-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2018; 7(5): 142-146
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20180705.02

Determinants of Bank Profitability before and during Crisis: Evidence from Bangladesh
Alamgir Hossain1, M. Saifullah Khalid2
1College of Business Administration, IUBAT-International University of Business, Agriculture and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh
2BRAC Business School, BRAC University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Alamgir Hossain, College of Business Administration, IUBAT-International University of Business, Agriculture and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

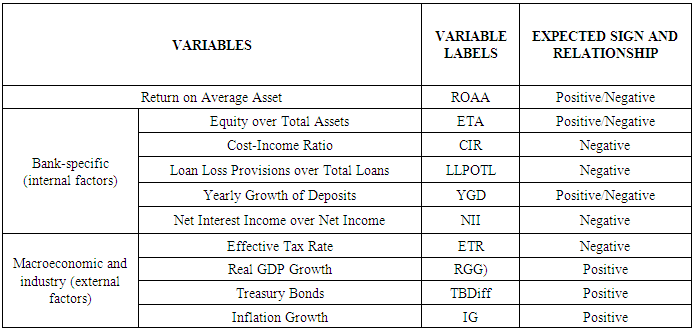
This paper examined the factors of profitability and as we know the main components of banks profitability is measured by the return on average asset and return on average equity. Moreover, this research examined to find the relationship between profitability and its determinants in Bangladesh context during recession and Pre-recession. Some others external and internal factors also considered to measure the banking profitability of bank. Return on average asset (ROAA) is considered as a dependent variable and which is the measurement of profitability in this study, whether, independent variables are divided into two segments: those are bank-specific characteristics (internal factors) such as - Equity Over Total Assets (ETA), Cost-Income Ratio (CIR), Loan Loss Provisions Over Total Loans (LLPOTL), Yearly Growth Of Deposits (YGD), Net Interest Income Over Net Income (NII) and industry-specific characteristics (external factors) such as - Effective Tax Rate (ETR), Real GDP Growth (RGG), Treasury Bonds (TBDiff), Inflation Growth (IG). To conduct the research the data for pre-crisis period (2002-2006) and, on the contrary, during crisis situation (2007-2008) was taken. The results show that bank-specific (internal) and market-specific (external) factors have influence on bank profitability, but macroeconomic factors do not.
Keywords: Bank profitability, Return on Average Asset, Financial crisis
Cite this paper: Alamgir Hossain, M. Saifullah Khalid, Determinants of Bank Profitability before and during Crisis: Evidence from Bangladesh, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 7 No. 5, 2018, pp. 142-146. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20180705.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The banking industry is very critical in the development of an economy and Bangladesh is not an exception. After the independence of Bangladesh, there was few commercial banks and now currently 56 banks are operate their activity and among those banks majority banks are private commercial. Profitability of commercial banking significantly influences the economy. This paper is discussing the determinants of the profitability of banking industries in Bangladesh, during the financial crisis of 2007-2008, and the pre-crisis period. This paper is evaluate the 7 years (2002-2008) relevant data for 4 nationalized commercial banks (NCBs), 5 government-owned development finance institutions (DFIs), 30 private commercial banks (PCBs) and 9 foreign commercial banks (FCBs).Several external and internal factors are work as determinants not only the bank management system and it also evident that the external and internal determinants have influence on the profitability (Samad, A., 2015; Yesmine, S., & Bhuiyah, M. S. U. 2015; Dietrich, A., & Wanzenried, G. 2011; Perera, S., Skully, M., & Chaudhry, Z. 2013).Bank profitability mostly measured by return on average asset and return on average equity, and by using this profitability measure this study is trying to illustrate the relationship between profitability and its determinants. Previously, several researches had been conducted to determine the determinants of bank profitability but no empirical study was precisely conducted to determine the determinant of profitability during and pre financial crisis period individually in the context of Bangladesh.
2. Literature Review
- Samad (2015) [12] conducted an analysis through the panel data to identify the bank specific characteristics and macroeconomic variables impact on the bank’s profitability. His study used bank specific factors as operational efficiency, financial risk and bank size for commercial banks, and economic growth as macroeconomic factors. His found that loan to deposit ratio, loan-loss provision, equity capital as bank specific factors are highly significant but no significance level of influence from macroeconomic factors and bank’s size.Rahman, Hamid and Khan (2015) [11] investigate several factors such as capital, credit, cost cutting efficiency, ownership, size of the bank, banks non-interest earning, off-balance sheet activities, liquidity condition and several macroeconomic variables to determine the profitability of banking sector of Bangladesh. They were used 25 Bangladeshi commercial bank’s data of 2006-2003 to conduct their empirical study. Their study used profitability for bank as net interest margin to assets, return from asset and equity. Their empirical analysis found that loan and capital strength has positively impact on banks profitability, but cost efficiency and off-balance sheet actions are negatively impact and all variables significant level was high. For net interest margin as profitability non-interest income, credit risk and economic growth are significant determinant.Dietrich and Wanzenried (2011) [3] was analyzed Switzerland’s 453 commercial banks profitability from the period of 1999-2008 and their research intend to examine the profitability determinant in two different individual term, the pre-financial crisis period and during the financial crisis period 2007-2008. They were selected their variables in two segments bank-specific characteristics and others were industry-specific and macroeconomic.Pasiouras, F. and Kosmidou, K., 2007 [8] empirically studied panel data of 19 Greek bank subsidiaries in different 11 nations from the term of 1995-2001 to identify the banking profitability. Their study reveals that subsidiaries profitability from different nations are positively influenced by the parents bank operating experience and the level of profits and others variables such as Liquidity condition, bank size, cost efficiency etc. are totally insignificant on banks profitability.Sufian, F. and Habibullah, M.S., 2009 [15] studied on thirty-seven commercial banks with period range from 1997 to 2004 from Bangladesh to evaluate their performance. Their findings indicate that cost efficiency, loans and credit conditions positively and significantly influence the banking performance but non-interest income negatively influence. They also found positive relation from bank size towards the return on asset but negative on return on equity and macroeconomic factors didn’t influence the significantly on bank performance.Yesmine, S., & Bhuiyah, M. S. U., 2015 [16] analyzed ten private commercial banks (PCB) and all nationalized commercial banks (NCB) of Bangladesh and used data from 2008-2014 to identify several factors that affecting the banks financial performance. Their empirical findings stated that, significant positive impact was visible from asset utilization and operating efficiency towards banks financial performance but no significant relationship wasn’t found from size and liquidity of the banks.Perera, S., Skully, M., & Chaudhry, Z., 2013 [9] studied particular South Asian countries (Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka) commercial banks profitability determinant. They found that competition between banks have negative impact on the profitability and slack legal system, bank size, efficient operation is positively related with banking profitability of those particular South Asian countries.Podder, B., Venkatesh, S., Wongsurawat, W., & Badir, Y., 2012 [10] attempt to examine the growth of private commercial banks through using several variables- banks total assets, total equity, net income, banks deposit and advances. Their study found most of those variables were important for the growth of the private commercial banks.
3. Data, Variables and Methodology
- Data source for variables of bank-specific characteristics and macroeconomics characteristics and variables of banking profitability are Bangladesh bank website which is provide all financial data of all bank of Bangladesh in their database (Bb.org.bd. 2018) [2]. This study is gathering data sample from4 nationalized commercial banks (NCBs), 5 government owned development finance institutions (DFIs), 30 private commercial banks (PCBs) and 9 foreign commercial banks (FCBs) data for the year of 2002-2008, where we consider 2002-2006 was the pre financial crisis period and 2007-2008 was financial crisis period.
3.1. Bank’s Profitability Determinants and Variables Selection
- Return on Average Asset (ROAA) is the dependent variable and which is considering as the measurement of profitability of this study. Independent Variables of this paper are divided into two segment those are Bank-specific characteristics (internal factors) and macroeconomic and industry-specific characteristics (external factors).Bank-specific characteristics (internal factors) are Equity over total assets, Cost-income ratio, Loan loss provisions over total loans, Yearly growth of deposits, Net interest income over net income. Dietrich, A., & Wanzenried, G., 2011 [3] consider equity over total assets is very useful indicator for profitability and higher capitalized bank low risky then the low capitalized bank and low share capital bank can make high return. Cost-income ratio indicate that the all kind of operating expense to generate revenue, and high operating create negative impact for the profitability of bank. Loan loss provisions over total loans is the ratio of Bank credit quality this ratio is calculate through the amount of loan loss provision out of total loan and Higher ratio influence the lower profitability then the lower ratio. Dietrich, A., & Wanzenried, G., 2011 [3] expect yearly growth of deposit ratio have negative and positive both effect on the dependent variable because high growth increase the profitability if bank can utilize deposit as earning assets, sometime high growth attract the competitors that lower the earning efficiency. In conventional banking interest income ratio is the prime indicator for profitability but in commercial banking huge amount of profit come from several fee, commission, trading spread, so this study is considering that the higher percentage of interest income in net income reduce the profitability.Macroeconomic and industry-specific characteristics (external factors) are including Effective tax, Real GDP growth, Treasury Bonds, Inflation. Effective tax rate is total taxes over pretax profit or mostly corporate income tax, we consider higher effective tax rate on bank have negative impact. Real GDP growth has a positive impact on the profitability. Term structure of interest rates-commercial bank use short term deposit to finance long term loan, we use the difference between the interest rate of a 5-year and a 1-year bond which impact the profitability. Samad, A., 2015 [12] expect Inflation affects most economic variables especially interest rate. High inflation raises the rate so it positively increases the profitability.
3.2. Methodology
- To investigate the profitability determinants of 48 banks of Bangladesh, this study uses the multiple regression model in equation (1) to empirically examine the relation between dependent variable and independent variable (internal and external factors). In first step this paper examine the data for all years (2002-2008) and in second step examine the data for pre-crisis period (2002-2006) and in final step this study examine data for during crisis situation (2007-2008).
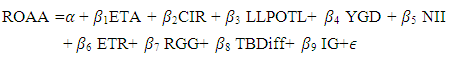 | (1) |
|
4. Empirical Result and Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
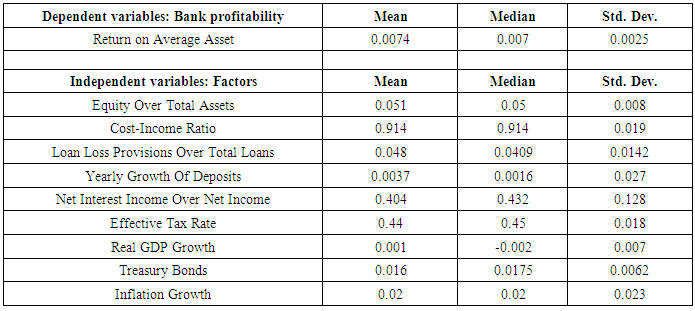
- Descriptive statistics presented in table 2 indicate ROAA average value is .0074 and standard deviation is .0025. On the other hand, the average of Equity over Total Assets, Cost-Income Ratio, and Loan Loss Provisions over Total Loans, Yearly Growth of Deposits, and Net Interest Income over Net Income, Effective Tax Rate and Real GDP Growth are 0.051, 0.914, 0.048, 0.0037, 0.404, 0.44 and 0.001, respectively. Moreover, the standard deviation of Equity Over Total Assets, Cost-Income Ratio, Loan Loss Provisions Over Total Loans, Yearly Growth Of Deposits, Net Interest Income Over Net Income, Effective Tax Rate and Real GDP Growth are 0.008, 0.019, 0.0142, 0.027, 0.128, 0.018 and 0.007 gradually.
|
4.2. Correlation Result
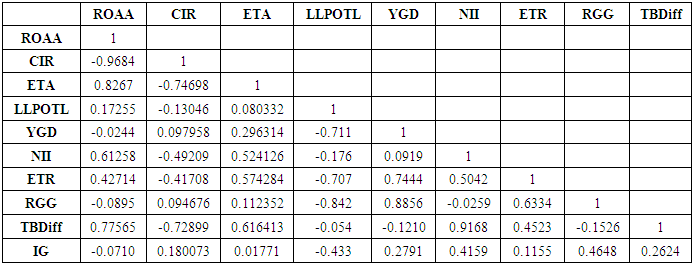
- Correlation matrix presented in table 3, and this correlation matrix indicates that very strong correlation exists between ROAA and CIR, ETA with value respectively -0.9684 and 0.8267 but ROAA and CIR are negatively related. NII and TBDiff also strongly and positively correlated with each other with value 0.9168. Good negative correlation between CIR and ETR are existing with value -0.7469. There is also good correlation visible between YGD and ETR with positive value 0.7444. Strong positive correlation exists between YGD and RGG, LLPOTL and RGG.
|
4.3. Multiple Regression Results
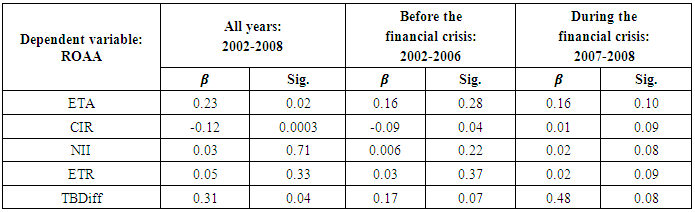
- Table 4 presenting the multiple regression result between dependent and independent in three segments; those are all periods (2002-2008), before the financial crisis periods (2002-2006) and during the financial crisis periods (2007-2008). Table 4 is including independent variables only those are statically significant in three segments individually to impact the dependent variable as return on average asset (ROAA).
|
5. Conclusions
- This paper analyzed aggregated data of all banks of Bangladesh in the year of 2002-2008 and also examines both independent and dependent variables to determine the specific determinates for bank profitability in pre-financial crisis period and during financial crisis period. Through the multiple regression analysis between ROAA and bank specific and macro-economic variables this study found change in determinants in different periods. Change of determinants for bank profitability only visible for bank specific characteristics but determinants were unchanged for macro-economic and industry specific characteristics.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML