the BF. This is the greatest value of the wedge-shaped dehydration method for the tasks of medical diagnostics. This method allows one to obtain valuable information characterizing all the features of metabolic processes inherent in a given organism. To date, it has been shown that the morphology of dehydrated BF samples adequately reflects both physiological and pathological changes occurring in highly dynamic spatiotemporal structures of living organisms. Our review of works shows that the human oral fluid is a quite suitable object, since the nature of the morphology of their microcrystals, which are formed during their dehydration, reflect the systemic organization of secretory processes in a given individual. So, for example, in work [4], the use of morphological analysis of the solid phase of the oral fluid as an effective indicator of the functional state of the organism was substantiated. [10]The phenomenological and quantitative morphological characteristics obtained by the authors of the salivary facies are in good agreement with the indicators of the level of the general nonspecific resistance of the organism. Thus, it can be expected that knowledge of the features of the morphology indices of saliva microcrystals formed as a result of their dehydration, depending on the initial vegetative status and prenosological functional states, will allow the development of a non-invasive test system for express diagnostics of the prenosological level of the functional state and health of the body, which was the goal of our research.The relevance of the study is due to the high prevalence of autonomic disorders in adolescents, as well as the fact that the indicators of the ANS state are of great importance for assessing the state of adaptive abilities, reliably characterizing the compensatory capabilities of a person at the level of the whole organism. There is a steady increase in the number of young people suffering from functional disorders of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, the triggering mechanism of which is often autonomic dysfunction, in connection with which the problem of early diagnosis of autonomic dysfunction syndrome becomes extremely urgent, the development of new methods of prenosological diagnosis and prevention of these conditions, which will allow you to maintain the health of a healthy person. Active targeted prenosological detection of autonomic disorders in practically healthy students and their correction in the preclinical stage can reduce the likelihood of developing somatic diseases in them.The study of saliva is connected with the fact that, on the one hand, the vegetative status of the body largely determines the levels of its functional state and, accordingly, health, and on the other, as already noted, through the salivary glands it affects the chemical composition of saliva. Thus, the indices of the morphology of saliva microcrystals, ranked according to the types and levels of vegetative status (VS), the influence of which on the functional state has already been established, can be used as criteria for assessing the VS and the level of health.Subject of the study: the level of health, the initial tone of the autonomic nervous system and the morphology of the oral fluid of practically healthy people.Research objectives: Elucidation of the dependence of the level of students' health on the type of the initial vegetative tone and the ratio of the tones of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the nervous system and on the morphological markers of their unstimulated oral fluid.
2. Objects and Research Methods
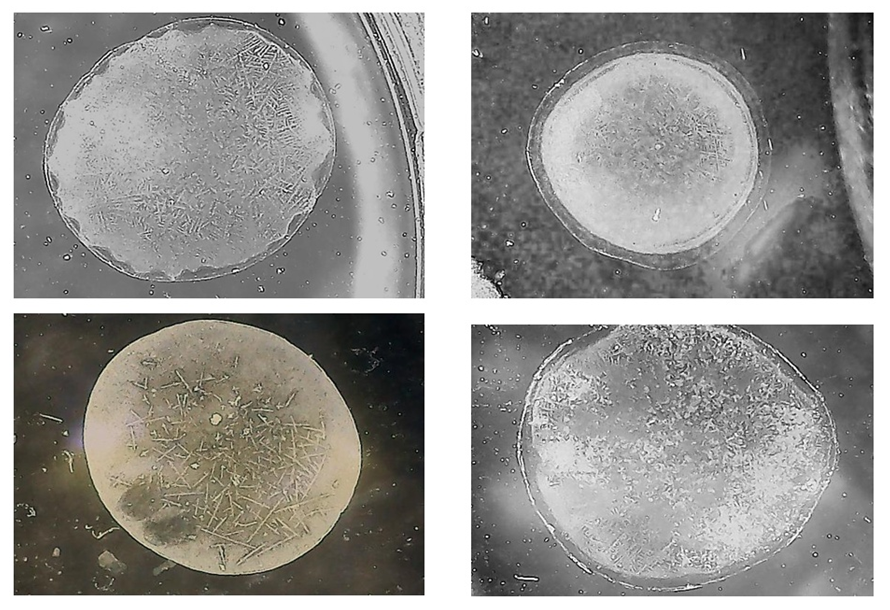
- The main criterion when choosing a contingent for the survey was the assessment of the level of health, but in no case, the diagnosis of diseases. In this regard, among the group of persons intended for the study, a survey was conducted using questionnaires specially compiled by us, and based on the results of their analysis, a preliminary selection of the contingent of the surveyed - practically healthy persons - was carried out. As a result, 43 students (19 boys and 24 girls) of 2–3 courses of the Fergana Medical Institute of Public Health were selected, aged 19–25, who do not systematically go in for sports. For a quantitative assessment of the level of the prevailing vegetative tone, we used the vegetative blood circulation index (BCI). It is known that the regulation of blood circulation in the body is carried out by the suprasegmental divisions of the autonomic nervous system. The circulatory system is not an independent functional system. The nervous and endocrine systems are certainly included. All these components are combined according to the principle of interaction. They form a single functional system that provides the working organs with sufficient blood pressure, a sufficient amount of blood, which provides the body metabolically and energetically. The cardiovascular system is included in the activity of other functional systems that provide the body with oxygen and necessary metabolites. According to the vegetative blood circulation index (BCI), all examined were divided into five groups: with normotonic, moderately sympathotonic, pronounced sympathotonic, and also moderately parasympathotonic and expressed by parasympathotonic types of autonomic regulation. The normotonic type of autonomic regulation can be characterized as a state of equilibrium of sympathetic-parasympathetic regulation of the functional systems of the body. Parasympathotonic and sympathotonic types of regulation can be defined as a state of functional tension of the body's activity, providing homeostasis. To determine the value of the VIC (vegetative index of blood circulation) we used the formula [5]:
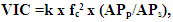 where, k - dimensional empirical coefficient equal to 2 s2; fc = (heart rate / 60) - heart rate, s-1; heart rate is the number of heartbeats in 1 minute; АPp - Arterial pulse blood pressure, mm Hg..; АPs - systolic blood pressure, mm Hg.The characteristic of the predominant vegetative tone of the cardiovascular contractions CVS based on a certain VIC is as follows: pronounced sympathicotonia —1.56 or more; moderately pronounced sympathicotonia — 1.06-1.55; eutonia — 1.05-0.95; moderately expressed parasympathicotonia 0.94-0.65; severe parasympathicotonia - 0.64 and below. The initial vegetative tone can be sympathicotonic, eutonic and parasympathicotonic. To study the morphological features of the solid phase of saliva, the method of edge dehydration of a drop proposed in [3] was used. In accordance with this methodology, the surveyed students, in the morning, before breakfast, 10 minutes after rinsing the mouth with boiled water, was collected in sterile test tubes, their non-stimulated oral fluid (OR). The samples were separated into sediment and supernatant fractions by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes at room temperature. The study used the supernatant fraction. The droplets were transferred to the solid phase [3] by drying them under standard conditions. For this, using a semi-automatic dispenser with a variable volume, 20 μL of the BF supernatant fraction was applied onto a defatted glass slide located in a strictly horizontal position and dehydrated by drying in air at 24-25°C and 60-65% relative humidity for 24 hours. Visualization of the obtained facies of the oral fluid was carried out using a light microscope in transmitted light, and with the help of a built-in digital camera, a computer atlas of the facies was created for their subsequent morphological analyzes. Figure 1 shows samples of the saliva facies of the individuals examined by us, belonging to different types.The next stage of the study is associated with morphological analysis and assessment of facies microcrystallization indices. At the same time, the homogeneity of the distribution of structural elements of the morphology of microcrystals of OF(oral fluid) over the entire volume of the facies (Fig. 1), which makes it possible to classify them with high reliability by type, in the samples of the saliva facies of some of the examined, was not fulfilled. The reason for this was that in different sectors of facies (Fig. 2), different morphological types of microcrystals were simultaneously formed, which made it difficult to classify them according to any type. Therefore, we used the method for determining the indicators of the morphology of microcrystals proposed in [6], in accordance with which, the samples of the OF facies, are divided into 4 equal quadrants, in each of which the type of microcrystallization is established, with the subsequent calculation of the indicator of its morphology.
where, k - dimensional empirical coefficient equal to 2 s2; fc = (heart rate / 60) - heart rate, s-1; heart rate is the number of heartbeats in 1 minute; АPp - Arterial pulse blood pressure, mm Hg..; АPs - systolic blood pressure, mm Hg.The characteristic of the predominant vegetative tone of the cardiovascular contractions CVS based on a certain VIC is as follows: pronounced sympathicotonia —1.56 or more; moderately pronounced sympathicotonia — 1.06-1.55; eutonia — 1.05-0.95; moderately expressed parasympathicotonia 0.94-0.65; severe parasympathicotonia - 0.64 and below. The initial vegetative tone can be sympathicotonic, eutonic and parasympathicotonic. To study the morphological features of the solid phase of saliva, the method of edge dehydration of a drop proposed in [3] was used. In accordance with this methodology, the surveyed students, in the morning, before breakfast, 10 minutes after rinsing the mouth with boiled water, was collected in sterile test tubes, their non-stimulated oral fluid (OR). The samples were separated into sediment and supernatant fractions by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes at room temperature. The study used the supernatant fraction. The droplets were transferred to the solid phase [3] by drying them under standard conditions. For this, using a semi-automatic dispenser with a variable volume, 20 μL of the BF supernatant fraction was applied onto a defatted glass slide located in a strictly horizontal position and dehydrated by drying in air at 24-25°C and 60-65% relative humidity for 24 hours. Visualization of the obtained facies of the oral fluid was carried out using a light microscope in transmitted light, and with the help of a built-in digital camera, a computer atlas of the facies was created for their subsequent morphological analyzes. Figure 1 shows samples of the saliva facies of the individuals examined by us, belonging to different types.The next stage of the study is associated with morphological analysis and assessment of facies microcrystallization indices. At the same time, the homogeneity of the distribution of structural elements of the morphology of microcrystals of OF(oral fluid) over the entire volume of the facies (Fig. 1), which makes it possible to classify them with high reliability by type, in the samples of the saliva facies of some of the examined, was not fulfilled. The reason for this was that in different sectors of facies (Fig. 2), different morphological types of microcrystals were simultaneously formed, which made it difficult to classify them according to any type. Therefore, we used the method for determining the indicators of the morphology of microcrystals proposed in [6], in accordance with which, the samples of the OF facies, are divided into 4 equal quadrants, in each of which the type of microcrystallization is established, with the subsequent calculation of the indicator of its morphology.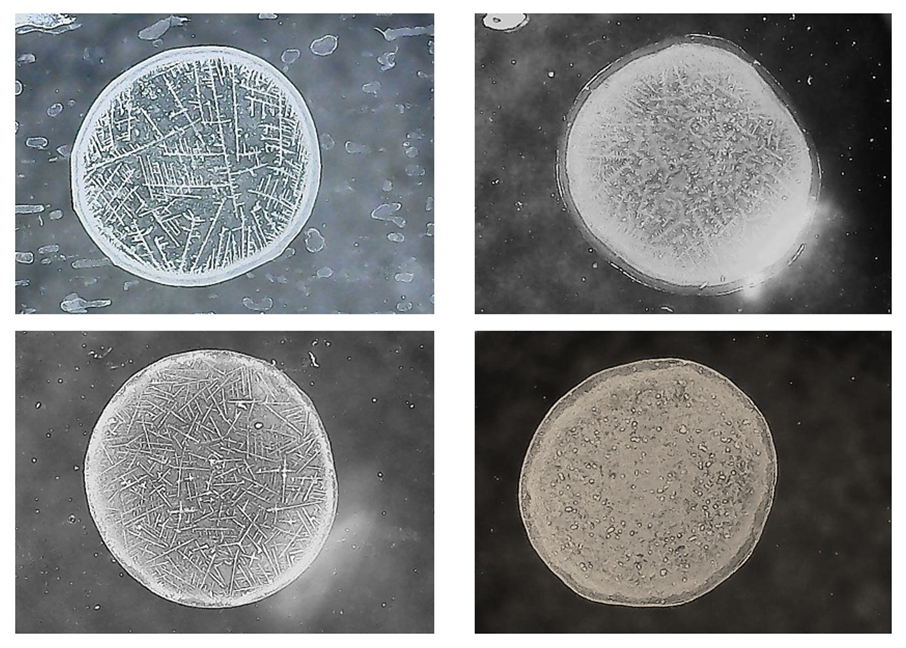 | Figure 1. Samples of saliva microcrystals of the persons examined by us, with different morphologies |
 | Figure 2. Morphological inhomogeneities of the salivary facies of some examined persons |
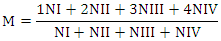 where NI, NII, NIII, NIV is the number of facies quadrants with microcrystallization of types I, II, III, IV, respectively; 1, 2, 3, 4 - weight factors for types of microcrystallization I, II, III, IV.It should be noted that this technique for analyzing the morphotexture of microcrystals of OF (oral fluids) makes it possible to identify more than 24 combinations of the structure of the facies, with 13 quantitative indicators, varying in the range from 1 to 4 conventional units, discretely in 0.25 increments. This makes it possible to almost double the sensitivity of this method to morphological changes in microcrystals of facies, in comparison with the existing ones [8], where only 7 morphological types of facies can be classified. There are several approaches to classifying the types of microcrystals. When classifying morphological types of the OF facies, we took into account the indicators of the visual morphometry method [9], namely, the severity of individual zones of the facies, the presence of crystalline and amorphous formations, the degree of their destruction and the uniformity of distribution over the texture of the sample, as well as the severity of the marginal zone due to the protein content in samples of OF. Four morphological types [6] of oral fluid microcrystals have been identified: Type I - a clear pattern of interconnected large crystal-prismatic structures of a tree-like (fern-like) shape, evenly distributed over the main layer of the drop. Single organic inclusions are observed along the entire perimeter (Fig. 3 a); Type II - in the central part, individual crystal-prismatic structures of a tree-like (fern-like) shape are determined, some of the crystals are not interconnected. On the periphery, there is a moderate amount of organic inclusions (Fig. 3b); Type III - a large number of randomly placed structures of irregular shape can be seen over the entire area, as well as a significant number of organic inclusions adhering to crystals (Fig. 3c); IV type - in the field of view along the entire perimeter, single small crystals of irregular shape are detected, without a clear orientation with signs of disaggregation or complete absence of crystals.
where NI, NII, NIII, NIV is the number of facies quadrants with microcrystallization of types I, II, III, IV, respectively; 1, 2, 3, 4 - weight factors for types of microcrystallization I, II, III, IV.It should be noted that this technique for analyzing the morphotexture of microcrystals of OF (oral fluids) makes it possible to identify more than 24 combinations of the structure of the facies, with 13 quantitative indicators, varying in the range from 1 to 4 conventional units, discretely in 0.25 increments. This makes it possible to almost double the sensitivity of this method to morphological changes in microcrystals of facies, in comparison with the existing ones [8], where only 7 morphological types of facies can be classified. There are several approaches to classifying the types of microcrystals. When classifying morphological types of the OF facies, we took into account the indicators of the visual morphometry method [9], namely, the severity of individual zones of the facies, the presence of crystalline and amorphous formations, the degree of their destruction and the uniformity of distribution over the texture of the sample, as well as the severity of the marginal zone due to the protein content in samples of OF. Four morphological types [6] of oral fluid microcrystals have been identified: Type I - a clear pattern of interconnected large crystal-prismatic structures of a tree-like (fern-like) shape, evenly distributed over the main layer of the drop. Single organic inclusions are observed along the entire perimeter (Fig. 3 a); Type II - in the central part, individual crystal-prismatic structures of a tree-like (fern-like) shape are determined, some of the crystals are not interconnected. On the periphery, there is a moderate amount of organic inclusions (Fig. 3b); Type III - a large number of randomly placed structures of irregular shape can be seen over the entire area, as well as a significant number of organic inclusions adhering to crystals (Fig. 3c); IV type - in the field of view along the entire perimeter, single small crystals of irregular shape are detected, without a clear orientation with signs of disaggregation or complete absence of crystals. | Figure 3. Classification of the morphological type of saliva microcrystals |
3. Research Results and Their Discussion
- Earlier [10], we presented the results of a study of the features of the morphological structures of saliva in practically healthy young people at various prenosological levels of the body's health. At the same time, for the first time, the presence of the fact of the dependence of the quantitative indicators of the visual morphometry of microcrystals of dehydrated gastric cancer in practically healthy young persons on the prenosological levels of their body health was established. At the same time, the value of the indicator microcrystallization of OF equal to -1, corresponds to the maximum crystallization ability of saliva, which takes place at a high level of health of the body, and when health deteriorates, its discrete increase is observed, at a low level of health, up to 4 units. Note that at a high level of health, when the crystallizing ability of saliva becomes maximum, facies with morphological indicators close to 1 unit are formed, and at low levels of health, its crystallizing ability sharply decreases and the formation of amorphous structures with morphological indicators of 4.0 units increases. and close to it, that is, the transition of the functional state of the body from the physiological norm to the prenosological state with its stress, and in some cases to the premorbid state, are accompanied by an increase in the values the morphological indicator of saliva microcrystals.In this work, we present the results of a comprehensive study of the dependence of the morphological parameters of saliva in practically healthy young people on their autonomic status, heart rate, type of self-regulation of blood circulation and health level. Table 1 shows the distribution of the surveyed according to the levels of vegetative status, established by us on the basis of data on their VIC.
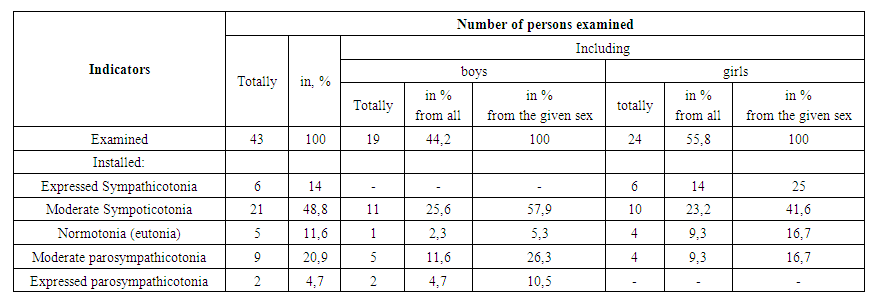 | Table 1. Distribution of the surveyed by levels of vegetative status |
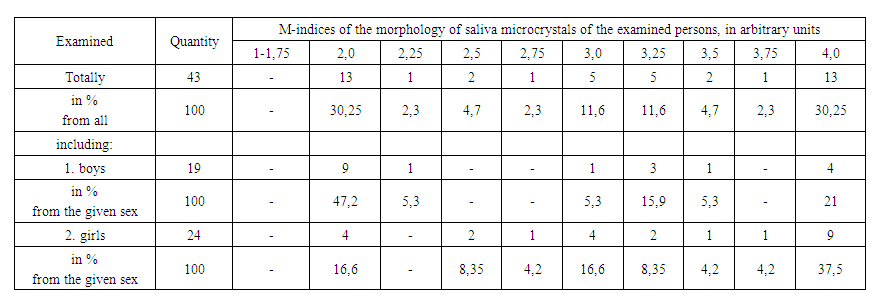 | Table 2. Distribution of the surveyed by the value of M in arbitrary units |
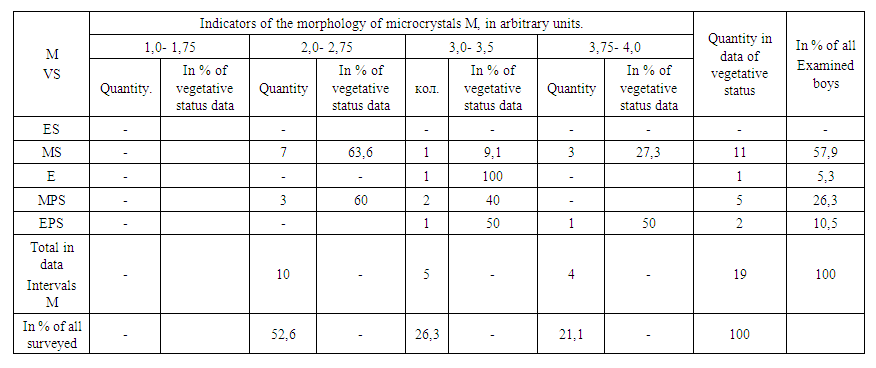 | Table 3. Indicators of the morphology of saliva microcrystals in boys |
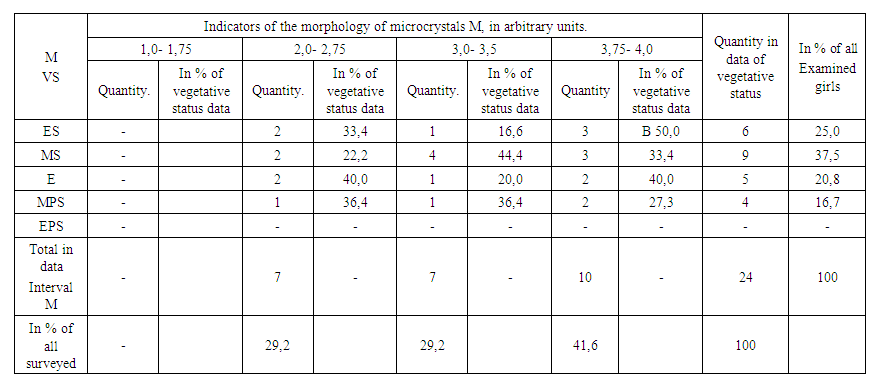 | Table 4. Indicators of the morphology of saliva microcrystals in girls |
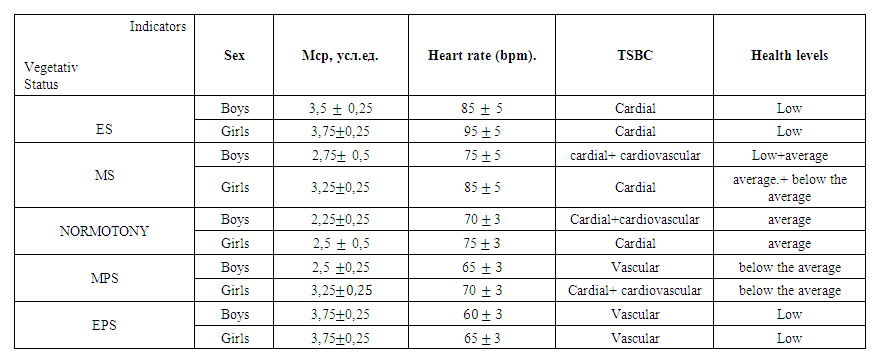 | Тable 5 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML