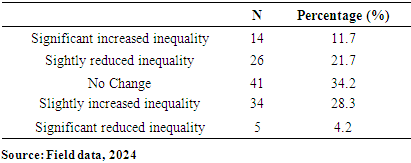-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2024; 13(3): 45-56
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20241303.01
Received: Nov. 2, 2024; Accepted: Nov. 26, 2024; Published: Nov. 30, 2024

Effects of International Monetary Fund Loans on Ghana’s Economy
Ramatu Ussif
Department of Applied Finance and Policy Management, University of Education, Winneba, Ghana
Correspondence to: Ramatu Ussif, Department of Applied Finance and Policy Management, University of Education, Winneba, Ghana.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article analyzes the impact of IMF loans on Ghana’s economy, focusing on economic impacts, social impacts, regulations, and challenges. It examines both the positive and negative outcomes of these programs. A total of 120 online, closed-ended questionnaires were completed by participants nationwide. The questionnaire was divided into different sections: demographics, awareness and understanding, economic impacts, social impacts, government regulations, challenges, and overall assessment. The response rate was 90%, indicating that the majority of distributed questionnaires were completed for data analysis. The article also addresses some challenges in Ghana related to IMF programs. The findings reveal an association between IMF loans, macroeconomic variables, and social services. Notably, the provision of social services shows a significant negative correlation, indicating that as Ghana receives financial assistance from the IMF, there is a decline in the accessibility and quality of essential social services, such as healthcare and education. In conclusion, while IMF programs have contributed to macroeconomic stability and some debt relief in Ghana, challenges remain in addressing economic and social impacts, inequality, and the difficulty of servicing external debt.
Keywords: International Monetary Fund, Multilateral Loans, Ghanaian Economy, Economic Growth, Social Impact, Ghana
Cite this paper: Ramatu Ussif, Effects of International Monetary Fund Loans on Ghana’s Economy, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 13 No. 3, 2024, pp. 45-56. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20241303.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The relationship between the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Government of Ghana (GoG) can be characterized as a cyclical pattern of dependency and adjustment. Like many developing nations in West Africa, Ghana has historically relied on multilateral loans to fund development initiatives and address economic challenges, with the IMF serving as a major source of such financial support. Despite the implementation of various IMF funds and programs from 1992 to the present, there remains a critical need to evaluate their economic and social impacts, as well as the challenges they present to Ghana’s economy (Adu-Gyamfi & Andoh, 2018; Osei-Assibey & Mohan, 2018). External debt arises when a country borrows from foreign creditors, such as global financial institutions, commercial banks, and other governments. A debt crisis often emerges when a nation with a fragile economy struggles to repay these obligations due to insufficient revenue generation from manufacturing and trade (IMF 2020). Although external borrowing may seem a viable solution during economic distress, consistent reliance on loans can lead to significant adverse consequences for both present and future generations, including deteriorating living standards, increased dependency on foreign aid, currency depreciation, and overall economic decline. From 1960 to 2019, Ghana’s foreign debt averaged approximately $6.58 billion, peaking at an all-time high of $26.95 billion in the fourth quarter of 2019 Abor, (2018). This escalating debt has consistently been linked to income shortfalls and excessive government expenditures (Amo-Yartey, 2014; Kusi, 2015; Kwakye, 2014). The role of external debt as a driver of growth has sparked intense debate among economists and policymakers IMF (2019). The recent COVID-19 pandemic compelled Ghana to elevate its spending to mitigate the pandemic's effects, highlighting the need for the government to borrow internally or externally from international financial markets, including the IMF and the World Bank, to finance development projects. By 2013, Ghana’s total debt had reached $15.83 billion, representing about 33% of GDP Abor (2018). The IMF programs enabled Ghana’s participation in the HIPC Initiative, resulting in considerable debt relief and easing the country’s debt repayment obligations (Abor, 2018; IMF, 2021). Through this initiative, Ghana secured substantial debt forgiveness from bilateral and multilateral creditors, including the IMF, allowing it to reduce external debt, redirect funds toward development goals, and increase fiscal space for investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare (Abor, 2018; IMF, 2021). The debt relief from IMF programs also enhanced Ghana’s debt sustainability, reducing the risk of debt distress and strengthening the country’s credit standing, which made it more feasible for Ghana to access international financial markets and attract foreign direct investment (FDI) (Abor, 2018; IMF, 2021). Similarly, Owusu, J. A. (2019) indicated that, Structural Adjustment Programs (SAPs) are economic reforms implemented by international financial institutions like the IMF to address balance of payments issues in developing countries. According to Mohammed et al. (2019), these programs typically include a suite of policy reforms aimed at enhancing a country’s export capacity and competitiveness. Following its transition to a republic, Ghana faced significant financial challenges that required IMF assistance. From 1960 to 1965, the Ghanaian economy experienced severe downturns, leading to hyperinflation, a deteriorating balance of payments, and dwindling foreign reserves (Gyasi et al., 2019). These economic struggles ultimately led Ghana to seek IMF support following its first military coup. Since 1966, Ghana has engaged in multiple loan agreements with the IMF across various administrations. Ghana’s renewed engagement with the IMF in 2022 has sparked widespread debate, raising questions about the implications of IMF loans on the national economy (IMF 2020). Working alongside development partners and stakeholders, the Ghanaian government has aimed to build on insights gained from IMF programs by implementing supportive policies and strategies for sustainable, inclusive growth (World bank 2021). These efforts focus on diversifying the economy, encouraging value addition in key sectors, advancing human capital development, and enhancing the business environment. The overarching goal is to establish a more resilient, inclusive economy that can better withstand external shocks, generate employment, and reduce poverty and inequality (Gyasi et al., 2019). Despite extensive implementation of IMF programs from 1992 to 2020, a thorough assessment of their impact on the Ghanaian economy is still needed (Adu-Gyamfi & Andoh, 2018; Osei-Assibey & Mohan, 2018). While these programs are often praised for fostering macroeconomic stability, providing debt relief, and supporting structural reforms (IMF, 2020), concerns remain regarding their effectiveness and long-term sustainability (Osei & Quartey, 2015). These concerns motivated the authors to research this topic.This study seeks to address the following objectives: assess the economic impacts of IMF loans on Ghana’s economy, examine the social impacts of these loans, evaluate potential risks associated with the loans in relation to Ghana’s economic development, and identify the challenges posed by IMF loans. To achieve these objectives, the paper addresses questions such as: What are the economic implications of IMF loans on Ghana’s economy? What are the social implications of IMF loans? What potential risks are associated with IMF loans for Ghana’s economic development? And what are the likely challenges of IMF loans in the country? Ultimately, the findings will serve as a valuable resource for policymakers and citizens, enabling a critical assessment of the effects of such loans on Ghana’s economy. According to Abor (2018) and the IMF (2021), debt relief has been an important impact of IMF programs in the country. These programs aim to alleviate Ghana’s external debt burden and improve debt sustainability through various initiatives and policy measures. To fully leverage the advantages of debt relief and external financing for sustainable, inclusive development, Ghana must maintain sound financial management practices and ensure efficient project execution (Abdallah et al., 2020; IMF, 2021).
2. Literature Review
2.1. Conceptual and Theoretical Review
- Macroeconomic StabilityBalance of Payments and Debt Relief: IMF loans are typically aimed at addressing short-term balance of payments deficits. By providing Ghana with needed foreign exchange, IMF loans can help stabilize the currency, prevent depletion of foreign reserves, and support the government's budget in times of fiscal shortfall (World Bank (2019).Stabilization Policies: IMF loans are often accompanied by stabilization policies, which include measures like fiscal consolidation, structural reforms, and monetary tightening to address underlying economic imbalances. In Ghana, this has generally involved efforts to reduce the fiscal deficit by curtailing public expenditure and increasing revenue through tax reforms (IMF, 2020).Fiscal Policy and Government SpendingAusterity and Fiscal Discipline: One of the hallmarks of IMF programs is the imposition of fiscal austerity to reduce public debt and budget deficits. In Ghana, this can mean reduced government spending on social services, public sector wages, and subsidies. This can lead to immediate economic challenges for the population, particularly for low-income groups that rely on government programs for support (World Bank (2019).Debt Sustainability: The IMF often provides support to ensure Ghana's debt remains sustainable by advising on debt restructuring or establishing strict borrowing limits. While this theoretically promotes long-term fiscal health, it can also restrict Ghana’s ability to finance essential infrastructure projects and social programs in the short term (IMF, 2020).Economic Growth and DevelopmentGrowth Trade-offs: IMF-supported policies often have a short-term contractionary effect on the economy due to austerity measures. Ghana's growth trajectory may be affected if reductions in public spending led to decreased investment in human capital and infrastructure, crucial elements for long-term growth (Huq, M 2018).Structural Reforms: In Ghana, IMF loans have sometimes come with conditions for structural reforms intended to promote long-term economic resilience. These reforms may include privatization of state-owned enterprises, deregulation, and labor market adjustments. Theoretically, these policies are designed to foster efficiency, increase competition, and enhance productivity, though they may also have adverse impacts on local employment and income distribution (IMF 2020).Social Impact and PovertyPoverty and Inequality: IMF programs can disproportionately impact low-income households due to reductions in government spending on social services, health, and education. For Ghana, IMF loan conditions may reduce social spending, limiting access to essential services for vulnerable groups (IMF 2019).Safety Nets and Social Programs: In recent years, the IMF has incorporated some flexibility, allowing countries to maintain critical social programs. However, maintaining an adequate social safety net while meeting IMF loan conditions remains challenging for Ghana, and the social impact remains a critical consideration in evaluating the effectiveness of IMF assistance (World Bank (2019).Exchange Rate and Inflation ControlExchange Rate Stabilization: IMF interventions are often designed to stabilize the currency and restore confidence in the exchange rate. For Ghana, this may involve policies aimed at preventing excessive depreciation of the Ghanaian cedi. A stable exchange rate can improve investor confidence, but restrictive measures may also limit the Central Bank’s ability to independently control the money supply (IMF, 2019).Inflation Control: High inflation can erode purchasing power and negatively impact economic stability. IMF programs usually include inflation-targeting policies, such as interest rate adjustments, which the Bank of Ghana has adopted under IMF guidance. However, such monetary tightening can constrain private sector investment and consumption, potentially slowing economic growth (World Bank 2021).
2.2. Empirical Review
- Upon gaining independence in 1957, Ghana’s new government adopted socialist economic practices that allowed for public engagement and regulation of industries. However, the country's economy remained heavily reliant on cocoa exports, which suffered a significant decline in global prices during the early 1960s. This downturn left the Nkrumah administration without the necessary revenue to support its socialist development agenda (Aryeetey & Kanbur, 2017). Additionally, the government faced intense criticism from the private sector for its market interventions, including import restrictions and price controls. Nkrumah and his administration were accused of crafting economic policies aimed at attracting foreign investment and undermining political opponents rather than genuinely fostering industrialization and supporting local businesses (Aryeetey & Kanbur, 2017). The military coup that ousted Nkrumah did not improve the economic situation in Ghana. The subsequent regime, known as the Provisional National Defense Council (PNDC), prioritized economic independence through the growth of the agricultural sector, leaving the industrial infrastructure developed in previous eras largely underutilized. This failure to maximize the industrial capacity, coupled with poorly executed economic development strategies during a politically volatile period, led to commodity shortages and escalating inflation rates (Aryeetey & Kanbur, 2017). Critics argue that the IMF’s broadening scope may diminish program effectiveness, fueling further discontent. They contend that much of the IMF criticism stems from a misalignment between its fundamental responsibilities and broader goals, such as achieving high economic growth, low inflation, and poverty alleviation. Empirical research examining the effects of IMF programs has utilized various methodologies, some of which have notable limitations (Barro & Lee, 2005; Haque & Khan, 1998). "Before-and-after" comparisons are often unreliable, as they assume that no changes occurred between the two periods except for the introduction of an IMF program. Evaluating program outcomes against targets can be problematic due to significant implementation issues and the potential for targets to be set either too optimistically or pessimistically. While simulations using economic models can provide insights into the effects of Fund-type policies, they do not reflect the actual impacts of IMF programs ((Kusi, et, al. 2015). Comparisons between program and non-program countries face the challenge of systematic differences that may influence economic performance (Adomako et. al 2017). Furthermore, several studies have suggested alternative methods for developing countries to raise funds for economic development projects while ensuring debt sustainability. For instance, A. G. Awan and Qasim (2020) propose that countries can generate funds through productivity improvements, increased tax revenues, and exports. A. G. Awan and Aslam (2015) argue that domestic borrowing, as it can be repaid in the country's currency, is preferable to external borrowing, which often imposes stringent conditions and pressures on governments.
2.3. Conceptual Framework
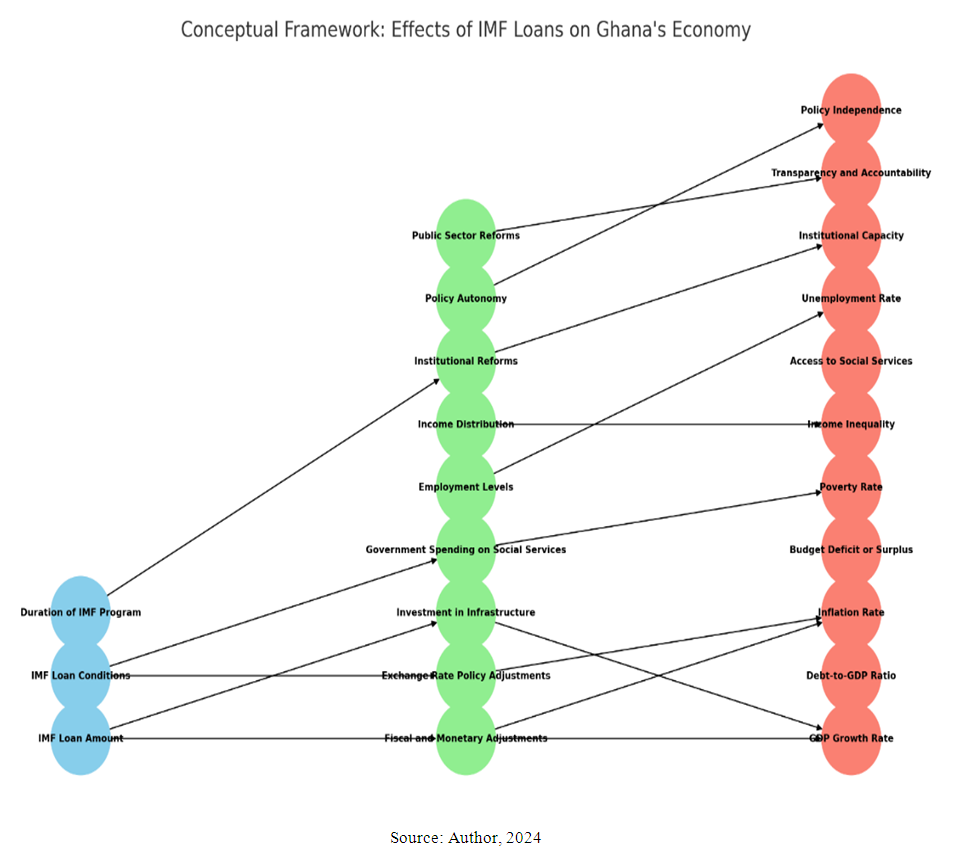
- The diagram below allows for an analysis of the causal chains through which IMF loans impact various aspects of Ghana’s economy: society, economic, and governance. The mediating variables highlight the mechanisms that transmit the influence of IMF loans to the economic and social outcomes observed.
 | Figure 1 |
3. Methodology
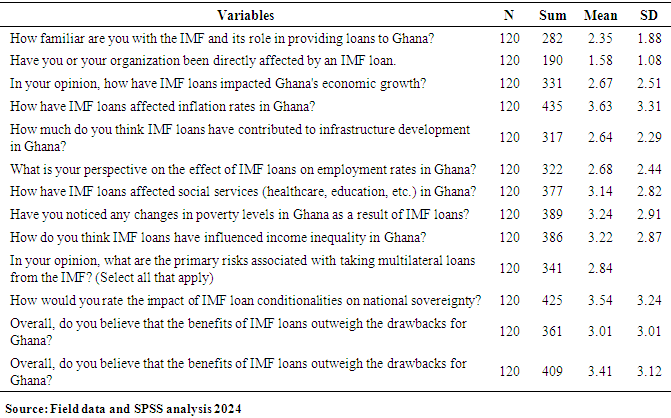
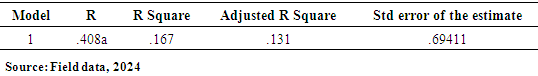
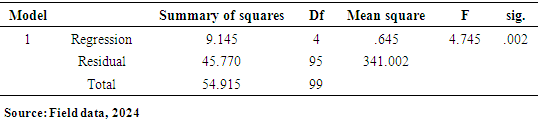
- This research on the Impact of IMF loans on the Economy of Ghana is purely quantitative. A quantitative research method involves gathering numerical data that can be converted into statistics for analysis. According to DeFranco (2011, para 3), this approach is used to measure and analyze variables like views, attitudes, behaviors, and opinions. The data gathered can be generalized to a larger population, helping researchers to establish facts, identify patterns, and provide evidence. Conducting quantitative research requires familiarity with statistical concepts like standard deviations and correlations for interpreting data. Data collection in this method can take various forms, including online or paper surveys, mobile surveys, kiosk surveys, and face-to-face or telephone interviews. Also, Creswell (2003) notes that knowledge is always an incomplete truth, suggesting that the evidence from research is inherently imperfect and subject to change (p. 7). This type of research method benefits scientists by enabling extensive, in-depth studies with accurate results. The clarity of quantitative data also facilitates easy comparisons across different datasets.Population and Sample SizeIn research, population and sample size are key concepts used to gather and analyze data effectively Creswell, J. W. (2014). Population: This refers to the entire group of individuals, items, or entities that a researcher is interested in studying. For example, if a study aims to understand the eating habits of college students in the U.S., the population would be all college students across the country. However, studying every single person in a large population can be impractical or impossible due to time and resource constraints. Sample Size: This is a smaller, manageable group selected from the population that represents the larger group. Researchers use sampling methods to select a sample that reflects the characteristics of the entire population as accurately as possible. For instance, instead of surveying all U.S. college students, researchers might select a sample of 1,000 students from different states, ages, and backgrounds. The sample size depends on the study's goals, the population size, and how precise the researcher wants the findings to be (Creswell, J. W. 2014). Using a well-chosen sample allows researchers to make inferences about the entire population without having to survey everyone. The target population consists of individuals living across the country. One hundred and twenty (120) individuals were interviewed online from this population. Primary data was collected using a structured questionnaire, which included both open-ended and closed-ended questions. Data AnalysisSaunders et. al (2009) explains data analysis is the process of examining, cleaning, transforming, and interpreting data to uncover meaningful insights, patterns, or trends. It’s a critical step in research that helps answer questions, test hypotheses, and inform decisions. The responses to each item in the questionnaire were tallied to determine the total number of respondents who answered each question. Each questionnaire was numbered and edited before coding. The raw scores were analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software. Descriptive statistics, such as frequencies and tables, were used in the data analysis. Additionally, regression analysis was applied to examine the effects of IMF loans on the Ghanaian economy, helping readers to better understand the findings. The regression model used in the study is presented below.Model SpecificationUsing the above conceptual framework, a multi-equation regression model below was set up to analyze the effects of IMF loans on economic, social, and governance outcomes in Ghana.Outcomei=α+β1(IMF Loan Amount)+β2(IMF Loan Conditions)+β3(Duration of IMF Program)+γZi+ϵiwhere:Outcomei represents the dependent variables (Economic Outcomes, Social Outcomes, or Governance Outcomes),α is the intercept term,β1\beta_1β1, β2\beta_2β2, and β3\beta_3β3 are the coefficients for the independent variables,ZiZ_iZi represents mediating variables (Economic Performance Mediators, Social Impact Mediators, Governance and Policy Reform Mediators),γ is the vector of coefficients for mediating variables,ϵi\epsilon_iϵi is the error term.Economic Outcomet=α+β1(IMF Loan Amountt)+β2(IMF Loan Conditionst)+β3(Duration of IMF Programt)+γ1(GDP Growtht)+γ2(Investment Levelst)+ϵtSocial Outcomet=α+β1(IMF Loan Amountt)+β2(IMF Loan Conditionst)+β3(Duration of IMF Programt)+γ1(Poverty Ratet)+γ2(Healthcare Accesst)+γ3(Education Qualityt)+ϵtGovernance Outcomet=α+β1(IMF Loan Amountt)+β2(IMF Loan Conditionst)+β3(Duration of IMF Programt)+γ1(Policy Reform Indext)+γ2(Transparency Indext)+ϵtVariable DefinitionsDependent Variables (Outcomes):• Economic Outcome: GDP per capita growth, debt-to-GDP ratio, fiscal stability.• Social Outcome: Standard of living index, healthcare accessibility score, education attainment score.• Governance Outcome: Governance quality index, regulatory effectiveness.Independent Variables:• IMF Loan Amount: Total amount of IMF loans provided to Ghana during the period ttt.• IMF Loan Conditions: A numerical index representing the strictness of loan conditions.• Duration of IMF Program: The number of years Ghana is enrolled in an IMF program during period ttt.Mediating Variables:Economic Performance Mediators: GDP growth, inflation rate, investment levels.Social Impact Mediators: Poverty rate, healthcare access index, education quality index.Governance and Policy Reform Mediators: Policy reform index, transparency index, governance effectiveness.Ethical ConsiderationsEthical considerations in research are principles and guidelines that ensure research is conducted responsibly, respecting the rights, dignity, and welfare of participants. Ethical guidelines are essential to maintaining trust, integrity, and accountability in research, protecting participants, and ensuring results are credible and reliable. Robson C. (2002). Ethical considerations were prioritized throughout the data collection process. Informed consent was obtained from all participants, ensuring they were fully aware of the research objectives, their voluntary involvement, and their rights as research subjects. Confidentiality was strictly maintained, with all personally identifiable information safeguarded and used solely for research purposes. The study adhered to established ethical guidelines and regulations to protect the welfare and privacy of all respondents involved.
4. Result and Discussion
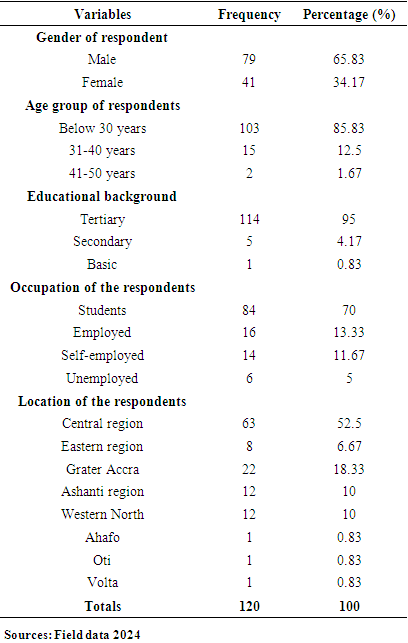
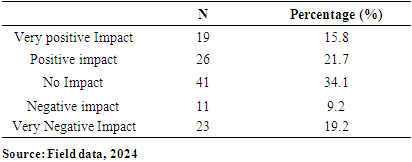
- Demographic Profile of the RespondentsThe background characteristics of the respondents were sought. This included the Gender, Age distribution (Group), Educational level, Occupation and Location of the respondents. The results were analysed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 | Table 10. Correlation |
|
|
|
5. Summary and Conclusions
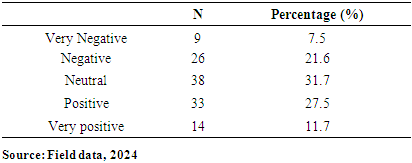
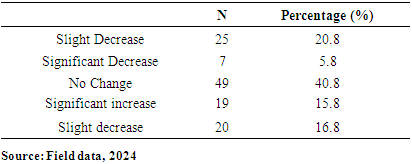
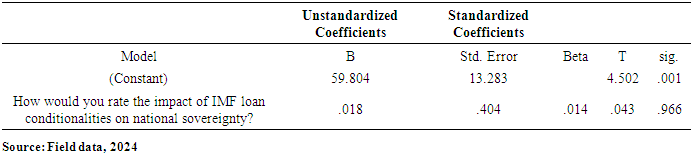
- The paper assessed the impacts of IMF loans on the economy of Ghana, with emphasis on the IMF and Ghana case. A total of 120 online closed-ended questionnaires filled by participants across the whole country by ticking the correct response to the best of their knowledge. The questionnaire is divided into key sections: demographic, awareness and understanding, economic impacts, social impacts, risks and overall assessment. Findings from this research revealed that most of the respondents for this study (n = 79; 65.83%), were males while the remaining were females (n = 41; 34.17%). It was found out that more than half of the total number of respondents (n = 103; 85.83%) were below 30years. This was followed by (n = 15; 12.5%) of the respondents who fall between 31years to 40years. This was also followed by (n=2; 1.67%) who were 41years and above. This suggests that most of the respondents were matured, hence, they could provide relevant information about their concern on IMF loans. To the educational background of the respondents, it was found that majority (n=114; 95%) of the respondents were Tertiary graduate. This was followed by (n=5; 4.17%) who were Secondary graduate. It was also found that (n=1; 0.83%) was basic graduate. It was clear that most of the respondents were having high educational level. Other findings were that majority of the respondents (n=84; 70%) were students. However, (n=16; 13.33%) of the respondents were Employed. This was followed by (n=14; 11.67%) who were self-employed. It was also found that, (n=6; 5%) of the respondents were unemployed. Another finding from this study was that, there is an association between loans from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the provision of social services exhibits a pronounced negative correlation. This observation indicates that as Ghana secures financial assistance from the IMF, there is a concomitant deterioration in the quality or accessibility of essential social services, such as healthcare and education. The adverse effects may be attributed to austerity measures or structural adjustments mandated by the IMF as prerequisites for these loans, which frequently prioritize fiscal rectitude over social expenditure.Also, another finding from this study was that the correlation between the conditionalities associated with IMF loans and the concept of national sovereignty is similarly negative. This finding implies that the stipulations linked to IMF loans, which typically necessitate economic reforms, can significantly erode Ghana's national sovereignty. Such conditions may compel the government to enact policies that do not necessarily align with the nation's socio-economic objectives or the preferences of its populace, thereby reflecting a possible relinquishment of national autonomy in pursuit of external financial support. The paper found through the study that, correlation between IMF loans and employment rates is weak yet positive association. The elevated significance value indicates that this relationship lacks statistical significance, implying that there is inadequate evidence to assert that IMF loans exert a substantial influence on employment rates within Ghana. This situation is particularly troubling, as stable employment is essential for fostering economic development and ensuring social stability. The correlation between IMF loans and income inequality reveals a moderate positive association. Conclusively, IMF programs have been pivotal in fostering macroeconomic stability, providing debt relief, and driving structural reforms in Ghana. The intervention of IMF was vital in economy’s stabilization, correcting fiscal imbalances, and alleviating external debt pressures. These programs offered Ghana a well-coordinated policy framework, technical guidance, and financial support which helped Ghana navigate economic challenges and implement essential reforms.
6. Recommendations
- Ghana should aim to reduce dependence on the IMF by harnessing local resources, expanding exports, reducing imports, strengthening partnerships with "Friends of Ghana," and shifting the economy toward production.The government should enhance financial restructuring and implement policies that drive economic growth, reducing reliance on foreign loans.Government spending should be carefully managed, with selective budget reductions where feasible.To address the balance of payments issue—often a reason for seeking IMF loans—the government should prioritize increasing exports and boosting indigenous revenue.Strong incentives are needed to foster a robust tax culture alongside necessary structural reforms.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML