-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2017; 6(4): 104-110
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20170604.02

The Determinants of Computerized Accounting System on Accurate Financial Report in Listed Banks on the Ghana Stock Exchange
Allan McBright Sekyere1, Augustine Kwasi Amoateng2, Kennedy Frimpong1
1Department of Accountancy, Sunyani Technical University, Brong Ahafo, Ghana
2Department of Secretaryship and Management Studies, Sunyani Technical University, Brong Ahafo, Ghana
Correspondence to: Allan McBright Sekyere, Department of Accountancy, Sunyani Technical University, Brong Ahafo, Ghana.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

With the recent development of information technology, accounting information system has made it easier and faster to use computers. This study was conducted to examine the factors affecting the accuracy of financial reports in listed banks in Ghana. The study was set to addressing the benefits of computerized accounting system and critically examined the qualities of financial reporting and the concept of financial reporting. The study used a descriptive research designed. A sample size of eighty (80) respondents was involved in the study. Questionnaires were used to collect data which was processed with the aid of SPSS. It was revealed that users with better understanding and expertise in computerized accounting affect the quality and accuracy of financial reports in banks in Ghana. Also, assessing the benefits of computerized accounting system, the findings indicated that 85% of the respondents were in agreement that computerized accounting systems minimize errors and duplications, 15% disagree with the view. The study further found that most banks in Ghana run a fully computerized accounting system in financial reporting where they maintained the financial report qualities of timeliness, reliability, accuracy because of computerized accounting system. The study recommended that banks should put in much emphasis on training of staff to match the information needs of the bank with available software.
Keywords: Accuracy, Banks, Computerized accounting, Financial report, Financial report quality
Cite this paper: Allan McBright Sekyere, Augustine Kwasi Amoateng, Kennedy Frimpong, The Determinants of Computerized Accounting System on Accurate Financial Report in Listed Banks on the Ghana Stock Exchange, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 6 No. 4, 2017, pp. 104-110. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20170604.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The modern trends in business organizations have progressively brought about tremendous growth in information technologies infrastructure, the manual accounting systems have become gradually inadequate for decision needs (Brecht and Martin, 1996). Consequently, public and private sector firms in both developing and developed economies see computerized accounting systems as a tool to ensure effective and efficient information flow in recording, processing, and analysis of financial data. This helps in managerial decision-making, thereby increasing the firm's ability to achieve organizational goals. (Manson, McCartney, and Sherer, 2001). The experience of advanced countries is that managing complex financial management information systems projects require considerable managerial skills. However, this is typically in short supply in distributed control system. Top level managers may not be computer literate. The consequence thereof is often the binding constraint when adapting a current financial management information systems is not the technical capacity to create them but the capacity to manage them.Computerized accounting system as defined by Muinde (2013) is the application of a computer-based software which serves as a tool for inputting, processing, storing, and transforming data into accounting information. Accurate financial reporting refers to the ability of the financial reports to portray the true financial position of the company in terms of profitability, assets, bad debts provisions and other measures (Abdulrazak, 2013). The statements need to give third parties looking at the information such as regulators and the potential investors the worth and strength of the company. The financial statements that should also be checked by independent auditors also need to show the weaknesses of the company to enable prudent decision-making (Barako et al., 2013). The accurate financial reporting is important due to several factors. The accurate financial reports form the basis for the valuation of the company and analyzing the operational results. It is easier to market the company to potential investors when there are financial reports that are sound and have integrity (Barako et al., 2013).Regardless of the size of an organization, an accounting system is designed to collect, process and report periodic financial information about the entity (Oluoch, 2014). Several tools such as annual reports, audits, quarterly reports, financial accounts, performance assessments and independent evaluations can be derived from computerized accounting systems. Munide (2013) indicated that the heart of fiscal management is any organization is a good accounting system that is appropriate to that organization. To achieve a prudent financial accountability, it is advisable to establish a standardized system of accounting practices. In order to determine the effectiveness of a computerized accounting system, one must set its objectives. Per the Ghanaian constitution, as stipulated in Section 123 of Ghana’s Companies Code (1963) ACT 179, it is a mandate for all companies to keep proper books of accounts with respect to their financial and changes therein. Hence, the need for an accurate financial report cannot be over emphasized, therefore, this study seeks to identify the determinants of computerized accounting systems on accurate financial reporting in listed Banks on the Ghana Stock Exchange.
2. Literature Review
- In recent times in Ghana, the banking industry has hugely adapted to the use of computerized accounting in many sections of their activities such as recording of daily collections, recording of customer's savings (account details), preparation and presentation of end of year financial reports etc. Therefore the study critically examined on the determinants of computerized accounting on accurate financial reporting in listed banks on the Ghana stock exchange. However, it is important to note that research findings and recommendations in the Ghanaian banking sector can largely reveal several important matters that need to be considered by investors and shareholders in developing the country’s financial base. Computerized accounting system in commercial organizations, helps to integrate, simplify and streamline all the business processes and transaction cost effectively and easily (Indira 2008). It's however noted that the way accounting data is entered, processed and stored has considerably changed because there are accuracy and efficiency in keeping records, a low case of omission and loss of accounting records using computers. According to McBride (2000), computerized packages can quickly generate all types of reports needed by management, for instance, budget analysis and variance analysis. Data processing and analysis are faster and more accurate and meet the managers' need for accurate and timely information for decision making. Wood (1999) consented to the speed with which accounting is done and also indicated that a computerized accounting system can retrieve balance sheets, income statement or other accounting reports within seconds and with less effort. He further added that computerized accounting system allows managers to easily identify and solve problems instantly.In a related studies, Kateeba (2000) his studies sought to establish the relationship between governance and quality of financial reports in NGOs in Kosovo, the research carried out in Kosovo focused on the Financial factor, when a question was asked about their financial resources based on their last financial year, 75% of NGOs answered that foreign donors are the only or main financial sources of their projects and activities. The study findings confirmed a strong relationship between accounting systems and quality of financial reports. It was therefore recommended that NGOs should review their current accounting systems to identify gaps and then put in place the necessary steps to fill in those gaps. Alshebeil (2010) conducted a study and sought to identify the role of accounting information systems in achieving competitive advantage for Jordanian commercial banks, and his findings showed that there is a statistically significant impact on accounting information systems on achieving the dimensions of competitive advantage by improving the pricing process for banking services, reducing costs of banking services, increasing the speed of provided services, and increasing market share. Amveko (2011) in a related research study aimed to identify the impact of computerized accounting information systems on financial reporting in Kampala, the financial reports generated to conform to some of the quality attributes of good financial information. This showed a positive correlation of response on quality attributes of timeliness and accuracy though it was on a low scale, the research findings revealed that computerized accounting system actually influences the quality of financial reports for publication purposes. El-Dalabeeh (2012) conducted a research into the role of computerized accounting information systems in reducing the costs of medical services at King Abdullah University Hospital, and his findings showed that computerized accounting information systems play an in important role in reducing the costs of medical services at King Abdullah University Hospital compared with non-computerized systems, which usually require bigger costs and do not contribute to reducing the costs of medical services. According to Luther and Boru (2013) on their studies conducted on the Use of Annual Financial Statements by Loan Officers in Kenya, the research findings revealed that financial statements are rated as a very important source of information by credit risk analyst however commercial banks do not rely on one source of information. The worry though was a lack of concern of social objectives when lending. Mwaura (2013) also undertook a related study to establish the relationship between the financial performance of NGOs in Kenya and financial accountability. The study showed that the NGOs that applied financial standards in ensuring accountability of finances in the organizations boosted Donor support which resulted in improved performance. Another recent study was done by Kamau and Mutiso (2013) on the Factors Influencing Complexity in Financial Reports Preparation Evidence from the Banking Sector in Kenya. The objectives included assessing whether the disclosures adoption of international reporting standards regulations and lack of competence by the preparers have contributed to the complexity of the reports, the findings revealed that the identified variables positively contributed to the complexity of financial reports preparation. Management interference, lack of guidance on interpretations and frequent updates of standards were identified as the main challenges of preparing financial reports.Tarus and Kawasira (2015), in their study determinants of the accuracy of financial reports accuracy, concluded that there is a significant positive relationship between financial report accuracy and Computerise Accounting.In a study by Amidu and Effah (2010) and their counterpart Abor (2005) argues that computerized accounting system is a means of recording accounting transactions and also keeping financial reports by the use of computer technology for recording and processing financial data for business support and decision-making purposes. Computerized record keeping system uses computer software to keep financial records. It computes and records faster but it will not know what to do unless clear instructions are given. The computer then processes the information automatically by a request. With these systems, computers are used to make more precise computations and instant financial reports but it takes many skills, resources and effort. Also, it is tedious to measure which accounting type is faster and economical. Thus computerized accounting system refers to any accounting system that relies on Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for carrying out its information functions to ensure reliability, quality and in an accurate manner.Undoubtedly, with the adoption of computerized Accounting Systems, problems and challenges such as; high purchase, installation and maintenance cost, computer failure, inadequate information technology expertise and time involving are to be expected. However, the advantages from the use of a computerized accounting System far outweigh the problems and challenges as it has impacted the financial reporting of the banks positively. This implies that banks listed on the Ghana stock exchange must aggressively adopt a Computerised Accounting System to ensure accurate financial reporting and more importantly for all banks to make the effort to migrate onto the digitalized and virtual systems as it comes with added advantages of being networked with other banks globally.
3. Methodology
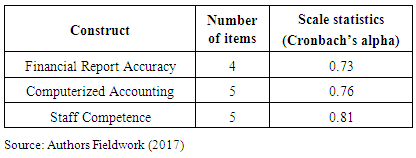
- The descriptive cross sectional survey design involving quantitative approaches was employed for this study. Cross sectional survey was used because it was a one-time study. The study population consisted of all the listed banks on the Ghana stock exchange. A total of 80 workers of the selected banks that use ICT/ accounting software were purposely selected for the study.Primary data was collected using structured questionnaires from the selected respondents. The questionnaire was designed in relation to the aim of the study and the study variables. Item scales were developed based on extensive review of related literature of recent empirical studies in computerized accounting. Constructs related to computerized accounting and financial reporting were measured on a five-point Likert scale ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (5). Of the 80 questionnaires distributed, all the 80 were sufficiently filled and returned translating to 100% response rate which was enough to facilitate the data analysis.A pilot study which involved 10 of the respondents was conducted to identify the challenges of understanding the questions, ambiguity, clarity and to assess reliability. Literature review and an in-depth discussion with banking experts and researchers were conducted to establish the basis of content validity for the instrument. The construct validity of the research instrument is guaranteed by subjecting the instrument to academic researchers and banking experts to critique for relevance and clarity.To check the reliability of the instrument in this study, Cronbach’s alpha was used. Cronbach’s coefficient was calculated for the items of each survey construct; the scale measuring financial report accuracy and the two scales measuring computerized accounting application. A lower limit of 0.6 is considered acceptable for newly developed scales and 0.7 for established scales (Nunnally, 1978).
|
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Demographics of Respondents
- Respondents were asked to indicate their gender, position and the number of years they have served in their current position and their highest level of education. They were asked to indicate the average number of years their banks have used accounting software. Results revealed that majority of the respondents were males (60.5%) as compared with females (39.5%). The results revealed that 27.5% of the respondents were operation managers, 22.5% of the respondents were tellers, 32.5% of the respondents were accountants and 17.5% were managers. The study shows that 27.5% of the respondents had worked for less than 3 years, 41.25% of the respondents had worked for between 3-6 years and 31.25% of the respondents had worked for more than 6 years. Duration in current position had a mean of 5.1 years. Out of the 80 respondents who took part in the study, 32.5 % were HND holders, 40% had a degree, 25% had a master degree and 2.5% were holding professional certificates. The majority of the respondents (43.9%) indicated that they have used accounting software for 2-5 years and above 5 years (42.7%).
4.2. Descriptive Statistics
4.2.1. Financial Reporting Accuracy
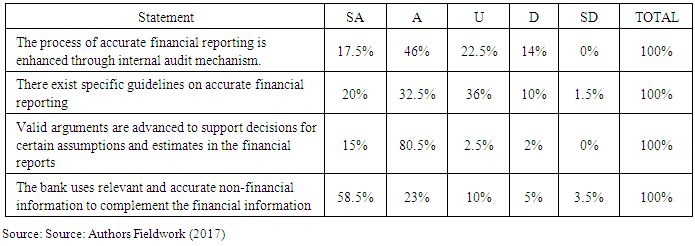
- Respondents were asked whether the process of accurate financial reporting is enhanced through internal audit mechanism, the majority of the respondents (46%) indicated that they agree whiles 17.5% indicated that they strongly agree. This shows that a cumulative percentage of 63.5% of the respondents are in support of the indicator. 22.5% of the respondents were uncertain and 14% of the respondents were not in agreement. With regards to the existence of specific guidelines for accurate financial reporting, 20% strongly agreed, 32.5% agreed, 36% were uncertain if there was, 10% disagreed and 1.5% strongly disagreed. When asked whether the bank valid arguments to support decisions for certain assumptions and estimates financial reports, a cumulative percentage of 95.5% indicated that they strongly agree and agree. This indicates that the metric is a significant indicator of financial reporting accuracy. Finally, in the context of the bank using relevant and accurate non-financial information to complement the financial information, 58.5% of the total respondents strongly agreed, 23% agreed, 10% of the respondents were uncertain and a cumulative percentage of 8.5% of the respondents disagreed and strongly disagreed. Table 4.1 below shows the descriptive statistics on different financial reporting metrics.
|
4.2.2. Influence of Computerized Accounting on Financial Reporting Accuracy
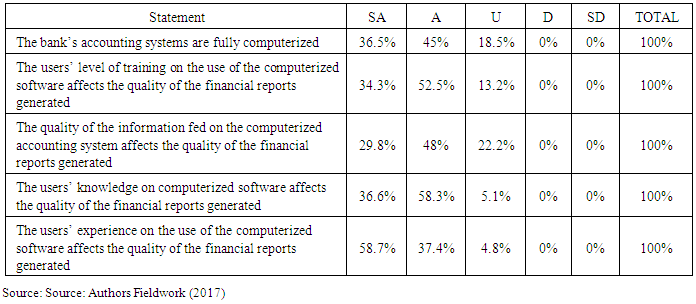
- As indicated by the results in Table 4.2 below, a cumulative percentage of 81.5% of respondents, representing a majority (81.5%) indicated that they agreed or strongly agreed that all the banking systems had been computerized. Only 18.5% of the respondents were uncertain whether the whole banking accounting processes had been computerized. The high number of respondents who were agreeing that all the bank's accounting systems had been computerized can be attributed to the fact that accounting software was easily available. In relations to the users' level of training on the use of computerized software on the impact of the financial reports generated, 34.3% indicated strongly agree, 52.5% indicated agree while 13.2% were uncertain. When asked about the impact of the quality of information fed into computerized accounting system on the financial reports, 29.8% of the respondents' indicated strongly agree, 48% agree, and 22.2% were uncertain. In relation to whether the user's knowledge on computerized software affected the quality of financial statements, 36.6% indicated strongly agree, 58.3% agreed, while 5.1% of the respondents were uncertain. Therefore, a cumulative figure of 94.9% of the respondents was agreeing that the user's knowledge on the accounting software played a critical role in the quality of the financial reports generated. In the context of the users' experience on the use of computerized accounting, only 4.8% of the respondents were uncertain on the metric.
|
4.2.3. Influence of Staff Competence on Financial Statement Accuracy
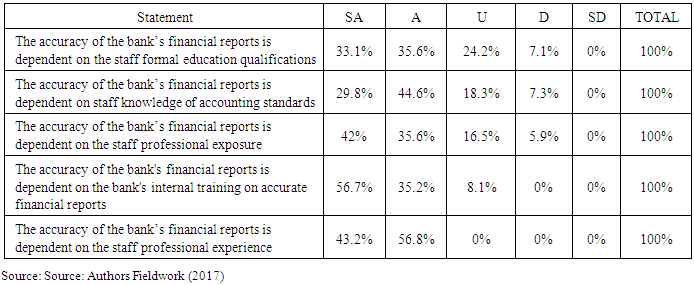
- In the context of the influence of the staff formal education on the financial statement, 33.1% strongly agree, 35.6% indicated agree, 24.2% indicated uncertain and 7.1% disagree. The staff knowledge of accounting standards was cited by 29.8% (strongly agree), 44.6% (agree), 18.3% (uncertain), and 7.3% (disagree). The professional exposure was cited by 42% (strongly agree), 35.6% (agree), 16.5% (uncertain), and disagree (5.9%) as an item that influenced the financial statement accuracy. The internal training on accurate financial reports was cited by 56.7% (strongly agree), 35.2% (agree), and uncertain (8.1%) as an influencing factor on financial statement accuracy. On the other hand, the staff professional experience influence on financial statement accuracy had 43.2% and 56.8% of the respondents indicating strongly agree and agree respectively. This showed that a cumulative percentage of 72.6% of the respondents answered in the affirmative.
|
4.3. Inferential Statistics
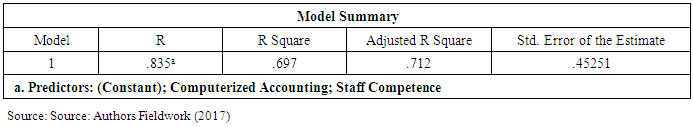
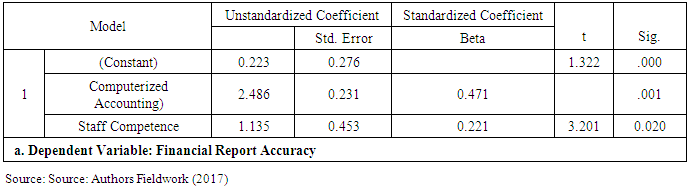
- To establish the effect of computerized accounting and staff competence on financial report accuracy, an ordinary least square analysis was conducted. The model summary (Table 4.4 below) provides the correlation coefficient (R) and the coefficient of determination (R2) values. The R value indicates there exists a very strong positive correlation between the dependent variable (financial report accuracy) and the predictors (computerized accounting and staff competence). The R2 value of 0.697 indicates how much of the variations in the dependent variable, was explained by the independent variables, Staff competence and Computerized Accounting. In this case, 69.7% was explained by staff competence and computerized accounting while the remaining 30.3% was explained by the other variables of the study. The P- Value of (0.003< 0.05) implies that the model of financial report accuracy is significant at 5% significance level.
|
|
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
- The main purpose of this study was to identify the determinants of computerized accounting systems on accurate financial reporting in selected banks listed on the Ghana Stock Exchange. The study also had another objective of finding out the effect of staff competence on accurate financial reporting. Banks are continuously searching for cost-effective, economic and efficient ways of doing business. Hence, there is the necessity for banks to be abreast of the current issues in technology to enhance their business and service delivery. This is to help gain a competitive advantage over their competitors especially in this period where there are more banks springing up in the Ghanaian economy.One of the ways to reduce cost in the Banking process is to ensure that resources allocated are well utilized to obtain maximum benefits at minimum cost. Thus, with the use of (input) like a Computerized Accounting System, it is expected that, the accounting system will be able to generate relevant and meaningful reports (output) for making strategic business decisions by users and managers. Computerized Accounting Systems are therefore used by these financial institutions in order to generate timely and accurate reports through a fast and efficient processing of accounting data. The researchers observed that, there are several benefits both financial and non-financial which are obtained from the use of a Computerised Accounting System. Amongst the non-financial benefits are: time-saving, improved quality of accounting information, minimized clerical error, improved report to stakeholders and provision of a better way of keeping accounting records. The financial benefits include a reduction in tax liability by way of enjoying capital allowance, reduction in labour cost, audit expenses, clerical expenses and stationery expenses.The study revealed that because of the numerous benefits that are associated with computerized accounting system, more importantly, its ability to produce and present relevant and faithful representative of financial reports to end users (Banks), management of the selected banks are trying to migrate all their activities onto the Banking Software System (Computerized Accounting System).Undoubtedly, the accuracy of the bank’s financial reports is dependent on the staff competence. Formal education qualification was the most significant metric in terms of staff competence in the use of the Computerized Accounting Software. The accuracy of the bank’s financial reports is also dependent on users’ knowledge of accounting standards on computerized software which affected the quality of financial reports generated. The study also revealed that the accuracy of the bank’s financial reports is dependent on the staff professional exposure and experience significantly affected the accuracy of financial reporting. Based on the empirical findings of the study, it can be concluded that there is a strong positive correlation (84%) between Computerized Accounting System and accurate financial reporting. Hence, Banks in Ghana need to adopt a Computerized Accounting System and most importantly link all their branches.
5.2. Recommendations
- Based on the findings of the study, it is recommended that the banks should invest in computerized accounting system since it is seen to affect the accuracy of financial reports to a great extent. The study further recommends that the banks should train its staff through seminars and workshops on the usage of the computerized accounting software in order to upgrade the competency level.The study recommends three areas for further research; first, more research should be done on the effect of computerized accounting systems on the Financial Reporting accuracy in Banking Institutions in Ghana so as to allow for generalization. Also, further research should be done on the extent of adaption of computerized accounting systems by Banks in Ghana. Lastly, a comparative study needs to be conducted on computerized accounting system compared to manual accounting systems on the quality and accuracy of financial reports in Banks in Ghana.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML