-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2016; 5(3): 158-164
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20160503.03

Analysis of Effect of Capital Structure, Company Size and Distribution of Funds against Third Party Financing and Its Implication on Profitability (Studies in Islamic Cooperative Baitul Maal Tamwil in Indonesia)
Oyong Lisa
STIE Widya Gama Lumajang, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Oyong Lisa, STIE Widya Gama Lumajang, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

One of the business activities of Islamic Cooperation is to finance the collection and distribution. Fund raising activities derived from the cooperative itself, of the depositor / members, financing from banks or third parties, and from other sources. This study aimed to analyze the effect of capital structure, company size, and third-party funds to finance portfolio as well as analyze the impact of capital structure, company size, third-party funds and the distribution of funding to profitability. The analysis showed that the capital structure, and third-party funds significantly influence the distribution of funding while the size of the company does not affect the distribution of funding. Capital structure, funding and distribution of third party financing a significant effect on profitability, while the size of the company does not affect the profitability of Islamic Cooperation BMT in Indonesia.
Keywords: Capital Structure, Company Size, Third Party Funds, Distribution Finance, Profitability
Cite this paper: Oyong Lisa, Analysis of Effect of Capital Structure, Company Size and Distribution of Funds against Third Party Financing and Its Implication on Profitability (Studies in Islamic Cooperative Baitul Maal Tamwil in Indonesia), International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 5 No. 3, 2016, pp. 158-164. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20160503.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Basically every company in the operations aimed at obtaining maximum profits by maintaining and continuously improving its business. This is not another in the continuity of the company in order to grow continuously in tune with the progress of time. One of the efforts made by the company is strengthening the capital structure of the right to obtain a profit, at least to cover operating costs in order to maintain its company. The capital structure of a company describes the balance between equity and long-term debt. Thus, companies should always pay attention to proper capital structure in order, so that if the funding will be able to minimize the cost of capital. Selection of alternative funding either from its own capital and foreign capital will greatly affect the amount of profitability obtained by the company. The greater profitability, means the greater the company's ability to generate profits for the owners of capital. Related to the company's capital structure, Gill et al [1] proves there is a positive relationship between short-term debt, long-term debt and total debt to profitability.In a cooperative operational activities, capital is an important factor in channeling funding to the Member. Cooperative capital can also be used to maintain the possibility of risks, including risks arising from the financing itself. To cope with possible risks that occur, then a cooperative must provide a minimum capital adequacy. With a substantial capital then a cooperative can channel more financing, in line with the increased funding will increase financing distribution to members.The size (size) of the company can be expressed in total assets, sales and market capitalization. These three variables used to determine the size of the company because it can represent how big the company is. The greater the assets the more capital invested, the more sales, the more the velocity of money and the greater the market capitalization, the greater the company is known in the community.One of the business activities of Islamic Cooperation is to finance the collection and distribution. Fund raising activities derived from the cooperative itself, of the depositor / members, financing from the bank or to a third party, and from other sources. Meanwhile, the distribution of financing activities can be done in various forms, such as the finance portfolio, investment activities, and in the form of fixed assets and inventory. Cooperative fund raising activities largely sourced from members' savings in the form of demand deposits, savings deposits, and time deposits. Member savings is often referred to as the Third Party Fund (DPK). DPK collected mostly distributed in the form of loans or financing.According Sun'an and Kaluge [2] the factors that influence the distribution of funding investment in Indonesia is the third party fund (DPK), interest rate financing, the rate of inflation. Similar research was also conducted and Munawaroh Akbar [3] proved that the factors affecting the Bank's loan portfolio in the Government of South Kalimantan is the third party funds collected by government banks, the interest rate specified financing, and the level of inflation in Borneo south. Both studies reached the same conclusion, namely third-party funds and financing interest rates positive effect on the distribution of funding, and the rate of inflation negatively affects the distribution of funding. This means that if third party funds that have been collected by the bank increased the distribution of funding the community will increase, so does the interest rate financing. Haron et al [4] conducted research on several factors that affect profitability in some Islamic bank in the world. According Haron et al. [4] factors that affect the profitability of Islamic banks are divided into two categories, namely internal and external variables. Internal factors such as liquidity, capital structure, the structure of deposits, and financing structures affect the profitability of Islamic banks. While external variables include market share, money supply, interest rates, inflation and the size of the bank.The use of total assets as tool size companies based on research Nugraheni and Hapsoro [5], and Arini [6]. Total assets chosen as a proxy for the size of the company taking into account that the value of assets relatively more stable than the market value capitalized and sales [7]. If the value of total assets, sales, or capital was big, then use the natural logarithm of that value [8]. The larger the size of the company will increase the company's ability to manage the assets owned, the greater the chances of cooperatives to channel funds to the community in the form of distribution of funding that have an impact on increased profitability.Funds owned by a cooperative the more, the greater the opportunity for the cooperative to undertake activities to achieve its goals. Taswan [9] explains that the growing number of third-party funds as a major source of funding in the bank, the bank put these funds in the form of productive assets eg financing. Placement in the form of financing will contribute to the bank's interest income that would have an impact on profitability (profit) bank. Research results Maulida [10] proved that the amount of third party funds affect profitability growth. The level of profitability demonstrate the company's ability to generate profits in a given period. Profitability is the ability of cooperatives to obtain profit in relation to total sales, total assets, own capital and the distribution of funding. The greater provision of financing, it will have an impact on increasing the income of the cooperative which will affect on increasing the profitability of the cooperative.The expected goals of this study are: To analyze the effect of capital structure, company size, and third-party funds to finance portfolio as well as to analyze the effect of capital structure, company size, third-party funds and the distribution of funding to profitability.
2. Research Methods
2.1. Research Design
- The design of this study is a causal research design. It is because of this study intends to examine the influence of the variables. This study is called explanatory research, as it aims to explain the influence between variables through hypothesis testing [11].
2.2. Population, Sample and Sampling Techniques
- The population in this study were all cooperative BMT Sharia in Indonesia is 98 BMT incorporated in Parent cooperative sharia in Indonesia. Sampling was done by using a non-probability and purposive sampling method, criteria routinely make financial reports for the period 2012 and 2013. Cooperative Sharia have a complete financial statement as much as 51 sharia cooperatives. Furthermore, of the 51 sharia cooperatives have a complete financial statement, the next meeting the criteria variables in this study were 44 cooperatives, so that cooperatives sharia consecutive for 2 years had a complete financial statement and meet kriteia variable as much as 44 sharia cooperatives. So the sample size in this study was 44 sharia cooperative.
2.3. Data Analysis
- The analysis used in this research is the analysis of multiple regression analysis. Figure 1 shows the research model, with multiple regression analysis. The model in this study consisted of two statistical equations as follows.
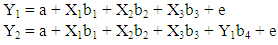
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Result
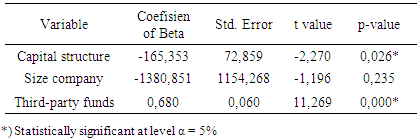
- Effect of Capital Structure, Size Company and Third-party funds to FinancingThe results of the analysis of the effect of capital structure, the size of the company and third-party funds to the financing are presented in the following table.
|
|
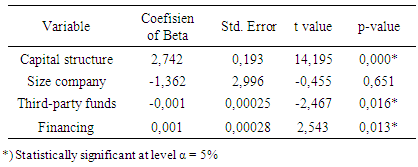
 with a regression coefficient of -0.001 and a standard error of 0.00025 and t value of -2.467 and a p value of 0.016. This means that third-party funds positive effect on profitability, which means an increase in third-party funds will be followed by a decline in profitability. Financing influence on profitability is positive at level = 5%, with a regression coefficient of 0.001 and a standard error of 0.00028 and t value of 2.543 and p value of 0.013. That is positive to the profitability of financing which means an increase in third-party funds will be followed by an increase in profitability. Based on tables 1 and 2, then the results of this research model is presented in the following figure.
with a regression coefficient of -0.001 and a standard error of 0.00025 and t value of -2.467 and a p value of 0.016. This means that third-party funds positive effect on profitability, which means an increase in third-party funds will be followed by a decline in profitability. Financing influence on profitability is positive at level = 5%, with a regression coefficient of 0.001 and a standard error of 0.00028 and t value of 2.543 and p value of 0.013. That is positive to the profitability of financing which means an increase in third-party funds will be followed by an increase in profitability. Based on tables 1 and 2, then the results of this research model is presented in the following figure.3.2. Discussion
- Effect Capital Structure to FinancingCapital structure significantly influence the distribution of funding, which means that the source of funds is the most important thing for the cooperative to be able to increase the amount of financing that will be distributed to the public. The more funds that are owned by the cooperative, the greater the chances of cooperatives to carry out its functions. Funds may include funds from the cooperative itself, the funds coming from other institutions, and funds from the public. Funds sourced from public or third party funds (DPK) is an important funding source for operations and is a measure of the success of the cooperative sharia if it is able to finance its operations from this funding source [12]. These funds can come from savings in the form of savings, current accounts and deposits. Dendawijaya [13] revealed third-party funds raised from the public is the largest funding source of the most reliable by banks (80% -90% of all funds managed by the bank).
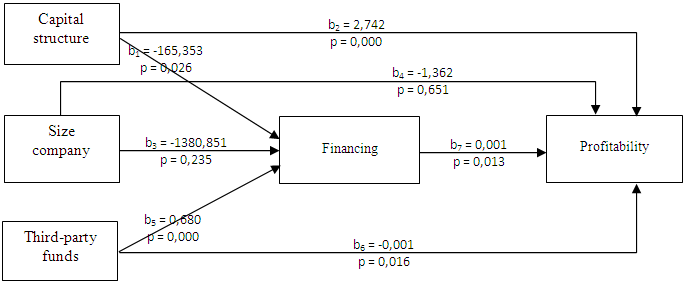 | Figure 2. Results of Research Model |
4. Conclusions
- Capital structure and third-party funds a positive effect on the financing, while the size of the company does not affect the financing. Capital structure, third-party funds and financing positive effect on profitability, while firm size has no effect on profitability. This suggests that the amount of financing is determined from the amount of capital structure and third-party funds, therefore Islamic banks need to set a specific target on the amount of debt to equity and the greater Third-party funds received, also increase the cooperative role of Syariah in channeling funds to the cash-strapped party financing forms that have an impact on increasing profitability.Financing needs to be maintained in order to be able to obtain the return of Islamic Cooperation are able to cover losses from financing problems, and if Syariah Cooperative intends to use long-term debt as a source of external funding, the cooperative should consider the structure of its assets, whether the amount of its fixed assets were able to secure the loan to be taken. Cooperatives that have high profitability need to maintain it, because with high profitability, the cooperative can finance most of the funding needs with retained earnings, thereby reducing dependence on external parties to finance their business activities. To achieve and maintain high profitability, the cooperative must manage its resources (total assets) efficiently.
5. Recommendations
- It is recommended to companies, capital structure determination using the debt at a certain level (as far greater benefits, additional debt is allowed) as a source of funding to improve profitability. While the positive growth of the company shows the company's ability to increase in assets has a high potential to generate high cash flows in the future. For further research is expected to examine the variables other than the variables in order to obtain a more varied results that can describe any matters that may affect the financing and profitability and may also extend the period of observation.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML