-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2020; 9(4): 91-97
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20200904.03
Received: Nov. 2, 2020; Accepted: Nov. 30, 2020; Published: Dec. 15, 2020

Impact of Working Capital Management on Profitability of Manufacturing Business: Evidence from Nigeria
Sani Alfred Ilemona1, Nwite S.2
1Department of Accounting and Business Administration, Federal University Kashere, Gombe State, Nigeria
2Department of Business Management, Ebonyi State University, Abakaliki, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Sani Alfred Ilemona, Department of Accounting and Business Administration, Federal University Kashere, Gombe State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The study investigated the impact of Working Capital Management (WCM) on profitability of business using Ashaka cement Plc as case study. The aim was to examine the importance of WCM to manufacturing firms. Data for the study were obtained from published financial statements of the company from 2015 – 2019. The explanatory variable of the study is WCM proxied by Inventory Conversion Period (ICP), Debtors’ Collection Period (DCP), Creditors’ Payment Period (CPP) and Cash Conversion cycle (CCC) while the dependent variable is profitability proxied by Return on Assets (ROA). Results of regression analysis revealed that while ICP and CCC have significant impact on ROA, DCP and CPP have negative impact. The result of multicolinearity test indicated that there exist a high/ severe and impairing correlation between all pair of the explanatory variables implying non significance and in ability of the variables (endogenous factors) to predict future likely changes in ROA. The study recommended in addition to implementation of effective Working Capital Cycle (WCC) by manufacturing firms particularly ICP and CCC, government should aid profitability of the sector through creation of business friendly environment particularly improved security and infrastructure.
Keywords: Working capital management, Manufacturing firm, Return on total assets, Improved security, Improved infrastructure
Cite this paper: Sani Alfred Ilemona, Nwite S., Impact of Working Capital Management on Profitability of Manufacturing Business: Evidence from Nigeria, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 9 No. 4, 2020, pp. 91-97. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20200904.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The amount of Working Capital (WC) available to an enterprise is one of the key indices to measure its success in business as the capital represents the total liquid asset available for operations. WC reflects a firm’s ability to meet day – to - day operating expenses and a good indicator of a firm short financial health and stability. Management decisions relating to its WC therefore, are decisions on short term financing aimed at ensuring that the firm has sufficient cash flow to meet its short term obligations and operating expenses (Pandey, 2004). A firm having the required cash to meet its obligations as they fall due is a good omen of ability to continue in business and achieving a proper tradeoff between profitability and liquidity necessary to maximize shareholders’ wealth.Working capital comprises four (4) statements of financial position items usually referred to as the short term areas of the statement of financial position (Delofta & Ann 2011) these are (i) Stock which include raw material, work in progress and finished goods (ii) Debtors and prepayments (iii) creditors and accruals and (iv) cash which include physical cash balances available in the company, cash balances in the banks, short terms investments inform of bank deposits, quoted investments and other cash equivalents that could be turned into cash within the shortest possible time. Working Capital Management (WCM) is concern with how to effectively manage each of these of components of WC by mangers of enterprises. The overall objective of WCM is to maximize profit and reducing the risk of not been able to satisfy maturing short term obligations (debt). A firm that is not able to effectively make its WC or is poorly managing its WC is an indication that such a business is either under – capitalized or doing over – trading. The ultimate negative effect of under – capitalization and over – trading is decrease in Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) with large sums of funds tied up and fall in profit margin. Manufacturing industry is a key sector in any economy particularly the developing ones like Nigeria where the application of WCM is critical for profitability . The growth of the sector in Nigeria is of interest to the people and government for the tremendous contribution of the sector to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment creation and poverty reduction in the society in 1960s to early part of 80s. Unfortunately, the growth and profitability prospect of the sector started dwindling in the 1990s due to factors that are within and outside the control of the players in the industry. One of the major endogenous factors responsible for the falling performance and collapse of the manufacturing sector of the Nigerian economy is poor management of the WC by managers of these firms (Galis & Enemah, 2010, Edem & Ebaiai 2016).Utsha (2019) remarked that the problem of WCM is so severe in the sector of Nigerian economy that most manufacturing enterprises cannot measure with certainty, the period it takes for their investment in materials and merchandise will turnover into cash. The most worrisome disadvantage of poor and inadequate WCM is ability of firms to keep abreast of technical improvements and loss of opportunity to grow and make profit (Utsha, 2020). The multiplier ugly effect of poor WCM in most manufacturing firms is slim employment opportunity that has further worsen poverty in Nigerian society (Edem & Ebiai, 2016; Utsha, 2019).Contrary to Edem & Ebiai (2016) and Utsha, (2019), Diyola and Oke (2020) and Lawal and Aduku (2020) asserted that profitability of manufacturing business in Nigerian environment is an issue beyond the players in the industry as factors such as poor state of infrastructure, insecurity, value of Nigerian currency, low purchasing power and demand for locally produced goods etcetera have all marred profitability vision of manufactures. Therefore, though effective WCM can trigger profitability of a manufacturing business in any environment, existence of negative exogenous factors beyond the control of entrepreneurs can truncate any internal efforts and policies targeted towards profitability (Diyola & Oke, 2020; Lawal & Aduku, 2020).It is against this backdrop of the contradictory arguments that the study empirically test the impact or otherwise of WCM (endogenous managerial policy) on profitability of manufacturing business in Nigeria.
2. Objectives of the Study
- The objective of the study is to investigate the impact of WCM on profitability of firm. However, the specific purposes are as follows:1. To ascertain the impact ICP on the profitability of manufacturing business.2. To investigate the impact DCP on profitability of manufacturing business.3. To determine the impact CPP on profitability on manufacturing enterprise.4. To evaluate the impact of CCC on profitability of manufacturing business.5. To ascertain the impact of WCM on revenue of manufacturing enterprise.
3. Hypotheses of the Study
- Drawing from the stated specific objectives, the following null hypotheses are formulated to guide the study: Ho1: ICP has no significant impact on profitability of manufacturing business.Ho2: DCP has no significant impact on profitability of manufacturing business. Ho3: CPP has no significant impact on profitability of manufacturing business.Ho4: CCC has no significant impact on profitability of manufacturing business.Ho5: WCM has no significant impact on revenue of manufacturing enterprise.
4. Literature Review
4.1. Conceptual Clarification
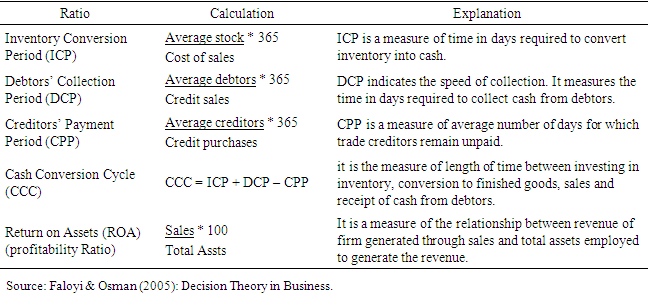
- Mycithan and Kane (2002) defined WC as excess Current Assets (CA) over Current Liabilities (CL). Examples of current assets of a typical manufacturing enterprise include cash, account receivables (debtors) and inventories and its current liabilities (Obligations) include salaries, wages. creditors (accounts payable) and taxes owed to government. For a manufacturing firm, WC represents the funds available to it to finance production, inventories and provide credit to customers (Kissitto, 2010; Ola & Mark: 2015). Shortage of WC in a firm or in any organization is synonymous with shortage of cash as such entity will not be able to meet its obligations (debts) as they fall due. Thus, Rahman (2001) refers to WC as the quantum of funds required to run a business or defray day-to-day operational expenses of an enterprise. To provide for WC in a business is the same with making provision for availability of cash as it is the most liquid asset required for daily operational expenses. Thus, Ellen (2012) Summarized WC of an enterprise as a total of a firm’s short term obligations that require effective management.Defining WCM Diallo and Obotto (2003) viewed that it as a concept involving effective control mechanism put in place by management of an enterprise or a firm to monitor relationship between short term assets and short term liability with a view to improving liquidity position of the business. Liquidity of a business at all times is important especially to a manufacturing firm. It is a means to meet daily operational expenses also essential for financing of seasonal trade and repayment of loans or other capital projects where these have not been anticipated in loan term plans. The overall essence of WCM is for profit maximization. Thus, Garrison (2004) asserted that WCM is a managerial policy of a firm implemented to attain optimal level in each of the four (4) components of WC namely: stock including raw materials and Work-In- Progress (WIP), finished goods, debtors and cash necessary for profit maximization. It is with intent of profit maximization that manufacturing enterprises hold cash (liquid) either for speculative motive to finance purchase of items in advance of price increase expectation or reasonably defer payments to creditors. Thus, Diego (2018) asserted that WCM of a firm is part of managerial policy to leverage on of its goods will with creditors to reasonably differ payment due to them and engaging in ventures with quick profit potential.Profitability is the ability of a firm to sell goods and services above cost and earn reasonable return (Adeniyi, 2004). It is the difference between the cost of providing goods and services by a firm and the price paid for those goods and services by consumers. Profit (P) will arise if the Selling Price (SP) of an item is higher than its Cost Price (CP) mathematically denoted as: SP-CP=P (Fadipe, 2002; Barlaya & Dele, 2007).Profitability is a performance indicator that can measured by Return on Assets (ROA), a component of Return on capital employed (ROCE) or return on Investment (ROI) of a business (Ogonia & Clement 2015). ROA is a performance evaluation criteria using ratios that show the relationship between sales and ROCE. The relationship is a division between sales (numerator) and ROCE (denominator) that could be expressed in terms of percentage or number of times (Adeniyi 2004). The denominator, according to Faloyi & Osman (2005) could be defined in terms of: (i) Total Assets of a firm that is Fixed Assets (FA) plus Current Assets (CA) (ii) Net Assets (NA) of firm that is share capital plus reserves and (iii) Total Assets less current liabilities. Adeniyi (2004) opined that ROA is a measure that shows the efficiency and how profitable a manufacturing enterprise operates in utilization of assets and investing its financial resources through paying for raw materials at the beginning of production process, making/ producing the product and recovery at the end through sales and collection of cash (revenue) from debtors.The WC of a typical manufacturing firm and profitability ratios are depicted in the table below
|
5. Empirical Review
5.1. Studies in Other Economies
- Farrah Noredi and Othman (2016) conducted a study on working capital management efficiency: A study of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Malaysia. The aim was to analyse the efficiency of WCM in selected SMEs in Malaysia. Data for the study were obtained from database of twenty four (24) SMEs randomly selected from 2010 – 2013. The results of the analysis of the indexes of the companies namely: Performance Index of WCM (PLWCM), Utilization Index of WCM (ULWCM) and Efficiency Index of WCM (ELWCM) revealed that the SMEs were less efficient in managing their WC with negative effects on profitability of the enterprises.Asghar and Syed (2012) examined Working capital Management and whether it affects profitability of organizations in Pakistan. The study is an exploratory research that investigated the impact of WCM decisions on profitability of enterprises. It was found from studies that WCM has positive impact on profitability of Organizations.Ishmael, venancio, Isaac and Widin (2018) did a study on working capital management and financial performance in UK listed firms: A contingency approach. The aim was to investigate the effects of WCM on firms’ financial performance. Specifically to establish a relationship between WCM and financial performance as affected by firms’ environment, resources and management capabilities. Data for the study were collected from 302 firms listed on London Stock Exchange (LSE) from 2004 to 2014. The analysis was done using series of interactive models to estimate the relationship. Findings suggest that the impact of WCM on performance changes to reflect a number of contingency Variables such as environmental resources and capability of firms.Tan veer, Muhammad, Muhammed and Muhammed (2016) did a study on impact of WCM on firm’s financial performance evidence from Pakistan. The aim was to empirically explore the impact of WCM on firm’s performance. Using purposive sampling, a random sample of 50 listed non-financial companies on Pakistan Stock Exchange (PES) were selected. Data obtained from financial statement of these firms were analyzed using multiple regression. The results indicated that financial performance (FP) proxied by ROA is influenced by WCM. Rahimah, Farha, Syahrul and Noraisah (2018) did a study on WCM and its effects on profitability: Empirical evidence from Malaysia capital market. The aim was to examine effects of WCM on profitability of firms. Data for 803 listed companies on Bursa Malaysia collected from 2010 to 2014 were analyzed using regression. It was found that WCM determines profitability of companies.
5.2. Studies in Nigeria
- Olayinka (2012) investigated the effect of WCM on profitability of selected quoted firms in Nigeria. The aim was to examine the relationship between WCM and profitability of businesses. Data obtained from a sample of 68 Nigerian non-financial firms for the period 1997-2007 were analyzed. Results suggest that firm’s profitability is reduced by lengthening the number of days of account receivable while shortening the CCC improves profitability.Akindele and Odusina (2015) studied WCM and firms’ profitability: Evidence from Nigeria quoted companies. Data for the study were obtained from audited financial statements of twenty-five (25) Nigerian companies from 2005-2011. The analysis of the data carried out using multiple regression. showed a negative relationship between WCM and profitability of firms. Oladele and Tasie (2011) conducted a study on the effects of WCM on profitability of Nigerian manufacturing firms. The aim was to provide empirical evidence of the relationship between WCM and profitability of manufacturing firms. Data for the study were obtained from audited annual reports of randomly selected six (6) listed manufacturing firms in Nigeria. Results of the analysis using correlation statistical tool suggest a negative correlation between WCM and profitability of firms. Dapo and Teju (2017) examined the impact of WCM on performance and profitability of manufacturing firms. Data for the study were obtained from a sample of twenty (20) manufacturing enterprises listed on Nigerian Stock Exchange (NSE) from 2005-2014. The results of multiple regression indicated that WCM has significant impact on profitability of the firms.Dauda, Martins and Luka (2016) studied WCM and profitability of listed Nigerian food product companies. The aim was to examine the effect of WCM on profitability of listed companies on NSE for the period 2002-2011. Data obtained from annual reports of the companies were analyzed using panel data regression technique. The result revealed a positive relationship between CCC and ROA of the firms.Lara and Martha (2018) conducted a study on the impact of WCM on the financial performance of manufacturing enterprises measured by ROA of firms. Data for the study were obtained from financial statements of twenty-two (22) manufacturing companies located in Lagos and Ogun states of Nigeria. Results of multiple regression revealed that WCM has significant impact on ROA of the companies.Nkechi, John and Natali (2016) did a study on WCM and its impact on profitability and growth of industry. The aim was to ascertain the relationship between WCM and profitability of manufacturing enterprises. Data for the study were obtained from financial statements of seven (7) beverage manufacturing enterprises located in Lokoja the capital of Kogi State-Nigeria. Results of multiple regression analysis revealed a significant impact of WCM on profitability of the enterprises.Ojoade and Tolu (2015) examined the role of WCM in liquidity management and profitability of firms. Data for the study were obtained from the financial statements of ten (10) manufacturing firms in Lagos state. Using panel analysis, Ordinary Least Square (OLS) and Fixed Effect Estimation (FEE), the result of the analysis showed that WCM can impact positively on ROA suggesting a relationship between WCM and ROA. Toby (2014) examined the relationship between WCM policy and corporate profitability of Nigerian quoted companies across 23 manufacturing sector for the period 2003-2007. The result of product moment correlation analysis indicated a positive correlation between ROA (measure of profitability) and WCM of the firms.
6. Theoretical Framework
- The study is anchored on the prescriptive theory of WC propounded by Ans Mcinnes in 1937 (Diallo & Obotto 2003). The theory assumed that if WC is managed to the optimum then, it would be expected that businesses would invest in WC and monitor factors that would influence it. That the essence of firm’s analysing and measuring the influence of cash management, accounts receivables (debtors), inventory, accounts payables (creditors) and cash conversion cycle is for evaluation to ensure that assets are utilized effectively and efficiently for overall attainment of efficiency, profitability and shareholders’ wealth maximization.Optimal management of WC for profitability is the key emphasis of the theory. The emphasis of the theory underscores its relevance to the study for the fact that effective WCM is one of the major endogenous policies needed in Nigerian manufacturing environment for profitable operation which other factors outside managerial policy (exogenous factor) have been negatively influencing the profitability objective of the firms (Diyola & Oke, 2020; Lawal & Aduku, 2020).
7. Methodology
- It is an exploratory study that made use secondary data. Data for the study were obtained from the published financial statement s of Ashaka cement Plc for 2015-2019. The figures of the variables of interest in the statement were empirically analyzed using regression statistically tool.
7.1. Model Estimation
- The regression analysis revealed the degree of variation of dependent variable caused by the independent variables. The aprior expectation was that
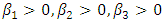 and
and 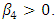
7.2. Model Specification
- In the study, Y (the dependent variable) is presented as profitability of the firm proxied by ROA. This is mathematically represented in equations as:
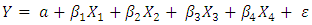 | (1) |
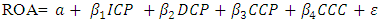 | (2) |
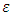 = Error term
= Error term 8. Results
|
|
|
|
9. Findings and Discussion
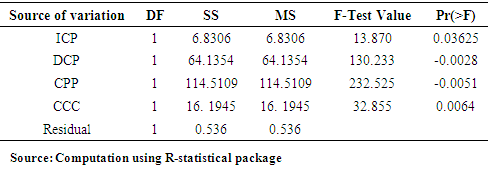
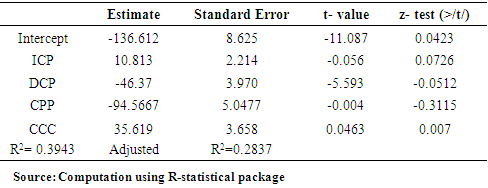
- The result of ANOVA indicates that while ICP has significant impact on ROA at 5% level of significance; that of CCC showed impact at 1%. Therefore the first and fourth hypotheses of this study are rejected. This result is consistent with that of Olayinka (2012) that shortening CCC improves profitability. However, the DCP and CPP impact are negative and therefore the second and third hypotheses of the study are accepted.Further, the result of regression analysis showed similar pattern with that of ANOVA. The impact of ICP on ROA is significant at 5% level of significance as decrease of 5.6% in ICP accounts for 7.26% increase of ROA of the firm. The CCC variable also showed impact. The variable has a positive coefficient of 35.19 and a P value of 0.007 implying the significance of the variable at 1% level. This further indicates that an increase in the number of days of CCC by 1 day accounts for a decline in ROA by 4.63%. The significance of this variable corroborate with the finding of Olayinka (2012).Contrary to the impact of ICP and CCC on ROA, the values of -0.028 and -0.0051 for DCP and CPP respectively indicate the negative impact of the variables on ROA and therefore not significant. Further, the apriori expectation of
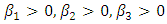 and
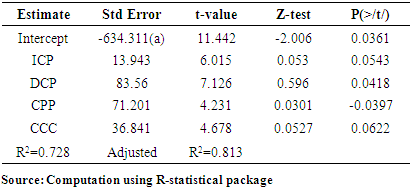
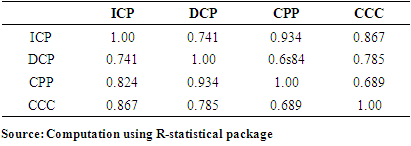
and 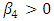 were not satisfied caused by the negative values of -46.37 and -94.5667 for DCP and CPP respectively conforming further that variables (DCP and CPP) have no significant impact on ROA.In terms of the predicatory ability of the explanatory variables of the likely changes in ROA caused by the predictors, the low value of the coefficient of determination (R2) at 0.2943 showed that only 29.43% of the variation in ROA can be explained by the predicators. This therefore implies that a small percentage of changes in ROA of the firm can be explained by managerial policy of WCM (endogenous factor) while a greater percentage of 70.57% changes in ROA are explained by exogenous factors. This result is consistent with findings of Diyo & Oke (2018) and Lawal & Adeku (2019) that the impact of WCM on firm’s ROA can be limited as exogenous factors such as negative socio-economic business environment can erode any effective managerial policy like WCM in a manufacturing outfit. However, for Revenue (R), all the explanatory variables have positive impact on R expect CPP. About 73% (0.728 of R2) of the changes in R of the enterprise can be explained by the variables (ICP, DCP and CCC) implying significant impact. Thus, the fifth hypothesis of the study is rejected. The result of multi co linearity test showed that there exist high correlations (multicolinearity) among the pairs of variables as all the pairs have between 0.6 to 1.00 with 1.00 or 100% being the maximum. Existence multicolinearity severe or impairs the predicatory ability of independent variable of the likely future changes in the dependent variable (Ogonia & Clement, 2015). The existence of multi co linearity among the independent variables further confirms the limited extent to which effective WCM of enterprise can impact on the profitability of firms (Diyo & Oke, 2018: Lawal & Aduku, 2019).
were not satisfied caused by the negative values of -46.37 and -94.5667 for DCP and CPP respectively conforming further that variables (DCP and CPP) have no significant impact on ROA.In terms of the predicatory ability of the explanatory variables of the likely changes in ROA caused by the predictors, the low value of the coefficient of determination (R2) at 0.2943 showed that only 29.43% of the variation in ROA can be explained by the predicators. This therefore implies that a small percentage of changes in ROA of the firm can be explained by managerial policy of WCM (endogenous factor) while a greater percentage of 70.57% changes in ROA are explained by exogenous factors. This result is consistent with findings of Diyo & Oke (2018) and Lawal & Adeku (2019) that the impact of WCM on firm’s ROA can be limited as exogenous factors such as negative socio-economic business environment can erode any effective managerial policy like WCM in a manufacturing outfit. However, for Revenue (R), all the explanatory variables have positive impact on R expect CPP. About 73% (0.728 of R2) of the changes in R of the enterprise can be explained by the variables (ICP, DCP and CCC) implying significant impact. Thus, the fifth hypothesis of the study is rejected. The result of multi co linearity test showed that there exist high correlations (multicolinearity) among the pairs of variables as all the pairs have between 0.6 to 1.00 with 1.00 or 100% being the maximum. Existence multicolinearity severe or impairs the predicatory ability of independent variable of the likely future changes in the dependent variable (Ogonia & Clement, 2015). The existence of multi co linearity among the independent variables further confirms the limited extent to which effective WCM of enterprise can impact on the profitability of firms (Diyo & Oke, 2018: Lawal & Aduku, 2019). 10. Conclusions and Recommendations
- The role of manufacturing sector in growth of any economy cannot be over emphasized. In the 70s and early part of 80s, the sector played key roles in Nigeria in her quest for industrialization, economic growth, expansion, employment generation and poverty reduction in the society.Unfortunately in the 2000s, the fortune of the sector started dwindling due to a myriad of factors beyond the control and imagination of the entrepreneurs and mangers in the sector. Prominent among these exogenous negative factors that contributed to the misfortune of manufacturing sector of the economy are insecurity, poor infrastructure, inflation, low purchasing power, low demand for the output, poverty etcetera. Though, firms in the sector tried to reposition the sector for growth and profitability through effective internal managerial policies such WCM, but, the influence of negative business environment has limited the profitability efforts of entrepreneurs in the sector.Profitability of the manufacturing business in Nigeria is a desirable attainment that requires deliberate efforts of both entrepreneurs, managers of the firms and government through viable policies. Therefore the following recommendations are put forward:1. Mangers of manufacturing enterprise in Nigeria should as much as possible manage their Working Capital Cycle (WCC) particularly through quality control necessary for quality output.2. Deliberate implementation of practical fair pricing policy to induce sales, patronage and profitability (SPP). The three business elements (SPP) are critical to survival of any enterprise especially manufacturing.3. Government should create conducive environment for manufacturers particularly improved security and infrastructure.These recommendations are both endogenous and exogenous factors that can impact positively on manufacturing business in Nigeria.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML