-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Finance and Accounting
p-ISSN: 2168-4812 e-ISSN: 2168-4820
2015; 4(3): 172-179
doi:10.5923/j.ijfa.20150403.04
An Empirical Analysis of Audited Financial Statements Reliability: Mediating Role of Auditor Quality
Abdelfatah M. Alrshah
School of Accountancy, Universiti Utara Malaysia, (Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business)
Correspondence to: Abdelfatah M. Alrshah, School of Accountancy, Universiti Utara Malaysia, (Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business).
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Current study seeks to analyze the impact of corporate governance mechanism on audited financial statements reliability by analysing mediating effect of auditor quality. Study based on primary data which was collected from 188 respondents of Libyan banking industry through convenience sampling. Multiple regression analysis was used to determine the relationship among independent variables and mediating variable and bivariate regression analysis used to analyze the relationship among mediating variable and dependent variable. The current study used reliability of audited financial statement as a dependent variable and auditor quality as mediating variables. The independent variables in current study are; non- audit services, auditor rotation, measures of audit firm size, measures of audit firm fees and measures of audit committee characteristics. Result of current study stated that there is a direct positive relationship between corporate governance practices and auditor quality. The results also reveal a direct strong positive relationship between auditor quality and the reliability of audited financial statements. In terms of mediation, the findings of the study show that auditor quality partially mediates the relationship between corporate governance mechanisms and the reliability of audited financial statements.
Keywords: Corporate Governance Mechanisms, Auditor Quality, Reliability of Audited Financial Statements, Libya, Banking Sector
Cite this paper: Abdelfatah M. Alrshah, An Empirical Analysis of Audited Financial Statements Reliability: Mediating Role of Auditor Quality, International Journal of Finance and Accounting , Vol. 4 No. 3, 2015, pp. 172-179. doi: 10.5923/j.ijfa.20150403.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Corporate governance has attained immense attention of business world and research scholars in today’s hypercompetitive and volatile business environment. Recent scandals of corporate word like Enron corporation, BCCI, WorldCom, Lehman brothers and HIH insurance group has fostered to consider corporate governance as significant field.Among the various corporate governance reforms, reliability of reported financial statements information is vital. The crux of corporate governance reforms and implementation are to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of financial statement reporting and audit quality [7, 12, 39, 55] Therefore scholars and policy makers are much interested to dig out and explore corporate governance related to financial statement reliability and audit quality in both developing and developed countries [43, 48, 51, 52]. Therefore outcome of corporate crises and scandals urged importance of reliability of financial statements, audit quality and corporate governance [5].There are few studies that investigated the impact of corporate governance mechanism on financial statement reliability in the context of Libya. Current study seeks to fill this gap by examining the impact of corporate governance on reported financial statements reliability with mediating effect of auditor quality in Libyan banking sector.
2. Literature Review
- Reliability of financial statements and reporting has its roots in industrial revolution and ancient trading [54, 58]. Current business models challenged the old rule of thumbs and separate the authority and power of management control from ownership [35]. This response was to be compatible with contemporary needs of stakeholders of financial statements for accountability [20].Reliability of audited financial statements is an among the core issues in a today’s corporate sector. It has gained more importance in recent time of financial crunch. Financial accounting standards Board [21] defined financial reporting as “Quality of information that assures that focus information is reasonably free from error or bias and faithfully represents what it purports to represent”.Bribesh [9] stressed that corporate financial reports should contain certain characteristics and attributes to be effective namely, reliability, relevance, completeness, comparability and understandability. These characteristics and attributes enable the investors to rely on financial statements while taking financial decision. Obaidat [46] and Elliot [19] delineated that reliability is the quality of financial statement that builds confidence of the investors. Reliable information is having characteristics of neutrality and faithful representation of the financial information.There is paucity of empirical studies that examine the collective impact of NAS, Audit fee, Auditor’s independence regarding reliability of financial statements [4, 25].
2.1. Provision of Non-Audit Services (NAS)
- After decay of Enron, the field of the provision of NAS and auditor independence emerged as burnning issue for scholars and pactitioners [36]. Intense literature revealed that independence of auditors is a serious threat to its corporate clients in many countris [4, 8, 11, 13, 18, 22, 26, 41]. Surely this issue urged the need to control external auditors to prevent from providing NAS that impair the impartiality and independence of auditors [53].
2.2. Auditor Rotation
- The relationship of firm auditor rotation, audit firm independence and audit quality is significant area of research and discussion in accounting literature. There is immense literature can be found that stress on quality of financial reporting by sustaining the auditor independence thorugh auditor rotation reporting [37, 40, 41, 56]. There are other views that posit contrary view point about having little faith in ability of auditor independence due to audit rotation [14, 32]. Salleh and Jasmani [49] conducted a study to analyze the relationship of reliability of audited financial statements and audit the auditors’ rotation. The association between the rotation of mandatory audit partner and reliability of audited financial statements seemed significant.
2.3. Size of Audit Firm
- Many researchers found positive linkage between firm size of the audit firm, auditor quality and reliability of the financial statements [2, 23, 42]. Several researchers have defined large firm size in terms of the provision of multi-services to many clients [15, 17, 27, 57], in respect of the proportion of fees charged for both non-auditing and audit services [49], in terms of the audit firm’s market share revenue [27, 47], in terms of the number of clients and the number of members of audit firm and on the basis of internationality [33, 38, 45].
2.4. Audit Firm Fees
- Many researcher indicate that audit quality much dependent on fees charging for audit services and consequently it effects reliability of the financial statements [1, 28, 31, 34].Security of the auditing profession has been increased deu level of NAS fee collected from audit customers and expected influance of theses fees on independence of auditors and audit quality consequently to reliability of financial statements [30].
2.5. Auditor Quality
- Auditor quality is one of the important elements to make financial reports more reliable and audit committees play significant role in it. The degree of audit quality is significantly affected by the audit committee [44]. More specifically, effective audit committees are anticipated to improve financial reporting quality by assuming responsibilities especially reviewing the financial statements prepared by the client’s management. Additionally, audit committees are also estimated to play a key role in ensuring the effectiveness of external auditors in the audit engagement process by, fulfilling a number of responsibilities including the selection and remuneration of external auditors, as well as reviewing the auditors work [16]. It is evident that prior and current research indicate that both the existence of the audit committee and the attributes of audit committee members affect the usefulness and reliability of financial reporting [3, 10].
3. Methodology and Variable Measurement
- The objectives of the study are to extend the evidence linking external corporate governance mechanisms to reliability of audited financial statements through analyzing the mediating effect of auditor quality. First, current study examines the relationship between internal corporate governance practices and auditor quality, than investigate the relationship between auditor quality and reliability of audited financial statements in the Libyan Banking Sector. The primary data for this study is gathered by opting survey technique so the data used in this study is primary in nature. Convenient sampling is used to gather the data and the main respondent of this study are auditors and loan officers of banking sector of Libya. Current study distributed 500 questionnaires and managed to get 188 respondents as sample size.
3.1. Model Specification
- First, a multiple regression equation is set up to investigate the hypothesized relationships among mediating variable and explanatory variables in current study. The econometric form of the equation is given as:
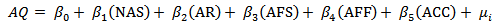 | (1) |
 | (2) |
4. Measurement of Variables
4.1. Reliability of Audited Financial Statement (Dependent variable)
- Reliability of Audited Financial Statement calculated thorough adding the values of seven indicators which derived from previous literature to operationalized this variable namely, “1) perceived audited financial statement as an indication that the company as free from fraud, 2) the extent of audit work performed is clearly communicated, 3) the financial statements give a true and fair view, 4) the auditor does not agree with the accounting policies used in the financial statement, 5) the current standards of audit practice give a clear guidance to auditors, 6) the extent of assurance given by the auditor is clearly indicated and 7) users can have absolute assurance that the financial statements contain no material misstatements.” Likert scale is used to measure all these indicators ranging from value 1 to 7. Value 1 denotes for strongly disagree and 7 for strongly agree.
4.2. Auditor Quality (Mediating Variables)
- Auditor independence takes as a proxy variable for measuring Auditor Quality (AQ). Auditor independence calculated thorough adding the values of eight indicators which derived from previous literature to operationalized this variable namely, “1) Auditor’s ability to be objective in disclosing a financial reporting problem, 2) Auditor’s ability to be unbiased in disclosing a financial reporting problems, 3) Freedom from managerial interference with the audit program, 4) Free access to all records, producers, and personnel relevant to the audit, 5) Active co-operation from management personnel during the audit examination, 6) Freedom from personal interests on the part of the auditor leading to exclusions form or limitations on the audit examination, 7) The auditor maintains independence in fact, and 8) The auditor maintains independence in appearance”. Likert scale is used to measure all these indicators ranging from value 1 to 7. Value 1 denotes for strongly disagree and 7 for strongly agree.
4.3. Non- audit Services (Independent varialbe)
- Non- audit services (NAS) also calculated thorough adding the values of eight indicators which derived from previous literature to operationalized this variable namely, “1) non- audit services from incumbent ≥ 100 percent audit fee, 2) non- audit services from incumbent ≥ 50 percent audit fee, 3) non- audit services from incumbent ≥ 25 percent fee, 4) The audit firms should not provide any find of non-audit service to its audit clients, 5) the prohibition of the provision of NAS to an audit client is only to maintain the perception of independence, 6) Non-audit services is provided to audit clients by as separate department within the audit firm give the auditor more credibility, 7) Non-audit services is provided by the auditor to all clients but full disclosure is made in the client financial statements and 8) The provision of NAS to an audit client leads to economic dependency on that client and causes a conflict of interest for the auditor”. Likert scale is used to measure all these indicators ranging from value 1 to 7. Value 1 denotes for strongly disagree and 7 for strongly agree.
4.4. Auditor Rotation (Independent varialbe)
- Auditor Rotation (AR) calculated thorough adding the values of nine indicators which derived from previous literature to operationalized this variable namely, “1) Risk of adverse market reaction to frequent auditor change threatening auditor independence, 2) Long tenure with a client gives an auditor more experience and leads to low audit hours by an auditor, 3) Long tenure should only be allowed with large companies, 4) The longer the duration an audit firm serves an audit client, the more likelihood that auditors’ independence will be impaired, 5) Mandatory audit firm rotation in the interest of independence is valid, 6) Mandatory rotation create a positive users’ perspective concerning independency in regards of financial statements reliability, 7) Mandatory rotation enhance the audit firm-client independency, 8) depending on audit partner rotation instead of audit firm rotation enhance independency and 9) Management time and costs incurred in changing auditors threatening auditor independence”. Likert scale is used to measure all these indicators ranging from value 1 to 7. Value 1 denotes for strongly disagree and 7 for strongly agree.
4.5. Measures of Audit Firm Size (Independent varialbe)
- Measures of Audit Firm Size (ASF) calculated thorough adding the values of six ne indicators which derived from previous literature to operationalized this variable namely, “1) Being a small, local audit firm, 2) Being a sole practitioner, 3) Being a sole practitioner, 4) The Big four firms can report the real financial situation of the clients more readily than other firms, 5) The Big four firms perform more powerful effective tests and are more credible than others and 6) The companies or banks audited by the Big firms are more attractive to investors and creditors”. Likert scale is used to measure all these indicators ranging from value 1 to 7. Value 1 denotes for strongly disagree and 7 for strongly agree.
4.6. Measures of Audit Firm Fees (Independent varialbe)
- Measures of Audit Firm fees (AFF) calculated thorough adding the values of eight indicators which derived from previous literature to operationalized this variable namely; A total of 8 items were derived from previous literature to operationalized this variable namely, “1) the external audit fee reasonable given the scope of the external audit, 2) there are differences between actual and estimated fees handled, 3) An assessment made on the amounts and relationship of audit and non-audit fee and services, 4) Disclosing audit and non-audit fees strengthens auditor independence, 5) the annual financial statements should include a management report which discloses the nature of other services provided by its external auditor, 6) Greater than 10% of total firm’s audit fees revenues are from one client, 7) the big audit firm usually charge higher audit fee and local firms usually charge lower fees, and 8) A company that pays higher fees in more likely to receive a clean audit opinion”. Likert scale is used to measure all these indicators ranging from value 1 to 7. 1 denotes for strongly disagree and 7 for strongly agree.
4.7. Measures of Audit Committee Characteristics (Independent varialbe)
- Measures of Audit Committee Characteristics (ACC) also calculated thorough adding the values of eight ne indicators which derived from previous literature to operationalized this variable namely, “1) The existence of an audit committee in a company or bank ensures that auditor is likely to be independence, 2) There is an active audit committee (meeting more than 3 times a year), 3) Existence of AC composed of nonexecutive directors, a majority of whom are independent, 4) AC is responsible for the selection of auditor, 5) AC is responsible for the determination of auditor’s fees before the services are provided, 6) AC is responsible for the dismissal of auditor, 7) There is a compulsory audit committee report describing activities and actions taken during the year, and 8) The average size of AC is 4 to 6 members”. Likert scale is used to measure all these indicators ranging from value 1 to 7. Value 1 denotes for strongly disagree and 7 for strongly agree.
5. Results and Discussions
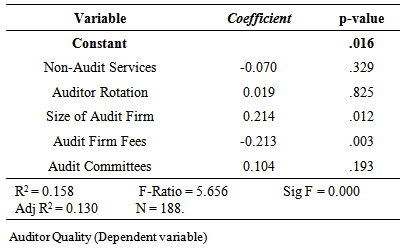
- The internal reliability of instrument has been ensured by computing Cronbach’s alpha for each construct. The estimated values show the internal consistency of data. The alpha values for auditor independence, provision of non-audit services, auditor rotation, audit firm size, audit firm fees and audit committee characteristics are 0.78, 0.89, 0.90, 0.75, 0.74 and 0.85 respectively. Likewise Cronbach’s alpha for reliability of audited financial statement is 0.71. These results show that all the items are internally consistent as the values are in acceptance region.
5.1. Correlations
- The correlation among variables shows in Table 1. It is established that auditor competence has a negative but weak or no relationship with the provision of NAS and auditor rotation. It is also established that auditor competence has a positive but weak or no relationship with size of audit firm, audit firm fees, and audit committee. Meanwhile, the correlation between auditor competence and RAFS at the 0.01 Significance level is weak (Table 1). Finally, Table 1 shows a positive but moderate relationship between auditor quality and auditor competence at the 0.01 level of significance.
|
6. Regressions Results
- Variables influencing Auditor Quality have been determined by applying multiple regression analysis. Here the dependent variable is Auditor Quality. The variables were taken as assuming that they have influence on Auditor Quality. Only five independent variables truly compose the model. The independent variables are: NAS, Provision of Non-Audit Services; AR, auditor rotation; AFS, audit firm size; AFF, audit firm fees; ACC, audit committee characteristics.Standard Multiple Regression was utilised to assess the ability of five independent variables to predict auditor quality. The first step was to check the sig. F value in this model. The value is 0.000 and thus we can accept the assumption that the model is statistically significantly and that the sample is unlikely to produce a large R2 when the population R2 is actually zero. As depicted in Table 2, all independent variables together explain 16 percent of the variance (R2) in the dependent variable (auditor quality), which is statistically significant [29]. The significance of the value is also supported by the F value of 5.66. Such results demonstrate the goodness of the model.
|
|
7. Conclusions and Recommendations
- Banking sector is known as the main sector of an economy. Same is the case of Libya. Libyan banking sector consists of 16 commercial banks which are basically performing the many important roles in the development of economy. So it becomes more important to investigate this sector. This study is basically added in the existing knowledge related to audit and its related features specifically in the reference of banking sector of Libya. This study investigates the relationship between corporate governance practices, auditor quality and financial reporting in the context of banking sector of Libya. The findings of this study revealed the impact of certain independent variables on auditor quality as well as on RAFS. Another key research aim of this study was to determine the mediating impact of auditor’s quality in the relationships between provision of NAS, auditor rotation, audit firm size, audit firm fees, audit committee characteristics, and the RAFS. There are two empirical associations that have been examined in this study. First, there is an examination of the association between auditor characteristics and auditor quality and in second, examine the relationship among auditor quality and RAFS. Auditor characteristics such as the provision of NAS and size of audit firms’ fees are shown to have an inverse relationship with auditor quality and RAFS. Auditor dimensions, namely, auditor rotation and size of audit firms are indicated as having a positive and significant relationship with auditor quality and RAFS.Meanwhile, the results of this study indicated that there is a positive and significant relationship between auditor quality and RAFS. Furthermore, the findings show that auditor quality has positively mediated the relationship between the following dimensions that is, auditor rotation, audit firms size, audit committee characteristics and RAFS. However, the findings of the study also demonstrated that auditor quality has negatively mediated the relationship between provision of NAS, audit firm fees and RAFS.Overall, the findings of this study were largely consistent with agency theory, which states that corporate governance mechanisms are essential monitoring devices that improve auditor quality which in turn helps to enhance financial reporting quality. Already, some emerging studies confirmed that external audit quality and board characteristics (particularly independence and diligence) are complementary mechanisms [24].Current study suggests future research may be beneficial, if more variables and better measures are integrated into the study to enrich the outcome variable. In this regard, it is important that other factors which affect audit quality such as accounting standards, competition in the audit market, regulatory and socio-economic dimensions are added to the conceptual framework. This would allow us to have a deeper knowledge of the factors that affect audit quality. Similarly, future studies should use all existing measures or proxies of audit quality including auditor’s reputational capital, financial restatements, auditor’s litigation, auditor performance, auditor responsibility and auditor statement reliability. This would allow us to draw more reliable conclusions about the effect of auditor quality on the RAFS. To put differently, future research should design a comprehensive measure of audit quality.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML