-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2017; 6(1): 19-36
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20170601.04

Antecedent Factors in the Implementation of Accounting System and Performance of Information System (A Case in Readiness to Success Accrual Base of Financial Reporting in South Kalimantan – Indonesia)
Syaiful Hifni
Lecturer at the Economic and Business Faculty Lambung Mangkurat University, Banjarmasin, South Kalimantan Province, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Syaiful Hifni, Lecturer at the Economic and Business Faculty Lambung Mangkurat University, Banjarmasin, South Kalimantan Province, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article presents how the government's readiness to achieve success of implementation of accounting system and the performance of information system through guidelines Government Accounting Standards (Government Regulation No. 71 year of 2010) which uses acrrual basis for financial reporting, which began since end year 2015. This research is explanatory survey which uses antecedent factors, namely: the role of regulation, management support, communication effectiveness. The role of internal supervision, the implementation of accounting system and performance of information systems. Population in this research are 386 (three hundred eighty six) of the government work units in the Province of South Kalimantan, Indonesia. Sampling method that was used is a multi stages of stratified sampling with proportional samples of government work units. Analysis of data was done using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with AMOS application program version 18. The findings of this study indicates that the role of regulation do not significantly affect the implementation of accounting systems and to the performance of information systems, and the role of internal supervision also do not significantly affect the performance of information system. This findings indicate that, Regional Government in South Kalimantan still not yet fully has readiness for the implementation of accrual based accounting due to weakness the role of regulation, and the role of internal supervision for the implementation of accrual based reporting. Meanwhile, there was a perspective of readiness, which can be accepted, because of management support, communication effectiveness, the role of internal supervision towards success in implementation of accounting system, and influence from this implementation towards performance of information systems.
Keywords: Implementation, Accounting Systems, Performance of Information Systems, The Role of Regulation, Management Support, Communication Effectiveness, and The Role of Internal Supervision, Accrual Based Accounting
Cite this paper: Syaiful Hifni, Antecedent Factors in the Implementation of Accounting System and Performance of Information System (A Case in Readiness to Success Accrual Base of Financial Reporting in South Kalimantan – Indonesia), International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 6 No. 1, 2017, pp. 19-36. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20170601.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Efforts to achieve good government governance in Indonesia has been done through the role of public sector accounting which is characterized by the establishment of a package of laws on finance State (Law No. 17 year of 2003, Law No. 1 year of 2004; and Law No. 15 year of 2004). This perspective is carried out through efforts implement the accounting system with the aim achieving to performance of information system of governmental organizations in Indonesia (governmental regulation No. 8 Year of 2006). In Following the development of public sector accounting's role for government organizations in Indonesia, showed that practices of accounting system and reporting or information system in Indonesia has began with apply the government accounting standards (government regulation No. 24 Year of 2005), which initially uses the cash basis toward accrual. This standard has been stated in line with the International Public Sector Accounting Standard (IPSAS) as guidelines in financial reporting with cash basis (IPSAS, 2014). This standard as reference has been applied to guide the implementation of accounting system and financial reporting in Indonesia until the year of 2014. Where, for each regional government as reporting entity should makes 4 (four) element of financial statement, namely: balance sheet with accrual basis, budget realization report-cash basis, statement of cash flows, and notes to financial statements. Financial reporting for government be described through the concept of accountability in fulfillment the responsibility by providing information that enables users (users) to make judgments about the performance, financial position, finance and investment, and compliance of reporting entity (Carnegie and West, 2005). Due to environment development, has gave influences to the establishment of a new accounting standard in Indonesia. This thing can not be separated with the development of the national accounting system in Indonesia, with a need for developing of accounting systems for performance of information systems. This phenomena referring to “financial accounting environment", where in forming an accounting policy is based on imposed accounting standard. Process to determine an accounting policy for organization are determined by the accounting theory, political factors, and economic conditions (Tearney, et al, 1997, Page 7). Implication of the effect of intended factors, such as, accounting theory, and political factor is the intervention of the government to develops guidelines for organization accounting policy which be codified from government accounting standard. Based on “omnibus regulation”, application of the Government Accounting Standard with accrual basis provides the basis for each regional government entities (also includes for each from central Government in Indonesia) to develop and arrange accounting policies (as one of regulation in accounting), and others rules for finance management for financial reporting of organization. Over the past two decades, a growing number of governments began moving away from pure cash accounting toward accrual accounting (IMF, 2016). Based on research with data collected from November 2015 to June 2016, show that: “Around three-quarters of OECD countries have adopted accrual based accounting for their year end financial reports as key priority. This means that governments’ financial reporting is more comprehensive, with not only cash movements in and out of the government treasury reported to the public, but a range of other financial operations, as well as inventories of government, assets and liabilities” (OECD, IFAC, 2017, P:4). Then, there was discussed the challenges and benefits from accruals basis, reforms, and considers that for steps ahead, countries which will taking an accounting system and financial reporting can be made better with use of accrual information for the future (Handbook of IPSAS, 2016). For reason of good governance in Indonesia, since year 2003-2004, from this time, Indonesia has been moving to implement reform in financial management country/regions. Aspects of financial management reforms (FMR) as a perspective be stated by Andrew Lawson, namely: first, FMR deliver results when 3 (three) conditions coincide, namely, when there is a strong political commitment to their implementation, when reform designs and implementation models are well tailored to the institutional and capacity context; and when strong coordination arrangements led by government officials are in place to monitor and guide reforms. Secondly, strong leadership and commitment to reform are also needed at the technical level. In the case of study countries, this emerged naturally where there was political commitment and leadership. By contrast, commitment at the technical level was not sufficient to generate political commitment” (Andrew, 2012; p.12-13). Consequences of the application of accounting standards for governmental sector in Indonesia is one that related to the work function of accounting in facilitating the implementation of accounting work, and review the accounting performance. Relate to structural of accounting, management of government requires an effort to implement the function of the accounting system for the performance of information systems that meet the qualitative characteristics of information (see, Bastian, 2006; 2009). An implementation of accounting systems gives achievements quality of information in the performance of financial reporting. Fulfillment of implementation of financial accounting system is the information perspective for decision usefulness. The information's perspective on decision usefulness is an approach to financial reporting by the fulfillment of a characteristic of information that can fulfill the usefulness of information in decision-making (Kam, 1986). In many cases, information systems is more about how they are used and in what ways they can contribute to a competitive advantage (Rackoff, Wiseman, Ullrich, 1985 in Krister, et al, 2014). Performance of information systems provides the benefits of information which is reached through financial reporting with accrual basis. Performance of information systems is measured by indicators of the benefits of information for: accountability, stewardship, managerial and external supervision (See Halim, 2004; Government Accounting Standard, Government Regulation No 71, 2010). The implementation process requires the participation of all levels and units of government organizations, as well as the involvement of other parties, which is influenced by forces outside their control (Ripley and Franklin, 1986, in Subarsono 2006; Hogwood and Gunn, 1984). An approach to research carried out in the implementation of the system, put related aspects situational as antecedents which put forth as a determinant in the implementation of the organizational system. Masri and Sofian (1995) suggested for aspects or antecedent variables was stated precede the variable's influences. Kren (1997) suggests a model of research in accounting control system as a model of control system research in accounting. The model proposed is the antecedents and consequences of using accounting information to evaluate subordinate performance. Their determining factors to the design of control systems in the form of an accounting system with antecedent variables (e.g. individual and organizational attributes and the environment). This model lays back in the theory of contingency with the variables of internal and external as antecedent variables that affect the organization's accounting system. In the explanation of the relationship between the needs of the key aspects of research in theoretical models, empirical facts noted from previous studies, so underlie the formation of a theoretical model that deserves to be tested with empirical data (Sugiyanto, 2002).Government Accounting Standards as guidelines for government of Indonesia are accounting principles applied in preparing and presenting the financial statements of the government. Government accounting standards (SAP) has been established by Government Regulation No. 24 of 2005 dated June 13. Application of government accounting standards for accounting systems and information systems has become new experience and be a challenge for the Government of Indonesia. Moreover, with the implementation of accrual based accounting standards (Government regulation No. 71 Year 2010), has becoming a new phenomenon in Indonesia and of course, provides a level of difficulty in its application. That is why, even though the year 2010 government accounting standards with accrual basis have been set, but 5 (five) years later the newly entered can into force. This study was conducted to assess the success of the implementation of accrual based government accounting standards on government entities in Indonesia as representation level of readiness of government to fulfill obligation of new system. Questions of the Study Based on the description in introduction, and also based on various studies as the empirical studies previously which put forward as the basis for an explanation of the relationship between variables of research, and presented in association with this research, as base to state research problem. Research problems be formulated and expressed as follows: (i) Does role of regulation, management support, communication effectiveness, the role of internal supervision influence towards Implementation of accounting system ?, (ii) Does role of regulation, the role of internal supervision influence towards the performance of information system ? (iii) Does implementation of system influence towards performance of information system ?.Objectives of the Study The aim of this research is to analyze and to prove the antecedent variables which not only relate with technical aspects but also relate with organizational behaviour, aspects from individual, group, and organizational attribute. This study was conducted: (1) to examine the antecedent factors, consists of: the role of regulation, management support, communication effectiveness, and the role of internal supervision, in determining implementation of regional financial accounting system, towards performance of information system with accrual basis in financial reporting; (2) to provide a justification of how the readiness of the Local Government in South Kalimantan, Indonesia, to achieve the success in implementation of accounting system and performance of information system for financial reporting system with accrual basis.
2. Literature Review
- Based on perspective for agency theory, the implementation of accounting must be based with a regulation (Bastian, 2009). The Regulation as a rule of practice be stated in the standard, and be adopted in the form of accounting policies of the organization. Accounting regulations limit the emergence of agency conflict in the form of moral hazard and adverse selection (Scott, 2006). Appropriate agency theory, Jensen and Meckling (1976) puts in perspective, the role of regulation with the concept and proposition, delegation of decision rights, and the issue of control over decision rights are delegated. Regulations goal is to achieve the degree of usefulness of information for users which is useful for decision support, and reducing the imbalance of information or information assymmetry (Eisenhartd, 1989; Smith and Bushman, 2001). Meanwhile, based on institutional theory, describes the accounting practices were selected for viewpoint that the organization operates within a social framework. Social framework includes norms, values, and a taken for granted of assumptions about what the formations of conformity and acceptance of economic behavior (Oliver, 1997, in Feroz and Carpenter, 2001). The application of the suitability of institutional theory is a theory to explain the phenomenon of accountability in the public sector. Success of the system accounting in implementation of accounting systems and performance of information system with government accounting standard as guidelines in Indonesia will depend on contingency aspects. Many aspects surround and correspond with the real situation in system implementation for government organization. Contingency theories dominant in accounting research through behavioral aspects, in explaining the success of the implementation of the accounting in organization. Contingency Theory, describe no information system that is universally applicable to all circumstances and at all locations of its application. This theory is concerned with styles of management and situations of environment (Otley, 1980; Brownell, 1982; Govindarajan 1986; Hazem, 2010). Brownell (1982) describes factors contingency in classification, such as: (1) culture, legal, (2) organizational include the stability, the environment, technology, uncertainty of tasks, organizational structure, (3) interpersonal include styles of leadership, task characteristics, group characteristics, and (4) personal for locus of control, authoritarian. Meanwhile, Govindarajan (1986) argued contingency factor into the perspective of the individual and contextual factors of the organization. Also, management factors, human factors, organizational factors such as support supervisor can determine the successful implementation for information technology systems (Bodnar and Hopwood, 1995; Latifah and Sabeni, 2007). This theory is concerned with styles and situations. The most favorable situations are defined by having a good leader-follower relation, defined tasks, and strong leader position power (Hazem, 2010).Performance of Information Systems In the context of the role, Wilkinson (1989) suggests the usefulness or purposes and benefits from the accounting information system to provide information, which used: (1) to support the operational and legal requirement, and (2) to support decision making. An accounting information system of fully achieving these two objectives of a value judgment usability and usefulness of information. For the uses and benefits of the first, is the results of the activity generated through transaction processing (transaction processing) as a function of the accounting system, and for the uses and benefits of the latter generated through the activity of processing information (information processing) as a function of information systems.Perfomance of information systems be achieved with referring to GASB (1999) which this guidelines has introduced a financial reporting model (in Statement no. 34). The model integrates the traditional focus of governmental fund financial statements relating to fiscal accountability (and the modified accrual basis of accounting) with new forms of reporting. Two levels of financial reporting are intended to: (i) provide more relevant information that will result in greater accountability, (ii) usefulness of the annual financial reports to users, to make more informed economic, social, and political decisions. (IES, NCES, Ch. 4, Governmental Accounting, 2003). Basically, government financial reporting requires of financial information, compliance with rules, performance, planning and budgeting, as well as narrative information (Martiningsih, 2009). There was the relationship between the formal authority to use of information systems of regional financial for management decision making and control (Syafrudin 2006). Scott (2006) points out the elements that make up the performance of information systems presented in accordance viewpoint of provider information, and with the concept of decision usefulness. Accrual accounting, therefore offers a number of benefits over traditional cash accounting (IMF, 2016), from the point of view of government transparency, accountability, and financial management. Halim (2004) presents performance of information system to the fulfillment in communicating financial information for purposes of accountability, stewardship, managerial and supervisory externally.Performance of information system can be fulfilled through: (i) benefit of information for accountability, (ii) benefit of information for stewardship, (iii) benefit of information for management, and (iv) benefit of information for external supervision, which all of this dimensions are considered determine and shape the performance of information system (see Halim, 2004). Substance of Performance of information system is available with quality of information is to support decision making process which be justified as reasoning for measuring performance of information system (Mahsun (2009, p. 25 and p. 93); performance of accounting information has been fulfilled with apply accrual basis, Governmental Accounting Standard (2010); Performance in line with the information perspective for decision usefulness (see, Scott, 2006, p. 123); Basuki (2007, p. 184-189). To be able taking the right decisions be needed quality information, quality information is influenced by the quality of accounting information systems (Meiryani, 2014). Implementation of Accounting System Accounting system as organized set of manual and computerized accounting methods, procedures, and control which established to gather, record, classify, analyze, summarize, interpret, and where present accurate and timely financial data for management decision. Referring to Russell and Joselito (1999: p. 66): “proposes a new classificatory framework to improve current understanding with the similarities and differences in national financial accounting systems. Meanwhile, "when we think about accounting functions, we are mainly thinking about a systematic and comprehensive recording of financial transactions which are important to the business. They also refer to the process of summarizing, analysing and reporting these transactions" (Antonio, et al, 2014: p.119). The successful of practice of public sector accounting is normatively can be expressed require the implementation of policies. Policy is part of the public policy process items, namely as the process for the implementation of management to achieve results. The implementation is influenced by 2 (two) variables, namely policy contents, and environment of implementation (context of implementation). Policy is decision which relates 'with' many parties. By definition, the policy: "is as decision which be characterized by behavioral consistency as the part for those who make "it" and those who abide by it”. Each determination of policy will relate “who” acquire “what” and “how” to find. (Subarsono, 2006, pp. 12-13; Jones, 1984, p.26; see, Hogwood and Gunn, 1984). Policy as implementation in the accounting process is a fulfillment of accounting cycle or accounting core activities (Siegel and Marconi, 1989). The entire process of the accounting cycle, according to Hackman and Oldham (1975) in the Quick and Nelson (2006), became the core activities (core job) accounting to meet the financial reporting output. The concept of core accounting job have characteristics, diversity of expertise, the identity of the task, meaning of the task, autonomy, feedback (job based feedback). The function of the accounting system from the standpoint of goal expressed by Wilson and Kattelus (2002) as a function of government accounting system with the function of the accounting system, namely: to present the fairness of financial statements and full disclosure of funding and activities of the government unit in conformity with accounting principles generally acceptable, and to establish and demonstrate compliance with the legal aspects related to financial reporting in financial management, and financial terms of the contract (Governmental Accounting Standards Boards, GASBs No. 34). The implementation of accounting system as policy which relate with how decision making for fulfillment, namely: (i) accounting process as core job, (ii) compliance to apply regulation, and (iii) completeness of financial reporting output (Wilkinson, 1989; Siegel and Marconi, 1989; GASBs, 1994; Wilson and Kattelus, 2004; Quick and Nelson, 2006; Kieso et al, 2011). Antecedent variables that influences performance of information system through the implementation of accounting system. These variables such as: Role of RegulationRegulation refers to legislative, administration and professional control over various aspects of accounting activities performed in the private and public sectors (Roberts and Kurtenback, 1998, in Hassan, 2008: 290). Scott (2006) points out the background of two (2) theory for the regulation, namely the public interest theory and the interest group theory. Fulfillment needs a regulatory framework, be stated based on guidelines of level legal on it. This is as the phenomenon of organization (Hassan, 2008). Meanwhile, in concept, the obstacles of role of regulatory be able to shape behavior in the irregularities, or in the form of illegal act (Kam, 1986). Perspective for formation of regulations is a requirement that the organization requires clarity in the formation process of regulation, the determination of the regulatory framework, and the attainment of the objectives of regulation in the implementation stage (Subarsono, 2006; Craig and Diga, 2007). To achieve a goal for regulation, we first need to ensure that we have complete clarity. Goal clarity be simply described as ability to set a clear and specific objectives that all affected parties can understand and work towards in achieving (Jon, 2012). A discretion in stages of formation of regulation for Local Government is the use of the concept of "self modifying power", as the ability to make adjustments of the normative legal that applies nationally, accordance with local conditions. Form of the regulatory framework is a dynamic document (live documents), in which case for this regulatory documents will be constantly updated (up date) following the regulatory changes on it, and in which Local Governments can adjust it according to the conditions of each area. Regulatory role requires dimensional requirements. The first indication is a form of reference of regulations which requires a compliance regulations, clarity of purpose, and the need for completeness form of regulation. In accordance Saudagaran and Diga (2000), Subarsono (2006), Parera and Baydoun (2007), this indication is described in its formative stage, and the application of regulations. This stage is put forward as a policy determination in answering how a regulation is set, how the process of adopting for regulation, and what the regulations and forms of its regulation. The second indication, from the situation which needs the application towards regulatory barriers, and obstacles in the regulatory acceptance in the ease of understanding the regulation content. For the second condition, is as explained in the proposed Habermas model (Hassan, 2008), as well as aspects of regulatory compliance (see, Craig and Diga, 2007). At its most basic level, regulation is designed to work according to three main steps: i) regulation is implemented, which leads to changes in; (ii). the behaviour of individuals or entities targeted or affected by regulation, which ultimately leads to changes in; (iii) outcomes, such as amelioration in an underlying problem or other (Cary, 2012).Indications implementation of regulations in accordance Craig and Diga (2007) is the regulatory acceptance process and ease regulation in its application. In context, regulatory acceptance is as an administrative feasibility (administrative operability) which are indicated with the support of the recipient of organization policies toward regulation that has been set. Implementation of regulations regarding the behavior in the form of knowledge, attitudes, and forms of action in response to regulations. The role of regulation be stated with dimension, namely: (i) goal clarity, (ii) completeness of regulation forms, (iii) acceptance of regulation, and (iv) easiness to apply. (see, Saudagaran and Diga, 2000; Scott, 2006; Parera and Baydoun, 2007; Craig and Diga, 2007; Hassan, 2008; and Cary, 2012).Management SupportThe importance of the support of the management in the implementation of accounting systems can be explained with the coherence of the concepts of behavioral organization, such as leadership (leadership), job involvement (job involvement), functions, managerial activities and decisions, and disposition thematic conception. Keban (2008), suggests a management approach that studied from normative management. The first approach, describe the nature of managerial work in the category of the contents to show the role, function, as well as managerial responsibilities (content catagories). Management support in regional government be needed to support organization in achievement a goal. There is arguement that the governments play an important role in building effective and inclusive financial systems and discusses policies with finance for development (Asli, 2008). Darise (2007) states the contexts of the management support in line with financial management. This description is in accordance with the formal principle (Government Regulation No. 100 of 2000), which mentions the structural position is a position that indicates the duties, responsibilities, powers, and privileges of a civil servant in order to lead an organizational unit of country. According the main tasks of the organization, the support of the manager as the holders of power of regional financial management is the header of the area, which has authority to establish policies in the area of financial management. Regional Head gives delegates part or all of the powers of planning, implementation, administration, reporting and accountability and financial oversight of regions to (1) the secretary of the region as the coordinator of financial management area, (2) head of regional finance management with task as officer of regional financial management, and (3) the head of work units as users of funds and assets referring to budget of work units. For every functions of regional government organization, there were corresponding structure of the levels of organization, such as: top level, middle level, lower level. Every level expressed the need for their expertise in management tasks, ie for strategic aspects, decision unstructure- non recurring, towards structured decisions are repetitive. (see, Saunders and Pearlson, 2004).Based on the description of theoretical and normative, can be stated indications which presented in the form of a manager support at the level of top management (top management), the coordination function, the function of the middle management and lower management functions in operational level. Management support be stated with dimensions, namely: (i) support for empowerment strategic, (ii) support for coordination, (iii) Support for management control, and (iv) Support for operational control (Darise, 2007; see management dimension, Keban (2008, pp. 91-123), and characteristic of public administrator (pp. 21-22); see, Basuki, organization of regional financial management (2007, pp.26-33); Saunders and Pearlson (2004). Communication EffectivenessCommunication stated as: "the abilitiy to share thoughts through text, images, and speech (Saunders and Pearlson, 2004: 7). Communication meaningful as the ability of members of the organization in the process of giving, sharing data and information in various forms to produce a common understanding. Robbins and Judges (2008) states communication as the transfer process (transfer) the meaning and understanding of the meaning. In the context of managerial activities, communication activities related to exchanging routine information and processing paperwork. The communication stated in the explanation of the basic concept of partnerships. Substantively, the behavioral aspects of communication can be stated with the proposition that explains the concept of willingness to cooperate (Barnard, 1973, in Wren, 1994). Effectiveness of communication according to Robbins and Judge (2008) includes the fulfillment of the criteria, the communication that meets the speed, accuracy, the emergence of a leader, and member satisfaction. It is associated with their advantages and disadvantages of each form of communication to meet the speed and accuracy, and performance feedback in communication. Written communication provides benefits with ease and can be verified, documented, accuracy in writing, and clear. Oral communication provides the benefits of speed and fulfillment of feedback. Horizontal communication provides effectiveness of time and establish a coordination process.Azwar (2009) state the behavioral perspective in communication which have relationship with the effectiveness of communication. Be stated, the effectiveness of communication and its impact on changes in attitude can be seen at least from of two (2) aspects, namely the organization of communication, and the communication contents. Messages communicated on formal channels are viewed as official and are transmitted via one or more of three different routes: (vertical-either upward or downward, (2) horizontal, and (3) external (Robert and Angelo, 2010, p. 416-417). Referring to Barnard (1973, in Wren, 1994), there were three (3) elements, which be needed to establish communication channel, formalized and defined as short as possible. According to these principles, meaningful communication need be established with channels to meet the clarity of the goals and objectives of an organization ideas. Effectiveness of communication expressed as communication between organizations or between people in translating policy content, distribute information and exchanging information in order to get the same perception about the contents of the policy. Communication is an important aspect that determines the success of the implementation of a policy (Edwards III, 1980; Subarsono, 2006), and the contents of the policy as one of the factors that affect the successful implementation.Characteristics of the communication effectiveness be formed as an indication of compliance with the principles, functions, and contents of the communications. Characteristics of the fulfillment of the principles of communication be stated, such as: horizontal communication for data communications, channel vertical communication, the process of channeling information, communication established with a discussion, forum as internal communication and external communication (Wren, 1994; Robbins and Judge, 2008). Champoux (2003) states function of communication, namely: information sharing, performance feedback, integration, persuasion, emotion, and inovation. Characteristics of the functioning of the communication can be described with details indication, such as: the activities for the needs of data consolidation / financial information, the expected benefits to meet the accounting system and financial reporting organization, the activities coordinated through the planning functions of local Government, the existence of a communication link connecting the policy makers with function for implementing accounting, and communication activities with information (see, Champoux, 2003; Darise, 2007; Robbins and Judge, 2008). Characteristics with contents of communication be stated, such as: information for the benefit of the integration of accounting functions of work units and for financial reporting of regional government, trending data / financial information and assets, activity data communications / financial information and assets for feedback achievement of performance accounting, fulfill informations to achieve of the degree accountability that is expected of the auditor's opinion with the performance of the accounting and financial reporting, information of performance (see, Champoux, 2003, Darise, 2007; Grindle, 1980; Subarsono, 2006). Effectiveness of communication is described with the fulfillment of the principles, functions and rules of communication in accordance with the contents of the policy implementation that is communicated (Champoux, 2003; Robbins and Judge, 2008, Azwar, 2009). Communication effectiveness be stated and are measured by (i) fulfillment for communication principles, (ii) fulfillment for communication functions, and (iii) fulfillment for communication contents (Champoux, aspect of Communication, 2003; see also Grindle, 1980, Subarsono, 2006; Azwar, 2009; Robert and Angelo, 2010).The role of Internal Supervision The concept of supervision can not be separated from the concept of control function. Where controls or controlling presented as an attempt to convince the organization is moving toward the achieve the goal. If parts of the organization are in the wrong direction, then the managers try to find the cause, and then arrange things properly (Saunders and Pearlson, 2004). The linkage of concept internal supervision with the concept of internal control are, internal supervision is a function for testing the implementation of the activities of the management control function or internal control of the organization. Internal supervision has grown as an organization's needs. Both of these concepts be managed with the same focus, which is assured under management aspects of the organization in achieving its objectives, the two concepts only differ in implementation time and those who carry out the activity. Supervision through internal audit activity be expressed Mardiasmo (2001) serves to provide a guarantee or assurance and consultancy, internal control, the process of governance, risk management (see, also, The Institute of Internal Auditors, 1999, Yudiono, 2006).In governmental organizations, internal oversight functions carried out by the Apparatus of Government Internal Supervisory (AGIS) with the principal task and function is to strengthen and support the effectiveness of the internal control system of Local Government. Internal supervision as the activities which performed by the AGIS is to ensure that the system of management control or internal control system has been able to be implemented properly. Fulfillment for supervision relate to the internal oversight activities with the evaluation function (STAN, 2007), Apparatus of Government Internal Supervisory (AGIS) has assignment perform supervision internal's functions through the internal audit activity, the review, monitoring, and evaluation (Minister Regulation No. 28/2007). The role of internal supervision to assess internal control proposed include 2 (two) indication, namely, clarity of purpose and clarity of process of supervision activities, and the quality of apparatus as requirements for implementing safeguards in supervisory activity (see, Sawyer, 1992; Fayol in Wren, 1994; STAN, 2007). There were authorities responsible with prudential supervision through supervisory boards as internal supervisor which has duty for supervising of management. Supervisory be acted based on the roles, objectives, methods and positions are different with management. The argument is made, that prudential supervision may be take on too big a role, as they are essentially disadvantaged relative as internal supervisors in terms of information and expertise (Kess and Jaap, 2013). AIGS is as independent party of management which should be involved in such supervision regularly. Referring to the role of internal supervision, can be stated and are measured by: (i) the role of internal audit, (ii) The role of review of financial statement (iii) the role of evaluation, (iv) the role of monitoring, and (iv) the role of internal supervisor quality (Basuki. 2007, pp. 178-183); Sawyer, 1992; Pickett, 2003; Saunders and Pearlson, 2004; also, Kess and Jaap, 2013).
3. Methods
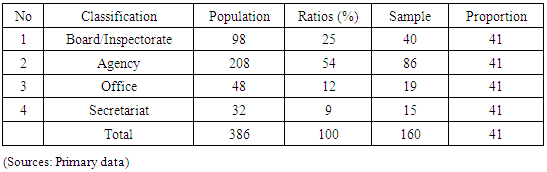
- Subject SelectionThe population of this research is all of Local Government work units of regional government in South Kalimantan- Indonesia. Respondents of research are Financial administrative officer of Government work units. These officer be considered has knowledge and practices in accounting of organization and as respondent with their perception which relate with the aspects of the research. Sampling technique using multi stages sampling with 2 (two) stages to determine: (1) taking sample for Local Government from 14 (fourteen) entities Regional Government, and (2) taking sample of Local Government work units of selected regional government in line with the forms of work unit as: Board, Agency, Office, and Secretariat. The amount of population target of research are 386 (three hundred eighty six) of work units. The amount of selected sample are 160 (one hundred sixty), which for each Government work unit is represented with 1 (one) respondent. List amount of work unit as population and as sample be stated in table 1 below:
|
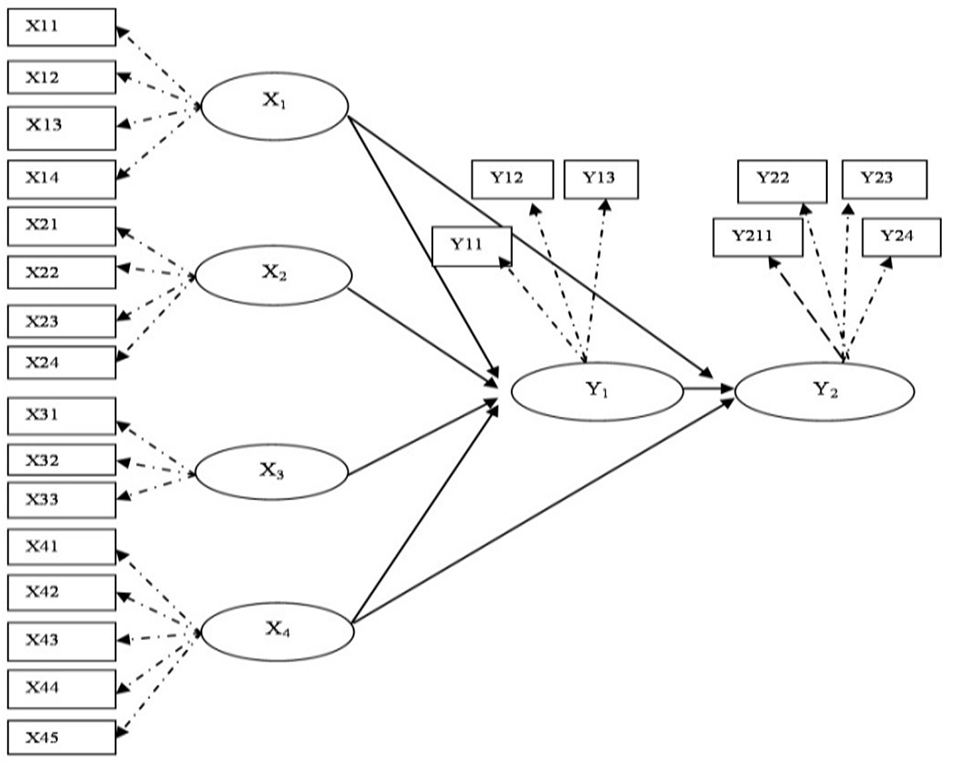 | Figure 1. Research Model |
4. Results
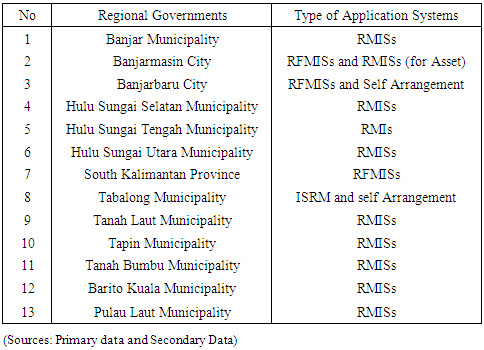
- Descriptive analysis Based on observation and documentation to collect information, showed type of application of information technology that was used regional government in South Kalimantan. Usage of data processing system as programme application to implement accounting system and financial reporting system uses 2 (two) types of programme application, namely: (i) The Regional Management Information Systems (RMISs), and (ii) The Regional Finance Management Information Systems ( RFMISs) of the entity of the Provincial / District / City in South Kalimantan. These models are used for regional government nationally. Description for usage of programme application for each regional government in South Kalimantan be stated through table 2 below:
|
|
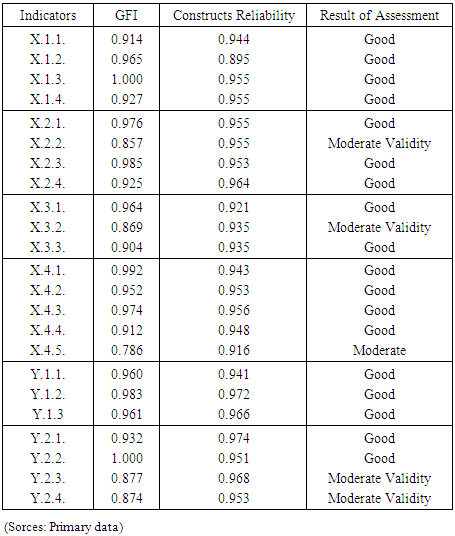
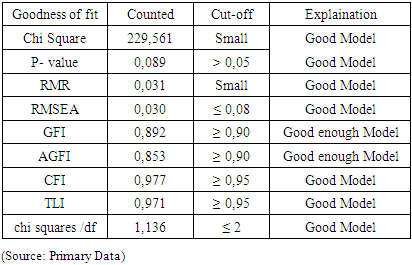
 | Figure 2. Result of Sem Analysis with Goodness of Fit Model |
|
|
|
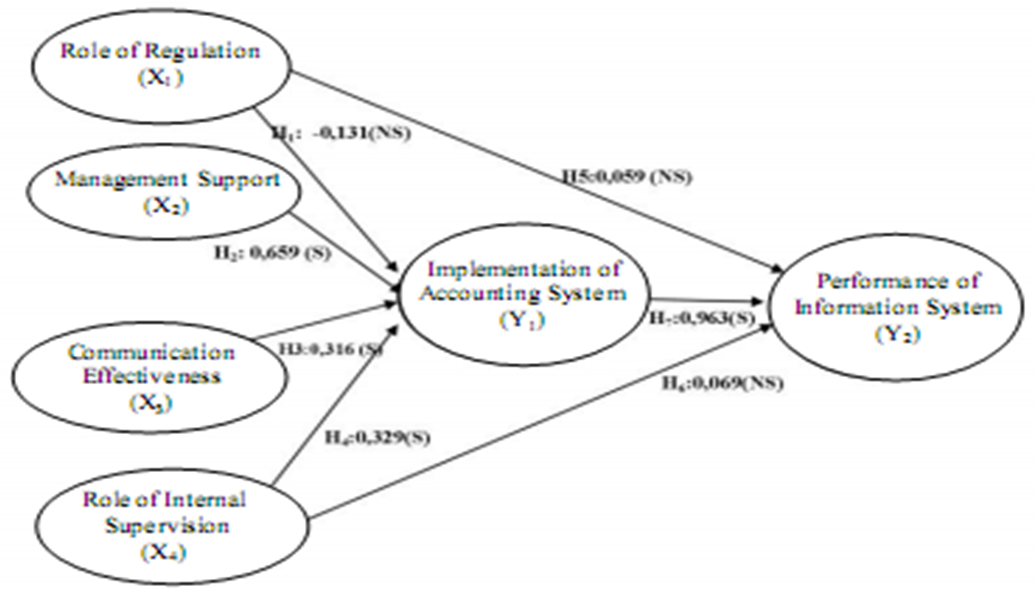 | Figure 3. Result of Hypotheses Testing |
5. Discussion and Conclusions
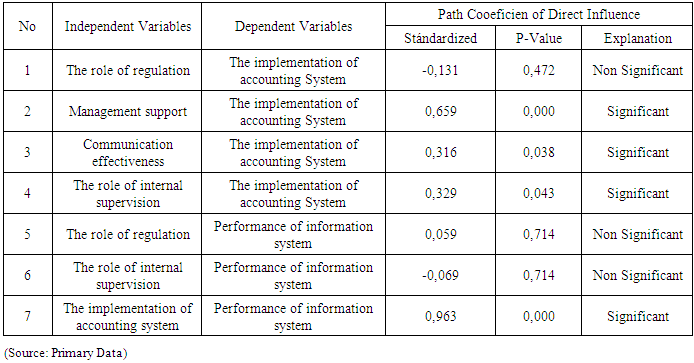
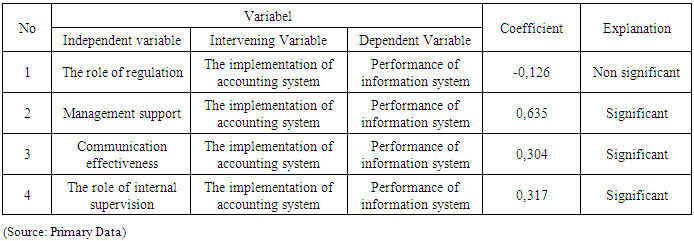
- DiscussionResult of study shows that 3 (three) hypotheses testing from 7 (seven) hypotheses can not reject Ho. It mean, that level of implementation of accounting system and performance of information system of local governments in South Kalimantan for accrual accounting system, showing still not yet fully has readiness. Implementation in accounting system has not been be supported through: non significant relationship from role of regulation toward accounting information system, non significant relationship from role of regulation toward performance of information system, and non significant relationship from role of regulation toward accounting information system. - This empirical facts show the existence of barriers of effectiveness to implement accrual base financial reporting in Local Government. This study provides evidence of the weakness role of regulation. This means that the reference which includes accounting standards, and accounting policy, regulation of financial management in financial management cycle, and the regulation of the internal control system still requires strengthening forward to the implementation of the accounting system and and performance of information system. See, (Kam, 1986) about obstacles of the role of regulatory. Constraint which appears of role of regulation is as failure to follow form and content of regulation that in line with preventive method "ex ante" that causes ineffectiveness of accounting system, and also towards performance of information system. Barriers for role of regulation also as failure to avoid punitive "ex post" in administrative punishment case from supervisory externally. Accounting Standards is a representation of preventive methods in keeping good accounting practices. Enforcement methods in accounting regulation and financial reporting with accrual basis was needed organization in relation with fulfillment of the principles of financial management for unity of organization, methods, responsibilities, and even for need integration with central government in integrated reporting. - Due to weakness in the role of internal supervision can influence ineffectiveness of accouting systems in achieving performance of information system with accrual based reporting. The study results showed that there were obstacles to the fulfillment of the purposes of supervision which was conducted by internal supervisor to the purposes and objects of supervision in order to realize the achievement of accountability. This situation in line with the analysis and interpretation (see, Mu’azu, 2012) for his major findings, such as: Local governments’ internal auditors lack of proper independence for their duties, fact that the independent as to verify various records of the various departments and to ensure control is still very weak, internal auditors do not evaluate the internal control system of the local government to the extent that it can prevent irregularities and fraud, iii. the internal audit unit of local governments are understaffed and they experience excessive work load, they have lack the compliance with general standard (professional proficiency), and also, with problem of organisational structure (clear line of reporting and responsibility). - Additionally, for empirical facts of the results of study also indicated an indirect effect on the performance of information systems through the implementation of the accounting system. This fact shows that there is the role of internal supervisor through the role of review of financial statement. The implications of an internal oversight role of government in the achievement of financial performance information system requires successful implementation of accounting system as administrative function of financial management of regional government. Mean while, we can take justification in line with the performance of information systems whch can be met through accounting system implementation, because of 4 (four) of 7 (seven) of hypotheses testing can reject Ho. It mean, that implementation in accounting system has been be supported through: significant relationship from management support toward implementation of accounting system, significant relationship from communication effectiveness toward implementation of accounting system, significant relationship from role of internal supervisión toward implementation of accounting system, and significant relationship from implementation of accounting system toward performance of information system. - There were arguments of antecedents factors which influence towards implementation of accounting systems, and this implementation gives influence towards the performance of information system. In implementation of accounting system, this thing referring to Government Accounting Standard (accrual base) in presenting and communicating financial reporting elements which gives benefit for the users in assessing accountability and decision making in economic, social, and political perspective. - Due to theoretical persepective, we can receive for understanding that an implementation of accounting system in South Kalimantan Province has suitable and relevant situation with the model, concepts, and propositions of Otley, 1980; DeLone and McLean (2003), (iii) Tearney et al, 1997; Kren, 1997; Soegiharto (2001). Also, in line with Jesse, et al, (2016). The results of this study gives evidence that using guidelines for government accounting standards (accrual base accounting) which has began in year of 2015 in Indonesia, as role evidence of agency theory which be applied. (see, (Jensen and Meckling, 1976; Eisenhartd, 1989). Also with the institutional theory (Feroz and Carpenter, 2001, Hassan, 2008).Implementation RMISs and RFMISs as implementation programme application for accounting system and to regional financial management information systems requires support from the organization management. Strategic Support to integrate RMISs and /or RMISs with technical operations, and administration, ideally should be done into the government resource management information system (GRMISs). Design of GRMISs contain of menu, such as: revenue, e-assets, human resources, minutes of payments, minutes of the project handover, e-procurement (through electronic procurement unit), deliberation of development planning, proposal list (e- plan), work plan of regional government, work plan for budgeting of regional government work units, determining budget list, contracts and standard, progress procurement directly for assets and services. Due to benefit of goal of GRMISs for e-government (President Instruction No 3 Year of 2003) is to increase the efficiency, monitoring, control and services of government towards good governance. So that, for the public administration service through RMISs/RFMISs with integration into e-government, also provides easiness of accessibility role better so will support good governance in public service with transparency. GRMISs with e-government can support Local Government to provide role model in communication more broad, namely: (i) government-to-citizen or government - to - customer (G2C), (ii) government-to-business (G2B), as well as (iii) government-to-government (G2G). Integration of 2 (two) types of systems into government resource management information system (GRMISs) need regulation that support. This systems will give advantage with an increase in efficiency, convenience, accessibility, and better for process and result of public service. ConclusionsDue to fulfill a good policy of government, be needed some efforts to meet the implementation of accounting system and performance of information system with accrual base financial reporting. The government has goal clarity with good practices of accounting, to support and achieve: (i) the effectiveness of regional government in financial planning and control; (ii) the effectiveness of regional government for financial administrative control; (iii) fulfillment for external supervision by the Supreme Audit Agency) and supervision activity through the Regional Representatives Council; (iv) Due to the meaning of accountability with fulfillment a qualifying criteria of quality information that meets the qualitative characteristics of information, compliance to apply the accounting standard or accounting policy for organizational referrence, has compliance with financial regulations, compliance with aspects of internal controls, and for the adequacy of the disclosure of information in financial reporting.Readiness for financial reporting with accrual based accounting is a national need, in line with goal the national system for development in accounting systems of the public sector in Indonesia. This need due to goal of good governance of public sector for meet the fiscal information by the integration of national fiscal position, to fulfill consolidated financial reporting between all entities of the Local Government and central government in Indonesia. The accounting system was developed towards the System National of Accounts (SNA), as well as in the fulfillment of Government Financial Statistics (GFS). This GFS system puts the conception for the integration of the Accounting System of Central Government (ASCG), the Accounting System of Regional Government (ASRG), Budgeting system, and accrual basis reporting system based on reference Government Accounting Standard (Government Regulation No. 71 Year of 2010). There is a need for Local Government organizations as part of the Unitary Republic of Indonesia in implementation and enforcement to implement Government Accounting Standards (Government Regulation No. 71 Year of 2010) started of end of year 2015.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I do appreciate Scientific & Academic Publishing (SA & P), which has supported through review, comments and suggestion to revise this writing. Also, many thanks to my Promotor, Prof Dr. H. Soegeng Soetedjo, SE, Ak, and mysecond promotor Drs. H. Basuki, M. Com (Hons), Ph.D, AK, CMA, from Airlangga University, Surabaya Indonesia, for all guidance in writing for dissertation.
Regulations
- RI Law Number 17 Year of 2003 About State Finance RI Law Number 1 Year of 2004 About State Treasury RI Law Number 15 Year of 2004 About Auditing Management and State Finance Accountability Government Regulation, Number 24 Year of 2005 About Governmental Accounting Standard (Cash towards Accrual )Governmental Regulation, Number 58 Year of 2005 About Regional Financial Management Governmental Regulation, Number 8 Year of 2006 About Financial Reporting and Performance of Governmental InstitutionGovernmental Regulation, Number 56 Year of 2005 About Regional Financial Information System Governmental Regulation, Number 71 Year of 2010, About Govenrmental Accounting Standard (Fully Accrual)Regulation of Ministry of Domestic Affairs, Number 4 Year of 2008 About Guidelines for Review of Financial Statement of Regional GovernmentRegulation of Ministry of Finance, Number 46 Year of 2006 About Communicating of Regional Financial Information Regultion of Ministry of Domestic Affairs, Number 59 Year of 2007 About Regional Financial Management Guidelines Indonesian Presidential Instruction, No. 3 of 2003 about National Policy and Strategy Development E –GovernmentRegulation of Minister Domestic Affairs No. 28 Year 2007 about Norm of Supervision and Code of Conduct of Supervisory Officers
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML