-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2017; 6(1): 13-18
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20170601.03

Talent Issue in Islamic Finance Industry
Selvarajah Krishnan1, Kamisan Gadar2, Muhammad Zahim Ghazali2, Norhafidah Nordi2, Mohd Iqbal Shahidan2
1International University of Malaya-Wales-Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
2University Kuala Lumpur Malaysia, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Selvarajah Krishnan, International University of Malaya-Wales-Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study aims to measure the demanding on Islamic Finance Accounting position in global business market that will affecting on fresh university graduate work opportunity and effects of Islamic Finance industry global. Data collected based on the qualitative data. The finding focus on qualification needed to fulfil position in Islamic finance industry, the rate of salary that can be offered, work quality, integrity of worker and the budgeting for company that applying this concept toward demand on Islamic finance work position. The qualitative data are used to apply accordingly to their needs, wants, satisfaction and other criteria and developing answer based on our research to satisfy need and wants of their particular group. Finding show the relationship between demand of work position and opportunity toward fresh university graduate. Additional point, research also found the difference between Islamic Finance concept and Finance Accounting concept that be used by company at global market. Furthermore, elaborated the demanding on Islamic Finance Accounting position toward fresh university graduate that affected work opportunity that been offer by company in global. Government should introduce or create as much as they can work opportunity that can offer to unemployment and fresh university graduate.
Keywords: Islamic Finance, Fresh Graduate, Global
Cite this paper: Selvarajah Krishnan, Kamisan Gadar, Muhammad Zahim Ghazali, Norhafidah Nordi, Mohd Iqbal Shahidan, Talent Issue in Islamic Finance Industry, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 6 No. 1, 2017, pp. 13-18. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20170601.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Worldwide, the financial services sector records the highest earnings and drives a country’s economic growth. The financial services sector contributed 11.6% to the real gross domestic product in Malaysia last year, according to the annual report of the Economic Transformation Programme (ETP) released earlier this year. The Islamic finance accounting industry has been growing at annual rates of 15-20% over the last decade and is expected to continue in the foreseeable future. The Malaysian Institute of Accountants (MIA) was established in 1967 to regulate and control the practise of the accountancy profession and to ensure that only suitably qualified graduated are admitted to the profession. According to Associate Professor Dr Noor Azina Ismail from Department of Applied Statistic, Faculty of Economics and Administration, University of Malaya (2011), for the past 20 years, the Malaysia higher education grows rapidly produce a high number graduates in multi disciplines. There only 7 public universities in 1990’s and currently there are 20 public universities, 24 polytechnics, 37 public community colleges, 33 private universities, 4 foreign university branch campuses and about 500 private college by 2007 (Ministry of Higher Education, 2007). The number of students enrolled into the universities significantly increased from 576,439 in 2002 to 748,797 in 2007.The demanding on Islamic Finance Accounting position in Malaysian business companies are high and they need the quality of the fresh graduates to grab the position. Greater attention need to be provided in monitoring the labour market as the expansion of higher education since there could imbalance of supply of graduate with the demand labour market (Ismail, 2011; Kartz-Gerro & Yaish, 2003; Teichler, 2000). Nowadays, there many fresh graduates who are unemployed and scarring to find a job that reasonable with their field of work. The demanding of Islamic finance position will reduce and solve the unemployment problem in global. A course in finance can be divided into 3 areas, which are corporate finance, investment and financial derivatives. They need to find new graduates who are proficient in controlling the position related to accounts such as financial manager, controller, credit manager, cash manager, risk and insurance manager, financial institution, branch manager, financial analysts and so on. The position is important because it can be influence the economic country. The high demand on Islamic Finance position in global business companies will effect on fresh university graduate work opportunity and business companies in global. In this case, the position that they offer will reduce or solve the unemployment phenomena in Malaysia. The fresh graduate will get the work and they will not have to be unemployed. Besides that, it will be strength the company potential according to have the labour that educated work. Employability from the employees perspective denote as “working readiness” which is skill, knowledge, attitude and profit making understanding possess by graduate the enable them to contribute in achieving the organizational goal (Zarina, et al, 2011; Mason, G., Williams G. & Cranmer, S., 2006). The demand of the Malaysia business company that offer the position will get the advantage from them also can be solving the unemployment problem. The demanding on Islamic Finance position also affected the company in Malaysia and global. The Malaysian financial system’s ability to allocate financial resources effectively and efficiently will be crucial to support Malaysia’s transformation to become a high value-added, high-income economy. Amid greater regional economic and financial integration, the financial sector will also have a more prominent role in intermediating funds in the region and other emerging economies. A more diversified, efficient, competitive and stable financial system is therefore a necessary precondition for Malaysia’s economic transformation. The financial sector today is well positioned to advance and benefit from the opportunities emanating from a more competitive and integrated environment.
2. Literature Review
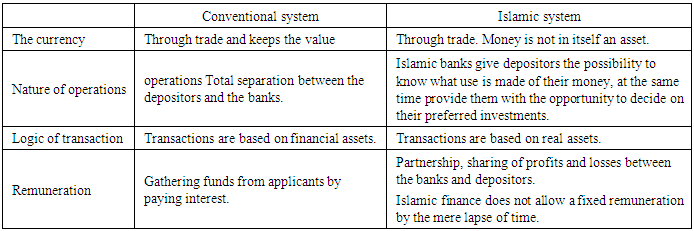
- Islamic Finance The questionnaire defined what would now call the labor force as those with a “gainful occupation” (Hauser, 1949; Ransom and Stuch, 1986). The demanding of Islamic finance position will reduce and solve the unemployment problem in Malaysia. A course in finance can be divided into 3 areas, which are corporate finance, investment and financial derivatives. They need to find new graduates who are proficient in controlling the position related to accounts such as financial manager, controller, credit manager, cash manager, risk and insurance manager, financial institution, branch manager, financial analysts and so on. Increased diversification in Malaysia’s economic structure, where the manufacturing and services sectors will increasingly advance up the value chain towards higher value-added activities. Economic growth will be increasingly driven by knowledge-intensive and more innovative industries, and a larger pool of more advanced SMEs, with improved processes, product innovation and market outreach. So that, they need to offer the variety of the position of Islamic finance accounting to the person especially fresh graduated. Fresh Graduate The ability to accurately crunch numbers is a unique skill set in high demand. As a result, graduates with degrees in accounting, finance, and related majors are reaping lucrative salaries and vast career opportunities. It is difficult to see why the ‘seeking working’ concept has not be more extensively used in unemployment survey: not as secondary sorter, but jointly with ’working’ as the best means of identifying the total labor supply like ‘working’, ’seeking work’ is an actively that can be reported in term of what the individual doing at the time of inquiry”. (Webb, 1939, p.4). Graduates of these programs are being highly sought after by employers, and enrolment in undergraduate and graduate accounting programs is at an all-time high. Accounting might also be a good choice for those with managerial or entrepreneurial aspirations. To support the demands of innovation-driven economic activities and start-up ventures, the fresh graduated are needed to join the offer of the position. It will be reduce and solve the unemployment issue in Malaysia. Effect on CompaniesWhen company add on new method or department in their organization it will give on effect to companies. They will increase on their expending and budget because they need to hire new employee and increase on capacity in their organization. The companies will more advance because using new method of finance. Furthermore, the environment of work will be change because effected that been given by new staff that had their own idea to improve the companies especially fresh graduate that will give 100% commitment on their work performance it can help increase motivation of other staff to compete with them in healthy competition. Employability from the employees perspective denote as “working readiness” which is skill, knowledge, attitude and profit making understanding possess by graduate the enable them to contribute in achieving the organizational goal (Zarina, et al, 2011; Mason, G., Williams G. & Cranmer, S., 2006). Islamic Finance can help to gain more investor totally helped companies to gain more capital, revenue and give good result to the company.Rate Salary Income in terms of salaries, wages, profit and professional incomes become the most important source of living for the majority of population. (Ezamshah Ismail, January 2011). The company that created job opportunities in Islamic finance position offers lucrative salaries to the employee accordance with their respective positions. The salary that satisfy the fresh graduated are attracted them to join the position. The company will increase their salary according to their work performance that makes the company success. The different position influence the different salary because it is depend on how they work and what the expertise that they have.
3. Methodology
- During the research study, we use the secondary data as our result to finish our journal. We use from existing journal. As the result we can detect our dependant variable and independents variable. As all know our dependant variable is demanding work position and our independents variable are fresh graduate work opportunity, effect on companies and rate of salary. Other than that we also use the data from the internet. We find the rate of salary for accounting, fresh graduate work opportunity and the word that we do not know. Sometime we found the data and information that we need but sometime we did not get the information because the information for this title still in limit and new in this industries.
4. Finding
- Through the research that been made, shows the finding about Islamic finance history. Much of the literature on Islamic finance is of a comparative nature. This is due to the fact that the question of identity or of the financial specificity of the Islamic banks is constantly questioned. Are Islamic banks, different or not? Does Islamic finance differentiate itself from conventional finance? This effort of clarification is sometimes underlined by a normative will to prove the superiority of one system compared to the other. Committed authors preferences are not always implicit. The vast majority of these comparative studies focus on the banking activity in a country (comparison between traditional finance and Islamic finance) but only some of those studies cover the banking sector in a panel of country’s where the Islamic banks are present: Asarpota & Kader (2007) compare conventional and Islamic banks in the United Arab Emirates over the period of 2000-2004, Hassan & Samad (2000) and Bakar & Rosly (2003) toke an interest in Malaysia, Ahmed and Hassan (2007) compare banks of Bangladesh, Naceur & Kandil (2009) present the case of Egyptian banks and Baldwin (1990) that of the Turkish banks. Other studies involve comparisons between countries: Malaysia and Bahrain (Cook & al. 2005), the Persian Gulf countries (Olson & Zoubi, 2008). The coexistence of both types of banks poses the question of the criteria’s used consumers to make their choices between the financial services offered by one and the other system. In addition, it leads to a comparison of performances between the two systems. Thus, Samad (2004) analysis the situation of the Bahrain over the period 1991-2001; He came to the conclusion that there is no major differences in performance in terms of profitability and liquidity.Research also, finding history of Islamic finance in Malaysia. According to statement that made by Bank Negara Malaysia, Islamic finance has grown tremendously since it first emerged in the 1970's. Current global Islamic banking assets and assets under management have reached USD750 billion and is expected to hit USD1 trillion by 2010. There are over 300 Islamic financial institutions worldwide across 75 countries According to the Asian Banker Research Group, The World's 100 largest Islamic banks have set an annual asset growth rate of 26.7% and the global Islamic Finance industry is experiencing average growth of 15-20% annually. Malaysia's Islamic finance industry has been in existence for over 30 years.The enactment of the Islamic Banking Act 1983 enabled the country's first Islamic Bank to be established and thereafter, with the liberalisation of the Islamic financial system, more Islamic financial institutions have been established Malaysia's long track record of building a successful domestic Islamic financial industry of over 30 years gives the country a solid foundation - financial bedrock of stability that adds to the richness, diversity and maturity of the financial system. Presently, Malaysia's Islamic banking assets reached USD65.6 billion with an average growth rate of 18-20% annually. Today, Malaysia's Islamic finance continues to grow rapidly, supported by a conducive environment that is renowned for continuous product innovation, a diversity of financial institutions from across the world, a broad range of innovative Islamic investment instruments, a comprehensive financial infrastructure and adopting global regulatory and legal best practices. Rapid liberalisation in the Islamic finance industry, coupled with facilitative business environment has encouraged foreign financial institutions to make Malaysia their destination of choice to conduct Islamic banking business. This has created a diverse and growing community of local and international financial institutions. Malaysia continues to progress and to build on the industry by inviting foreign financial institutions to establish international Islamic banking business in Malaysia to conduct foreign currency business. (Bank Negara Malaysia 2016).Every year, over 200,000 students graduate from institutions of higher learning. Shockingly, 1 out of 4 graduates remain unemployed 6 months after graduation, with the majority being Degree holders. These graduates make up 35.3% of those who are unemployed (Michelle Leo, 2016). It shows high amount of fresh graduate become jobless after finish their studies. The amount can be increase year by years if didn’t take serious for this problem. Malaysia has also placed a strong emphasis on human capital development alongside the development of the Islamic financial industry to ensure the availability of Islamic finance talent. All of these value propositions have transformed Malaysia into one of the most developed Islamic banking markets in the world (Bank Negara Malaysia, 2016). According Bank Negara Statement, it show Islamic Finance in Malaysia already stable and become more valuable it totally can give many work opportunity to fresh university graduated. Previous finding tell about history of Islamic finance and unemployment rate that had correlation with third finding, Malaysia has developed a progressive and comprehensive Islamic financial system that contributes to the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the Malaysian financial sector. (Financial Sector Master Plan, 2011). Many universities graduated facing same problem with their self confident level and problem of lack communication skill. ‘’In my 25 years of experience in HR, I’ve conducted many job interviews with graduates who, on paper, were incredibly bright. CGPAs of 4.0, made from Dean’s List, you name it – but when it came to analysing case studies or even just answering standard questions during the interview, in English especially, they were unable to give voice to their ideas.’’ (Rasidah, 2015). Other finding that been found was action that been made by government to help undergraduate university student to prepare their self to enter job world and university graduate to find job. To enhance graduate employability, Talent Corp continued to provide tax incentives on expenses incurred by companies in hosting 17,967 undergraduates for structured internships; and co-funded training programmes with the industry to upskill 7,153 fresh graduates to meet industry requirements in 2015. (National Transformation Programme, 2015). Researches finding about work opportunity that had at Middle East. There are many private company at middle east want hire person that had qualification in Islamic finance because local residency more interested to work at government sector because the benefit and rewards that offer by government. In the Middle East in particular, the traditionally high wages of the public sector provide stiff competition to banks. One recruitment manager at a major UAE-based retail bank comments that: “The war for talent is pretty intense and it is getting more intense as the market picks up.” (IFN, 2016). It shows the work opportunity to fresh graduate are not only in Malaysia. “According to Malaysia’s Financial Sector Blueprint 2011-20 up to 56,000 new finance industry positions will be needed in the next 10 years; including up to 40,000 Islamic finance industry jobs. A recent survey by Bank Indonesia suggested that the country would need 17,000 qualified Islamic finance professionals over the next three to five years, while some estimates go as high as 39,000 (IFN, 2016).
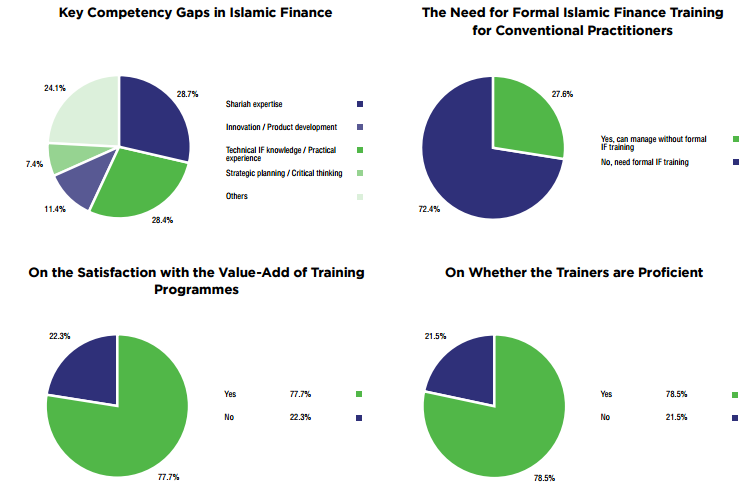 | Figure 1. Key Finding on Talents Gaps and training capacity in Islamic Finance (Talent Development Survey 2014) |
|
5. Conclusions
- As developing country, Malaysia needs to decrease the rate of unemployment. Government should introduce or create as much as they can work opportunity that can offer to unemployment and fresh university graduate. Other than that, Islamic finance will give work opportunity to both which is Muslim or non-Muslim. It given many benefit to citizen, companies and country. In next 5 years Islamic finance and banking needed around 50 000 professional to fulfil their market demand. Base on research be made Islamic Finance can give many benefit to companies and can attract investor from outside especially companies from Middle East to invest in Malaysia and Malaysian companies. The action will help Malaysia economy more active and stable. Besides that, university in Malaysia needed to revise the syllabus of education in Institut Pengajian Tinggi (IPT) that quite old version to new version. It automatically helped the student more knowledgeable and ready to compete at work field. Furthermore, it can increase level of Malaysian education that can produce great quality product for work sector. Thus H, can be accepted. It can be concluded that fresh graduate certificate had relationship with work opportunity. Future graduates should take opportunity of internship program as a training ground to improve their employability skills and try makes the best of it (Yusof, Mohd Fauzi, Abidin, Awang, 2013). Even better, if future graduates able to secure a job after internship program from the same employers. Even though unemployment is not serious as it look as reported by The Star (2013, 23 October) as Malaysia is said to achieve full employment as the unemployment rate is below 4%. Future graduates should not take this lightly as a number of unemployed graduates moderately increased through the year.
6. Limitation
- The major limitation of this study is to recognize either company are owner by Muslim or non-muslim. The information is important because to know result how many company are already applied Islamic Finance concept. Every owner had their own method or strategy to manage their company and the information quit private and confidential. Other limitation was to find accurate number of companies in Malaysia some of companies did not respond our questionnaire so it effect to our study for collecting the accurate data and result. Limited period is one of limitation of this study because we had limited time to make research for this study so that it need revise back the time period for next research. Other than that, lack of source information such as journal and news article because Islamic Finance still newbies in Malaysia work field it will totally not many journalist and reporter are attracted with this topic.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML