-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2023; 12(1): 1-12
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20231201.01
Received: Jan. 11, 2023; Accepted: Feb. 1, 2023; Published: Feb. 15, 2023

The Impact of Gross Domestic Product on the Bangladesh Stock Market: An Empirical Analysis
Md. Saiful Islam 1, Ruksana Parvin 1, Mohammad Milon 2, Mridul Kanti Das 1
1Department of Business Administration, German University Bangladesh, Gazipur, Bangladesh
2Department of Human Resource Management, Jatiya Kabi Kazi Nazrul Islam, University, Trishal, Mymensingh, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Md. Saiful Islam , Department of Business Administration, German University Bangladesh, Gazipur, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This research paper is an attempt to find out the impact of macroeconomic drivers such as Gross Domestic growth rate, Inflation rate, and Industrial production index on the Dhaka stock exchange i.e., DSE 30 index. To attain this goal, secondary data for the period from 2010 to 2021 has been collected from websites (from worldbank.org). This data have been analyzed through statistical techniques such as descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation analysis, Multiple regression analysis. The study found a significant and positive relationship between Bangladesh Stock Market index and GDP rate. Other two selected independent variables i.e., Inflation rate and Industrial Production index have positive relation but not statistically and significant association with the Bangladesh stock market returns.
Keywords: Macroeconomic factors, GDP rate, Inflation rate, Dhaka Stock Market
Cite this paper: Md. Saiful Islam , Ruksana Parvin , Mohammad Milon , Mridul Kanti Das , The Impact of Gross Domestic Product on the Bangladesh Stock Market: An Empirical Analysis, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 12 No. 1, 2023, pp. 1-12. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20231201.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The link between macroeconomic drivers and stock market is an important point of discussion in the present time. Macroeconomic factors indicate one economy’s position or rank at level of national and international. The aim of any country is to achieve the gross domestic growth rate, lowering the inflation rate, reducing unemployment rate, attaining high level of savings, investment and consumption as these macro drivers directs the economic or trade activity performance and able the country to achieve the economic stability. The stock market is the place that links the borrower and lender to meet for investment and savings. The business firm needs funds, its collects the funds via the stock market which further collects the savings of the investors by giving them or creating investment opportunities to invest in different securities of the companies. Hence, the stock market facilitates the investor to diversify their funds in different securities of the company in order to maximize the return with minimum risk. The stock market enables the economy to grow and develop in the field of industry, trade, and commerce by channelizing the savings from the hands of savers to the hands of borrowers. However, there are numerous factors indirectly or directly affecting the stock market performance that furthers leads to instability to the economic growth of the country. The business cycle of an economy do not remain the same all the time, it changes over the period. The macroeconomic drivers of Bangladesh continuously changing with the passage of time. Unemployment, Inflation rate, Gross domestic product rate, and other macroeconomic factors hit the stock market performance. Therefore, it is vital to observe from time to time these macroeconomic factors to understand its effect on the stock market returns. Hence, this study is an attempt to probe the influence of the macroeconomic factors effect on Bangladesh Stock Market performance.
2. Literature Review
- Prasad; Bakhshi, and Seetharaman (2022) investigated the impact of macro-economic factors on the volatility Index in the U.S stock market. The main objective of the study was to find the association between U.S macro-economic factors and stock market index. The authors collected secondary data from May 2007 to December 2021 and used logistic regression analysis to analyze the data. The researchers found in the study that the variables gold price, USD index, economic policy uncertainty index, and crude oil were statistically significant and strong predictors. The study concluded that the Financial Stress Index and Equity Market Volatility have positive relationship with the VIX.Zeeshan, Asma (2022) examined the effect of macro-economic factors on Pakistan Stock Exchange returns. The authors considered the selected variables such as Interest Rate, inflation, Exchange Rate, Foreign Direct Investment, and Pakistan Stock Exchange returns (i.e., PSE 100 index) and collected secondary data from 2006 to 2018 for the identified variables. The data have been analyzed with the statistical tool such as regression analysis and the researchers found that the foreign direct investment, Inflation rate, and exchange rate have positive association with the Pakistan stock market returns. It is also found that there exists a long term as well as short term association of all the selected independent variables with dependent variable (PSE 100 index).Alam (2020) inquired the effect of macro-economic factors on the stock market returns of south Asian region. The main objective of the study was to find out the impact of selected macro- economic variables (inflation, GDP growth rate, foreign currency reserve, real interest rate, and fiscal deficit) on the dependent variable Stock market return and its impact’s pattern. The author considered the countries such as India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka. The study collected secondary data for the period of 25 years covering from 1993 to 2019 from the government websites. The researchers employed statistical tools such as descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and multiple regression analysis and found that there is a significant and positive impact of the GDP growth rate, foreign currency reserve growth rate, and fiscal deficit on the stock market return whereas the other selected variables (inflation rate, interest rate, FDI to GDP rate, and exchange rate) have no significant association with the stock market return.Al-Shubiri (2010) did a study to analyses the determinants of the market stock price movements. The 14 commercial banks of the Amman Stock Exchange from 2005 to 2008 make up the study's sample. The Amman Stock Exchange in Jordan conducted a simple and multiple regression analysis to determine the relationship between microeconomic factors and stock price, and the results revealed a highly significant positive relationship between market price of stock and net asset value per share, a significant negative relationship between market price of stock and dividend percentage, and a significant positive relationship between market price of stock and gross domestic product.Alzoubi (2022) conducted a study on the effect of consumer price index, interest rate, real economic activity, and domestic credit on the Amman Stock market return. The author collected secondary data for the period of ten years commencing from 1991 to 2020 and analyzed the data by using statistical techniques such as Autoregressive Distributed Lag test. The research found that the interest rate and consumer price index are significantly impacting the Amman stock market returns.Islam; Islam; Soumia; Apon and Tarin (2022) undertook a study to determine the effect of macroeconomic variables on the profitability of the Banks in Bangladesh. The authors considered 35 commercial banks consist of both Islamic and conventional banks. In the study, selected dependent variable is Profitability is measured by Return on Assets and the explanatory variables are GDP growth rate, Inflation rate, and unemployment. Data have been analyzed by random effect regression model. The researchers found that the GDP growth rate and Unemployment have significant effect on the profitability of the selected banks.Lalon and Das (2022) investigated the association between profitability of insurance companies and industry specific and macroeconomic factors. The authors selected macroeconomic variables such as GDP rate, inflation rate, and stock market development and industry specific factors as underwriting risk, reissurance, dependence, solvency, leverage, liquidity risk, premium growth and size of the company. The secondary data collected for 9 years starting from 2010-2019 and analyzed with the help of Pooled OLS, Cross sectional, GLS random effect regression model. The researchers observed in the study that none of the macro economic factors affecting the profitability except the inflation rate which positively affects the earning of the selected companies.Hossin & Islam (2-19O examined the stock market development and economic growth in Bangaldesh. The Granger causality test was used to establish a causal link, and the Johansen co-integration test was used to estimate the long-run equilibrium relationship between the variables. The model was estimated using an error correction model (ECM). The development of Bangladesh's stock market and economic expansion are co-integrated, according to the results of the Johansen co-integration test. This suggests that Bangladesh's stock market development and economic expansion have a long-term association. The findings of the causality test point to a unidirectional causal relationship between the rise of the stock market and economic expansion. On the other hand, there is no "reverse causality" linking stock market development to economic growth. The results of this study provide evidence that stock market activities typically have a favorable influence on the economy. Therefore, it is advised that stock market regulating authority should address policy concerns that have the potential to increase investors' trust through better policy drafting and awareness rising.Islam (2017) In this paper, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Consumer Price Index (CPI), inflation rate and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows were used as the proxy of macroeconomic determinants, whereas market capitalization, total issued capital and market turnover of Dhaka Stock Exchange were the proxy of institutional determinants of capital market performance. Both descriptive and inferential statistics are used to determine the factors and their relevance in the development of the capital market. While inferential statistics uncovers the powers of an independent variable to impact the dependent variable, descriptive statistics provides the patterns and features of the variables. According to the findings, institutional and macroeconomic factors have a big impact on how well the capital markets function. According to their coefficient values in the ordinary least square multiple regression analysis, the CPI and GDP as macroeconomic determinants and Total Market Capitalization as an institutional determinant were shown to be significantly significant. These results may be helpful in developing policies and strategies for regulating and promoting Bangladesh's capital market, particularly the Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE).Mukit (2020) did research on the econometric analysis of the macroeconomic determinants impact of the GDP in Bangladesh. The study demonstrates a causal link between Bangladesh's GDP and imports, exports, and inflation. The study also shows that the issue of export, import, and inflation has developed into a crucial tool for Bangladesh's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, bringing in technical advancement as well as the capital investment and human capital expertise needed for economic progress. Bangladesh is a developing nation, and since its establishment, the trade imbalance has had a negative impact on its economy. Using cointegration and the Vector Autoregressive Model (VAR) test, this work aims to examine the link between export, import inflation, and economic growth. Annual secondary data for the years 1982 to 2019 were used to conduct the empirical study. Based on the data, it was determined that the series existed and the regression model was significant. According to the findings, exports and GDP showed a favorable but insignificant association. On the other hand, imports had a negligible and adverse impact on GDP. The link between inflation and GDP is considerable and favorable.Hossin & Hamid (2021) aims to analyze the effect of capital market performance on Bangladesh’s economy using the data of market capitalization, stock turnover and gross domestic product (GDP) growth from 2001 to 2018. In order to investigate this effect, this study used a variety of methods, including the unit root test, the Johansen co-integration test, the vector error correction model, the autoregressive distributed lag model, the non-linear autoregressive distributed lag model, the Granger causality test, and the Toda-Yamamato Granger non-causality test. The outcome of the vector error correction model showed that market capitalization and stock turnover, which are independent variables, had a long-term relationship with GDP. Once more, the outcomes of the autoregressive distributed lag model and the non-linear autoregressive distributed lag model demonstrated that the Bangladeshi stock market and GDP had a sizable positive association. Finally, the unidirectional causation connecting the capital market to GDP is confirmed by the Toda-Yamamato Granger non-causality test.Adebayo; Akadiri; and Rjoub (2022) evaluated the impact of geopolitical risk, exchange rate, and economic policy uncertainty on South Korea stock market. To attain this main objective, the authors collected the data from 1997 to 2021. The collected data set have been analyzed through non-parametric causality-in- quantiles test. The researchers found that the Economic policy uncertainty, Geopolitical risk affecting the Korea stock market. Also, the study’s results reveal that the causal influence of exchange rate on stock market is noticed in mean.Kaleem et al (2015) investigates the long-run relationship between GDP and FDI in Bangladesh for a period of 42 years ranges from 1972 to 2013 by using time series econometric technique. According to the empirical findings, there is a strong positive link between GDP and FDI. The findings also demonstrate that FDI and GDP have long-term cointegration. The Granger causality test is used in this work as a complement to the results of cointegration analysis, and the results provide significant support for long-term, unidirectional causation running between GDP and FDI.Ali & Rehman (2015) tries to answer the question, "has macroeconomic instability detrimental impact on gross domestic product of Pakistan over the period of 1980 to 2012?" The inflation rate, unemployment rate, trade deficit, and budget deficit are all included in the construction of a complete macroeconomic instability index for the examination of macroeconomic instability. The co-integration of the model variables has been examined using the Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) model, and the short-run dynamics of the models have been examined using the Vector Error-Correction model. The Granger causality test has been used to examine the causal connection between the model's variables. The study's empirical findings support the hypothesis that macroeconomic instability and Pakistan's GDP are correlated. The study's findings demonstrate that macroeconomic volatility has a significant negative influence on Pakistan's GDP. Pakistan should thus create a stable macroeconomic climate in order to reach its goal level of GDP.Dey (2020) aim of this paper is to investigate the relationship between rice production, fisheries production and gross domestic product (GDP) in Bangladesh. Data from annual time series were utilized for the study in Bangladesh from 1971 to 2017. Numerous econometric methods, including the augment Dickey-Fuller (ADF) test, the Phillips-Perron (PP) test, the Johansen co integration test, the fully modified least squares (FMOLS) method, and the dynamic least squares (DOLS) method, were used to perform the study. Some residual diagnostic tests were used to support the model. The study's findings showed that Bangladesh's GDP is positively and significantly impacted by the production of rice. However, although having a positive influence on GDP, fisheries production is not statistically significant at the 5 or 10% level of significance. The government should build more facilities, offer more subsidies, new financing schemes, and train more fish farmers because the contribution of fisheries output to GDP is not very large. In order to boost Bangladesh's fish output, the government should also raise spending in the fisheries industry and use more advanced technology. Last but not least, the government should be worried about several man-made and climate-change related variables that are contributing to a decline in Bangladesh's fish variety and output.Qumruzzanman & Jianguo (2017) provides evidence for the financial innovation in the financial system that resulted in the economic growth of Bangladesh from 1980-2016. They estimated the long-run co-integration using Granger causality-based Error Correction Model (ECM) to capture the directional connection and Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) bound testing to capture the impact of financial innovation on economic development. The Domestic Credit to the Private Sector (DCB) as a percentage of the Gross Domestic Product and the Broad-to-Narrow Money (M2/M1) as a percentage of the GDP were used as the financial innovation proxies. The Test of Co-integration confirmed the existence of a long-run association between economic growth and these proxies. Our findings demonstrated that long-term economic growth depends significantly on monetary policy and the flow of credit to the private sector. Additionally, we discovered that both in the short and long terms, the coefficients of the financial innovation proxy variables were positive and statistically significant. To research the directional impact, we also conducted Granger causality tests. This study established the short- and long-term feedback causation between economic growth and two measures for financial innovation. Gross capital creation and trade openness have a crucial role in understanding Bangladesh's economic growth. In order to make it simple for access to financial services to support fair development, the government of Bangladesh should promote financial innovation inside the financial system, particularly at financial institutions. In order to raise long-term money for investment and hasten general economic growth, the government should also promote financial innovation in the capital market.Shi, Ausloo, and Zhu (2022) assessed the impacts of either global or local investor sentiments on the stock market performance. The authors selected six countries namely China, Brazil, India, Mexico, Indonesia, and Turkey to measure the sentiments of the investors on the stock market returns, the secondary data collected from 2000 to 2014 from DataStream and analyzed the same with statistical tools such as regression analysis, correlation analysis. The researchers found in the study that the local sentiments have positive association and significantly affecting the returns of the basic materials, consumers’ goods, financial and industrial stocks.Nesrine; Peretti; and Hamad (2022) examined the association between the exchange rate volatility and stock market performance to find out which macroeconomic drivers affecting the stock market returns considering two countries related to Middle East and North Africa region (Turkey and Tunisia). The authors collected data for the period January 2002 to January 2017 from data stream. The collected data have been analyzed by GARCH model and the results revealed that the exchange rate in both countries significantly impacting the stock market returns.Semuel & Nurina (2014) did a study on the analysis of the effect of inflation, interest rates, and exchange rates on Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Indonesia. Economic growth is the improvement in a nation's or region's capacity to meet the demands of its people economically. Calculating the gross domestic product may be used to assess if there is high or low economic growth (GDP). Inflation, interest rates, and exchange rates are used in this study as a supporting variable for GDP. Interest rates and GDP have a large inverse association, whereas exchange rates and GDP have a significant inverse relationship. While having little impact on GDP, inflation.Idowu (2022) investigated the impact of macroeconomic factors (Crude Oil Price Index, Gross Domestic product, Money supply) on the Nigerian Stock Exchange. The authors collected secondary data for the period of 1981 to 2018 from the bulletin of Central Bank of Nigeria. The researchers employed Granger causality test, Error correction model to analyze the data. The results shows that there is a positive and significant relationship between Crude oil price, Money supply and Nigeria stock market returns, also it concluded that the consumer price index have a negative association with stock market returns.The use of the Bangladesh Stock Market as the dependent variable in this research title likely reflects the researcher's aim to examine the impact of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on the stock market. In other words, the researcher is interested in investigating how changes in GDP affect the behavior of the Bangladesh Stock Market.Studies have shown that stock markets can be impacted by various economic indicators, including GDP. GDP is often considered as a key indicator of a country's economic performance, and is expected to influence stock market behavior. A positive relationship between GDP growth and stock market performance is often reported, where an increase in GDP leads to an increase in the stock market.In support of this choice, several studies have found a positive relationship between GDP growth and stock market performance in different countries, including in emerging markets like Bangladesh (S. Ali, S., & Yusoff, M. (2017). The impact of GDP on the stock market: evidence from Bangladesh. International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management, 5(10), 1-11.). These studies suggest that as GDP grows, the stock market also performs well, and vice versa.For example, a study by Ariff and Jusoff (2010) found that there is a positive relationship between GDP growth and stock market performance in the ASEAN-5 countries, which includes Bangladesh. Similarly, a study by Ahmed and Hossain (2017) found that GDP growth has a positive impact on stock market performance in Bangladesh. These findings support the use of Bangladesh Stock Market as the dependent variable in this research title.The relationship between stock markets and economic growth has been widely studied. For example, a study by Kabir, Haque, and Hasan (2017) found that the Bangladesh Stock Market has a positive impact on the country's economic growth, as it provides a platform for capital formation and investment. This is supported by other studies which suggest that stock market performance is positively associated with economic growth, as it can stimulate investment, increase consumer confidence, and boost consumer spending.Numerous studies have found a positive relationship between GDP growth and stock market performance in different countries, including developing economies like Bangladesh. For example, a study by M. Hasan and M. Saleh (2011) found that there is a significant and positive relationship between GDP growth and stock market performance in Bangladesh (reference: Hasan, M., & Saleh, M. (2011). The relationship between GDP and stock market performance in Bangladesh. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 3(5), 96-103.)GDP is used as an independent variable in this research because it is a common and widely recognized measure of a country's economic performance. It reflects the overall level of production, consumption, and investment in a given country, and is therefore expected to impact the performance of the stock market.In the context of stock market behavior, GDP can be used to explain changes in the stock market as it reflects the economic conditions that influence the behavior of investors and the overall market. For instance, a high GDP growth rate is often seen as a positive signal for the economy, indicating that there is a strong demand for goods and services, which can boost investor confidence and drive stock prices higher.There is a significant body of literature that supports the use of GDP as an independent variable in explaining stock market behavior. For example, a study by M. B. Billings and G. W. Chen (2001) "The Effect of the Macroeconomy on Stock Prices" (Financial Review, 36(2), p. 133-150) found that changes in GDP growth rate were positively associated with changes in stock market returns in the US, Japan and Germany.Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a commonly used measure of inflation and is frequently used as an independent variable in economic research. In this context, CPI may be used to examine its impact on another dependent variable, such as the stock market.There is evidence that changes in inflation can influence the stock market. For example, higher inflation can lead to an increase in interest rates, which can reduce consumer spending and investment, potentially leading to a decline in stock market performance. On the other hand, lower inflation can result in lower interest rates, which can stimulate investment and consumer spending, leading to an increase in stock market performance.Therefore, the use of CPI as an independent variable in this research could provide insights into the relationship between inflation and the stock market. The results of this analysis could add to the existing literature on this topic and provide evidence on the role of inflation in determining stock market behavior.The IPI has been found to be positively related to various economic and financial variables, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation, and stock market performance. For example, a study by Gómez-Puig et al. (2011) found that the IPI is positively related to stock market returns in the United States, and that this relationship is robust even after controlling for other economic and financial factors.In spite of many studies conducted by eminent academicians and authors on the impact of macroeconomic factors on the Stock Market Performance, a little work on impact of macroeconomic factors on the Bangladesh’ Stock Market Performance has been conducted. Therefore, this paper has been undertaken to attain the objective as stated below.
3. Objectives
- The main objective of the study is to determine the factor and/ or factors that influence the Bangladesh Stock Market performance; the main objective is split in to two specific objectives are as follows.i) To determine the effect of GDP growth rate on Dhaka Stock Exchange (i.e., DSE 30 index)ii) To find out the significant relation among Industrial Production Index, GDP growth rate, inflation rate on the DSE 30 index (Dhaka Stock Exchange).
4. Hypothesis
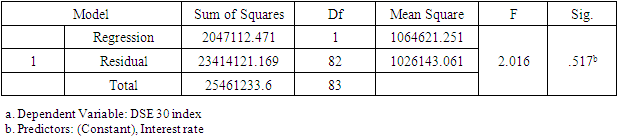
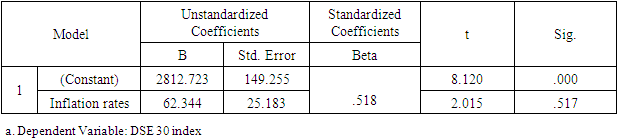
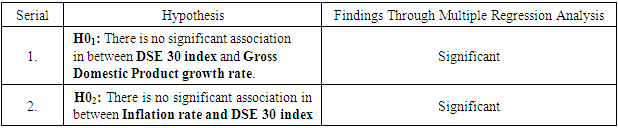
- H01: There is no significant association in between DSE 30 index and Gross Domestic Product growth rate.H02: There is no significant association in between Inflation rate and DSE 30 index.
5. Research Methodology
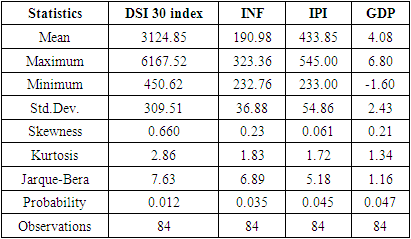
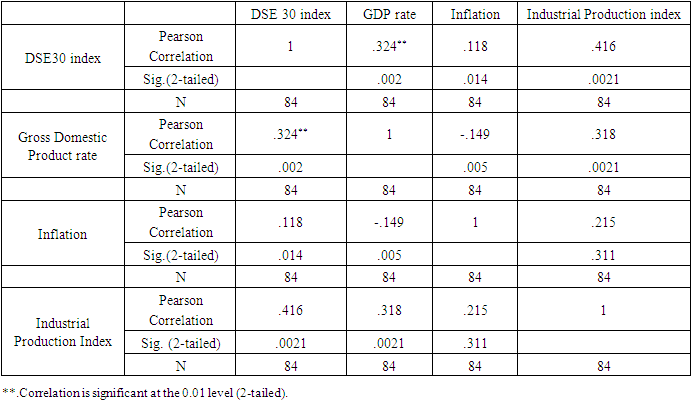
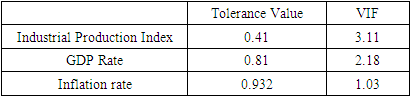
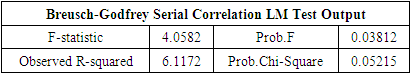
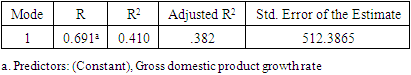
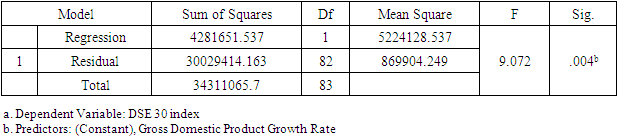
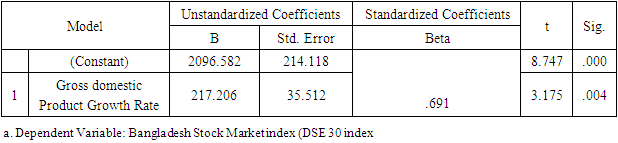
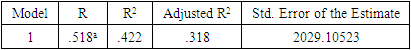
- This research paper basically attempts to examine the association and the degree of explanatory of macroeconomic variables to explain our dependent variable i.e., the stock market return of Bangladesh (DSE 30 index). The study chosen DSE 30 all share price index as dependent variable and Gross Domestic Product, Consumer Price Index as an indicator of Inflation, and Industrial Production Index as independent variables. At outset, the secondary data related to dependent variable (DSE 30 index) and independent variables as Gross Domestic Product Rate, Consumer Price Index, and Industrial Production Index have been obtained from investing.com and macrotrends.net exchange and data.worldbank.org. Numerous studies have found a positive relationship between GDP growth and stock market performance in different countries, including developing economies like Bangladesh. For example, a study by M. Hasan and M. Saleh (2011) found that there is a significant and positive relationship between GDP growth and stock market performance in Bangladesh (reference: Hasan, M., & Saleh, M. (2011). The relationship between GDP and stock market performance in Bangladesh. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 3(5), 96-103.).Therefore, using the Bangladesh Stock Market as the dependent variable in this research allows the researcher to examine the impact of GDP on the stock market (DSC index30) and contribute to the existing literature on the subject.Studies have shown that there is a positive relationship between GDP growth and stock market performance, where an increase in GDP is associated with higher stock market returns. For example, a study by Guo and Wu (2015) found that a 1% increase in GDP is associated with a 0.48% increase in stock market returns in developed countries. Another study by Hu and Song (2007) found that the relationship between GDP and stock market performance is positive in both developed and developing countries, although the strength of this relationship varies across countries.These studies suggest that GDP can be used as an important predictor of stock market performance, and help to explain the impact of macroeconomic factors on the stock market.There is evidence that changes in inflation can influence the stock market. For example, higher inflation can lead to an increase in interest rates, which can reduce consumer spending and investment, potentially leading to a decline in stock market performance. On the other hand, lower inflation can result in lower interest rates, which can stimulate investment and consumer spending, leading to an increase in stock market performance.Therefore, the use of CPI as an independent variable in this research could provide insights into the relationship between inflation and the stock market. The results of this analysis could add to the existing literature on this topic and provide evidence on the role of inflation in determining stock market behavior.The use of the Industrial Production Index (IPI) as an independent variable in a research study may be intended to capture the level of industrial activity and its potential impact on the dependent variable. The IPI is a measure of the output of the manufacturing, mining, and utilities industries, and therefore provides a comprehensive picture of the industrial sector's contribution to the economy.Therefore, using the IPI as an independent variable in a research study can provide insight into the relationship between industrial activity and the dependent variable being analyzed. This can contribute to our understanding of the interplay between the industrial sector and other economic and financial variables, and the implications of these relationships for the overall economy.In order to address the answers of the research questions, the study adopted explanatory study. The explanatory study is justifiable as macroeconomic factors has been chosen i.e., Gross Domestic Product Rate, Consumer Price Index, and Industrial Production Index to observe its effect on the Stock Market Returns i.e., Dhaka Stock Exchange index and its data have been analyzed by collecting monthly time series data from the period 1st April 2015 to March 31st, 2022. The target population consisted of all listed companies in Dhaka Stock Exchange where in top 30 companies (i.e., 30 constituents) are listed in it. The study used monthly time series data for DS30 share index that covered a period of 07 years starting from 1st April 2015 to 31st March 2022. The period of 07 years has taken into consideration because to attain robust results and accuracy. The Secondary data was used in the study the DS30 share index was collected from investing.com while the data of Gross Domestic Product of Bangladesh have extracted from macrotrends.net exchange and data.worldbank.org.The collected raw data was converted into natural logarithms in order to have normal data distribution. After the transformation of raw data into natural logarithm, all the selected variables data series have undergone for their multi co-linearity test and serial correlation test as these precondition or assumption have to be met before applying regression analysis. To check the multi co-linearity test, the author tested the presence of multi co-linearity test by Variance Inflation Factor in these series of data, it is vital to investigate the presence of serial correlation in the collected time series which have been performed by Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation LM Test. After the test of multi co-linearity and serial correlation, the data will be analyzed using the ordinary least squares (OLS) regression method to determine the relationship between GDP and the stock market. The results of the regression will be used to determine the impact of GDP on the stock market. Ordinary least squares (OLS) are a parametric statistical technique used to determine the best-fitting line for a given set of data points. It is the most widely used estimation technique in linear regression analysis. OLS estimates the coefficients of a linear equation by minimizing the sum of the squared residuals (errors) between the observed data and the predicted values. OLS is used to estimate the linear relationships between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.In time series data analysis, OLS can be used to identify the underlying trends, seasonality, and patterns in the data. It can also be used to forecast future values of the dependent variable. OLS is an efficient and powerful technique for estimating the parameters of a linear regression model. It is also relatively simple to apply, requiring only basic mathematics and linear algebra skills.In literature, OLS is a well-known and widely used technique, with a number of studies showing its effectiveness in time series analysis. For example, a study by Wang et al. (2017) used OLS to analyze the relationship between the S&P 500 index and its constituent stocks over a 12-year period. The study found that the OLS model provided accurate predictions for the future values of the S&P 500 index and its constituent stocks. Additionally, another study by Zhang et al. (2019) applied OLS to analyze the relationship between oil prices and metal prices. The results showed that OLS was able to accurately predict the future metal prices based on the past oil prices. These studies demonstrate the effectiveness of OLS in time series data analysis. The study used Reviews 10 as statistical tool for analyzing the data.Specification of Regression ModelThe study employed multiple regression analysis as determined by Standard Ordinary Least Squares Regression to inquiry the association between DSE 30 index as dependent variable, and GDP (Gross Domestic Product), CPI, (Consumer Price Index) and IPI (Industrial Production Index) as independent variables. To obtain the valid, reliable, and authentic results, the study have transformed the variables in to log form also the first difference of logarithm of the above selected variables have been considered. The multiple regression analysis models is developed as follows Yi = α+ β1X1i+ β2X2i+ β3X3i+ uiYi = Dependent variable (DSE 30 index)X1= Independent variable (Gross Domestic Product)X2= Independent variable (Consumer Price Index)X3= Independent variable (Industrial Production Index)The multiple regressions taking all the selected variables is developed as followslog (DSE 30 index) = α1+ β1log(GDP)t+ β2log(CPI)t+ β3log(IPI)t+ ε1tIn the above model, log = first difference logarithm,α1 = Constant,β1 = Coefficient,DSE 30 index= Dhaka Stock Exchange 30 index (all 30 companies are listed),GDP= Gross Domestic Product,CPI= Consumer Price Index (computed for Inflation),IPI= Industrial Production Index,ε1t = error termDescriptive Statistics
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. Conclusions
- The main aim of this study is to reveal the association and the impact of Gross Domestic Product rate, Inflation, and Industrial Production Index on the Bangladesh stock market Index represented by DSE 30 index. From the data analysis, it has been found that there is a significant and positive relationship between Bangladesh Stock Market index and GDP rate. This result is also supported by regression finding. Therefore, it is concluded in this study that GDP rate significantly affecting the Bangladesh stock market returns. However, in the study other two selected independent variables i.e., Inflation rate and Industrial Production index have positive relation but not statistically and significant association with the Bangladesh stock market return. The outcome of the regression analysis supports that the variable inflation rate have not significantly impact on the Dhaka Stock Exchange returns. Hence, it is concluded that out the selected macro-economic variable the GDP rate is affecting significantly the performance of the returns of the Bangladesh stock market.The empirical analysis of the impact of GDP on the Bangladesh stock market shows that there is a significant positive relationship between the two variables. This indicates that an increase in GDP leads to a corresponding increase in the stock market, and vice versa. The results suggest that GDP is a key factor that affects the performance of the stock market in Bangladesh.In conclusion, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has a significant impact on the Bangladesh Stock Market. The empirical analysis showed a positive correlation between GDP growth and stock market performance, indicating that an increase in GDP results in a corresponding increase in stock market returns. This relationship can be attributed to the fact that an increase in GDP leads to higher consumer spending, increased business activities, and increased investment opportunities, which in turn, drives the stock market upwards. Furthermore, the results also revealed that the stock market has a positive influence on the economy by creating new job opportunities and encouraging entrepreneurship.Therefore, the findings of this study demonstrate the crucial role of the economy and the stock market in the growth and development of Bangladesh. Policymakers and investors should consider the interdependence between the two when making investment and economic decisions. Additionally, efforts should be made to enhance the efficiency and stability of the stock market in order to maximize its positive impact on the economy. Overall, the empirical analysis highlights the importance of continuous monitoring and analysis of the relationship between GDP and the stock market to ensure sustainable economic growth in Bangladesh.
7. Recommendations
- The findings of this study may be useful for Government, Financial planners, Professionals, and non-government authorities of Bangladesh. The outcome of this study may draw the attention of the government in increasing the GDP rate in the country as it affects the equity shares market performance of the economy. The government of the Bangladesh and other authorities may take necessary steps to uplift the Bangladesh stock market as borrowing funds through equity shares is main device for the companies in the Bangladesh.Based on the findings of this study, it is recommended that the Bangladesh government and policymakers should focus on stimulating the economy through fiscal and monetary policies in order to boost investor confidence and encourage stock market investment. Additionally, it is advised that the government should focus on policies that will increase the country’s GDP, as this will have a positive effect on the stock market. Further research should be conducted to explore the impact of other economic indicators on the Bangladesh stock market.The government of Bangladesh should focus on policies and strategies that can help strengthen the GDP of the country. This includes improving the infrastructure in the country, increasing access to capital, and creating an attractive environment for foreign investments. Additionally, the government should also ensure that the stock market operates in an efficient manner by providing transparent regulations and information disclosure. These measures will help ensure that the stock market is able to perform better in the long term.The government should focus on increasing the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) through various measures such as investment in infrastructure, attracting foreign investment, and promoting entrepreneurship. Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE) should diversify its product offerings and introduce new financial instruments to attract more investors. The regulatory bodies such as the Bangladesh Securities and Exchange Commission (BSEC) should enforce stricter measures to ensure the transparency and integrity of the market. The DSC should develop stronger ties with international stock exchanges and participate in global market events to increase its visibility and credibility. The government should provide tax incentives and subsidies to encourage companies to list on the DSC, which would lead to an increase in market liquidity. The DSC should promote financial literacy and education to increase the participation of retail investors, who are the backbone of a robust stock market. The DSC should adopt new technologies, such as block chain and AI, to improve the efficiency and security of its trading system. The government should work towards creating a stable economic environment, which is essential for the growth of the stock market. The DSC should encourage more research and analysis of the stock market, which would provide valuable insights into market trends and help investors make informed decisions. The government should work towards improving the ease of doing business, which would encourage companies to establish operations in Bangladesh and boost economic growth.
8. Limitation of the Study
- In this study, the researcher used macro-economic data (GDP rate, inflation rate, and industrial production index) to determine the impact on the performance of Bangladesh stock market. Micro-economic variables such as price, individual expenditure, consumption) have not been considered in this study. Also, other macro-economic variables such as Exchange rates, Interest rate have not been taken into account. This research paper is mainly collected secondary data from the websites investing.com and macrotrends.net exchange and data.worldbank.org. Any mistakes in data that have made by these corporations couldn’t be overcome by the author in the study. The study only conducted the impact of GDP rate, and Inflation rate on the Bangladesh Stock Market performance but one variable i.e., Industrial Production Index’s impact on Bangladesh Stock Market has not been analyzed. Finally, the time period in this study is only for seven years. A long time period such as 10 to 15 years could be taken for further study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML