-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2016; 5(2): 98-119
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20160502.04

The Role of Control of Corporate Governance Mechanisms in Improving the Quality of Accounting Information and Its Impact on Developing the Performance of the External Auditor in Saudi Arabia Environment
Azza H. Shalaby 1, Shehab Yehia Mohamed Ahmed Eltobgey 2
1College of Business Admiration- Al Rass, University of Qassim, Saudi Arabia
2University of Jena, Germany
Correspondence to: Azza H. Shalaby , College of Business Admiration- Al Rass, University of Qassim, Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study aimed to demonstrate the impact of the application of a set of independent variables in providing and communicating information which affecting the corporate governance mechanisms and its impact on all parties concerned (the external auditor, subject of the study) as the dependent variable. The sample is derived from a Population of internal auditing managers, external auditing managers and audit committee managers at Monetary and financial companies listed on the stock exchange and office auditors in Saudi Arabia in Jeddah and Riyadh. To achieve the objective of the study, the researchers developed a questionnaire. Validity and reliability were established in the questionnaire and administrated to the sample of the study, and (100) usable questionnaires were returned and entered into the SPSS statistical software, the researcher use a number of statistical procedures in data analysis using Statistical Package for Social Studies (SPSS) & (Minitab) to identify the response rates of the sample subjects on the questionnaire's items by using Linear and stepwise regression methods to test the relationship between the dependent and independent variables of the study, besides using Spearman coefficient to clarify the link among variables, in addition to the use of Cronbach's alpha statistical to test the hypotheses of the study. The goal of this study is to strengthen and expand the previous findings by evaluating the interrelationship among all the variables of corporate governance mechanisms and the combined effects among them in audit office. And thus increase the Job Performance of the External Auditor. The results of the study indicate that there is a positive relationship between the application of corporate governance mechanisms, and the quality of the performance of the external auditor. The study recommends the need of the companies in different economic units in Saudi Arabia for applying the controls of corporate governance, with an attempt to develop a special guide in line with the conditions of Saudi Arabia economic environment.
Keywords: Corporate governance mechanisms, Accounting information, The quality of the performance of the external auditor
Cite this paper: Azza H. Shalaby , Shehab Yehia Mohamed Ahmed Eltobgey , The Role of Control of Corporate Governance Mechanisms in Improving the Quality of Accounting Information and Its Impact on Developing the Performance of the External Auditor in Saudi Arabia Environment, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 5 No. 2, 2016, pp. 98-119. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20160502.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The international economic world has witnessed a series of contemporary financial crises, most notably the collapse of several major international companies, most notably Enron Corp., and WorldCom Inc. And the resulting losses from shareholders' money. And followed by several money market fallout reflected in administrative and financial corruption in General and particular accounting corruption which were due to the weakness of mechanisms of control over the activities of financial institutions and mechanisms, lack of experience, skill, the disruption of financing structures and the inability to generate sufficient internal cash flow to repay the obligations owed, and the lack of interest in the application of accounting principles that meet the disclosure and transparency, by not showing the accounting information of the company's financial reality (ALKhodary, ND), this resulted in loss of confidence in the various financial markets, and also in accounting and auditing offices as a result of faking in the accounting information in the financial statements of different companies (Hassan, 2002) (Gujler, 2003) Which led to the emergence of the term Corporate Governance, as a contemporary input to tighten control companies.The nature of the problem and study:The non-disclosure of information that reflect the financial reality of economic units and weak oversight mechanisms in some large companies which are accused of serious professional mistakes and unreal audit reports causes the collapse of many economic units, lost many rights of stakeholders, loss of investor confidence in the information included in the accounting reports and financial statements and the increase the expectations gap between investors and the Auditors (Dahmash, 2003), there is a real source of interest in the concept of corporate governance, which is considered to be the cornerstone upon which many economic units can come up with new visions of the appropriate degree of transparency and credibility to shareholders and all the groups concerned of financial statements. As a result, the problem of the research focused on the need to apply the standards and criteria to meet challenges and cope with stress on auditing profession and its impact on the quality of information in the financial statements published degree of confidence and credibility in the Saudi economic environment, to satisfy the relevant parties (the external auditor). Therefore, the ignorance of this study leads to the creation of varying degrees of confidence and credibility in the Saudi economic environment, which leads to varying degrees of accuracy on the job performance of the external auditor, and then leads to some fundamental error such as lump appreciation, wasted ledgers and, Thus negative impact on the Job Performance on the External Auditor.
2. Purposes and Significance of the Study
- Based on the above introduction, this study aimed to illustrate the impact of Corporate Governance mechanisms - combined - with the quality of published financial statements, and its impact on the job performance of the external auditor, In order to regain confidence to meet the challenges of the coming period under the current financial crisis, its effects on investors’ decisions and relevant parties in the business environment.
3. Questions about the Study
- The study has one question that has been generated for the purposes what is the effect of the relationship between the Corporate Governance mechanisms combined with the quality of published financial statements and its impact on the job performance of the external auditor?
4. Literature Review
- Analytical study of the impact of corporate governance controls on the quality of accounting information, (National Bank of Egypt, 2003) (Darwish, 2003) (Lutfi, 2001) (Melies, Andrea, 1998) (Basel, September 1999) indicated that Corporate governance is the system of company management and control comprehensively through a variety of mechanisms that can be relied upon to achieve its goals., the beginning phase of accounting control and actual practice is the commitment to the application of accounting standards and evaluation and follow-up by the shareholders and stakeholders of the Board of directors and managers’s performance and management’s profit, to disclose as a result of this practice in the form of reports and financial statements by achieving regulatory governance dimension of fairness and transparencyith disclosure, accountability and integrity in corporate governance process, despite the multiplicity of different controls, only this accounting side cannot be applied without governance and, that is done through the application of the principles of corporate governance system in economic unit under clear authorities and responsibilities organizational structure of economic unit. This application represents a set of integrated procedures and controls to adjust the performance of the economic unit is working on effective accounting information system, especially for the giant fund companies, this feedback is one of the important sources correct some formal and substantive errors which are impeding the process of governance in preparation of the final report and financial statements at least in an environment encourages financial and economic objective and effective performance of governance, i.e. the proper application of corporate governance controls will be an effective entrance to achieve accounting information quality, it has been formulated as follows:
4.1. Accounting Control and Accountability
- To configure the system for internal control and accountability and evaluate the performance of economic units which come as a result of the lack of credibility of the lists, and financial reports, lack of confidence in the regulatory system in enterprises, and conflict of interest, resulting in what follows (National Bank of Egypt, 2003), (Darwish, 2003):- Emergence of bankruptcies, financial failure and recurring financial crises.- The goal of corporate governance is to ensure the effectiveness of internal control procedures, and adherence to established standards and focus on variables influencing decision-making.- Hiring of the members of the Board of Directors non-executive directors who have competence and experience in the examination and audit of internal control procedures and to ensure effectiveness, (Symposium on the role of accountant in corporate governance, 2004), check and review the accounting policies applied in the preparation of financial statements, actual and estimated, examination and evaluation of internal and external audits, verification of the company's management response to the external auditor's observations.- Verification of the tight system of internal control through the examination and audit of the accounting policies used in preparing the financial statements (actual and estimated) through verification of the quality standard of the unit's performance and economic impact on the quality of financial reporting. - Achieving effectiveness and efficiency in economic units and the protection of assets is one of the main mechanisms of corporate governance (The World Bank, 2007) (Hassanin, 2003) (Brennan, 1989) (Ashiq & Hwang, 2000).- Achieve economic oversight, so that the resulting benefits outweigh the burdens.- More confidence and credibility in the financial environmental control, it is a good tool of governance to ensure compliance with the rules and criteria established. More efficient use of resources and maximize quality economic unit and strengthen their competitiveness in the market, helping to expand and create new jobs (Winkler, 1998) (Teddy, 2002), It is already clear that the urgent need to exercise governance for protection of investors’ interests in companies, and strengthen the regulatory structure for these companies to face the prospects of a lack of confidence in the system regading Regulatory and accounting issue between senior management and lower administrative levels, and between all of the Board of Directors and stakeholders by the external auditor and about evaluation of the internal control system, and to ensure that the financial statements do not contain any substantial misrepresentation misleading information.
4.2. Interactive Relationship between the Internal Audit Function and the Other Parties to Corporate Governance
- Traditionally, the internal audit function is designed to protect the company's assets and help Producing accounting information that is reliable for decision-making (Ebaid, 2011) (Mahdi Salehi, 2010). Due to effective internal controls and working with the Board and the Audit Committee for risk management and control, and as a result of independence and dependence of the Chairman of the Board of Directors. The Chairman of the Audit Committee, and thus the parties to corporate governance have access to information needed to perform their functions to affect the quality of reports and financial information through:I. Objectivity and independence of the internal audit functionThe effectiveness of the internal audit function, and the fficienc of Internal Auditors’ fficiency, promotion through the Audit Committee or senior management, external members in the internal audit functions, working to achieve the independence, integrity, transperancy and impartiality internal auditors when performing audits functions even with their participation in the initial stages and the final budgeting system.II. Capacity for internal auditorsWhich is determined by the internal level of education, experience, professionalism, level of training and qualification and continuing education and the quality of the performance of the tasks entrusted to him, which reflected positively Consequently the quality of the internal audit.III. Accuracy and integrity of interpretation of internal auditorBy discovering errors made by robberies of analytical procedures, and acceptable explanations increase with increasing experience, gained from working with companies (Church, 1995). The relationship between the internal audit function And the Audit Committee is a result of the internal audit function reports to the Audit Committee, including the appropriate information for business report (ILA, 2003B).IV. Audit feesSome studies (Wallace, 1989) (Felix & al, 2001) revealed that the external audit work hours are increasing at a rate of 10% on average in the case of non-participation of the internal audit function in reviewing financial statements, i.e., so it reduces Audit team members work hours, thus reducing the percentage range of detailed tests (Haron, 2004), and reflected the quality of the reports and financial information.V. The integrity and effectiveness of the Department- The higher the integrity of management, the more reliance on internal auditor (Margheimand Label; 1990)- Interdependence between internal audit and Audit Committee, when examining internal control system leads to increase the effectiveness and quality management and strengthen the infrastructure of the enterprise (Carcello, 2002).VI. Measurement of the level of riskIn circumstances where the inherent danger is low, the larger the company becomes, the increase in the complexity of the activity, the more difficulty for external auditors and management. So the company is facing higher risk, and here is the internal auditor's vital role in defining the risk and control procedures, which means improving the quality of corporate governance (IIA, 2002).It already is clear that there is a positive relationship between good interaction for the internal audit function with other parties to corporate governance, reduce repreparing the financial statements, and fraud in order to overcome the problem. So, there is a need or increasing the credibility of financial statements by an independent external auditor for the purpose of the reliability of the financial statements prepared by management to shareholders.
4.3. The External Audit Role in Activating the Mechanisms of Governance and Its Impact on the Quality of Financial Reporting and the Performance of the External Auditor
- The role of external audit has become essential and effective in the field of corporate governance because it reduces conflicts between owners and economic management, it also reduces the problem of information asymmetry., studies indicate that some shareholders still believe that audited financial statements contain some reliable information (Kothra, 2001) (Jean C. & others, 2012). In order to overcome the problem of credibility of the financial statements, the appointment of an external auditor is an independent investigation of the information contained in the financial statements and submit findings to shareholders (Al-Thuneibal et al., 2011(.I. The importance of complementarity between the internal audit function and the external auditorRecently has become the role of the external auditor and the internal audit function more integrated serving each party to corporate governance in support of the other parties (Abbott et al. 2007), as follows:- The capacity of the internal auditor to detect manipulation of financial statements enables the external auditor to evaluate and assess the risks of manipulation (Church, 2001).- The American Institute of certified public accountants issued Criterion No (65) which encourages external auditors on internal audit activities in the planning and implementation of audit and, where the planning for external audit (Brody, 1998) and in each internal control test and detailed tests (Mills, 1996), (Whittington & Margheim, 1993).- Auditing standards issued Criterion (55) requiring external auditors to understand internal control, internal audit, as part of internal control, should therefore the external auditor's understanding of the work of internal audit (Colbert, 2002).- The work of the internal audit function affects (in PCAOB, 2004) on the nature, timing, and extent of the annual external audit work, affecting the actions carried out by the external auditor in order to understand the internal control system, Risk assessment procedures, procedures for collecting of evidence needed for detailed tests when performing the external audit functions.II. Strengthening the independence of the external auditor are reflected positively on the quality of accounting informationThe strengthening of the independence of the audit function for the organization helps the external auditor to perform the audit, this is evident in the following:- Ensure the commitment of the Board of Directors to work on the external auditor's observations took interest, and strengthening their independence (Ashiq, 2000).- Achieve effective coordination with external auditors through the area of audit of financial statements identified before and after deployment.- To review and evaluate the performance of management accounts and financial management, and discuss the procedures and internal controls, and financial policies of the organization.- Examination and evaluation of the work of the internal audit department to ascertain the adequacy of its programs, and evaluate the adequacy of the internal audit team to fulfil the tasks entrusted to do.- Audit Committee responsible for the integrity and ensure strong internal control procedures, and oversee the activities of the external audit, and responsibility to oversee annual financial reports prepared by the management (DeZoort et al., 2002).- (IIA-UK & USA) and the Institute of internal auditors in England and America the efforts of many scholars and writers in accounting thought in this area in recent years (Kamal, Faraj, 1996) (Wabil, 1996) study the role Strengthening the independence of the audit function and improving quality, audit committees are communication channel between management and the Auditors. It already is a clear positive relationship between good interaction, to external audit function with other parties to corporate governance, and affected the role to be played by the internal audit function in the audit of financial statements And reduce the incidence of fraud and thus improve the quality of corporate governance.
4.4. The Interactive Relationship between the Function of Audit Committees and Other Parties to Corporate Governance
- Most of the studies and reports on corporate governance about the need for audit committees in the economic units that seek to apply corporate governance (Andrew, 2004) (OECD, 2014).I. Practices that contribute to the effectiveness of the Audit Committee depends on the following:- Availability of appropriate information, good preparation before the meetings, arrange contacts with internal and external auditors, prepare a list of goals and responsibilities.- Establishing of objective criteria for the selection and the independence of the members is that the members of audit committees with sufficient expertise in industry, finance and investment, audit, and having the Chairman of the Committee with Leadership personality. - The accuracy and efficiency of the scope of internal audit work programs, And Chairman Audit Committee in the absence of a fundamental distortion in the annual and periodic lists.- Make sure internal auditors are having professional care necessary when performing their duties with the support of the internal audit function.- Provide sufficient and appropriate information to the Audit Committee and assist them in the performance of their supervisory functions.II. The role and importance of audit committees on corporate governance and its impact on the quality of financial reports- Strengthen the independence of the audit function and improving its quality through Committee with the task of nominating the external auditors.- The importance of the active role of audit committees in strengthening behavior of executives (Larry, 2002).- Assist the Board of Directors of the company to meet its legal responsibilities as a which seem like a proxy for shareholders, through formal channels of communication between Board committees on the one hand and customers entering and leaving the internal control structure on the other.- Strengthening the economic status of the organization by providing the rest of the members of the Board of Directors an adequate and sufficient information to improve the Council's decisions in managing the affairs of the organization, thus reducing the problem of inconsistency Information within the Board and reducing the costs of the Agency. Also, the provisions of the control of the Board Organization (Younes, 1996).- Supervision of internal and external audits and resist pressure from the Administration on the review process, in addition to, Declare the formation of a Committee to review the impact the movement of the shares Stock market (Defond).- Published review criteria (61) regarding communication with audit committees and governing communication between the external auditor and the audit Committee on the information to be reported to the external auditor Audit Committee (Statement on Auditing, 1988), and extending the responsibility of the external auditor, and to ensure its obligations, fulfil its supervisory responsibilities for reporting and disclosure, with the aim of improving and activating the central role Audit committees to ensure quality of the performance of different companies.It is already clear that there is a positive relationship between good interaction to audit function of the Audit Committee with other parties to corporate governance, which are affected by the role of the function can play in strengthening the independence of the Audit Committee Internal auditor, to protect the impartiality and independence of the external auditor for the purpose of the reliability of the financial statements prepared by management to shareholders and reduce fraud and then improve the quality of governance.
4.5. The Role of Disclosure and Transparency in the Quality of Accounting Information and the Performance of the External Auditor
- A better disclosure and transparency in the presentation of financial and non-financial information is one of the main pillars and principles underlying corporate governance. It is one important indicator for judging application system determining whether governance within various economic units or not, so that the principles of corporate governance developed by OECD and amended on 12 February 2004 that includes accurate disclosure about all important matters pertaining to contingents Economical with regard to its financial position, financial performance and cash and operational and other aspects related to the members of the Board of Directors and management, preparation and review of information and disclosure Timely and appropriate cost. and it has been found prior evidence of a positive relationship between corporate governance and disclosure standards (Mangena & Pike, 2012) and weak governance and disclosure standards (Ettredge, Johnstone, Stone & Wang, 2011).I. Important role of disclosure and its impact on the quality of accounting information to:- Discover inaccurate Accounting information, and its errors due to landslides that struck a lot of giant corporations. - The Importance of timely property when disclosure of accounting information and its impact on the prices of financial investments, as any delay in the dissemination of information, inaccurate and biased view and lack of dependence on Principles and an agreed accounting standards has a negative effect on investor behavior (Douban, 1985).- Alleviation of heterogeneity between multiple departments, and increase the value of information to employees on the company level, increase customer confidence in the company (Dorothy, 1996).- Increase the value of the company as it became clear documentation of a direct correlation between the value of the company and the quality of corporate governance (Bebchuk, Cohen and Ferrell, 2009).- To predict the capacity of accounting information, whether annual or alftret.- One of the basic standards of corporate governance is the accuracy and objectivity of financial reports beside abiding by laws and legislations (ALSiad, without) (Cuneyt Yuksel, 2008).- It can be said that there is a link between corporate governance and accurate disclosure lists and financial reports as a source of data and accounting information, accounting disclosure must be contained lists, and financial reports to reflect a certain amount of information that must be disclosed. It is already clear that there is a strong correlation between the existence of corporate governance mechanisms and the level of quality and reliability of financial reports, corporate governance controls to take advantage of views Other parties and take necessary corrective action, through the implementation of Audit Committee principles and criteria generally accepted accounting GAAP with its ability to achieve full coordination between the members of the Commission Audit and the external auditor, on the one hand, and between the members of the Audit Committee and the internal auditor on the other hand, to make sure to evaluate the application of the system of internal control. And resolve disputes that arise between the management and the external auditor, any achieving governance society is producing accounting information with multiple uses of the various parties, thereby sustaining The rights of those parties towards economic unity, so this information is important to a degree that prepares the comprehensive level of quality so dependable, and at the same time reflect the confidence of other parties On economic integration and management, thus, the results of several previous studies have established a strong relationship between corporate governance mechanisms and job performance of the external auditor . And, the goal of this study will be to strengthen and expand the previous findings by evaluating the interrelationship among all variables of corporate governance mechanisms and job performance in the audit office through a field study.
5. Hypotheses of the Study
- Based on the research objectives, the following hypotheses were derived are as follows:H1: There is a relationship between controls and procedures of corporate governance (independent variable) and improving the quality of accounting information (dependent variable). H2: There is a relationship between the quality of accounting information for corporate governments (independent variable) and the Job performance of the external Auditor (Dependent variable). The researcher will test the hypothesis researches through field study.
6. The Field Study
- The field study aims to explore the common points of views in the study about the impact of a set of independent variables of corporate governance, which provides and communicates information and its effect on the confidence of all parties concerned (the external auditor) as the dependent variable, In light of the problem, the importance of this research and to achieve its objectives.
6.1. Research Methodology
- This study will be designed using a correlation framework and employ a survey through a questionnaire, in a common format in terms of the contents of the questions from fund listed companies in the Saudi stock market and the audit offices of Jeddah and Riyadh in Saudi Arabia. The questionnaire was distributed among big and middle levels of different firms. Both inferential and differential statistical methods were used the results of this study will be carried out through statistical calculations, making use of both the Pearson r technique and regression methods for measuring correlations, and Cronbach's alpha test to make sure of the reliability of study tool.
6.2. Data Collection and Sample
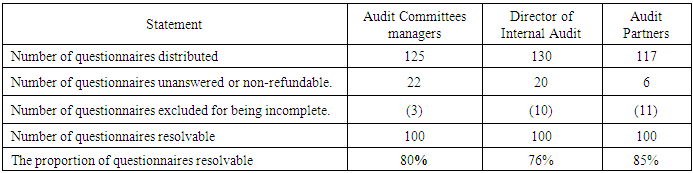
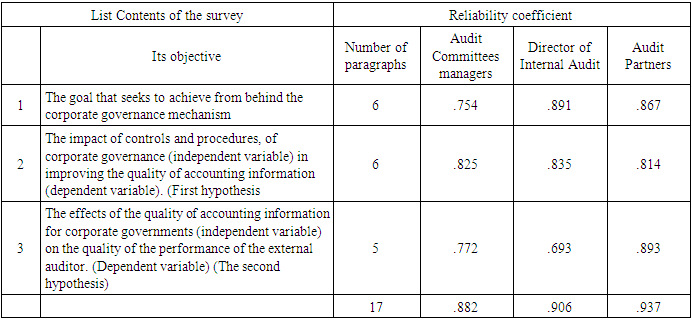
- The present study makes a questionnaire survey approach to collect data for testing the research hypotheses. Data are analyzed using principal components analysis and relationships are tested using linear regression. The majority of this sample of male, due to the long working hours and the nature of the community and the most of the respondents has higher education, qualifications, skills, knowledge and experience as to help facilitate data collection, and reduce the risk of measurement errors.This percentage is undoubtedly considered appropriate proportion due to the researches which used to close-style interviews to overcome differences, cultural, and educational Validity and reliability of study tool:The study tested the stability of the tool using Cronbach's alpha, in order to check the internal consistency. Ranging Krumbach value of the alpha coefficient between the (.70. -- 0.93) for study variables, and this means the result providing a high degree of credibility in the answers, and therefore we can disseminate the results of this study, and the table (2) shows the most important results of this test.
6.3. Collect, Dump and Analysis Questionnaire List
- The researcher has divided the questionnaire into a set of queries relating to the problem of research with a group inquiries regarding testing hypothetical research. All independent and dependent variables require five-point Likert style responses ranging from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”.
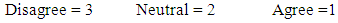 - Y refers to the dependent variable- X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 ........ Refers to a set of independent variables.1 - Inquiries relating to research range.From the table above analysis, it is clear that most of the participants in the survey find that the stage of knowledge reader about audit reports had received support in determining the perception messages. With the necessity to define a minimum quality of the service level, the threat to the independence of the Audit Office, the lack of internal control system, and the accounting reports not keep pace with the ongoing changes in society, all of these make the form and content of the report of the current audit office does not reflect the sincerity and integrity of the information contained in the financial statements, Shareholders need effective tool can be turned on accounting thought by eliminating of deficiencies that hit the content of accounting information and reports which affect on the output away from the rumors and speculation, to make it easier for auditors and maintain shareholders' equity, and that's what ended with theoretical study of research.2- Inquiries relating to the hypothesis of the research.
- Y refers to the dependent variable- X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 ........ Refers to a set of independent variables.1 - Inquiries relating to research range.From the table above analysis, it is clear that most of the participants in the survey find that the stage of knowledge reader about audit reports had received support in determining the perception messages. With the necessity to define a minimum quality of the service level, the threat to the independence of the Audit Office, the lack of internal control system, and the accounting reports not keep pace with the ongoing changes in society, all of these make the form and content of the report of the current audit office does not reflect the sincerity and integrity of the information contained in the financial statements, Shareholders need effective tool can be turned on accounting thought by eliminating of deficiencies that hit the content of accounting information and reports which affect on the output away from the rumors and speculation, to make it easier for auditors and maintain shareholders' equity, and that's what ended with theoretical study of research.2- Inquiries relating to the hypothesis of the research.
|
|
 | Table (3). Shows the goal that seeks to achieve from behind the corporate governance mechanism |
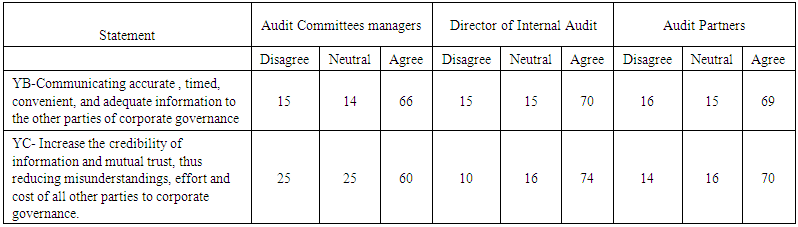 | Table (4). Shows the importance of the criteria of the quality of accounting information and, the quality of the performance of the external auditor as dependent variables |
6.4. The Results of Statistical Analysis Using Linear Regression and Step Wise and Spearman Coefficient
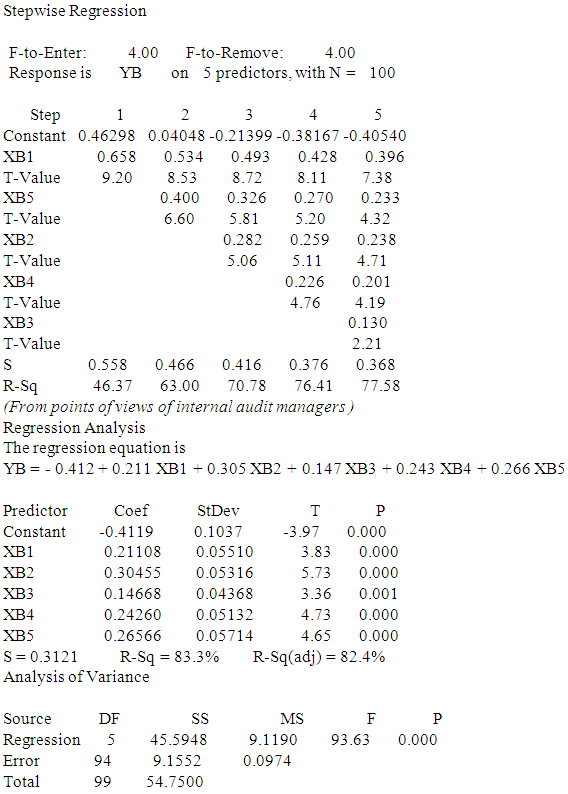
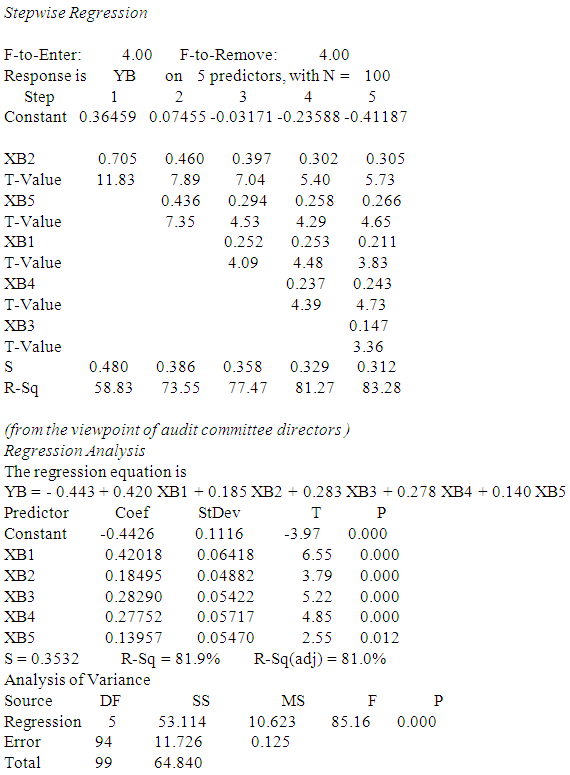
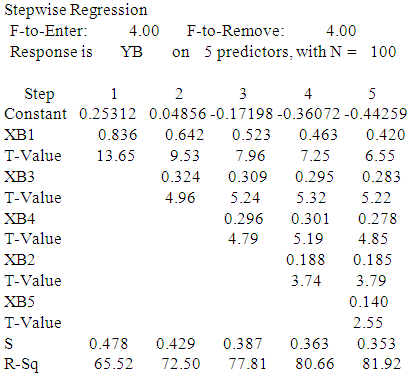
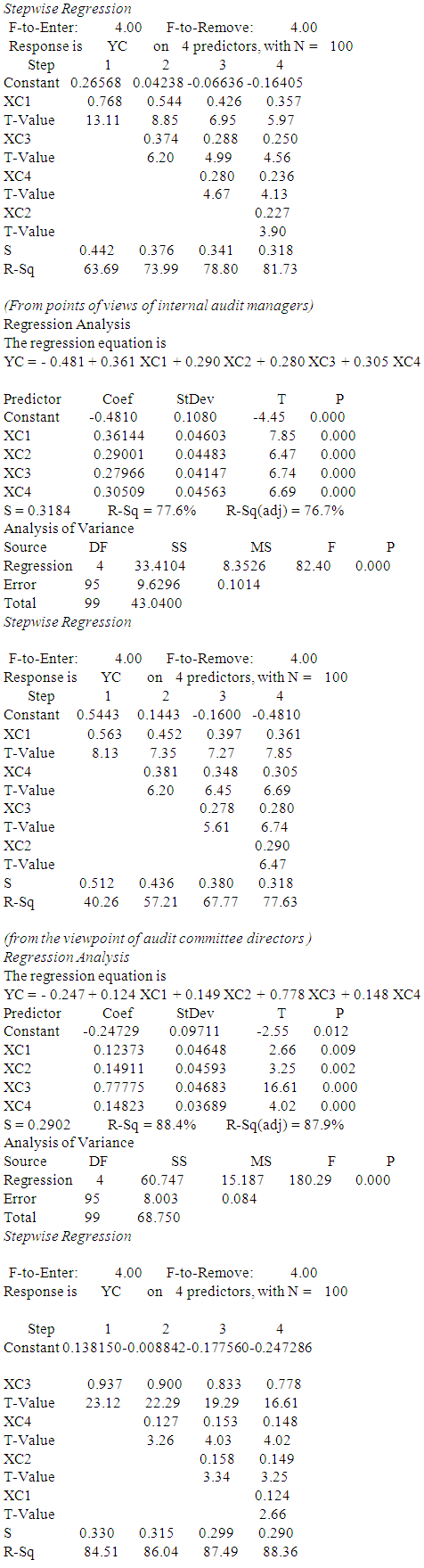
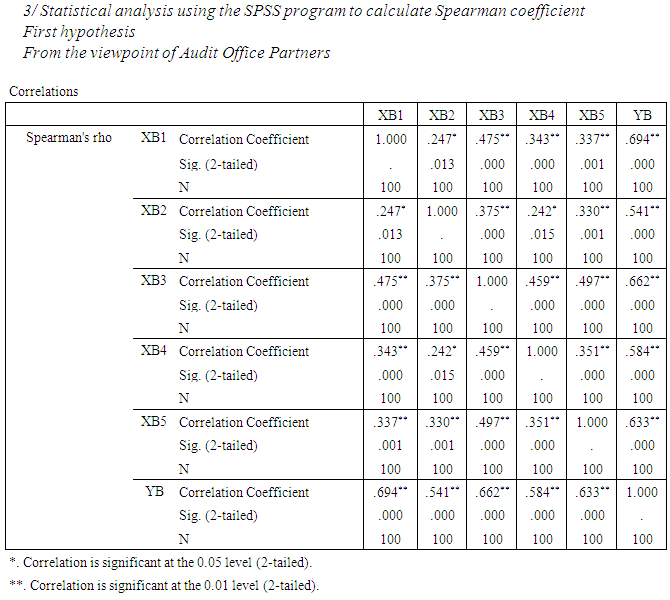
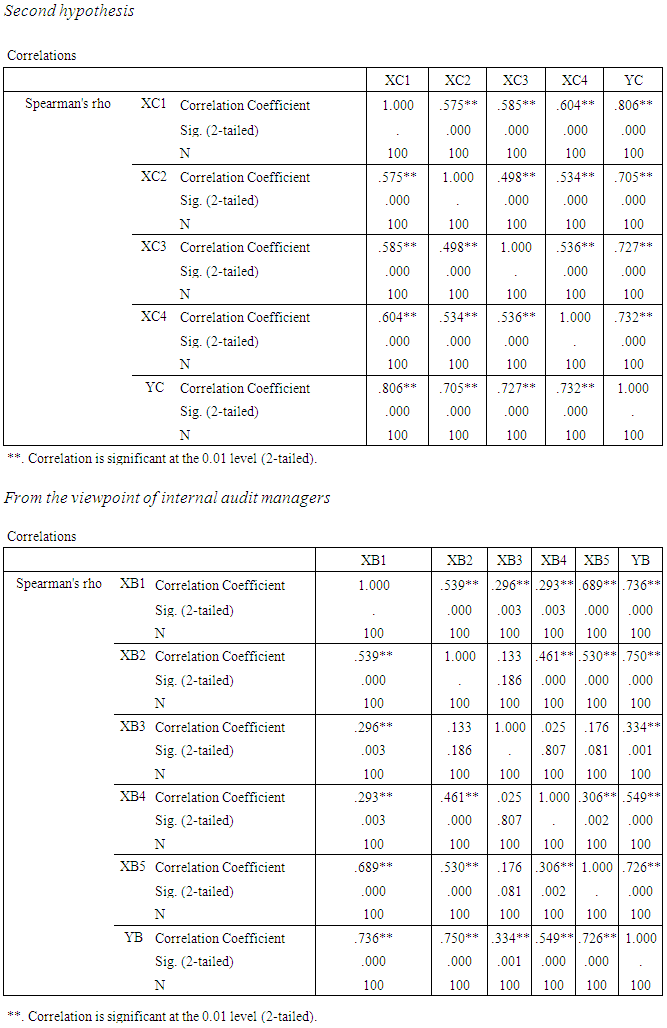
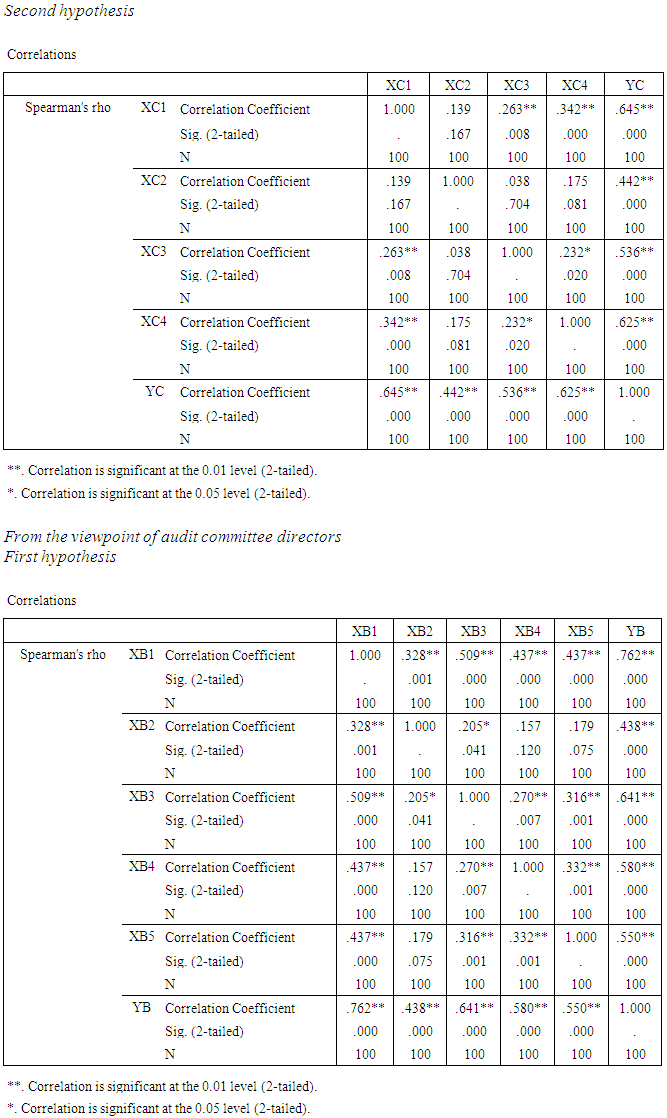
- a. First hypothesis: The impact of controls and procedures, of corporate governance (independent variable) in improving the quality of accounting information (dependent variable). With regard to the quality of accounting information as the dependent variable which symbolized YB to determine the impact of the following independent variables:XB1 - Internal control XB2 - Internal Audit XB3 - Audit Committee XB4 - External Audit XB5 - Disclosure From the point of view of both partners Audit Office, internal audit managers and audit committee directors, using simple linear regression and stepwise regression:First: using Linear regression analysis:Equation (1) from the viewpoint of Audit Office PartnersIt has been shown all of the independent variables in Table (5) Where the coefficient of determination rate was 76.4% and thus becomes the effect of independent variables on the standard represents 76.4% and 23.6 % due to other factors.Equation (2) from the viewpoint of internal audit managersIt has been shown all of the independent variables in Table (5) Where the coefficient of determination rate was 82.4% and thus becomes the effect of independent variables on the standard represents 82.4% and 17.6% due to other factors.Equation (3) from the viewpoint of audit committee directorsIt has been shown all of the independent variables in Table (5) Where the coefficient of determination rate was 81.0% and thus becomes the effect of independent variables on the standard represents 81.0% and 19 % due to other factors.Second: the most influential factors using stepwiseFrom the viewpoint of Audit Office Partners- The most important factors that impact on the quality of accounting information is XB1 then XB5 then XB2 then XB4 and then XB3.- The most impact Factors on the dependent variable is XB1 where the degree of influence 46.37%, then variable XB1, XB5 The degree of influence collectively 63.00%, after that the variable XB1, XB5, XB2 degree of influence collectively 70.78%, then the variable XB1, XB5, XB2, XB4 The degree of influence collectively 76.41% finally, variable XB1, XB5, XB2, XB4, XB3 The degree of influence collectively 77.58%.From the viewpoint of internal audit managersThe most influential factor is XB2 then XB5 then XB1 then XB4 and then XB3- The most important factor impact on the dependent variable is XB2, where the degree of influence 58.83%, and then XB2, XB5 The degree of influence collectively 73.55%, after that XB2, XB5, XB1 The degree of influence collectively 77.47% and then XB2, XB5, XB1, XB4 The degree of influence collectively 81.27%, and finally, XB2, XB5, XB1, XB4, XB3 The degree of influence collectively 83.28%.From the viewpoint of audit committee directors- The most impact factor is XB1 then XB3 and then XB2 after that XB4 and finally XB5- The most impact factor on the dependent variable is XB1 where the degree of influence 65.52%, and then XB1, XB3 The degree of influence collectively 72.50% after that XB1 XB3 XB4 where the degree of influence collectively 77.81% and then XB1 XB3 XB4 XB2, where the degree of influence collectively 80.66% and finally XB1 XB3 XB4 XB2 XB5 where the degree of influence collectively 81.92%.Moral relationship has been proven at the level 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively. (from P estimated value) for all parties.
 | Table (5). Shows the impact of controls and procedures, of corporate governance (independent variable) in improving the quality of accounting information (dependent variable) |
 | Table (6). Shows the effects of the quality of accounting information for corporate governments (independent variable) on the quality of the performance of the external auditor. (Dependent variable) |
6.5. Analysis the Results
- - It already is clear that from the point of view of all parties (partners of audit office, internal audit directors and managers of audit committees) that:- There is a strong and positive correlation between corporate governance mechanism as independent variable and the quality of accounting information as a dependent variable - There is a strong and positive correlation between the quality of accounting information for corporate governments (independent variable) and the quality of the performance of the external auditor. (Dependent variable).- The researcher concluded through field studies the corporate governance controls increases accounting information’s quality and consequently increase the degree of confidence on all parties (external auditor under study) so undoubtedly proves the validity of hypotheses that the researcher put it on sound scientific grounds.
7. Conclusion the Findings and Recommendations
7.1. Study Findings
- The application of corporate governance is to confirm and increase the reliability and credibility of financial statements and to promote the concept of information quality in order to achieve quality with multiple criteria, which means achieving the comprehensive concept of information accounting quality - There is a direct correlation between the internal audit function with other parties and the quality of financial reports.-There is a direct correlation between the external audit function with other parties and the quality of financial reports. - There is a direct correlation between Audit Committee function with other parties and the quality of financial reports. - There is a direct correlation between Disclosure to other parties and the quality of financial reports.- There is a direct correlation between corporate governance mechanism and quality performance of the external auditor.- There is a positive relationship between the application aspects of corporate governance, quality of financial accounting information and quality performance of the external auditor.
7.2. Study Recommendations
- The researcher recommends the following:- Professional organizations develop awareness among shareholders and investors by highlighting the role of corporate governance mechanisms in improving the quality of reports and financial statements and increased Credibility and transparency to the masses of users. And, commit to specific legislative controls for audit Committees to ensure effectiveness.- Impose effective control over the performance of economic units and strengthen the accountability of accounting.- Taking into account the interests of the various parties to activate communication with them.- The expansion of the application of corporate governance in different economic units, with an attempt to develop a special guide corporate governance in line with the Saudi economic environment conditions and achieve the maximum benefit from the application of corporate governance.
Appendix
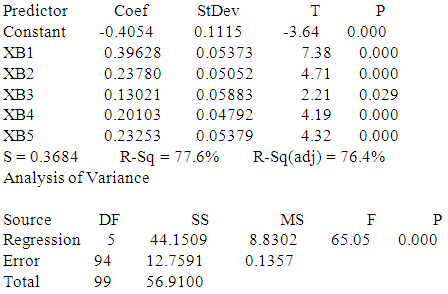
- First hypothesis: The impact of controls and procedures, of corporate governance (independent variable) in improving the quality of accounting information (dependent variable). First: from the perspective of the external auditorRegression AnalysisThe regression equation isYB = - 0.405 + 0.396 XB1 + 0.238 XB2 + 0.130 XB3 + 0.201 XB4 + 0.233 XB5
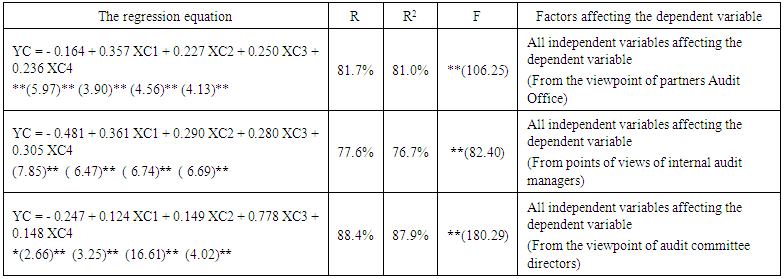
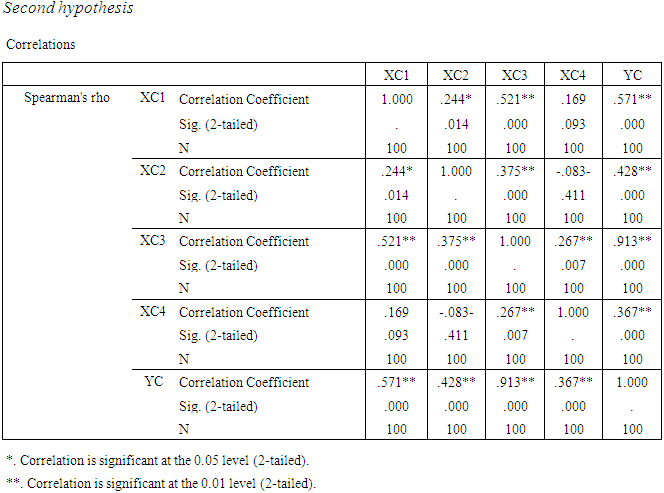
 b. The second hypothesis: The effects of the quality of accounting information for corporate governments (independent variable) on the quality of the performance of the external auditor. (Dependent variable) First: from the perspective of the external auditorRegression AnalysisThe regression equation isYC = - 0.164 + 0.357 XC1 + 0.227 XC2 + 0.250 XC3 + 0.236 XC4
b. The second hypothesis: The effects of the quality of accounting information for corporate governments (independent variable) on the quality of the performance of the external auditor. (Dependent variable) First: from the perspective of the external auditorRegression AnalysisThe regression equation isYC = - 0.164 + 0.357 XC1 + 0.227 XC2 + 0.250 XC3 + 0.236 XC4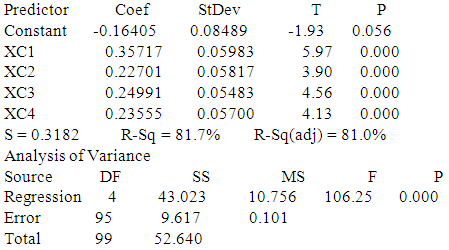
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML