-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Genetic Engineering
p-ISSN: 2167-7239 e-ISSN: 2167-7220
2022; 10(3): 29-32
doi:10.5923/j.ijge.20221003.01
Received: Nov. 8, 2022; Accepted: Nov. 20, 2022; Published: Nov. 24, 2022

Creative Approach to the Formation of Pedagogical Competences of Young Biology Teachers
Achilova Nazifa Rahmonqulovna
Lecturer at the Department of Biology Teaching Methods, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Navoi State Pedagogical Institute, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Achilova Nazifa Rahmonqulovna, Lecturer at the Department of Biology Teaching Methods, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Navoi State Pedagogical Institute, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article provides interesting and historical information on creativity in the formation of pedagogical competencies of future biology teachers, independent learning, as well as the organization of non-traditional biology lessons and increasing students' interest in teaching biology, the stages of improving the methodology of using modern teaching methods, its structure, content, and introduction into educational practice, the formation of skills are studied. It also provides information on the level of knowledge and skills of beginner teachers of biology in designing lesson plans based on interactive technologies.
Keywords: Pedagogical technology, Interactive teaching methods, Pedagogical competence, Creativity, Information technology, Designing, Organizational-managerial, Explanatory-motivational, Cognitive, Technological map, Skills
Cite this paper: Achilova Nazifa Rahmonqulovna, Creative Approach to the Formation of Pedagogical Competences of Young Biology Teachers, International Journal of Genetic Engineering, Vol. 10 No. 3, 2022, pp. 29-32. doi: 10.5923/j.ijge.20221003.01.
1. Introduction
- Particular attention is paid to the development of interactive technologies for the formation of competencies in young teachers in the world, the improvement of pedagogical mechanisms for making a creative learning environment. Furthermore, on the basis of the formation of pedagogical competence to ensure the professional activity of newteachers’ priority is given to improving the mechanisms.On the basis of a creative approach in the world, the issues of formation of pedagogical competencies in future biology teachers, improvement of methodological support, development of professional competence of students, wide and mass use of multimedia, information and communication technologies in lessons are being studied. In higher education institutions, the priorities are to develop students' creative thinking skills, improve their professional competencies, ensure the harmony of theory and practice in teaching, introduce new information technologies, provide students with innovative knowledge in their fields, continuous improvement of professional skills and abilities. The transition to new paradigms of education requires not only innovative approaches to the creative development of students, but also the improvement of the methodological framework that allows to ensure the same process.In today's global environment, being a highly competitive workforce, which is a priority in the labor market, requires every specialist to have pedagogical competence and gradually increase it. So what is competence? What qualities are reflected in the basis of pedagogical competence? What competency qualities a future biology teacher should be able to articulate.The concept of "competence" entered in the field of education as a result of psychological research. So, competence means that “how a teacher behaves in unusual situations and unexpected cases, a culture of communication, a new way of interacting with competitors, in the performance of uncertain tasks, the use of conflicting information, having a clear plan of action in a constantly evolving and complex process". Pedagogical competence - possession the knowledge, skills and competencies required to perform professional activity by a specialist and application of them at a high level in practice.Pedagogical competence is not acquisition of a special knowledge and the skills by teacher, but assumes the acquisition of integrative knowledge and actions for each independent direction. Also, the competence requires always enrich specialized knowledge, learning new information, to be able to understand the important social requirements, to find new information, processing them and a high level of application in their work. Psychological competence - the ability to create a healthy psychological environment in the pedagogical process, the organization of positive communication with students and other participants in the educational process, the ability to timely understand and eliminate various negative psychological contradictions;Methodical competence - methodologically rational organization of pedagogical process, correct definition of forms of educational or pedagogical activity, choice of methods and means according to the purpose, effective application of methods, successful application of means;Information competence - search, collect, sorting, processing of necessary, important, useful information in the information environment and their purposeful, appropriate, effective use;Creative competence - a critical, creative approach to pedagogical activity, the ability to demonstrate their creative skills;Innovative competence - improve the pedagogical process and the quality of education, the promotion of new ideas to increase the effectiveness of the educational process, their effective implementation in practice; Communicative competence - to communicate sincerely with the whole participants of the educational process including students, being able to listen to them and make a positive impact on them.Technological competence - mastering advanced technologies that enrich professional and pedagogical knowledge, skills and abilities, the use of modern tools, techniques and technologies.
 | Figure 1. Structural bases of pedagogical activity |
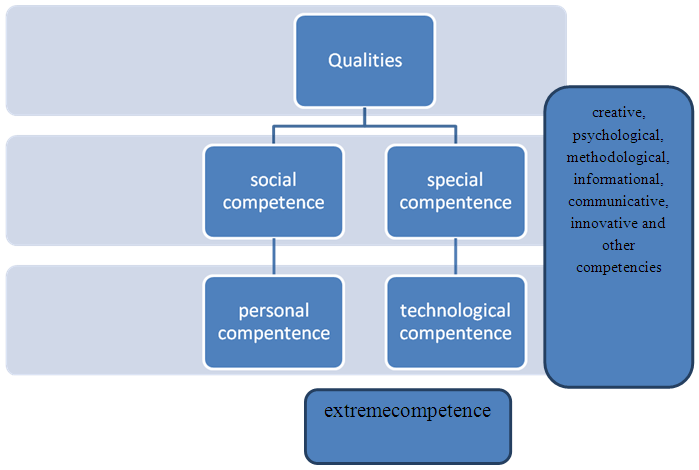 | Figure 2. Qualities of professional and pedagogical competence are based on the following qualities |
2. Numbers Speak in Biology
- The average statistical number of needles of the hedgehog reaches 10 thousand.Throughout their lives bees can produce honey as 1/12 of a teaspoon.To collect 100 grams of honey, bees fly a distance of 46 thousand km. This is equivalent to traveling the entire globe around the equator.The hen lays an average of 190 eggs a year.The elephant's teeth can weigh up to 9 kg.Ants never sleep. Instead, they “rest” from 8 minutes twice a day. The queen of ants rests for 90 minutes a day.The ficus that grows in South Africa is the longest rooted flowering plant. Its roots reach up to 120 meters.The horse breathes about 8-16 times a minute.The whale's heart beats 9 times a minute.In cow's suck, milk is stored at 37.7°C.The number of swan feathers is around 25,000, making it the most feathered bird.You can make 120 pencils out of a medium-sized tree.For example, here are some interesting facts and figures about the plant of Alhagi.
 About Alhagi- a bush can transpire up to 2.5 liters of water throughout the day. Using this unique physiological process of Alhagi, it is possible to obtain 2-2.5 liters of healing thirst-quenching fluid per day in the desert by the method of closing 1 m2 polyethylene bag. A hectare area of saplings has the capacity to receive 350 tons of groundwater and evaporate it. Another great feature of Alhagi is that by sowing seeds of melon crops (melons, watermelons, squash) in its roots, high yields allow to grow melons even in the desert.
About Alhagi- a bush can transpire up to 2.5 liters of water throughout the day. Using this unique physiological process of Alhagi, it is possible to obtain 2-2.5 liters of healing thirst-quenching fluid per day in the desert by the method of closing 1 m2 polyethylene bag. A hectare area of saplings has the capacity to receive 350 tons of groundwater and evaporate it. Another great feature of Alhagi is that by sowing seeds of melon crops (melons, watermelons, squash) in its roots, high yields allow to grow melons even in the desert. How do figs bloom? Who has seen a fig flower? These questions are asked to students in the form of a problem situation. Figs bloom in the evening, its flowers are not visible. There is a saying among the people that about it whoever sees a fig flower will crazy. Indeed, the fig flower secretes a substance that has a strong effect on human brain activity. Figs are self-pollinating. The famous botanist Carl Linnaeus discovered two types of figs, the plant has two form: female and male. As a result of this discovery, figs were found to be two pests. In female plants inflorescences-fig (siconia) are connected - flowers with long or short columns. In male specimens - kaprifigami - smaller inflorescences are formed. Both inflorescences are oval-spherical as a result of the growth of the axis, hollow and have a small hole at the top. Several varieties of self-pollinating figs have now been grown, but mainly this plant is pollinated by a special type of arps called blastophages. Fertilized female blastophages enter the flower beds of male fig plants, lay eggs there, and fly through a hole at the top of the inflorescence. The larvae that emerge from the eggs live and
How do figs bloom? Who has seen a fig flower? These questions are asked to students in the form of a problem situation. Figs bloom in the evening, its flowers are not visible. There is a saying among the people that about it whoever sees a fig flower will crazy. Indeed, the fig flower secretes a substance that has a strong effect on human brain activity. Figs are self-pollinating. The famous botanist Carl Linnaeus discovered two types of figs, the plant has two form: female and male. As a result of this discovery, figs were found to be two pests. In female plants inflorescences-fig (siconia) are connected - flowers with long or short columns. In male specimens - kaprifigami - smaller inflorescences are formed. Both inflorescences are oval-spherical as a result of the growth of the axis, hollow and have a small hole at the top. Several varieties of self-pollinating figs have now been grown, but mainly this plant is pollinated by a special type of arps called blastophages. Fertilized female blastophages enter the flower beds of male fig plants, lay eggs there, and fly through a hole at the top of the inflorescence. The larvae that emerge from the eggs live and  feed on substances derived from the inflorescence.Why don’t the grains that the ants have collected underground grow out of the ground? Scientists have found that the ant gathers the grain and seeds it needs underground and splits it in two after it has accumulated. Because if the grain and the seed are divided into two, no matter how fertile the land, it will not grow. But when the ant saw that the kashnich grain was divided into four pieces, the scientists were surprised. After conducting the necessary research in this regard, they discovered the following. The kashnich grain would grow even if it was divided into two. But if it is divided into four parts, it will not grow. In the teaching of biology, accordance with the unique and modern requirements each theme is required training. It is also planned to provide additional types of education and upbringing in teaching each lesson to young students. For example, in the process of teaching topics in botany classes, students are taught the importance of a number of plants, their care, observation growth and development, and the issues of organize scientific research work will be possible to teach to students. But because students are small groups, they can be limited to learning the plant nutrition, growth of height or width, and so on.Conducting research in biology and teaching using the results in the reading process, gives great results in the acquisition of theoretical and practical knowledge of students. This leads to 15-20% positive results compared to normal types of training.The creative approach of future biology teachers is very useful in subject of biology, extracurricular and extralesson activities, and it creates good conditions for students to gain in-depth knowledge and positive forms of education, as well as increase their interest in studying biology and the profession.Thus, it can be concluded from the above that the task of the teacher in the classroom is to organize the activities of students in such a way that they apply as much as possible their knowledge of general and specialized disciplines, mobilize them to develop skills to perform assigned tasks. At this stage, explanatory notes, processes from working material drafts to the end are designed, and this serves to improve the professional quality of the students.
feed on substances derived from the inflorescence.Why don’t the grains that the ants have collected underground grow out of the ground? Scientists have found that the ant gathers the grain and seeds it needs underground and splits it in two after it has accumulated. Because if the grain and the seed are divided into two, no matter how fertile the land, it will not grow. But when the ant saw that the kashnich grain was divided into four pieces, the scientists were surprised. After conducting the necessary research in this regard, they discovered the following. The kashnich grain would grow even if it was divided into two. But if it is divided into four parts, it will not grow. In the teaching of biology, accordance with the unique and modern requirements each theme is required training. It is also planned to provide additional types of education and upbringing in teaching each lesson to young students. For example, in the process of teaching topics in botany classes, students are taught the importance of a number of plants, their care, observation growth and development, and the issues of organize scientific research work will be possible to teach to students. But because students are small groups, they can be limited to learning the plant nutrition, growth of height or width, and so on.Conducting research in biology and teaching using the results in the reading process, gives great results in the acquisition of theoretical and practical knowledge of students. This leads to 15-20% positive results compared to normal types of training.The creative approach of future biology teachers is very useful in subject of biology, extracurricular and extralesson activities, and it creates good conditions for students to gain in-depth knowledge and positive forms of education, as well as increase their interest in studying biology and the profession.Thus, it can be concluded from the above that the task of the teacher in the classroom is to organize the activities of students in such a way that they apply as much as possible their knowledge of general and specialized disciplines, mobilize them to develop skills to perform assigned tasks. At this stage, explanatory notes, processes from working material drafts to the end are designed, and this serves to improve the professional quality of the students. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML