-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Genetic Engineering
p-ISSN: 2167-7239 e-ISSN: 2167-7220
2012; 2(1): 1-11
doi:10.5923/j.ijge.20120201.01
Biocompatibility and Gene Expression Associated with Streptococcus Infection in Myocarditis
Soha S. S. Abdou1, Kholoud S. Ramadan2, Iman M. K. Abumourad3, Rasha E. Hassan1
1Biochemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
2Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Girls Science, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
3Department of hydrobiology, National Research Center, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Iman M. K. Abumourad, Department of hydrobiology, National Research Center, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Myocardial inflammation is a nonspecific response to various triggers such as viral and bacterial infection. This study was designed to examine the Streptococcus induction of myocarditis in rat and induction of CRP, SAP, LBP and Cytokines on the transcriptional activity of the inflammation / related genes expression using a semi-quantitative RT-PCR in liver and heart tissues. Experimental myocarditis was established with intra-peritoneal injection of 108 CFU/ ml of Streptococcus faecalis in three groups of rats and sacrificed after one, two and seven days post infection, respectively. Heart and liver functions were highly elevated while kidney functions were not affected. Histopathological examination for heart and liver showed damage effect for the bacterial infection. Expression pattern of CRP, SAP, LBP & IL6 genes were investigated, in liver these genes were highly expressed while some of them showed no expression pattern in heart tissues.
Keywords: Myocarditis, Rat, Streptococcus Faecalis, C-Reactive Protein, Serum Amyloid P Component, Interleukin 6 & Lipopoly Saccharide Binding Protein
Cite this paper: Soha S. S. Abdou, Kholoud S. Ramadan, Iman M. K. Abumourad, Rasha E. Hassan, Biocompatibility and Gene Expression Associated with Streptococcus Infection in Myocarditis, International Journal of Genetic Engineering, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2012, pp. 1-11. doi: 10.5923/j.ijge.20120201.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Myocarditis, a heterogeneous myocardial inflammatory disease, leads to both acute and chronic heart failure manifested by dilated cardiomyopathy. The etiology of myocarditis appears to be rather complicated involving idiopathic, infectious or autoimmune factors (Caforio and Iliceto, 2008). Bacteremia from any source may result in myocarditis, with the most common pathogens being meningococcus, streptococcus, and Listeria (Lori and Cooper, 2010). Myocarditis is an uncommon disease, usually difficult to diagnose because its clinical behavior may be entirely asymptomatic until sudden death. (Dec, 2002 & Jared et al., 2006) Myocarditis has been reported in up to 12% of young adults presenting with sudden death (Fabre & Sheppard, 2006) and is an important underlying etiology of other myocardial diseases (Puranik et al., 2005) such as dilated (Kawai, 1999)and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (Calabrese et al., 2006). Research over the last 15 years has provided that there is unequivocal evidence for a local inflammation in the artery wall which is accompanied by a systemic low-grade inflammatory response. (Feinstein & Spagnuolo, 1993 and Narula et al., 1999). Inflammatory response can be measured by a variety of inflammatorybiomarkers. The largest database so far has been accumu- lated for C-reactive protein (Kolz et al., 2008). C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute phase reactant with roles in innate host defense, clearance of damaged cells, and regulation of the inflammatory response. Cytokines released from jeopardized tissues stimulate the liver to synthesize acute phase proteins, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and serum amyloid P component (SAP). IL-6 is the chief stimulator for the production of most acute phase proteins. (Kushner, 1982 and Gotschilich, 1989). Serum amyloid P component (SAP), the murine homologue to CRP, is a relatively low concentration constitutive serum protein in man. Paradoxically, in mouse SAP is the major acute phase reactant. (Jiang et al., 1995) Therefore, mRNA expression levels of CRP and SAP may provide sensitive markers of systemic acute phase response (Saber et al., 2009). Lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP), a key participant in the inflammatory response to infection, may be a useful marker for diagnosis and prognosis of patients with bacterial infections (Schumann et al., 1990). The present study sought to investigate the association and biocompatibility between C - reactive protein (CRP), Serum amyeloid P component (SAP), Lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP) and cytokines exemplified by interleukin 6 (IL6) genes expression involved in the inflammatory pathway in a rat group experimentally infected with streptococcus bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental animals
- Ten weeks old male Swiss albino rats (n=40) weighing 150-200 g were maintained on a diet of ad libitum and tap water. These experiments have been approved by Ain Shams University committee on the use and care of Laboratory animals. After 2-weeks as a conditioning period, the animals were randomly distributed into 2 groups. One group (n=10) was treated as a control group and injected with saline. The other group (n=30) was treated as the experimental group, anesthetized with ketamine, and were intraperitoneal injected with a fresh culture of Streptococcus faecalis. Rats were sacrificed after 1, 2 and 7 days from infection with bacteria.
2.2. Bacterial Challenge
- Enterococcus faecalis bacteria strain refrence ATCC: 29212, supplied from the faculty of veterinary medicine, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt was used. The bacteria was grown for 18 hours at 37℃ in glucose broth medium (Enriched media) and aliquots of the initial culture were inoculated into fresh media with 15 % glycerol for storing and frozen at -20℃ until used. Frozen aliquots were thawed, kept at 37℃ for 6 hours, and sub cultured in fresh media for 18 hours prior to injection. The bacteria were cultured to approximately 108 CFU/ml. Estimations of cell density were determined by measuring the absorbance at 620 nm and verified by plate counts. Quantization of cultures was done by serial dilutions & plates were counted after overnight incubation with a bright light source. A fresh culture of bacteria was prepared (24 hours culture) and 1 ml of this culture was injected in the experimental rat groups.
2.3. Tissue Specific Expression of CRP, IL-6, LBP and SAP Genes by Semi-Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
- I) RNA extraction from tissueRNA was extracted from rat livers and hearts according to the method of Nicholas, (2004) using BIOZOL BioFlux™ Reagent (ready to use) that was purchased from BioFlux (South San Francisco, U.S.A).II) Reverse transcription The extracted total RNA was then reverse transcribed with Oligo d(T) primer according to Revert Aid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit™ (purchased from Fermentas life science Co. (Invitrogen Corporation) (Van Allen Way, Carlsbad, Canada). Positive and negative control reactions were used to verify the results of the first strand cDNA synthesis steps. GAPDH gene RNA was used as positive control.III) Polymerase chain reactionThe resulting cDNA was subjected to PCR for 35 cycles with respective primers designated from the sequence of the CRP, IL-6, LBP and SAP genes (table 1) using primer premier 5.0 software and were purchased from Invitrogen Corporation (Van Allen Way, Carlsbad, Canada). Dream Taq™Green PCR Master Mix (Invitrogen Corporation) was used in the PCR. Products of PCR were then displayed on an appropriate agarose gel (2%) and examined for yield and specificity. Analysis of gel images was done using Gel analyzer Pro (version 3.1) software. PCR product for each gene was sequenced. The obtained nucleotide sequences were blasted on gene bank site (http://www.ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/) to ensure that the obtained PCR product is our target gene. The nucleotide sequence for each gene was analyzed using the web site for sequence manipulation suite (version 2): http://www.bioinformatics.org/sms2/ to characterize some target genes like the open reading frames, prediction and characterization for the protein sequences and the signal P 3.0 Sever using the expasy website (http:// expasy.org/tools/) to predicts the presence and location of signal peptide cleavage sites in amino acid sequence. This method incorporates a prediction of cleavage sites and a signal peptide/non-signal peptide prediction based on a combination of several artificial neural networks and hidden Markov models.
3. Results
- a) C- reactive protein gene expressionCRP gene was highly expressed by hepatocytes and heart after bacterial infection by 1 day, 2 days and 7 days (Fig. 1-A). In both tissues the bands molecular weight on agarose gel were 433 bp. While, there was no expression for CRP in the liver and heart of normal non-infected control group. GADPH gene expression was used as +ve control in examining all the studied genes. Rat CRP gene/GAPDH gene ratio was determined by densitometry (Fig.2), which was performed by measuring the photo stimulated luminescence values using gel analyzer pro version software.
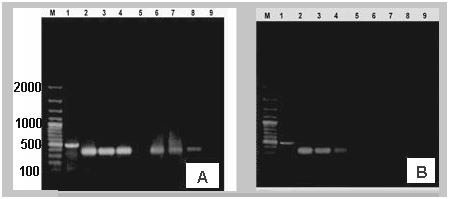 | Figure 1. A) The C-reactive protein (CRP) gene expression in accordance to GAPDH. (B) SAP gene expression in accordance to GAPDH (lane: 1) obtained by RT-PCR in liver (lane: 2, 3 & 4) & heart (6, 7 & 8) of infected groups with bacteria and control group (lanes 5 & 9) (M: DNA marker) |
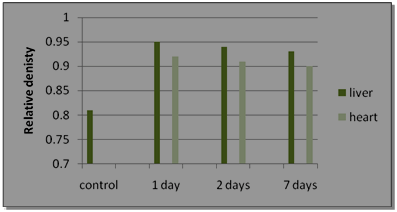 | Figure 2. The relative density of expressed rat CRP gene bands in liver and heart tissues |
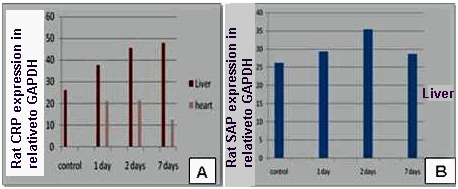 | Figure 3. (A) Effect of bacterial infection (1, 2 and 7 days) on expression of rat CRP ⁄ GAPDH genes in liver and heart. (B): Effect of bacterial infection (1, 2 and 7 days) on expression of rat SAP⁄ GAPDH genes in liver and heart |
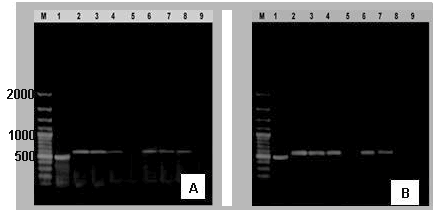 | Figure 4. (A) IL6 gene expression in accordance to GAPDH. (B) LBP gene expression in accordance to GAPDH (Lane: 1) obtained by RT-PCR in liver (2, 3 & 4) & heart (6, 7 & 8) of infected groups with bacteria and control group (lanes 5 & 9) (M: DNA marker) |
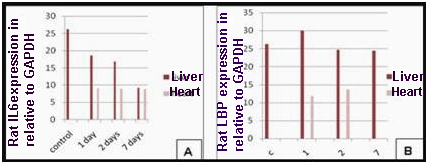 | Figure 5. (A) Effect of bacterial infection (1, 2 and 7 days) on expression of rat IL6 & GAPDH genes in liver and heart. (B) Effect of bacterial infection (1, 2 and 7 days) on expression of rat LBP & GAPDH genes in liver and heart |
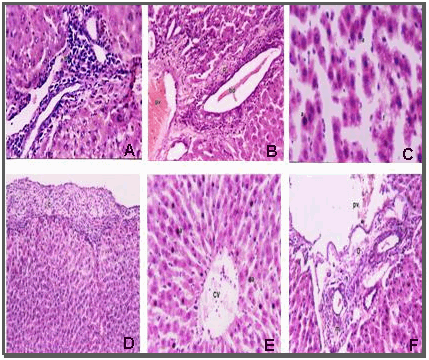 | Figure 6. Histological appearance of liver sections stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin of: (A) Massive number of inflammatory cell infiltration in the portal area after one day from infection. (B)dilation and congestion in the portal vein (pv) and dilation of bile duct (bd) with periductal inflammatory cells infiltration after one day from infection. (C)Apoptosis (a) and mild fatty change (f) in hepatocytes after bacterial infection by two days. (D) thickening of the hepatic capsule (c) and infiltrated by inflammatory cells and fibrin threads after seven days from infection.(E)Apoptosis in most of hepatocytes (a).(F) Dilation in the portal vein (pv) with inflammatory cells infiltration (m) in the portal area surrounding the bile duct (o) after seven days from infection |
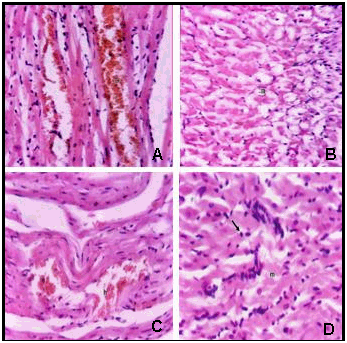 | Figure 7. Histological appearance of heart sections stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin of: (A) Infected heart rat after one day showing focal hemorrhages in between the myocardial bundles (h). (B) infected rat after two days showing degeneration of myocardial muscle cells (m). (C) focal hemorrhages (h) in between the myocardial bundles after bacterial infection by two days. (D) infected rat showing inflammatory cells infiltration (arrow) in between myocardial bundles (m) after bacterial infection by seven days |
4. Discussion
- Myocardial inflammation is a nonspecific response to various triggers such as viral or bacterial infection, cardio toxic agents, catecholamine, infarction, or mechanical injury (Skouri et al., 2006). Myocarditis is a potentially life- threatening disease that primarily affects children and young adults with sometimes devastating consequences, including sudden death (Drory et al., 1991). Myocarditis is defined as: a process characterized by an inflammatory infiltrate of the myocardium, with necrosis or degeneration of adjacent myocytes not typical of the ischemic damage associated with coronary artery disease (Dominiczak et al., 2005). Bacteremia from any source may result in myocarditis, with the most common pathogens being meningococcus, streptococcus, and Listeria (Blauwet and Cooper, 2010).More than a dozen different enterococcal species have been associated with human disease; the majority of human enterococcal infections are due to the species Enterococcus faecalis (Jett et al., 1994, Evans & Chinn (1947), Facklam & Collins (1989), Murray (1990) & Moellering (1992)). The present study was concerned with bacterial myocarditis where it was carried out on four groups of rats, each group is composed of ten rats (n= 10). Three of the four groups were injected by Streptococcus faecalis intra- peritoneally and the fourth group was treated as control group and was injected by saline. All rats in the experimental three groups developed myocarditis, this was proved, after sacrificing the animals on different intervals of time (after 1 day, 2 days and 7 days), through a series of biochemical, molecular and histological investigations. In this study we investigated numerous biochemical markers (Data not shown) for inflammation and gene expression pattern for group of inflammation related genes. These investigations were carried out on different intervals of time (one, two and seven days) after bacterial infection.C-reactive protein is an acute-phase reactant protein synthesized primarily by liver cells in response to the proinflammatory cytokines including interleukin-6 and TNF-α (Castell et al., 1990). The major function of CRP by binding phosphocholine is to recognize some foreign pathogens and phospholipid constituents in damaged cells (Gotschlich and Edelman, 1967). It also activates the complement system and contributes to the induction of inflammatory cytokines and tissue factors in monocytes (Ballou and Kushner, 1992). Inflammatory molecules as mildly raised C- reactive protein (CRP) are among the most extensively studied CVD biomarkers and is considered one underlying cause of CVD development and progression (Libby, 2000). Animal studies also support the proinflammatory and pro-atherogenic role of CRP, because administration of human CRP or over- expression of CRP in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice promotes the development of spontaneous atherosclerosis (Paul et al., 2004). CRP is mainly expressed by hepatocytes, but can be synthesized in other tissues (Black, Kushner & Samols, 2005 & Marnell, Mold & Du Clos, (2005), although the liver has been assumed as the only source of CRP synthesis and release, this protein has been demonstrated (Calabro, Willerson & Yeh, 2003) to be produced also in other districts, such as the vascular walls.Mouse CRP (moCRP) is classified as a minor APR since its highest concentration was estimated at only~2µg/ml, as against levels of ≥300, µg/ml in humans that are undergoing an inflammatory response (Kushner, 1988 and Ballou & Kushner, 1992). HuCRP and moCRP are each encoded by a single-copy gene on chromosome 1 of both species as part of a syntenic group of genes (Yunis & Whitehead, 1990). Both genes have a very similar organization, with two exons and a single intron within the codon for the third residue of the mature protein (Lei et al., 1985 & Ohnishi et al 1988). The amino acid sequences from cDNA clones for human and mouse CRP show an identity of 71 % (Ohnishi et al., 1988 & Whitehead et al., 1990). The extent of the increase in moCRP seems likely to be a function of the gene structure, since the human CRP gene is expressed as a major APR in transgenic mice (Ciliberto et al., 1987).In the current study, the injection of rats by Streptococcus feacalis induces a “priming” of the host immune response characterized by increased expression of CRP genes in liver and heart tissues by 24 h after infection with a peak at 48 h when compared with the uninfected control rats that showed no expression for the gene. (Analysis of images to show the peak) Tissue-specific gene expression is regulated at the transcriptional initiation step through the recognition of promoter sites by transcription factors (Maniatis, Goodbourn, & Fischer, 1987). This general scheme for tissue-specific gene expression has been documented for many cell types, including pancreatic endocrine cells (Ohlssen & Edlund, 1986), hepatocytes (De Simone & Cortese 1988), erythrocytes (Tsai et al., 1989) muscle cells (Lassar et al, 1989) and B cells (Muller et al, 1988 & Scheiderei et al., 1988). It seems likely therefore that the expression of the mouse acute-phase genes is regulated by liver-specific trans-acting factors and cis acting elements within the 5' flanking region of the genes (Namon & Richard, 1993). The pathogenesis and severity of both experimental and human myocarditis has been lied to the intramyocardial production of these cytokines, as well as that of interferon-)! (IFN-y)(Lane et al., 1991, 1992, 1993).(70)In rats infected with S.mansoni, a sudden increase in cytokine mRNA expression was observed only during the early stages of infection, during which the parasite passes through the lung. This result indicates that the immune response is associated to the parasitic infection pathway (Cetre et al., 1998).IL-6, which is Th2 cytokine and the principal mediator of the acute phase response in rats, plays certain roles in immunity in vivo. However, the mechanism by which this cytokine operates has been reported to vary widely. The mechanisms inherent to responses to foreign antigens differ depending on the kinds of parasites, host and infection period. When we set a standard with rates of increase or decrease in cytokine expression in the spleen, it was determined to increase principally in the early stages of infection, and it was unbiased toward the Th1 or Th2 cytokine (KIM et al., 2007).Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a proinflammatory cytokine, elicits pleiotropic effects on a variety of biological functions, including regulation of the immune response, hem-atopoiesis, inflammation and cellular differentiation (LE & Vilcek, 1989) & Hirano et al., 1990. However, IL-6 serves not only as an inducer of acute phase reactions but is also an important factor in the elicitation of cellular immune responses against infected cells and of mucosal humoral responses against re-infection (Romani et al., 1996). IL-6 is the chief stimulator for the production of most acute phase proteins (Gabay & Kushner, 1999). Recent studies have indicated the additional importance of cytokines in the pathogenesis of myocardial injury in viral myocarditis (Shioi et al. 1996). Evidence that IL-6 generates distinct signal only in the combination with IL-6 receptor in cardiac myocyte is based on the low expression level of IL-6 receptor (Saito et al. 1992; Yamauchi-Takihara et al. 1995). Independently of high cholesterol or myocardial damage markers, IL-6 predicts future adverse cardiovascular events and reflects increased inflammatory activity in plaques and is therefore a strong marker of increased risk for mortality in coronary artery diseases (Lindmark et al., 2004 & Ridker et al., 2000). The cytokine IL-6 is synthesized, e.g., by mononuclear phagocytes, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts (Soderquist et al., 1995). IL-6 is known to be secreted from several cell types, including endothelial cells, macrophages, lymphocytes, and adipocytes, and exerts its biological actions through a complex yet well-defined fashion (Tsugiyasu & Takashi, 2004). The most potent inducer of huCRP gene expression at the level of transcription is IL-6 (Ganapathi et al., 1988 & Ganter et al., 1989). A recent study has shown increased myocardial IL-6 expression is associated with the progression of heart failure (Plenz, Song & Reichenberg et al., 1998). IL-6 mRNA is reportedly induced in the myocardium of a canine model of ischemia and reperfusion (Chandrasekar et al., 1999 & Kukielka et al., 1995).In the present study, we investigate the expression pattern of IL-6 gene expression pattern in liver and heart tissues. We found that there was no abundance of IL-6 expression pattern in control non infected rat’s liver and cardiac tissue and that bacterial infection led to a marked increase in IL-6 gene expression in both liver and heat tissues detected after one, two and seven days post infection. Some investigators as Erodgan & Ongen, 1997, Mohler et al., 1997, Ridker et al., 2000 & Kanada et al., 2000 have suggested that IL6 enhances development of myocardial injury. Several mouse models have been used to analyze the direct relationship between IL-6 and infection. IL-6 deficient mice were reported to be susceptible to both microbial and viral infections (Lane et al., 1991). Elevated production of IL-6 has been reported in autoimmune and infectious diseases as well as traumatic injury. Many other studies were in harmony with our results as the studies of (Lane et al., 1991, 1992, 1993) which support that the pathogenesis and severity of both experimental and human myocarditis has been lied to the intra-myocardial production of interleukin-l β (IL-lβ) and interleukin-6 (IL 6), as well as that of interferon- IFN-y (Black et al., 2004) Also the studies of Hartmut et al., 1995 support our findings as they stated that cytokines may be released locally within the heart by vascular endothelial cells, fibroblasts, macrophages, and leukocytes in response to a variety of stimuli including ischemia-reperfusion, cardiopulmonary bypass, septic shock, heart transplant rejection, and myocarditis. The heart may also be exposed to cytokines released from other sites such as the liver or lungs in septic or inflammatory conditions (Gotschlich and Edelman, 1967).Serum amyloid P component (SAP) is a member of pentraxins. Previous studies indicate that SAP exists in human atherosclerotic aortic intima and the plasma SAP levels are associated with cardiovascular disease. (Hirano et al., 1990) SAP is produced mainly in the liver and secreted into the blood circulation. The average plasma concentration of SAP is about 40 mg/ l (160 nM) in human. (Puranik et al, 2005) In man and rabbit, one of the serum proteins that exhibit the highest proportional increase, from trace resting levels to several hundred micrograms per ml, is CRP. SAP is a relatively low concentration constitutive serum protein in man. Paradoxically, in mouse it is SAP that is a 'major' acute phase reactant, increasing from resting levels of around 60, µg/ml or less to peak concentrations of several hundred micrograms/ml during acute inflammation [Gabay, 1999]. Although mouse CRP is poorly defined, it has been reported as a trace serum component [Shioi et al, 1996] that increases slightly in concentration during the acute-phase response [Saito et al, 1992). These studies support our present study where by analysis of our PCR product images for both CRP and SAP genes expression in liver tissue, we found that the relative density for SAP genes bands was higher than that of CRP genes bands which gives a confirmed figure about that SAP represent the major acute phase protein in rat.Numerous studies using primary mouse hepatocytes (Lin et al., 1990) have shown that the mouse SAP gene can be induced by the direct action of either IL-1 or IL-6. Thus, both CRP and SAP are usually considered to be class 1 acute- phase gene products.Serum levels of SAP in mouse start to rise approximately 8 h after an acute-phase stimulus and peak at 24-48 h (Pepys, M.B., 1979) the serum half-life is 7-8 h and is independent of the SAP level (Baltz, Dyck & pepys, 1985). Increases are therefore proportional to the rate of synthesis and secretion of SAP rather than to changes in clearance. One of the most potent stimuli to SAP production is bacterial endotoxin. Recently it has been shown that this effect is mediated via certain cytokines produced by activated monocytes and macrophages (Le, Muller & Mortensen, 1982).In this study, the data showed that there was no expression for SAP genes in normal uninfected rat’s liver while SAP expression markedly increase in liver tissue after the bacterial infection at one, two and seven days. Also, in the present study, no expressions for SAP genes were observed in heart tissue after bacterial infection when compared to the control. These findings are contradicted with those of Zhiqing et al, 2010 which indicates that SAP is produced by non-hepatic cells (Hirano et al, 1990).In summary, our data demonstrate that in rats, during S. facalis infection, the expression of SAP is rapidly and strongly in liver parenchyma but not in the heart during the bacterial induced acute phase response. In this regard, SAP might be referred to as an early intracellular acute phase protein. Taken together, these data point to an important role of SAP in cytoprotection of hepatocytes, which might become damaged during their intensive function under inflammatory conditions.Indirect evidence for LBP participation in sepsis comes from clinical investigations showing that levels of LBP in several body fluids were increased significantly in patients with bacteremia, sepsis, major surgery and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and were associated with clinical outcome. (Cermak et al., 2005). Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) is a protein that is up-regulated and secreted in stress situations. Its exact role in modulating the cellular response to endotoxin remains unclear. As an acute phase response, protein LBP is especially interesting because of findings indicating a potential dual role in the regulation of LPS action on target cells: low baseline level concentrations of LBP have been shown to enhance LPS potency, whereas the high concentrations seen during the acute phase can decrease the suppressive effect of LPS by shunting it into the HDL clearance pathway. It has been demonstrated in a mouse model that the high serum concentrations of LBP are protective in the setting of sepsis and bacteremia [Yunis, and Whitehead, 1990]. LBP is present at low levels (ca. 100–200 ng/ml in the blood) under normal conditions whereas it is highly increased during infections (ca. 10–20 µg/ml) to neutralize LPS for the prevention of overwhelming inflammation (Zweigner et al., 2001). Liver is considered to be the central organ regulating this acute phase response by releasing specific acute phase protein including LBP which has been defined as a class I acute phase protein. (Kushner, 1988). Previous data showed that LBP mRNA expression in liver and kidneys markedly increased after burns. (Marnell et al, 2005) LBP expression in several cell types was demonstrated in vitro to be dramatically up-regulated by exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. (Calabro et al, 2003) Our data showed that there was no expression for LBP genes in normal uninfected rat’s liver while LBP expression markedly increases in liver tissue compared to GAPDH after the bacterial infection at one, two and seven days. These findings are in harmony with those of (Grace et al., 1994) and dog (Usui et al., 1998), which stated that LBP gene expression occur in tissues such as liver, kidney, spleen and lung was reported in rat. (Ciliberto et al, 1987) Also, this agree with the studies of Su et al., 1994 as they reported that rat LBP mRNA is expressed mainly in the liver and slightly in kidneys and lungs, and that its levels increase markedly in the liver, kidneys and lungs in bacterial infections (Maniatis et al, 1987). Rat and rabbit models as well as in-vivo experiments with primary human hepatocytes and human hepatoma cell lines demonstrated that LBP is a secretory class 1 acute-phase protein whose gene is transcriptionally activated by the acute-phase response element/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (APRF/STAT3) and other cytokine-inducible nuclear proteins [Ohnishi et al, 1988], where Our study indicated that the predicted signal p for the predicted protein sequence of rat LBP is a non- secretory protein.There was no expression for LBP genes in normal uninfected rat’s heart in our study while we found that LBP genes expression pattern increased after 24 and 48 hours post infection and no expression for the gene was detected after seven days post infection. These findings can be supported by the findings of Dentener et al, 2000 which stated that the transcriptional regulation of the LBP gene is induced by interleukin (IL)-1 alone or synergistically by IL-1 and IL-6, leading to a maximal LBP concentration within 24-48 h after stimulation, a response that can be strongly enhanced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-a and dexamethasone [Whitehead et al., 1990].
References
| [1] | Ballou, S. P. and Kushner, I. (1992): Adv. Intern Med. 37, 313-337 |
| [2] | Baltz, M.L., Dyck, R.F. and pepys, M.B. (1985): Studies on the in vivo synthesis and catabolism of serum amyloid P component (SAP) in the mouse. Clin. exp. Immunol. 59: 235 |
| [3] | Banchroft, J.D., Stevens, A. and Turner, D.R. (1996): Theory and practice Of Histological Techniques. Fourth Ed. Churchil Livingstone, New York, London, San Francisco, Tokyo. Black S, Kushner I, Samols D. (2004): C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem., 279:48487-48490 |
| [4] | Blauwet LA, Cooper LT. (2010): Myocarditis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 52:274–288 |
| [5] | Bodmer, B. & Siboo, R. (1977): J. Immunol. 118, 1086-1089 |
| [6] | Caforio, A.L., Iliceto, S. (2008): Genetically determined myocarditis: clinical presentation and immunological characteristics. Curr Opin Cardiol 23: 219–226 |
| [7] | Calabrese F, Basso C, Carturan E, Valente M, Thiene G. (2006): Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: is there a role for Calabro` P, Willerson JT, Yeh ET. (2003): Inflammatory cytokines stimulated C-reactive protein production by human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Circulation, 108: 1930–1932 |
| [8] | Castell JV, Gomez-Lechon MJ, David M, Fabra R, Trullenque R, Heinrich PC. (1990): Acute-phase response of human hepatocytes: regulation of acute-phase protein synthesis by interleukin-6. Hepatology; 12(5):1179–86. [PubMed: 1699862] |
| [9] | Catherine W.H. Fang, Yong-Ming Yao, Hong-Xia Zhai, Yan Yu, Ye Wu, Lian-Rong Lu, Zhi-Yong Sheng, C. Y Sheng (2004): Tissue lipopolysaccharide-binding protein expression in rats after thermal injury: potential role of TNF-α. Burns 30:225–231 |
| [10] | Cermak J., Key N.S., Bach R.R., Balla J., Jacob H.S. and Vercellotti(1993): C-reactive protein induces human peripheral blood monocytes to synthesize tissue factor. J. Blood. 15;82(2):513-20 |
| [11] | Cêtre C, Pierrot C, Cocude C, Lafitte S, Capron A, Capron M, Khalife J (1999): Profiles of Th1 and Th2 cytokines after primary and secondary infection by Schistosoma mansoni in the semipermissive rat host. Infect Immun 67: 2713-2719 |
| [12] | Chandrasekar B, Mitchell DH, Colston JT, and Freeman GL. (1999): Regulation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein, interleukin- 6, interleukin-6 receptor, and gp130 expression during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation ,99: 427–433 |
| [13] | Ciliberto, G., Arcone, R., Wagner, E. and Ruther, U. (1987): EMBO J., 6: 4017-4022 |
| [14] | Dalrymple SA, Lucian LA, Slattery R, McNell T, Aud DM, Fushino S, Lee F, Murray R. (1995): Interleukin 6-deficient mice are highly susceptible to Listeria monocytogenes infection: correlation with inefficient neutrophilia. Infect Immun; 63: 2262–2268 |
| [15] | De Simone, V. and Cortese, R. (1988): Oxford Surv. Eukaryotic Genes, 5: 51-90 |
| [16] | Dec GW. (2002): Introduction to clinical myocarditis. In: Cooper LT, ed. Myocarditis: From Bench to Bedside. Totowa: Humana Press: 257−281 |
| [17] | Dentener MA, Vreugdenhil AC, Hoet PH, Vernooy JH, Nieman FH, Heumann D, et al. (2000): Production of the acute-phase protein lipopolysaccharide-binding protein by respiratory type II epithelial cells: implications for local defense to bacterial endotoxins. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol; 23:146–53 |
| [18] | diagnosis and treatment. Circulation;113:876−890 |
| [19] | Dominiczak, A.F. et al. (2005): Cardiovascular genomics and oxidative stress. Hypertension, 45: 636–642. Citted from: Christian Delles, Martin W. |
| [20] | Drory, Y., Turetz, Y., Hiss, Y., Lev, B., Fisman, E.Z., Pines, A., Kramer, M.R. (1991): Sudden unexpected death in persons less than 40 years of age. Am J Cardiol 68: 1388–1392 |
| [21] | Erodgan O, Ongen Z. (1997): The role of CRP and IL-6 in unstable angina. Circulation; 96: 2099–2101 |
| [22] | Naoki Hiki, Dieter Berger, Yoshikazu Mimura, Julia Frick, Mieke A. Dentener, Wim A. Buurman, Manuela Seidelmann, Michio Kaminishi and Hans G. Beger (2000): Release of endotoxin-binding proteins during major elective surgery: role of soluble CD14 in phagocytic activation. World J Surg ;24:499–506 |
| [23] | Evans AC, Chinn AL (1947): The Enterococci: With Special Reference to Their Association with Human Disease. J.Bacteriol. 54: 495–512 |
| [24] | Fabre A, Sheppard MN (2006): Sudden adult death syndrome and other non-ischaemic causes of sudden cardiac death. Heart, 92: 316 –320 |
| [25] | Facklam RR, Collins MD (1989): Identification of Enterococcus species isolated from human infections by a conventional test scheme. J.Clin.Microbiol. 27: 731–734 |
| [26] | Feinstein, A.R., Spagnuolo M. (1993): The clinical pattern of acute rheumatic fever: a reappraisal. Medicine 72: 272-283 |
| [27] | G.L. Su, P.D. Freeswick, D.A. Geller, Q. Wang, R.A. Shapiro, Y.-H. Wan, T.R. Billiar, D.J. Tweardy, R.L. Simmons, S.C. Wang, (1994): J. Immunol. 153: 743–752 |
| [28] | G.M. (1993): C-reactive protein induces human peripheral blood Gabay C, Kushner I (1999): Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med, 340:448-454 |
| [29] | Ganapathi, M. K., Schultz, D., Mackiewicz, A., Samols, D., Hu, S-1., Brabenec, A., Macintyre, S. S. and Kushner, I. (1988): J. Immunol. 141:564-572 |
| [30] | Ganter, U., R. Arcone, C. Toniatti, G. Morrone, and G. Ciliberto. (1989): Dual control of C-reactive protein gene expression by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. EMBO J. 8:3773-3779 |
| [31] | Gotschilich EC (1982): C-reactive protein: A historical overview. Ann NY Acad Sci, 557:19–30 |
| [32] | Gotschlich, E. C., and Edelman, G. M. (1967): Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 47: 706-712 |
| [33] | Grace, L.S., Freeswick, P.D., Geller, D.A., Wang, Q., Shapiro, R.A., Grube BJ, Cochane CC, Ye RD, Green CE, McPhail ME, Ulevitch RJ, et al. (1994): Lipopolysaccharide binding protein expression in primary human hepatocytes and HepG2 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem ;269:8477–82 |
| [34] | Hartmut Luss, Simon C. Watkins, Paul D. Freeswick, Amy K. Imro, Andreas K. Nussler*, Timothy R. Billiar, Richard L. Simmons, Pedro J. de1 Nido and Francis X. McGowan, Jr. (1995): Characterization of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Endotoxemic Rat Cardiac Myocytes in viva and Following Cytokine Exposure in vitro. J Mol Cell Cardiol 27. 201 S-2029 |
| [35] | Hiki N, Berger D, Mimura Y, Frick J, Dentener MA, Buurman WA, Hirano T, Akira S, Taga T, Kishmoto T. (1990): Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin-6. Immunol Today; 11: 443–449 |
| [36] | Hirano T, Matsuda T, Turner M , Miyasaka N, Buchan G , Tang B, Sato K , Shimizu M , Maini R , Feldmann M et al. (1988): Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol; 18: 1797–1801 |
| [37] | Hubacek JA, Stuber F, Frohlich D, Book M, Wetegrove S, Ritter M, et al. (2001): Gene variants of the bactericidal/permeability increasing protein and lipopolysaccharide binding protein in sepsis patients: gender-specific genetic predisposition to sepsis. Crit Care Med; 29:557–61 |
| [38] | Jared W, Magnani G, Dec W. (2006): Myocarditis—current trends in Jett BD, Huycke MM, Gilmore MS (1994): Virulence of enterococci. Clin.Microbiol.Rev. 7: 462–478 |
| [39] | Jiang S.L., Samols D., Rzewnicki D. et al., (1995): Kinetic modeling and mathematical analysis indicate that acute phase gene expression in Hep 3B cells is regulated by both transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. J Clin Invest, 95: 1253-1261 |
| [40] | Kanada T, Kobayashi I, Nagai R.(2000): Cardiac interleukin6 in ischemic myocardium. Circulation; 101:E 86 |
| [41] | Kawai C. (1999): From myocarditis to cardiomyopathy: mechanisms of inflammation and cell death: learning from the past for the future Circulation 99:1091-1100 |
| [42] | Kim YK et al (2007): Imbalance between pro-inflammatory and anito- inflammatory cytokines in bipolar disorder. Journal of Affective Disorder 104: 91-95 |
| [43] | Kolz W., Koenig W., Muller M., Andreani M., Greven S., Illig T., Khuseyinova N., Panagiotakos D., Pershagen G., Salomaa V., Sunyer J., and Peters A. (2008): DNA variants, plasma levels and variability of C-reactive protein in myocardial infarction survivors: results from the AIRGENE study. European Heart Journal, 29:1250–1258 |
| [44] | Kukielka GL, Smith W, Manning AM, Youker KA, Michael LH, and Entman ML. (1995): Induction of interleukin-6 synthesis in the myocardium: potential role in postreperfusion inflammatory injury. Circulation ,92:1866–1875 |
| [45] | Kushner I. (1982): The phenomenon of the acute phase response. AnnNY Acad Sci, 389:39–48 |
| [46] | Kushner, I. (1988): Methods Enzymol., 163: 373-383 |
| [47] | Lamping N, Dettmer R, Schroder NW(1998): LPS-binding protein protects mice from septic shock caused by LPS or gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Invest;101:2065 |
| [48] | Lane JR, Neumann Da, Lafond-Walker A, Herskovitz A. Rose NR. (1993): Role of IL-l and tumor necrosis factor in coxsackie virus-induced autoimmune myocarditis. J Immunol, 151: 1682-l 690 |
| [49] | Lane: JR, Neumann DA, Lafond-Walker A, Herskowitz A. Rose NR. (1992): Interleukin-1 or tumor necrosis factor can promote Coxsackie B3-induced myocarditis in resistant BlO A mice. Exp Med, 175: 1123-1129 |
| [50] | Lane: JR, Neumann DA, Lafond-Walker A, Herskowitz A. Rose NR. (1991): LPS promotes CB3-induced myocardilis in resistant BlO A mice. Cell Immunol, 136: 219-225 |
| [51] | Lassar, A. B., Buskin, J. N., Lockshon, D., Davis, R. L., Apone, S., Hauschka, S. D. and Weintraub, H. (1989): Cell, 58: 823-831 |
| [52] | LE JM, Vilcek J. (1989): Interleukin 6: a multifunctional cytokine regulating immune reactions and the acute phase protein response. Lab Invest; 61: 588–602 |
| [53] | Le, P. T., M. T. Muller, and R. F. Mortensen. (1982): Acute phase reactants of mice. I. Isolation of serum amyloid P-component (SAP) and its induction by a monokine. J. Immunol. 129:665 |
| [54] | Lei, K., Liu, T., Zon, G., Soravia, E., Liu, T. and Goldman, N. (1985): J. Biol. Chem., 260, 13377-13383 |
| [55] | Libby P (2002): Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420: 868–874 |
| [56] | Lin, B. F., Ku, N. O., Zahedi, K., Whitehead, A. S. and Morensen, R. F. (1990): IL-1 and IL-6 mediate increased production and synthesis by hepatocytes of acute-phase reactant mouse serum amyloid P-component (SAP). Inflammation,14:297-313 |
| [57] | Lindmark E, Diderholm E, Wallentin L, Siegbahn A (2001): Relationship between interleukin 6 and mortality in patients with unstable coronary artery disease: Effects of an early invasive or noninvasive strategy. JAMA 286: 2107–2113 |
| [58] | Lori A. Blauwet, Leslie T. Cooper (2010): Myocarditis. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 52: 274–288 |
| [59] | M.A. Dentener, A.C. Vreugdenhil, P.H. Hoet, J.H. Vernooy, F.H. Nieman, D. Heumann, Y.M. Janssen, W.A. Buurman, E.F. Wouters, (2000): Production of the acute-phase protein lipopolysaccharidebinding protein by respiratory type II epithelial cells: implications for local defense to bacterial endotoxins, Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 23: 146e153 |
| [60] | Maaløe Ole (1955): Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, Volume 21, Issue 3, September 1956, Pages 448-458 |
| [61] | McBride, Sandosh Padmanabhan and Anna F. Dominiczak (2008): The genetics of cardiovascular disease. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 19: 309-316 |
| [62] | Maizels RM. (2005): Infections and allergy - helminths, hygiene and host immune regulation. curr. opin. immunol, 17(6): 656-661. Epub |
| [63] | Maniatis, T., Goodbourn, S. and Fischer, J. A. (1987): Science, 236: 1237-1245 |
| [64] | Marnell L, Mold C, Du Clos TW. (2005): C-reactive protein: ligands,receptors and role of inflammation. Clin Immunol., 117:104-111 |
| [65] | Martin TR, Rubenfeld GD, Ruzinski JT, Goodman RB, Steinberg KP, Leturcq DJ, et al. (1997): Relationship between soluble CD14, lipopolysaccharide binding protein, and the alveolar inflammatory response in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med;155:937–44 |
| [66] | Moellering RC Jr (1992): Emergence of Enterococcus as a significant pathogen. Clin.Infect.Dis. 14: 1173–1176 |
| [67] | Mohler ER, 3RD, Soresen LC, Ghali JK, Schocken DD,Willis PW, Bowers JA, Cropp AB, Presseler ML. (1997): Role of cytokines in the mechanism of action of amlodipine: the PRAISE Heart Failure Trial. Prospective Randomized Amodipine Survival Evaluation. J Am Coll Cardiol; 30: 35–41 |
| [68] | monocytes to synthesize tissue factor. Blood 82, 513-520 |
| [69] | Mortensen, R. F., Beisel, K., Zeleznik, N. J. & Le, P. T. (1983): J. Immunol. 130, 885-889 |
| [70] | Muller, M. M., Ruppert, S., Schaffner, W. and Matthias, P. (1988): Nature (London) 336, 544-551 |
| [71] | Murray BE (1990): The life and times of the Enterococcus. Clin.Microbiol.Rev. 3: 46–65 |
| [72] | Nakajima K, Martinez Maza O, Hirano T, Breen EC, Nishanian PG, Salazar Gonzalez JF, Fahey JL, Kishimoto T . (1989): induction of IL-6 (B cell stimulatory factor-2/IFN-beta 2) production by HIV. J Immunol; 142: 531–536 |
| [73] | Nam-on KU and Richard F. Mortensent (1993): Cloning and tissue-specific expression of the gene for mouse C-reactive Protein. Biochem. J., 295: 379-386 |
| [74] | Narula, J., Virmani R., Reddy K. S., Tandon R. (1999): Rheumatic Fever 504 American Registry of Pathology, Washington. |
| [75] | Nicholas F. Marko (2004): RNA extraction from human or animal tissue samples. The institute for genomic research standard operating procedure. SOP #: M019: 1-12. Ohlssen, H. and Edlund, T. (1986): Cell, 45: 35-44 |
| [76] | Ohnishi, S., Maeda, S., Nishiguchi, S., Arao, T. and Shimada, K. (1988): Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 156: 814-822. |
| [77] | Opal SM, Scannon PJ, Vincent JL, White M, Carroll SF, Palardy JE, et al. (1999): Relationship between plasma levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS-binding protein in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. J Infect Dis;180:1584–9 |
| [78] | Paul A, Ko KW, Li L, Yechoor V, McCrory MA, et al. (2004): C-reactive protein accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 109: 647–655 |
| [79] | Pearce EJ, Kane CM, Sun J (2006): Regulation of dendritic cell function by pathogen-derived molecules plays a key role in dictating the outcome of the adaptive immune response. Chem Immunol Allergy 90: 82–90 |
| [80] | Pepys M. B., D.R. Booth, W.L. Hutchinson, J.R. Gallimore, P.M. Collins, E. Hohenester, (1997): Amyloid P component. A critical review, Amyloid: Int. J. Exp. Clin. Invest. 4: 274–295 |
| [81] | Pepys, M. B., Baltz, M., Gomer, K., Davis, A. J. S. & Doenhoff, M. (1979): Nature (London) 278, 259-261 |
| [82] | Plenz G, Song ZF, Reichenberg S, et al. (1998): Left-ventricular expression of interleukin-6 messenger-RNA higher in idiopathic dilated than in ischemic cardiomyopathy. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg , 46: 213-216 |
| [83] | Puranik R, Chow CK, Duflou JA, Kilborn MJ, McGuire MA. (2005): Sudden death in the young Heart Rhythm 2:1277-1282 |
| [84] | R.R. Schumann, C.J. Kirschning, A. Unbehaun, H.P. Aberle, H.P. Knope, N. Lamping, R.J. Ulevitch, F. Herrmann, (1996): The lipopolysaccharide-binding protein is a secretory class 1 acute-phase protein whose gene is transcriptionally activated by APRF/STAT/3 and other cytokine-inducible nuclear proteins, Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 3490e3503 |
| [85] | Ridker PM, Rafai N, Stampfer MJ, Hennekens CH. (2000):Plasma concentration of interleukin-6 and the risk of future myocardial infarction among apparently healthy men. Circulation; 101: 1767–1772 |
| [86] | Romani L, Mencacci A, Cenci E, Spaccapelo R, Toniatti C, Pucitti P, Bistoni F, Poli V. (1996): Impared neutrophil response and CD4+ T helper cell 1 development in interleukin-6-deficient mice infected with Candida albicans. J Exp Med; 183: 1345–1355 |
| [87] | Saber A.T., Halappanavar S., Folkmann J.K. et al., (2009): Lack of acute phase response in the livers of mice exposed to diesel exhaust particles or carbon black by inhalation. Paeticle and Fibre Toxicology, 8977:6-12 |
| [88] | Saito M., Yoshida K., Hibi M., Taga T. & Kishimoto T. (1992): Molecular cloning of a murine IL-6 receptor-associated signal transducer, gp130, and its regulated expression in vivo. J. Immunol. 148, 4066–4071 |
| [89] | Scheidereit, C., Cromlish, J. A., Gerster, T., Kawakami, K., Balmaceda, C.-G., Currie, R. A. and Roeder, R. G. (1988): Nature (London) 336, 551-557 |
| [90] | Schumann RR, Leong SR, Flaggs DW, Gray PW, Wright SD, et al. (1990): Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science, 249:1429–1431 |
| [91] | Schumann RR, Kirschning CJ, Unbehaun A, et al. (1996): The lipopolysaccharide- binding protein is a secretory class 1 acute-phase protein whose gene is transcriptionally activated by APRF/STAT-3 and other cytokine-inducible nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol;16:3490–503 |
| [92] | Shioi T., Matsumori A. & Sasayama S. (1996): Persistent expression of cytokine in the chronic stage of viral myocarditis in mice. Circulation 94, 1930–1937 |
| [93] | Siboo, R. & Kulisek, E. (1978): J. Immunol. Methods 23, 59-67 |
| [94] | Skouri Hadi N., MD, G. William Dec, MD, FACC, Matthias G. Friedrich, MD, FESC, Leslie T. Cooper, MD, FACC (2006): Non invasive imaging in Myocarditis. JACC, 48: 2085–2093 |
| [95] | Soderquist B, Sundqvist KG, Jones I, Holmberg H, Vikerfors T. (1995): Interleukin- 6, C-reactive protein, lactoferrin and white blood cell count in patients with S. aureus septicemia. Scand J Infect Dis, 27:375–380 |
| [96] | Tsai, S. F., Martin, D. I. K., Zon, L. I., D'Andrea, A. D., Wong, G. G. and Orkin, S. H.(1989): Nature (London), 339: 446-451 |
| [97] | Tsugiyasu Kanada and Takashi Takahashi (2004): Interleukin-6 and Cardiovascular Diseases. Jpn Heart J, 45(2): 183-193. |
| [98] | Usui, M., Hanamura, N., Hayashi, T., Kawarada, Y., Suzuki, K., (1998): Molecular cloning, expression and tissue distribution of canine lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1397: 202–212 |
| [99] | Vreugdenhil AC, Snoek AM, Greve JW, Buurman WA. (2000): Lipopolysaccharide- binding protein is vectorially secreted and transported by Wang, Y.-H., Billiar, T.R., Tweardy, D.J., Simmons, R.L., Wang, S.C., (1994): Molecular cloning, characterization, and tissue distribution of rat lipopolysaccharide binding protein. J. Immunol. 153: 743–752 |
| [100] | Whitehead, A. S., K. Zahedi, M. Rits, R. F. Mortensen, and J. M. Lelias. (1990): Mouse C-reactive protein: generation of complementary DNA clones, structural analysis, and induction of messenger RNA during inflammation. Biochem. J. 266:238-290 |
| [101] | Woodroofe MN, Sarna GS, Wodhwa M, Hayes GM, Loughlin AJ, Tinker A, Cuzer ML.(1991): Detection of interleukin-1 and interleukin -6 in adult rat brain following mechanical injury, by in vivo microdialysis: evidence of a role for microglia in cytokine production. J Neuroimmunol; 33: 227–236 |
| [102] | Yamauchi-takihara k., ihara y., yoshizaki k. & kishimoto t. (1995b): Hypoxic stress induced cardiac myocyte derived interleukin-6. – Activation of IL-6 is mediated by NF-IL6 and NF-Kb binding sites – In Cardiac Development and Gene Regulation (Ed. Y. YAZAKI. )Tokyo: Excerpta Medica Ltd, pp. 111–126 |
| [103] | Yunis, I. and Whitehead, A. S. (1990): Immunogenetics, 32: 361-365 |
| [104] | Zahedi, K. & Whitehead, A. S. (1989): J. Immunol. 143, 2880-2886 |
| [105] | Zhiqing Songa,e, Lei Caib, Ling Guoa, Yoshitane Tsukamotoc,d, Chikao Yutanic, Xiang-An Li a (2010): 95Accumulation and expression of serum amyloid P component in human atherosclerotic lesions. Atherosclerosis 211:90–95 |
| [106] | Zweigner, J., Gramm, H.J., Singer, O.C., Wegscheider, K., Schumann, R.R., (2001): High concentrations of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in serum of patients with severe sepsis or septic shock inhibit the lipopolysaccharide response in human monocytes. Blood 98: 3800–3808 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML